A Review of Automatic Pain Assessment from Facial Information Using Machine Learning
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Highlight the limitations of self-reporting pain levels and emphasize the power of automated pain detection through spatial facial recognition and machine learning in healthcare settings.
- Present a background about the pain intensity scales, pain datasets and method performance evaluation criteria used in automatic pain assessment.
- Analyze the state-of-the-art spatial facial information and machine learning-based pain assessment methods to determine the areas in which their accuracies and resilience can be enhanced.
- Encourage the application of this cutting-edge technology in clinical settings for better pain management.
2. Review Methodology
2.1. Search Strategy
- For pain assessment, we used “pain assessment”, “pain intensity”, “pain estimation”, “pain diagnosis” and “pain recognition” keywords.
- For facial information, we used “facial information”, “facial expressions”, “facial traits” and “faces” keywords.
- For machine learning, we used “machine learning”, “deep learning” and “artificial intelligence” keywords.
2.2. Inclusion/Exclusion Criteria
2.3. Categorization Method
3. Background
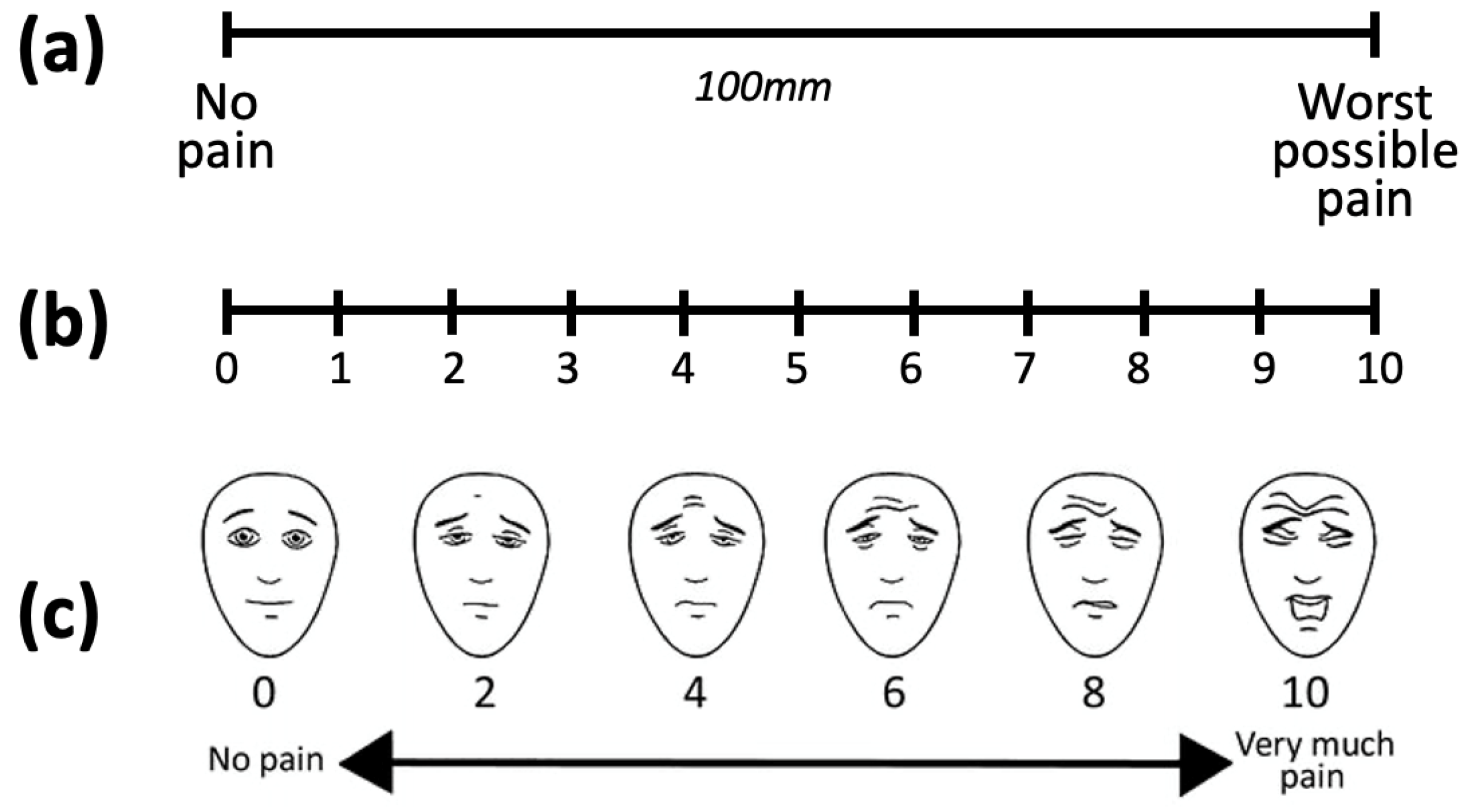
3.1. Pain Intensity Scales
3.2. Publicly Accessible Pain Assessment Datasets
3.3. Criteria for Performance Evaluation
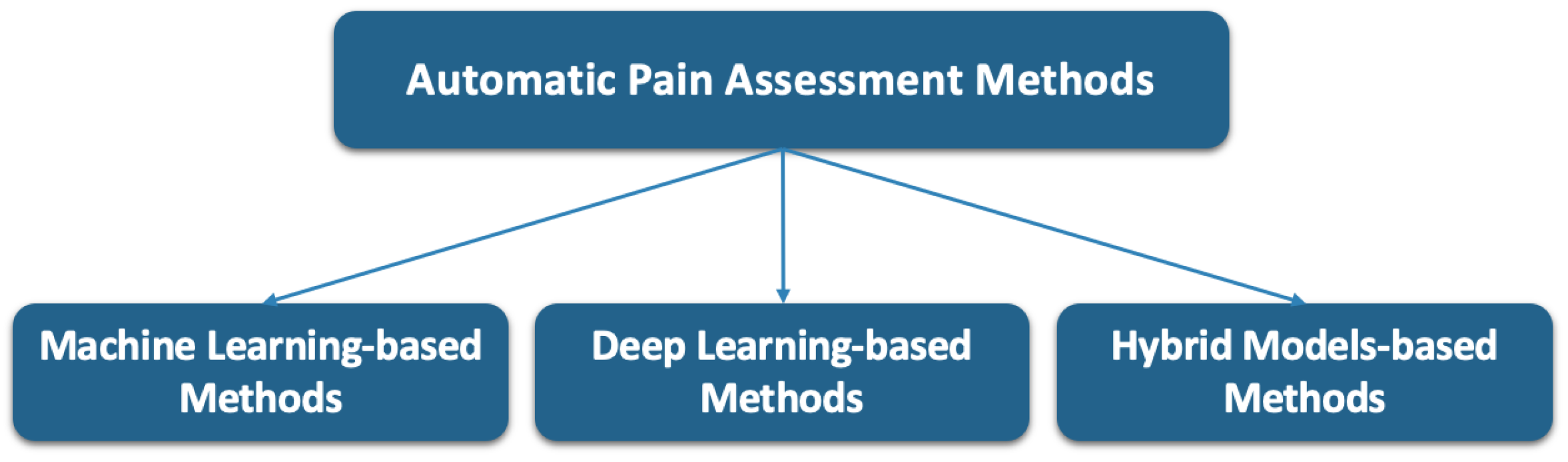
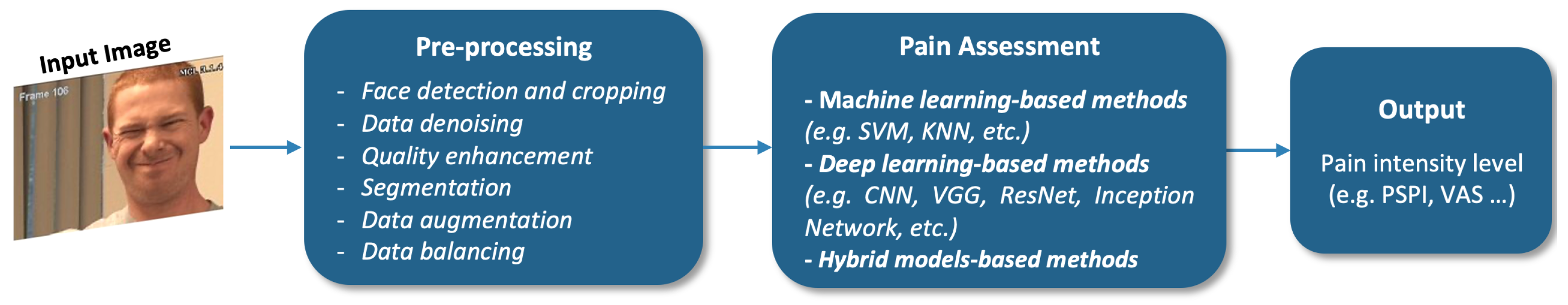
4. Facial Information-Based Pain Assessment Methods
4.1. Machine-Learning-Based Methods
4.2. Deep Learning-Based Methods
4.3. Hybrid Model Methods
5. Discussion
5.1. Result Analysis
5.2. Automatic Pain Assessment Challenges
5.3. Limitations of This Review
6. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Semwal, A.; Londhe, N.D. Automated Pain Severity Detection Using Convolutional Neural Network. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Computational Techniques, Electronics and Mechanical Systems (CTEMS), Belagavi, India, 21–22 December 2018; pp. 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Hong, X.; Peng, J.; Feng, X.; Zhao, G. Incorporating high-level and low-level cues for pain intensity estimation. In Proceedings of the 2018 24th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR), Beijing, China, 20–24 August 2018; pp. 3495–3500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Morabit, S.; Rivenq, A.; Zighem, M.E.N.; Hadid, A.; Ouahabi, A.; Taleb-Ahmed, A. Automatic Pain Estimation from Facial Expressions: A Comparative Analysis Using Off-the-Shelf CNN Architectures. Electronics 2021, 10, 1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barua, P.; Baygin, N.; Dogan, S.; Baygin, M.; Arunkumar, N.; Fujita, H.; Tuncer, T.; Tan, R.; Palmer, E.; Azizan, M.; et al. Automated detection of pain levels using deep feature extraction from shutter blinds-based dynamic-sized horizontal patches with facial images. Sci. Rep. 1022, 12, 17297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casti, P.; Mencattini, A.; Comes, M.C.; Callari, G.; Di Giuseppe, D.; Natoli, S.; Dauri, M.; Daprati, E.; Martinelli, E. Calibration of Vision-Based Measurement of Pain Intensity with Multiple Expert Observers. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2019, 68, 2442–2450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragomir, M.C.; Florea, C.; Pupezescu, V. Automatic Subject Independent Pain Intensity Estimation using a Deep Learning Approach. In Proceedings of the International Conference on e-Health and Bioengineering (EHB), Iasi, Romania, 29–30 October 2020; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, X.; Lin, X.; Yang, S.; Zheng, X. Pain intensity estimation based on a spatial transformation and attention CNN. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0232412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, X.; Li, X.; Yang, S.; Lin, X.; Zheng, X. Pain expression assessment based on a locality and identity aware network. IET Image Process. 2021, 15, 2948–2958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathee, N.; Pahal, S.; Sheoran, P. Pain detection from facial expressions using domain adaptation technique. Pattern Anal. Appl. 2021, 25, 567–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, S.; Huang, D.; Ni, Y.; Feng, X. Multi-Scale Regional Attention Networks for Pain Estimation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedical Technology (ICBBT), Xi’an, China, 21–23 May 2021; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karamitsos, I.; Seladji, I.; Modak, S. A Modified CNN Network for Automatic Pain Identification Using Facial Expressions. J. Softw. Eng. Appl. 2021, 14, 400–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semwal, A.; Londhe, N. S-PANET: A Shallow Convolutional Neural Network for Pain Severity Assessment in Uncontrolled Environment. In Proceedings of the IEEE 11th Annual Computing and Communication Workshop and Conference (CCWC), Virtual, 27–30 January 2021; pp. 800–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghamdi, T.; Alaghband, G. Facial Expressions Based Automatic Pain Assessment System. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 6423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semwal, A.; Londhe, N. ECCNet: An Ensemble of Compact Convolution Neural Network for Pain Severity Assessment from Face images. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Cloud Computing, Data Science and Engineering (Confluence), Noida, India, 28–29 January 2021; pp. 761–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semwal, A.; Londhe, N. MVFNet: A multi-view fusion network for pain intensity assessment in unconstrained environment. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2021, 67, 102537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bargshady, G.; Zhou, X.; Deo, R.C.; Soar, J.; Whittaker, F.; Wang, H. Ensemble neural network approach detecting pain intensity from facial expressions. Artif. Intell. Med. 2020, 109, 101954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Xia, Z.; Li, L.; Wang, K.; Feng, X. Pain-awareness multistream convolutional neural network for pain estimation. J. Electron. Imaging 2019, 28, 043008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Xia, Z.; Li, L.; Ma, Y. Pain estimation with integrating global-wise and region-wise convolutional networks. IET Image Process. 2022, 17, 637–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.; Liang, X.; Hu, J.; Xie, Y. Image-Based Pain Intensity Estimation Using Parallel CNNs with Regional Attention. Bioengineering 2022, 9, 804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghamdi, T.; Alaghband, G. SAFEPA: An Expandable Multi-Pose Facial Expressions Pain Assessment Method. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 7206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sait, A.; Dutta, A. Ensemble Learning-Based Pain Intensity Identification Model Using Facial Expressions. J. Disabil. Res. 2024, 3, e20240029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salekin, M.; Zamzmi, G.; Goldgof, D.; Kasturi, R.; Ho, T.; Sun, Y. Multimodal spatio-temporal deep learning approach for neonatal postoperative pain assessment. Comput. Biol. Med. 2021, 129, 104150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczapa, B.; Daoudi, M.; Berretti, S.; Pala, P.; Del Bimbo, A.; Hammal, Z. Automatic Estimation of Self-Reported Pain by Trajectory Analysis in the Manifold of Fixed Rank Positive Semi-Definite Matrices. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2022, 13, 1813–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiam, P.; Hihn, H.; Braun, D.; Kestler, H.; Schwenker, F. Multi-Modal Pain Intensity Assessment Based on Physiological Signals: A Deep Learning Perspective. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 720464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, K.N.; Iyortsuun, N.K.; Pant, S.; Yang, H.J.; Kim, S.H. Pain Recognition with Physiological Signals Using Multi-Level Context Information. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 20114–20127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gkikas, S.; Chatzaki, C.; Pavlidou, E.; Verigou, F.; Kalkanis, K.; Tsiknakis, M. Automatic Pain Intensity Estimation based on Electrocardiogram and Demographic Factors. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Information and Communication Technologies for Ageing Well and e-Health, Virtual, 23–25 April 2022; pp. 155–162. [Google Scholar]
- Mieronkoski, R.; Syrjälä, E.; Jiang, M.; Rahmani, A.; Pahikkala, T.; Liljeberg, P.; Salanterä, S. Developing a pain intensity prediction model using facial expression: A feasibility study with electromyography. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, 0235545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, R.A.; Meyer, A.; Konik, H.; Bouakaz, S. Pain detection through shape and appearance features. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo (ICME), San Jose, CA, USA, 15–19 July 2013; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafar, Z.; Khan, N. Pain Intensity Evaluation through Facial Action Units. In Proceedings of the 2014 22nd International Conference on Pattern Recognition, Stockholm, Sweden, 24–28 August 2014; pp. 4696–4701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brahimi, S.; Ben Aoun, N.; Ben Amar, C.; Benoit, A.; Lambert, P. Multiscale Fully Convolutional DenseNet for Semantic Segmentation. J. WSCG 2018, 26, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Aoun, N.; Mejdoub, M.; Ben Amar, C. Bag of sub-graphs for video event recognition. In Proceedings of the 39th IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing (ICASSP’14), Florence, Italy, 4–9 May 2014; pp. 1566–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brahimi, S.; Ben Aoun, N.; Ben Amar, C. Very Deep Recurrent Convolutional Neural Network for Object Recognition. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Vision (ICMV’2016), Nice, France, 18–20 November 2016; Volume 10341, p. 1034107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nhidi, W.; Ben Aoun, N.; Ejbali, R. Deep Learning-Based Parasitic Egg Identification from a Slender-Billed Gull’s Nest. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 37194–37202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nhidi, W.; Ben Aoun, N.; Ejbali, R. Ensemble Machine Learning-Based Egg Parasitism Identification for Endangered Bird Conservation. In Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on Advances in Computational Collective Intelligence (ICCCI’2023), Communications in Computer and Information Science, Budapest, Hungary, 27–29 September 2023; Volume 1864, pp. 364–375. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Ansari, R.; Wilkie, D.J. Automated Pain Detection from Facial Expressions using FACS: A Review. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1811.07988. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Eidan, R.; Al-Khalifa, H.; Al-Salman, A. Deep-Learning-Based Models for Pain Recognition: A Systematic Review. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 5984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, T.; Seus, D.; Wollenberg, J.; Weitz, K.; Kunz, M.; Lautenbacher, S.; Garbas, J.; Schmid, U. Automatic Detection of Pain from Facial Expressions: A Survey. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2021, 43, 1815–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, P.; Lopez-Martinez, D.; Walter, S.; Al-Hamadi, A.; Gruss, S.; Picard, R.W. Automatic Recognition Methods Supporting Pain Assessment: A Survey. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2022, 13, 530–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsangidou, M.; Liampas, A.; Pittara, M.; Pattichi, C.; Zis, P. Machine Learning in Pain Medicine: An Up-To-Date Systematic Review. Pain Ther. 2021, 10, 1067–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gkikas, S.; Tsiknakis, M. Automatic assessment of pain based on deep learning methods: A systematic review. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2023, 231, 107365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Sario, G.; Haider, C.; Maita, K.; Torres-Guzman, R.; Emam, O.; Avila, F.; Garcia, J.; Borna, S.; McLeod, C.; Bruce, C.; et al. Using AI to Detect Pain through Facial Expressions: A Review. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cascella, M.; Schiavo, D.; Cuomo, A.; Ottaiano, A.; Perri, F.; Patrone, R.; Migliarelli, S.; Bignami, E.G.; Vittori, A.; Cutugno, F. Artificial Intelligence for Automatic Pain Assessment: Research Methods and Perspectives. Pain Res. Manag. 2023, 2023, 6018736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, J.; Yu, Y.; Lin, W.; Hu, A.; Wu, C. Application of AI in Multilevel Pain Assessment Using Facial Images: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Med. Internet Res. 2024, 26, e51250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucey, P.; Cohn, J.; Prkachin, K.; Solomon, P.; Matthews, I. Painful data: The UNBC-McMaster shoulder pain expression archive database. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face and Gesture Recognition (FG), Santa Barbara, CA, USA, 21–23 March 2011; pp. 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kächele, M.; Werner, P.; Al-Hamadi, A.; Palm, G.; Walter, S.; Schwenker, F. Bio-Visual Fusion for Person-Independent Recognition of Pain Intensity. In Proceedings of the International Workshop on Multiple Classifier Systems (MCS), Nanjing, China, 15–17 May 2015; Volume 132, pp. 220–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, M.; Bautista, R.; Noroozi, F.; Kulkarni, K.; Laursen, C.; Irani, R.; Bellantonio, M.; Escalera, S.; Anbarjafari, G.; Nasrollahi, K.; et al. Deep Multimodal Pain Recognition: A Database and Comparison of Spatio-Temporal Visual Modalities. In Proceedings of the 2018 13th IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face and Gesture Recognition (FG 2018), Xi’an, China, 15–19 May 2018; pp. 250–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, M.A.; Bedi, S. Survey on SVM and their application in image classification. Int. J. Inf. Technol. 2021, 13, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taunk, K.; De, S.; Verma, S.; Swetapadma, A. A Brief Review of Nearest Neighbor Algorithm for Learning and Classification. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Intelligent Computing and Control Systems (ICCS), Madurai, India, 15–17 May 2019; pp. 1255–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. ImageNet Classification with Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2012, 25, 1097–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very Deep Convolutional Networks for Large-Scale Image Recognition. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR), San Diego, CA, USA, 7–9 May 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Szegedy, C.; Ioffe, S.; Vanhoucke, V. Inception-v4, Inception-ResNet and the Impact of Residual Connections on Learning. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1602.07261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karcioglu, O.; Topacoglu, H.; Dikme, O.; Dikme, O. A systematic review of the pain scales in adults: Which to use? Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2018, 36, 707–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prkachin, K.; Solomon, P.E. The structure, reliability and validity of pain expression: Evidence from patients with shoulder pain. Pain 2008, 139, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekman, P.; Friesen, W. Facial Action Coding System: A Technique for the Measurement of Facial Movements; Consulting Psychologists Press: Palo Alto, CA, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Hammal, Z.; Cohn, J. Automatic detection of pain intensity. In Proceedings of the ACM International Conference on Multimodal Interaction (ICMI), Santa Monica, CA, USA, 22–26 October 2012; pp. 47–52. [Google Scholar]
- Breivik, H.; Borchgrevink, P.C.; Allen, S.M.; Rossel, L.A.; Romundstad, L.; Breivik Hals, E.K.; Kvarstein, G.; Stubhaug, A. Assessment of pain. Br. J. Anaesth. 2008, 101, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hicks, C.L.; von Baeyer, C.L.; Spafford, P.A.; van Korlaar, I.; Goodenough, B. The Faces Pain Scale—Revised: Toward a common metric in pediatric pain measurement. Pain 2001, 93, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, S.; Gruss, S.; Ehleiter, H.; Tan, J.; Traue, H.; Werner, P.; Al-Hamadi, A.; Crawcour, S.; Andrade, A.; Moreira da Silva, G. The biovid heat pain database data for the advancement and systematic validation of an automated pain recognition system. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Cybernetics (CYBCO), Lausanne, Switzerland, 13–15 June 2013; pp. 128–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, P.; Al-Hamadi, A.; Gruss, S.; Walter, S. Twofold-Multimodal Pain Recognition with the X-ITE Pain Database. In Proceedings of the 2019 8th International Conference on Affective Computing and Intelligent Interaction Workshops and Demos (ACIIW), Cambridge, UK, 3–6 September 2019; pp. 290–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aung, M.S.H.; Kaltwang, S.; Romera-Paredes, B.; Martinez, B.; Singh, A.; Cella, M.; Valstar, M.; Meng, H.; Kemp, A.; Shafizadeh, M.; et al. The Automatic Detection of Chronic Pain-Related Expression: Requirements, Challenges and the Multimodal EmoPain Dataset. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2016, 7, 435–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Liu, Z.; Van Der Maaten, L.; Weinberger, K.Q. Densely connected convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 4700–4708. [Google Scholar]
- Redmon, J.; Farhadi, A. YOLO9000: Better, Faster, Stronger. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 6517–6525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szegedy, C.; Vanhoucke, V.; Ioffe, S.; Shlens, J.; Wojna, Z. Rethinking the Inception Architecture for Computer Vision. In Proceedings of the 33rd International Conference on Machine Learning, New York, NY, USA, 20–22 June 2016; pp. 2818–2826. [Google Scholar]
- Howard, A.G.; Zhu, M.; Chen, B.; Kalenichenko, D.; Wang, W.; Weyand, T.; Andreetto, M.; Adam, H. MobileNets: Efficient Convolutional Neural Networks for Mobile Vision Applications. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 1382–1391. [Google Scholar]
- Szegedy, C.; Liu, W.; Jia, Y.; Sermanet, P.; Reed, S.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Vanhoucke, V.; Rabinovich, A. Going deeper with convolutions. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, N.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, H.; Sun, J. ShuffleNet V2: Practical Guidelines for Efficient CNN Architecture Design. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 122–138. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.; Cui, G.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, C.; Liu, Z.; Sun, M. Graph Neural Networks: A Review of Methods and Applications. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1812.08434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
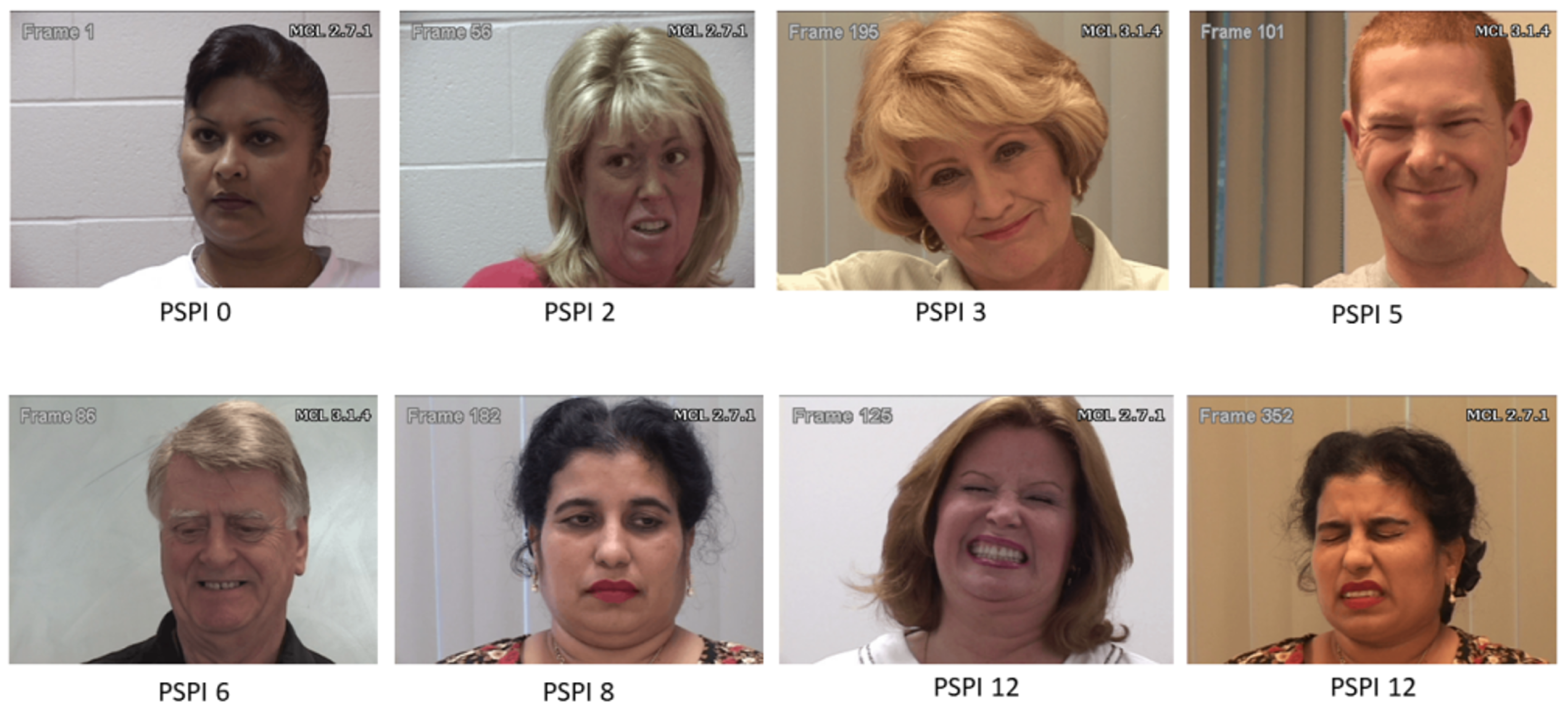


| Attribute | UNBC–McMaster (2011) [44] | BioVid Database (2013) [45] | MIntPain Database (2018) [46] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of subjects | 25 adults with shoulder pain | 90 subjects (87 are available) | 20 subjects |
| Subject type | Self-identified pain patient | Healthy volunteers | Healthy volunteers |
| Pain nature | Natural shoulder pain | Inducted heat pain | Stimulated electrical pain |
| Pain levels | 0–16 (PSPI) and 0–10 (VAS) | 1–4 (Stimuli) | 0–4 (Stimuli) |
| Modalities | RGB | RGB | RGB, Depth and Thermal |
| Dataset size | 48,398 frames issued from 200 variable-length videos | 17,300 5 s videos (25 fps) | 9366 variable-length videos with 187,939 frames |
| Method | Feature Extraction | Machine Learning Model | Main Contribution | Performance on UNBC–McMaster |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Semwal and Londhe [1] | CNN-based deep features | 3-layer CNN | Optimize the model parameters | ACC: 93.34% |
| Yang et al. [2] | Low-level image patches features + CNN-based deep learning features | SVR | A hierarchical network architecture with two feature modules to extract low-level and deep learning features. | MSE: 1.45 |
| Morabit et al. [3] | Deep features extracted with a fine-tuned DenseNet-161 model | SVR | Adopting the transfer learning technique to fine-tune a pre-trained DenseNet-161 model for feature extraction | MSE: 0.34 |
| Barua et al. [4] | Deep features extracted with a fine-tuned DarkNet19 and selected with INCA | KNN | Using a pre-trained DarkNet19 model to generate deep features that were optimized by the INCA algorithm | ACC: 95.57% |
| Method | Deep Learning Model | Main Contribution | Performance | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| UNBC–McMaster | BioVid | |||
| Casti et al. [5] | Pre-trained AlexNet | Re-annotating the dataset with seven experts to improve the ground truth and translating the frames to illumination-invariant 3D space using the multidimensional scaling | ACC: 80% | - |
| Dragomir et al. [6] | ResNet | Hyper-parameters optimization + data augmentation | - | ACC: 36.6% |
| Xi et al. [7] | 9-layer CNN | Including an attention mechanism to focus on the region-related pain | ACC: 51.1% | - |
| Xi et al. [8] | CNN | Incorporating locality-aware and identity-aware modules. | ACC: 89.17% | ACC: 40.4% |
| Rathee et al. [9] | CNN | Efficiently initializing CNN parameters with an MAML++ module. | ACC: 90.3% | - |
| Cui et al. [10] | Multi-scale regional attention network (MSRAN) | Integrating self-attention and relation attention modules to emphasize the pain-related face parts and their inter-relationships | ACC: 91.13% | - |
| Karamitsos et al. [11] | Customized and Deeper VGG16 | Feeding the model with effectively pre-processed images (e.g., gray-scaling, histogram equalization, face detection, image cropping, mean filtering and normalization). | ACC: 92.5% | - |
| Semwal and Londhe [12] | SPANET | Shallow CNN including a false positive reduction strategy. | ACC: 97.48% | - |
| Alghamdi and Alaghband [13] | InceptionV3 | The convolutional block is frozen and a shallow CNN is used instead of the prediction layer. | ACC: 99.1% | - |
| Method | Hybrid Model | Main Contribution | Performance | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UNBC–McMaster | BioVid | MIntPain | |||
| Bargshady et al. [16] | EDLM: three independent CNN-RNN deep learners with different weights | Extract face features with a fine-tuned VGGFace and optimize them with the PCA algorithm. | ACC: 86% | - | ACC: 92.26% |
| Huang et al. [17] | Pain-awareness multi-stream convolutional neural network with 4 CNNs | 4 pain related-face region features are extracted with 4 CNNs, weighted according to their contribution to the pain expression and classified to estimate the pain intensity | ACC: 88.19% | - | - |
| Huang et al. [18] | Hierarchical Deep Network (HDN) | Two scale branches are performed to extract local facial patches features with a multi-stream CNN and their inter-dependencies with a multi-task learning technique | MSE: 0.49 | - | - |
| Alghamdi and Alaghband [20] | SAFEPA: 2 fine-tuned concurrent and coupled CNNs | Placing greater emphasis on the upper part of the face to extract pose-invariant face features which are coupled with global face feature leading to better pain assessment. | ACC: 89.93% | ACC: 33.28% | - |
| Semwal and Londhe [14] | ECCNET = VGG-16 + MobileNet + GoogleNet | Averaging the prediction of three deep learning models | ACC: 93.87% | - | - |
| Ye et al. [19] | Parallel CNN framework with regional attention: VGGNet + ResNet | Used VGGNet + ResNet to extract the face features with regional attention and the SogtMax algorithm to classify them. | ACC: 95.11% | - | - |
| Semwal and Londhe [15] | 3 CNNs: VGG-TL + ETNet + DSCNN | Used multiple neural networks with high-level spatial features with local and global geometric cues. | ACC: 96% | - | - |
| Sait and Dutta [21] | Stacking XGBoost and CatBoost models with an SVM as meta-learner | Relevant spatial features are extracted with fine-tuned ShuffleNet V2 model + Application of class activation map and fusion feature approaches | ACC: 98.7% | - | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ben Aoun, N. A Review of Automatic Pain Assessment from Facial Information Using Machine Learning. Technologies 2024, 12, 92. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies12060092
Ben Aoun N. A Review of Automatic Pain Assessment from Facial Information Using Machine Learning. Technologies. 2024; 12(6):92. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies12060092
Chicago/Turabian StyleBen Aoun, Najib. 2024. "A Review of Automatic Pain Assessment from Facial Information Using Machine Learning" Technologies 12, no. 6: 92. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies12060092
APA StyleBen Aoun, N. (2024). A Review of Automatic Pain Assessment from Facial Information Using Machine Learning. Technologies, 12(6), 92. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies12060092






