Long-Baseline Real-Time Kinematic Positioning: Utilizing Kalman Filtering and Partial Ambiguity Resolution with Dual-Frequency Signals from BDS, GPS, and Galileo
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Design
2.1.1. IGS Station Experiment
2.1.2. Shipborne Measurement Experiment
2.2. Long-Baseline Real-Time Kinematic Algorithm Based on Dual-Frequency Signals
2.2.1. Traditional Real-Time Kinematic Model
2.2.2. Wide Lane Observations
2.2.3. Adjustments for Tropospheric and Ionospheric Effects
2.2.4. Dual-Frequency Long-Baseline Real-Time Kinematic
3. Results
3.1. Factors Affecting the Positioning Performance of Long-Baseline RTK Systems
3.1.1. Broadcast Ephemeris Error
3.1.2. Tropospheric Error
3.1.3. Ionospheric Error
3.2. Evaluation of RTK Positioning Performance for Different Baseline Lengths
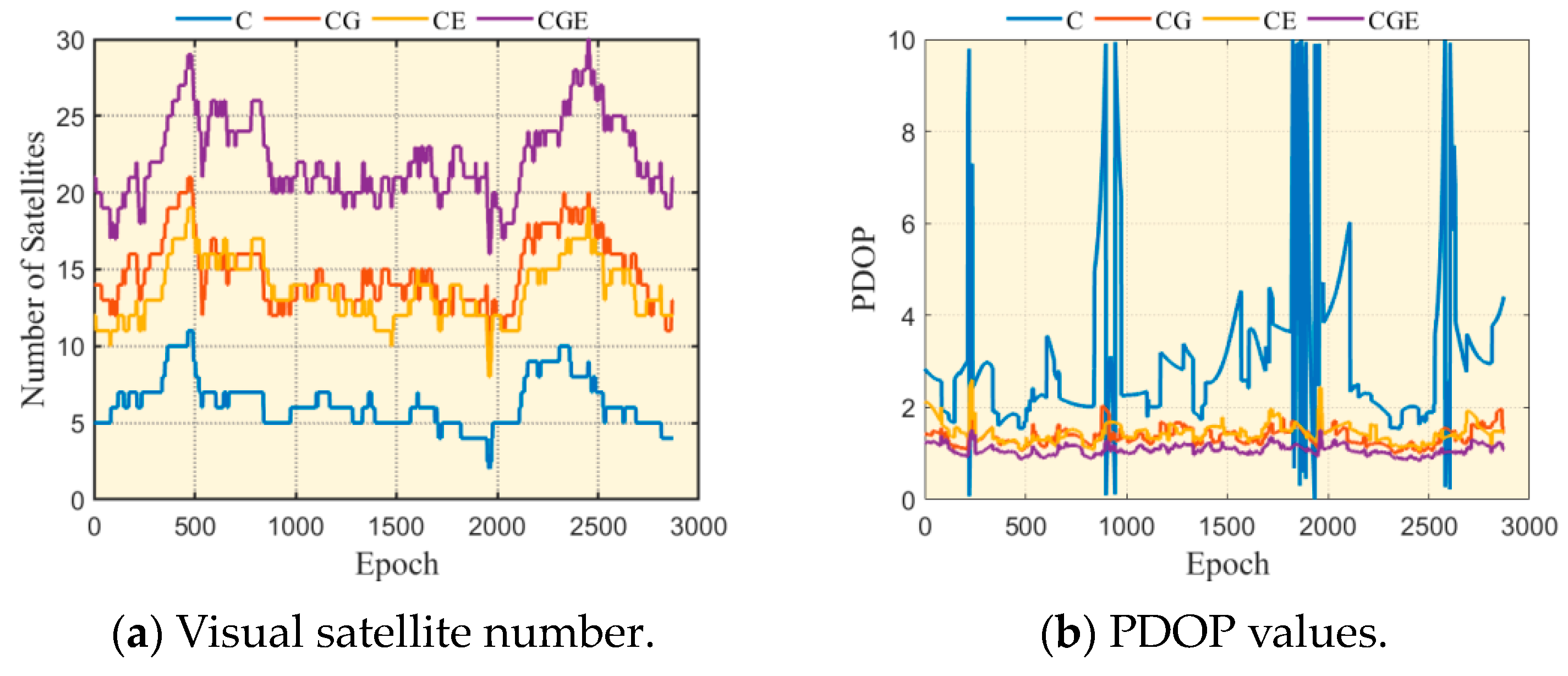
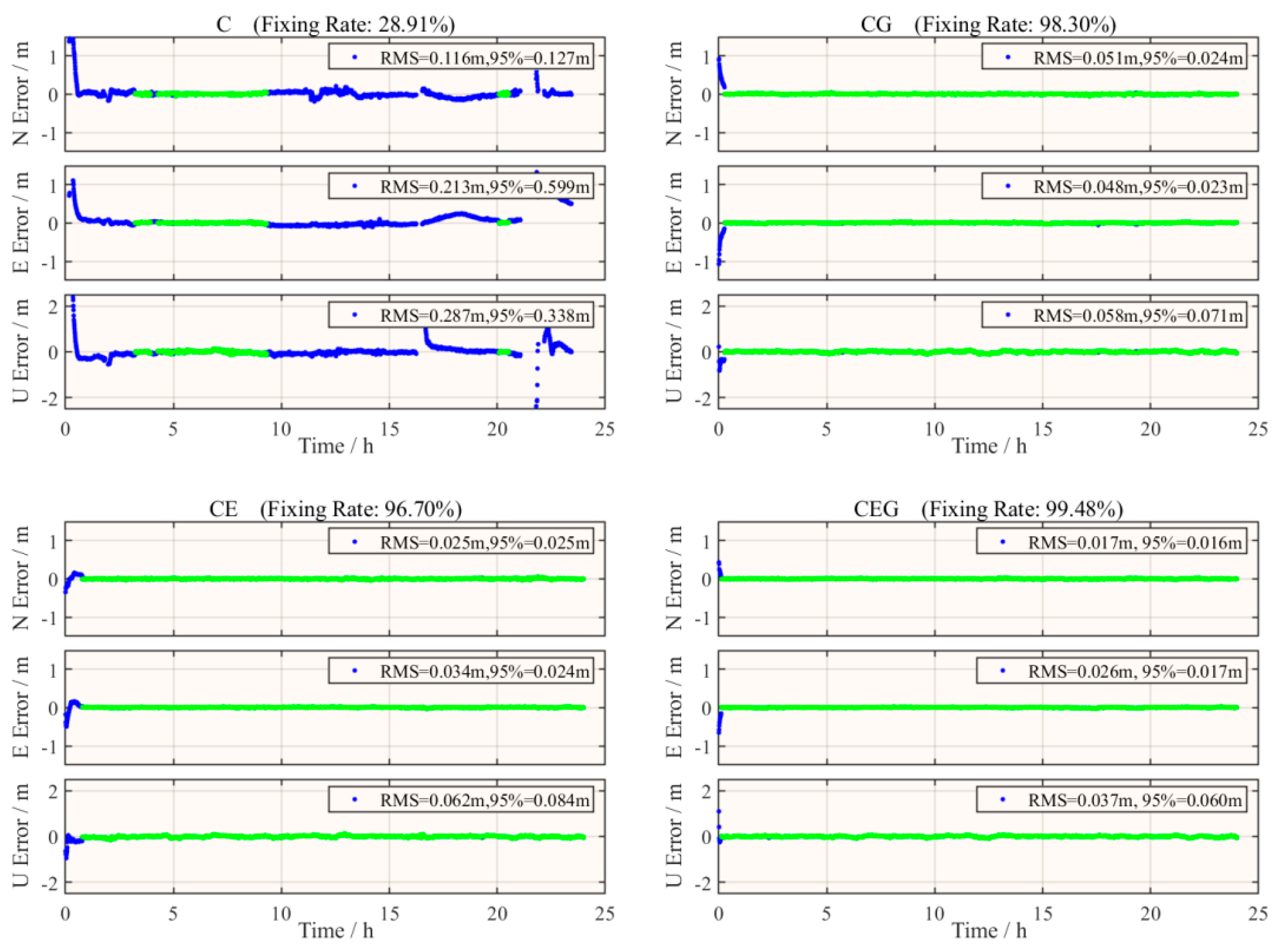
3.2.1. IGS Station Experiment
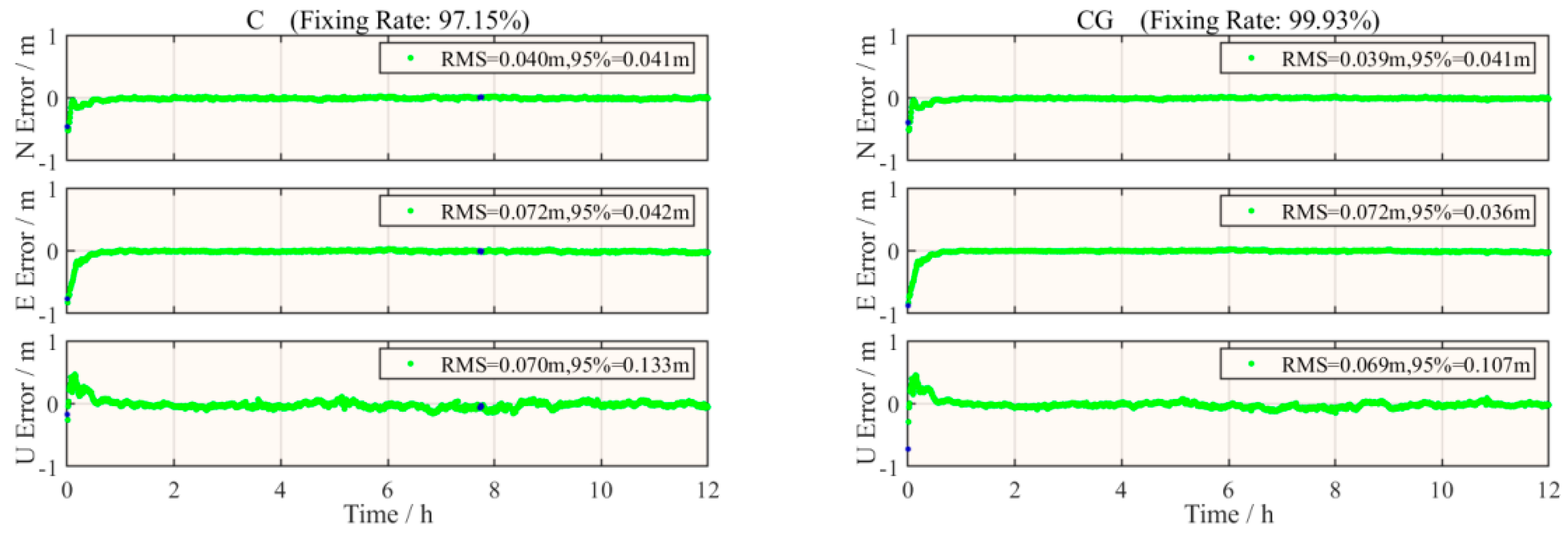
3.2.2. Shipborne Measurement Experiment
4. Discussion
4.1. Is the Approach of Treating Atmospheric Delays as Unknown Parameters the Only Feasible Solution?
4.2. Are There Any Potential Negative Aspects or Disadvantages Associated with the Integration of Multiple GNSSs?
4.3. To What Extent Must a Subset of Ambiguities Be Fixed for the Partial Ambiguity Resolution (PAR) Technique to Be More Efficient than Full Ambiguity Resolution (FAR)?
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, X.; Liu, H.; Yu, B.; Sheng, C.; Huang, G.; Hui, S.; Ying, J. BeiDou/GNSS wide-area precise positioning technology and service: Current situation and prospects. Geomat. Inf. Sci. Wuhan Univ. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Zhang, S.; Deng, C.; Qi, K.; Nie, X.; Zou, X.; Li, Y. Analysis and evaluation of network real-time kinematic positioning performance based on standalone BDS receivers. Geomat. Inf. Sci. Wuhan Univ. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Gu, S.; Lou, Y.; Zheng, F.; Song, W.; Zhang, D.; Mao, F. Real-time wide-area precise positioning and precise timing service system. Acta Geod. Cartogr. Sin. 2022, 51, 1206–1214. [Google Scholar]
- Remondi, B.W. Performing centimeter-level surveys in seconds with GPS carrier phase: Initial results. Navigation 1985, 32, 386–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, S.J.; Cross, P.A.; Barnes, J.B.; Bétaille, D. A methodology for benchmarking real time kinematic GPS. Surv. Rev. 1999, 35, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Miao, W.; Chen, G. Key technologies and challenges of multi-frequency and multi-GNSS high-precision positioning. Geomat. Inf. Sci. Wuhan Univ. 2023, 48, 1769–1783. [Google Scholar]
- Song, W.; Mao, W.; Zhang, Y. Achievements and opportunities in the development of GNSS RTK positioning technology. World Sci-Tech R D 2023, 45, 294–305. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, W.; Pan, S.; Huang, G. Medium-baseline RTK positioning method based on BDS-3 and Galileo multi-frequency ionosphere-reduced combinations. J. Chin. Inert. Technol. 2020, 28, 783–788. [Google Scholar]
- Pirti, A.; Gümüş, K.; Erkaya, H.; Hoşbaş, R.G. Evaluating repeatability of RTK GPS/GLONASS near/under forest environment. Croat. J. For. Eng. J. Theory Appl. For. Eng. 2010, 31, 23–33. [Google Scholar]
- He, H.; Li, J.; Yang, Y.; Xu, J.; Guo, H.; Wang, A. Performance assessment of single-and dual-frequency BeiDou/GPS single-epoch kinematic positioning. GPS Solut. 2014, 18, 393–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, Z.; Yuan, H.; Zhou, K. Validation and analysis of the performance of dual-frequency single-epoch BDS/GPS/GLONASS relative positioning. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2015, 60, 857–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Kubo, N.; Chen, J.; Chu, F.Y.; Wang, H.; Wang, J. Contribution of QZSS with four satellites to multi-GNSS long baseline RTK. J. Spat. Sci. 2020, 65, 41–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odolinski, R.; Teunissen, P.J.G.; Odijk, D. Combined GPS+BDS for short to long baseline RTK positioning. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2015, 26, 045801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odolinski, R.; Teunissen, P.J.G.; Odijk, D. Combined GPS+BDS+Galileo+QZSS for Long Baseline RTK Positioning. In Proceedings of the 27th International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of The Institute of Navigation (ION GNSS+ 2014), Tampa, FL, USA, 8–12 September 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Feng, Y.; Shen, Y. Three carrier ambiguity resolution: Distance-independent performance demonstrated using semi-generated triple frequency GPS signals. GPS Solut. 2010, 14, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takasu, T.; Yasuda, A. Kalman-filter-based integer ambiguity resolution strategy for long-baseline RTK with ionosphere and troposphere estimation. In Proceedings of the 23rd International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of the Institute of Navigation (ION GNSS 2010), Portland, OR, USA, 21–24 September 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Bramanto, B.; Gumilar, I.; Taufik, M.; Hermawan, I.M.D.A. Long-range single baseline RTK GNSS positioning for land cadastral survey map. E3S Web Conf. 2019, 94, 1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wang, J.; Khodabandeh, A. Regional ionospheric correction generation for GNSS PPP-RTK: Theoretical analyses and a new interpolation method. GPS Solut. 2024, 28, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Chai, H.; El-Mowafy, A.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Du, Z. Modeling and assessment of atmospheric delay for GPS/Galileo/BDS PPP-RTK in regional-scale. Measurement 2022, 194, 111043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, R.; Ye, F.; Odolinski, R.; Satirapod, C.; Zhang, B. Mitigating ionospheric scintillation effects on RTK-based long-span bridge deformation monitoring. Measurement 2025, 242, 115957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubo, Y.; Tanaka, H.; Ohashi, M.; Sugimoto, S. Long baseline GNSS relative positioning with estimating ionospheric and tropospheric delays and their gradients. In Proceedings of the 42th ISCIE International Symposium on Stochastic Systems Theory and its Applications, Okayama, Japan, 26–27 November 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Q.; Zhu, F. A method of dynamic positioning with the medium and long baseline for aerial measurement scenarios. Acta Geod. Cartogr. Sin. 2019, 48, 871–878. [Google Scholar]
- Shu, B.; Liu, H.; Xu, L.; Qian, C.; Gong, X.; An, X. Performance analysis of BDS medium-long baseline RTK positioning using an empirical troposphere model. Sensors 2018, 18, 1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, P.; Zhang, B.; Liu, T. Integer-estimable GLONASS FDMA model as applied to Kalman-filter-based short-to long-baseline RTK positioning. GPS Solut. 2020, 24, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, B.K.; Roh, K.M.; Lee, S.J. Long baseline GPS RTK with estimating tropospheric delays. J. Position. Navig. Timing 2014, 3, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Wu, C.; Li, L.; Yan, L.; Liu, M.; Wang, S. GPS/BDS medium/long-range RTK constrained with tropospheric delay parameters from NWP model. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, B.; Liu, H.; Zhang, J.; Pan, G.; Jiang, J. Performance assessment of partial ambiguity resolution based on BDS/GPS combined positioning. Geomat. Inf. Sci. Wuhan Univ. 2017, 42, 989–994+1001. [Google Scholar]
- Teunissen, P.J.G.; Joosten, P.; Tiberius, C. Geometry-free ambiguity success rates in case of partial fixing. In Proceedings of the 1999 National Technical Meeting of the Institute of Navigation, San Diego, CA, USA, 25–27 January 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, L.L.; Eslinger, D.J.; Sharpe, R.T.; Hatch, R.R. Partial Search Carrier-Phase Integer Ambiguity Resolution. U.S. Patent 7,961,143, 14 June 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Vollath, U.; Doucet, K.D. GNSS Signal Processing with Partial Fixing of Ambiguities. U.S. Patent 7,538,721, 26 May 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Teunissen, P.J.G.; Verhagen, S. The GNSS ambiguity ratio-test revisited: A better way of using it. Surv. Rev. 2009, 41, 138–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Verhagen, S. Model and data driven partial ambiguity resolution for multi-constellation GNSS. In Proceedings of the 5th China Satellite Navigation Conference (CSNC 2014) Proceedings, Nanjing, China, 21 May 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, L.; Ma, L.; Liu, W.; Wu, T.; Chen, B. A triple checked partial ambiguity resolution for GPS/BDS RTK positioning. Sensors 2019, 19, 5034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, F.Y.; Yang, M. GPS/Galileo long baseline computation: Method and performance analyses. GPS Solut. 2014, 18, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Wu, J.; Zhao, C.; Tian, Y. Double differencing within GNSS constellations. GPS Solut. 2017, 21, 1161–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odijk, D.; Teunissen, P.J.G. Estimation of differential inter-system biases between the overlapping frequencies of GPS, Galileo, BeiDou and QZSS. In Proceedings of the 4th International Colloquium Scientific and Fundamental Aspects of the Galileo Programme, Prague, CZ, USA, 4–6 December 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Odijk, D.; Nadarajah, N.; Zaminpardaz, S.; Teunissen, P.J.G. GPS, Galileo, QZSS and IRNSS differential ISBs: Estimation and application. GPS Solut. 2017, 21, 439–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, M.; Gendt, G.; Rothacher, M.; Shi, C.; Liu, J. Resolution of GPS carrier-phase ambiguities in precise point positioning (PPP) with daily observations. J. Geod. 2008, 82, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsigianni, G.; Loyer, S.; Perosanz, F. PPP and PPP-AR kinematic post-processed performance of GPS-only, Galileo-only and multi-GNSS. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odijk, D. Weighting ionospheric corrections to improve fast GPS positioning over medium distances. In Proceedings of the 13th International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of the Institute of Navigation (ION GPS 2000), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 19–22 September 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Teunissen, P. Springer Handbook of Global Navigation Satellite Systems; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Teunnissen, P.J.G. The least-square ambiguity decorrelation adjustment: A method for fast GPS integer ambiguity estimation. J. Geod. 1995, 70, 65–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhagen, S.; Li, B.; Geodesy, M. LAMBDA Software Package: Matlab Implementation, version 3.0; Delft University of Technology and Curtin University: Perth, Australia, 2012.
- Verhagen, S.; Teunissen, P.J.G. The ratio test for future GNSS ambiguity resolution. GPS Solut. 2013, 17, 535–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkins, A. Increasing GNSS RTK availability with a new single-epoch batch partial ambiguity resolution algorithm. GPS Solut. 2011, 15, 391–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Gao, C.; Pan, S.; Wang, D.; Deng, J. Improving ambiguity resolution for medium baselines using combined GPS and BDS dual/triple-frequency observations. Sensors 2015, 15, 27525–27542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhao, L.; Li, X.; Cheng, B. A sequential and partial ambiguity resolution strategy for improving the initialization performance of medium-baseline relative positioning. Earth Planets Space 2016, 68, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Verhagen, S.; Wu, J. A data driven partial ambiguity resolution: Two step success rate criterion, and its simulation demonstration. Adv. Space Res. 2016, 58, 2435–2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odijk, D.; Teunissen, P.J.G. ADOP in closed form for a hierarchy of multi-frequency single-baseline GNSS models. J. Geod. 2008, 82, 473–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böhm, J.; Möller, G.; Schindelegger, M.; Pain, G.; Weber, R. Development of an improved empirical model for slant delays in the troposphere (GPT2w). GPS Solut. 2015, 19, 433–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanninger, L. Effects of the equatorial ionosphere on. GPS World 1993, 48–54. [Google Scholar]
- Foster, J.C. Quantitative investigation of ionospheric density gradients at mid latitudes. In Proceedings of the 2000 National Technical Meeting of The Institute of Navigation, Anaheim, CA, USA, 26–28 January 2000. [Google Scholar]
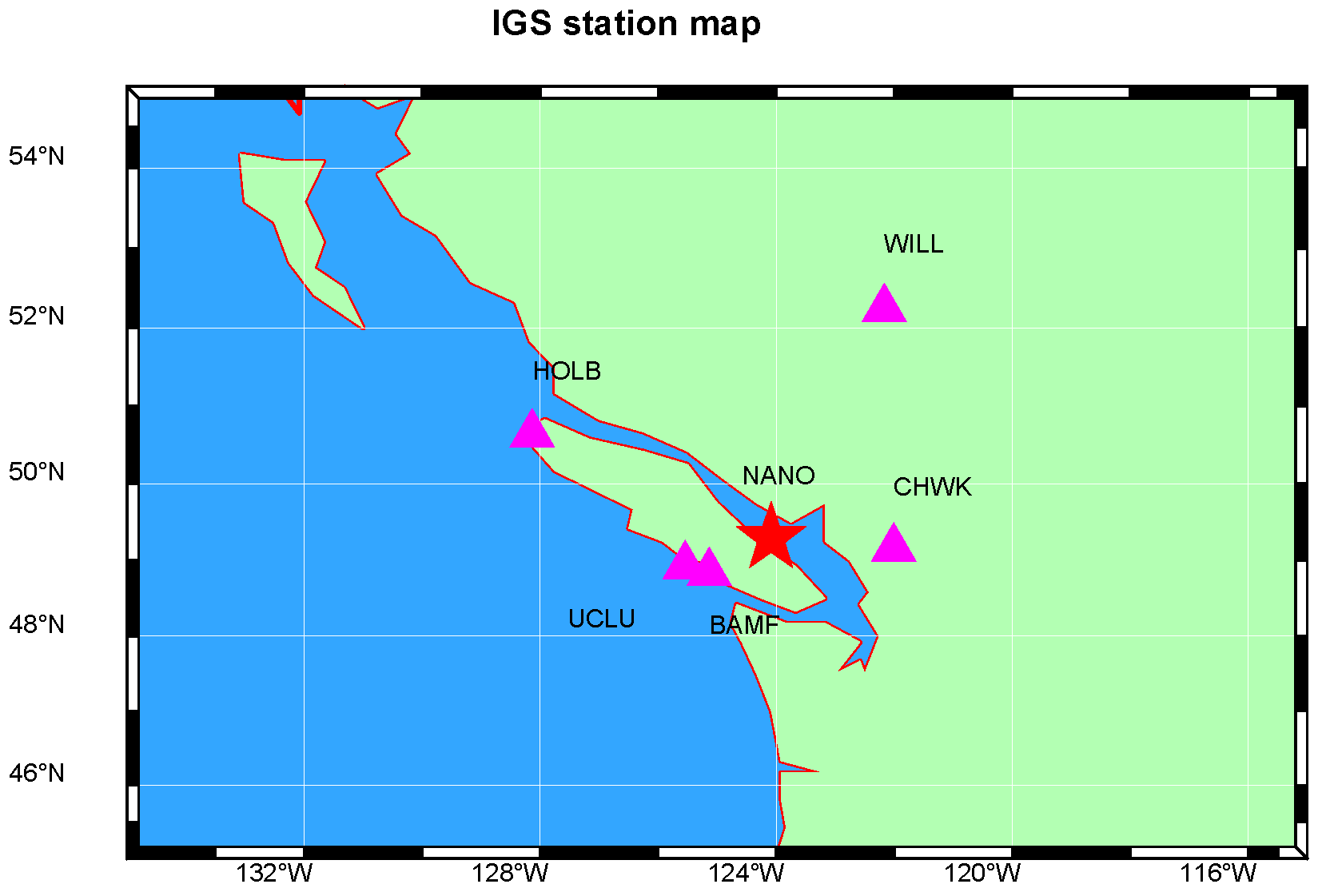
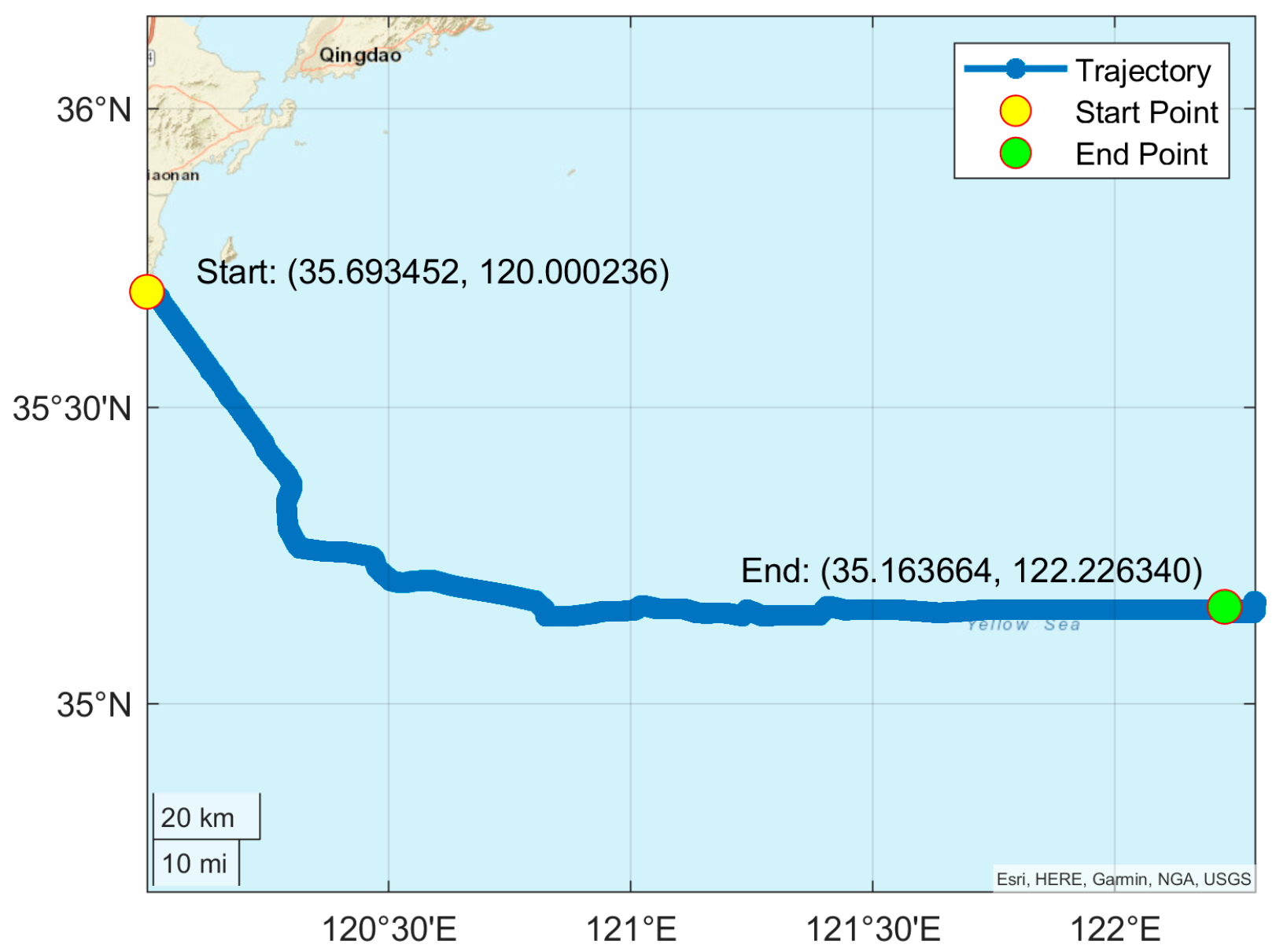

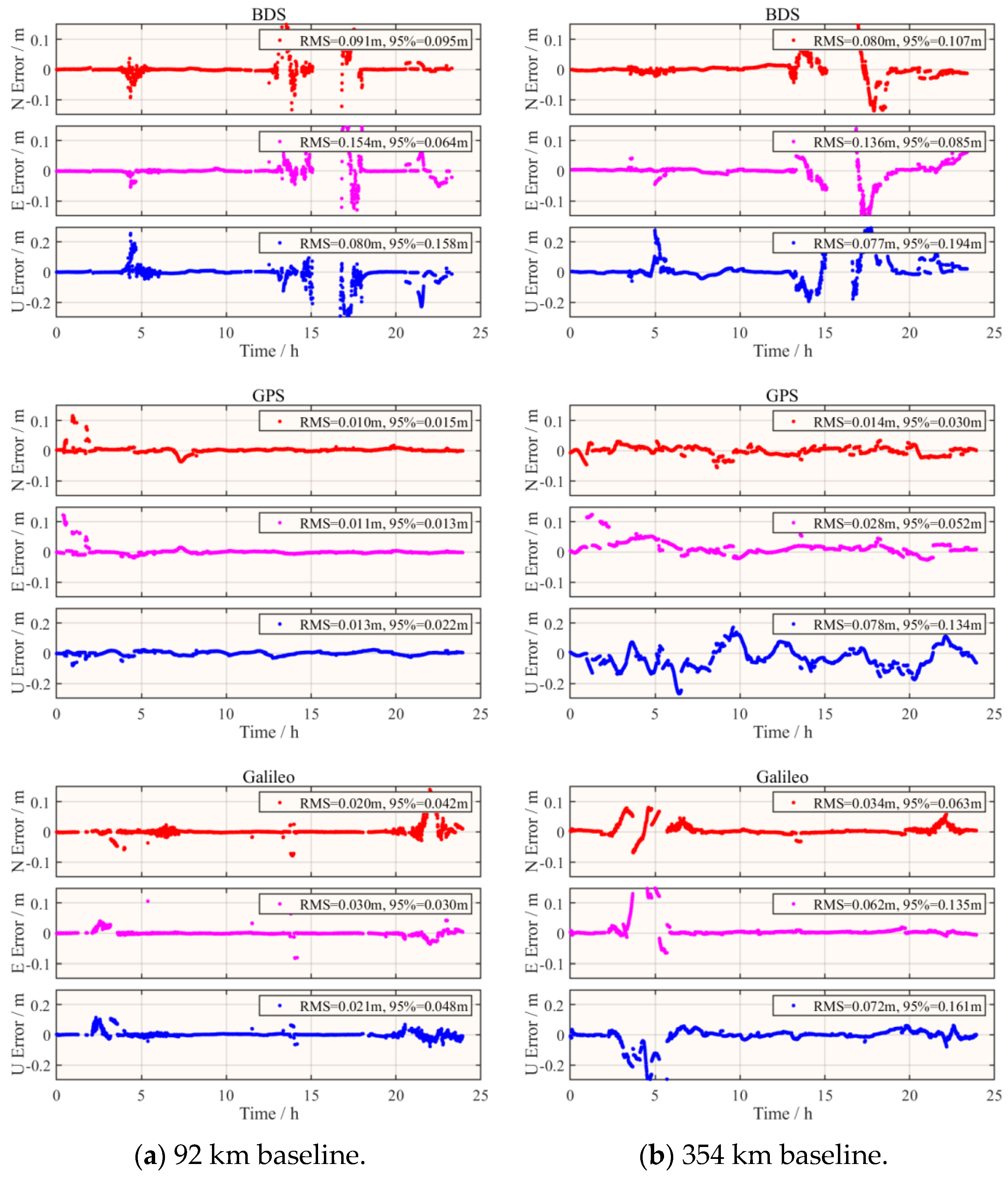
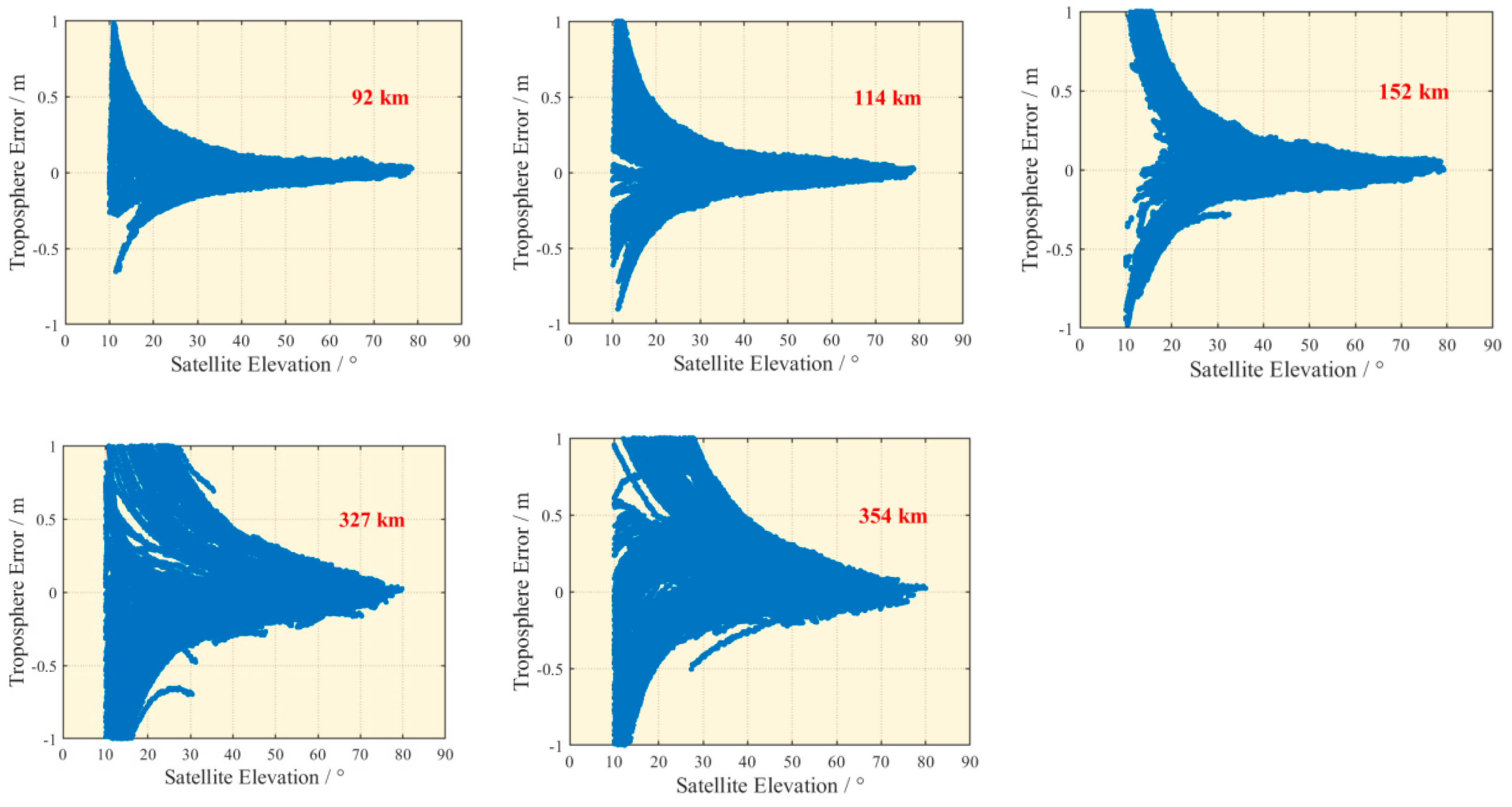
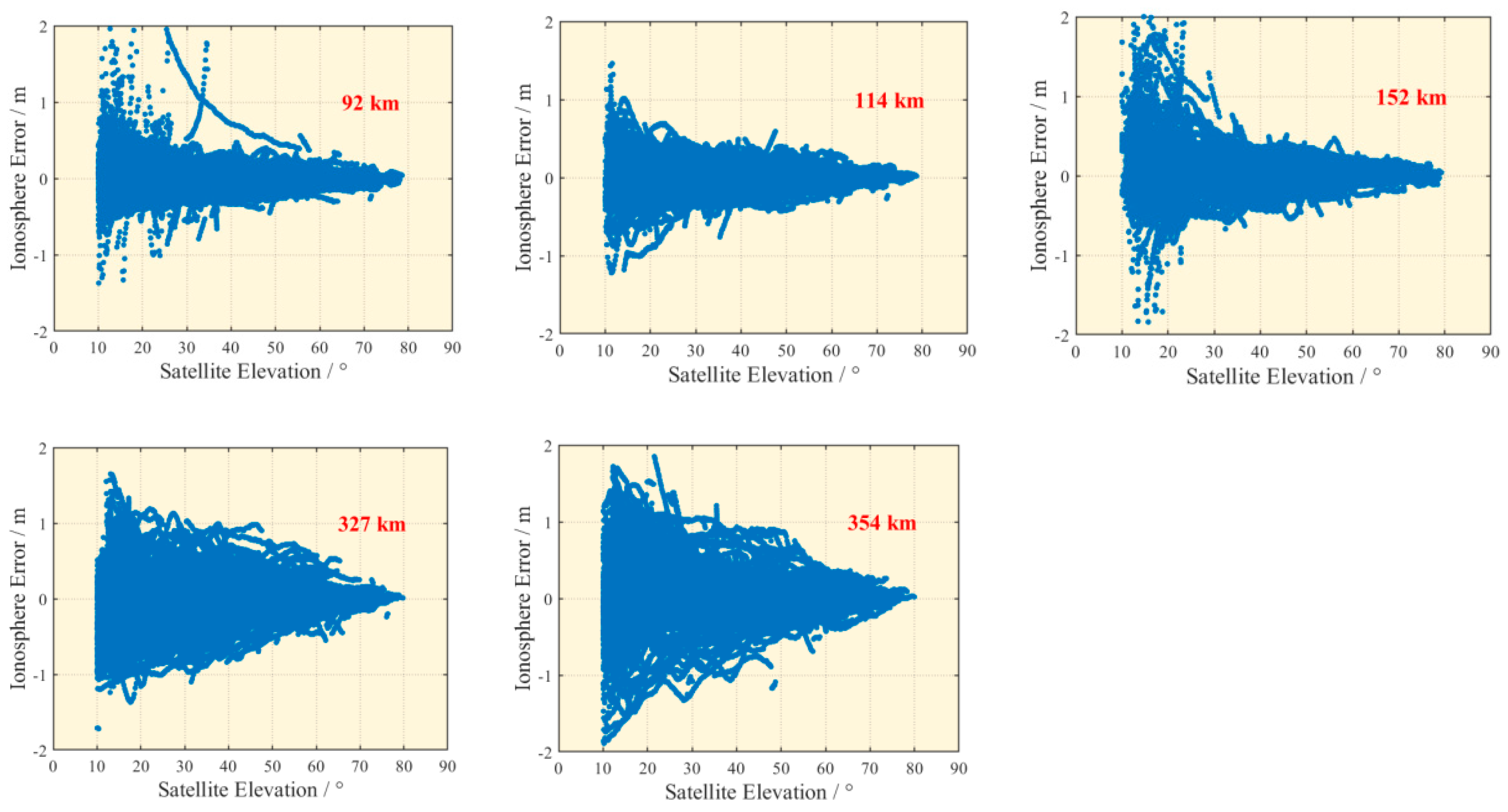


| Serial Number | Baseline | Length/km |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | NANO-BAMF | 92 |
| 2 | NANO-UCLU | 114 |
| 3 | NANO-CHWK | 152 |
| 4 | NANO-HOLB | 327 |
| 5 | NANO-WILL | 354 |
| Item | Processing Strategy | |
|---|---|---|
| Satellite Orbit/Clock | Broadcast Ephemeris | |
| Data Interval | 30 s | |
| Satellite Elevation Cutoff | 10° | |
| Troposphere Delay | Meteorological Parameter | GPT2w Model |
| Zenith Delay | Saastamoinen Model | |
| Mapping Function | VMF1 | |
| Residual Zenith Wet Delay | Parameter Estimation | |
| Ionosphere Delay | Parameter Estimation | |
| Positioning Mode | Kinematic | |
| Frequency | Dual | |
| Estimation Method | Kalman Filter | |
| Cycle Slip Method | GF and MW | |
| Code Observation Noise | 0.3 m | |
| Phase Observation Noise | 0.003 m | |
| Stochastic Model | Elevation Dependent | |
| Antenna File | IGS_20.atx | |
| System | Positioning Error/m | Fixing Rate/% | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| North | East | Up | ||
| BDS | 0.040 | 0.072 | 0.070 | 97.15 |
| BDS/GPS | 0.039 | 0.072 | 0.069 | 99.93 |
| Baseline | PAR | FAR | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fixed Number | Fixed Epoch | Fixing Rate/% | N/m | E/m | U/m | Fixed Number | Fixed Epoch | Fixing Rate/% | N/m | E/m | U/m | |
| NANO-BAMF | 24.9 | 2853 | 99.06 | 0.011 | 0.013 | 0.048 | 26.25 | 1442 | 50.07% | 0.012 | 0.015 | 0.051 |
| NANO-UCLU | 19 | 2841 | 98.65 | 0.011 | 0.029 | 0.033 | 20.42 | 1454 | 50.49 | 0.012 | 0.03 | 0.036 |
| NANO-CHWK | 20.79 | 2865 | 99.48 | 0.017 | 0.026 | 0.037 | 27.14 | 258 | 8.96 | 0.022 | 0.031 | 0.046 |
| NANO-HOLB | 19.79 | 2773 | 96.28 | 0.015 | 0.019 | 0.041 | 27.33 | 254 | 8.82 | 0.018 | 0.021 | 0.047 |
| NANO-WILL | 18.94 | 2717 | 94.34 | 0.020 | 0.051 | 0.053 | 27.35 | 154 | 5.35 | 0.019 | 0.060 | 0.066 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, D.; Li, H.; Wang, Z.; Wu, S.; Liu, Y.; Ju, K.; Zhu, C. Long-Baseline Real-Time Kinematic Positioning: Utilizing Kalman Filtering and Partial Ambiguity Resolution with Dual-Frequency Signals from BDS, GPS, and Galileo. Aerospace 2024, 11, 970. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace11120970
Yu D, Li H, Wang Z, Wu S, Liu Y, Ju K, Zhu C. Long-Baseline Real-Time Kinematic Positioning: Utilizing Kalman Filtering and Partial Ambiguity Resolution with Dual-Frequency Signals from BDS, GPS, and Galileo. Aerospace. 2024; 11(12):970. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace11120970
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Deying, Houpu Li, Zhiguo Wang, Shuguang Wu, Yi Liu, Kaizhong Ju, and Chen Zhu. 2024. "Long-Baseline Real-Time Kinematic Positioning: Utilizing Kalman Filtering and Partial Ambiguity Resolution with Dual-Frequency Signals from BDS, GPS, and Galileo" Aerospace 11, no. 12: 970. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace11120970
APA StyleYu, D., Li, H., Wang, Z., Wu, S., Liu, Y., Ju, K., & Zhu, C. (2024). Long-Baseline Real-Time Kinematic Positioning: Utilizing Kalman Filtering and Partial Ambiguity Resolution with Dual-Frequency Signals from BDS, GPS, and Galileo. Aerospace, 11(12), 970. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace11120970






