Numerical Investigation of Mach 2.5 Axisymmetric Turbulent Shock Wave Boundary Layer Interactions
Abstract
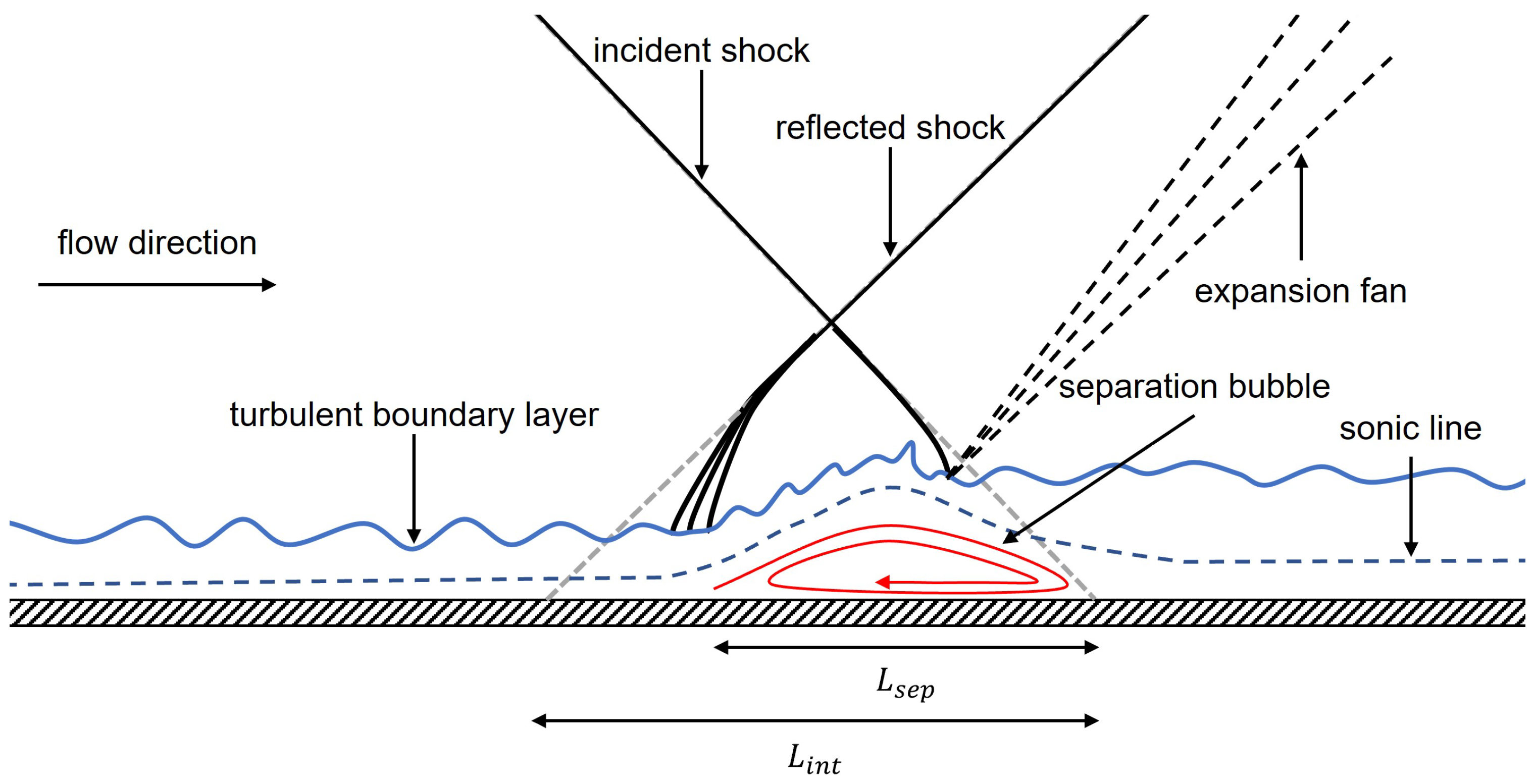
:1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Governing Equations and Discretization
2.2. Non-Dimensionalization
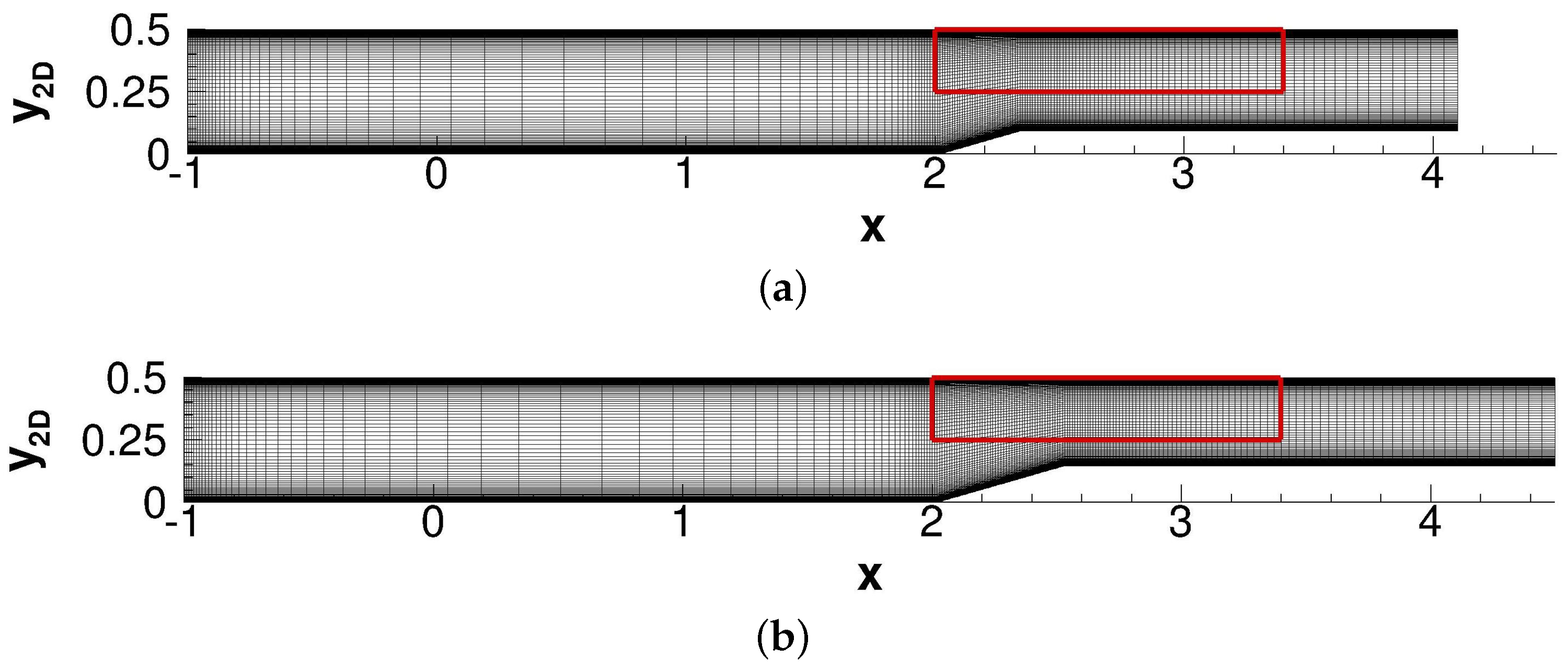
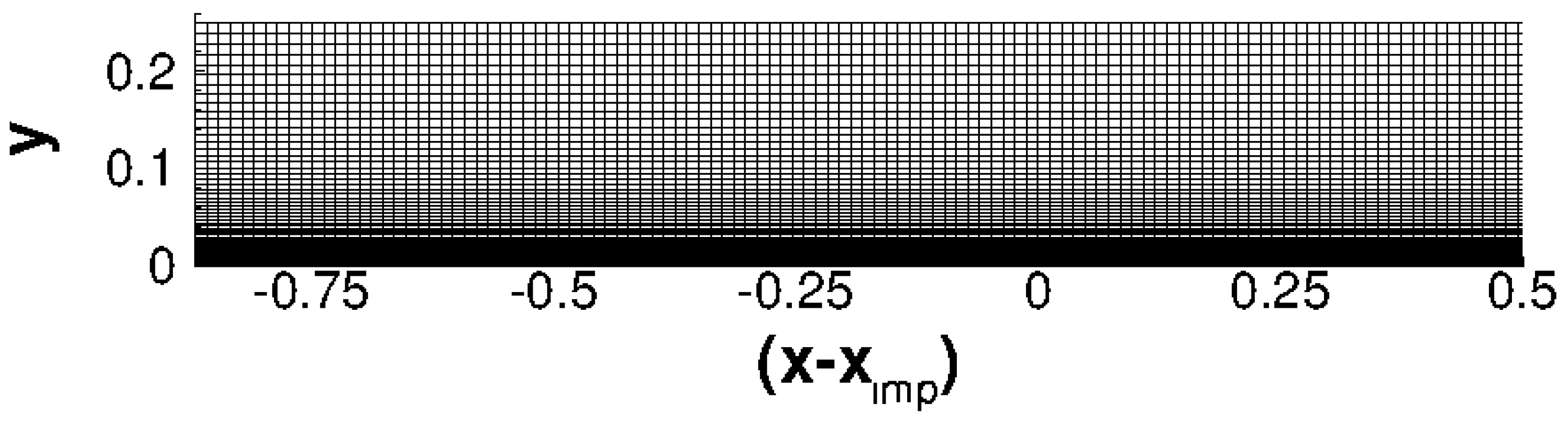
2.3. Computational Grids
2.4. Boundary Conditions
2.5. Proper Orthogonal Decomposition and Fourier Transforms
3. Results
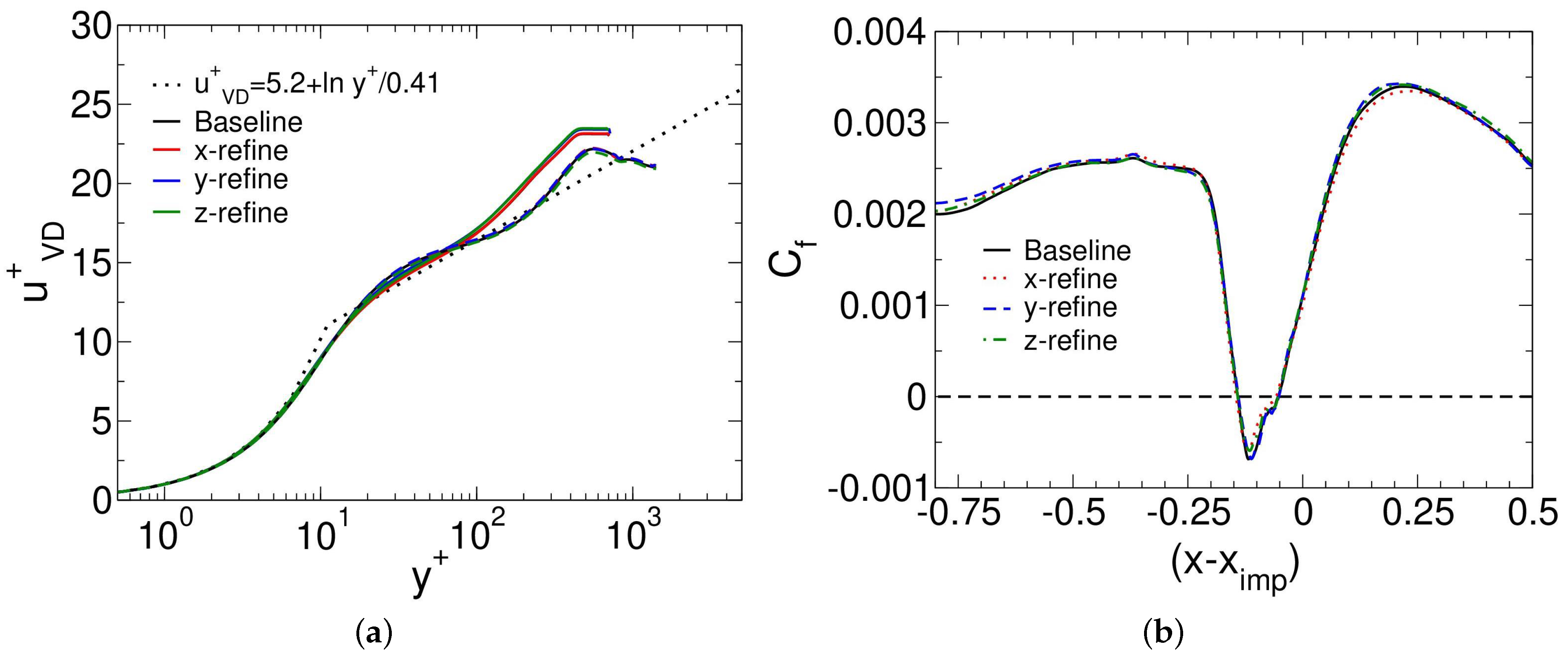
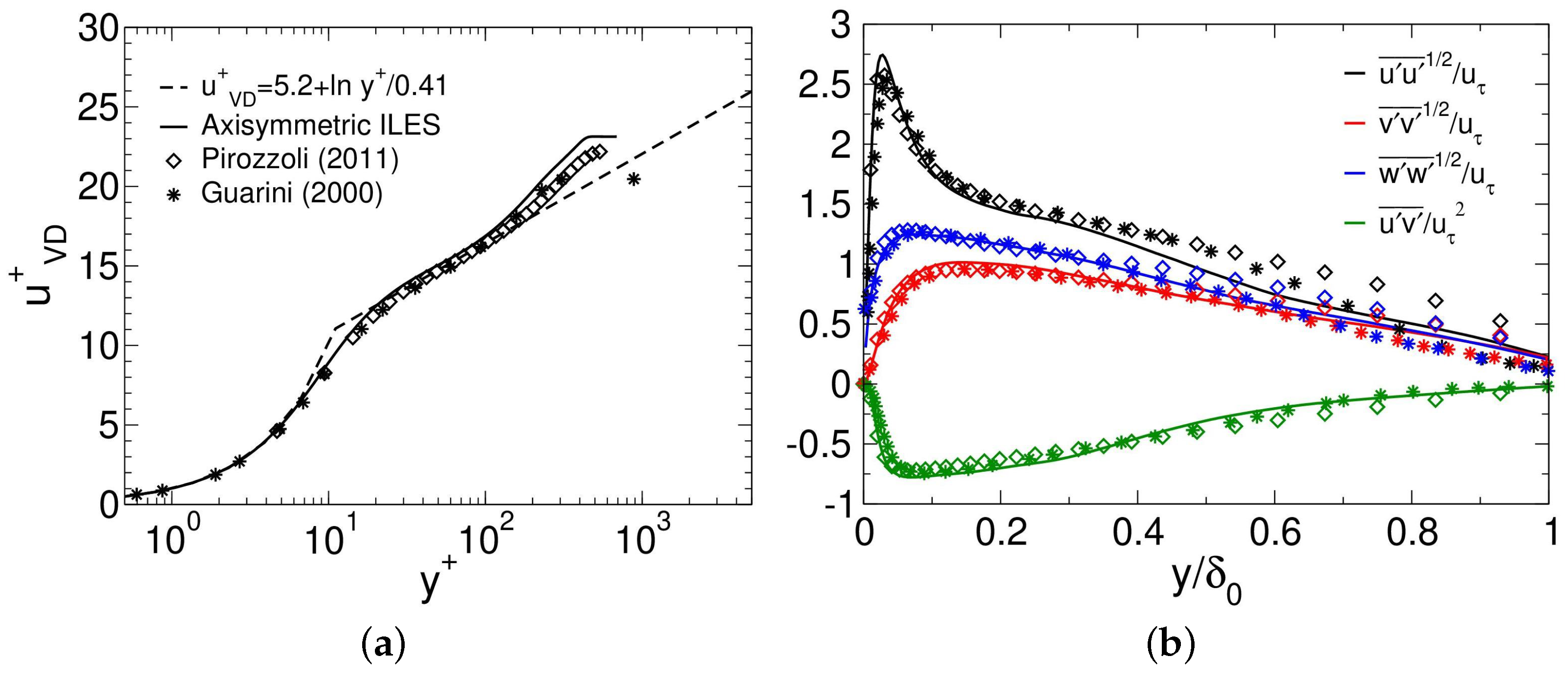
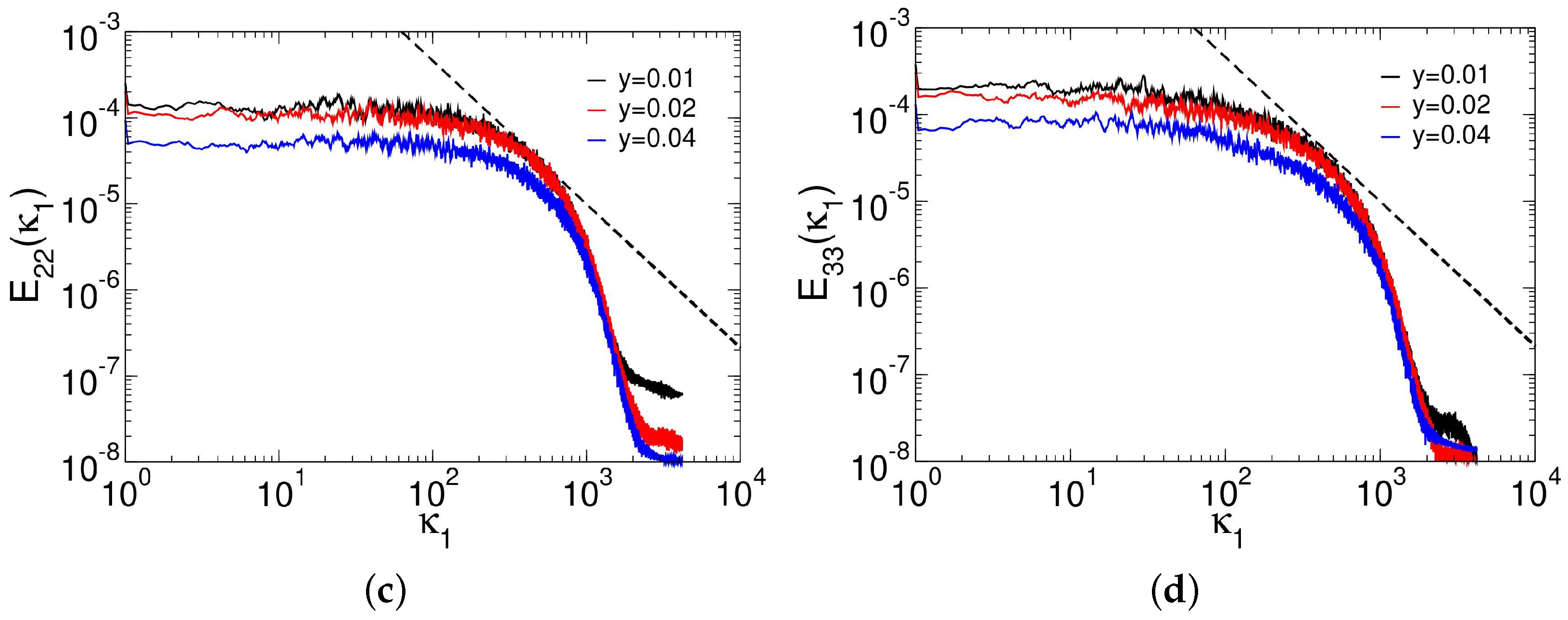
3.1. Turbulent Approach Boundary Layer
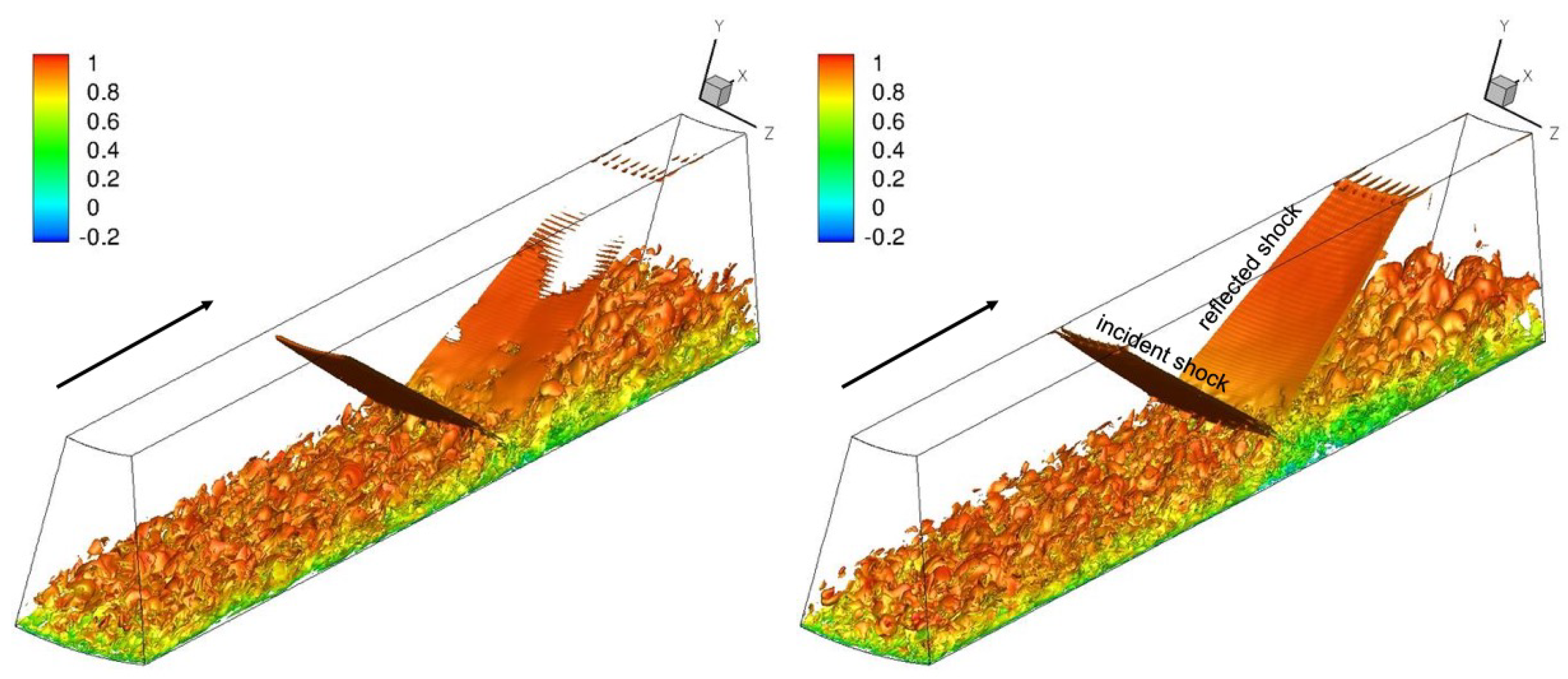
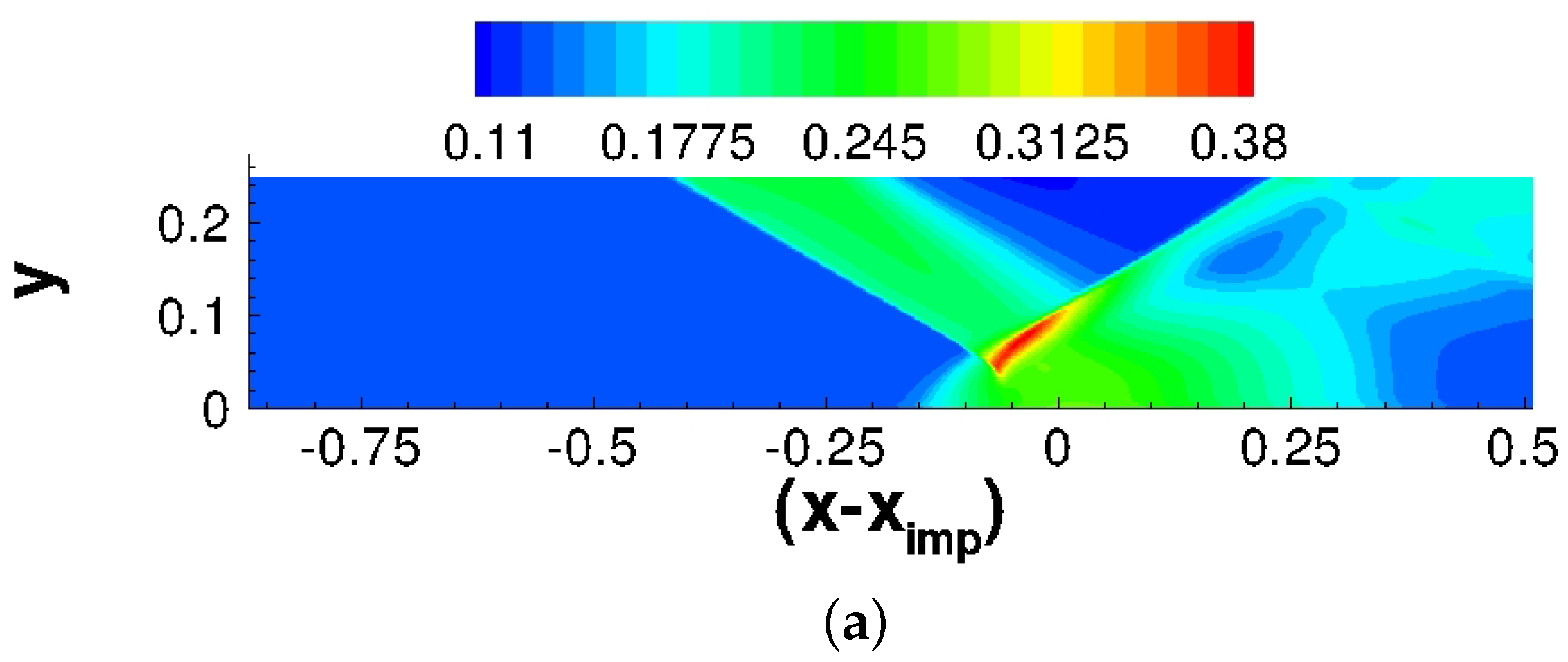
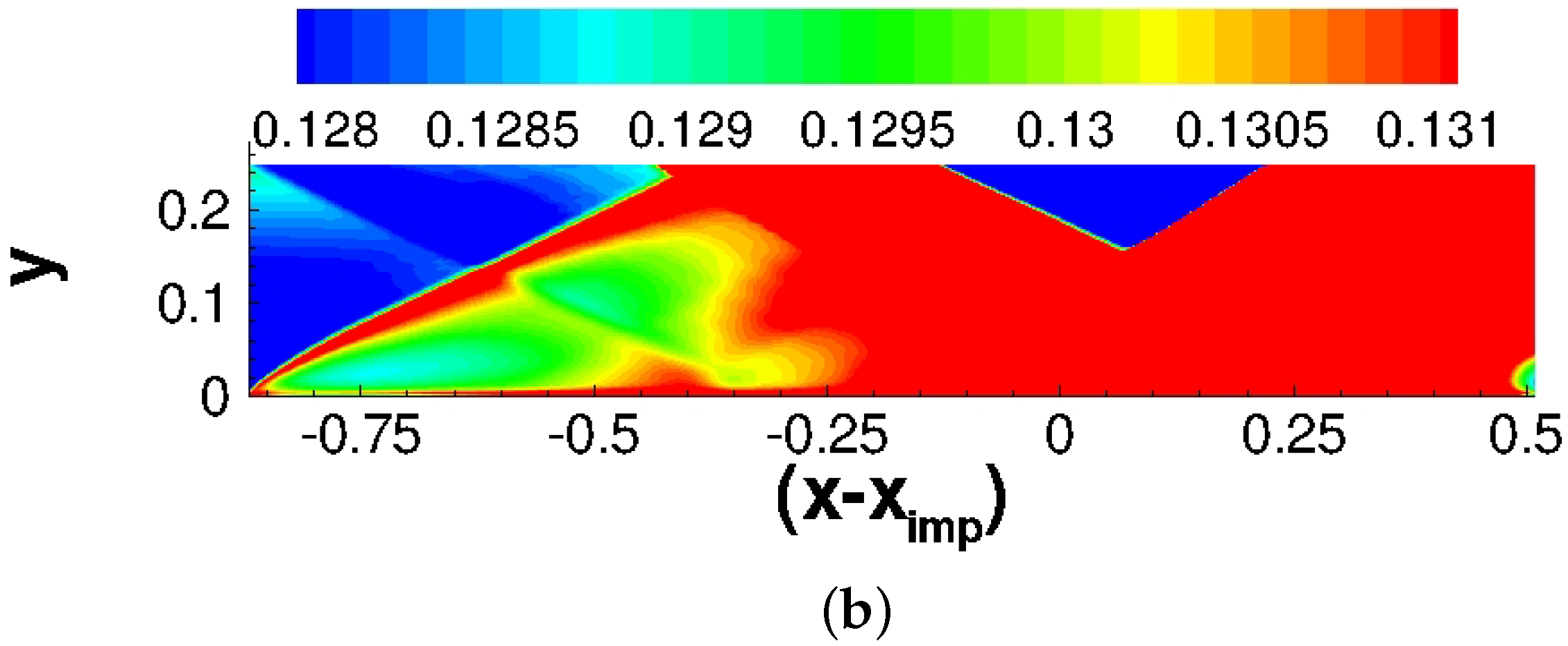
3.2. Instantaneous Flow Fields
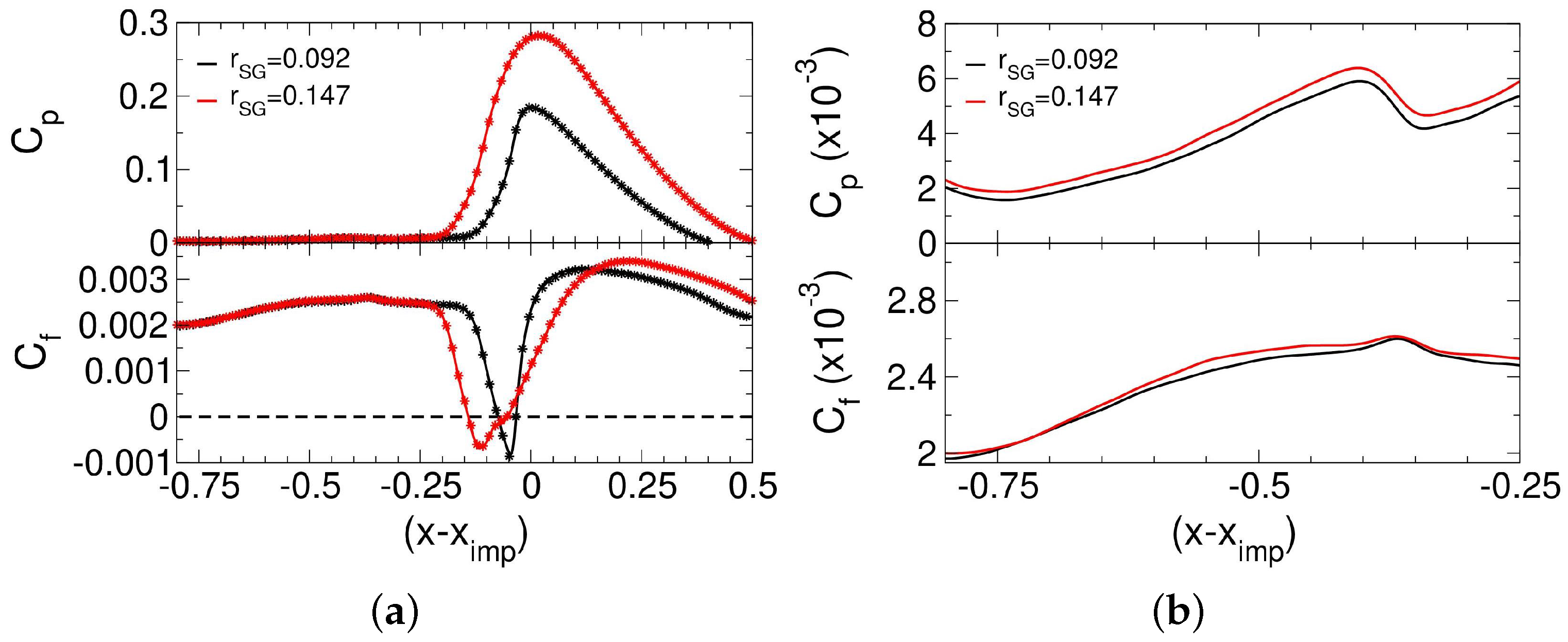
3.3. Mean Flow Analysis
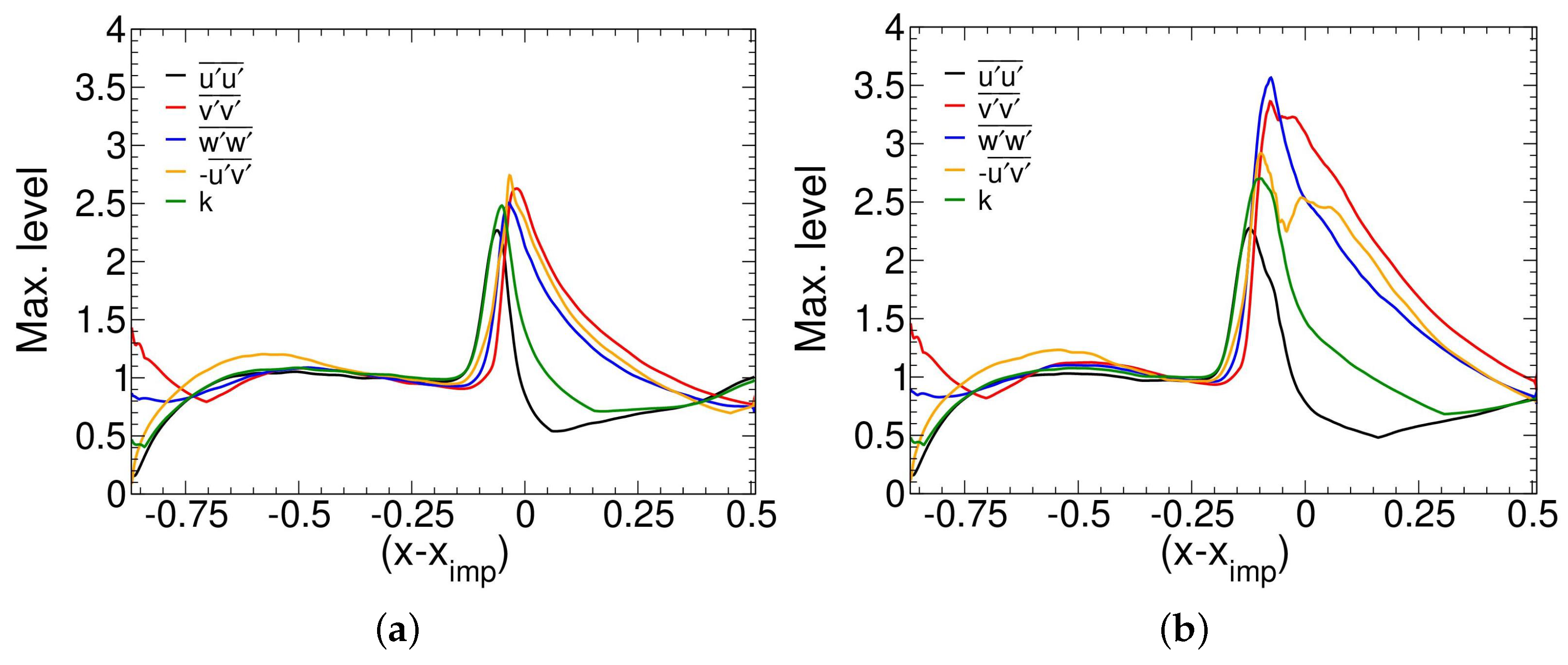
3.4. Unsteady Flow Analysis
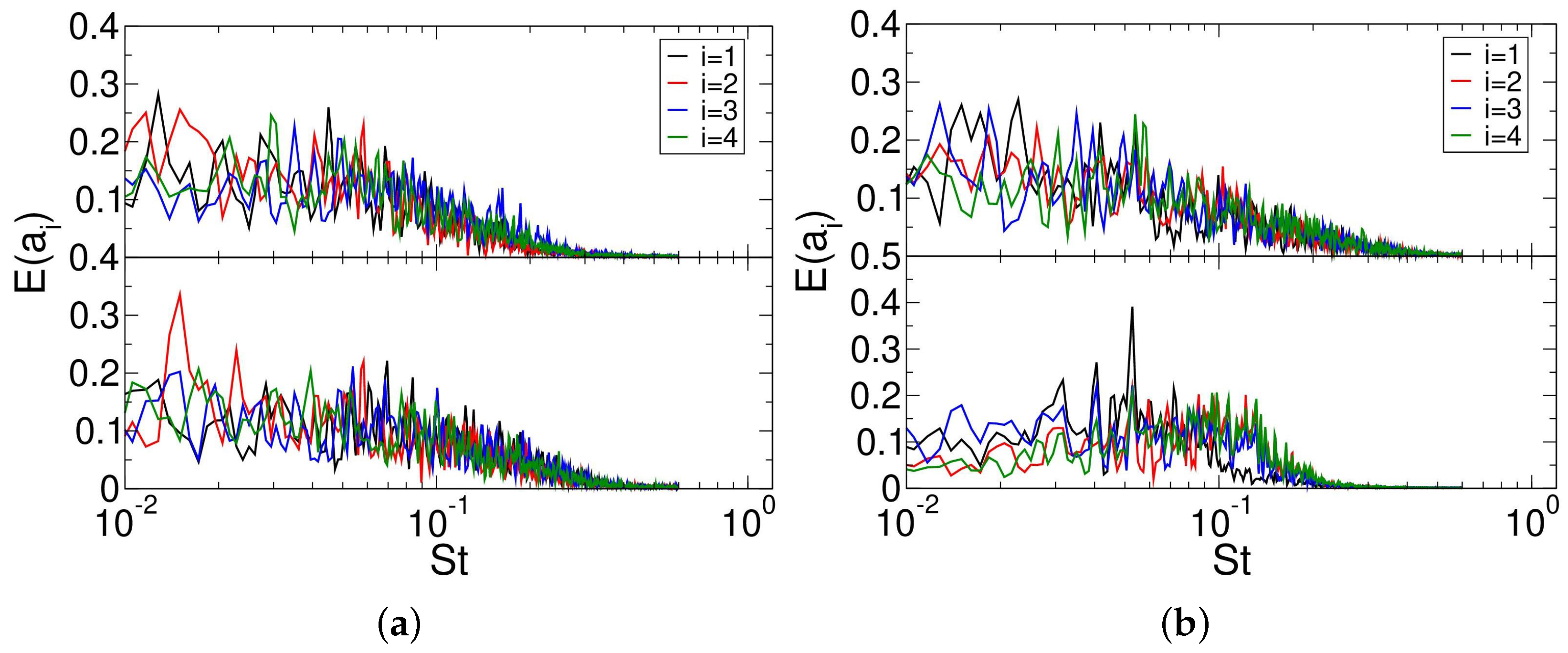
3.4.1. Fourier-Transforms of Wall-Pressure Coefficient
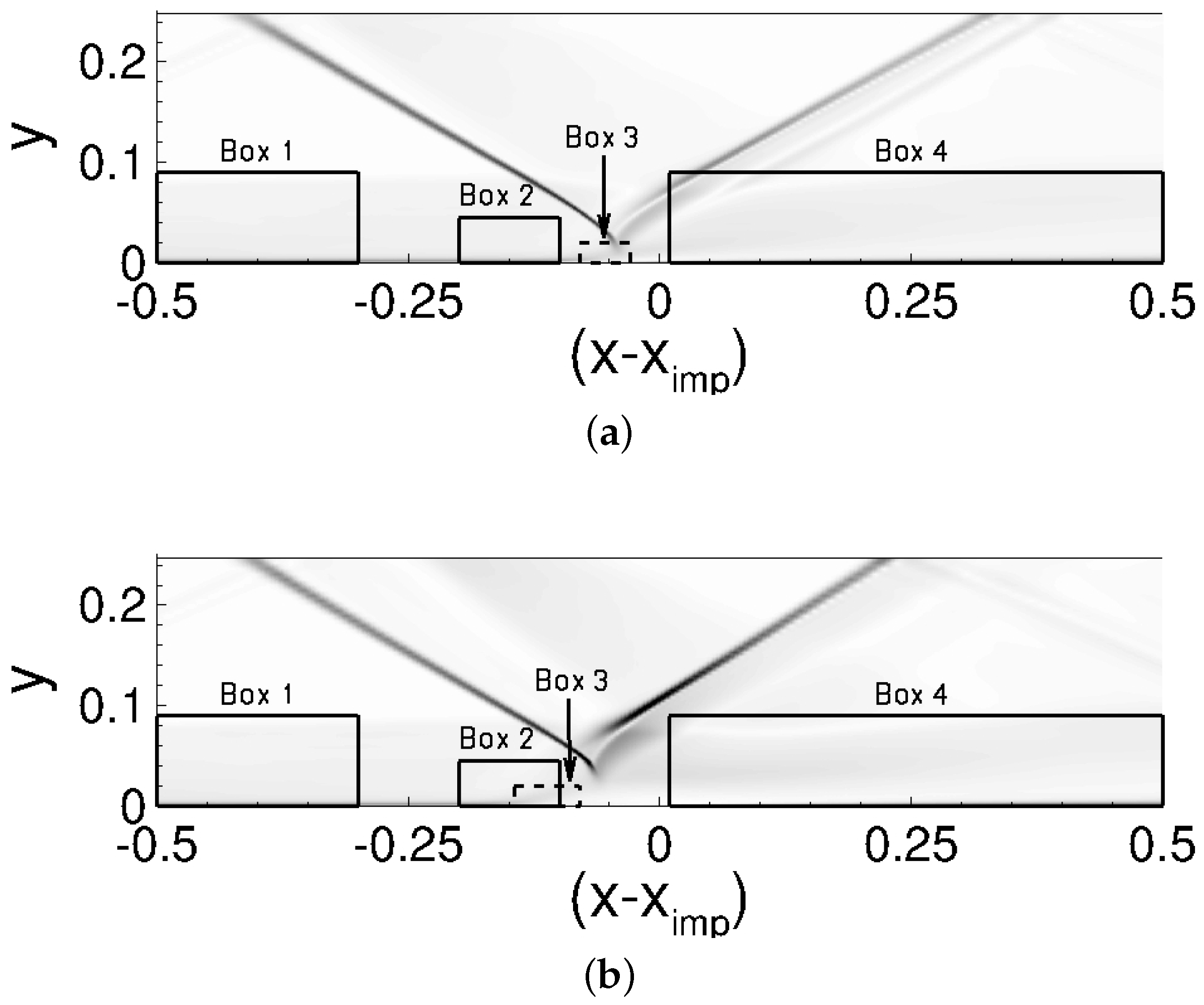
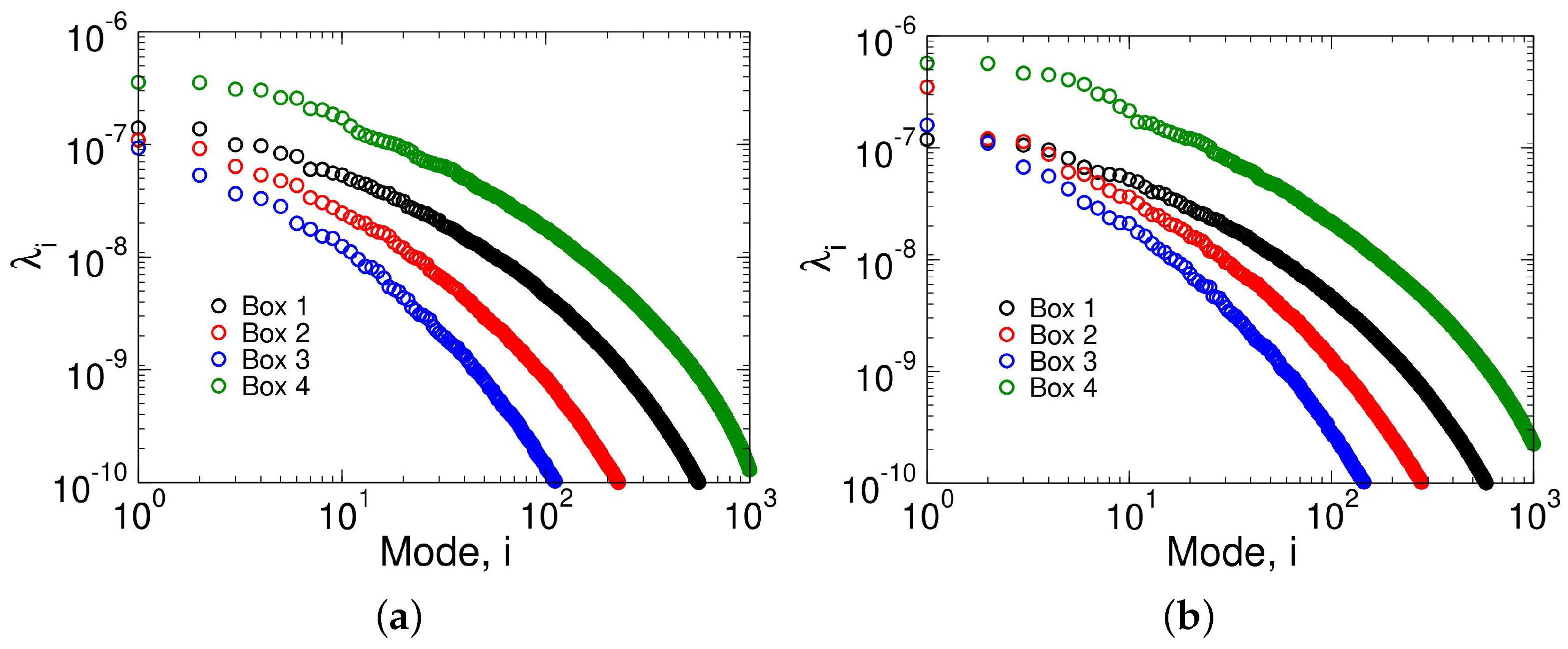
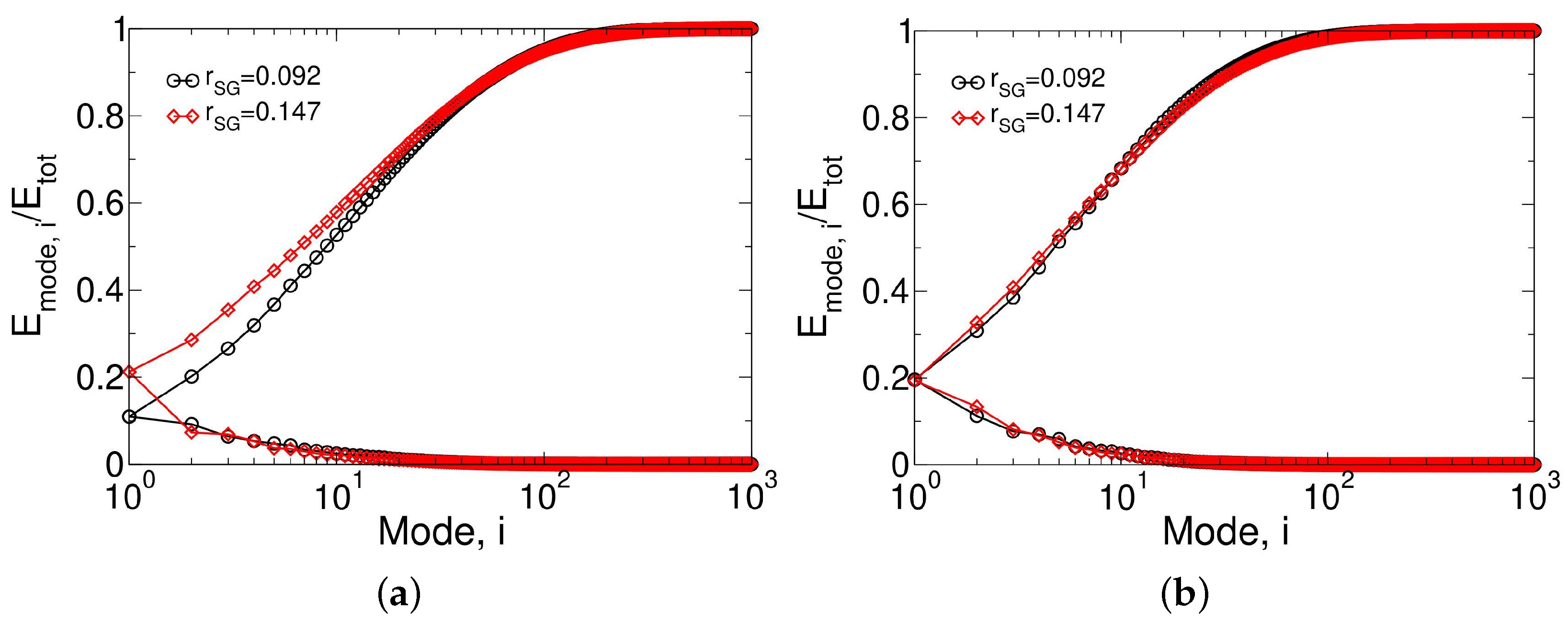
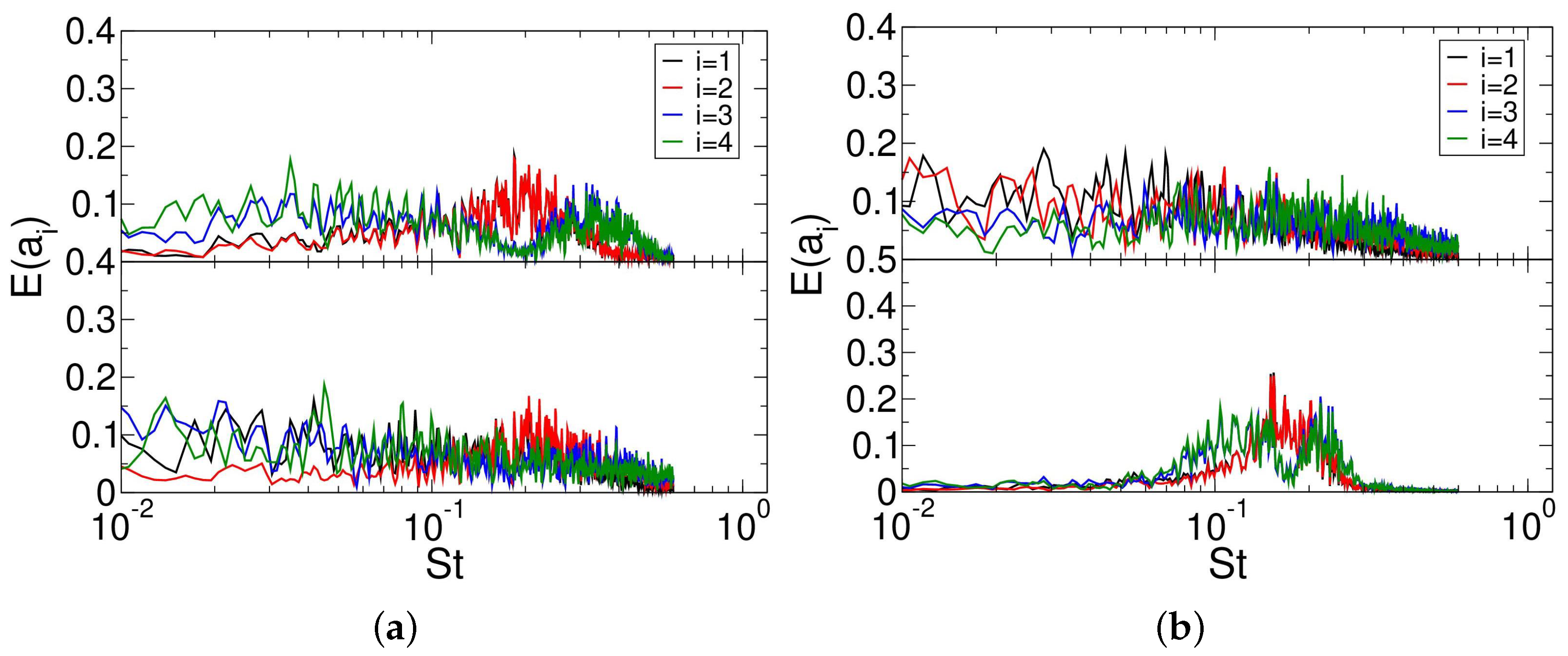
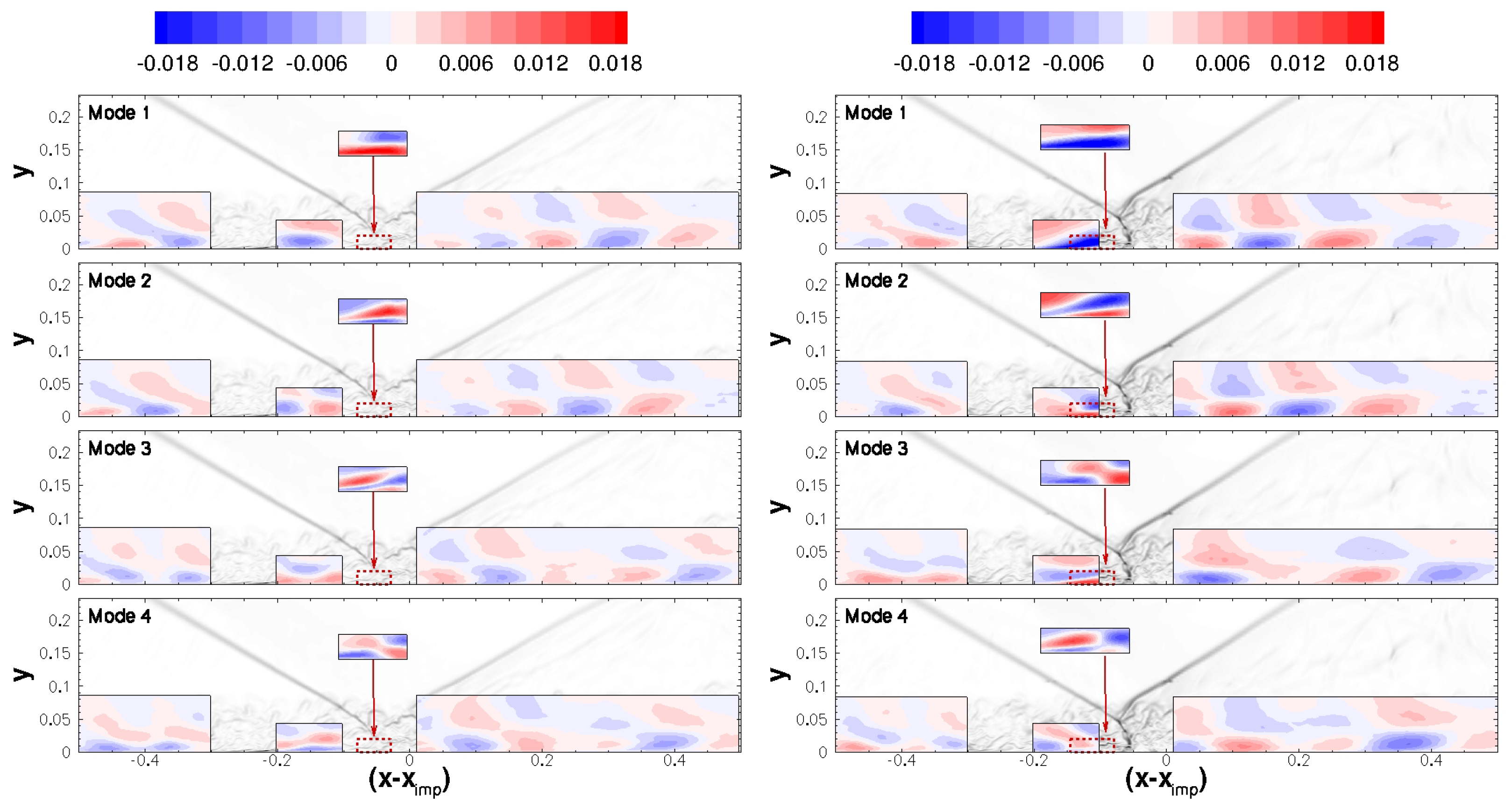
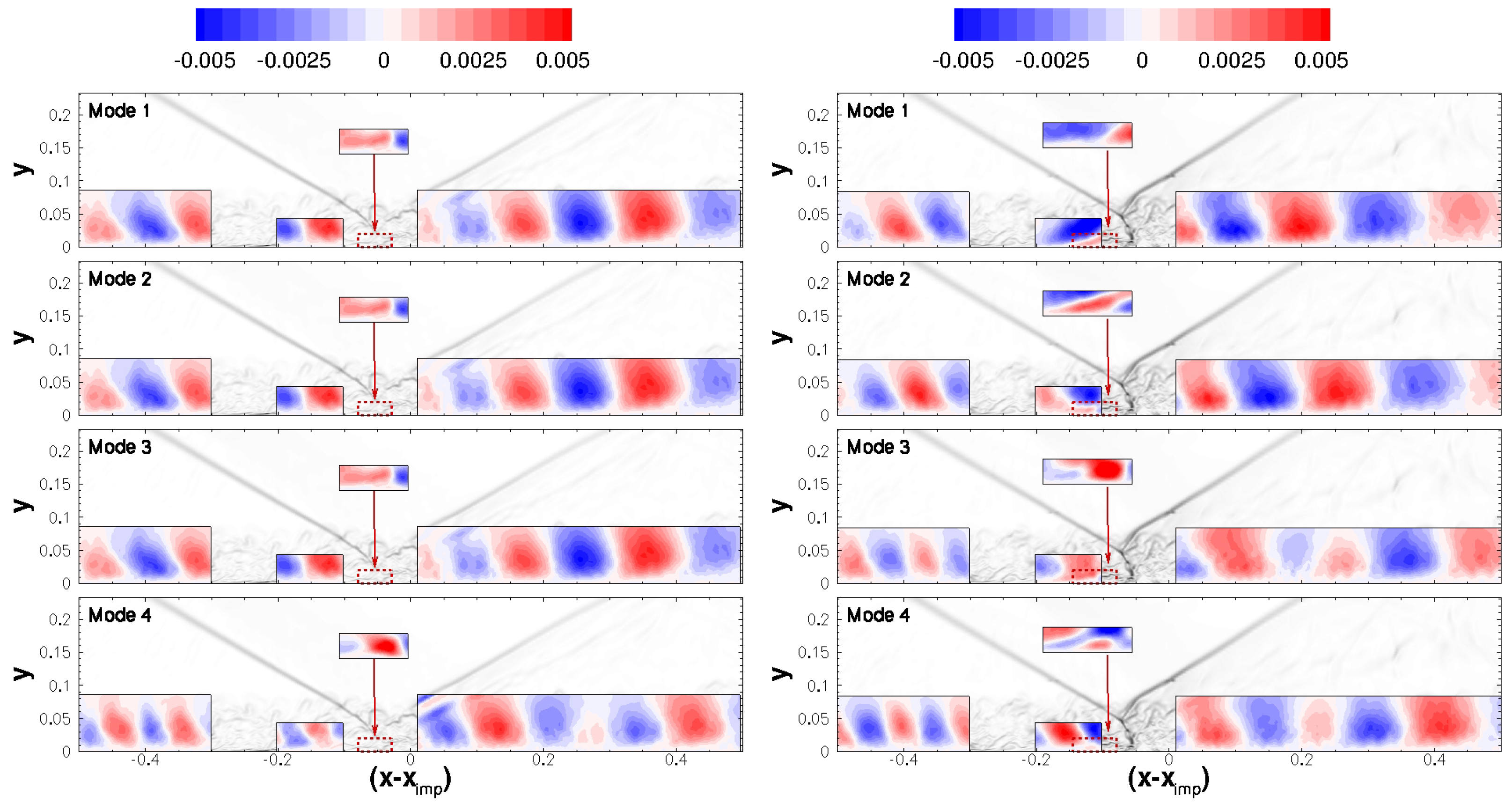
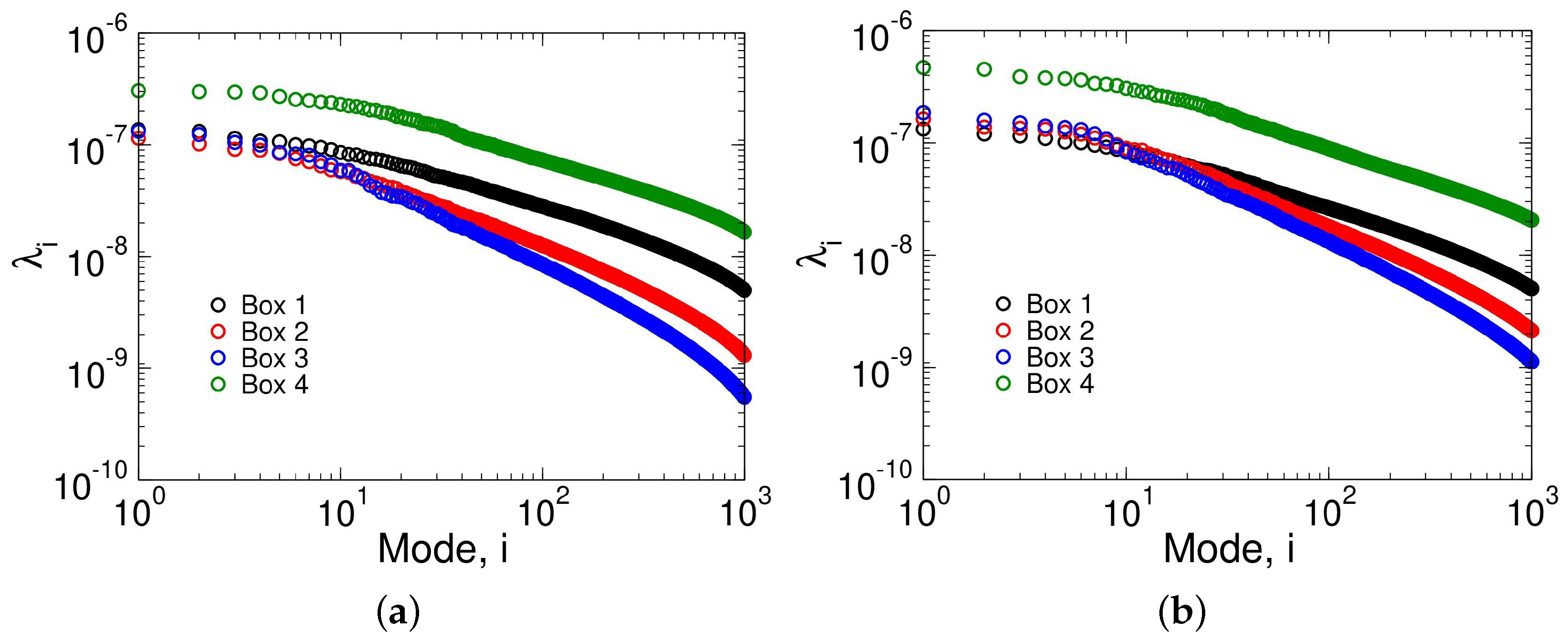
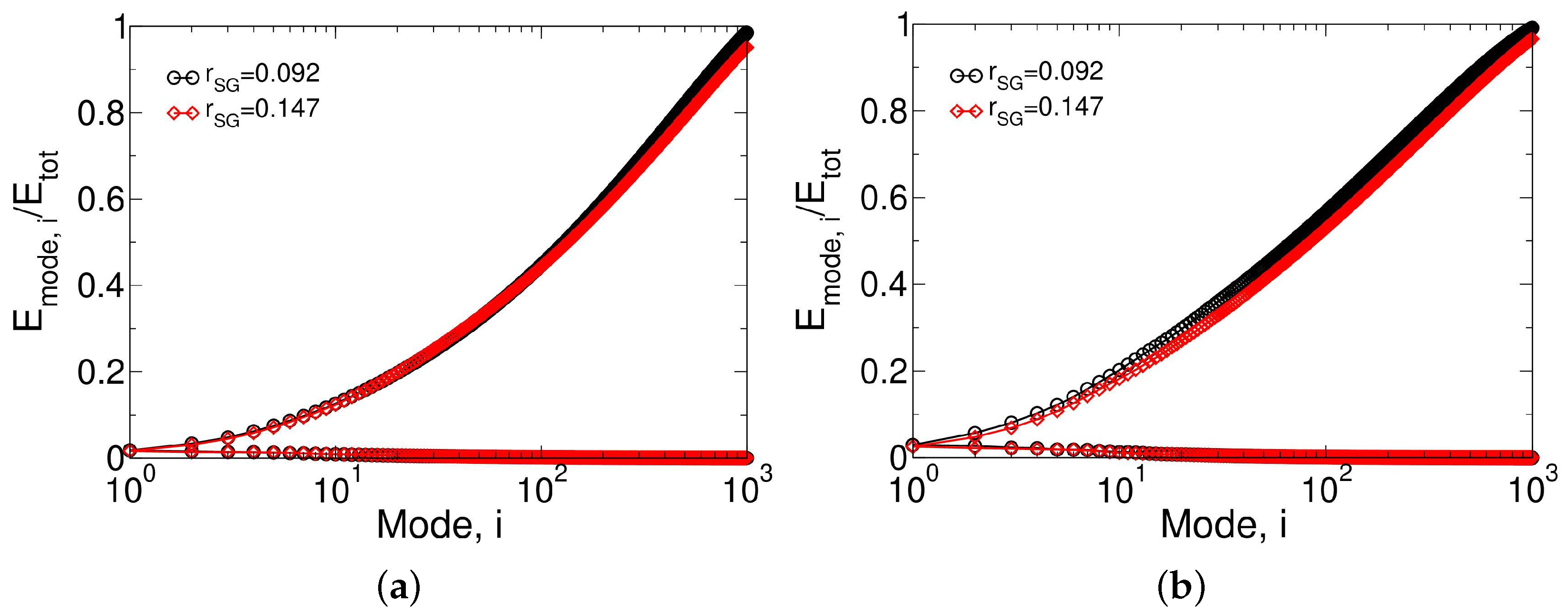
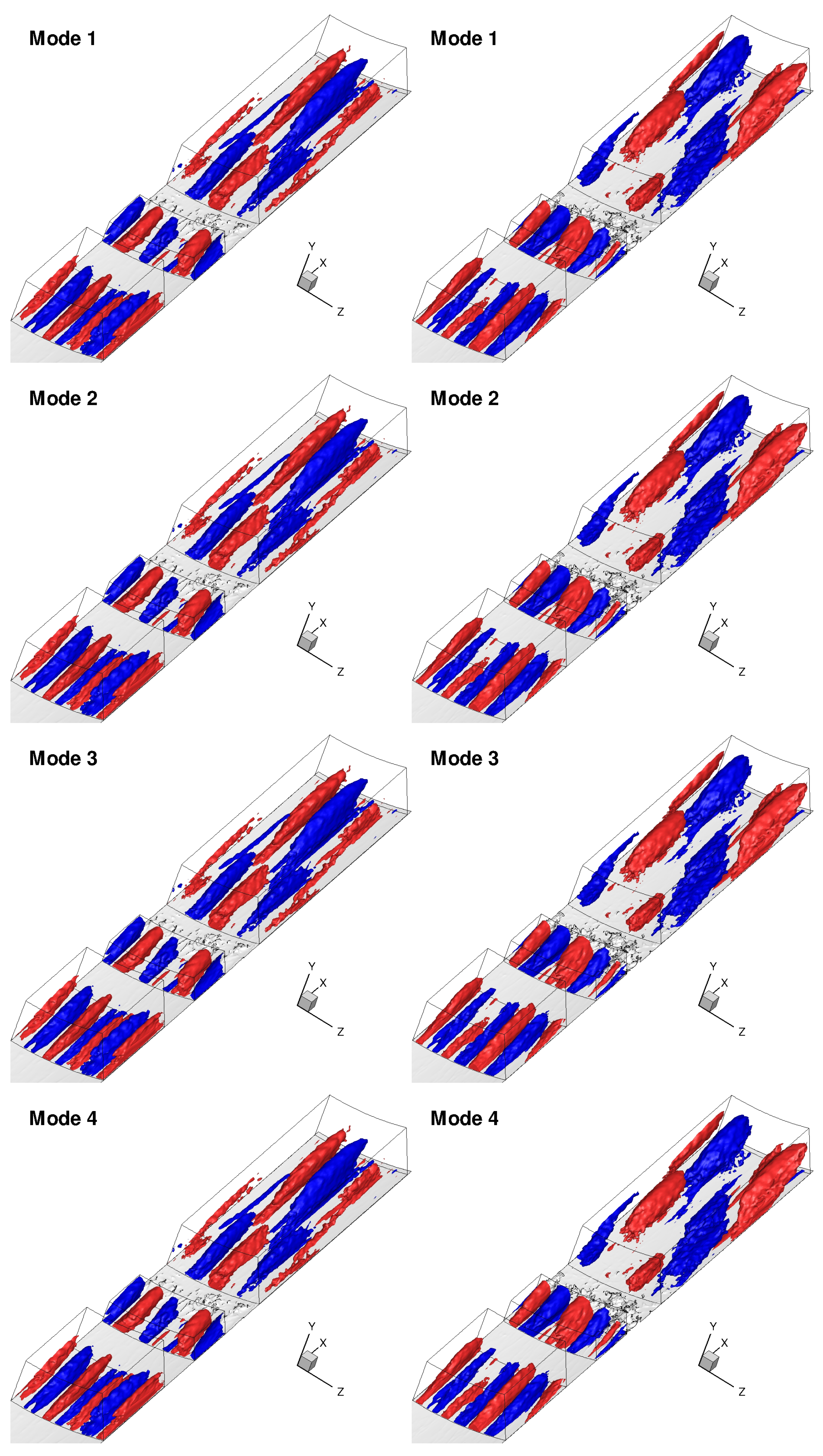
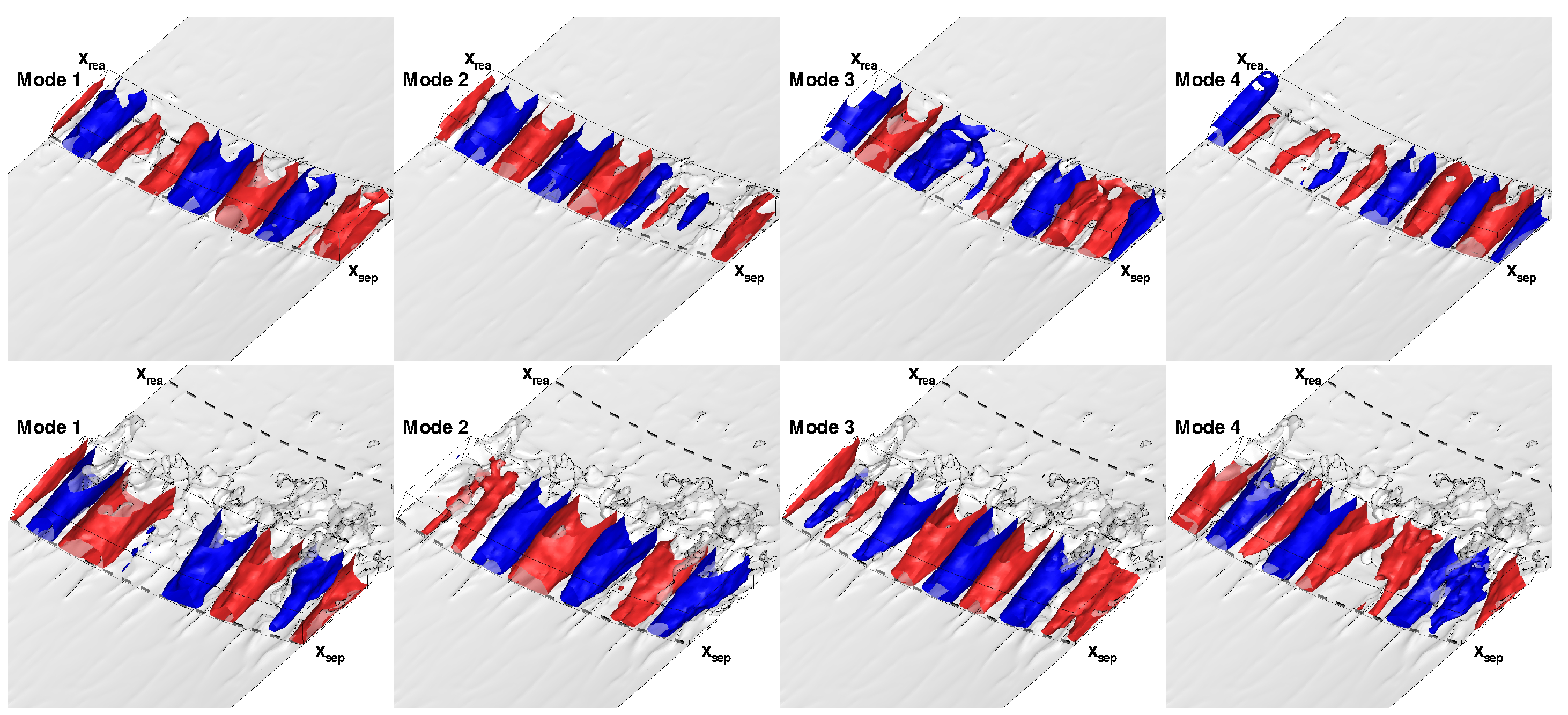
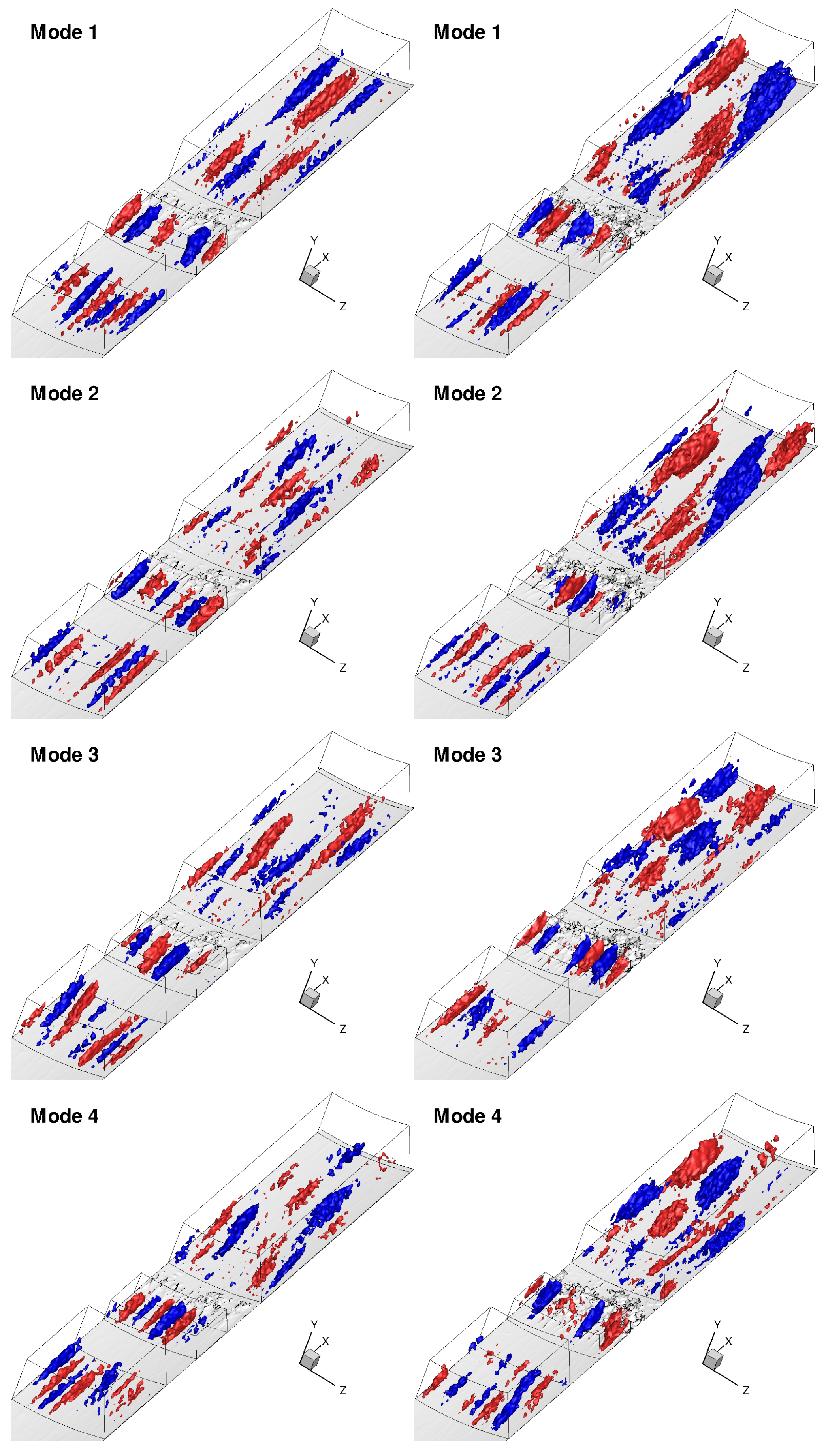
3.4.2. Proper Orthogonal Decomposition of Azimuthal Average of Data
3.4.3. Proper Orthogonal Decomposition of Three-Dimensional Data
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Green, J. Interactions between shock waves and turbulent boundary layers. Prog. Aerosp. Sci. 1970, 11, 235–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babinsky, H.; Harvey, J. Shock Wave-Boundary-Layer Interactions; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2011; Volume 32. [Google Scholar]
- Dolling, D.S. Fifty Years of Shock-Wave/Boundary-Layer Interaction Research: What Next? AIAA J. 2001, 39, 1517–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaitonde, D.V. Progress in shock wave/boundary layer interactions. Prog. Aerosp. Sci. 2015, 72, 80–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Délery, J.; Dussauge, J.P. Some physical aspects of shock wave/boundary layer interactions. Shock Waves 2009, 19, 453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smits, A.; Dussauge, J.P. Turbulent Shear Layers in Supersonic Flow; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Souverein, L.; Bakker, P.; Dupont, P. A scaling analysis for turbulent shock-wave/boundary-layer interactions. J. Fluid Mech. 2013, 714, 505–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemens, N.; Narayanaswamy, V. Low-Frequency Unsteadiness of Shock Wave/Turbulent Boundary Layer Interactions. Ann. Rev. Fluid Mech. 2014, 46, 469–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piponniau, S.; Dussauge, J.P.; Debieve, J.F.; Dupont, P. A simple model for low-frequency unsteadiness in shock-induced separation. J. Fluid Mech. 2009, 629, 87–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dussauge, J.P.; Dupont, P.; Debiève, J.F. Unsteadiness in shock wave boundary layer interactions with separation. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2006, 10, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganapathisubramani, B.; Clemens, N.; Dolling, D. Low-frequency dynamics of shock-induced separation in a compression ramp interaction. J. Fluid Mech. 2009, 636, 397–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humble, R.; Elsinga, G.; Scarano, F.; Van Oudheusden, B. Three-dimensional instantaneous structure of a shock wave/turbulent boundary layer interaction. J. Fluid Mech. 2009, 622, 33–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Porter, K.M.; Poggie, J. Selective upstream influence on the unsteadiness of a separated turbulent compression ramp flow. Phys. Fluids 2019, 31, 016104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beresh, S.; Clemens, N.; Dolling, D. Relationship Between Upstream Turbulent Boundary-Layer Velocity Fluctuations and Separation Shock Unsteadiness. AIAA J. 2002, 40, 2412–2422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganapathisubramani, B.; Clemens, N.; Dolling, D. Effects of upstream boundary layer on the unsteadiness of shock-induced separation. J. Fluid Mech. 2007, 585, 369–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanstone, L.; Clemens, N.T. Proper Orthogonal Decomposition Analysis of Swept-Ramp Shock-Wave/Boundary-Layer Unsteadiness at Mach 2. AIAA J. 2019, 57, 3395–3409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priebe, S.; Martín, M.P. Low-frequency unsteadiness in shock wave–turbulent boundary layer interaction. J. Fluid Mech. 2012, 699, 1–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priebe, S.; Tu, J.H.; Rowley, C.W.; Martín, M.P. Low-frequency dynamics in a shock-induced separated flow. J. Fluid Mech. 2016, 807, 441–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupont, P.; Haddad, C.; Debieve, J. Space and time organization in a shock-induced separated boundary layer. J. Fluid Mech. 2006, 559, 255–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirozzoli, S.; Grasso, F. Direct numerical simulation of impinging shock wave/turbulent boundary layer interaction at M = 2.25. Phys. Fluids 2006, 18, 065113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souverein, L.J.; Dupont, P.; Debieve, J.F.; Dussauge, J.P.; Van Oudheusden, B.W.; Scarano, F. Effect of Interaction Strength on Unsteadiness in Shock-Wave-Induced Separations. AIAA J. 2010, 48, 1480–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agostini, L.; Larchevêque, L.; Dupont, P.; Debiève, J.F.; Dussauge, J.P. Zones of Influence and Shock Motion in a Shock/Boundary-Layer Interaction. AIAA J. 2012, 50, 1377–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Threadgill, J.A.; Bruce, P.J. Unsteady Flow Features Across Different Shock/Boundary-Layer Interaction Configurations. AIAA J. 2020, 58, 3063–3075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolling, D.; Bogdonoff, S. Blunt Fin-Induced Shock Wave/Turbulent Boundary-Layer Interaction. AIAA J. 1982, 20, 1674–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, C.M.; Buning, P.G. Simulation of blunt-fin-induced shock-wave and turbulent boundary-layer interaction. J. Fluid Mech. 1985, 154, 163–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruce, P.; Burton, D.; Titchener, N.; Babinsky, H. Corner effect and separation in transonic channel flows. J. Fluid Mech. 2011, 679, 247–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, D.; Babinsky, H. Corner separation effects for normal shock wave/turbulent boundary layer interactions in rectangular channels. J. Fluid Mech. 2012, 707, 287–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seebaugh, W.R.; Childs, M.E. Conical Shock-Wave Turbulent Boundary-Layer Interaction Including Suction Effects. J. Aircr. 1970, 7, 334–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, W.C. The Behavior of a Compressible Turbulent Boundary Layer in a Shock-Wave-Induced Adverse Pressure Gradient. Ph.D. Thesis, Washington University, Seattle, WA, USA, 1973. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, D.O. CFD Validation Experiment of a Mach 2.5 Axisymmetric Shock-Wave/Boundary-Layer Interaction. In Proceedings of the Fluids Engineering Division Summer Meeting, New York, NY, USA, 9–12 August 2015; Volume 57212, p. V001T06A001. [Google Scholar]
- Sasson, J.; Reising, H.H.; Davis, D.O.; Barnhart, P.J. Summary of Shock Wave Turbulent Boundary Layer Interaction Experiments In a Circular Test Section; AIAA Paper 2023-0442; American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics: Reston, VA, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Funderburk, M.L.; Narayanaswamy, V. Investigation of Negative Surface Curvature Effects in Axisymmetric Shock/Boundary-Layer Interaction. AIAA J. 2019, 57, 1594–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, B.; Duraisamy, K.; Nguyen, N.; Kawai, S.; Lele, S. Flow physics and RANS modelling of oblique shock/turbulent boundary layer interaction. J. Fluid Mech. 2013, 729, 231–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lumley, J.L. The structure of inhomogeneous turbulent flows. In Atmospheric Turbulence and Radio Wave Propagation; National Institute of Informatics: Tokyo, Japan, 1967; pp. 166–178. [Google Scholar]
- Gross, A.; Fasel, H.F. High-Order Accurate Numerical Method for Complex Flows. AIAA J. 2008, 46, 204–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, A.; Fasel, H.F. Numerical investigation of supersonic flow for axisymmetric cones. Math. Comput. Simul. 2010, 81, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilcox, D.C. Turbulence Modeling for CFD, 3rd ed.; DCW Industries: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Wilcox, D.C. Formulation of the k-w Turbulence Model Revisited. AIAA J. 2008, 46, 2823–2838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balsara, D.S.; Shu, C.W. Monotonicity preserving weighted essentially non-oscillatory schemes with increasingly high order of accuracy. J. Computat. Phys. 2000, 160, 405–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yee, H.C. Upwind and Symmetric Shock-Capturing Schemes; NASA-TM-89464; NASA: Washington, DC, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Touber, E.; Sandham, N.D. Large-eddy simulation of low-frequency unsteadiness in a turbulent shock-induced separation bubble. Theor. Computat. Fluid Dyn. 2009, 23, 79–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poggie, J.; Bisek, N.J.; Gosse, R. Resolution effects in compressible, turbulent boundary layer simulations. Comput. Fluids 2015, 120, 57–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, A.; Little, J.; Fasel, H.F. Numerical investigation of unswept and swept turbulent shock-wave boundary layer interactions. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2022, 123, 107455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Gross, A. Numerical Investigation of Sweep Effect on Turbulent Shock-Wave Boundary-Layer Interaction. AIAA J. 2022, 60, 712–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poletto, R.; Craft, T.; Revell, A. A New Divergence Free Synthetic Eddy Method for the Reproduction of Inlet Flow Conditions for LES. Flow Turbul. Combust. 2013, 91, 519–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Gross, A. Large-Eddy Simulation of Supersonic Turbulent Boundary Layer. In Proceedings of the AIAA AVIATION 2020 FORUM, Virtual Event, 15–19 June 2020; American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics: Reston, VA, USA, 15–19 June 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Sirovich, L. Turbulence and the Dynamics of Coherent Structures. Q. Appl. Math. 1987, 45, 561–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, M.; Parziale, N.; Smith, M.; Marineau, E. Amplification and structure of streamwise-velocity fluctuations in compression-corner shock-wave/turbulent boundary-layer interactions. J. Fluid Mech. 2019, 863, 1091–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo Gomez, P.; Gross, A.; Guildenbecher, D.R.; Miller, N.E.; Lynch, K.P. Wall-Modeled Large-Eddy Simulations of Turbulent Mach 3.5, 8, and 14 Boundary Layers-Effect of Mach Number on Aero-Optical Distortions. In Proceedings of the AIAA AVIATION 2022 Forum, Chicago, IL, USA, 27 June–1 July 2022; p. 3441. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, J.D. Modern Compressible Flow: With Historical Perspective; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1990; Volume 12. [Google Scholar]
- Pirozzoli, S.; Bernardini, M. Direct Numerical Simulation Database for Impinging Shock Wave/Turbulent Boundary-Layer Interaction. AIAA J. 2011, 49, 1307–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guarini, S.E.; Moser, R.D.; Shariff, K.; Wray, A. Direct numerical simulation of a supersonic turbulent boundary layer at Mach 2.5. J. Fluid Mech. 2000, 414, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purtell, L.; Klebanoff, P.; Buckley, F. Turbulent boundary layer at low Reynolds number. Phys. Fluids 1981, 24, 802–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, E.J.; Inouye, M. An Evaluation of Theories for Predicting Turbulent Skin Friction and Heat Transfer on Flat Plates at Supersonic and Hypersonic Mach Numbers. AIAA J. 1971, 9, 993–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandham, N. Effects of Compressibility and Shock-Wave Interactions on Turbulent Shear Flows. Flow Turbul. Combust. 2016, 97, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Zheltovodov, A.A.; Yao, Y.; Moulinec, C.; Emerson, D.R. On the turbulence amplification in shock-wave/turbulent boundary layer interaction. J. Fluid Mech. 2020, 897, A32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Martin, M.P. Analysis of shock motion in shockwave and turbulent boundary layer interaction using direct numerical simulation data. J. Fluid Mech. 2008, 594, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasquariello, V.; Hickel, S.; Adams, N.A. Unsteady effects of strong shock-wave/boundary-layer interaction at high Reynolds number. J. Fluid Mech. 2017, 823, 617–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grilli, M.; Schmid, P.J.; Hickel, S.; Adams, N.A. Analysis of unsteady behaviour in shockwave turbulent boundary layer interaction. J. Fluid Mech. 2012, 700, 16–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nichols, J.W.; Larsson, J.; Bernardini, M.; Pirozzoli, S. Stability and modal analysis of shock/boundary layer interactions. Theor. Comput. Fluid Dyn. 2017, 31, 33–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piponniau, S.; Collin, E.; Dupont, P.; Debiève, J.f. Reconstruction of velocity fields from wall pressure measurements in a shock wave/turbulent boundary layer interaction. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 2012, 35, 176–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agostini, L.; Larchevêque, L.; Dupont, P. Mechanism of shock unsteadiness in separated shock/boundary-layer interactions. Phys. Fluids 2015, 27, 126103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loginov, M.S.; Adams, N.A.; Zheltovodov, A.A. Large-eddy simulation of shock-wave/turbulent-boundary-layer interaction. J. Fluid Mech. 2006, 565, 135–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humble, R.; Scarano, F.; Van Oudheusden, B. Unsteady aspects of an incident shock wave/turbulent boundary layer interaction. J. Fluid Mech. 2009, 635, 47–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]






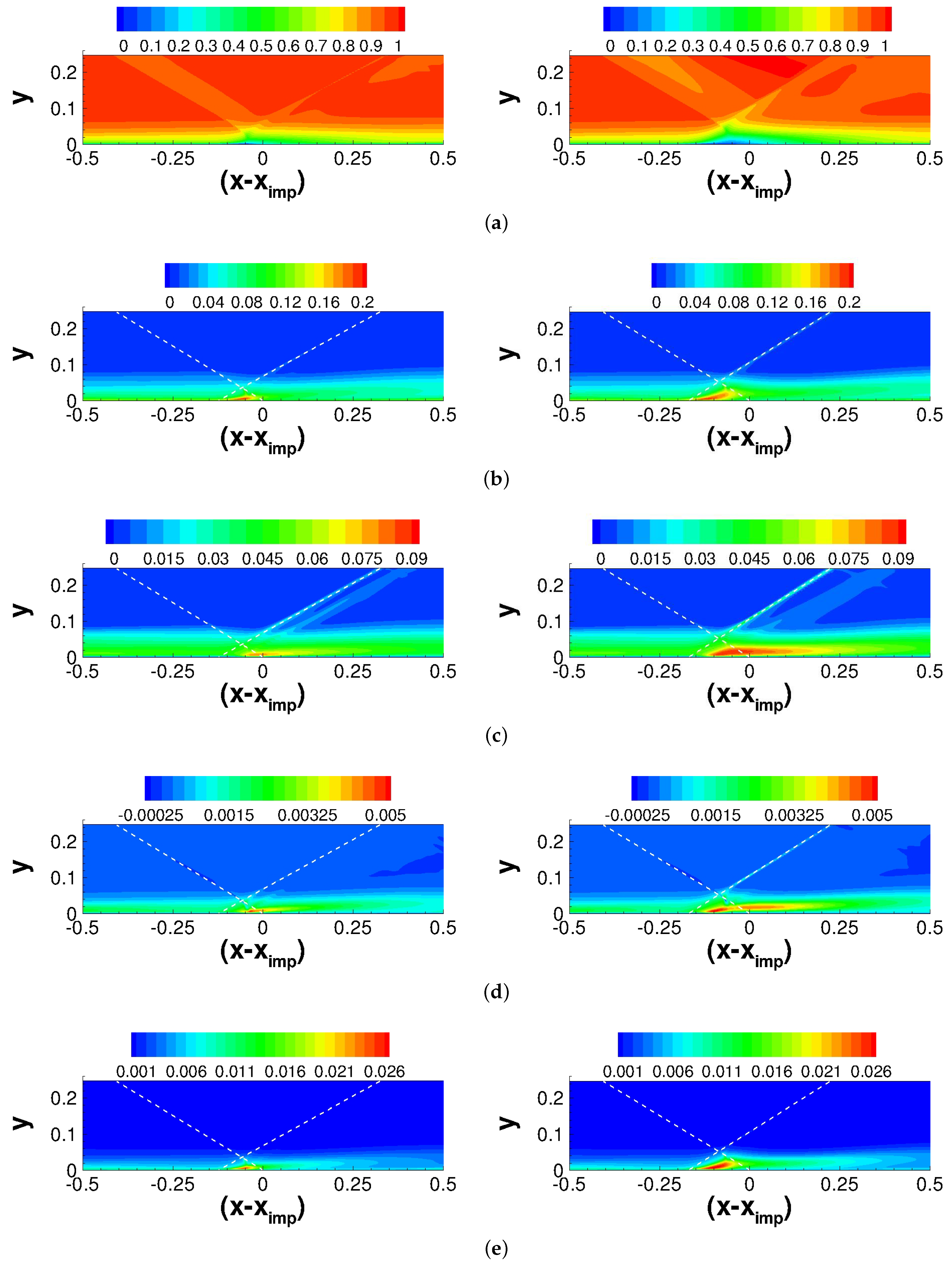
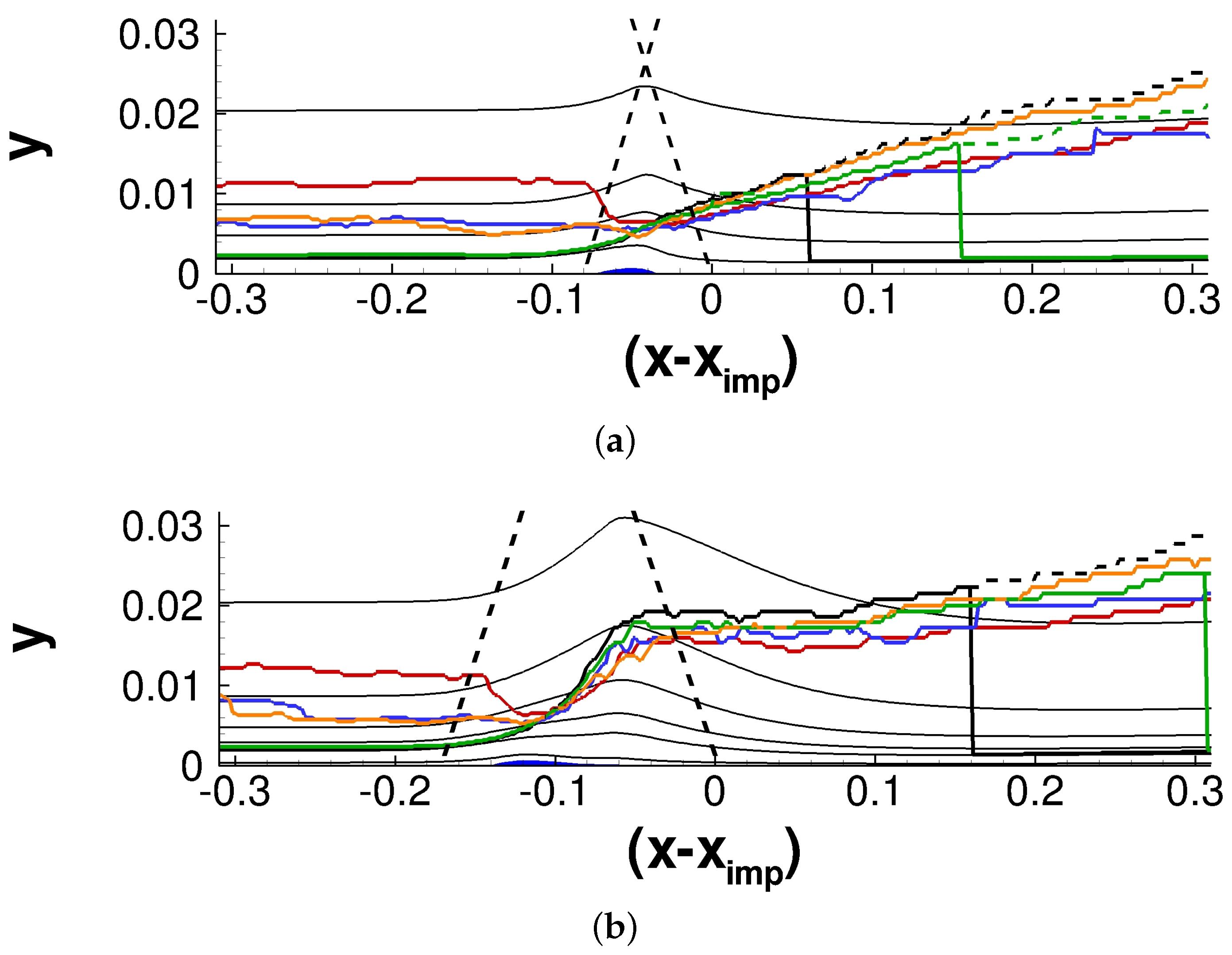
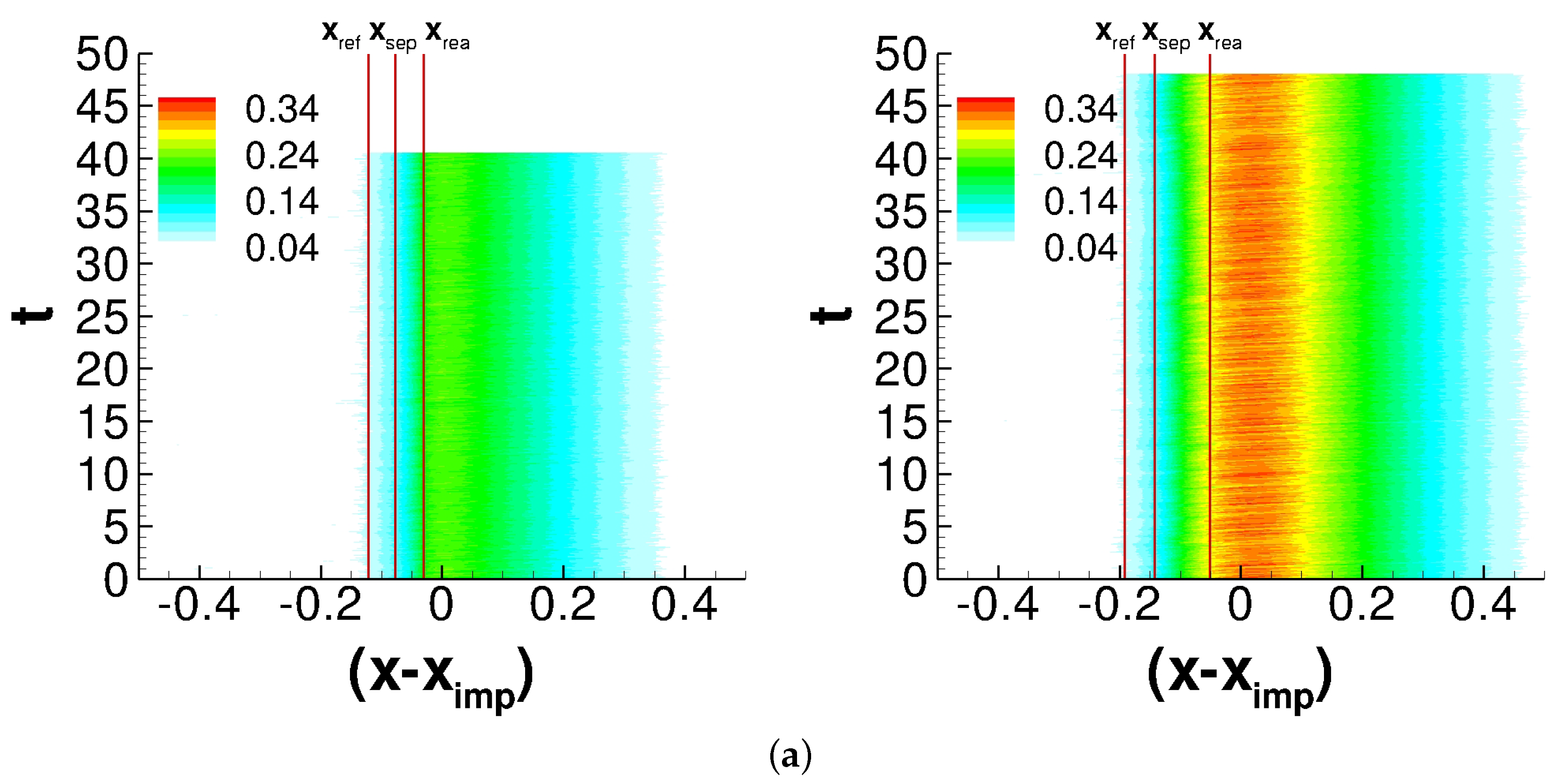

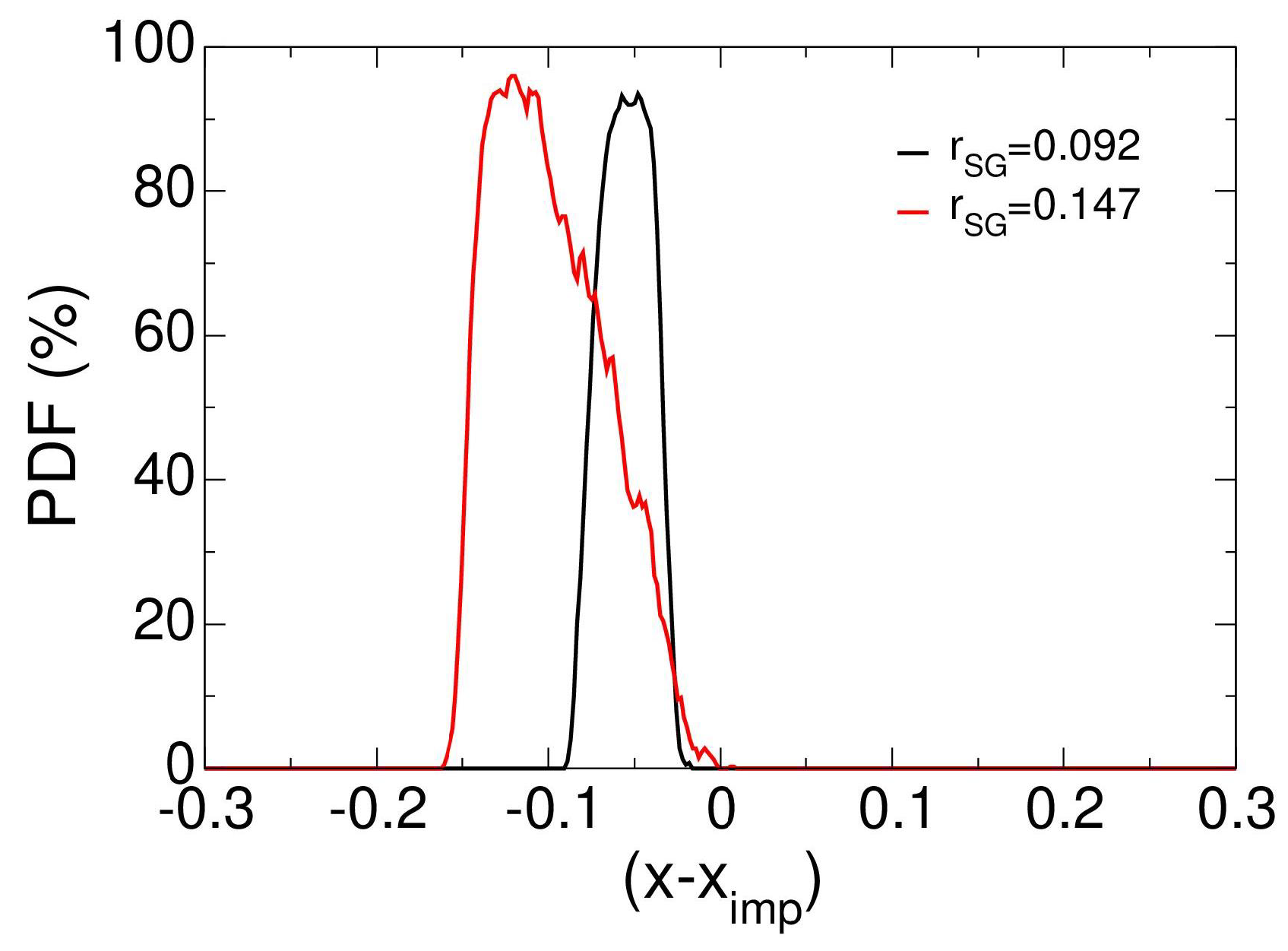



| Case | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | |||
| x-refine | |||
| y-refine | |||
| z-refine | |||
| Centerbody Radius | Time-Interval for Obtaining Stationary Flow | Time-Interval for Time Averaging | Time-Interval for Computing Statistics |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.092 | 0–3 | 3–18 | 18–36 |
| 0.147 | 0–3 | 3–18 | 18–36 |
| Analytical | Simulation, | Simulation, | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | |
| M | 2.40 | 2.15 | 2.40 | 2.11 | 2.40 | 2.10 |
| 1 | 0.941 | 0.982 | 0.912 | 0.981 | 0.908 | |
| 0 | 0.103 | 0 | 0.125 | 0 | 0.129 | |
| 1 | 1.12 | 1.05 | 1.19 | 1.05 | 1.20 | |
| k | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mosele, J.-P.; Gross, A.; Slater, J. Numerical Investigation of Mach 2.5 Axisymmetric Turbulent Shock Wave Boundary Layer Interactions. Aerospace 2023, 10, 159. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace10020159
Mosele J-P, Gross A, Slater J. Numerical Investigation of Mach 2.5 Axisymmetric Turbulent Shock Wave Boundary Layer Interactions. Aerospace. 2023; 10(2):159. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace10020159
Chicago/Turabian StyleMosele, John-Paul, Andreas Gross, and John Slater. 2023. "Numerical Investigation of Mach 2.5 Axisymmetric Turbulent Shock Wave Boundary Layer Interactions" Aerospace 10, no. 2: 159. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace10020159
APA StyleMosele, J.-P., Gross, A., & Slater, J. (2023). Numerical Investigation of Mach 2.5 Axisymmetric Turbulent Shock Wave Boundary Layer Interactions. Aerospace, 10(2), 159. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace10020159






