Static and Dynamic Performance of a Morphing Trailing Edge Concept with High-Damping Elastomeric Skin
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Summary and Investigation Strategy
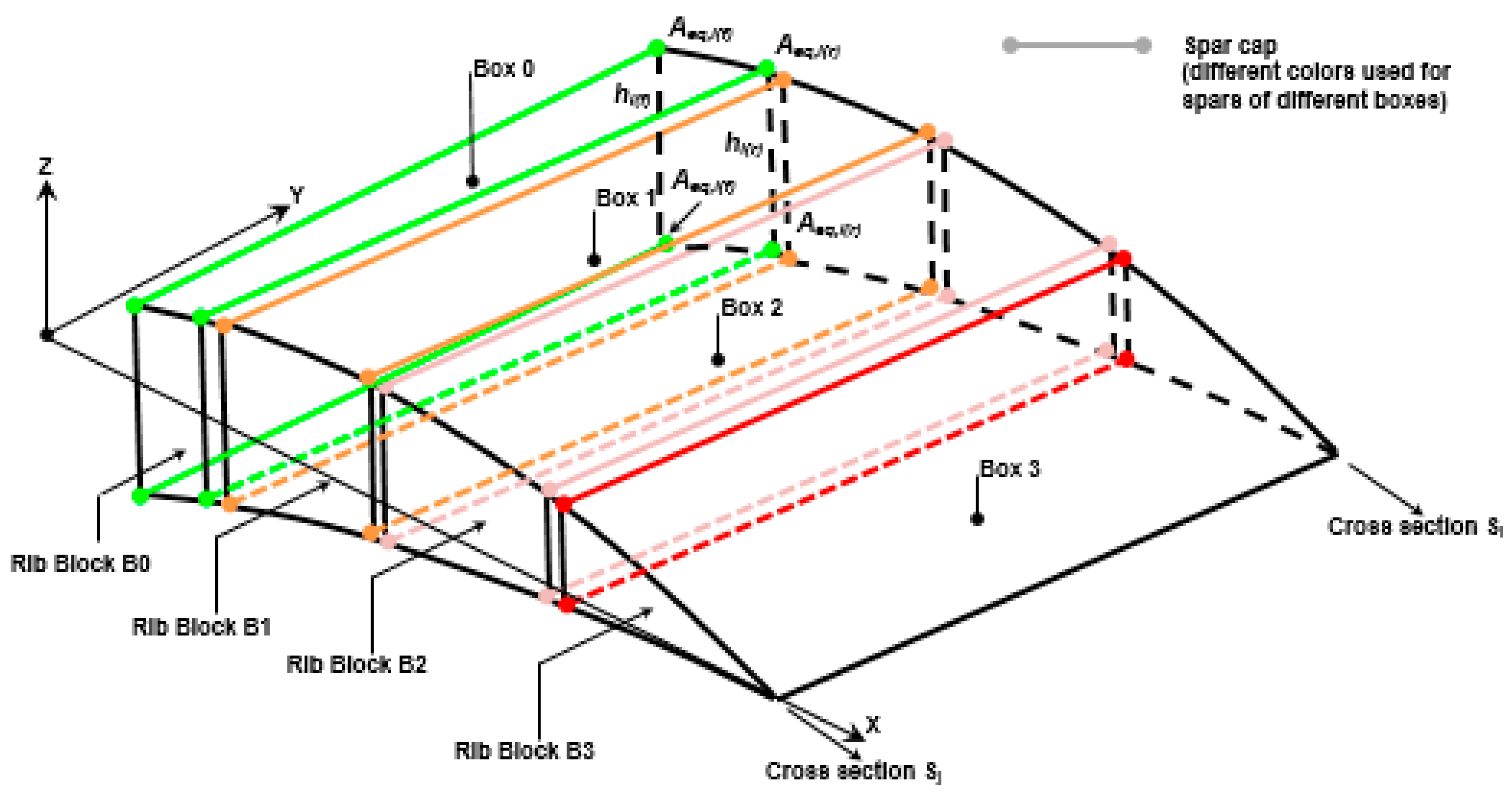
3. Morphing Architecture Description
4. Skeleton Structural Sizing
- Al2024-T5 alloy for all primary elements comprising rib plates, spars and skin panels;
- limit load condition associated to a trimmed flight symmetric manoeuvre, at dive speed, limit load factor and maximum take-off weight);
- no coupling among the hinged blocks along the chord-wise direction (in more detail, each cell of the multi-block arrangement was analysed independently);
5. Hyperelastic Compliant Skin
5.1. Design Aspects
5.2. Damping Properties’ Characterization
6. Numerical Model Overview
6.1. Structural Modelling
- An aluminium sheet (plate-cquad4), connected to the rib;
- A hyperelastic sheet (plate-cquad4), covering all the structure;
- Foam strips (solid-chexa8), applied in span-wise direction and located close to the hinges to guarantee the morphing capability to the skin.
6.2. Parametric Normal Modes Analysis
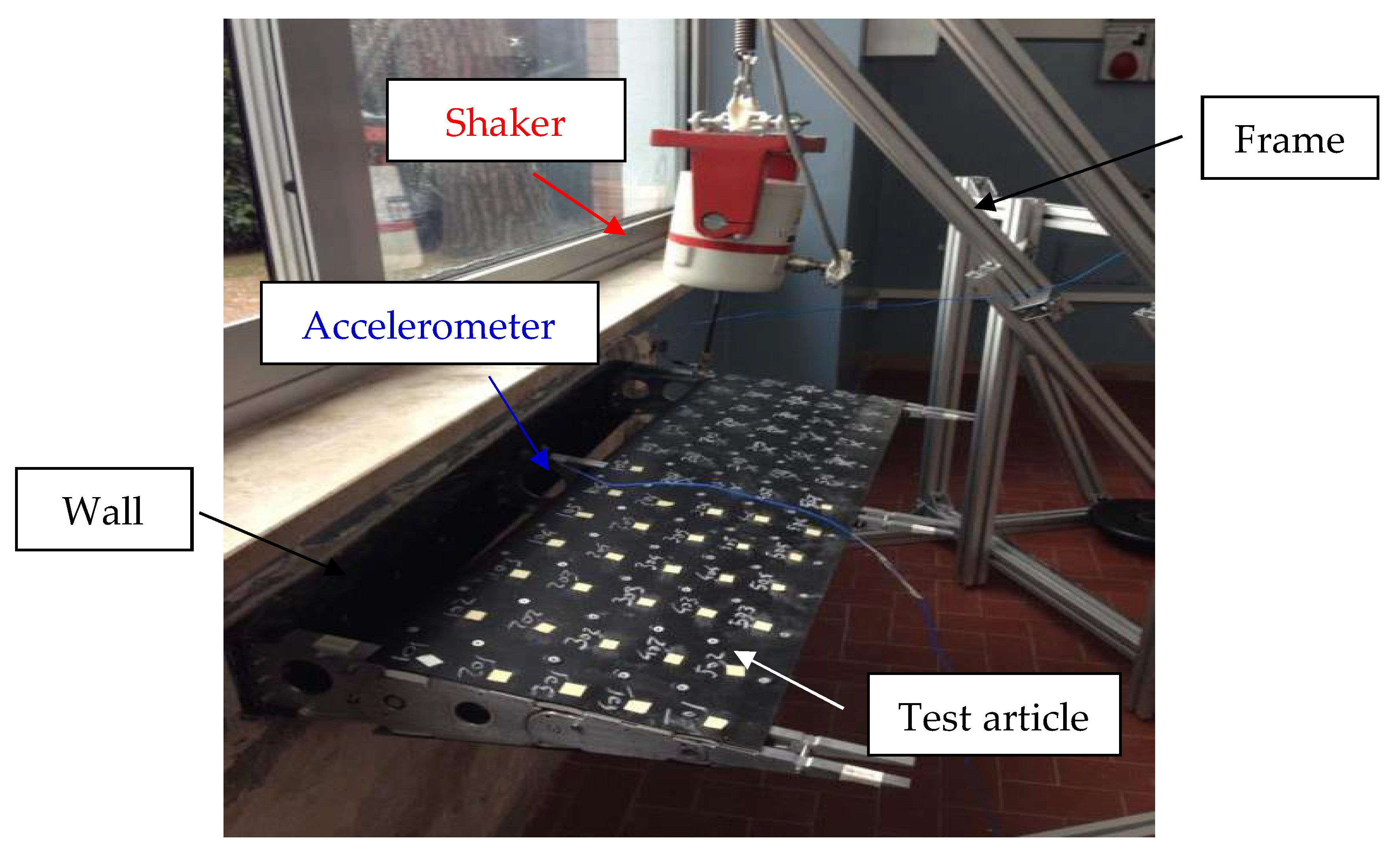
7. Experimental Investigation of Dummy Device
7.1. Test Setup Description
7.2. Ground Vibration Test Results
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References and Note
- Sofla, A.Y.N.; Meguid, S.A.; Tan, K.T.; Yeo, W.K. Shape morphing of aircraft wing: Status and challenges. Mater. Des. 2010, 31, 1284–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbarino, S.; Bilgen, O.; Ajaj, R.M.; Friswell, M.I.; Inman, D.J. A review of morphing aircraft. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2011, 22, 823–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thill, C.; Etches, J.; Bond, I.; Potter, K.; Weaver, P. Morphing skins. Aeronaut. J. 2008, 112, 117–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thornburgh, R.P.; Kreshock, A.R.; Wilbur, M.L.; Sekula, M.K.; Shen, J. Continuous Trailing-Edge Flaps for Primary Flight Control of a Helicopter Main Rotor. In Proceedings of the 20th American Helicopter Society (AHS) Annual Forum, Montreal, QC, Canada, 20–22 May 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Wilbur, M.L.; Mistry, M.P.; Lorber, P.E.; Blackwell, R., Jr.; Barbarino, S.; Lawrence, T.H.; Arnold, U.T.P. Chapter 24—Rotary Wings Morphing Technologies: State of the Art and Perspectives, Morphing Wing Technologies Large Commercial Aircraft and Civil Helicopters; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 759–797. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, J.; Wang, C.; Huang, C.; Ji, H.; Xu, Z. Smart skin and actuators for morphing structures, 23rd International Congress of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics. Procedia IUTAM 2014, 10, 427–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ermakova, A.; Dayyani, I. Shape optimisation of composite corrugated morphing skins. Compos. Part B Eng. 2017, 115, 87–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Airoldi, A.; Crespi, M.; Quaranti, G.; Sala, G. Design of a Morphing Airfoil with Composite Chiral. Struct. J. Aircr. 2012, 49, 1008–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.; Sun, J.; Chang, Z.; Bai, R.; Leng, J. Elastic composite skin for a pure shear morphing wing structures. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2014, 26, 352–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Woods, B.K.S.; Friswell, M.I. The Adaptive Aspect Ratio Morphing Wing: Design Concept and Low Fidelity Skin Optimization. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2015, 42, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaverstock, C.S.; Woods, B.K.S.; Fincham, J.H.S.; Friswell, M.I. Performance Comparison between Optimised Camber and Span for a Morphing Wing. Aerospace 2015, 2, 524–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gurses, E.; Tuncoz, I.O.; Yang, Y.; Arslan, P.; Kalkan, U.; Tıras, H.; Sahin, M.; Ozgen, S.; Yaman, Y. Structural and aerodynamic analyses of a hybrid trailing edge control surface of a fully morphing wing. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2016, 28, 979–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, H. Shape sensing a morphed wing with an optical fiber Bragg grating. In Proceedings of the SPIE Conference on Smart Structures and Materials, Nondestructive Evaluation and Health Monitoring, San Diego, CA, USA, 19 May 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Viscardi, M.; Arena, M.; Barra, G.; Vertuccio, L.; Ciminello, M.; Guadagno, L. Piezoresistive strain sensing of carbon nanotubes-based composite skin for aeronautical morphing structures. In Proceedings of the SPIE 10599, Nondestructive Characterization and Monitoring of Advanced Materials, Aerospace, Civil Infrastructure, and Transportation, Denver, CO, USA, 27 March 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Viscardi, M.; Arena, M.; Guadagno, L.; Vertuccio, L.; Barra, G. Multi-functional nanotechnology integration for aeronautical structures performance enhancement. Int. J. Struct. Integr. 2018, 9, 737–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.; Wua, Y.; Lia, H.; Zhua, L. 3D shape sensing of flexible morphing wing using fiber Bragg grating sensing method. Optik 2018, 156, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jodin, G.; Scheller, J.; Rouchon, J.F.; Braza, M. On the multidisciplinary control and sensing of a smart hybrid morphing wing. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Workshop of Electronics, Control, Measurement, Signals and their Application to Mechatronics (ECMSM), Donostia-San Sebastian, Spain, 24–26 May 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Ciminello, M.; Ameduri, S.; Concilio, A.; Dimino, I.; Bettini, P. Fiber Optic Shape Sensor System for a Morphing Wing Trailing Edge. Smart Struct. Syst. 2017, 20, 441–450. [Google Scholar]
- Gomez, J.C.; Garcia, E. Morphing unmanned aerial vehicles. Smart Mater. Struct. 2011, 20, 103001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimino, I.; Diodati, G.; Concilio, A.; Volovick, A.; Zivan, L. Distributed electromechanical actuation system design for a morphing trailing edge wing. In Proceedings of the SPIE—The International Society for Optical Engineering, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 20–24 March 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Botez, R.M.; Tchatchueng Kammegne, M.J.; Grigorie, L.T. Design, numerical simulation and experimental testing of a controlled electrical actuation system in a real aircraft morphing wing model. Aeronaut. J. 2015, 119, 1047–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbarino, S.; Flores, E.S.; Ajaj, R.M.; Dayyani, I.; Friswell, M.I. A review on shape memory alloys with applications to morphing aircraft. Smart Mater. Struct. 2014, 23, 063001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roh, J.H.; Kim, K.S.; Lee, I. Shape adaptive airfoil actuated by a shape memory alloy and its aerodynamic characteristics. Mech. Adv. Mater. Struct. 2009, 16, 260–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarselli, G.; Nicassio, F.; Maffezzoli, A. Mechanical characterization of bistable laminates for very small aircraft morphing applications. In Proceedings of the SPIE 10600, Health Monitoring of Structural and Biological Systems, Denver, CO, USA, 27 March 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Scarselli, G.; Nicassio, F.; Pinto, F. A novel bistable energy harvesting concept. Smart Mater. Struct. 2016, 25, 055001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabawy, M.R.A.; ElNomrossy, M.M.; Abdelrahman, M.M.; ElBayoumi, G.M. Aerodynamic shape optimisation, wind tunnel measurements and CFD analysis of a MAV wing. Aeronaut. J. 2012, 116, 685–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.R.; Abdelrahman, M.M.; ElBayoumi, G.M.; ElNomrossy, M.M. Optimal wing twist distribution for roll control of MAVs. Aeronaut. J. 2011, 115, 641–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roccia, B.A.; Preidikman, S.; Balachandran, B. Computational Dynamics of Flapping Wings in Hover Flight: A Co-Simulation Strategy. AIAA J. 2017, 55, 1806–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulrahim, M.; Lind, R. Flight testing and response characteristics of a variable gull-wing morphing aircraft. In Proceedings of the AIAA Guidance, Navigation, and Control Conference and Exhibit, Providence, Rhode Island, 16–19 August 2004; p. 5113. [Google Scholar]
- Abdulrahim, M.; Garcia, H.; Lind, R. Flight characteristics of shaping the membrane wing of a micro air vehicle. J. Aircr. 2005, 42, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Concilio, A.; Dimino, I.; Diodati, G.; Pecora, R.; Magnifico, M.; Schorsch, O. Damping levels induced by morphing skin on an adaptive trailing edge device (ATED). In Proceedings of the 24th AIAA/AHS Adaptive Structures Conference, San Diego, CA, USA, 4–8 January 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Wölcken, P.C.; Papadopoulos, M. Smart Intelligent Aircraft Structures (SARISTU); Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pecora, R.; Concilio, A.; Dimino, I.; Amoroso, F.; Ciminello, M. Structural design of an adaptive wing trailing edge for enhanced cruise performances. In Proceedings of the 24th AIAA/AHS Adaptive Structures Conference AIAA SciTech, San Diego, CA, USA, 4–8 January 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Pecora, R.; Amoroso, F.; Magnifico, M.; Dimino, I.; Concilio, A. KRISTINA: Kinematic rib-based structural system for innovative adaptive trailing edge. In Proceedings of the SPIE—The International Society for Optical Engineering, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 20–24 March 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Arena, M.; Noviello, M.C.; Rea, F.; Amoroso, F.; Pecora, R.; Amendola, G. Modal stability assessment for a morphing aileron subjected to actuation system failures: Numerical analysis supported by test evidence. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering, London, UK, 18–20 July 2016; pp. 437–442. [Google Scholar]
- Bruhn, E.F. Analysis & Design of Flight Vehicle Structures; Chapter A19; Tri-State Offset Company: Cincinnati, OH, USA, 1969. [Google Scholar]
- Nagel, C.; Fiedler, A.; Schorsch, O.; Lühring, A. Design, manufacture, and testing of a seamless morphing concept for a smart aircraft wingtip. In Proceedings of the 7th ECCOMAS thematic conference on smart structures and materials (SMART 2015), Ponta Delgada, Azores, Portugal, 3–6 June 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Schorsch, O.; Nagel, C.; Lühring, A. Morphing Skin: Foams Morphing Wing Technologies; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 207–230. [Google Scholar]
- Schorsch, O.; Lühring, A.; Nagel, C. Elastomer-Based Skin for Seamless Morphing of Adaptive Wings, Smart Intelligent Aircraft Structures (SARISTU); Springer Nature Switzerland: Basel, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 187–197. [Google Scholar]
- Nagel, C.; Fiedler, A.; Schorsch, O. Seamless Morphing Concepts for Smart Aircraft Wing Tip Smart Intelligent Aircraft Structures (SARISTU); Springer Nature Switzerland: Basel, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 275–291. [Google Scholar]
- Sarlin, E.; Liu, Y.; Vippola, M.; Zogg, M.; Ermanni, P.; Vuorinen, J.; Lepistö, T. Vibration damping properties of steel/rubber/composite hybrid structures. Compos. Struct. 2012, 94, 3327–3335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MSC-MD/NASTRAN®; Software Package, Ver. R3–2006, “Reference Manual”.























| Amplitude | Dissipated Energy | Elastic Energy | Loss Factor | Nominal Strain | Specific Dissipated Energy | Specific Elastic Energy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| u | Ud | Uel | Ud,spec | Uel,spec | ||
| (mm) | (mJ) | (mJ) | (--) | (--) | (mJ/mm3) | (mJ/mm3) |
| 1.0 | 10 | 45 | 0.0354 | 0.03 | 9.71 × 10−4 | 4.29 × 10−3 |
| 1.5 | 24 | 86 | 0.0444 | 0.05 | 2.26 × 10−3 | 8.19 × 10−3 |
| 2.0 | 44 | 139 | 0.0504 | 0.07 | 4.16 × 10−3 | 1.32 × 10−2 |
| 2.5 | 68 | 197 | 0.0550 | 0.08 | 6.48 × 10−3 | 1.88 × 10−2 |
| 3.0 | 96 | 259 | 0.0590 | 0.10 | 9.12 × 10−3 | 2.47 × 10−2 |
| 4.0 | 157 | 412 | 0.0607 | 0.13 | 1.50 × 10−2 | 3.92 × 10−2 |
| 5.0 | 226 | 599 | 0.0601 | 0.17 | 2.15 × 10−2 | 5.70 × 10−2 |
| 6.0 | 299 | 813 | 0.0586 | 0.20 | 2.84 × 10−2 | 7.74 × 10−2 |
| 7.0 | 377 | 1062 | 0.0565 | 0.23 | 3.59 × 10−2 | 1.01 × 10−1 |
| 8.0 | 462 | 1325 | 0.0555 | 0.27 | 4.40 × 10−2 | 1.26 × 10−1 |
| 9.0 | 553 | 1605 | 0.0549 | 0.30 | 5.26 × 10−2 | 1.53 × 10−1 |
| 10.0 | 637 | 1828 | 0.0555 | 0.33 | 6.07 × 10−2 | 1.74 × 10−1 |
| Material | E (MPa) | ρ (Kg/m3) | ν | Items |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al 2024-T3 | 70,000 | 2780 | 0.33 | Ribs; Spars |
| Hyperelastic layer | 1.83–2.30 | 10 | 0.46–0.47 | Skin |
| Foam | 2.30–3.97 | 10 | 0.15–0.24 | Skin |
| FEM Entity | Number | Items |
|---|---|---|
| Node | 177,548 | All |
| Bar | 255 | Pins, fasteners, links |
| Plate | 177,221 | Ribs, spars, skin |
| MPC | 226 | Hinges, holes |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Arena, M.; Nagel, C.; Pecora, R.; Schorsch, O.; Concilio, A.; Dimino, I. Static and Dynamic Performance of a Morphing Trailing Edge Concept with High-Damping Elastomeric Skin. Aerospace 2019, 6, 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace6020022
Arena M, Nagel C, Pecora R, Schorsch O, Concilio A, Dimino I. Static and Dynamic Performance of a Morphing Trailing Edge Concept with High-Damping Elastomeric Skin. Aerospace. 2019; 6(2):22. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace6020022
Chicago/Turabian StyleArena, Maurizio, Christof Nagel, Rosario Pecora, Oliver Schorsch, Antonio Concilio, and Ignazio Dimino. 2019. "Static and Dynamic Performance of a Morphing Trailing Edge Concept with High-Damping Elastomeric Skin" Aerospace 6, no. 2: 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace6020022
APA StyleArena, M., Nagel, C., Pecora, R., Schorsch, O., Concilio, A., & Dimino, I. (2019). Static and Dynamic Performance of a Morphing Trailing Edge Concept with High-Damping Elastomeric Skin. Aerospace, 6(2), 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace6020022









