A Stage Flow Parameter Analytical Model for Transonic Counter-Rotating Compressor and Its Application
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Analytical Model to Calculate Counter-Rotating Compressor Stage Parameters
2.1. Aim and Method
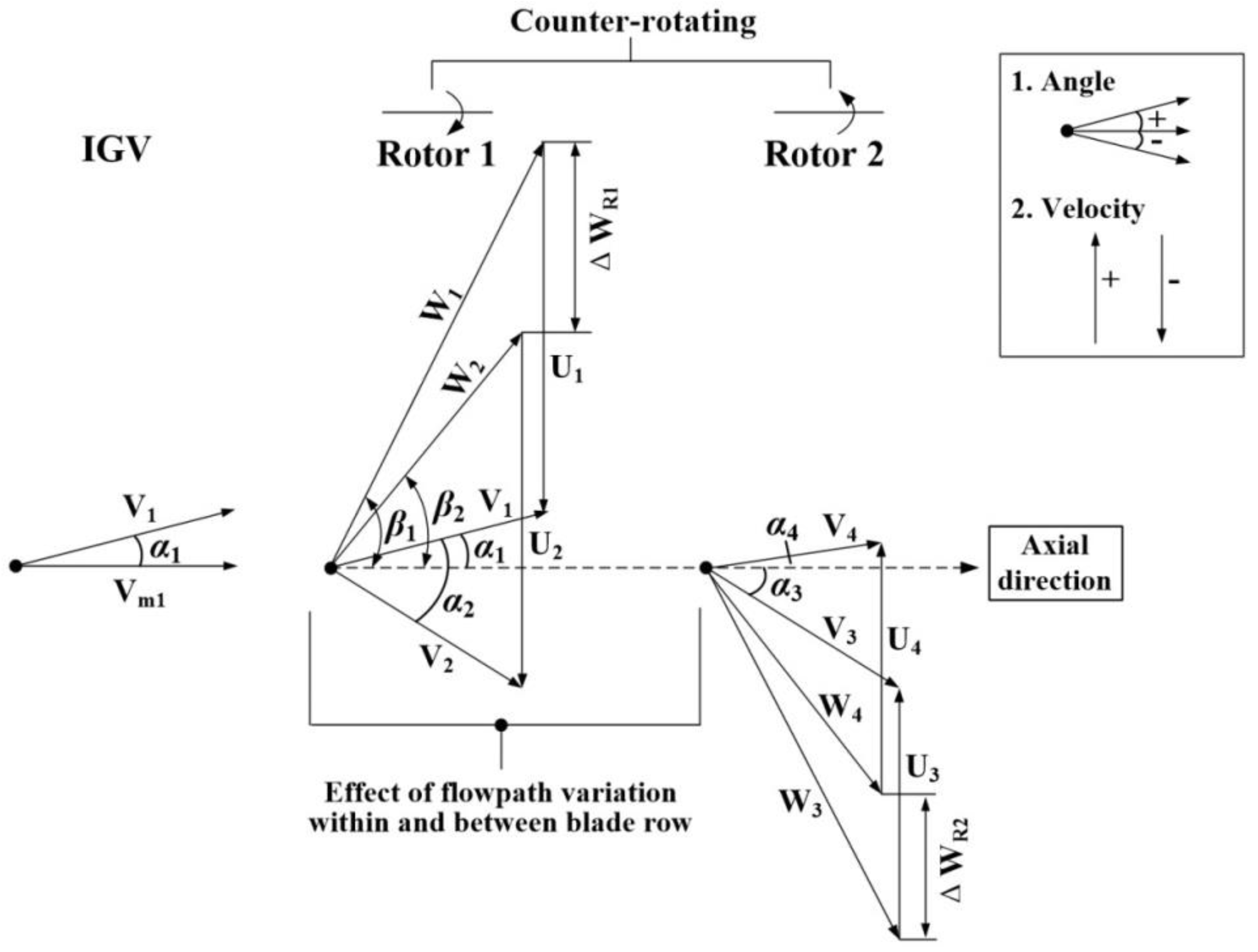
2.2. IGV + Upstream Rotor (R1)
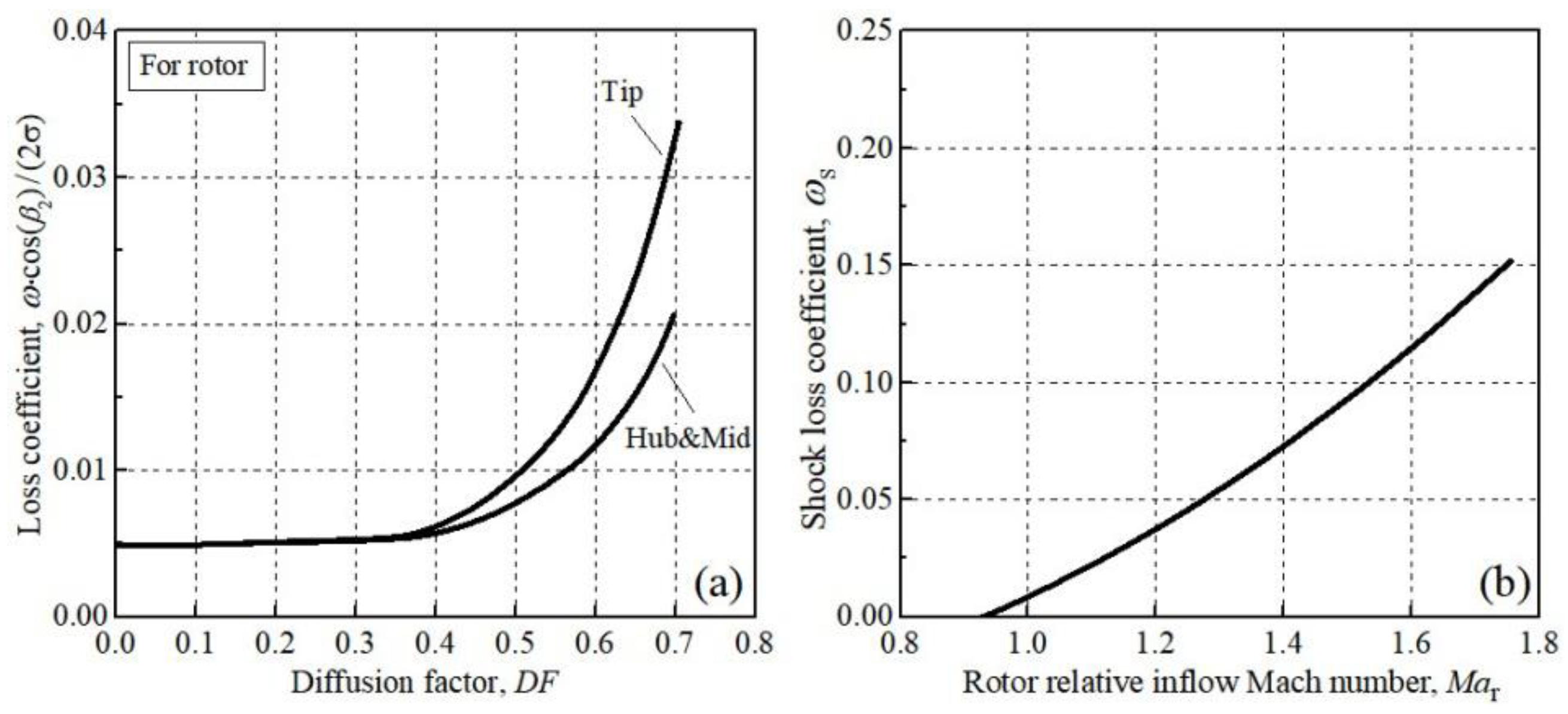
2.3. Prediction of Loss Coefficient
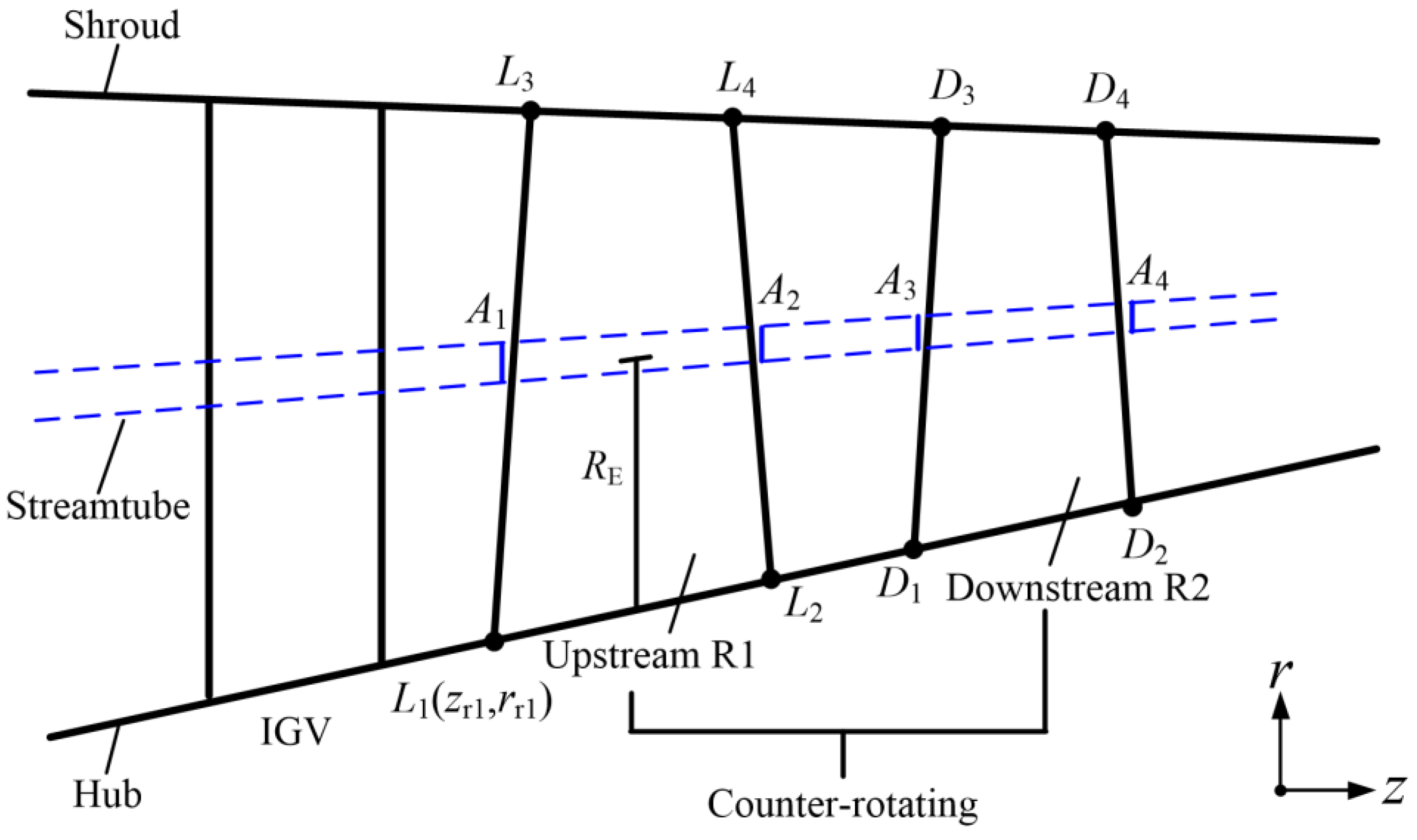
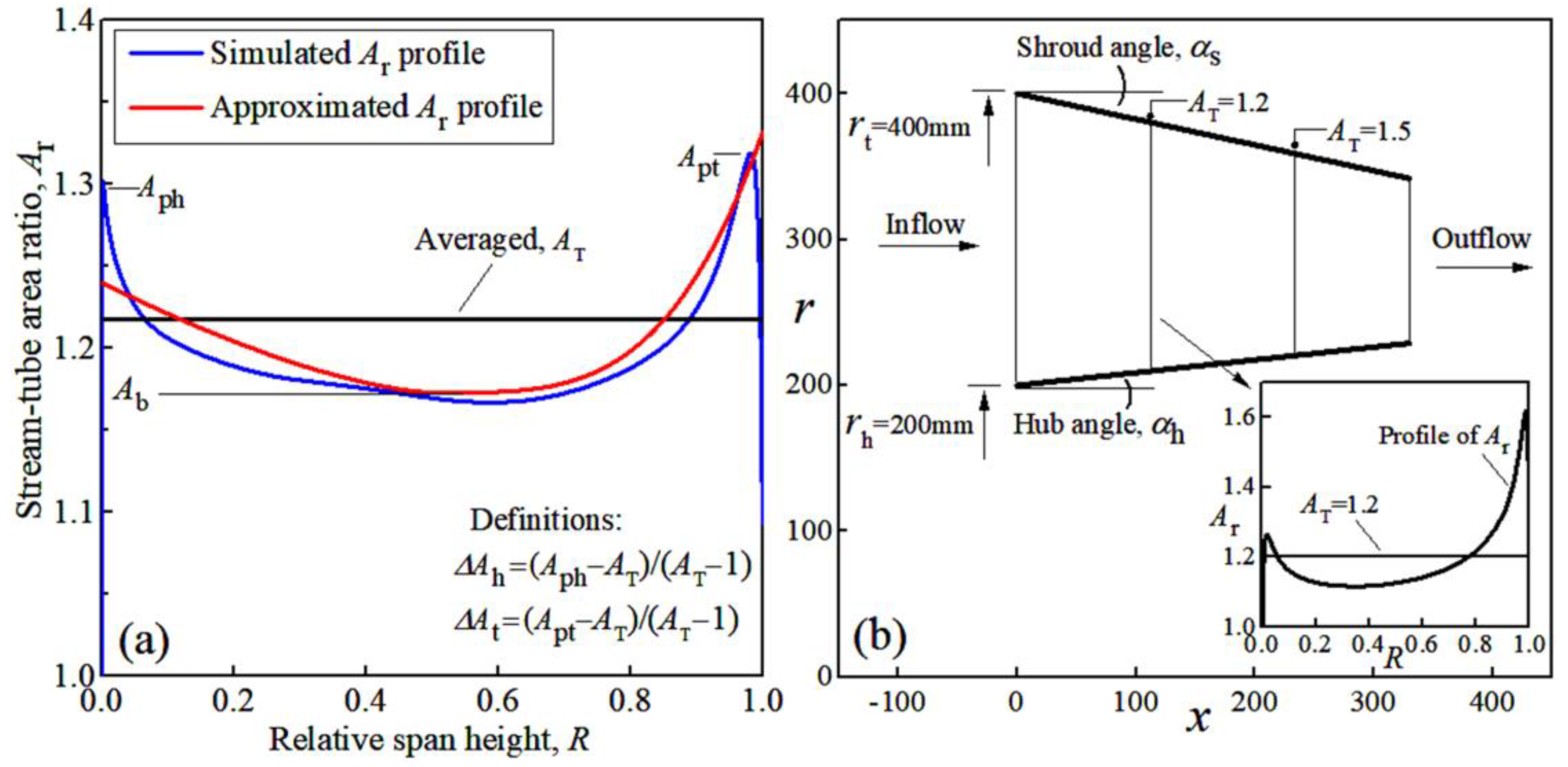
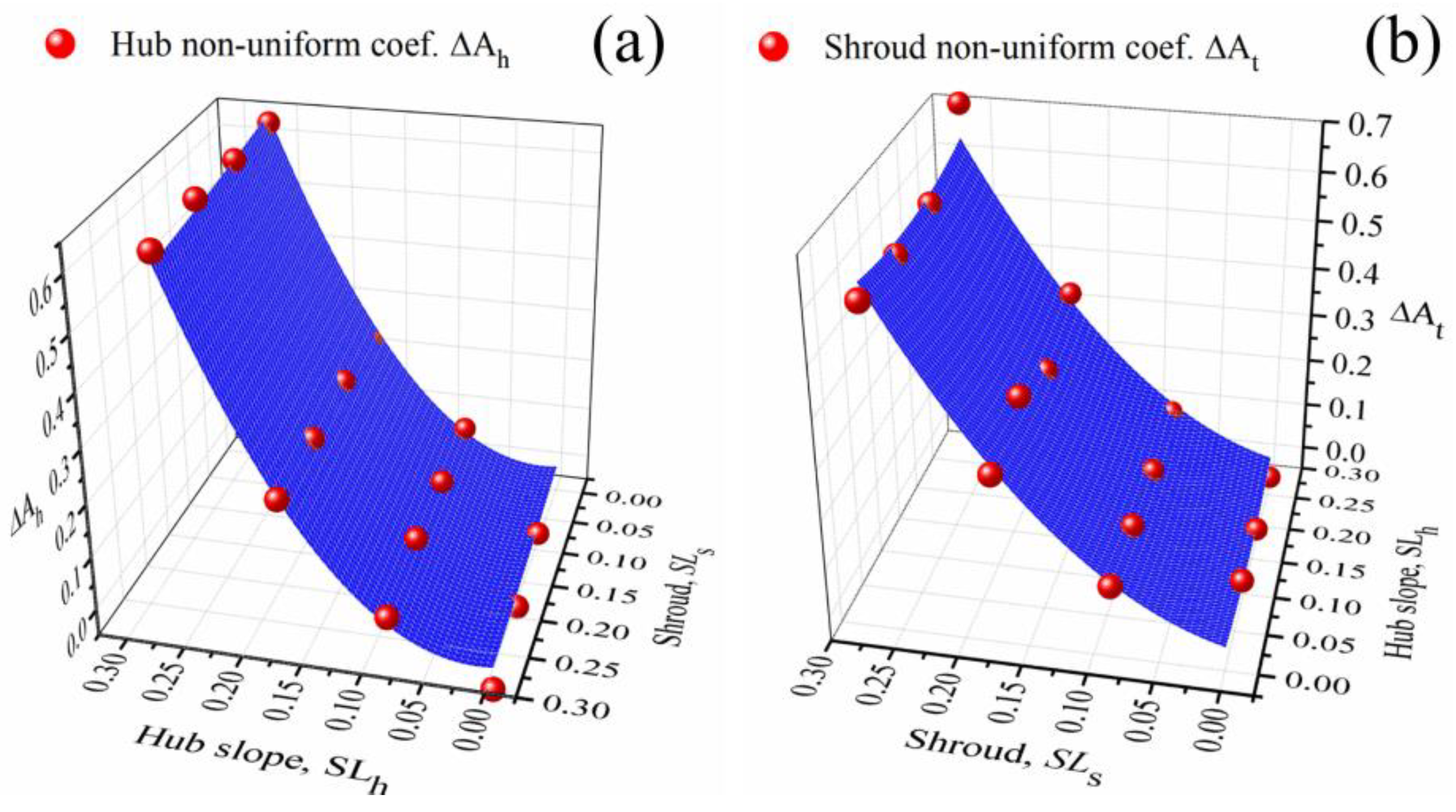
2.4. Flow-Path Variation Effect
2.5. Counter-Rotating Rotor R2
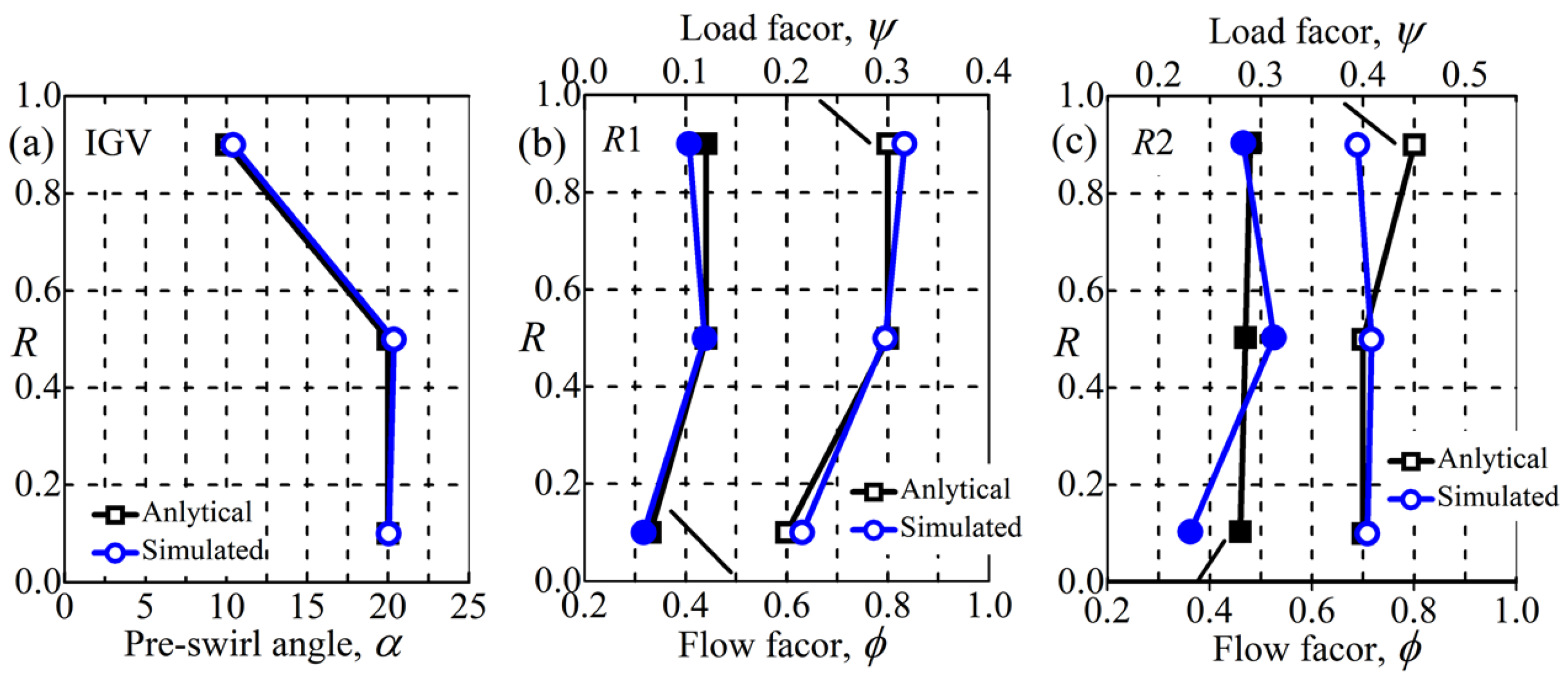
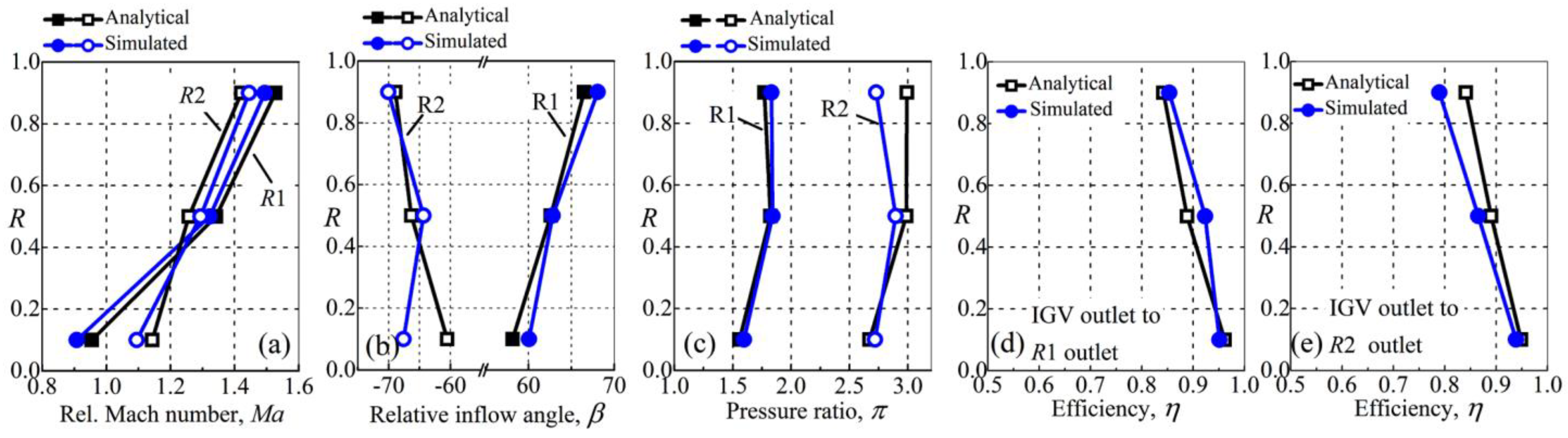
3. Analytical Model Aided the Aerodynamic Design of a Transonic Counter-Rotating Fan Stage
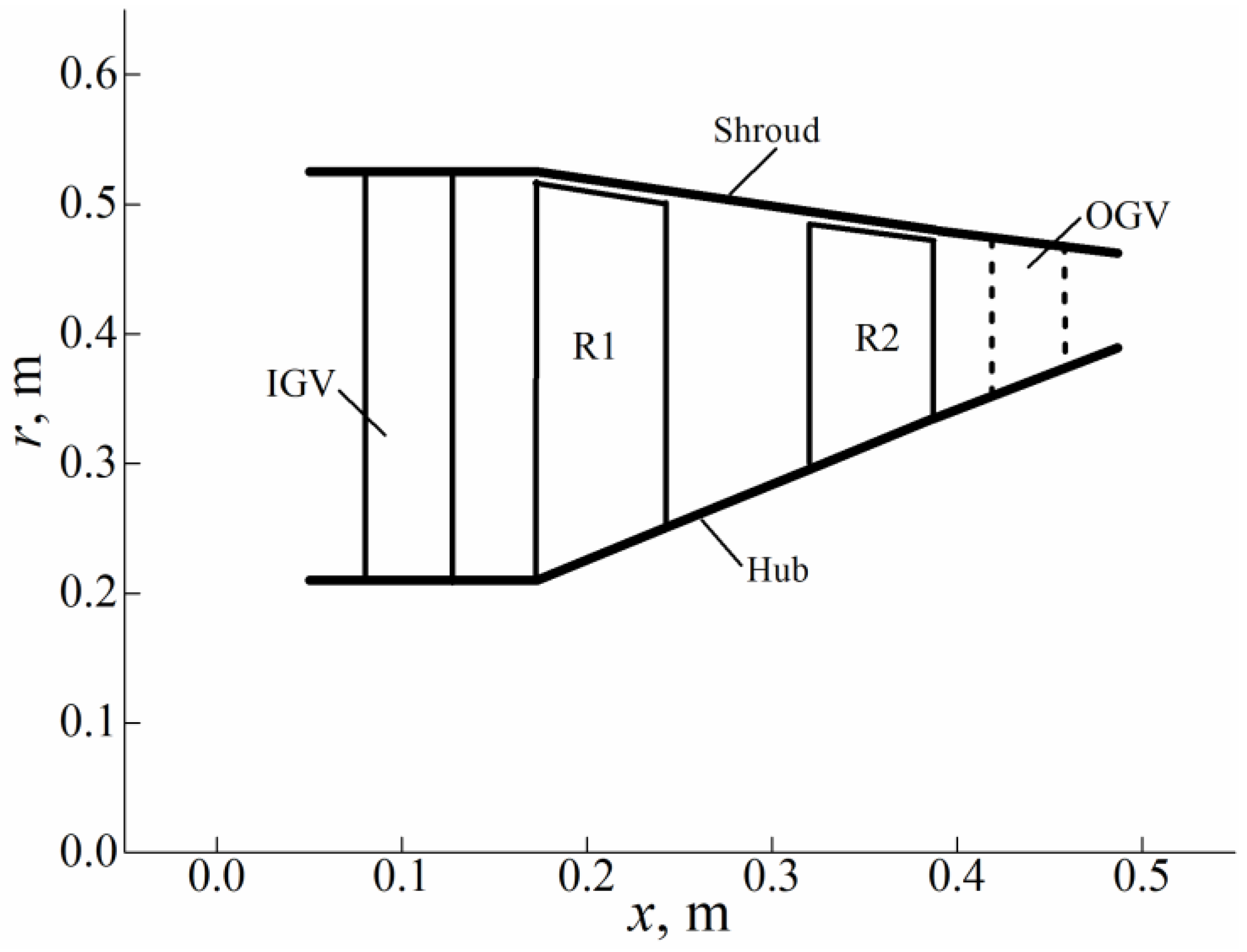
3.1. Introduction of the Design Case
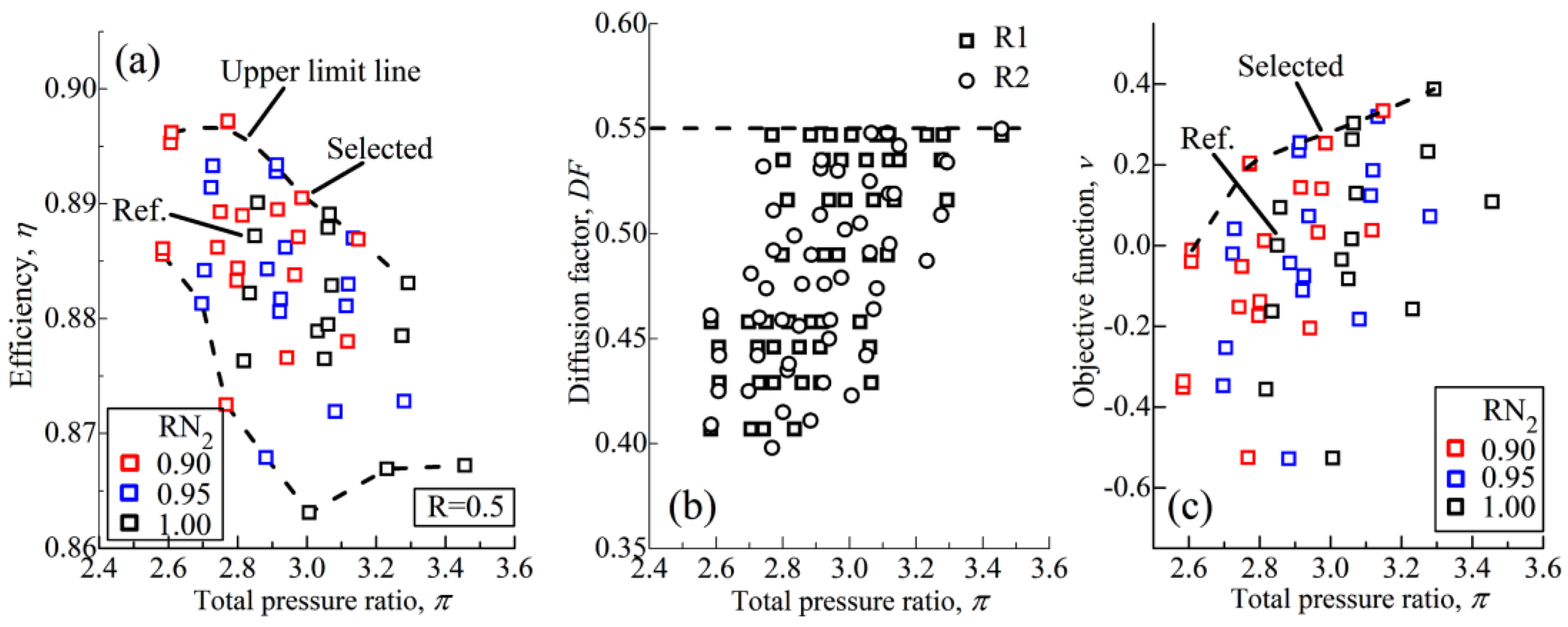
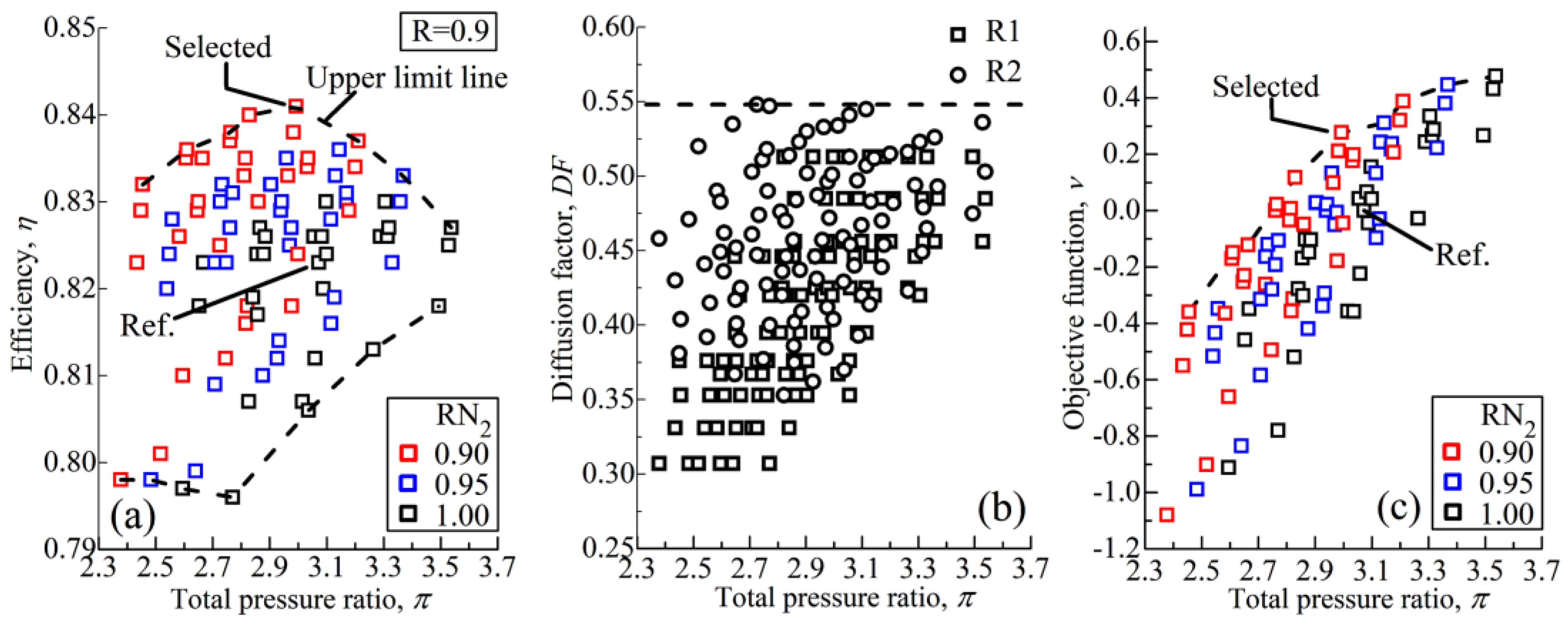
3.2. Analytical Model Calculated Results
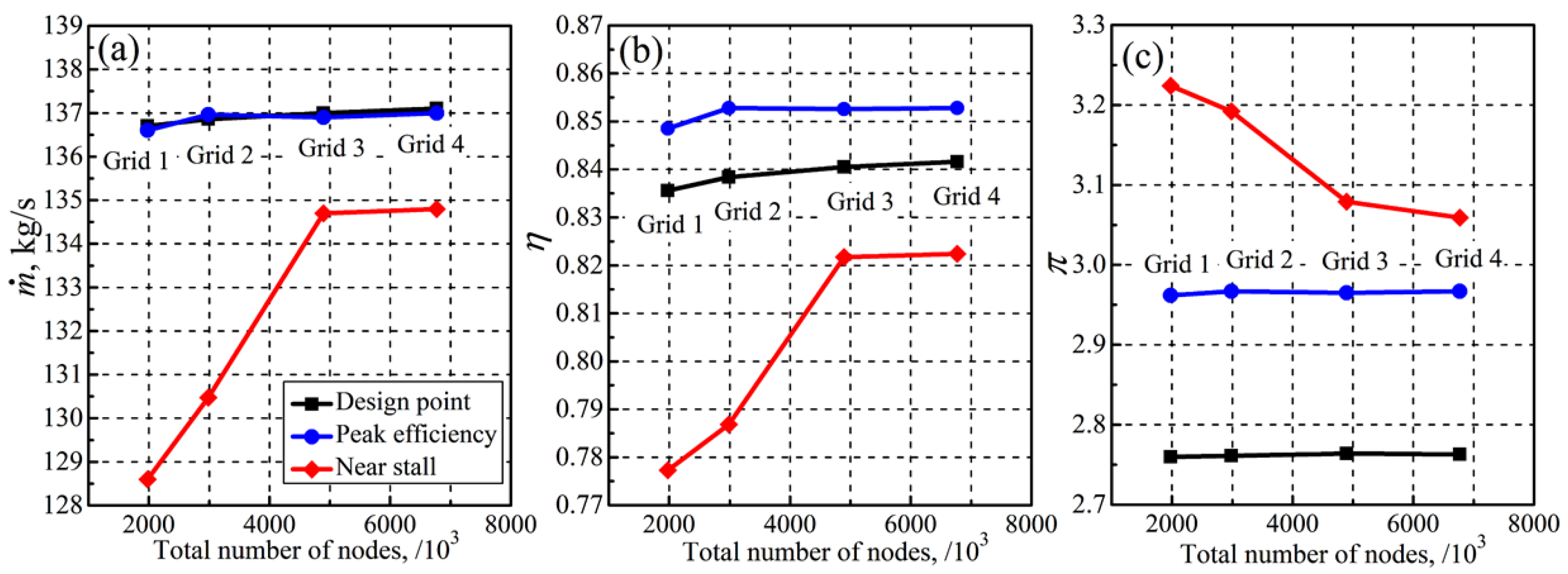
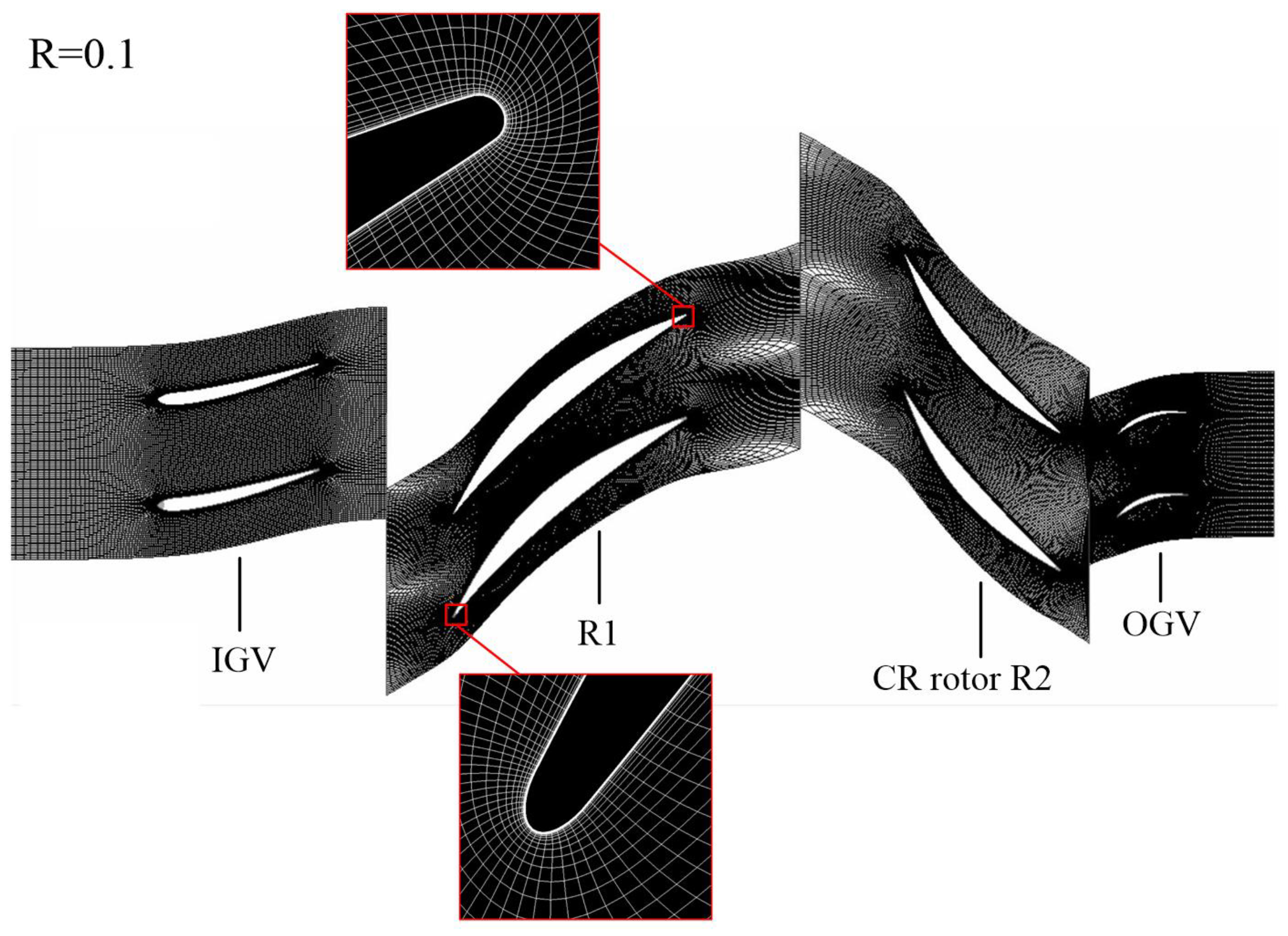
3.3. Numerical Method
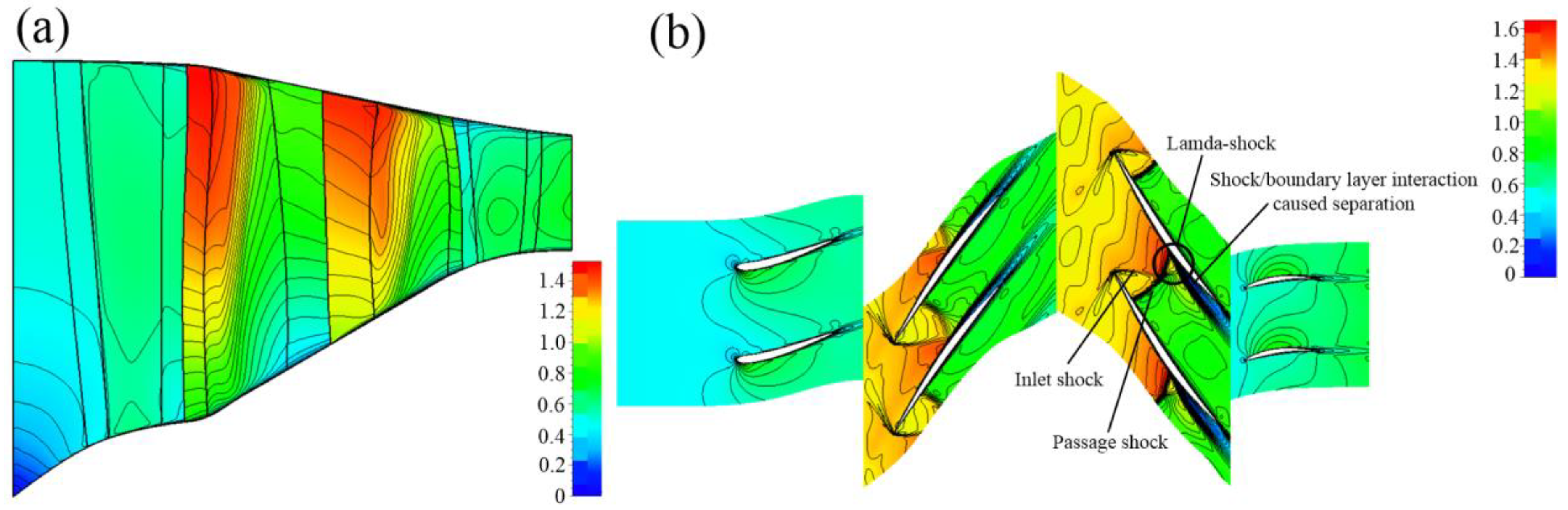
4. Aerodynamic Characteristic and Flow Analysis of the Transonic Counter-Rotating Fan
4.1. Aerodynamic Characteristic
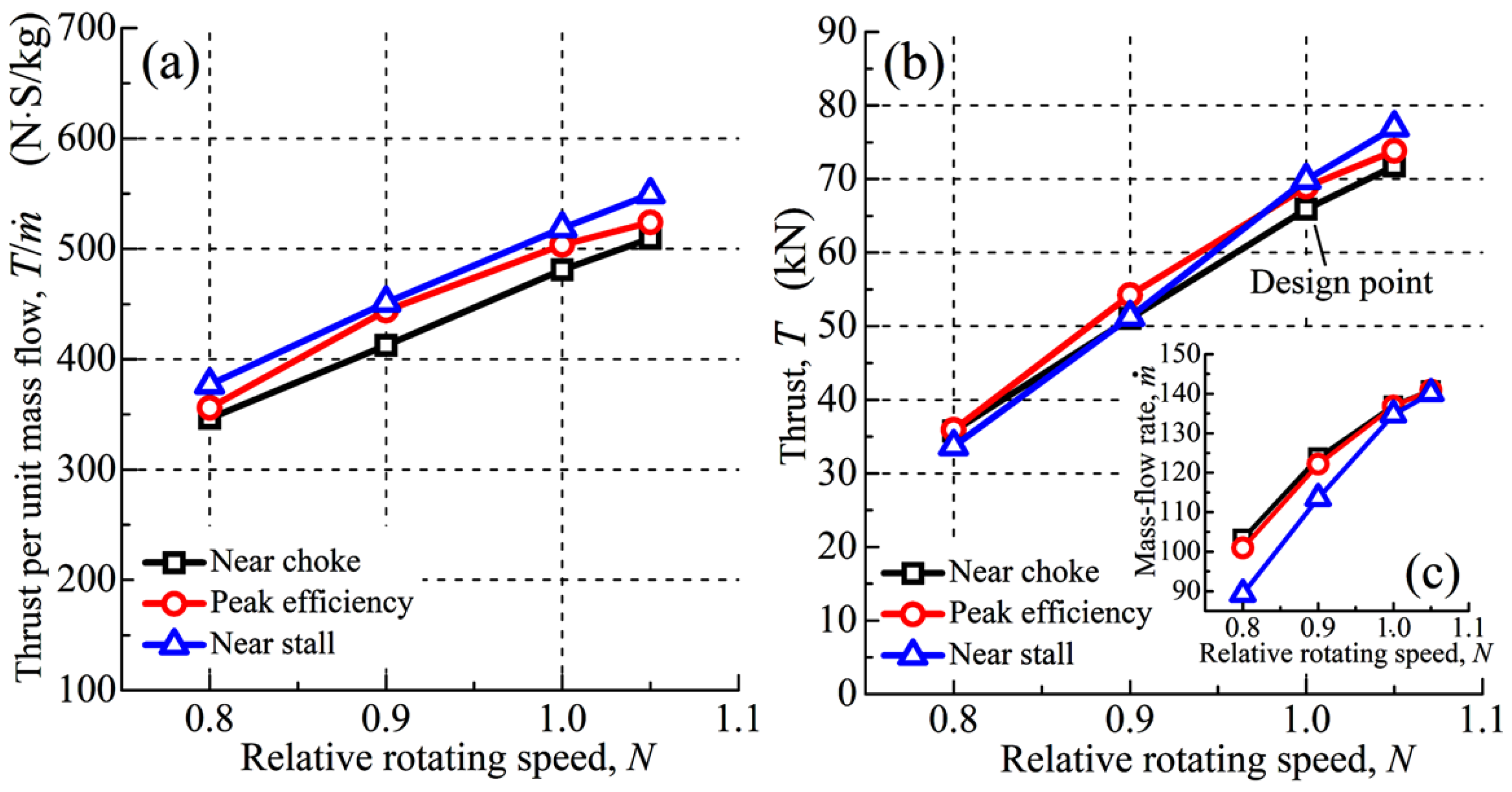
4.2. Calculation of Thrust
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| p | Static pressure (Pa) |
| Mass-flow rate (kg/s) | |
| i | Incidence angle |
| k | Specific heat ratio, k = 1.4 |
| Radius of blade section (mm) | |
| Stream-tube area ratio, | |
| C | Chord (mm) |
| Diffusion factor, for rotor | |
| Ma | Mach number |
| N | Rotating speed (rpm) |
| P | Total pressure (Pa) |
| R | Blade relative height |
| Specific gas constant for air, | |
| T | Total temperature (K) |
| Blade section tangential velocity (m/s) | |
| Absolute axial velocity (m/s) | |
| Absolute radial velocity (m/s) | |
| Absolute meridian velocity (m/s), | |
| Relative flow angle measured from axial direction (degree) | |
| Relative error | |
| Total pressure ratio, | |
| Efficiency, | |
| Solidity, | |
| Flow coefficient based on blade tip (LE side) tangential velocity, | |
| Load coefficient based on blade tip (LE side) tangential velocity, | |
| Increment of enthalpy by the rotor section | |
| CR | Counter-rotating |
| LE | Leading edge |
| TE | Trailing edge |
References
- Lynam, F.C.; Hawes, S.P. Contra Rotating Axial Flow Fans. Engineers 1946, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Young, R.H. Counter Rotating Fans. JHIVE 1952, 18, 187. [Google Scholar]
- Sabel, E.; Sabatiuk, A. Turbojet Engine Development: Design of Phase I Compressor; Curtiss-Wright Corporation: Davidson, NC, USA, 1957. [Google Scholar]
- Sabel, E.; Sabatiuk, A. Turbojet Engine Development: Phase I Compressor Test Results; Curtiss-Wright Corporation: Davidson, NC, USA, 1957. [Google Scholar]
- Millar, D.A.J.; Chappell, M.S.; Okelah, R. The Co-Turbo Shaft: A Novel Gas Turbine Power Plant for Heavy Equipment. In Proceedings of the ASME 1979 International Gas Turbine Conference and Exhibit and Solar Energy Conference, San Diego, CA, USA, 12–15 March 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Kirchner, J. Aerodynamic Design of an Aspirated Counter-Rotating Compressor; Massachusetts Institute of Technology: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Merchant, A.; Kerrebrock, J.L.; Epstein, A.H. Compressors with aspirated flow control and counter-rotation. In Proceedings of the 2nd AIAA Flow Control Conference, Portland, OR, USA, 28 June–1 July 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Kerrebrock, J.L.; Epstein, A.H.; Merchant, A.; Guenette Gerald, R.; David, P. Design and test of an aspirated counter-rotating fan. ASME J. Turbomach. 2008, 130, 021004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knapke, R.D.; Turner, M.G. Unsteady simulations of a counter-rotating aspirated compressor. In Proceedings of the ASME Turbo Expo 2013: Turbine Technical Conference and Exposition, San Antonio, TX, USA, 3–7 June 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Talbotec, J.; Vernet, M. SNECMA Counter rotating Fan aerodynamic design logic & tests results. In Proceedings of the 27th International Congress of Aeronautical Sciences, Nice, France, 19–24 September 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Lengyel, T.; Nicke, E.; Rüd, K.-P.; Schaber, R. Optimization and examination of a counter-rotating fan stage: The possible improvement of the efficiency compared with a single rotating fan. In Proceedings of the ISABE, Gothenburg, Sweden, 12–16 September 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Schmid, T.; Lengyel-Kampmann, T.; Schmidt, T.; Nicke, E. Optimization of a carbon-fiber composite blade of a counter-rotating fan for aircraft engines. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Turbomachinery Fluid Dynamics and Thermodynamics, Lausanne, Switzerland, 8–12 April 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Ly, T.; Koc, K.; Meillard, L.; Schnell, R. Evaluation of the aerodynamic performance of the counter rotating turbo fan COBRA by means of experimental and numerical data. CEAS Aeronaut. J. 2022, 13, 385–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vijayraj, K.; Govardhan, M. Aerodynamics of contra-rotating fans with swept blades. In Proceedings of the ASME 2015 Gas Turbine India Conference, Hyderabad, India, 2–3 December 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Wang, Y.; Xian, S.; Hu, W. Effect of inlet distortion on the performance of axial transonic contra-rotating compressor. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part G J. Aerosp. Eng. 2016, 232, 42–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, X.; Liu, B.; Zhao, H. Effects of tip clearance size on the unsteady flow behaviors and performance in a counter-rotating axial flow compressor. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part G J. Aerosp. Eng. 2017, 233, 1059–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Wang, S.; Chen, S. Aerodynamic Design and Analysis of a Two-Stage High-Load Low-Reaction Transonic Aspirated Counter-Rotating Compressor. In Proceedings of the ASME Turbo Expo 2017: Turbomachinery Technical Conference and Exposition, Charlotte, NC, USA, 26–30 June 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Joshi, N.; Payyappalli, M.M.; Pradeep, A.M. Performance evaluation of contra-rotating fans operating under different speed combinations. In Proceedings of the ASME 2019 Gas Turbine India Conference, Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India, 5–6 December 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, T.; Liu, B.; Spence, S.; Jiao, L. Numerical analysis of the effects of circumferential groove casing suction in a counter-rotating axial flow compressor. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part A J. Power Energy 2020, 235, 944–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnsen, I.A.; Bullock, R.O. Aerodynamic Design of Axial-Flow Compressors; NASA: Washington, DC, USA, 1965. [Google Scholar]
- Wennerstrom, A.J.; Puterbaugh, S.L. A Three-Dimensional Model for the Prediction of Shock Losses in Compressor Blade Rows. ASME J. Eng. Gas Turbines Power 1984, 106, 295–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, C.C.; Smith, L.H., Jr. Loss Sources and Magnitudes in Axial-Flow Compressors. ASME J. Eng. Power 1976, 98, 411–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H. A Parametric Blade Design Method for High-Speed Axial Compressor. Aerospace 2021, 8, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H. Parametric Research and Aerodynamic Characteristic of a Two-Stage Transonic Compressor for a Turbine Based Combined Cycle Engine. Aerospace 2022, 9, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Liu, B.; Yu, X. Criteria for designing low-loss and wide operation range variable inlet guide vanes. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2018, 80, 177–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravanamuttoo, H.I.H.; Rogers, G.F.C.; Cohen, H.; Straznicky, P.V.; Nix, A.C. Gas Turbine Theory; Pearson: Harlow, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]



| Input Parameters | Symbol |
|---|---|
| IGV outflow property and angle | |
| R1 load and flow coefficients | |
| R1 rotating speed | |
| Coordinates of points | |
| R1 chord length radial distribution | |
| R2 load coefficient | |
| Relative rotating speed of R2 (relative to R1) | |
| Coordinates of points | |
| Downstream rotor (R2) chord length radial distribution | |
| Output Parameters | Symbol |
| Relative Mach number and inflow angle of rotors R1 and R2 | |
| Total pressure ratio of R1 and R2 | |
| Efficiency of R1 and R2 | |
| Specified Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| Rotating speed of R1, | 8200 rpm |
| Shroud radius of R1, | 525 mm |
| R1 hub to tip ratio at leading edge | 0.40 |
| R1 flow coefficient for R = 0.1, 0.5, and 0.9, | 0.330/0.440/0.440 |
| R1 and R2 chord length radial distribution | , |
| Hub and shroud slope from R1 LE to R2 TE | 0.582, −0.207 |
| Design variables | Symbol |
| Upstream rotor (R1) load coefficient | |
| IGV pre-swirl angle | |
| CR rotor R2 relative rotating speed | |
| CR rotor R2 load coefficient | |
| Output parameters | Symbol |
| Relative Mach number and inflow angle of rotors R1 and R2 | |
| Diffusion factor of rotors R1 and R2 | , |
| Transonic CR fan total pressure ratio and efficiency | and |
| Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| Blade section relative height, | 0.1, 0.5, 0.9 |
| IGV pre-swirl angle, | 0, 10, 20, 30 |
| Upstream rotor (R1) load coefficient, | 0.20, 0.25, 0.30 for R = 0.1; 0.25, 0.30, 0.35 for R = 0.5, 0.9 |
| CR rotor R2 relative rotating speed, | 0.90, 0.95, 1.0 |
| CR rotor R2 load coefficient, | 0.35, 0.40, 0.45 |
| Research samples for blade section R = 0.1, 0.5, and 0.9 | 108 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shi, H.; Yu, X. A Stage Flow Parameter Analytical Model for Transonic Counter-Rotating Compressor and Its Application. Aerospace 2023, 10, 144. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace10020144
Shi H, Yu X. A Stage Flow Parameter Analytical Model for Transonic Counter-Rotating Compressor and Its Application. Aerospace. 2023; 10(2):144. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace10020144
Chicago/Turabian StyleShi, Hengtao, and Xianjun Yu. 2023. "A Stage Flow Parameter Analytical Model for Transonic Counter-Rotating Compressor and Its Application" Aerospace 10, no. 2: 144. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace10020144
APA StyleShi, H., & Yu, X. (2023). A Stage Flow Parameter Analytical Model for Transonic Counter-Rotating Compressor and Its Application. Aerospace, 10(2), 144. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace10020144






