A Subregional Model of System Dynamics Research on Surface Water Resource Assessment for Paddy Rice Production under Climate Change in the Vietnamese Mekong Delta
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Model Development
2.2. Study Area
2.3. Subregional Temperature and Rainfall
2.4. Socioeconomic Assumptions by Subregions
2.5. Actual Water Demand
2.6. Scenarios of Climate and Land Use Change
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Actual Water Demand for Paddy Rice
3.2. Climate Change Impact
3.2.1. In the Dry Season
3.2.2. In the Wet Season
3.3. Land Use Change Responds to Climate Change
3.3.1. Dry Season
3.3.2. Wet Season
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vörösmarty, C.J. Global Water Resources: Vulnerability from Climate Change and Population Growth. Science 2000, 289, 284–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnell, N. Climate change and global water resources. Glob. Environ. Chang. 1999, 9, S31–S49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenters, J.D.; Coe, M.T.; Foley, J.A. Surface water balance of the continental United States, 1963–1995: Regional evaluation of a terrestrial biosphere model and the NCEP/NCAR reanalysis. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2000, 105, 22393–22425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granier, A.; Bréda, N.; Biron, P.; Villette, S. A lumped water balance model to evaluate duration and intensity of drought constraints in forest stands. Ecol. Modell. 1999, 116, 269–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chahine, M.T. The hydrological cycle and its influence on climate. Nature 1992, 359, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, E.G.R. Modelling feedback in the society-Biosphere-Climate System. Ph.D. Thesis, The University of Western Ontario, London, ON, Canada, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Hanasaki, N.; Kanae, S.; Oki, T.; Masuda, K.; Motoya, K.; Shirakawa, N.; Shen, Y.; Tanaka, K. An integrated model for the assessment of global water resources—Part 2: Applications and assessments. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2008, 12, 1027–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcamo, J.; Döll, P.; Henrichs, T.; Kaspar, F.; Rösch, T.; Siebert, S. Development and testing of the WaterGAP 2 global model of water use and availability. Hydrol. Sci. 2003, 48, 317–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, E.G.R.; Simonovic, S.P. Global water resources modeling with an integrated model of the social–economic–environmental system. Adv. Water Resour. 2011, 34, 684–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiddaman, T. Feedback Complexity in Integrated Climate-Economy Models. Ph.D. Thesis, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, MA, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Döll, P.; Hoffmann-Dobrev, H.; Portmann, F.T.; Siebert, S.; Eicker, A.; Rodell, M.; Strassberg, G.; Scanlon, B.R. Impact of water withdrawals from groundwater and surface water on continental water storage variations. J. Geodyn. 2012, 59, 143–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholls, R.J.; Cazenave, A. Sea-Level Rise and Its Impact on Coastal Zones. Science 2010, 328, 1518–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, M.D.; Howard, K.W.F. Modeling the Transient Response of Saline Intrusion to Rising Sea-Levels. Groundwater 2011, 49, 560–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ketabchi, H.; Mahmoodzadeh, D.; Ataie-Ashtiani, B.; Simmons, C.T. Sea-level rise impacts on seawater intrusion in coastal aquifers: Review and integration. J. Hydrol. 2016, 535, 235–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusuf, A.A.; Francisco, H. Climate Change Vulnerability Mapping for Southeast Asia Vulnerability Mapping for Southeast Asia. East 2009, 181, 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Darby, S.E.; Hackney, C.R.; Leyland, J.; Kummu, M.; Lauri, H.; Parsons, D.R.; Best, J.L.; Nicholas, A.P.; Aalto, R. Fluvial sediment supply to a mega-delta reduced by shifting tropical-cyclone activity. Nature 2016, 539, 276–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, K.H.; Le, T.A.; Nguyen, K. Van Urban design principles for flood resilience: Learning from the ecological wisdom of living with floods in the Vietnamese Mekong Delta. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2016, 155, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanington, P.; To, Q.T.; Van, P.D.T.; Doan, N.A.V.; Kiem, A.S. A hydrological model for interprovincial water resource planning and management: A case study in the Long Xuyen Quadrangle, Mekong Delta, Vietnam. J. Hydrol. 2017, 547, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, T.V.H.; Nguyen, H.N.; Wolanski, E.; Tran, T.C.; Haruyama, S. The combined impact on the flooding in Vietnam’s Mekong River delta of local man-made structures, sea level rise, and dams upstream in the river catchment. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2007, 71, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karila, K.; Nevalainen, O.; Krooks, A.; Karjalainen, M.; Kaasalainen, S. Monitoring changes in rice cultivated area from SAR and optical satellite images in ben tre and tra vinh provinces in mekong delta, vietnam. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 4090–4108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, H.N.; Huynh, H.X.; Nguyen, T.H. Simulation of salinity intrusion in the context of the Mekong Delta Region (Viet Nam). In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE RIVF International Conference on Computing & Communication Technologies, Research, Innovation, and Vision for the Future, Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam, 27 February–1 March 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, N.A. Historic drought and salinity intrusion in the Mekong Delta in 2016: Lessons learned and response solutions. Vietnam J. Sci. Technol. Eng. 2017, 59, 93–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smajgl, A.; Toan, T.Q.; Nhan, D.K.; Ward, J.; Trung, N.H.; Tri, L.Q.; Tri, V.P.D.; Vu, P.T. Responding to rising sea levels in the Mekong Delta. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2015, 5, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minderhoud, P.S.J.; Erkens, G.; Pham, V.H.; Bui, V.T.; Erban, L.; Kooi, H.; Stouthamer, E. Impacts of 25 years of groundwater extraction on subsidence in the Mekong delta, Vietnam. Environ. Res. Lett. 2017, 12, 064006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thoang, T.T.; Giao, P.H. Subsurface characterization and prediction of land subsidence for HCM City, Vietnam. Eng. Geol. 2015, 199, 107–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Government, V. Resolution 120/NQ-CP on Sustainable Development of the Mekong Delta in Response to Climate Change; Government of Vietnam: Ha Noi, Vietnam, 2017.
- Osman, A.; Crundwell, F.K.; Harding, K.G.; Sheridan, C.; Hines, K.; Du Toit, A. Water Accountability and Efficiency at a Base Metals Refinery. In Proceedings of the Water in Mining Conference, Brisbane, Queenland, Australia, 26–28 November 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Abedin, M.A.; Shaw, R. Safe Water Adaptability for Salinity, Arsenic and Drought Risks in Southwest of Bangladesh. Risk Hazards Cris. Public Policy 2013, 4, 62–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goff, M.; Crow, B. What is water equity? The unfortunate consequences of a global focus on “drinking water”. Water Int. 2014, 39, 159–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, T.P.; Dieperink, C.; Dang Tri, V.P.; Otter, H.S.; Hoekstra, P. Governance conditions for adaptive freshwater management in the Vietnamese Mekong Delta. J. Hydrol. 2018, 557, 116–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vensim. Ventana Simulation Environment—User’s Guide Version 6; Ventana Systems, Inc.: Havard, MA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Chapman, A.; Darby, S. Evaluating sustainable adaptation strategies for vulnerable mega-deltas using system dynamics modelling: Rice agriculture in the Mekong Delta’s An Giang Province, Vietnam. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 559, 326–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, T.M.; Bosch, O.J.H.; Nguyen, N.C.; Trinh, C.T. System dynamics modelling for defining livelihood strategies for women smallholder farmers in lowland and upland regions of northern Vietnam: A comparative analysis. Agric. Syst. 2017, 150, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuu, N.T.; Lim, J.; Kim, S.; Tri, V.P.D.; Kim, H.; Kim, J. Surface water resource assessment of paddy rice production under climate change in the Vietnamese Mekong Delta: A system dynamics modeling approach. J. Water Clim. Chang. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choukr-Allah, R.; Ragab, R.; Rodriguez-Clemente, R. Integrated Water Resources Management in the Mediterranean Region Dialogue towards New Strategy; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2012; pp. 1–364. [Google Scholar]
- Moorhead, J.E.; Gowda, P.H.; Singh, V.P.; Porter, D.O.; Marek, T.H.; Howell, T.A.; Stewart, B.A. Identifying and Evaluating a Suitable Index for Agricultural Drought Monitoring in the Texas High Plains. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2015, 51, 807–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prime Minister, V. Decision 417/QD-TTg in Implementing the Government’s Resolution 120/NQ-CP on Sustainable Development of the Mekong Delta in Response to Climate Change; Government of Vietnam: Ha Noi, Vietnam, 2019.
- Law, M.; Collins, A. Getting to Know ArcGIS; ESRI Press: Redlands, CA, USA, 2015; ISBN 1589483820. [Google Scholar]
- DIVA-GIS Free Spatial Data. Available online: http://www.diva-gis.org/Data (accessed on 10 February 2019).
- Kottek, M.; Grieser, J.; Beck, C.; Rudolf, B.; Rubel, F. World map of the Köppen-Geiger climate classification updated. Meteorol. Z. 2006, 15, 259–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cimate-Data.org. Climate Data for Cities Worldwide. Available online: https://en.climate-data.org/ (accessed on 15 February 2019).
- MONRE (Ministry of Natural Resources and Environement of Vietnam). Scenarios of Climate Change and Sea Level Rise for Vietnam; MONRE: Ha Noi, Vietnam, 2016.
- IPCC. Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- FAO (Food and Agriculture Organization). Irrigation in Southern and Eastern Asia in Figures; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Kuenzer, C.; Campbell, I.; Roch, M.; Leinenkugel, P.; Tuan, V.Q.; Dech, S. Erratum to: Understanding the impact of hydropower developments in the context of upstream–downstream relations in the Mekong river basin. Sustain. Sci. 2015, 10, 185–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kantoush, S.; Van Binh, D.; Sumi, T.; Trung, L.V. Impact of Upstream Hydropower Dams and Climate Change on Hydrodynamics of Vietnamese Mekong Delta. J. Jpn. Soc. Civ. Eng. Ser. B1 Hydraul. Eng. 2017, 73, I_109–I_114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.D.N.; Le Hang, T.T.; Van Trien, T.; Linh, V.T.P.; Vu, P.T.; Tri, V.P.D. Evaluating adaptive ability to floods by people at the full-dyke system in Cho Moi district, An Giang province. Can. Tho Univ. J. Sci. Environ. 2017, 159–165, Special Issue on Environment and Climate Change. [Google Scholar]
- Whitehead, P.G.; Jin, L.; Bussi, G.; Voepel, H.E.; Darby, S.E.; Vasilopoulos, G.; Manley, R.; Rodda, H.; Hutton, C.; Hackney, C.; et al. Water quality modelling of the Mekong River basin: Climate change and socioeconomics drive flow and nutrient flux changes to the Mekong Delta. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 673, 218–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuyen, N.Q. Systematization of rice-based production models in the freshwater ecological zone of the Mekong Delta. Can. Tho Univ. J. Sci. 2013, 29, 60–69. [Google Scholar]
- Vu, P.T.; Minh, V.Q.; Huy, V.T.; Nguyen, P.C. Effect of flooding and salinity as a result of climate change on land use suitability in the coastal zone of the Vietnamese Mekong Delta. Can. Tho Univ. J. Sci. Agric. 2016, 71–83, Special Issue on Agriculture. [Google Scholar]
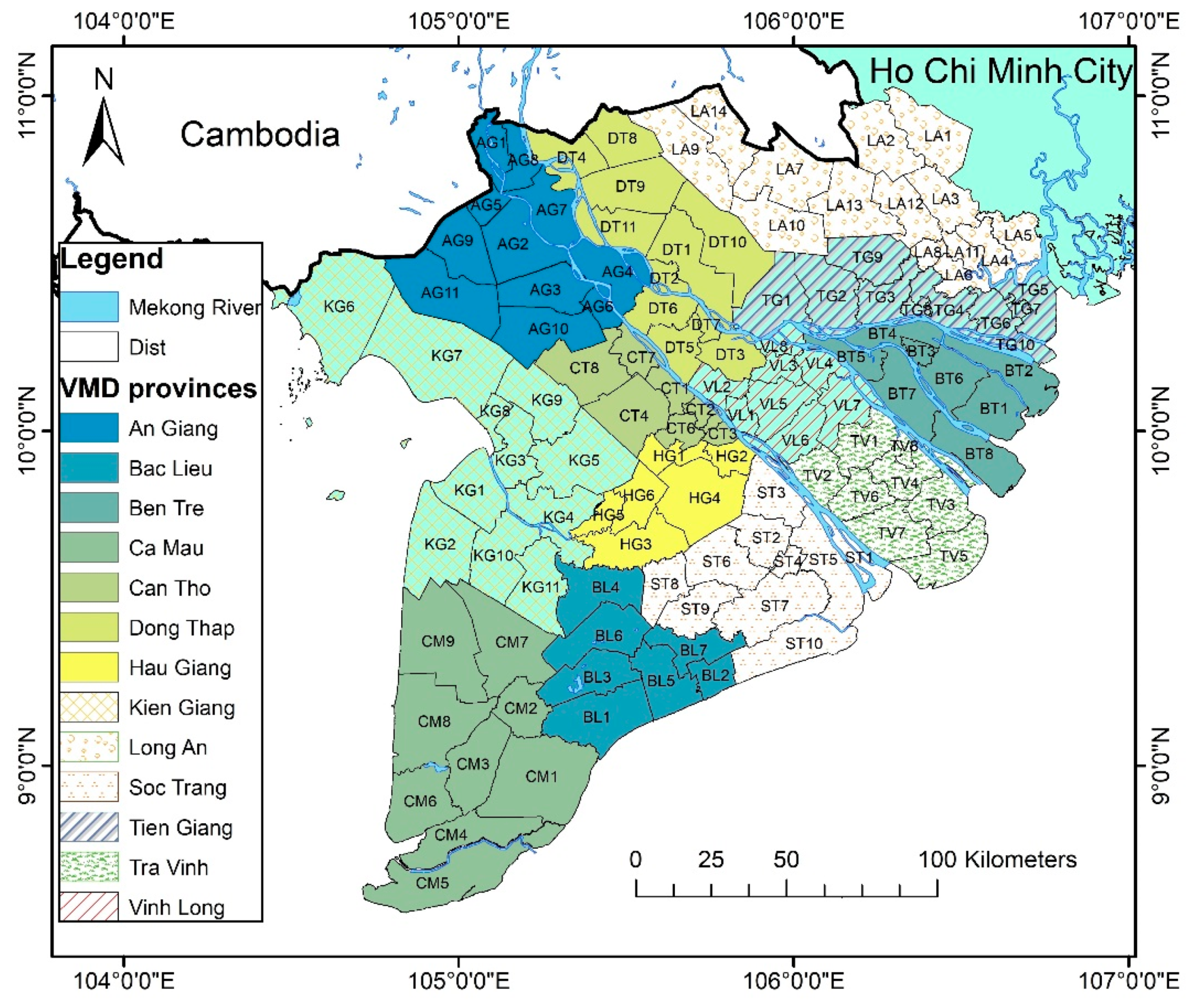










| Province (pro) | Subregion (k) | Name of Subregion |
|---|---|---|
| Dong Thap | DT1-DT11 | Cao Lanh, Cao Lanh City, Chau Thanh, Hong Ngu, Lai Vung, Lap Vo, Sa Dec City, Tan Hong, Tam Nong, Thap Muoi and Thanh Binh. |
| An Giang | AG1-AG11 | An Phu, Chau Phu, Chau Thanh, Cho Moi, Chau Doc City, Long Xuyen, Phu Tan, Tan Chau, Tinh Bien, Thoai Son and Tri Ton. |
| Bac Lieu | BL1-BL7 | Dong Hai, Bac Lieu City, Gia Rai, Hong Dan, Hoa Binh, Phuoc Long and Vinh Loi. |
| Ben Tre | BT1-BT8 | Ba Tri, Binh Dai, Ben Tre City, Chau Thanh, Cho Lach, Giong Trom, Mo Cay and Thanh Phu. |
| Ca Mau | CM1-CM9 | Dam Doi, Ca Mau City, Cai Nuoc, Nam Can, Ngoc Hien, Phu Tan, Thoi Binh, Tran Van Thoi and U Minh. |
| Can Tho | CT1-CT9 | O Mon, Binh Thuy, Cai Rang, Co Do, Ninh Kieu, Phong Dien, Thot Not and Vinh Thanh. |
| Hau Giang | HG1-HG6 | Chau Thanh A, Chau Thanh, Long My, Phung Hiep, Vi Thanh City and Vi Thuy. |
| Kien Giang | KG1-KG11 | An Bien, An Minh, Chau Thanh, Go Quao, Giong Rieng, Ha Tien City, Hon Dat, Rach Gia City, Tan Hiep, U Minh Thuong and Vinh Thuan. |
| Long An | LA1-LA14 | Duc Hoa, Duc Hue, Ben Luc, Can Duoc, Can Giuoc, Chau Thanh, Moc Hoa, Tan An City, Tan Hung, Tan Thanh, Tan Tru, Thu Thua, Thanh Hoa and Vinh Hung. |
| Soc Trang | ST1-ST10 | Cu Lao Dung, Chau Thanh, Ke Sach, Soc Trang City, Long Phu, My Tu, My Xuyen, Nga Nam, Thanh Tri and Vinh Chau. |
| Tien Giang | TG1-TG10 | Cai Be, Cai Lay, Chau Thanh, Cho Gao, Go Cong Dong, Go Cong Tay, Go Cong, My Tho City, Tan Phuoc and Tan Phu Dong. |
| Tra Vinh | TV1-TV8 | Cang Long, Cau Ke, Cau Ngang, Chau Thanh, Duyen Hai, Tieu Can, Tra Cu and Tra Vinh City. |
| Vinh Long | VL1-VL8 | Binh Minh, Binh Tan, Long Ho, Mang Thit, Tam Binh, Tra on, Vung Liem and Vinh Long City. |
| Scenario | Climate | Land Use | Simulated Year | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Base period | Base land use system in 2010 | 2015 | [34]; Can Tho University |
| 2 | RCP4.5 | Unchanged land use in 2010 | 2050 | |
| 3 | RCP8.5 | |||
| 4 | RCP4.5 | Land use change in the whole VMD: Triple rice systems in both upper and coastal zones is shifted to Winter Spring—Summer Autumn (WS-SA) and Summer Autumn—Autumn Winter (SA-AW), respectively | 2050 | [34]; Resolution 120 of the Government of Vietnam |
| 5 | RCP8.5 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nguyen Thanh, T.; Tri, V.P.D.; Kim, S.; Nguyen Phuong, T.; Lam Mong, T.; Vuong Tuan, P. A Subregional Model of System Dynamics Research on Surface Water Resource Assessment for Paddy Rice Production under Climate Change in the Vietnamese Mekong Delta. Climate 2020, 8, 41. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli8030041
Nguyen Thanh T, Tri VPD, Kim S, Nguyen Phuong T, Lam Mong T, Vuong Tuan P. A Subregional Model of System Dynamics Research on Surface Water Resource Assessment for Paddy Rice Production under Climate Change in the Vietnamese Mekong Delta. Climate. 2020; 8(3):41. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli8030041
Chicago/Turabian StyleNguyen Thanh, Tuu, Van Pham Dang Tri, Seungdo Kim, Thuy Nguyen Phuong, Thuy Lam Mong, and Phong Vuong Tuan. 2020. "A Subregional Model of System Dynamics Research on Surface Water Resource Assessment for Paddy Rice Production under Climate Change in the Vietnamese Mekong Delta" Climate 8, no. 3: 41. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli8030041
APA StyleNguyen Thanh, T., Tri, V. P. D., Kim, S., Nguyen Phuong, T., Lam Mong, T., & Vuong Tuan, P. (2020). A Subregional Model of System Dynamics Research on Surface Water Resource Assessment for Paddy Rice Production under Climate Change in the Vietnamese Mekong Delta. Climate, 8(3), 41. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli8030041





