Flood Hazard and Management in Cambodia: A Review of Activities, Knowledge Gaps, and Research Direction
Abstract
1. Overview of Flood Hazard in Cambodia
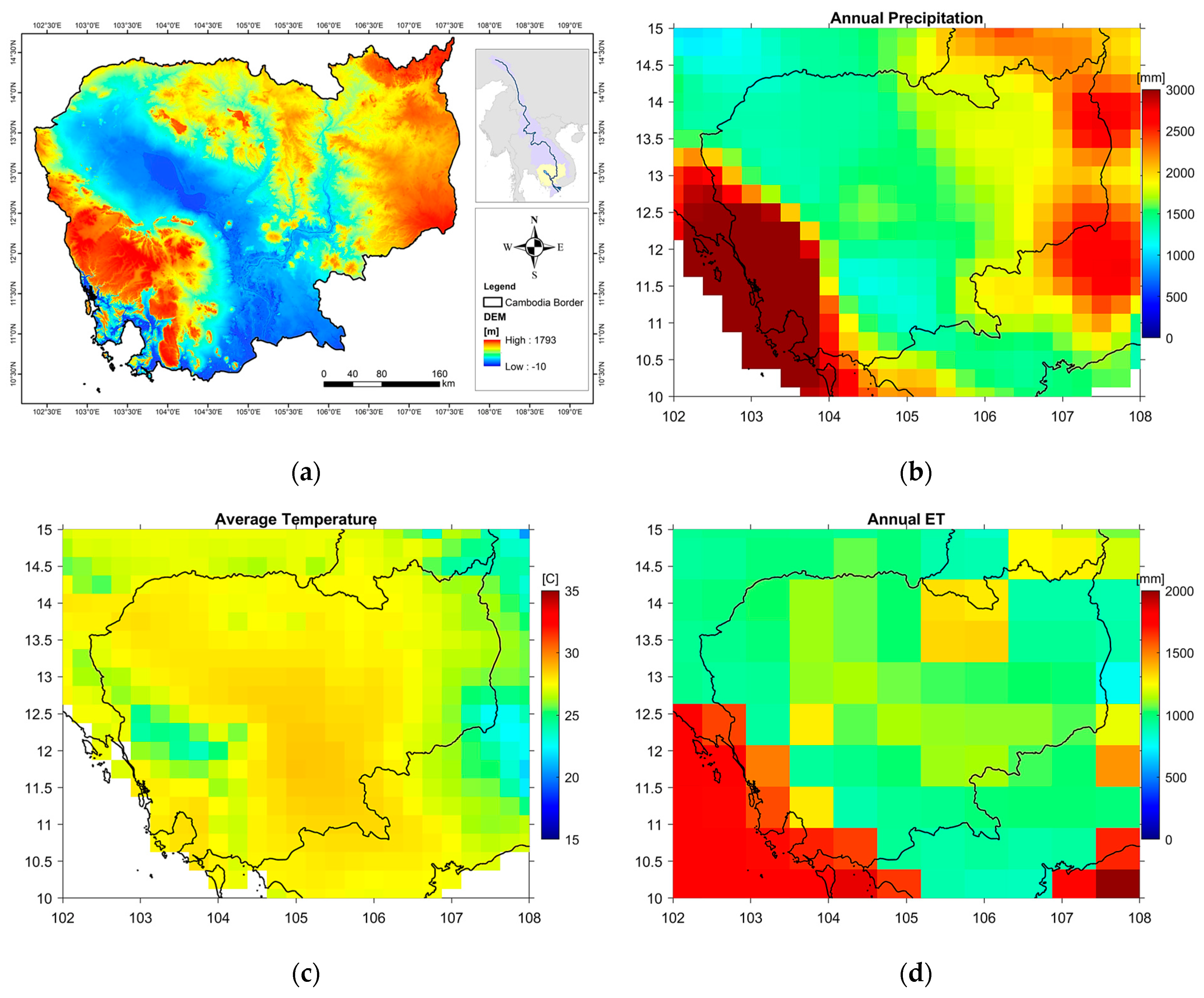
1.1. Cambodia and Natural Hazards
1.2. Flood Hazard and Its Impacts
2. Existing Studies on Flood Hazard and Management in Cambodia
3. Driving Factors on Flood in Cambodia
3.1. Climate Change
3.2. Water Infrastructure Development
3.3. Weather Extremes
3.4. Land-Use Change
4. Related Institutions and Efforts in Flood Management
5. Future Research Directions on Flood in Cambodia
5.1. Land Use/Land Cover
5.2. Water Infrastructure
5.3. Flood Forecasting
5.4. Flood Assessment and Surveys
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AHP | Analytic Hierarchy Process |
| APHRODITE | Asian Precipitation—Highly-Resolved Observational Data Integration Towards Evaluation |
| CNMC | Cambodia National Mekong Committee |
| CRC | Cambodian Red Cross |
| DEM | Digital Elevation Model |
| DRR | Disaster Risk Reduction |
| ENSO | El Niño-Southern Oscillation |
| ERA | European Centre for Medium-range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF) Reanalysis |
| EVI | Enhanced Vegetation Index |
| EWS | Early Warning System |
| FAO | Food and Agriculture Organization |
| GIS | Geographic Information System |
| GLDAS-NOAH | Global Land Data Assimilation System NOAH model |
| GRACE | Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment |
| HEC-RAS | Hydrological Engineering Center—River Analysis System |
| IFRC | International Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies |
| JRA-55 | Japanese 55-year Reanalysis |
| LMB | Lower Mekong Basin |
| LOADEST | LOAD ESTimator |
| LSWI | Land Surface Water Index |
| LUM | Linear Unmixing Model |
| MNDWI | Modified Normalized Difference Water Index |
| MODIS | Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer |
| MOWRAM | Ministry of Water Resources and Meteorology |
| MR | Mekong River |
| MRC | Mekong River Commission |
| NCDM | National Committee for Disaster Management |
| NDVI | Normalized Difference Vegetation Index |
| NGOs | Non-Governmental Organizations |
| PCR-GLOBWB | PCRaster GLOBal Water Balance |
| RF | Random Forests |
| RGC | Royal Government of Cambodia |
| ROC | Receiver Operating Characteristics |
| RRI | Rainfall-Runoff-Inundation |
| RS | Remote Sensing |
| SNAP | Strategic National Action Plan |
| SRTM | Shuttle Radar Topography Mission |
| SVM | Support Vector Machines |
| SWAT | Soil and Water Assessment Tool |
| T-SAS | Time-Space Accounting Scheme |
| TSL | Tonle Sap Lake |
| TSR | Tonle Sap River |
| UNDP | United Nations Development Programme |
| WFFI | Wavelet-based Filter for detecting spatio-temporal changes in Flood Inundation |
| WFP | World Food Programme |
References
- MoE. Cambodia Environment Outlook; Ministry of Environment: Phnom Penh, Cambodia, 2009; ISBN 978-974-300-197-0.
- Yatagai, A.; Kamiguchi, K.; Arakawa, O.; Hamada, A.; Yasutomi, N.; Kitoh, A. APHRODITE: Constructing a Long-Term Daily Gridded Precipitation Dataset for Asia Based on a Dense Network of Rain Gauges. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2012, 93, 1401–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasutomi, N.; Hamada, A.; Yatagai, A. Development of a Long-Term Daily Gridded Temperature Dataset and Its Application to Rain/Snow Discrimination of Daily Precipitation. Glob. Environ. Res. 2011, 15, 165–172. [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi, S.; Ota, Y.; Harada, Y.; Ebita, A.; Moriya, M.; Onoda, H.; Onogi, K.; Kamahori, H.; Kobayashi, C.; Endo, H.; et al. The JRA-55 Reanalysis: General Specifications and Basic Characteristics. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. 2015, 93, 5–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ADB; IHE Delft. Characterizing Water Supply and Demand in Cambodia’s River Basins; Asian Development Bank and IHE Delft Institute for Water Education: Metro Manila, Philippines, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Piman, T.; Lennaerts, T.; Southalack, P. Assessment of Hydrological Changes in the Lower Mekong Basin from Basin-Wide Development Scenarios. Hydrol. Process. 2013, 27, 2115–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uk, S.; Yoshimura, C.; Siev, S.; Try, S.; Yang, H.; Oeurng, C.; Li, S.; Hul, S. Tonle Sap Lake: Current Status and Important Research Directions for Environmental Management. Lakes Reserv. 2018, 23, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pekel, J.-F.; Cottam, A.; Gorelick, N.; Belward, A.S. High-Resolution Mapping of Global Surface Water and Its Long-Term Changes. Nature 2016, 540, 418–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO; RIMES. Managing Climate Change Risks for Food Security in Cambodia; Food and Agriculture Organization & Regional Integrated Multi-Hazard Early Warning System: Bangkok, Thailand, 2011; p. 23. [Google Scholar]
- UNDRR. Disaster Risk Reduction in Cambodia: Status Report 2019; United Nations Office for Disaster Risk Reduction: Bangkok, Thailand, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- NCDM; UNDP. Cambodia Disaster Loss and Damage Analysis Report 1996–2013; National Committee for Disaster Management & United Nations Development Programme: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014; p. 98. [Google Scholar]
- NCDM. National Action Plan for Disaster Risk Reduction (NAP-DRR) 2014–2018; National Committee for Disaster Management: Phnom Penh, Cambodia, 2013.
- KEI. Environmental Sustainability in Asia: Progress, Challenges and Opportunities in the Implementation of the Sustainable Development Goals, Series 2—Cambodia; Korea Environment Institute: Sejong, Korea, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- NCDM; MoP. Strategic National Action Plan for Disaster Risk Reduction 2008–2013; National Committee for Disaster Management & Ministry of Planning: Phnom Penh, Cambodia, 2008.
- MRC. Annual Mekong Flood Report 2011; Mekong River Commission: Vientiane, Laos, 2015; p. 72. [Google Scholar]
- JICA. Country Report Cambodia: Natural Disaster Risk Assessment and Area Business Continuity Plan Formulation for Industrial Agglomerated Areas in the ASEAN Region; Japan International Cooperation Agency: Tokyo, Japan, 2015.
- Ros, B.; Nang, P.; Chhim, C. Agricultural Development and Climate Change: The Case of Cambodia; Cambodia Development Resource Institute (CDRI): Phnom Penh, Cambodia, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- NCDM. Annual Report on Disaster Management Activities 2000; National Committee for Disaster Management: Phnom Penh, Cambodia, 2000.
- IFRC. Cambodia: Floods 2001 (Appeal No. 29/01); International Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies: Geneva, Switzerland, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- NCDM. Cambodia: Disaster Situation Report 01–17 August 2002; National Committee for Disaster Management: Phnom Penh, Cambodia, 2002.
- RGC. Cambodia–Post Ketsana Disaster Needs Assessment; National Committee for Disaster Management: Phnom Penh, Cambodia, 2010.
- ADB. Flood Damage Emergency Reconstruction: Preliminary Damage and Loss Assessment; Asian Development Bank: Mandaluyong, Philippines, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Cambodia HRF. Floods Humanitarian Response Forum (HRF) Final Report No. 07 (as of 07 December 2013); Cambodia Humanitarian Response Forum: Phnom Penh, Cambodia, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Cambodia HRF. Cambodia: Cambodia Disaster 2018 Humanitarian Response Forum (HRF) Report–No. 11 (as of August, 13 2018); Cambodia Humanitarian Response Forum: Phnom Penh, Cambodia, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Cambodia HRF. Situation Report No. 1–Floods in Cambodia (As of 20 September 2019); Cambodia Humanitarian Response Forum: Phnom Penh, Cambodia, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Cambodia HRF. Floods in Cambodia: Version 1.0–Situation Report No. 1–Humanitarian Response Forum, as of 12 October 2020; Cambodia Humanitarian Response Forum: Phnom Penh, Cambodia, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Cambodia HRF. Situation Report No. 6–Flood in Cambodia–Humanitarian Response Forum, as of 26 October 2020; Cambodia Humanitarian Response Forum: Phnom Penh, Cambodia, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Davies, G.; McIver, L.; Kim, Y.; Hashizume, M.; Iddings, S.; Chan, V. Water-Borne Diseases and Extreme Weather Events in Cambodia: Review of Impacts and Implications of Climate Change. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2014, 12, 191–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chantarat, S.; Oum, S.; Samphantharak, K.; Sann, V. Natural Disasters, Preferences, and Behaviors: Evidence from the 2011 Mega Flood in Cambodia. J. Asian Econ. 2019, 63, 44–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, A.K.; Bloch, R.; Lamond, J. Cities and Flooding: A Guide to Integrated Urban Flood Risk Management for the 21st Century; World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2012; ISBN 978-0-8213-8866-2. [Google Scholar]
- MRC. Working Paper 2011–2015: The Impact & Management of Floods & Droughts in the Lower Mekong Basin & the Implications of Possible Climate Change; Mekong River Commission: Vientiane, Laos, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Dutta, D.; Alam, J.; Umeda, K.; Hayashi, M.; Hironaka, S. A Two-Dimensional Hydrodynamic Model for Flood Inundation Simulation: A Case Study in the Lower Mekong River Basin. Hydrol. Process 2007, 21, 1223–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hai, P.T.; Masumoto, T.; Shimizu, K. Development of a Two-Dimensional Finite Element Model for Inundation Processes in the Tonle Sap and Its Environs. Hydrol. Process 2008, 22, 1329–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, V.; Tantanee, S.; Suparta, W. Gis-based flood hazard mapping using hec-ras model: A case study of lower Mekong River, Cambodia. Geogr. Tech. 2020, 15, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Koem, C.; Tantanee, S. Flood Disaster Studies: A Review of Remote Sensing Perspective in Cambodia. Geogr. Tech. 2021, 16, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, N.-T.; Chen, C.-F.; Chen, C.-R. Flood Assessment Using Multi-Temporal Remotely Sensed Data in Cambodia. Geocarto Int. 2019, 36, 1044–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tangdamrongsub, N.; Ditmar, P.G.; Steele-Dunne, S.C.; Gunter, B.C.; Sutanudjaja, E.H. Assessing Total Water Storage and Identifying Flood Events over Tonlé Sap Basin in Cambodia Using GRACE and MODIS Satellite Observations Combined with Hydrological Models. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 181, 162–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siev, S.; Paringit, E.; Yoshimura, C.; Hul, S. Seasonal Changes in the Inundation Area and Water Volume of the Tonle Sap River and Its Floodplain. Hydrology 2016, 3, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, S.; Takeuchi, J.; Fujihara, M.; Oeurng, C. Flood Damage Assessment on Rice Crop in the Stung Sen River Basin of Cambodia. Paddy Water Environ. 2019, 17, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanh Son, N.; Thi Thu Trang, N.; Bui, X.T.; Thi Da, C. Remote Sensing and GIS for Urbanization and Flood Risk Assessment in Phnom Penh, Cambodia. Geocarto Int. 2021, 37, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazarika, M.K.; Bormudoi, A.; Kafle, T.P.; Samarkoon, L.; Nuon, K.; Savuth, Y.; Narith, R. Flood Hazard Mapping in Four Provinces of Cambodia under the Mekong River Basin. In Proceedings of the 5th Annual Mekong Flood Forum, Ho Chi Minh, Vietnam, 17–18 May 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Ly, S.; Kim, L.; Demerre, S.; Heng, S. Flood Mapping along the Lower Mekong River in Cambodia. Eng. J. 2018, 22, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Try, S.; Tanaka, S.; Tanaka, K.; Sayama, T.; Khujanazarov, T.; Oeurng, C. Comparison of CMIP5 and CMIP6 GCM Performance for Flood Projections in the Mekong River Basin. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2022, 40, 101035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Try, S.; Tanaka, S.; Tanaka, K.; Sayama, T.; Hu, M.; Sok, T.; Oeurng, C. Projection of Extreme Flood Inundation in the Mekong River Basin under 4K Increasing Scenario Using Large Ensemble Climate Data. Hydrol. Processes 2020, 34, 4350–4364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Try, S.; Tanaka, S.; Tanaka, K.; Sayama, T.; Lee, G.; Oeurng, C. Assessing the Effects of Climate Change on Flood Inundation in the Lower Mekong Basin Using High-Resolution AGCM Outputs. Prog. Earth Planet Sci. 2020, 7, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Try, S.; Sayama, T.; Oeurng, C.; Sok, T.; Ly, S.; Uk, S. Identification of the Spatio-Temporal and Fluvial-Pluvial Sources of Flood Inundation in the Lower Mekong Basin. Geosci. Lett. 2022, 9, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, I.N.; Bolten, J.D.; Srinivasan, R.; Lakshmi, V. Satellite Observations and Modeling to Understand the Lower Mekong River Basin Streamflow Variability. J. Hydrol. 2018, 564, 559–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakamoto, T.; Van Nguyen, N.; Kotera, A.; Ohno, H.; Ishitsuka, N.; Yokozawa, M. Detecting Temporal Changes in the Extent of Annual Flooding within the Cambodia and the Vietnamese Mekong Delta from MODIS Time-Series Imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 109, 295–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Try, S.; Lee, G.; Yu, W.; Oeurng, C. Delineation of Flood-Prone Areas Using Geomorphological Approach in the Mekong River Basin. Quat. Int. 2019, 503, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sok, T.; Oeurng, C.; Kaing, V.; Sauvage, S.; Kondolf, G.M.; Sánchez-Pérez, J.M. Assessment of Suspended Sediment Load Variability in the Tonle Sap and Lower Mekong Rivers, Cambodia. CATENA 2021, 202, 105291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sok, T.; Oeurng, C.; Ich, I.; Sauvage, S.; Miguel Sánchez-Pérez, J. Assessment of Hydrology and Sediment Yield in the Mekong River Basin Using SWAT Model. Water 2020, 12, 3503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Try, S.; Tanaka, S.; Tanaka, K.; Sayama, T.; Oeurng, C.; Uk, S.; Takara, K.; Hu, M.; Han, D. Comparison of Gridded Precipitation Datasets for Rainfall-Runoff and Inundation Modeling in the Mekong River Basin. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0226814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Sohn, H.-G.; Kim, M.-K.; Lee, H. Analysis of the Relationship among Flood Severity, Precipitation, and Deforestation in the Tonle Sap Lake Area, Cambodia Using Multi-Sensor Approach. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2019, 23, 1330–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Kim, Y.; Lee, D.; Lee, G. Hydrological Assessment of Basin Development Scenarios: Impacts on the Tonle Sap Lake in Cambodia. Quat. Int. 2019, 503, 115–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oeurng, C.; Cochrane, T.A.; Chung, S.; Kondolf, M.G.; Piman, T.; Arias, M.E. Assessing Climate Change Impacts on River Flows in the Tonle Sap Lake Basin, Cambodia. Water 2019, 11, 618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vichet, N.; Kawamura, K.; Trong, D.P.; On, N.V.; Gong, Z.; Lim, J.; Khom, S.; Bunly, C. MODIS-Based Investigation of Flood Areas in Southern Cambodia from 2002–2013. Environments 2019, 6, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Xu, Z.; Chen, F.; Chen, F.; Zhang, L. Flood Hazard Mapping and Assessment on the Angkor World Heritage Site, Cambodia. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- RGC. Cambodia Climate Change Strategic Plan 2014–2023; Royal Government of Cambodia: Phnom Penh, Cambodia, 2013; p. 62.
- MRC. Adaptation to Climate Change in the Countries of the Lower Mekong Basin: Regional Synthesis Report; MRC Technical Paper No. 24; Mekong River Commission: Vientiane, Laos, 2009; p. 89. [Google Scholar]
- RGC. Climate Change Action Plan 2016–2018; Royal Government of Cambodia: Phnom Penh, Cambodia, 2016.
- Arias, M.E.; Cochrane, T.A.; Piman, T.; Kummu, M.; Caruso, B.S.; Killeen, T.J. Quantifying Changes in Flooding and Habitats in the Tonle Sap Lake (Cambodia) Caused by Water Infrastructure Development and Climate Change in the Mekong Basin. J. Environ. Manag. 2012, 112, 53–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siev, S.; Yang, H.; Sok, T.; Uk, S.; Song, L.; Kodikara, D.; Oeurng, C.; Hul, S.; Yoshimura, C. Sediment Dynamics in a Large Shallow Lake Characterized by Seasonal Flood Pulse in Southeast Asia. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 631–632, 597–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uk, S.; Yang, H.; Vouchlay, T.; Ty, S.; Sokly, S.; Sophal, T.; Chantha, O.; Chihiro, Y. Dynamics of Phosphorus Fractions and Bioavailability in a Large Shallow Tropical Lake Characterized by Monotonal Flood Pulse in Southeast Asia. J. Great Lakes Res. 2022, 48, 944–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WBG; ADB. Climate Risk Profile: Cambodia; The World Bank Group and Asian Development Bank: Mandaluyong, Philippines, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.; Siev, S.; Sovannara, U.; Yoshimura, C. Flood Pulse and Water Level. In Water and Life in Tonle Sap Lake; Yoshimura, C., Khanal, R., Sovannara, U., Eds.; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2022; pp. 101–109. ISBN 9789811666315. [Google Scholar]
- Shrestha, B.; Cochrane, T.A.; Caruso, B.S.; Arias, M.E.; Piman, T. Uncertainty in Flow and Sediment Projections Due to Future Climate Scenarios for the 3S Rivers in the Mekong Basin. J. Hydrol. 2016, 540, 1088–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ICEM. MRC Strategic Environmental Assessment (SEA) of Hydropower on the Mekong Mainstream: Summary of the Final Report; International Centre for Environmental Management: Hanoi, Vietnam, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Kann, V. Thousands of Cambodians Displaced After Laos Dam Collapse. Available online: https://www.voacambodia.com/a/thousands-of-cambodians-displaced-after-laos-dam-collapse/4503890.html#:~:text=Thousands%20of%20residents%20in%20northern,Nam%20Noy%20Dam%20on%20Monday (accessed on 3 October 2021).
- Sok, S.; Chhinh, N.; Hor, S.; Nguonphan, P. Climate Change Impacts on Rice Cultivation: A Comparative Study of the Tonle Sap and Mekong River. Sustainability 2021, 13, 8979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baird, I.G. Catastrophic and Slow Violence: Thinking about the Impacts of the Xe Pian Xe Namnoy Dam in Southern Laos. J. Peasant Stud. 2021, 48, 1167–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sithirith, M. Downstream State and Water Security in the Mekong Region: A Case of Cambodia between Too Much and Too Little Water. Water 2021, 13, 802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, T.; Cochrane, T.; Arias, M.E.; Van, T.P.D.; Vries, T.T.D. Analysis of Water Level Changes in the Mekong Floodplain Impacted by Flood Prevention System and Upstream Dams. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Association for Hydro-Environment Engineering and Research World Congress (IAHR), Hague, The Netherlands, 28 June–3 July 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Collentine, D.; Futter, M.N. Realising the Potential of Natural Water Retention Measures in Catchment Flood Management: Trade-Offs and Matching Interests: Realising the Potential of Natural Water Retention Measures. J. Flood Risk Manag. 2018, 11, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thoms, M.C. Floodplain–River Ecosystems: Lateral Connections and the Implications of Human Interference. Geomorphology 2003, 56, 335–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, P.J.; Kummu, M.; Lall, U. Flood Frequencies and Durations and Their Response to El Niño Southern Oscillation: Global Analysis. J. Hydrol. 2016, 539, 358–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabeya, N.; Shimizu, A.; Shimizu, T.; Iida, S.; Tamai, K.; Miyamoto, A.; Chann, S.; Araki, M.; Ohnuki, Y. Long-Term Hydrological Observations in a Lowland Dry Evergreen Forest Catchment Area of the Lower Mekong River, Cambodia. Jpn. Agric. Res. Q. 2021, 55, 177–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton, W.R.; Srivastava, J.P.; Koo, J.; Vasileiou, I.; Pradesha, A. Striking a Balance: Managing El Niño and La Niña in Cambodia’s Agriculture; World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Cosslett, T.L.; Cosslett, P.D. The Lower Mekong Basin: Rice Production, Climate Change, ENSO, and Mekong Dams. In Sustainable Development of Rice and Water Resources in Mainland Southeast Asia and Mekong River Basin; Springer: Singapore, 2018; pp. 85–114. ISBN 978-981-10-5612-3. [Google Scholar]
- Saghafian, B.; Farazjoo, H.; Bozorgy, B.; Yazdandoost, F. Flood Intensification Due to Changes in Land Use. Water Resour. Manage. 2008, 22, 1051–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nut, N.; Mihara, M.; Jeong, J.; Ngo, B.; Sigua, G.; Prasad, P.V.V.; Reyes, M.R. Land Use and Land Cover Changes and Its Impact on Soil Erosion in Stung Sangkae Catchment of Cambodia. Sustainability 2021, 13, 9276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sourn, T.; Pok, S.; Chou, P.; Nut, N.; Theng, D.; Rath, P.; Reyes, M.R.; Prasad, P.V.V. Evaluation of Land Use and Land Cover Change and Its Drivers in Battambang Province, Cambodia from 1998 to 2018. Sustainability 2021, 13, 11170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, L.H. Country Report of Cambodia Disaster Management; Asian Disaster Reduction Center: Kobe, Japan, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- CFE-DM. Cambodia: Disaster Management Reference Handbook, Ford Island: Center for Excellence in Disaster Management and Humanitarian Assistance; Center for Excellence in Disaster Management and Humanitarian Assistance: Ford Island, HI, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Law on Water Resources Management of the Kingdom of Cambodia 2007. Available online: https://ppp.worldbank.org/public-private-partnership/library/law-water-resources-management-kingdom-cambodia (accessed on 3 October 2021).
- Apollonio, C.; Balacco, G.; Novelli, A.; Tarantino, E.; Piccinni, A. Land Use Change Impact on Flooding Areas: The Case Study of Cervaro Basin (Italy). Sustainability 2016, 8, 996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Feng, P.; Chen, F. Effects of Land Use Change on Flood Characteristics in Mountainous Area of Daqinghe Watershed, China. Nat. Hazards 2014, 70, 593–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, R.; Basnayake, S.; Ahmed, A.K. Assessing Gaps and Strengthening Early Warning System to Manage Disasters in Cambodia. J. Integr. Disaster Risk Manag. 2015, 5, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ming, X.; Liang, Q.; Xia, X.; Li, D.; Fowler, H.J. Real-Time Flood Forecasting Based on a High-Performance 2-D Hydrodynamic Model and Numerical Weather Predictions. Water Resour. Res. 2020, 56, e2019WR025583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ab Razak, N.H.; Aris, A.Z.; Ramli, M.F.; Looi, L.J.; Juahir, H. Temporal Flood Incidence Forecasting for Segamat River (Malaysia) Using Autoregressive Integrated Moving Average Modelling. J. Flood Risk Manag. 2018, 11, S794–S804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Emerton, R.; Duan, Q.; Wood, A.W.; Wetterhall, F.; Robertson, D.E. Ensemble Flood Forecasting: Current Status and Future Opportunities. WIREs Water 2020, 7, e1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosavi, A.; Ozturk, P.; Chau, K. Flood Prediction Using Machine Learning Models: Literature Review. Water 2018, 10, 1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampurno, J.; Vallaeys, V.; Ardianto, R.; Hanert, E. Integrated Hydrodynamic and Machine Learning Models for Compound Flooding Prediction in a Data-Scarce Estuarine Delta. Nonlinear Processes Geophys. Discuss. 2022, 29, 301–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koem, C.; Tantanee, S. Flash Flood Hazard Mapping Based on AHP with GIS and Satellite Information in Kampong Speu Province, Cambodia. Int. J. Disaster Resil. Built Environ. 2021, 12, 457–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha Anh, H.; Da Hanh, T.M.; Thi Tuong Vi, N.; Shunbo, Y. Examining the Interaction of Flood Vulnerability Determinants in Cambodia and Vietnam Using Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modeling. Water Policy 2018, 20, 1256–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okazumi, T.; Tanaka, S.; Kwak, Y.; Shrestha, B.B.; Sugiura, A. Flood Vulnerability Assessment in the Light of Rice Cultivation Characteristics in Mekong River Flood Plain in Cambodia. Paddy Water Environ. 2014, 12, 275–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heng, S.; Ly, S.; Chhem, S.; Kruy, P. Analysis of Public Perceptions on Urban Flood in Phnom Penh, Cambodia. In Water Security in Asia; Babel, M., Haarstrick, A., Ribbe, L., Shinde, V.R., Dichtl, N., Eds.; Springer Water; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 687–701. ISBN 978-3-319-54611-7. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, M. Options in Flood Management and Mitigation: Findings of the FAO TCP Project. In Flood Management and Mitigation in the Mekong River Basin; FAO RAP Publication 1999/14; Food and Agriculture Organization: Bangkok, Thailand, 1999. [Google Scholar]

| Area | Method | Focus | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lower Mekong Basin | HEC-RAS model and AHP method | Flood hazard mapping and flood frequency | [34,41] |
| HEC-RAS model | Flood map | [42] | |
| RRI model | Flood inundation and climate change | [43,44,45] | |
| RRI model and T-SAS method | Hydrograph separation and fluvial-pluvial flood | [46] | |
| SWAT model | Streamflow variability | [47] | |
| Mekong River Basin | EVI or NDVI LSWI WFFI | Temporal change in annual flood | [48] |
| Linear binary classifier and ROC analysis | Flood hazard mapping | [49] | |
| LOADEST method | Sediment load variability | [50] | |
| SWAT model | Hydrology and sediment yield | [51] | |
| RRI model | Evaluation of gridded rainfall products | [52] | |
| Tonle Sap River Basin | NDVI index | Seasonal changes in inundation area and water volume | [38] |
| Regression Monte Carlo simulation | Relationship between flood, precipitation, and deforestation | [53] | |
| GLDAS-NOAH ERA PCR-GLOBWB | Water storage and flood identification | [37] | |
| CAESAR-LISFLOOD model | Hydrological impacts on Tonle Sap Lake | [54] | |
| Tonle Sap tributaries | SWAT model | Climate change and extreme flow | [55] |
| RRI model | Rice crop damage | [39] | |
| Whole Cambodia | NDVI Comparison Probability of flood | Multi-temporal flood mapping | [36] |
| Southern Cambodia, Along the Mekong | WFFI MNDWI | Spatiotemporal flood inundation and land cover change | [56] |
| Angkor Wat site | AHP | Flood hazard zonation map | [57] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Phy, S.R.; Sok, T.; Try, S.; Chan, R.; Uk, S.; Hen, C.; Oeurng, C. Flood Hazard and Management in Cambodia: A Review of Activities, Knowledge Gaps, and Research Direction. Climate 2022, 10, 162. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli10110162
Phy SR, Sok T, Try S, Chan R, Uk S, Hen C, Oeurng C. Flood Hazard and Management in Cambodia: A Review of Activities, Knowledge Gaps, and Research Direction. Climate. 2022; 10(11):162. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli10110162
Chicago/Turabian StylePhy, Sophea Rom, Ty Sok, Sophal Try, Ratboren Chan, Sovannara Uk, Chhordaneath Hen, and Chantha Oeurng. 2022. "Flood Hazard and Management in Cambodia: A Review of Activities, Knowledge Gaps, and Research Direction" Climate 10, no. 11: 162. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli10110162
APA StylePhy, S. R., Sok, T., Try, S., Chan, R., Uk, S., Hen, C., & Oeurng, C. (2022). Flood Hazard and Management in Cambodia: A Review of Activities, Knowledge Gaps, and Research Direction. Climate, 10(11), 162. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli10110162









