Risks to the Health of Russian Population from Floods and Droughts in 2010–2020: A Scoping Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
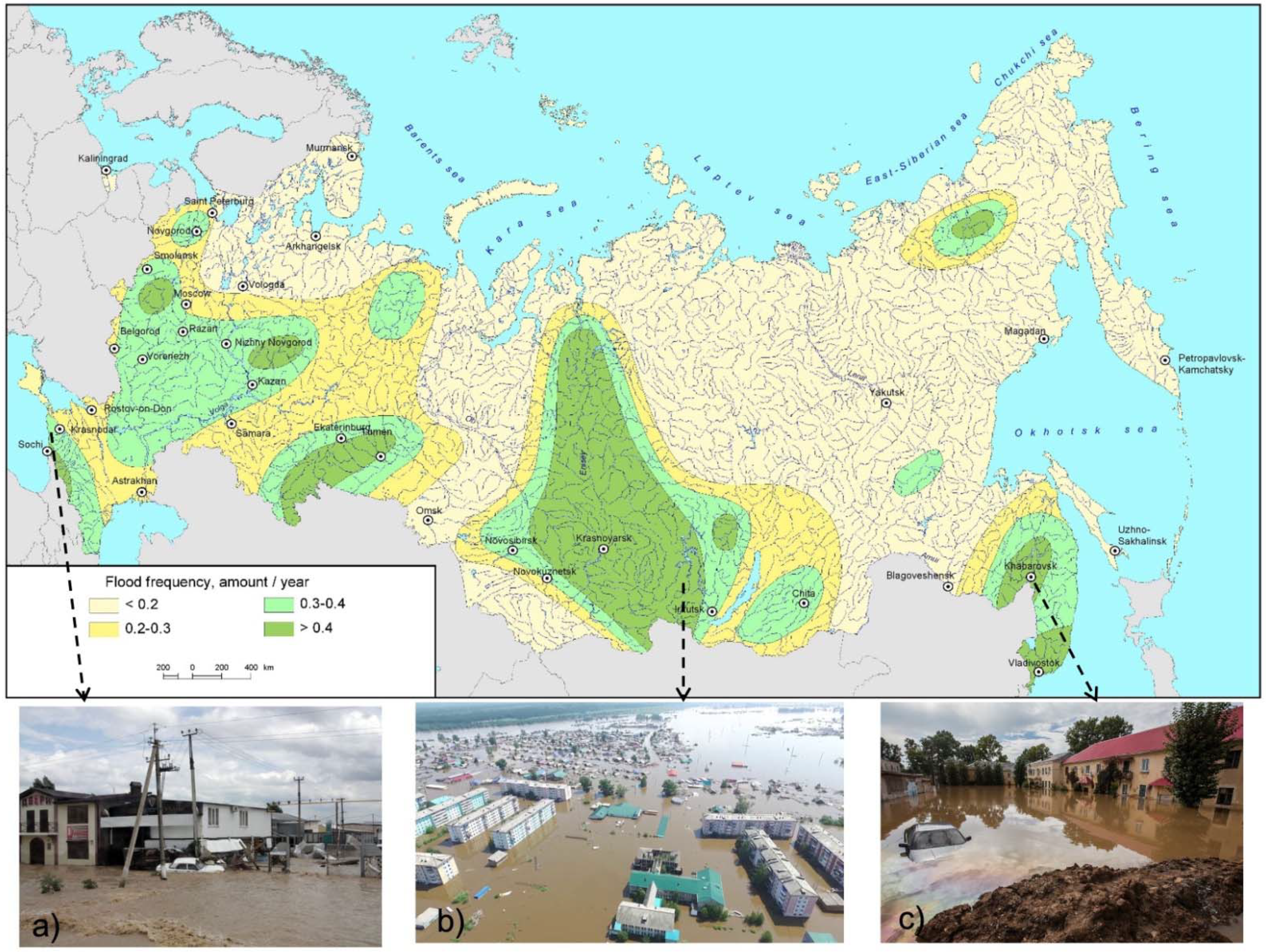
3.1. Floods in Russia
3.2. Droughts in Russia
4. Concluding Comments
4.1. Floods, Mental Health and Social Outcomes
4.2. Mitigation of Flood Risk: Problems and Solutions
4.3. Droughts, Drinking Water and Public Health Preparedness
4.4. Floods and Droughts: Noah and Joseph Effects
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alderman, K.; Turner, L.R.; Tong, S. Floods and Human Health: A Systematic Review. Environ. Int. 2012, 47, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bykov, A.A.; Bashkin, V.N. On Extreme Natural Phenomena and Assessment of Natural and Environmental Risks. Issues Risk Anal. 2018, 15, 4–5. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokolov, Y.I. Risks of Extreme Weather Events. Issues Risk Anal. 2018, 15, 6–21. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banwell, N.; Rutherford, S.; Mackey, B.; Street, R.; Chu, C. Commonalities between Disaster and Climate Change Risks for Health: A Theoretical Framework. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Alwis, D.; Noy, I. The Cost of Being Under the Weather: Droughts, Floods, and Health-Care Costs in Sri Lanka. Asian Dev. Rev. 2019, 36, 185–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebi, K.L.; Vanos, J.; Baldwin, J.W.; Bell, J.E.; Hondula, D.M.; Errett, N.A.; Hayes, K.; Reid, C.E.; Saha, S.; Spector, J.; et al. Extreme Weather and Climate Change: Population Health and Health System Implications. Annu. Rev. Public Health 2021, 42, 293–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grigorieva, E.A.; Revich, B.A. Health Risks to the Russian Population from Temperature Extremes at the Beginning of the XXI Century. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC. IPCC, Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Sixth Assessment Report Fact. Sheet. 2021. Available online: https://www.ipcc.ch/site/assets/uploads/2021/06/fact_sheet_ar6.pdf (accessed on 30 January 2022).
- Yusa, A.; Berry, P.; Cheng, J.; Ogden, N.; Bonsal, B.; Stewart, R.; Waldick, R. Climate Change, Drought and Human Health in Canada. IJERPH 2015, 12, 8359–8412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, R.; Kuriqi, A.; Kisi, O. Human–Environment Natural Disasters Interconnection in China: A Review. Climate 2020, 8, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saborío-Rodríguez, M.; Alpízar, F.; Aguilar-Solano, L.; Martínez-Rodríguez, M.R.; Vignola, R.; Viguera, B.; Harvey, C.A. Perceptions of Extreme Weather Events and Adaptation Decisions: A Case Study of Maize and Bean Farmers in Guatemala and Honduras. In Extreme Events and Climate Change; Castillo, F., Wehner, M., Stone, D.A., Eds.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 89–106. [Google Scholar]
- Şen, Z. Noah and Joseph Effects: Floods and Droughts under Global Warming. Int. J. Glob. Warm. 2018, 16, 347–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, M.A.R.; Renaud, F.G.; Anderson, C.C.; Wild, A.; Domeneghetti, A.; Polderman, A.; Votsis, A.; Pulvirenti, B.; Basu, B.; Thomson, C.; et al. A Review of Hydro-Meteorological Hazard, Vulnerability, and Risk Assessment Frameworks and Indicators in the Context of Nature-Based Solutions. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2020, 50, 101728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, B.A. The Organizational and Interorganizational Development of Disasters. Adm. Sci. Q. 1976, 21, 378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, D. Natural Disasters. Springer Science & Business Media; Kluwer Academic Publisher: London, UK, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- UNISDR. Terminology on Disaster Risk Reduction; United Nations International Strategy for Disaster Reduction: Geneva, Switzerland, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Guha-Sapir, D.; Vos, F.; Below, R.; Ponserre, S. Annual Disaster Statistical Review 2011: The Numbers and Trends; Centre for Research on the Epidemiology of Disasters (CRED): Brussels, Belgium, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- WHO World Health Organization. Flooding: Managing Health Risks in the WHO European Region. 2017. Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/329518/9789289052795-eng.pdf?sequence=1&isallowed=y (accessed on 23 February 2022).
- Dobrovolsky, S.G.; Istomina, M.N.; Pasechkina, V.Y. Changes in the Natural Parameters of Extreme Hydrological Phenomena in Russia and in the World and the Damage Caused by Them: Floods and Droughts. Issues Geogr. 2018, 145, 183–193. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Dobrovolsky, S.G.; Istomina, M.N.; Lebedeva, I.P.; Solomonova, I.V. The Main Regions of Droughts and Floods in the World: Natural Parameters, Damage Characteristics, Dynamics Features, Identification Using the SPEI Index. In Improvement of Russian Rivers: Scientific Problems and Ways to Solve Them. Collection of Scientific Papers; Studia F1: Nizhny Novgorod, Russia, 2019; pp. 46–51. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Fasihi, S.; Lim, W.Z.; Wu, W.; Proverbs, D. Systematic Review of Flood and Drought Literature Based on Science Mapping and Content Analysis. Water 2021, 13, 2788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, P.J.; de Ruiter, M.C.; Mard, J.; Schröter, K.; van Loon, A.; Veldkamp, T.; von Uexkull, N.; Wanders, N.; AghaKouchak, A.; Arnbjerg-Nielsen, K.; et al. The Need to Integrate Flood and Drought Disaster Risk Reduction Strategies. Water Secur. 2020, 11, 100070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunner, M.I.; Slater, L.; Tallaksen, L.M.; Clark, M. Challenges in Modeling and Predicting Floods and Droughts: A Review. WIREs Water 2021, 8, e1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EM-DAT. Human Cost of Disasters. An Overview of the Last 20 Years 2000-2019. Brussels Centre for Research on the Epidemiology of Disasters (CRED), UNDRR. 2020. Available online: http://www.emdat.be/database (accessed on 15 January 2022).
- Jonkman, S.N. Global Perspectives on Loss of Human Life Caused by Floods. Nat. Hazards 2005, 34, 151–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razumov, V.V.; Kachanov, S.A.; Razumova, N.V. Scales and Danger of Floods in the Regions of Russia; FC VNII GOChS Emercom of Russia: Moscow, Russia, 2018. (In Russan) [Google Scholar]
- Hu, P.; Zhang, Q.; Shi, P.; Chen, B.; Fang, J. Flood-Induced Mortality across the Globe: Spatiotemporal Pattern and Influencing Factors. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 643, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FEMA (Federal Emergency Management Agency). Glossary. Terms Frequently Used by FEMA, 2022. Available online: https://www.fema.gov/about/glossary (accessed on 23 February 2022).
- Ward, D.R. Water Wars: Drought, Flood, Folly, and the Politics of Thirst; Penguin: New York, NY, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Lo, S.S. Glossary of Hydrology; Water Resources Publications: Littleton, CO, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Carter, R. Flood Risk, Insurance and Emergency Management in Australia; Australian Institute for Disaster Resilience: Melbourne, Australia, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Hirabayashi, Y.; Mahendran, R.; Koirala, S.; Konoshima, L.; Yamazaki, D.; Watanabe, S.; Kim, H.; Kanae, S. Global Flood Risk under Climate Change. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2013, 3, 816–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundzewicz, Z.W.; Kanae, S.; Seneviratne, S.I.; Handmer, J.; Nicholls, N.; Peduzzi, P.; Mechler, R.; Bouwer, L.M.; Arnell, N.; Mach, K.; et al. Flood Risk and Climate Change: Global and Regional Perspectives. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2014, 59, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danilov-Danilyan, V.I.; Gelfan, A.N. Catastrophe of National Scale. Sci. Life 2014, 1, 32–39. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Kononova, N.K. Changes in the Nature of Atmospheric Circulation-the Reason for the Increase in the Frequency of Extremes. Scientific notes of the Crimean Federal University named after V.I. Vernadsky. Geogr. Geol. 2017, 3, 174–191. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Vinober, A.V. Natural and Anthropogenic Causes of Flooding in the Irkutsk Region in 2019. Biosph. Econ. Theory Pract. 2019, 5, 41–48. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Revich, B.A.; Maleev, V.V.; Smirnova, M.D. Climate Change and Health: Estimates, Indicators, Forecasts; Revich, B.A., Kokorin, A.O., Eds.; World Health Organization: Moscow, Russia, 2019. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Fowler, H.J.; Lenderink, G.; Prein, A.F.; Westra, S.; Allan, R.P.; Ban, N.; Barbero, R.; Berg, P.; Blenkinsop, S.; Do, H.X.; et al. Anthropogenic Intensification of Short-Duration Rainfall Extremes. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2021, 2, 107–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, J.W.; Evans, E.P.; Penning-Rowsell, E.C. Quantified Scenarios Analysis of Drivers and Impacts of Changing Flood Risk in England and Wales: 2030-2100. Glob. Environ. Chang. Part B Environ. Hazards 2003, 5, 51–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigi, V.; Comino, E.; Fontana, M.; Pezzoli, A.; Rosso, M. Flood Vulnerability Analysis in Urban Context: A Socioeconomic Sub-Indicators Overview. Climate 2021, 9, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alekseevsky, N.I.; Magritsky, D.V.; Koltermann, P.K.; Toropov, P.A.; Shkolny, D.I.; Belyakova, P.A. Floods on the Black Sea Coast of the Krasnodarsky Krai. Water Resour. 2016, 43, 3–17. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonov, E.A.; Nikitina, O.I.; Osipov, P.E.; Egidarev, E.; Shalikovsky, A. We and the Amur Floods: Lessons (Un)Learned? Shalikovsky, A.V., Ed.; World Wildlife Fund (WWF): Moscow, Russia, 2016. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- McMichael, A.J.; Woodruff, R.E.; Hales, S. Climate Change and Human Health: Present and Future Risks. Lancet 2006, 367, 859–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, W.; FitzGerald, G.J.; Clark, M.; Hou, X.-Y. Health Impacts of Floods. Prehosp Disaster Med. 2010, 25, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zolotokrylin, A.N.; Vinogradova, V.V.; Glezer, O.B. (Eds.) Natural and Climatic Conditions and Sociogeographical Space of Russia; Institute of Geography, RAS: Moscow, Russia, 2018. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Diaz, J.H. The Public Health Impact of Hurricanes and Major Flooding. J. La. State Med. Soc. 2004, 156, 145–150. [Google Scholar]
- Lowe, D.; Ebi, K.; Forsberg, B. Factors Increasing Vulnerability to Health Effects before, during and after Floods. IJERPH 2013, 10, 7015–7067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ligon, B.L. Infectious Diseases That Pose Specific Challenges After Natural Disasters: A Review. Semin. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. 2006, 17, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shokri, A.; Sabzevari, S.; Hashemi, S.A. Impacts of Flood on Health of Iranian Population: Infectious Diseases with an Emphasis on Parasitic Infections. Parasite Epidemiol. Control 2020, 9, e00144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Flooding and Communicable Diseases Fact Sheet. 2021. Available online: http://www.who.int/hac/techguidance/ems/flood_cds/en/ (accessed on 27 January 2022).
- Johanning, E.; Auger, P.; Morey, P.R.; Yang, C.S.; Olmsted, E. Review of Health Hazards and Prevention Measures for Response and Recovery Workers and Volunteers after Natural Disasters, Flooding, and Water Damage: Mold and Dampness. Environ. Health Prev. Med. 2014, 19, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grigorieva, E.A.; Suprun, E.N. Climate and Children with Bronchial Asthma: Case Study for the Russian Far East. Reg. Probl. 2018, 21, 26–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorobyov, Y.L.; Akimov, V.A.; Sokolov, Y.I. Catastrophic Floods at the Beginning of the XXI Century: Lessons and Conclusions; Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Developmen: Moscow, Russia, 2003. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Mason, V.; Andrews, H.; Upton, D. The Psychological Impact of Exposure to Floods. Psychol. Health Med. 2010, 15, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greene, G.; Paranjothy, S.; Palmer, S.R. Resilience and Vulnerability to the Psychological Harm from Flooding: The Role of Social Cohesion. Am. J. Public Health 2015, 105, 1792–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalashnikov, D.I.; Portnova, A.A.; Shport, S.V. Remote Consequences of the Flood in Krymsk for the Mental Health of the Affected Population. Public Mental Health: Present and Future. In Proceedings of the VI National Congress on Social Psychiatry and Narcology, Moscow, Russia, 7–8 October 2016; p. 150. (In Russian). [Google Scholar]
- Sokolova, Y.A. The Reaction of Rural Residents to a Long-Term Extreme Situation. Extreme natural events: Problems factors, consequences. In Proceedings of the International Scientific and Practical Internet Conference, Kharkiv, Ukraine, 4–6 October 2016; pp. 130–138. (In Russian). [Google Scholar]
- Simonovic, S.P.; Kundzewicz, Z.W.; Wright, N. Floods and the COVID-19 Pandemic—A New Double Hazard Problem. WIREs Water 2021, 8, e1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rufat, S.; Tate, E.; Burton, C.G.; Maroof, A.S. Social Vulnerability to Floods: Review of Case Studies and Implications for Measurement. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2015, 14, 470–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinet, F.; Boissier, L.; Saint-Martin, C. Flashflood-Related Mortality in Southern France: First Results from a New Database. E3S Web Conf. 2016, 7, 06001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Runkle, J.D.; Brock-Martin, A.; Karmaus, W.; Svendsen, E.R. Secondary Surge Capacity: A Framework for Understanding Long-Term Access to Primary Care for Medically Vulnerable Populations in Disaster Recovery. Am. J. Public Health 2012, 102, e24–e32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadiq, A.-A.; Tyler, J.; Noonan, D.S. A Review of Community Flood Risk Management Studies in the United States. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2019, 41, 101327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nofal, O.M.; van de Lindt, J.W. Understanding Flood Risk in the Context of Community Resilience Modeling for the Built Environment: Research Needs and Trends. Sustain. Resilient Infrastruct. 2020, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Mooty, M.N.; Yosri, A.; El-Dakhakhni, W.; Coulibaly, P. Community Flood Resilience Categorization Framework. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2021, 61, 102349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedritsky, A.I. (Ed.) Russian Hydrometeorological Encyclopedia; Letny Sad: St. Petersburg, Russia; Moscow, Russia, 2008; Volume 1: A‒I. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Ebi, K.L.; Bowen, K. Extreme Events as Sources of Health Vulnerability: Drought as an Example. Weather Clim. Extrem. 2016, 11, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvador, C.; Nieto, R.; Linares, C.; Díaz, J.; Gimeno, L. Effects of Droughts on Health: Diagnosis, Repercussion, and Adaptation in Vulnerable Regions under Climate Change. Challenges for Future Research. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 703, 134912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petkova, E.P.; Celovsky, A.S.; Tsai, W.-Y.; Eisenman, D.P. Mental Health Impacts of Droughts: Lessons for the U.S. from Australia. In Climate Change Adaptation in North America; Leal Filho, W., Keenan, J.M., Eds.; Climate Change Management; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 289–304. [Google Scholar]
- Stanke, C.; Kerac, M.; Prudhomme, C.; Medlock, J.; Murray, V. Health Effects of Drought: A Systematic Review of the Evidence. PLoS Curr. 2013, 5, ecurrents.dis.7a2cee9e980f91ad7697b570bcc4b004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomina, O.N.; Bushueva, I.S.; Dolgova, E.A.; Zolotokrilin, A.N.; Kuznetsova, V.V.; Kuznetsova, T.O.; Kukhta, A.E.; Lazukova, L.I.; Lomakin, N.A.; Matskovsky, V.V.; et al. Droughts of the East European Plain According to Hydrometeorological and Dendrochronological Data; Nestor-Istoriya: Moscow, Russia; St. Petersburg, Russia, 2017. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Berman, J.D.; Ebisu, K.; Peng, R.D.; Dominici, F.; Bell, M.L. Drought and the Risk of Hospital Admissions and Mortality in Older Adults in Western USA from 2000 to 2013: A Retrospective Study. Lancet Planet Health 2017, 1, e17–e25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sena, A.; Ebi, K.L.; Freitas, C.; Corvalan, C.; Barcellos, C. Indicators to Measure Risk of Disaster Associated with Drought: Implications for the Health Sector. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0181394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, A.L.; Savin, I.Y.; Stolbovoy, V.S.; Dukhanin, A.Y.; Kozlov, D.N.; Bamatov, I.M. Global Climate and Soil Cover in Russia: Assessment of Risks and Ecological and Economic Consequences of Land Degradation. Adaptive Systems and Technologies for Environmental Management: (Agriculture and Forestry): National Report; Bedritsky, A.I., Ed.; Soil Institute Named after V. V. Dokuchaev, GEOS: Moscow, Russia, 2018; p. 286. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Gu, L.; Chen, J.; Yin, J.; Sullivan, S.C.; Wang, H.-M.; Guo, S.; Zhang, L.; Kim, J.-S. Projected Increases in Magnitude and Socioeconomic Exposure of Global Droughts in 1.5 and 2 °C Warmer Climates. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2020, 24, 451–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zolotokrylin, A.N.; Cherenkova, E.A.; Titkova, T.B. Aridization of Arid Lands of the European Part of Russia and Connection with Droughts. News Russ. Acad. Sci. Ser. Geogr. 2020, 2, 207–217. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Kuzmin, S.B. Natural Disasters in the Russian Federation. Issues Risk Anal. 2019, 16, 10–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asmus, V.V.; Ioffe, G.M.; Kramareva, L.S.; Krovotyntsev, V.A.; Milekhin, O.E.; Solov’eva, I.A. Satellite Monitoring of Natural Hazards on the Territory of Russia. Russ. Meteorol. Hydrol. 2019, 44, 719–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roshydromet (2014) Second Roshydromet Assessment Report on Climate Change and Its Consequences in the Russian Federation: General Summary. Available online: http://downloads.igce.ru/publications/od_2_2014/v2014/pdf/resume_ob_eng.pdf (accessed on 23 February 2022).
- Dobroumov, B.M.; Tumanovskaya, S.M. Floods on the Rivers of Russia: Their Formation and Zoning. Meteorol. Hydrol. 2002, 12, 70–78. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Koronkevich, N.I.; Barabanova, E.A.; Zaitseva, I.S. (Eds.) Extreme Hydrological Situations; Geological Survey: Moscow, Russia, 2010. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Dobrovolsky, S.G.; Istomina, M.N. On the Development of the Concept of “Damage Management” from Floods in the Russian Federation. Civ. Saf. Strategy Probl. Res. 2016, 6, 30–36. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Kattsov, V.M.; Porfiriev, B.N. (Eds.) Report on the Scientific and Methodological Basis for the Development of Strategies for Adaptation to Climate Change in the Russian Federation (in the Area of Competence of Roshydromet); Amirit: St. Petersburg, Russia; Saratov, Russia, 2020. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Shalikovsky, A.V.; Lepikhin, A.P.; Tiunov, A.A.; Kurganovich, K.A.; Morozov, M.G. The 2019 Floods in Irkutsk Region. Water Sect. Russ. 2019, 6, 48–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kichigina, N.V. Flood Hazard Within the Basins of the Left Tributaries of the Angara. Geogr. Nat. Resour. 2020, 41, 344–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlov, E.A.; Chernov, K.A. Results of Emergency Recovery Work and Analysis of Medical Support during the Flood Elimination in the Territory of the Irkutsk Region by the Airmobile Group of the Tula Rescue Center of EMERCOM of Russia (6–15 July 2019). Med.-Biol. Soc.-Psihol. Probl. Bezop. Črezvyčajnyh Situac. 2019, 3, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Porfiriev, B.N. Economic Consequences of the Catastrophic Flood in the Far East in 2013. Reg. Econ. Sociol. 2015, 3, 257–272. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A Contractor Who Died in a Flood in the Far Eastern Federal District Will Be Presented with an Award. RIA Novosti. 5 September 2013. Available online: https://ria.ru/20130905/961110122.html (accessed on 15 January 2022). (In Russian).
- Makhinov, A.N.; Kim, V.I. Influence of Climate Changes on the Hydrological Regime of the Amur River. Pac. Geogr. 2020, 1, 30–39. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolgov, S.V.; Shaporenko, S.I. On the Geographical and Hydrographic Prerequisites for the Formation of Floods and Their Consequences in the North-West Caucasus. Probl. Reg. Ecol. 2018, 2, 84–90. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondarev, V.P.; Bolkhovitinova, Y.A. Social Consequences of Catastrophic Floods. Bull. Mosc. Univ. Ser. 5 Geogr. 2019, 5, 21–29. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Kosachev, A. Flood in the Altai Krai. Engineering Protection in Russia. 2014. 3 (July–August). Available online: https://territoryengineering.ru/vyzov/navodnenie-v-altajskom-krae/ (accessed on 15 January 2022). (In Russian).
- Nefedkin, V. Flood-2014 and Flood of 2018: How the Altai Krai Was Flooded. Arguments and Facts 30 March 2018. Available online: https://altai.aif.ru/society/navodnenie-2014_i_pavodok_2018_godov_kak_topilo_altayskiy_kray (accessed on 15 January 2022). (In Russian).
- Nigmetov, G.M.; Larionov, V.I.; Filatov, Y.A.; Pchelkin, V.I.; Ulyanov, S.V.; Sorogin, A.A.; Yuzbekov, N.S. Zoning of the the Russian Federation According to the Magnitude of the Risk from Floods. Technol. Civ. Secur. 2003, 1, 30–36. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- MESRF (Ministry of Emergency Situations of the Russian Federation). Available online: https://www.mchs.gov.ru/ (accessed on 27 December 2018).
- Anoshkin, A.V.; Egidarev, E.G.; Fetisov, D.M.; Grigorieva, E.A. Catastrophic Flooding in the Amur River Basin, Russia, 2013. Atlas Silk Road Disaster Risk Beijing Sci. Press. 2022, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Flood in Krasnodarsky Krai, Year 2012. Available online: https://aif.ru/society/gallery/navodnenie_v_krasnodarskom_krae_2012_goda_kak_eto_bylo#id=12054721 (accessed on 27 January 2022).
- Flood in Tulun, Year 2019. Available online: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7fsyqf3gm3g (accessed on 27 January 2022).
- Flood 2013, Khabarovsk. Available online: https://senyoro.livejournal.com/944142.html (accessed on 27 January 2022).
- Strashnaya, A.I.; Maksimenkova, T.A.; Chub, O.V. Agrometeorological Features of the 2010 Drought in Russia in Comparison with the Droughts of Previous Years. Proc. Hydrometeorol. Res. Cent. Russ. Fed. 2011, 345, 171–188. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Meshcherskaya, A.V.; Golod, M.P.; Mirvis, V.M. Drought of 2010 against the Background of Long-Term Changes in Aridity in the Main Grain-Producing Regions of Russia. Proc. Main Geophys. Obs. Named A.I. Voeikov. 2011, 563, 94–121. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Vasiliev, D.Y.; Vodopyanov, V.V.; Semenov, V.A.; Chibilev, A.A. Assessment of Trends in Aridity for the Territory of the Southern Urals in the Period 1960–2019 Using Various Methods. Rep. Russ. Acad. Sci. Earth Sci. 2020, 494, 91–96. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zolotokrylin, A.N.; Titkova, T.B.; Cherenkova, E.A.; Vinogradova, V.V. Comparative Studies of Droughts in 2010 and 2012 in the European Territory of Russia Based on Meteorological and MODIS Data. Mod. Probl. Earth’s Remote Sens. Space 2013, 10, 246–253. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Strashnaya, A.I.; Birman, B.A.; Bereza, O.V. Features of the 2012 Drought in the Urals and Western Siberia and Its Impact on the Yield of Spring Grain Crops. Hydrometeorol. Res. Forecast 2018, 2, 154–169. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Voropay, N.N.; Ryazanova, A.A. Droughts on the Territory of the Tomsk Region. Russ. Meteorol. Hydrol. 2020, 12, 39–51. [Google Scholar]
- On the State of Protection of the Population and Territories of the Russian Federation from Natural and Man-Made Emergencies: State Report; Russian Federation: Moscow, Russia, 2019; p. 344. (In Russian)
- Report on the Peculiarities of the Climate on the Territory of the Russian Federation for 2017; European Forest Institute: Moscow, Russia, 2018. (In Russian)
- Kleshchenko, A.D.; Asmus, V.V.; Strashnaya, A.I.; Krovotyntsev, V.A.; Virchenko, O.V.; Savitskaya, O.V.; Bereza, O.V.; Vasilenko, E.V.; Sukhareva, V.V.; Morgunov, Y.A.; et al. Drought Monitoring Based on Ground and Satellite Data. Russ. Meteorol. Hydrol. 2019, 44, 772–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuznetsova, N.F. Droughts in the Forest-Steppe Zone of the Central Chernozem Region and Criteria for Assessing Their Intensity. News Saratov Univ. New Ser. Ser. Earth Sci. 2019, 19, 142–148. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Polyakov, D.V.; Barashkova, N.K.; Kuzhevskaya, I.V. Weather and Climate Description of Anomalous Summer 2012 in Tomsk Region. Russ. Meteorol. Hydrol. 2014, 39, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanyo, Y.M.; Petrova, S.A.; Polkovskaya, M.N. Probabilistic Assessment of the Frequency of Droughts and Determination of the Risks of Agricultural Production. Bull. Irkutsk State Tech. Univ. 2018, 22, 73–82. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalikovskiy, A.; Kurganovich, K. Flood Hazard and Risk Assessment in Russia. Nat. Hazards 2017, 88, 133–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirschenbaum, A. Disaster Preparedness: A Conceptual and Empirical Reevaluation. Int. J. Mass Emerg. Disasters 2002, 20, 5–28. [Google Scholar]
- Medd, W.; Deeming, H.; Walker, G.; Whittle, R.; Mort, M.; Twigger-Ross, C.; Walker, M.; Watson, N.; Kashefi, E. The Flood Recovery Gap: A Real-Time Study of Local Recovery Following the Floods of June 2007 in Hull, North East England. J. Flood Risk Manag. 2015, 8, 315–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrucci, O. Review Article: Factors Leading to the Occurrence of Flood Fatalities: A Systematic Review of Research Papers Published between 2010 and 2020. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2022, 22, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- State Report “On the State of Sanitary and Epidemiological Well-Being of the Population in the Republic of Kalmykia”, 2020. Department of the Federal Service for Supervision of Consumer Rights Protection and Human Welfare in the Republic of Kalmykia. Available online: http//08.rospotrebnadzor.ru (accessed on 26 February 2021). (In Russian).
- Cutter, S.L.; Ismail-Zadeh, A.; Alcántara-Ayala, I.; Altan, O.; Baker, D.N.; Briceño, S.; Gupta, H.; Holloway, A.; Johnston, D.; McBean, G.A.; et al. Global Risks: Pool Knowledge to Stem Losses from Disasters. Nature 2015, 522, 277–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandelbrot, B.B. The Fractal Geometry of Nature; W. H. Freeman and Co.: New York, NY, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar]
| Natural Disaster | Region | Period | Impact on Human Health, Well-Being and Economy | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Floods | Irkutsk Region | Summer 2019 | More than 45,000 people suffered; according to various sources, 25–26 people died, including one child; 6–7 people were missing; 496 people were hospitalized; the economic damage caused estimated at several billion rubles | [36,83,85,105] |
| Applications to primary healthcare for diseases of the skin, respiratory, and digestion diseases; cases of infected blister feet, other wounds of feet | [85] | |||
| Far East, Amur River Basin | August–September 2013 | More than 360 settlements were affected; more than 25,000 people evacuated from flooded areas, the total number of victims exceeded 170,000 people; the total direct damage estimated at RUB 34 to 90 billion | [26,34,57,86,87] | |
| August–September 2019 | More than 360 settlements flooded, about 70,000 people suffered, about 3000 people were saved | [105] | ||
| Far East, Primorsky Krai | August–September 2016 | Many settlements flooded, all crops and livestock killed; risks to public health increased due to contamination of drinking water; the total damage estimated to about EUR 500 million | [45] | |
| Krasnodarsky Krai | Summer 2012 | 171 people died in Krymsk, Novorossiysk and Gelendzhik; more than 34,000 people suffered; total damage about USD 600 million | [3,106] | |
| June 2015 | Mediterranean cyclone caused heavy rains, thunderstorms, and squalls, which led to rising water level in the rivers and mudflows; emergency mode declared in Sochi | [35] | ||
| Fall 2018 | 29 settlements flooded; 6 people died | [106] | ||
| Altaisky Krai | Spring 2014 | Flood affected 25 municipal formations, about 18,000 people; damage estimated from RUB 5 to 5.9 billion | [19,92] | |
| Drought | ETR, southern Urals, southwestern regions of Western Siberia | Summer 2010 | Crop loss recorded on 13.3 million hectares of yield reduction on the remaining area down to 56% of the maximum harvest in 2008 | [107] |
| Spring and winter wheat harvested 67% of the 2009 harvest | [100] | |||
| Seed offspring of the 2010 harvest turned out to be non-viable | [108] | |||
| North of the Southern Federal District, the Volga region, the south of Siberia and the Urals | June–July 2012 | Atmospheric and soil droughts, combined with frequent dry winds, led to the death of grain crops on an area of almost 6 million hectares and a significant decrease in the gross grain harvest | [73,102] | |
| In the Tomsk Region, because of abnormally hot and dry weather, most crops damaged; yield less than 50% of planned indicators; because of the shallowing of the rivers, navigation stopped, which led to the failure of contracts for the supply of goods, causing damage to river transport | [104,109] | |||
| Irkutsk Region | Spring–summer 2015 | 13 municipal formations affected, grain harvest was significantly smaller. The greatest damage caused to the Cheremkhovsky District: the volume of lost products here amounted to about 20,000 tons. Crops of grains and perennial grasses, potatoes and vegetables suffered from dry weather; the total damage is estimated at RUB 308.3 million | [110] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Grigorieva, E.A.; Livenets, A.S. Risks to the Health of Russian Population from Floods and Droughts in 2010–2020: A Scoping Review. Climate 2022, 10, 37. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli10030037
Grigorieva EA, Livenets AS. Risks to the Health of Russian Population from Floods and Droughts in 2010–2020: A Scoping Review. Climate. 2022; 10(3):37. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli10030037
Chicago/Turabian StyleGrigorieva, Elena A., and Alexandra S. Livenets. 2022. "Risks to the Health of Russian Population from Floods and Droughts in 2010–2020: A Scoping Review" Climate 10, no. 3: 37. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli10030037
APA StyleGrigorieva, E. A., & Livenets, A. S. (2022). Risks to the Health of Russian Population from Floods and Droughts in 2010–2020: A Scoping Review. Climate, 10(3), 37. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli10030037







