Fractional-Order Sliding Mode Guidance Law for Intercepting Hypersonic Vehicles
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- Aiming at the scenario of a low-speed missile intercepting a hypersonic vehicle in the longitudinal plane, a guidance law based on the SMC method is proposed that can effectively overcome the disadvantage of the PN to avoid the divergence of the LOS angular rate at the end of the interception moment;
- By introducing the fractional-order operator into the sliding surface, a fractional-order fast power reaching (FOFPR) guidance law is proposed based on the fast power reaching law. It can not only improve the convergence speed of the guidance command, but can also effectively consume less energy in the interception process.
2. Problem Formulation
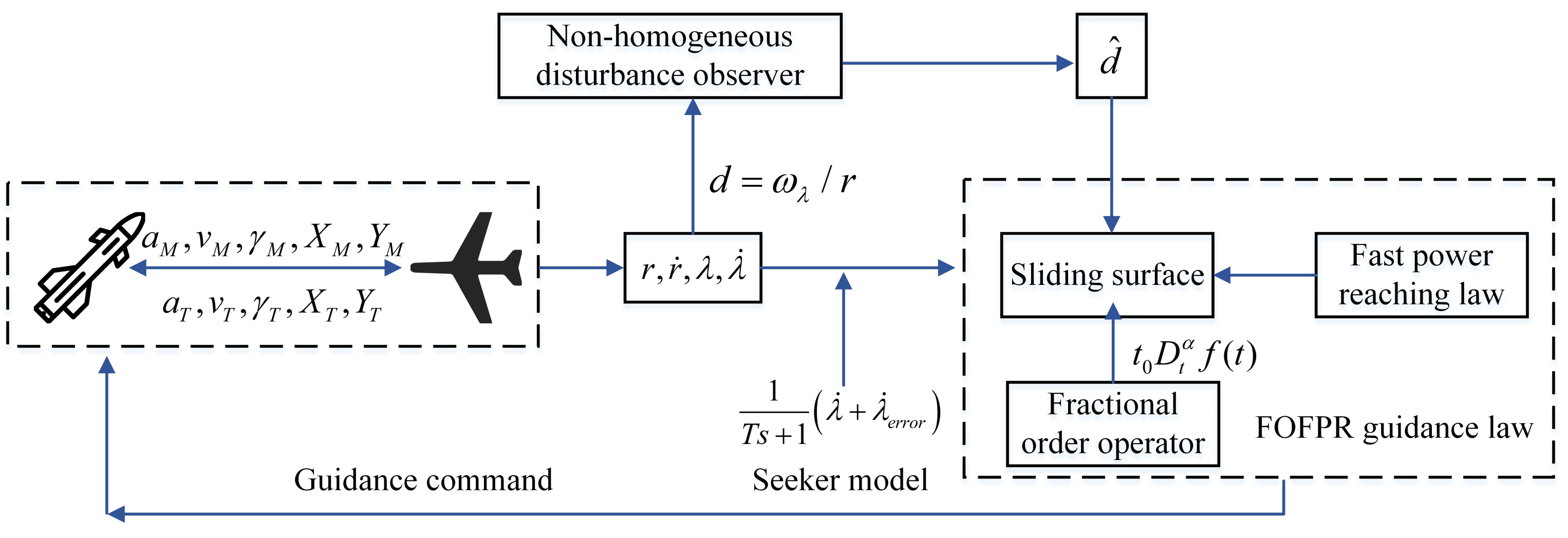
3. Guidance Law Design
3.1. Fundamentals of Fractional-Order Calculus
3.2. Design of a Non-Homogeneous Disturbance Observer
3.3. Guidance Law Design and Stability Analysis
4. Simulation Analysis
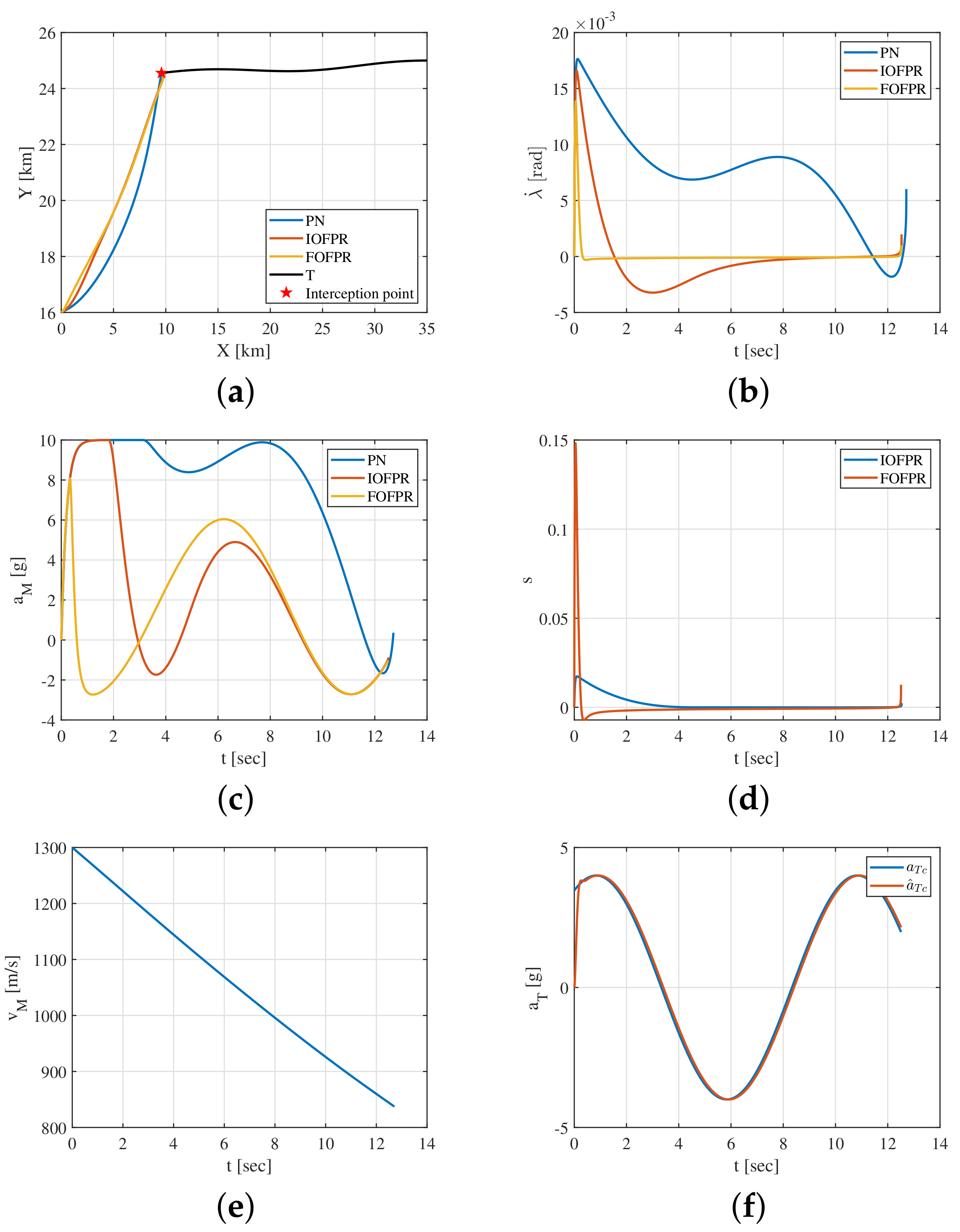
4.1. Hypersonic Vehicle Adopts the Bang-Bang Maneuver Mode
4.2. Hypersonic Vehicle Adopts the Sinusoidal Maneuver Mode
5. Conclusions and Future Discussion
- The FOFPR guidance law can accurately and effectively intercept the hypersonic vehicle with different maneuver modes, and the guidance command changes reasonably and smoothly without a chattering phenomenon;
- When the hypersonic vehicle adopts the bang-bang maneuver mode, under the action of the FOFPR, the interception accuracy is improved by and and consumes and less energy compared to the PN and IOFPR guidance laws, respectively;
- When the hypersonic vehicle adopts the sinusoidal maneuver mode, under the action of the FOFPR, the interception accuracy is improved by and and consumes and less energy compared to the PN and IOFPR guidance laws, respectively.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xu, B.; Shi, Z. An overview on flight dynamics and control approaches for hypersonic vehicles. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 2015, 58, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Yan, B.; Liu, R.; Dai, P.; Yan, J.; Xin, G. Cooperative guidance law for intercepting a hypersonic target with impact angle constraint. AERONAUT J. 2022, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.T.; Wang, Z.G.; Huang, W.; Li, S.B. A design approach of wide-speed-range vehicles based on the cone-derived theory. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2017, 71, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Huang, W.; Zhang, T.T.; Yan, L. Parametric modeling and aerodynamic optimization of EXPERT configuration at hypersonic speeds. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2019, 84, 641–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, K. Closed-form solution of pure proportional navigation. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 1990, 26, 526–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, U.S.; Mahapatra, P.R. The proportional navigation dilemma-pure or true? IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 1990, 26, 382–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Dong, X.; Li, Q.; Ren, Z. A Combined Guidance Law for Intercepting Hypersonic Large Maneuvering Targets. In Proceedings of the IEEE 2020 Chinese Automation Congress (CAC), Shanghai, China, 6–8 November 2020; pp. 1425–1430. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, A.; Ojha, A.; Padhy, P.K. Anticipated trajectory based proportional navigation guidance scheme for intercepting high maneuvering targets. Int. J. Control. Autom. Syst. 2017, 15, 1351–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, B.; Dai, P.; Liu, R.; Xing, M.; Liu, S. Adaptive super-twisting sliding mode control of variable sweep morphing aircraft. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2019, 92, 198–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Liu, W.; Yan, B.; Liu, S.; Yin, Y. Impact Time Control Guidance Law for Large Initial Lead Angles Based on Sliding Mode Control. In Journal of Physics: Conference Series; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2021; Volume 2031, p. 012050. [Google Scholar]
- Babaei, A.R.; Malekzadeh, M.; Madhkhan, D. Adaptive super-twisting sliding mode control of 6-DOF nonlinear and uncertain air vehicle. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2019, 84, 361–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kada, B. A new methodology to design sliding-pid controllers: Application to missile flight control system. IFAC Proc. Vol. 2012, 45, 673–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shtessel, Y.B.; Tournes, C.H. Integrated higher-order sliding mode guidance and autopilot for dual control missiles. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 2009, 32, 79–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idan, M.; Shima, T.; Golan, O.M. Integrated sliding mode autopilot-guidance for dual-control missiles. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 2007, 30, 1081–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; He, G.; He, Q. A finite-time-convergent composite guidance law with strong fault-tolerant performance. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part G J. Aerosp. Eng. 2019, 233, 3120–3130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Yan, B.; Zhang, T.; Dai, P.; Yan, J. Guidance Law with Desired Impact Time and FOV Constrained for Antiship Missiles Based on Equivalent Sliding Mode Control. Int. J. Aerosp. Eng. 2021, 2021, 9923332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Yang, S. Fast Convergent Nonsingular Terminal Sliding Mode Guidance Law with Impact Angle Constraint. In Proceedings of the IEEE 2018 37th Chinese Control Conference (CCC), Wuhan, China, 25–27 July 2018; pp. 2963–2968. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Qiu, X. Study on Fuzzy Neural Sliding Mode Guidance Law with Terminal Angle Constraint for Maneuvering Target. Math. Probl. Eng. 2020, 2020, 4597937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Guo, Z. Design of head-pursuit guidance law based on backstepping sliding mode control. Int. J. Aerosp. Eng. 2019, 2019, 8214042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monje, C.A.; Chen, Y.; Vinagre, B.M.; Xue, D.; Feliu-Batlle, V. Fractional-Order Systems and Controls: Fundamentals and Applications; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.; Li, X. Trajectory tracking control for electro-optical tracking system based on fractional-order sliding mode controller with super-twisting extended state observer. ISA Trans. 2021, 117, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboelela, M.A.; Ahmed, M.F.; Dorrah, H.T. Design of aerospace control systems using fractional PID controller. J. Adv. Res. 2012, 3, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahmed, M.F.; Dorrah, H.T. Design of gain schedule fractional PID control for nonlinear thrust vector control missile with uncertainty. Automatika 2018, 59, 357–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Xia, L. Fractional-order sliding mode control based guidance law with impact angle constraint. Nonlinear Dyn. 2021, 106, 425–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Wang, W.; Liu, Z.; Liang, C.; Lai, C. Impact angle constrained three-dimensional integrated guidance and control based on fractional integral terminal sliding mode control. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 126857–126870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golestani, M.; Ahmadi, P.; Fakharian, A. Fractional order sliding mode guidance law: Improving performance and robustness. In Proceedings of the IEEE 2016 4th International Conference on Control, Instrumentation, and Automation (ICCIA), Qazvin, Iran, 27–28 January 2016; pp. 469–474. [Google Scholar]
- Eray, O.; Tokat, S. The design of a fractional-order sliding mode controller with a time-varying sliding surface. Trans. Inst. Meas. Control 2020, 42, 3196–3215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Li, Z.; Wang, H.N.; Xiong, T. Fractional order sliding mode control based on single parameter adaptive law for nano-positioning of piezoelectric actuators. IET Control Theory Appl. 2021, 15, 1422–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podlubny, I. Fractional Differential Equations: An Introduction to Fractional Derivatives, Fractional Differential Equations, to Methods of Their Solution and Some of Their Applications; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Levant, A. Non-homogeneous finite-time-convergent differentiator. In Proceedings of the 48h IEEE Conference on Decision and Control (CDC) Held Jointly with 2009 28th Chinese Control Conference, Shanghai, China, 15–18 December 2009; pp. 8399–8404. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, W.; Li, C.; Lü, J. Stability analysis of linear fractional differential system with multiple time delays. Nonlinear Dyn. 2007, 48, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokat, S.; Fadali, M.S.; Eray, O. A classification and overview of sliding mode controller sliding surface design methods. In Recent Advances in Sliding Modes: From Control to Intelligent Mechatronics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 417–439. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, D.; Yi, J. Hierarchical Sliding Mode Control for Under-Actuated Cranes; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, Y.; Fu, M. Compound Control Methodology for Flight Vehicles; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; Volume 438. [Google Scholar]
- Valerio, D.; Da Costa, J.S. Ninteger: A non-integer control toolbox for MatLab. In Proceedings of the Fractional Differentiation and Its Applications, Bordeaux, France, 19–21 July 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, F.; Cai, Y.L. Optimal cooperative guidance with guaranteed miss distance in three-body engagement. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part G J. Aerosp. Eng. 2018, 232, 492–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Position | Speed | Path Angle | |
|---|---|---|---|
| T | 2000 | 180 | |
| M | 1300 | 8 |
| Mach Number | 0.2 | 0.78 | 0.94 | 1.07 | 1.32 | 1.61 | 2.43 | 3.5 |
| 0.241 | 0.213 | 0.258 | 0.407 | 0.445 | 0.372 | 0.255 | 0.190 |
| L | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.1 | 1.1 | 1.5 | 2 | 3 | 6 | 8 |
| Type | Parameter Values |
|---|---|
| PN | |
| IOFPR | |
| FOFPR | , , , |
| Reaching law | , , |
| Guidance Law | Interception Time | Miss Distance | Energy |
|---|---|---|---|
| PN | 12.424 | 1.74 | 4.9944 |
| IOFPR | 12.358 | 1.33 | 2.4613 |
| FOFPR | 12.334 | 0.24 | 2.9275 |
| Guidance Law | Interception Time | Miss Distance | Energy |
|---|---|---|---|
| PN | 12.713 | 2.14 | 8.3284 |
| IOFPR | 12.530 | 1.48 | 2.5246 |
| FOFPR | 12.510 | 0.86 | 1.4412 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, S.; Yan, B.; Zhang, X.; Liu, W.; Yan, J. Fractional-Order Sliding Mode Guidance Law for Intercepting Hypersonic Vehicles. Aerospace 2022, 9, 53. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace9020053
Liu S, Yan B, Zhang X, Liu W, Yan J. Fractional-Order Sliding Mode Guidance Law for Intercepting Hypersonic Vehicles. Aerospace. 2022; 9(2):53. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace9020053
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Shuangxi, Binbin Yan, Xu Zhang, Wei Liu, and Jie Yan. 2022. "Fractional-Order Sliding Mode Guidance Law for Intercepting Hypersonic Vehicles" Aerospace 9, no. 2: 53. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace9020053
APA StyleLiu, S., Yan, B., Zhang, X., Liu, W., & Yan, J. (2022). Fractional-Order Sliding Mode Guidance Law for Intercepting Hypersonic Vehicles. Aerospace, 9(2), 53. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace9020053







