Hydroclimatic Variability in the Bilate Watershed, Ethiopia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Datasets
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Variability Analysis
Coefficient of Variation (CV)
Standardized Anomaly Index (SAI)
2.3.2. Changing Point Detection Test
2.3.3. Trend Analysis
2.3.4. Calculation of Potential Evapotranspiration (PET) and Evapotranspiration (ET)
3. Results
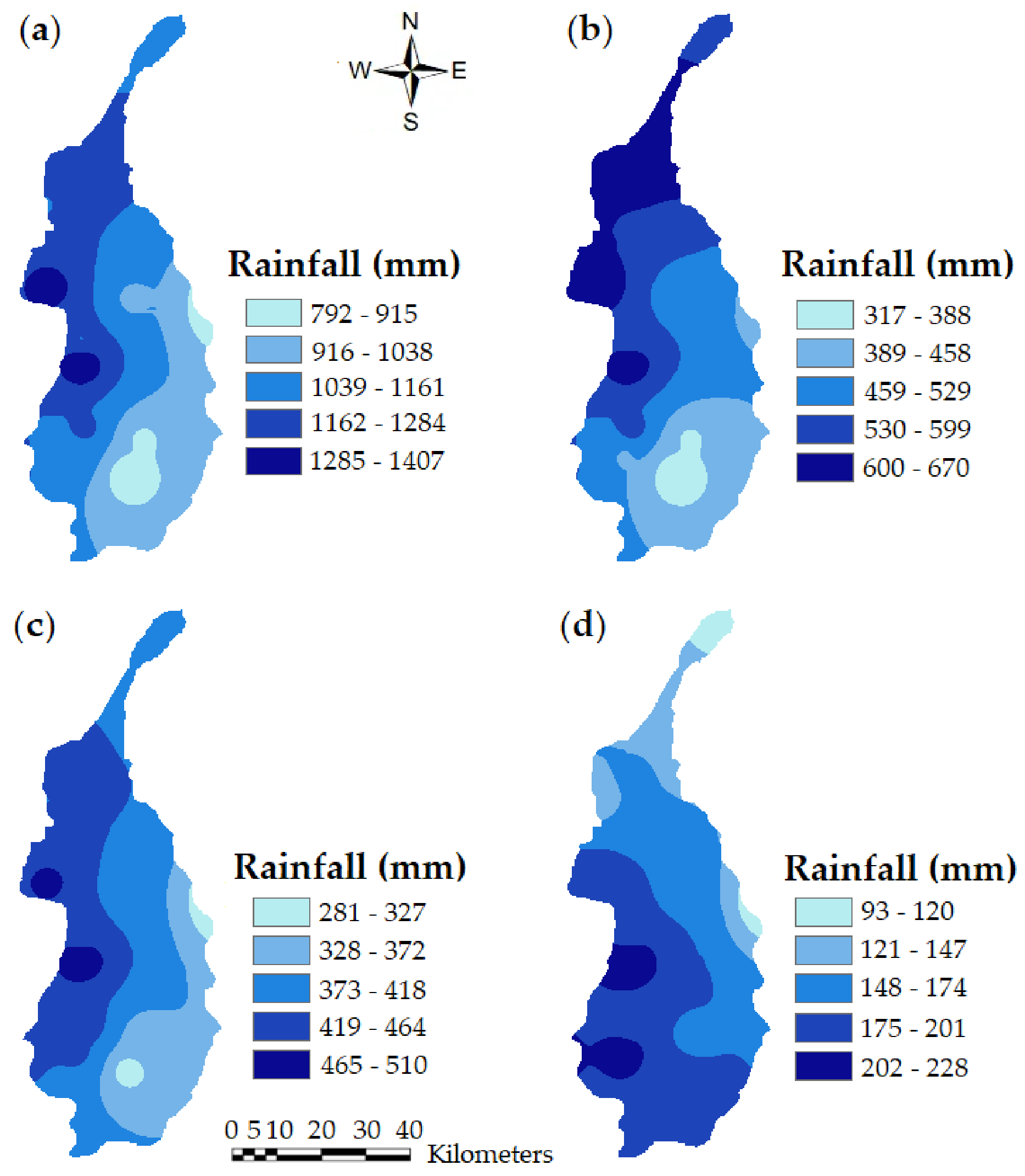
3.1. Climatology of Study Area
3.2. Variability Analysis
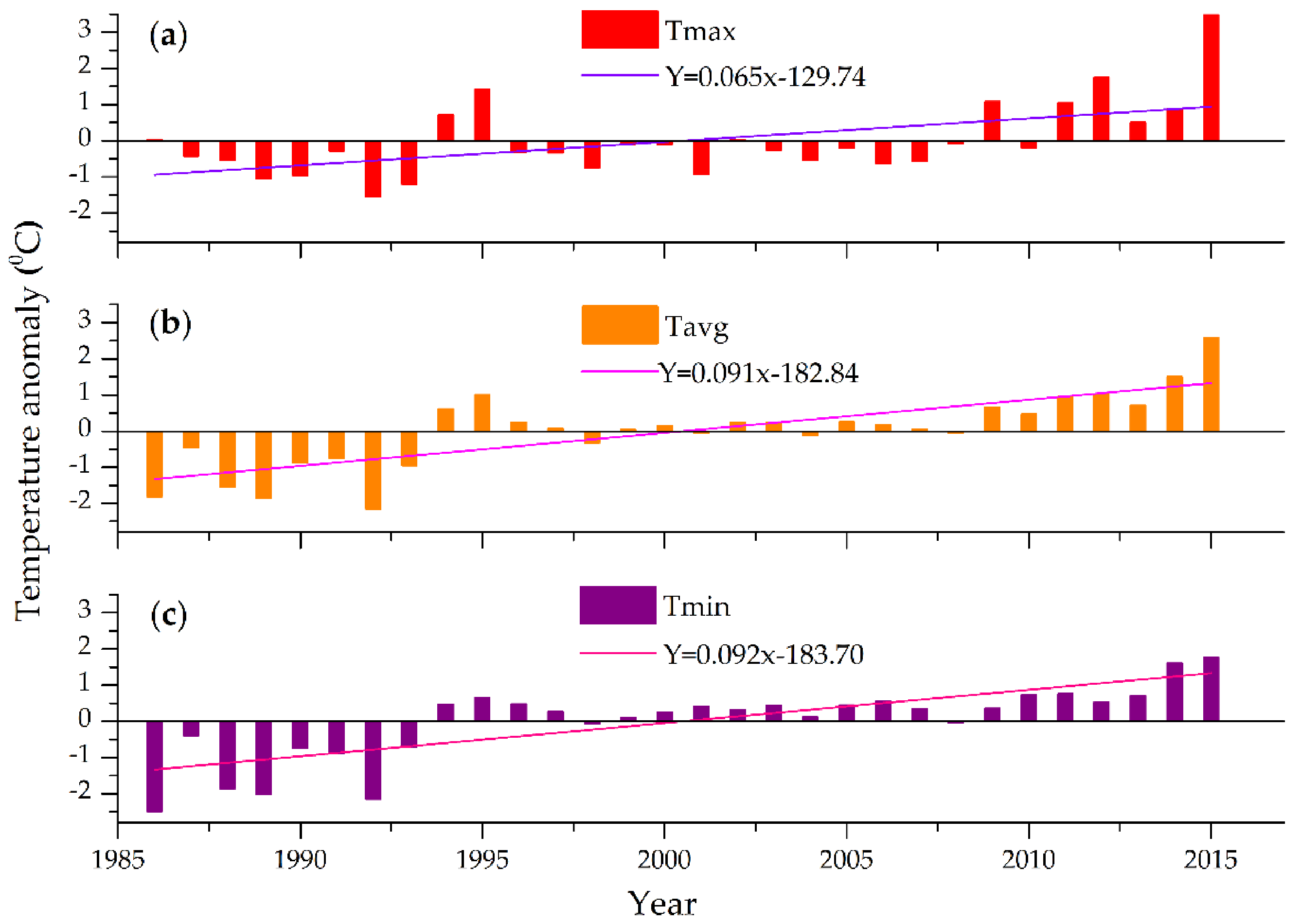
3.2.1. Temperature Variability Analysis
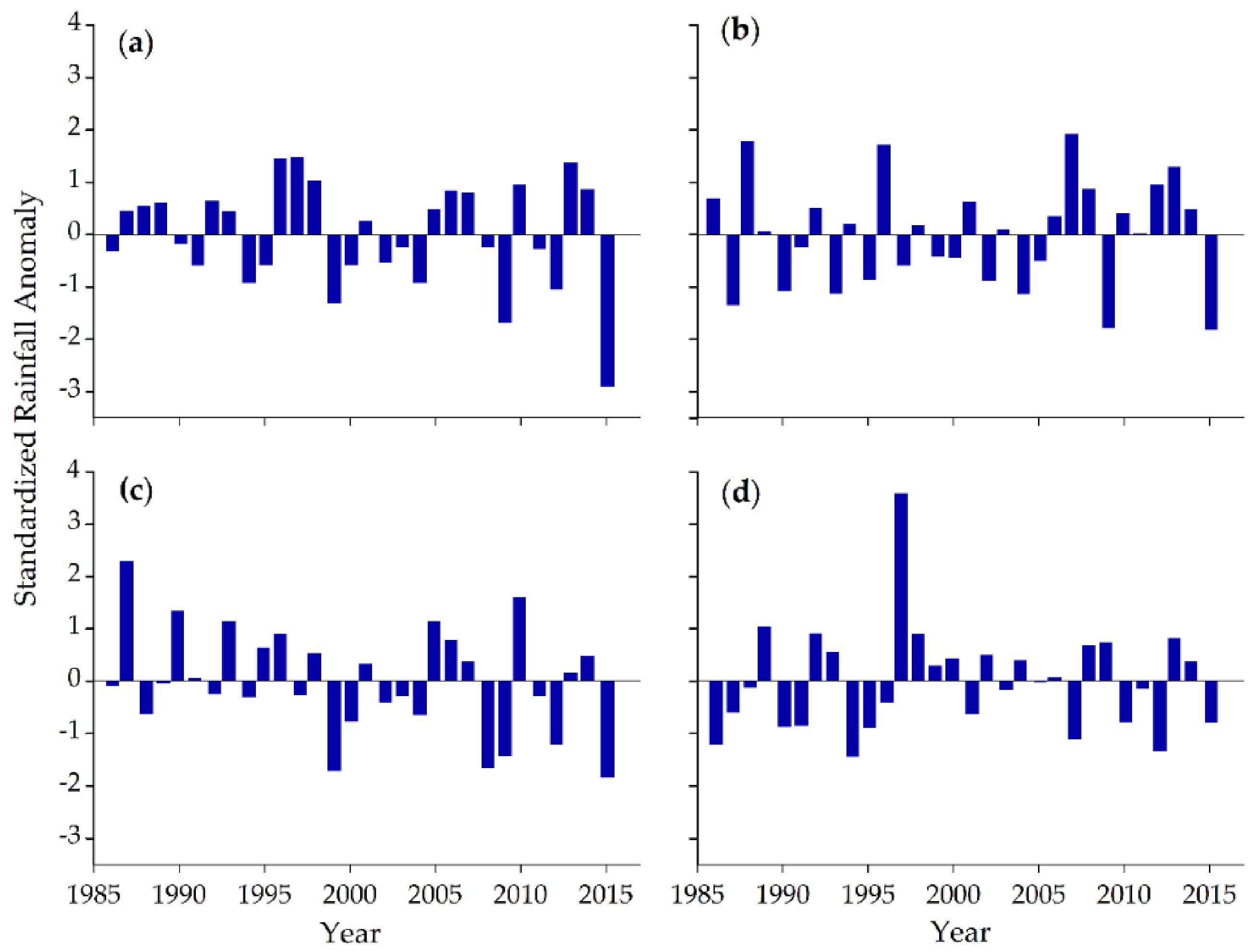
3.2.2. Rainfall Variability Analysis
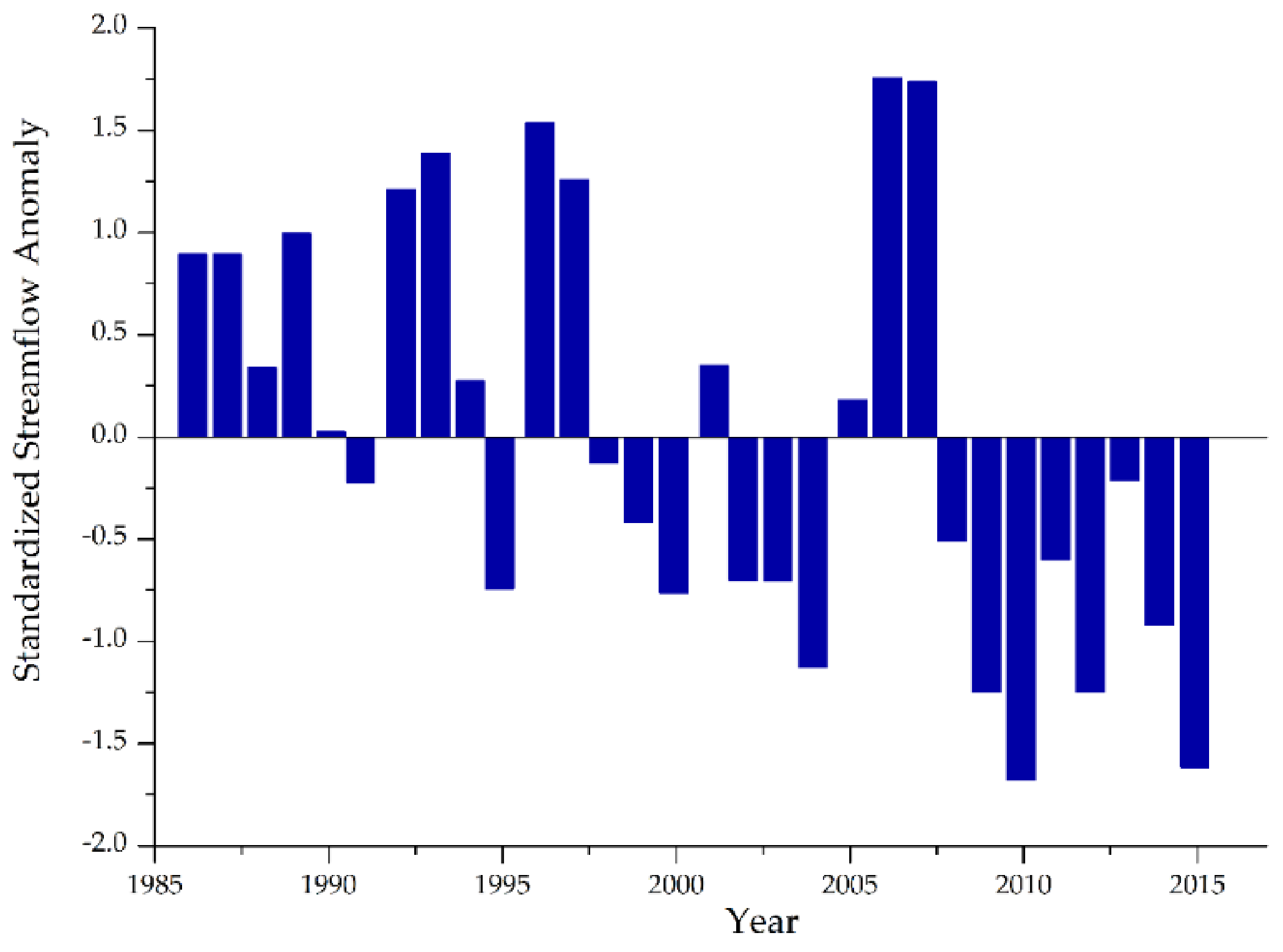
3.2.3. Streamflow Variability Analysis
3.3. Changing Point Detection Tests
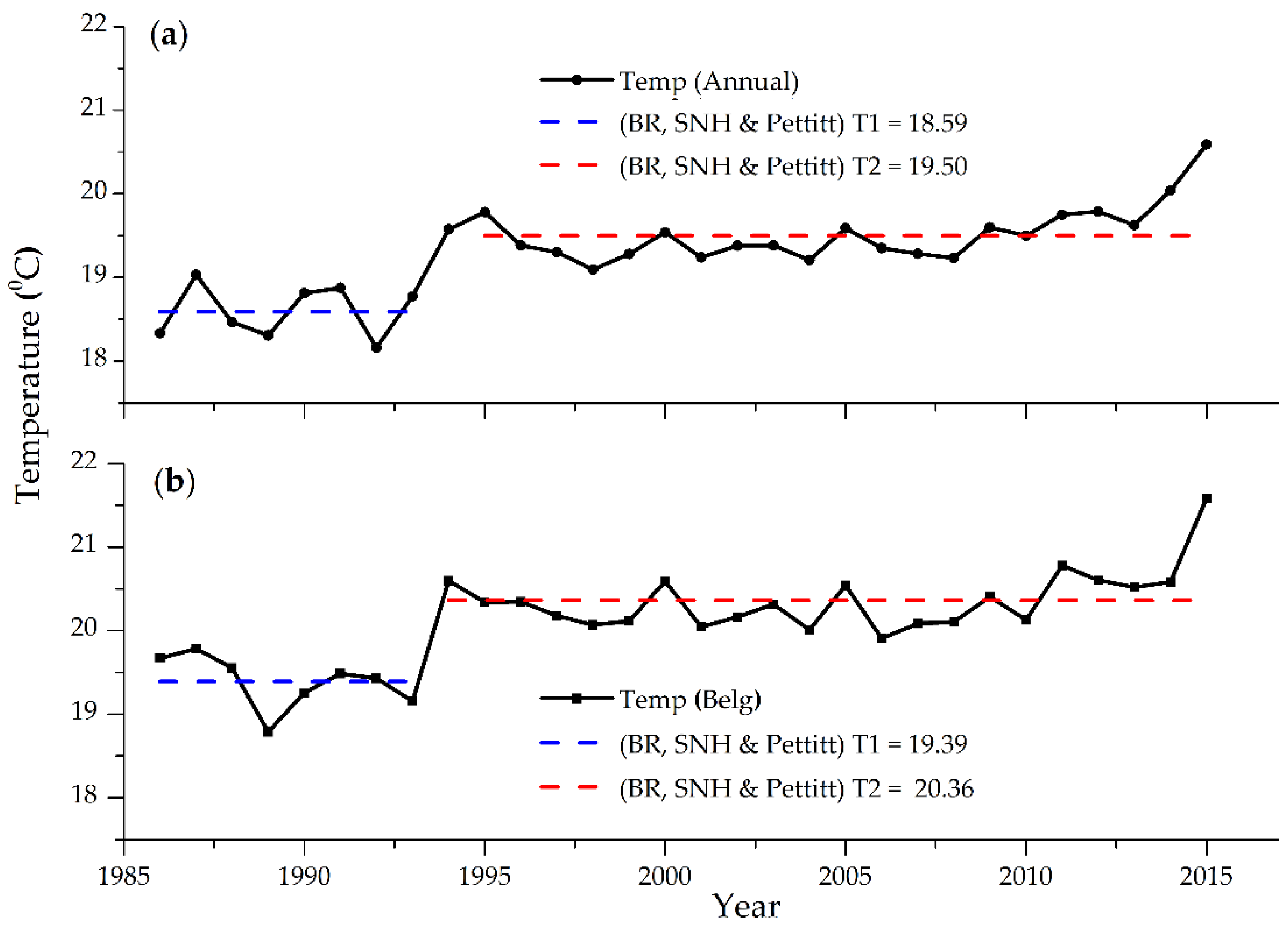
3.3.1. Temperature Changing Point Detection Test
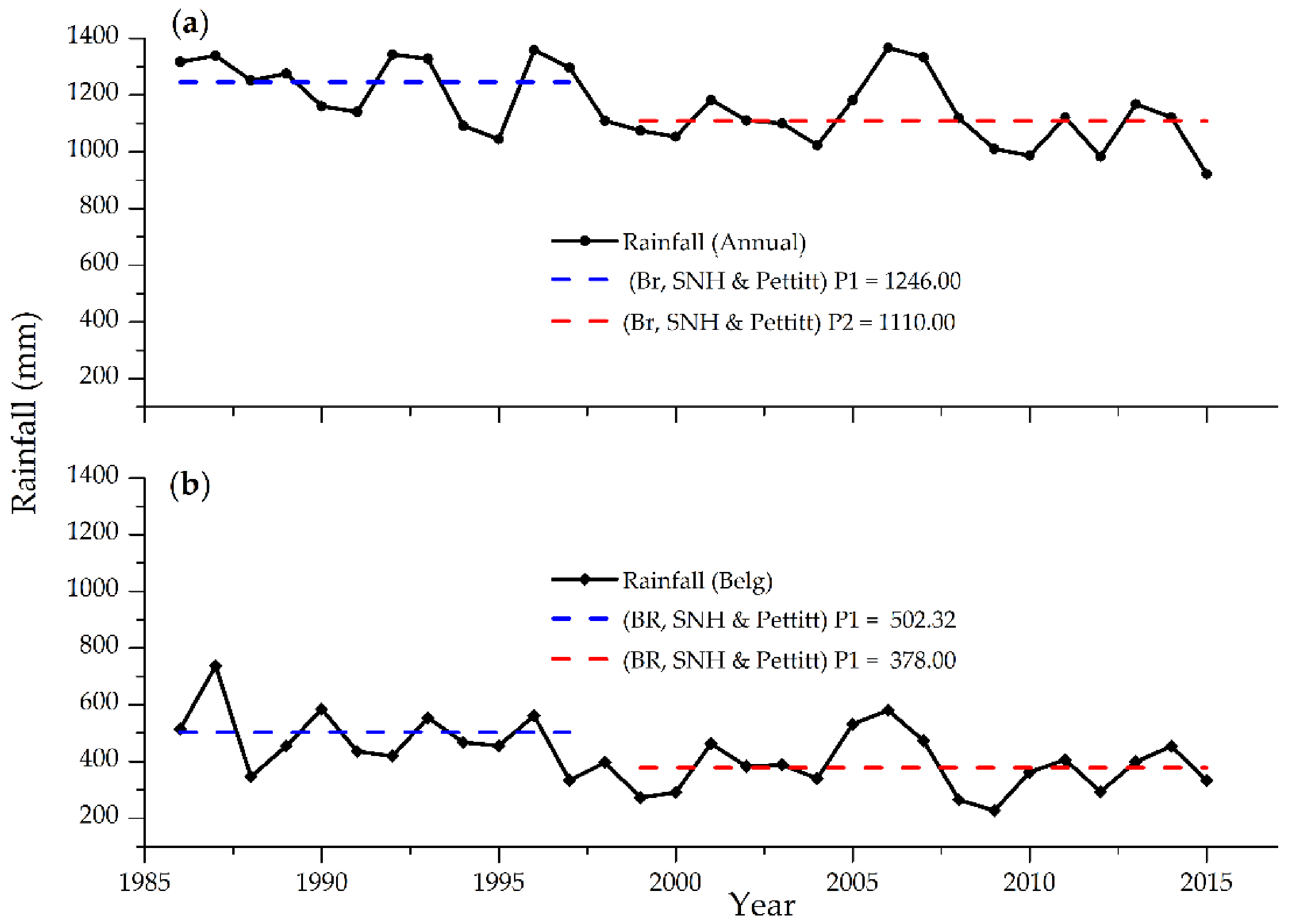
3.3.2. Rainfall Changing Point Detection Test
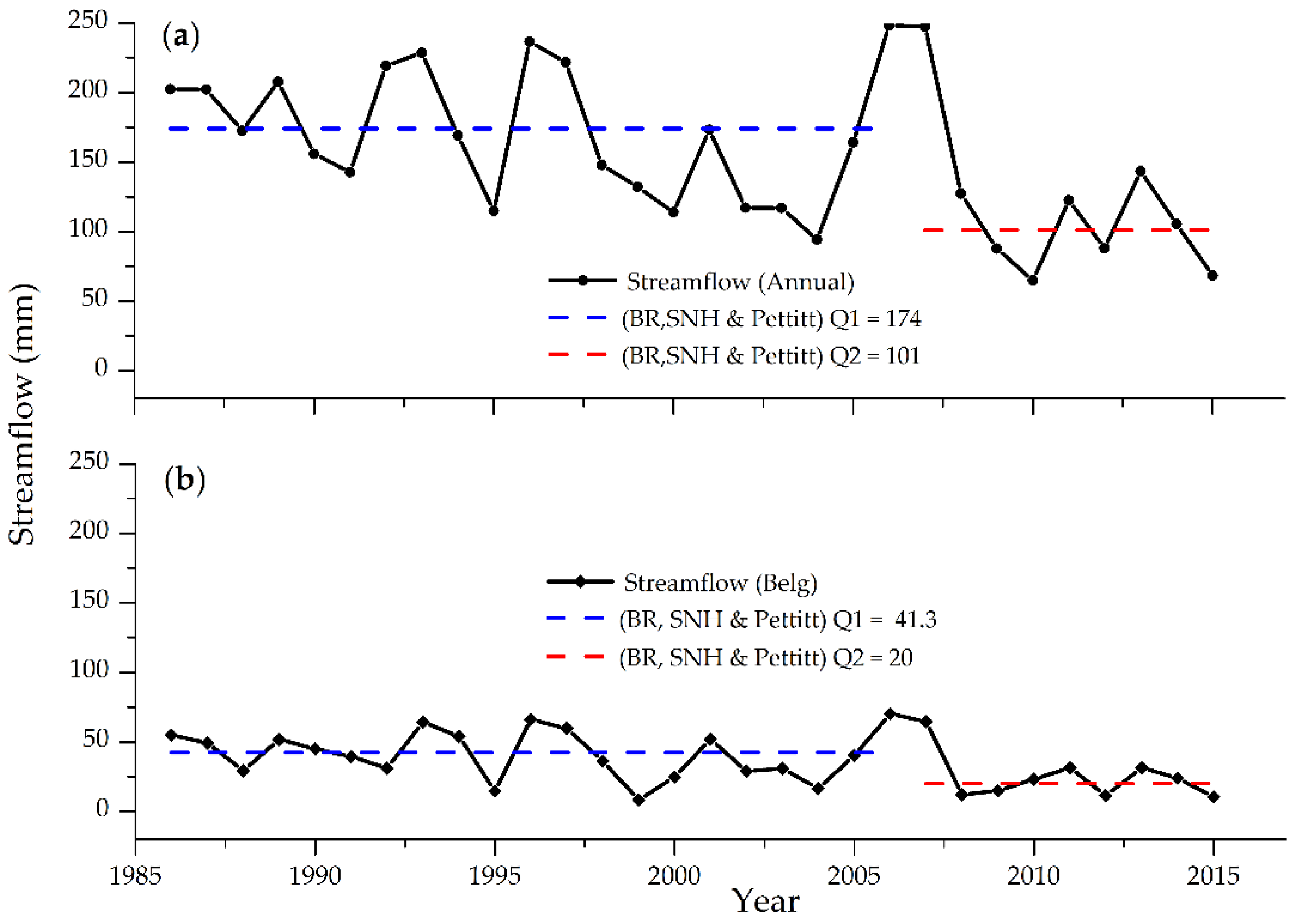
3.3.3. Streamflow Changing Point Detection Test
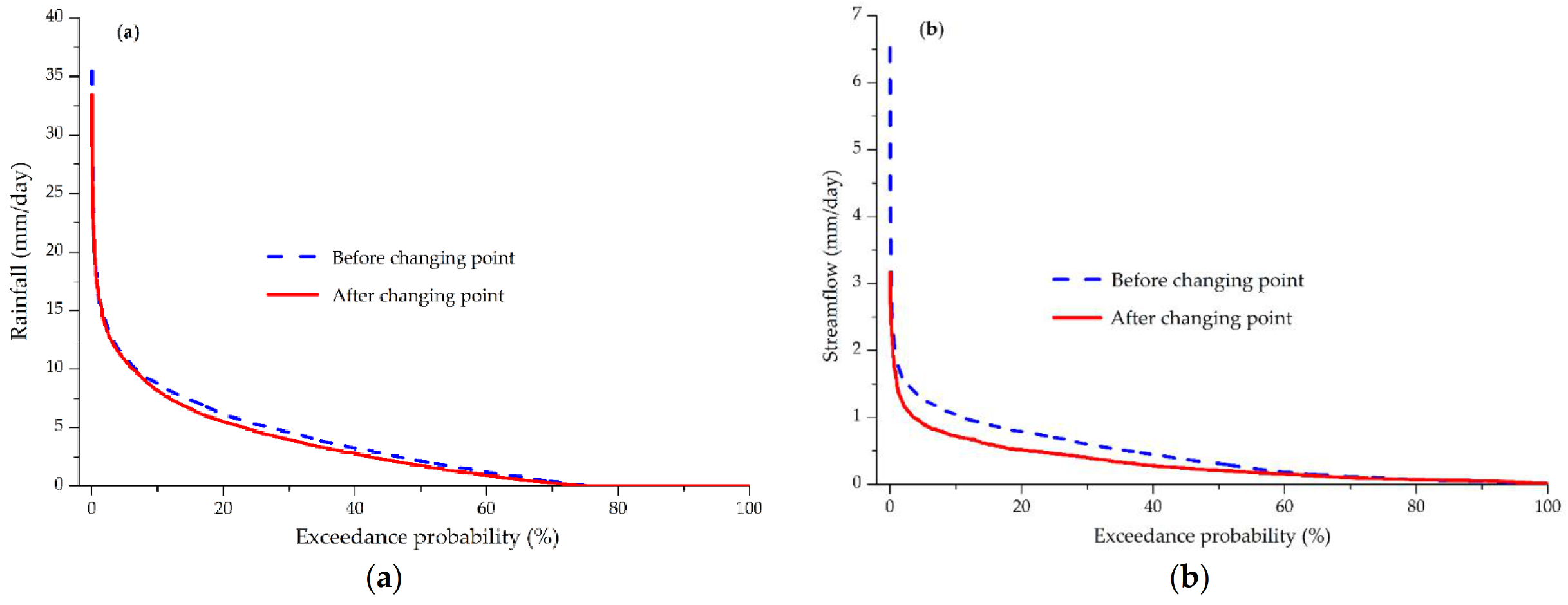
3.4. Implication of Changes in Hydrological Cycles
3.5. Trend Analysis
3.5.1. Temperature Trend Analysis
3.5.2. Rainfall Trend Analysis
3.5.3. Streamflow Trend Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Variability Analysis of Hydroclimatic Variables
4.2. Detection of Hydroclimatic Variables Changing Points
4.3. Hydroclimatic Variables Trend Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alemu, M.M.; Bawoke, G.T. Analysis of spatial variability and temporal trends of rainfall in Amhara region, Ethiopia. J. Water Clim. Chang. 2020, 11, 1505–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadese, M.T.; Kumar, L.; Koech, R.; Zemadim, B. Hydro-Climatic Variability: A Characterisation and Trend Study of the Awash River Basin, Ethiopia. J. Hydrol. 2019, 6, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharma, T.; Vittal, H.; Karmakar, S.; Ghosh, S. Increasing agricultural risk to hydro-climatic extremes in India. J. Environ. Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, A.; Haider, M.Z. Stern review on the economics of climate change: Implications for Bangladesh. Int. J. Clim. Chang. Strateg. Manag. 2019, 11, 100–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pichs-Madruga, O.R.; Sokona, Y.; Farahani, E.; Kadner, S.; Seyboth, K.; Adler, A.; Baum, I.; Brunner, S.; Eickemeier, P.; Kriemann, J.; et al. (Eds.) IPCC. Mitigation of Climate Change. Contribution of Working Group III to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 1–1435. [Google Scholar]
- Boko, M.; Niang, I.; Nyong, A.; Vogel, C.; Githeko, A.; Medany, M.; Osman Elasha, B.; Tabo, R.; Yanda, P. Climate change: Impacts, adaptation and vulnerability. Contribution of working group II to the fourth assessment report of the intergovernmental panel on climate change. J. Environ. Qual. 2007, 37, 433–467. [Google Scholar]
- Viste, E.; Korecha, D.; Sorteberg, A. Recent drought and precipitation tendencies in Ethiopia. J. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2013, 112, 535–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ministry of Environment and Forest (MEF). Ethiopia’s Second National Communication to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC); Ministry of Environment and Forest (MEF): Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 2015; pp. 1–235.
- Prevention, D. Preparedness Agency (DPPA) Flash Appeal for the 2006 Flood Disaster in Ethiopia; Joint government and humanitarian Partners: Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 2006; pp. 1–29. [Google Scholar]
- Moges, S.; Alemu, Y.; Mcfeeters, S. Flooding in Ethiopia: Recent History and 2006 Flood: Implications for the Nile Basin in Water Resources Management in Ethiopia: Implications for the Nile Basin; Helmut Kloos, W.L., Ed.; Cambria Press: Amherst, MA, USA, 2010; pp. 285–305. [Google Scholar]
- Tazeze, A.; Haji, J.; Ketema, M. Climate change adaptation strategies of smallholder farmers: The case of Babilie District, East Harerghe Zone of Oromia Regional State of Ethiopia. J. Econ. Sustain. Dev. 2012, 3, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Thiemann, S.; Förch, G. Water resources assessment in the Bilate river catchment-precipitation variability. In Proceedings of the Lake Abaya Research Symposium, Arba Minch, Ethiopia, 4–7 June 2005; pp. 53–78. [Google Scholar]
- Korecha, D.; Barnston, A.G. Predictability of June–September rainfall in Ethiopia. J. Mon. Weather Rev. 2007, 135, 628–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayele, H.S.; Li, M.-H.; Tung, C.-P.; Liu, T.-M. Impact of climate change on runoff in the Gilgel Abbay watershed, the upper Blue Nile Basin, Ethiopia. Water 2016, 8, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nyssen, J.; Vandenreyken, H.; Poesen, J.; Moeyersons, J.; Deckers, J.; Haile, M.; Salles, C.; Govers, G. Rainfall erosivity and variability in the Northern Ethiopian Highlands. J. Hydrol. 2005, 311, 172–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berhanu, B.; Seleshi, Y.; Melesse, A.M. Surface water and groundwater resources of Ethiopia: Potentials and challenges of water resources development. In Nile River Basin: Ecohydrological Challenges, Climate Change and Hydropolitics; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2014; pp. 97–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dralle, D.N.; Karst, N.J.; Thompson, S.E. Dry season streamflow persistence in seasonal climates. J. Water Resour. Res. 2016, 52, 90–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Belihu, M.; Abate, B.; Tekleab, S.; Bewket, W. Hydro-meteorological trends in the Gidabo catchment of the Rift Valley Lakes Basin of Ethiopia. J. Phys. Chem. Earth 2018, 104, 84–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matewos, T.; Tefera, T. Local level rainfall and temperature variability in drought-prone districts of rural Sidama, central rift valley region of Ethiopia. J. Phys. Geogr. 2020, 41, 36–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gedefaw, M.; Wang, H.; Yan, D.; Song, X.; Yan, D.; Dong, G.; Wang, J.; Girma, A.; Ali, B.A.; Batsuren, D. Trend analysis of climatic and hydrological variables in the Awash River Basin, Ethiopia. Water 2018, 10, 1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tekleab, S.; Mohamed, Y.; Uhlenbrook, S. Hydro-climatic trends in the Abay/upper Blue Nile basin, Ethiopia. J. Phys. Chem. Earth 2013, 61, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elzeiny, R.; Khadr, M.; Zahran, S.; Rashwan, E. Homogeneity Analysis of Rainfall Series in the Upper Blue Nile River Basin, Ethiopia. J. Eng. Res. 2019, 3, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djan’na, H.K.; Tall, M.; Amoussou, E.; Mumtaz, M.; Adounkpe, J.; Atchonouglo, K. Trend Analysis of Hydroclimatic Historical Data and Future Scenarios of Climate Extreme Indices over Mono River Basin in West Africa. Am. J. Rural Dev. 2020, 8, 37–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesemma, Z.K.; Mohamed, Y.A.; Steenhuis, T.S. Trends in rainfall and runoff in the Blue Nile Basin: 1964–2003. J. Hydrol. Process. 2010, 24, 3747–3758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tekle, A. Assessment of climate change impact on water availability of Bilate watershed, Ethiopian Rift Valley Basin. In Proceedings of the AFRICON 2015, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 14–17 September 2015; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Esayas, B.; Simane, B.; Teferi, E.; Ongoma, V.; Tefera, N. Climate variability and farmers’ perception in Southern Ethiopia. J. Adv. Meteorol. 2019, 2019, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girma, M.M.A.; Seleshi, B. Irrigation Practices in Ethiopia: Characteristics of Selected Irrigation Schemes; IWMI: Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 2007; Volume 124. [Google Scholar]
- Molla, D.D.; Tegaye, T.A.; Fletcher, C.G. Simulated surface and shallow groundwater resources in the Abaya-Chamo Lake basin, Ethiopia using a spatially-distributed water balance model. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2019, 24, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moloro, T.L. Spatio-Temporal Analysis of Rainfall Variability and Meteorological Drought: A Case Study in Bilate River Basin, Southern Rift Valley, Ethiopia. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Nat. Res. 2018, 14, 76–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wodaje, G.G.; Eshetu, Z.; Argaw, M. Temporal and spatial variability of rainfall distribution and evapotranspiration across altitudinal gradient in the Bilate River Watershed, Southern Ethiopia. J. AJEST 2016, 10, 167–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaweso, D.; Abate, B.; Bauwe, A.; Lennartz, B. Hydro-meteorological trends in the upper Omo-Ghibe river basin, Ethiopia. Water 2019, 11, 1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pingale, S.M.; Mekonnen, A.; Hatiye, S.D. Trends and abrupt changes in hydro-climatic variables in a Kulfo catchment, Ethiopia. In Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Sustainable Water Resources Development, Arba Minch, Ethiopia, 8–9 June 2018; pp. 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Tesfamariam, B.G.; Gessesse, B.; Melgani, F. Characterizing the spatiotemporal distribution of meteorological drought as a response to climate variability: The case of rift valley lakes basin of Ethiopia. J. Weather. Clim. Extrem. 2019, 26, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eshetu, M. Hydro-Climatic Variability and Trend Analysis of Modjo River Watershed, Awash River Basin of Ethiopia. J. Hydrol. Curr. Res. 2020, 11, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Hussen, B.; Mekonnen, A.; Pingale, S.M. Integrated water resources management under climate change scenarios in the sub-basin of Abaya-Chamo, Ethiopia. J. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2018, 4, 221–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolde-Georgis, T.; Aweke, D.; Hagos, Y. The Case of Ethiopia Reducing the Impacts of Environmental Emergencies through Early Warning and Preparedness: The Case of the 1997–98 El Niño; National Meteorological Service Agency (NMSA): Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 2000; pp. 1–73. [Google Scholar]
- Wagesho, N.; Goel, N.; Jain, M. Temporal and spatial variability of annual and seasonal rainfall over Ethiopia. J. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2013, 58, 354–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraus, E. Subtropical droughts and cross-equatorial energy transports. J. Mon. Weather. Rev. 1977, 105, 1009–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Everitt, B.; Skrondal, A. The Cambridge Dictionary of Statistics, 4th ed.; Cambridge University Press Cambridge: Cambrige, UK, 2002; Volume 106. [Google Scholar]
- Kendall, M. Rank Correlation Methods, 4th ed.; Charles Griffin: London, UK, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Mann, H.B. Nonparametric tests against trend. J. Econom. Soc. 1945, 13, 245–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, P.K. Estimates of the regression coefficient based on Kendall’s tau. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1968, 63, 1379–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartier, P.M.; Keller, C.P. Multivariate interpolation to incorporate thematic surface data using inverse distance weighting (IDW). J. Comput. Geosci. 1996, 22, 795–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, G.Y.; Wong, D.W. An adaptive inverse-distance weighting spatial interpolation technique. J. Comput. Geosci. 2008, 34, 1044–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nalder, I.A.; Wein, R.W. Spatial interpolation of climatic normals: Test of a new method in the Canadian boreal forest. Agric. For. Meteorol. 1998, 92, 211–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiegel, M.R.; Stephens, L. Theory and Problems of Statistics, Schaum’s Outline Series; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1961; pp. 1–549. [Google Scholar]
- Phogat, V.; Yadav, A.; Malik, R.; Kumar, S.; Cox, J. Simulation of salt and water movement and estimation of water productivity of rice crop irrigated with saline water. Paddy Water Environ. 2010, 8, 333–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokal, R.R. The Principles and Practice of Statistics in Biological Research, 3rd ed.; W.H. Freeman: New York, NY, USA, 1995; Volume 15, pp. 451–554. [Google Scholar]
- Bekele, D.; Alamirew, T.; Kebede, A.; Zeleke, G.; Melese, A.M. Analysis of rainfall trend and variability for agricultural water management in Awash River Basin, Ethiopia. J. Water Clim. Chang. 2017, 8, 127–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Asfaw, A.; Simane, B.; Hassen, A.; Bantider, A. Variability and time series trend analysis of rainfall and temperature in northcentral Ethiopia: A case study in Woleka sub-basin. J. Weather. Earth Clim. Extrem. 2018, 19, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eshetu, G.; Johansson, T.; Garedew, W. Rainfall trend and variability analysis in Setema-Gatira area of Jimma, Southwestern Ethiopia. Afr. J. Agric. Res. 2016, 11, 3037–3045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, L.; Guo, S. Trend test and change-point detection for the annual discharge series of the Yangtze River at the Yichang hydrological station. J. Hydrol. Sci. 2011, 49, 99–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Buishand, T.A. Some methods for testing the homogeneity of rainfall records. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 1982, 58, 11–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandersson, H.; Moberg, A. Homogenization of Swedish temperature data. Part I: Homogeneity test for linear trends. Int. J. Climatol. 1997, 17, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettitt, A.N. A non-parametric approach to the change-point problem. J. R. Stat. Soc. 1979, 28, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarenistanak, M.; Dhorde, A.G.; Kripalani, R. Trend analysis and change point detection of annual and seasonal precipitation and temperature series over southwest Iran. J. Earth Syst. Sci. 2014, 123, 281–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praveen, B.; Talukdar, S.; Mahato, S.; Mondal, J.; Sharma, P.; Islam, A.R.M.T.; Rahman, A. Analyzing trend and forecasting of rainfall changes in India using non-parametrical and machine learning approaches. J. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaiswal, R.; Lohani, A.; Tiwari, H. Statistical analysis for change detection and trend assessment in climatological parameters. J. Environ. Process. 2015, 2, 729–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adeboye, O.B.; Alatise, M.O. Performance of probability distributions and plotting positions in estimating the flood of river Osun at Apoje Sub-basin, Nigeria. Int. J. Agric. Eng. 2007, 9, 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Kundzewicz, Z.W.; Radziejewski, M. Methodologies for trend detection. J. IAHS 2006, 308, 538. [Google Scholar]
- Huth, R. Parametric versus non-parametric estimates of climatic trends. J. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2004, 77, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, S.; Pilon, P.; Cavadias, G. Power of the Mann–Kendall and Spearman’s rho tests for detecting monotonic trends in hydrological series. J. Hydrol. 2002, 259, 254–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, E.; Vogel, R.; Kroll, C. Trends in floods and low flows in the United States: Impact of spatial correlation. J. Hydrol. 2000, 240, 90–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, F.; Nabi, G.; Boota, M.W. Rainfall trend analysis by using the Mann-Kendall test & Sen’s slope estimates: A case study of district Chakwal rain gauge, barani area, northern Punjab province, Pakistan. Int. J. Agric. Eng. 2015, 27, 3159–3165. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Hasani, A. Trend analysis and abrupt change detection of streamflow variations in the lower Tigris River Basin, Iraq. Int. J. River Basin Manag. 2020, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, I.; Tang, D.; Wang, T.; Wang, M.; Wagan, B. Precipitation trends over time using Mann-Kendall and spearman’s rho tests in swat river basin, Pakistan. J. Adv. Meteorol. 2015, 2015, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weldegerima, T.M.; Zeleke, T.T.; Birhanu, B.S.; Zaitchik, B.F.; Fetene, Z.A. Analysis of rainfall trends and its relationship with SST signals in the Lake Tana Basin, Ethiopia. J. Adv. Meteorol. 2018, 2018, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aguilar, C.; Polo, M. Generating reference evapotranspiration surfaces from the Hargreaves equation at watershed scale. J. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 15, 2495–2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dingman, S.L. Physical Hydrology, 3rd ed.; Waveland Press: Long Grove, IL, USA, 2015; pp. 1–657. [Google Scholar]
- Senay, G.; Leake, S.; Nagler, P.; Artan, G.; Dickinson, J.; Cordova, J.; Glenn, E. Estimating basin scale evapotranspiration (ET) by water balance and remote sensing methods. J. Hydrol. Process. 2011, 25, 4037–4049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pike, J. The estimation of annual runoff from meteorological data in a tropical climate. J. Hydrol. 1964, 2, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enyew, B.; Steeneveld, G. Analysing the impact of topography on precipitation and flooding on the Ethiopian highlands. J. Geol. Geosci. 2014, 3, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Teyso, T.A.; Anjulo, A. Reports. Spatio-temporal Variability and Trends of Rainfall and Temperature over Gamo Gofa Zone, Ethiopia. J. Sci. Res. 2016, 12, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hessebo, M.T.; Woldeamanuel, T.; Tadesse, M. Spatial and temporal climate variability and change in the Bilate catchment, central Rift Valley lakes region, Ethiopia. J. Phys. Geogr. 2019, 42, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suryabhagavan, K. GIS-based climate variability and drought characterization in Ethiopia over three decades. J.Weather. Clim. Extrem. 2017, 15, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abtew, W.; Melesse, A.M. Dessalegne. El Niño southern oscillation link to the Blue Nile River basin hydrology. J. Hydrol. Process. 2009, 23, 3653–3660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seleshi, Y.; Zanke, U. Recent changes in rainfall and rainy days in Ethiopia. Int. J. Climatol. 2004, 24, 973–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndikumana, J. Coping Mechanisms and Their Efficacy in Disaster-Prone Pastoral Systems of the Greater Horn of Africa: Effects of the 1995-97 Drought and the 1997-98 El Niño Rains and the Responses of Pastoralists and Livestock; International Livestock Research Institute: Nairobi, Kenya, 2000; pp. 1–111. [Google Scholar]
- Zena, K.; Adugna, T.; Fufa, F. Trend Analysis of Climate variables, Streamflow and their Linkage at Modjo River Watershed, Central Ethiopia. J. Environ. Syst. Res. 2020, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolde-Georgis, T. El Nino and drought early warning in Ethiopia. J. Afr. Stud. 1997, 1, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Schultz, H. Water in a warmer world—Is atmospheric evaporative demand changing in viticultural areas. In Proceedings of the BIO Web of Conferences, Geisenheim, Germany, 19 February 2019; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Getahun, Y.S.; Li, M.-H.; Chen, P.-Y. Assessing Impact of Climate Change on Hydrology of Melka Kuntrie Subbasin, Ethiopia with Ar4 and Ar5 Projections. Water 2020, 12, 1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berhane, A.; Hadgu, G.; Worku, W.; Abrha, B. Trends in extreme temperature and rainfall indices in the semi-arid areas of Western Tigray, Ethiopia. J. Environ. Syst. Res. 2020, 9, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Degefu, M.A.; Rowell, D.P.; Bewket, W. Teleconnections between Ethiopian rainfall variability and global SSTs: Observations and methods for model evaluation. J. Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 2017, 129, 173–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Samy, A.; Ibrahim, M.G.; Mahmod, W.E. Analysis of Stream Flow Trends in Sub-basins of the Upper Blue Nile Basin. In Recent Advances in Environmental Science from the Euro-Mediterranean and Surrounding Regions; Kallel, A., Ksibi, M., Ben Dhia, H., Khélifi, N., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Germany, 2018; Volume 1, pp. 819–822. [Google Scholar]
- Devereux, S. Food Insecurity in Ethiopia: A Discussion Paper for DFID; Institute of Development Studies: Brighton, UK, 2000; Volume 14, pp. 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammed, Y.; Yimer, F.; Tadesse, M.; Tesfaye, K. Meteorological drought assessment in north east highlands of Ethiopia. Int. J. Clim. Chang. Strateg. Manag. 2018, 10, 142–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, J.; Huang, S.; Huang, Q.; Wang, H.; Leng, G. Detecting the dominant cause of streamflow decline in the Loess Plateau of china based on the latest Budyko equation. Water 2018, 10, 1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gunta, S.; Manjunatha, B.; Bhta, H.G. Monthly to Inter-Decadal Rainfall Variability of the Southern Regional Sate of Ethiopia, Links with El Niño-Southern Oscillation. Glob. J. Sci. Front. Res. 2019, 19, 21p. [Google Scholar]
- Almazroui, M.; Hasanean, H.; Al-Khalaf, A.; Basset, H.A. Detecting climate change signals in Saudi Arabia using mean annual surface air temperatures. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2013, 113, 585–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, T.; Gemmer, M.; Liu, L.; Su, B. Change-points in climate extremes in the Zhujiang River Basin, South China, 1961–2007. J. Clim. Chang. 2012, 110, 783–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suhaila, J.; Yusop, Z. Trend analysis and change point detection of annual and seasonal temperature series in Peninsular Malaysia. Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 2018, 130, 565–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho Ming, K.; Yusof, F. Homogeneity Tests on Daily Rainfall Series in Peninsular Malaysia. Int. J. Contemp. Math. Sci. 2012, 7, 9–22. [Google Scholar]
- Moges, S.A.; Taye, M.T.; Willems, P.; Gebremichael, M. Exceptional pattern of extreme rainfall variability at urban centre of Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. Urban Water J. 2014, 11, 596–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- World Meteorological Organization Geneva. World Meteorological Organization (WMO) Guidelines on the Calculation of Climate Normals; World Meteorological Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Medina, Y.; Muñoz, E. Estimation of Annual Maximum and Minimum Flow Trends in a Data-Scarce Basin. Case Study of the Allipén River Watershed, Chile. Water 2020, 12, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]



| SAI Value | Category |
|---|---|
| 2.00 and above 1.50 to 1.99 1.00 to 1.49 −0.99 to 0.99 −1.49 to −1.00 −1.99 to −1.50 −2.00 and less | Extremely Wet Very wet Moderately Wet Near Normal Moderately Dry Severely Dry Extremely Dry |
| EP (%) | Rainfall (mm) | Streamflow (mm) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| before CP | after CP | before CP | after CP | |
| 0.1 | 27.67 | 25.82 | 3.7 | 2.6 |
| 1 | 16.6 | 16.4 | 1.9 | 1.5 |
| 10 | 8.76 | 8.15 | 1 | 0.7 |
| 25 | 5.28 | 4.67 | 0.7 | 0.5 |
| 50 | 2.14 | 1.75 | 0.3 | 0.2 |
| 75 | 0.06 | 0.02 | 0.1 | 0.1 |
| 99 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| PET | ET | Tmax − Tmin | (Tmax + Tmin)/2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sen’s Slope | −0.38 | −2.71 | −0.046 | 0.044 |
| Zs | −0.88 | −5.86 | −5.86 | 5.89 |
| Trend | - | - | - | + |
| Seasons | Tmax | Tavg | Tmin | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zs | Sen’s Slope | Zs | Sen’s Slope | Zs | Sen’s Slope | |
| Bega | 1.67 | 0.021 | 4.82 * | 0.047 | 4.02 * | 0.068 |
| Belg | 2.28 * | 0.031 | 3.68 * | 0.041 | 4.00 * | 0.058 |
| Kiremt | 2.18 * | 0.024 | 4.39 * | 0.039 | 4.07 * | 0.059 |
| Annual | 2.93 * | 0.019 | 5.89 * | 0.044 | 3.64 * | 0.056 |
| Seasons | Full Period | Before CP | After CP | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zs | Sen’s Slope | Zs | Sen’s Slope | Zs | Sen’s Slope | |
| Bega | 4.82 * | 0.047 | 1.09 | 0.05 | 3.01 * | 0.04 |
| Belg | 3.68 * | 0.041 | −3.48 * | −0.06 | 1.65 | 0.01 |
| Kiremt | 4.39 * | 0.039 | 0.36 | 0.02 | 4.38 * | 0.03 |
| Annual | 5.89 * | 0.044 | −0.38 | −0.01 | 2.81 * | 0.02 |
| Seasons | Full Period | Before CP | After CP | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zs | Sen’s Slope | Zs | Sen’s Slope | Zs | Sen’s Slope | |
| Bega | −0.31 | −0.34 | 2.15 * | 7.76 | −5.15 * | −3.56 |
| Belg | −6.11 * | −5.57 | −2.18 * | −9.85 | 0.17 | 0.22 |
| Kiremt | −1.46 | −0.89 | −2.36 * | −9.25 | 0.0 | 0.07 |
| Annual | −7.53 * | −8.32 | −1.21 | −8.56 | −1.28 | −5.84 |
| Seasons | Full Period | Before CP | After CP | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zs | Sen’s Slope | Zs | Sen’s Slope | Zs | Sen’s Slope | |
| Bega | −0.21 * | −0.47 | −0.09 | −0.07 | −0.16 | −0.43 |
| Belg | −6.42 * | −1.08 | −2.17 * | −0.79 | −1.37 | −0.53 |
| Kiremt | −8.77 * | −2.04 | −3.98 * | −2.33 | −3.62 * | −7.15 |
| Annual | −8.19 * | −3.64 | −3.42 * | −3.45 | −1.84 | −7.50 |
| Parameters | Kiremt | Belg | Bega | Annual | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bilate | Mojo | Kulfo | Bilate | Mojo | Kulfo | Bilate | Mojo | Kulfo | Bilate | Mojo | Kulfo | |
| Tmax (°C) | 0.02 | 0.06 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.05 | 0.01 | 0.02 | NA | 0.0 | 0.02 | 0.06 | 0.02 |
| Tavg (°C) | 0.03 | NA | 0.04 | 0.04 | NA | 0.04 | 0.05 | NA | 0.02 | 0.04 | NA | 0.02 |
| Tmin (°C) | 0.06 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.06 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.07 | NA | 0.0 | 0.06 | 0.01 | 0.0 |
| Rainfall (mm) | −0.89 | 2.64 | 1.01 | −5.57 | −0.03 | 0.23 | −0.34 | NA | 1.99 | −8.32 | 3.85 | 3.89 |
| Streamflow (mm) | −2.04 | −0.10 | 0.22 | −1.08 | 0.0 | 0.27 | −0.47 | NA | 0.21 | −3.64 | −0.04 | 0.25 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Orke, Y.A.; Li, M.-H. Hydroclimatic Variability in the Bilate Watershed, Ethiopia. Climate 2021, 9, 98. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli9060098
Orke YA, Li M-H. Hydroclimatic Variability in the Bilate Watershed, Ethiopia. Climate. 2021; 9(6):98. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli9060098
Chicago/Turabian StyleOrke, Yoseph Arba, and Ming-Hsu Li. 2021. "Hydroclimatic Variability in the Bilate Watershed, Ethiopia" Climate 9, no. 6: 98. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli9060098
APA StyleOrke, Y. A., & Li, M.-H. (2021). Hydroclimatic Variability in the Bilate Watershed, Ethiopia. Climate, 9(6), 98. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli9060098







