Wearable Fall Detectors Based on Low Power Transmission Systems: A Systematic Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
- It provides an overview of FDSs using wearable devices and LPWAN technologies.
- It offers a detailed examination of the predominant algorithms used in fall detection within the context of integrating LPWAN technologies.
- It conducts a comprehensive analysis of the recent state of the art, covering studies that implement LPWAN wearable technologies for fall detection and considers aspects such as the wearable devices used, their placement on the body, the sensors, and energy efficiency.
- It evaluates performance parameters such as accuracy, sensitivity, and specificity in different combinations of LPWAN technologies, detection algorithms, and sensors.
- It presents a detailed discussion on emerging trends in applying LPWAN in fall detection, as well as future research directions.
2. Methodology
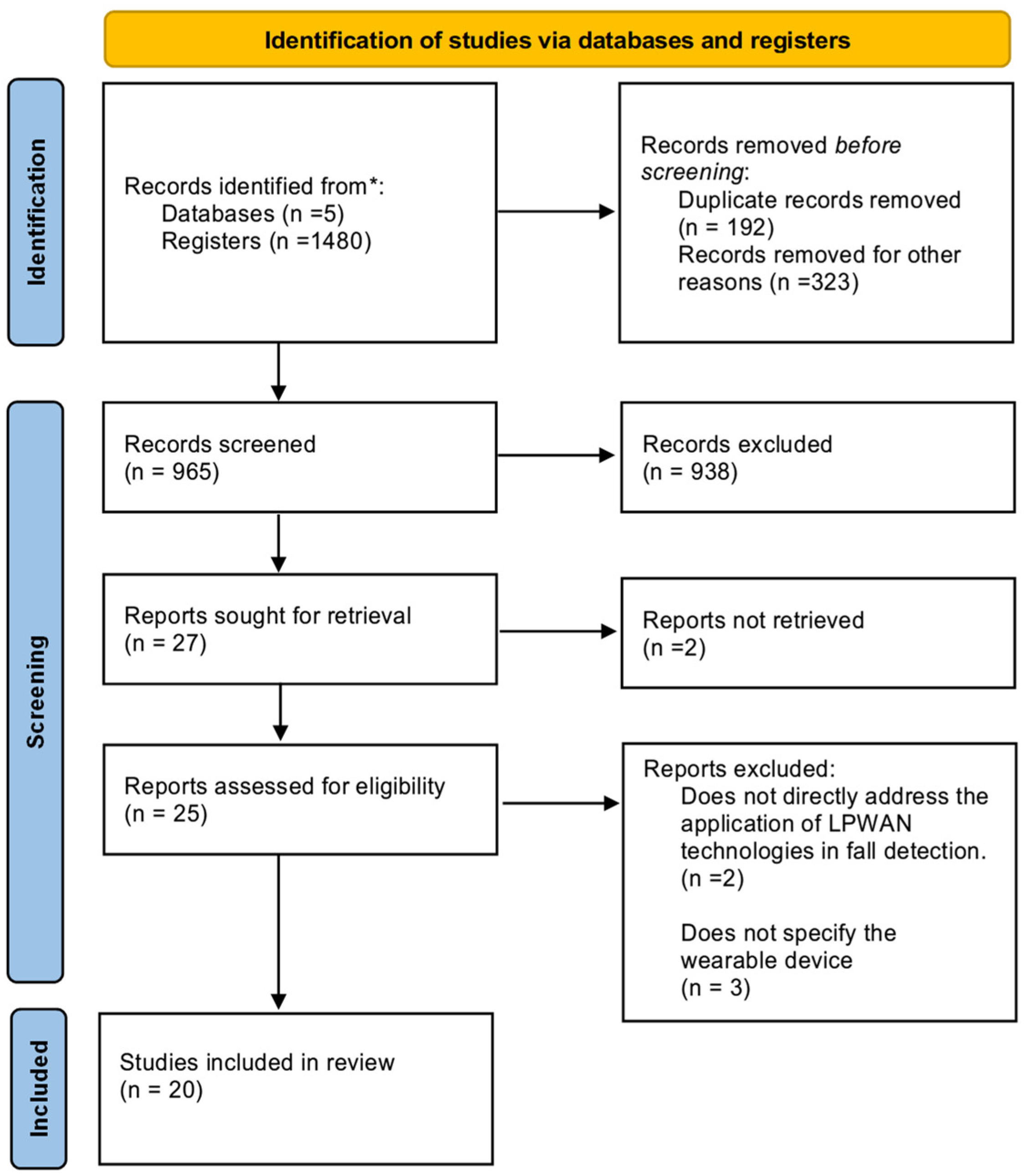
2.1. Phase 1: Identification Relevant Studies (Identification)
2.1.1. Definition of the Research Question
2.1.2. Eligibility Criteria
Inclusion
- Full original articles published in peer-reviewed journals between 2010 and 2023.
- Research addressing the application of LPWAN technologies in wearable devices for fall detection.
- Focus on evaluating the accuracy and effectiveness of technologies in fall detection.
- Studies using inertial sensors combined with functional tests and/or daily life activities for fall detection.
- Articles that present the keywords defined in the search string in the abstract or title.
Exclusion
- Duplicated records that appear in more than one database.
- Papers not available in full-text format or not written in English.
- Works published before 2010, the year of Sigfox technology conception.
- Studies that do not present a prototype aimed at detecting falls and sending the corresponding alarm.
- Articles describing systems in which the alarm transmission technology does not involve the use of LPWAN technologies.
- Studies that do not include any type of evaluation of the developed prototype.
- Records about fall detection architecture that, although incorporating the use of LPWAN standards, are not based on wearable devices.
2.1.3. Information Sources
2.2. Phase 2: Selection of Relevant Studies (Screening)
2.2.1. Search
2.2.2. Title and Abstract Exploration
2.2.3. Potentially Relevant Studies Selection
2.3. Phase 3: Study Inclusion (Inclusion)
Data Analysis and Quality Analysis of Articles
- Classification of LPWAN technologies: Identifying and categorizing the LPWAN technologies (LoRaWAN, Sigfox, NB-IoT) used in each study.
- Sensor analysis: Evaluating the types of sensors (accelerometers, gyroscopes, magnetometers) and their placement on the body.
- Detection algorithm performance: Analyzing the performance of detection algorithms, focusing on accuracy, sensitivity, and specificity.
- Characteristics of the evaluation samples: Review sample sizes and the number of falls evaluated.
- Energy consumption analysis: Comparing reported battery life and power consumption of the devices.
- Comparative analysis: Highlighting strengths, weaknesses, and key findings across studies.
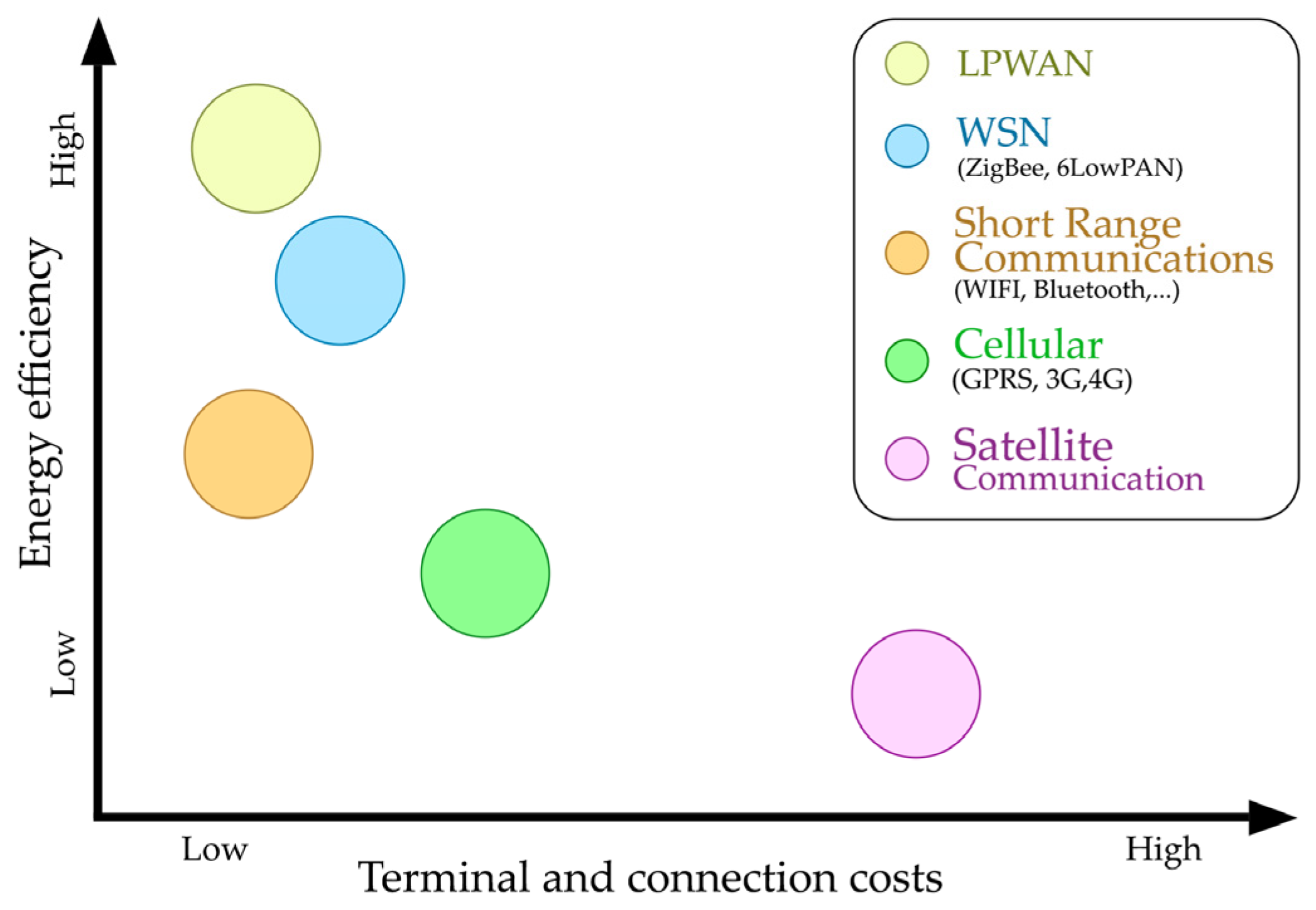
3. Overview of the LPWAN Concept
Comparison of Most Popular LPWAN Technologies
4. Analysis of Selected Studies
4.1. Selected Studies
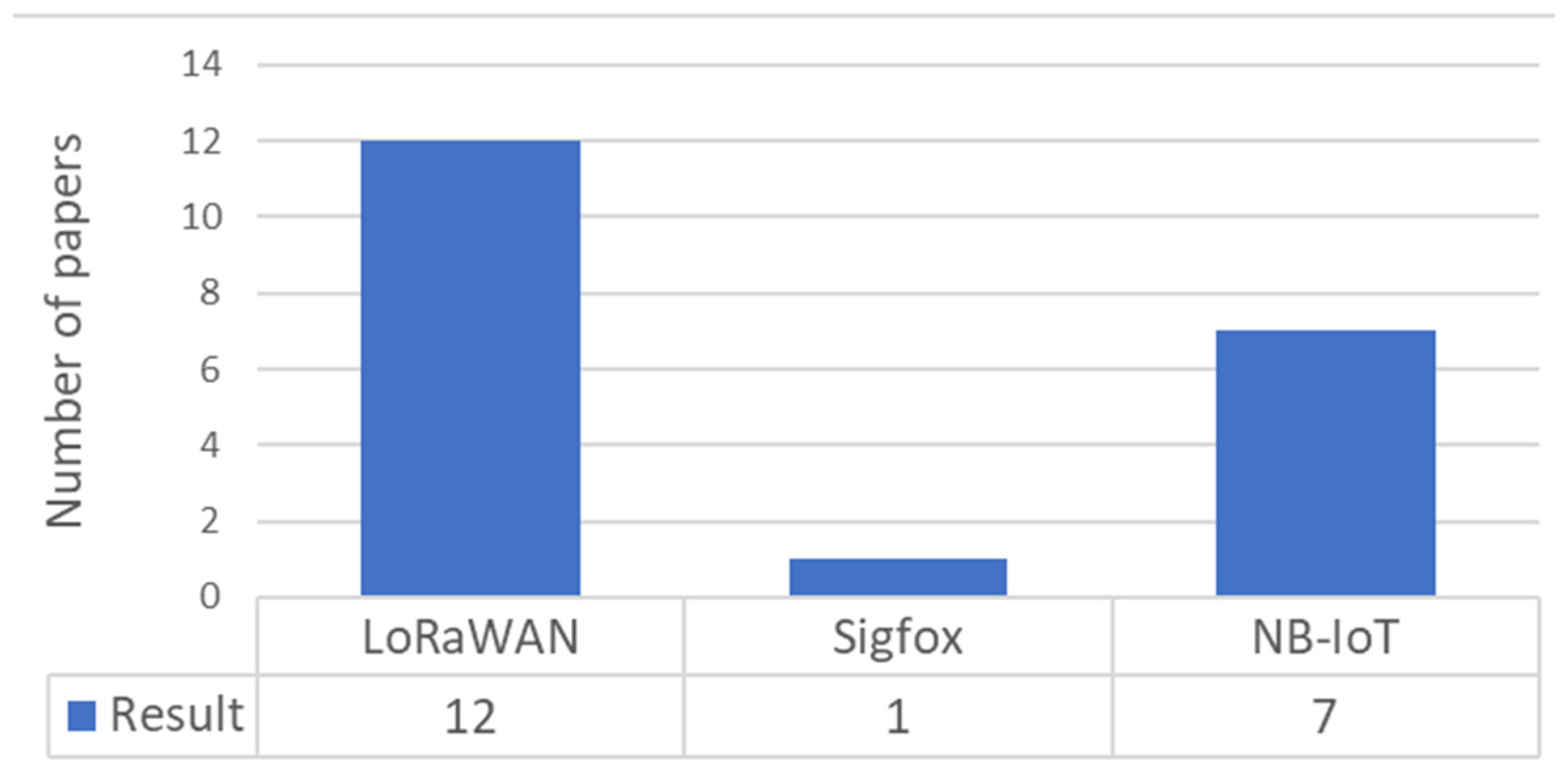
4.2. Selection of the LPWAN Technology
4.3. Comparative Insights on LPWAN Technologies
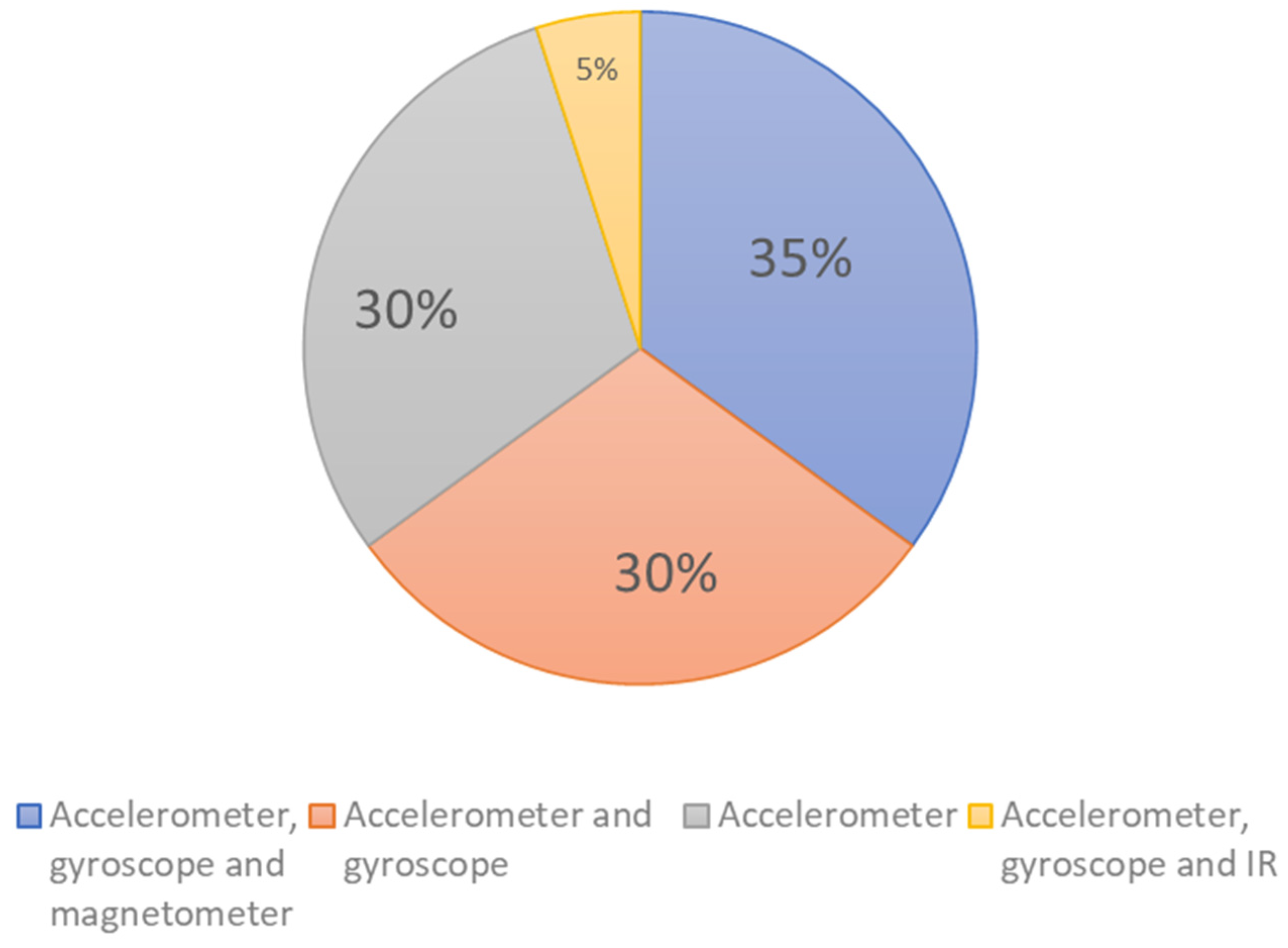
4.4. Employed Sensors
4.5. Location of the Wearable Device
4.6. Employed Detection Algorithms
4.7. Energy Consumption
4.8. LPWAN Transceivers
5. Discussion
6. Criticisms and Limitations
- From the study conducted, it can be inferred that the application of LPWAN technologies to wearable FDSs is still in an embryonic state, having neither exploited nor systematically analyzed its main benefits. Therefore, it is necessary to remark on the following weaknesses in the reviewed literature:
- Limited coverage: Signal reliability can be challenging in low-visibility areas. However, the developed prototypes do not investigate realistic usage scenarios where coverage might fail.
- Energy consumption: When compared to short-range and local area technologies, LPWAN standards may excel in energy efficiency, which is a key factor in increasing the battery life of wearables. Nevertheless, the existing studies to date have barely evaluated the quantitative benefits of using LPWAN compared not only to other transmission technologies but also to other sources of consumption present in the detector, mainly the detection algorithm.
- Implementation difficulty and reliability: LPWAN networks offer greater flexibility than other types of networks, but they still involve certain operational costs (subscription to operators) or deployment costs (e.g., location, installation, and management of base stations) that the literature does not evaluate. Likewise, the low bandwidth provided for LPWAN networks may be sufficient to send certain types of alarms (encodable in a few bytes) but may be clearly insufficient if more complex information needs to be sent to an external node in real-time (such as long samples of inertial signals). This limitation is scarcely addressed in the reviewed works.
- Lack of large-scale and clinical studies: In any case, as with almost all literature dedicated to FDS systems (whether based on contextual or wearable sensor systems), there is an almost complete lack of large-scale clinical trials.
7. Recommendations
- Based on the limitations and deficiencies identified, we outline the main areas of action that future proposals for LPWAN-based FDS should consider to develop viable products for real-world applications:
- Analyze coverage: Prototypes should be tested in realistic environments to demonstrate that users can be monitored over long distances (both outdoors and indoors) without compromising signal quality.
- Characterize energy consumption: The energy consumption of prototypes should be ‘budgeted’ and characterized in detail to demonstrate that using LPWAN technologies contributes to a significant increase in wearable autonomy. In this regard, the consumption (not only of energy but also of hardware resources) of the transmission system should be compared with that required by the detection algorithm.
- Conduct large-scale clinical studies: Develop large-scale longitudinal studies to appraise the actual effectiveness of LPWAN-based FDSs. In that sense, clinical field tests and massive evaluations of the long-term performance of the detectors in real-world scenarios should be prioritized.
- Integrate with emerging technologies: Investigate the integration of LPWAN technologies with emerging technologies such as 5G and edge computing to enhance data processing capabilities and reduce latency. This could improve the overall performance and responsiveness of FDSs.
- Develop user-centric designs: Evaluate the prototypes not only from a purely technical point-of-view but also consider a user-centric perspective that does not neglect key aspects such as ergonomics or usability. Focus on developing user-friendly wearable devices that ensure comfort and social acceptability. Consider different placement locations on the body and the specific needs of various user groups to maximize the practicality and adoption of these devices.
- Remote Rural Areas: LPWAN technologies such as LoRaWAN and Sigfox are highly beneficial in remote rural areas where traditional communication infrastructures, such as cellular networks, are limited or nonexistent. The long-range and low-power characteristics of LPWAN make it an ideal choice for monitoring fall detection in environments where other communication networks might be impractical or too costly to implement.
- Urban Environments with High Building Density: NB-IoT is particularly well-suited for urban environments with high building density and potential signal interference. Its ability to penetrate buildings and provide reliable communication in densely populated areas makes it a valuable asset for FDSs deployed in cities, ensuring consistent performance even in challenging urban landscapes.
- Elder Care in Low-Cost Public Health Initiatives: In scenarios where cost-effectiveness is crucial, such as large-scale public health initiatives aimed at elder care in developing regions, the low operational costs and minimal infrastructure requirements of LPWAN provide a scalable solution for deploying FDSs to a broader population, making healthcare more accessible.
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aledhari, M.; Razzak, R.; Qolomany, B.; Al-Fuqaha, A.; Saeed, F. Biomedical IoT: Enabling Technologies, Architectural Elements, Challenges, and Future Directions. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 31306–31339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costin, H.; Rotariu, C.; Adochiei, F.; Ciobotariu, R.; Andruseac, G.; Corciova, F. Telemonitoring of vital signs—An effective tool for ambient assisted living. IFMBE Proc. 2011, 36, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. WHO Global Report on Falls Prevention in Older Age. Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/43811 (accessed on 26 February 2023).
- World Health Organization. Falls. Available online: https://www.who.int/en/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/falls (accessed on 26 February 2023).
- World Health Organization. Ageing and Health. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/ageing-and-health (accessed on 10 April 2023).
- Huynh, Q.T.; Nguyen, U.D.; Tran, B.Q. A Cloud-Based System for In-Home Fall Detection and Activity Assessment. In IFMBE Proceedings, Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on the Development of Biomedical Engineering in Vietnam (BME 7), Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam, 27–29 June 2018; Springer: Singapore, 2020; Volume 69, pp. 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanaj, E.; Disha, D.; Spinsante, S.; Gambi, E. A wearable fall detection system based on LoRa LPWAN technology. J. Commun. Softw. Syst. 2020, 16, 232–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, W.J.; Chen, L.B.; Chen, M.C.; Su, J.P.; Sie, C.Y.; Yang, C.H. Design and Implementation of an Intelligent Assistive System for Visually Impaired People for Aerial Obstacle Avoidance and Fall Detection. IEEE Sens. J. 2020, 20, 10199–10210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newaz, N.T.; Hanada, E. The Methods of Fall Detection: A Literature Review. Sensors 2023, 23, 5212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanutama, L.; Wijaya, H.; Ardianti, D. Elderly Fall Detection and Warning System. In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Eco Engineering Development 2020, Banten, Indonesia, 10–11 November 2020; IOP Publishing Ltd.: Bristol, UK, 2021; Volume 794, p. 794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachtar, A.; Val, T.; Kachouri, A. Elderly monitoring system in a smart city environment using LoRa and MQTT. IET Wirel. Sens. Syst. 2020, 10, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valach, A.; Macko, D. Exploration of the LoRa Technology Utilization Possibilities in Healthcare IoT Devices. In Proceedings of the 2018 16th International Conference on Emerging eLearning Technologies and Applications (ICETA), Stary Smokovec, Slovakia, 15–16 November 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lousado, J.P.; Pires, I.M.; Zdravevski, E.; Antunes, S. Monitoring the health and residence conditions of elderly people, using lora and the things network. Electronics 2021, 10, 1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, W.D.; Ramani, B.; Pandya, S.; Bhaskar, S.; Koyuncu, B.; Ghayvat, H. NXTGeUH: LoRaWAN based NEXT Generation Ubiquitous Healthcare System for Vital Signs Monitoring & Falls Detection. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Punecon, Pune, India, 30 November–2 December 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.H.; Lee, D.H. Monitoring of driver’s biomedical signals using LoRa-based wireless communications. IEICE Electron. Express 2021, 18, 20210104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Lin, Z.; Huang, Z.; Cai, Z.; Huang, L.; Wei, Z. A Channel Hopping LoRa Technology Based Emergency Communication System for Elderly People Living Alone. In Proceedings of the 2022 21st International Symposium on Communications and Information Technologies ISCIT, Xi’an, China, 27–30 September 2022; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2022; pp. 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Song, W.; Gozho, A.; Sung, Y.; Ji, S.; Song, L.; Wen, L.; Zhang, Q. LoRa-Based smart iot application for smart city: An Example of Human Posture Detection. Wirel. Commun. Mob. Comput. 2020, 2020, 8822555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes Carvalho, D.; Ferrari, P.; Sisinni, E.; Bellitti, P.; Lopomo, N.F.; Serpelloni, M. Using LPWAN Connectivity for Elderly Activity Monitoring in Smartcity Scenarios. Lect. Notes Electr. Eng. 2020, 627, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vimal, S.; Robinson, Y.H.; Kadry, S.; Long, H.V.; Nam, Y. IoT Based Smart Health Monitoring with CNN Using Edge Computing. J. Internet Technol. 2021, 22, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escriba, C.; Roux, J.; Hajjine, B.; Fourniols, J.Y. Smart wearable active patch for elderly health prevention. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Computational Science and Computational Intelligence (CSCI), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 2018, 12–14 December 2018; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 1040–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Much, M.D.; Marcon, C.; Hessel, F.; Cataldo Neto, A. LifeSenior—A Health Monitoring IoT System Based on Deep Learning Architecture. In Lecture Notes in Computer Science (Including Subseries Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence and Lecture Notes in Bioinformatics), Proceedings of the 7th International Conference, ITAP 2021, Washington, DC, USA 24–29 July 2021; Springer Science and Business Media Deutschland GmbH: Berlin, Germany, 2021; Volume 12787, pp. 293–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manatarinat, W.; Poomrittigul, S.; Tantatsanawong, P. Narrowband-internet of things (NB-IoT) system for elderly healthcare services. In Proceedings of the 2019 5th International Conference on Engineering, Applied Sciences and Technology (ICEAST), Luang Prabang, Laos, 2–5 July 2019; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.S.; Islam, M.T.; Almutairi, A.F.; Beng, G.K.; Misran, N.; Amin, N. Monitoring of the Human Body Signal through the Internet of Things (IoT) Based LoRa Wireless Network System. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dammak, B.; Turki, M.; Cheikhrouhou, S.; Baklouti, M.; Mars, R.; Dhahbi, A. LoRaChainCare: An IoT Architecture Integrating Blockchain and LoRa Network for Personal Health Care Data Monitoring. Sensors 2022, 22, 1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, W.; Liao, J.; Han, J. A Real-Time Human Posture Recognition System Using Internet of Things (IoT) Based on LoRa Wireless Network. In Lecture Notes in Electrical Engineering, Proceedings of the CSA-CUTE 2019, Macau, China, 18–20 December 2019; Springer Science and Business Media Deutschland GmbH: Berlin, Germany, 2021; Volume 715, pp. 379–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Z.; Lin, Y.; Jing, W.; Ma, Z.; Liu, H.; Yin, R.; Li, Z.; Bi, Z.; Zhang, W. Development of a Real-Time Wearable Fall Detection System in the Context of Internet of Things. IEEE Internet Things J. 2022, 9, 21999–22007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Li, Z.; Zhang, L. Design and Implementation of Fall Detection Equipment for the Elderly Based on NB-IoT. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Computer Information Technology (AICIT), Yichang, China, 16–18 September 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Pan, J.; Zhu, H.; Li, Y. A Wearable Fall Detection System Based on 1D CNN. In Proceedings of the 2021 2nd International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Computer Engineering (ICAICE), Hangzhou, China, 5–7 November 2021; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 200–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh Alhassoun, N. Cross-Layer Energy Optimization for IoT-Enabled Smart Spaces. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Pervasive Computing and Communications Workshops (PerCom Workshops), Austin, TX, USA, 23–27 March 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Jiang, S.; Lo, B. Subject-Independent Slow Fall Detection with Wearable Sensors via Deep Learning. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE Sensors, Rotterdam, Netherlands, 25–28 October 2020; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierleoni, P.; Belli, A.; Maurizi, L.; Palma, L.; Pernini, L.; Paniccia, M.; Valenti, S. A Wearable Fall Detector for Elderly People Based on AHRS and Barometric Sensor. IEEE Sens. J. 2016, 16, 6733–6744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makma, J.; Thanapatay, D.; Isshiki, T.; Chinrungrueng, J.; Thiemjarus, S. Toward Accurate Fall Detection with a Combined Use of Wearable and Ambient Sensors. In Proceedings of the 2022 Joint International Conference on Digital Arts, Media and Technology with ECTI Northern Section Conference on Electrical, Electronics, Computer and Telecommunications Engineering (ECTI DAMT & NCON), Chiang Rai, Thailand, 26–28 January 2022; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2022; pp. 298–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, W.-K.; Hou, L.-Y.; Pan, T.; Wu, C.-C.; Chen, Y.-H. An IoT Application Based on LoRa Data Transmission. InternatIonal J. IntellIgent Technol. Appl. Stat. 2022, 15, 87–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zeng, P.; Ge, H. A Research of Fall Detection Module Based on NB-IOT. In Proceedings of the 2022 7th International Conference on Computer and Communication Systems (ICCCS), Wuhan, China, 22–25 April 2022; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2022; pp. 197–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L.; Peng, Y. Research of fall detection and fall prevention technologies: A systematic review. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 77702–77722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salah, O.Z.; Selvaperumal, S.K.; Abdulla, R. Accelerometer-based elderly fall detection system using edge artificial intelligence architecture. Int. J. Electr. Comput. Eng. 2022, 12, 4430–4438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanca, A.; Puscasiu, A.; Gota, D.I.; Valean, H. Methods to minimize false detection in accidental fall warning systems. In Proceedings of the 2019 23rd International Conference on System Theory, Control and Computing (ICSTCC), Sinaia, Romania, 9–11 October 2019; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 851–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igual, R.; Medrano, C.; Plaza, I. Challenges, issues and trends in fall detection systems. Biomed. Eng. Online 2013, 12, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özdemir, A.T. An analysis on sensor locations of the human body for wearable fall detection devices: Principles and practice. Sensors 2016, 16, 1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen Gia, T.; Sarker, V.K.; Tcarenko, I.; Rahmani, A.M.; Westerlund, T.; Liljeberg, P.; Tenhunen, H. Energy efficient wearable sensor node for IoT-based fall detection systems. Microprocess. Microsyst. 2018, 56, 34–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Park, S.; Kim, D.; Kim, E.; Kim, J.; Kim, W.; An, Y.; Xiong, S. A practical wearable fall detection system based on tiny convolutional neural networks. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2023, 86, 105325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Raeve, N.; Shahid, A.; De Schepper, M.; De Poorter, E.; Moerman, I.; Verhaevert, J.; Van Torre, P.; Rogier, H. Bluetooth-Low-Energy-Based Fall Detection and Warning System for Elderly People in Nursing Homes. J. Sens. 2022, 2022, 9930681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, R.; Terroso, M.; Marques, M.; Gabriel, J.; Marques, A.T.; Simoes, R. Wearable sensor networks supported by mobile devices for fall detection. Proc. IEEE Sens. 2014, 2014, 2246–2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, F.R.G.; Sejera, M.P.; Bunnao, M.B.G.; Jovellanos, B.R.; Maaño, P.L.C.; Santos, C.J.R. Fall Detection Wearable Device Interconnected Through ZigBee Network. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 9th International Conference on Humanoid, Nanotechnology, Information Technology, Communication and Control, Environment and Management (HNICEM), Manila, Philippines, 1–3 December 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao Gannapathy, V.; Fayeez, A.; Ibrahim, B.T.; Zakaria, Z.B.; Rani, A.; Othman, B.; Latiff, A.A. Zigbee-based smart fall detection and notification system with wearable sensor (e-safe). IJRET: Int. J. Res. Eng. Technol. 2013, 2, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Huang, C.N.; Chan, C.T. A ZigBee-Based Location-Aware Fall Detection System for Improving Elderly Telecare. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2014, 11, 4233–4248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekki, K.; Bajic, E.; Chaxel, F.; Meyer, F. A comparative study of LPWAN technologies for large-scale IoT deployment. ICT Express 2019, 5, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devalal, S.; Karthikeyan, A. LoRa Technology—An Overview. In Proceedings of the 2018 Second International Conference on Electronics, Communication and Aerospace Technology (ICECA), Coimbatore, India, 29–31 March 2018; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 284–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhayyal, M.; Mostafa, A. Recent Developments in AI and ML for IoT: A Systematic Literature Review on LoRaWAN Energy Efficiency and Performance Optimization. Sensors 2024, 24, 4482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhari, B.S.; Zennaro, M.; Borkar, S. LPWAN technologies: Emerging application characteristics, requirements, and design considerations. Future Internet 2020, 12, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chilamkurthy, N.S.; Pandey, O.J.; Ghosh, A.; Cenkeramaddi, L.R.; Dai, H.N. Low-Power Wide-Area Networks: A Broad Overview of Its Different Aspects. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 81926–81959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nolan, K.E.; Guibene, W.; Kelly, M.Y. An evaluation of low power wide area network technologies for the Internet of Things. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing Conference (IWCMC), Paphos, Cyprus, 5–9 September 2016; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 439–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pena Queralta, J.; Gia, T.N.; Tenhunen, H.; Westerlund, T. Edge-AI in LoRa-based health monitoring: Fall detection system with fog computing and LSTM recurrent neural networks. In Proceedings of the 2019 42nd International Conference on Telecommunications and Signal Processing (TSP), Budapest, Hungary, 1–3 July 2019; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 601–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.Y.; Guo, J.H.; Zhang, M.Y.; Ruan, Z.X.; Zheng, X.C.; Lv, S.S. GBDT-Based Fall Detection with Comprehensive Data from Posture Sensor and Human Skeleton Extraction. J. Healthc. Eng. 2020, 2020, 8887340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, J.; Tan, K.K.; Lee, T.H.; Koh, G.C.H. Power-efficient interrupt-driven algorithms for fall detection and classification of activities of daily living. IEEE Sens. J. 2015, 15, 1377–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siong Jun, S.; Rashidi Ramli, H.; Che Soh, A.; Ain Kamsani, N.; Kamil Raja Ahmad, R.; Anom Ahmad, S.; Juraiza Ishak, A. Development of fall detection and activity recognition using threshold based method and neural network. Indones. J. Electr. Eng. Comput. Sci. 2020, 17, 1338–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luque, R.; Casilari, E.; Morón, M.J.; Redondo, G. Comparison and Characterization of Android-Based Fall Detection Systems. Sensors 2014, 14, 18543–18574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kausar, F.; Mesbah, M.; Iqbal, W.; Ahmad, A.; Sayyed, I. Fall Detection in the Elderly using Different Machine Learning Algorithms with Optimal Window Size. Mob. Netw. Appl. 2023, 1, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, X.; Lee, B.G.; Pike, M.; Wu, R.; Chieng, D.; Chung, W.Y. Pre-Impact Firefighter Fall Detection Using Machine Learning on the Edge. IEEE Sens. J. 2023, 23, 14997–15009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astriani, M.S.; Bahana, R.; Kurniawan, A.; Yi, L.H. Threshold-based low power consumption human fall detection for health care and monitoring system. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of 2020 International Conference on Information Management and Technology (ICIMTech), Bandung, Indonesia, 13–14 August 2020; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 853–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šeketa, G.; Vugrin, J.; Lacković, I. Optimal threshold selection for acceleration-based fall detection. IFMBE Proc. 2018, 66, 151–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigfox, S.A. Sigfox 0G Technology. Available online: https://www.sigfox.com/what-is-sigfox/ (accessed on 16 May 2024).
- Mekki, K.; Bajic, E.; Chaxel, F.; Meyer, F. Overview of Cellular LPWAN Technologies for IoT Deployment: Sigfox, LoRaWAN, and NB-IoT. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Pervasive Computing and Communications Workshops (PerCom Workshops), Athens, Greece, 19–23 March 2018; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheurer, S.; Koch, J.; Kucera, M.; Bryn, H.; Bärtschi, M.; Meerstetter, T.; Nef, T.; Urwyler, P. Optimization and technical validation of the AIDE-MOI fall detection algorithm in a real-life setting with older adults. Sensors 2019, 19, 1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierleoni, P.; Belli, A.; Palma, L.; Concetti, R.; Sabbatini, L.; Raggiunto, S. A complete architecture for Ambient Assisted Living scenarios using a cross protocol proxy. J. Ambient. Intell. Humaniz. Comput. 2023, 15, 2757–2764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kautsarina; Kusumawati, D. The Potential Adoption of the Internet of Things in Rural Areas. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on ICT for Rural Development: Rural Development through ICT: Concept, Design, and Implication (IC-ICTRuDEv), Badung, Indonesia, 17–18 October 2018; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lykov, Y.; Paniotova, A.; Shatalova, V.; Lykova, A. Energy Efficiency Comparison LPWANs: LoRaWAN vs Sigfox. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Problems of Infocommunications Science and Technology (PIC S & T), Kharkiv, Ukraine, 6–9 October 2020; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 485–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qadir, Q.M.; Rashid, T.A.; Al-Salihi, N.K.; Ismael, B.; Kist, A.A.; Zhang, Z. Low power wide area networks: A survey of enabling technologies, applications and interoperability needs. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 77454–77473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rama, Y.; Alper Özpınar, M. A Comparison of Long-Range Licensed and Unlicensed LPWAN Technologies According to Their Geolocation Services and Commercial Opportunities. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 18th Mediterranean Microwave Symposium (MMS), Istanbul, Turkey, 31 October–2 November 2018; pp. 398–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanco, G.; Botta, A.; Frattini, F.; Giordano, U.; Ventre, G. On the performance of IoT LPWAN technologies: The case of Sigfox, LoRaWAN and NB-IoT. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Communications, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 16–20 May 2022; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2022; Volume 2022, pp. 2096–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Se, H.; Liu, J. A fusion fall detection algorithm combining threshold-based method and convolutional neural network. Microprocess. Microsyst. 2021, 82, 103828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sucerquia, A.; López, J.D.; Vargas-Bonilla, J.F. SisFall: A fall and movement dataset. Sensors 2017, 17, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vavoulas, G.; Pediaditis, M.; Spanakis, E.G.; Tsiknakis, M. The MobiFall dataset: An initial evaluation of fall detection algorithms using smartphones. In Proceedings of the 13th IEEE International Conference on BioInformatics and BioEngineering, Chania, Greece, 10–13 November 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casilari, E.; Santoyo-Ramón, J.A.; Cano-García, J.M. Analysis of public datasets for wearable fall detection systems. Sensors 2017, 17, 1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, M.; Jeannes, R.L.B. Elderly Fall Detection Using Wearable Sensors: A Low Cost Highly Accurate Algorithm. IEEE Sens. J. 2019, 19, 3156–3164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guvensan, M.A.; Kansiz, A.O.; Camgoz, N.C.; Turkmen, H.I.; Yavuz, A.G.; Karsligil, M.E. An Energy-Efficient Multi-Tier Architecture for Fall Detection on Smartphones. Sensors 2017, 17, 1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lampoltshammer, T.J.; de Freitas, E.P.; Nowotny, T.; Plank, S.; da Costa, J.P.C.L.; Larsson, T.; Heistracher, T. Use of Local Intelligence to Reduce Energy Consumption of Wireless Sensor Nodes in Elderly Health Monitoring Systems. Sensors 2014, 14, 4932–4947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musci, M.; De Martini, D.; Blago, N.; Facchinetti, T.; Piastra, M. Online Fall Detection Using Recurrent Neural Networks on Smart Wearable Devices. IEEE Trans. Emerg. Top. Comput. 2021, 9, 1276–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Bermejo, J.; Martinez-del-Rincon, J.; Dorado, J.; del Toro, X.; Santof imia, M.J.; Lopez, J.C. Edge computing transformers for fall detection in older adults. Int. J. Neural Syst. 2024, 34, 2450026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casamassima, F.; Farella, E.; Benini, L. Context aware power management for motion-sensing body area network nodes. In Proceedings of the 2014 Design, Automation & Test in Europe Conference & Exhibition (DATE), Dresden, Germany, 24–28 March 2014; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Bourke, A.K.; Nelson, J. Evaluation of accelerometer based multi-sensor versus single-sensor activity recognition systems. Med. Eng. Phys. 2014, 36, 779–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noor, M.H.M.; Salcic, Z.; Wang, K.I.K. Dynamic sliding window method for physical activity recognition using a single tri-axial accelerometer. In Proceedings of the 2015 10th IEEE Conference on Industrial Electronics and Applications (ICIEA), Auckland, New Zealand, 15–17 June 2015; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 102–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharghan, S.K.; Fakhrulddin, S.S.; Al-Naji, A.; Chahl, J. Energy-efficient elderly fall detection system based on power reduction and wireless power transfer. Sensors 2019, 19, 4452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballerini, M.; Polonelli, T.; Brunelli, D.; Magno, M.; Benini, L. NB-IoT Versus LoRaWAN: An Experimental Evaluation for Industrial Applications. IEEE Trans. Industr Inform. 2020, 16, 7802–7811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semtech SX1257 Datasheet. Available online: https://www.semtech.com/products/wireless-rf/lora-core/sx1257 (accessed on 22 August 2024).
- HopeRF. RFM95/96/97/98(W) LoRa Transceiver Module Datasheet. Available online: https://www.hoperf.com/modules/lora/RFM95W.html (accessed on 22 August 2024).
- Semtech. SX1276/77/78/79 Datasheet. Available online: https://www.semtech.com/products/wireless-rf/lora-connect/sx1276 (accessed on 22 August 2024).
- Quectel. BC95 NB-IoT Module Datasheet. Available online: https://www.es.co.th/Schemetic/PDF/QUECTEL_BC95B.PDF (accessed on 22 August 2024).
- China Mobile IoT Company. M5310A AT Command Manual. Available online: https://iot.10086.cn/Uploads/file/product/20180827/M5310A%20AT%20%E5%91%BD%E4%BB%A4%E7%94%A8%E4%B9%A6%E4%BD%BF%E7%94%A8%E6%89%8B%E5%86%8C_V1_20180827154312_20506.pdf (accessed on 22 August 2024).
- Nordic Semiconductor. nRF9160 System-in-Package Datasheet. Nordic Semiconductor. Available online: https://www.nordicsemi.com/Products/nRF9160 (accessed on 22 August 2024).
- Sinha, R.S.; Wei, Y.; Hwang, S.H. A survey on LPWA technology: LoRa and NB-IoT. ICT Express 2017, 3, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bet, P.; Castro, P.C.; Ponti, M.A. Fall detection and fall risk assessment in older person using wearable sensors: A systematic review. Int. J. Med. Inform. 2019, 130, 103946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, C.M.S.; Oliveira, R.A.R.; Silva, J.S. Low-energy smart cities network with lora and bluetooth. In Proceedings of the 2019 7th IEEE International Conference on Mobile Cloud Computing, Services, and Engineering (MobileCloud), Newark, CA, USA, 4–9 April 2019; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muteba, F.; Djouani, K.; Olwal, T. A comparative Survey Study on LPWA IoT Technologies: Design, considerations, challenges and solutions. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2019, 155, 636–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gemperle, F.; Kasabach, C.; Stivoric, J.; Bauer, M.; Martin, R. Design for Wearability. In Proceedings of the 2nd IEEE International Symposium on Wearable Computers, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 19–20 October 1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasher, E.; Popper, Z.; Raz, H.; Lawo, M. WearIT@work: A wearable computing solution for knowledge-based development. Int. J. Knowl.-Based Dev. 2010, 1, 346–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thilo, F.J.S.; Bilger, S.; Halfens, R.J.G.; Schols, J.M.G.A.; Hahn, S. Involvement of the end user: Exploration of older people’s needs and preferences for a wearable fall detection device—A qualitative descriptive study. Patient Prefer. Adherence 2017, 11, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Features | LoRaWAN | NB-IoT | Sigfox |
|---|---|---|---|
| Range | 5 km (urban), 20 km (rural) | 1 km (urban), 10 km (rural) | 10 km (urban), 40 km (rural) |
| Bidirectional | Yes/half-duplex | Yes/half-duplex | Limited/half-duplex |
| Frequency | Unlicensed ISM band (915 MHz in North America, 433 MHz in Asia, 868 MHz in Europe) | Licensed LTE frequency | Unlicensed ISM band (868 MHz in Europe, 915 MHz in North America, 433 MHz in Asia) |
| Modulation | CSS | QPSK | BPSK |
| Maximum Bit Rate (“on-the-air”) | 50 kbps | 250 kbps | 100 bps |
| Standardization | LoRa Alliance | 3GPP | Sigfox collaborates with ETSI on Sigfox-based network standardization |
| TX (Transmission) power consumption | 28 mA | 74–220 mA | 10–50 mA |
| RX (Reception) power consumption | 10.5 mA | 46 mA | 10 mA |
| Sleep mode power consumption | 1 µA | 3 µA | 6 µA |
| Ref. | Year | LPWAN Technology * | Sensor ** |
|---|---|---|---|
| Escriba et al. [20] | 2018 | Sigfox | Accelerometer |
| Patel et al. [14] | 2018 | LoRaWAN | Accelerometer |
| Valach et al. [12] | 2018 | LoRaWAN | Accelerometer |
| Manatarinat et al. [22] | 2019 | NB-IoT | Accelerometer and gyroscope |
| Pena Queralta et al. [53] | 2019 | LoRaWAN | Accelerometer, gyroscope and magnetometer |
| Scheurer et al. [65] | 2019 | LoRaWAN | Accelerometer |
| Cai et al. [54] | 2020 | NB-IoT | Accelerometer and gyroscope |
| Chang et al. [8] | 2020 | LoRaWAN | Accelerometer, gyroscope and IR (Infrared) |
| Huynh et al. [6] | 2020 | LoRaWAN | Accelerometer, gyroscope and magnetometer |
| Lachtar et al. [11] | 2020 | LoRaWAN | Accelerometer, gyroscope and magnetometer |
| Zanaj et al. [7] | 2020 | LoRaWAN | Accelerometer, gyroscope and magnetometer |
| Liu et al. [28] | 2021 | NB-IoT | Accelerometer, gyroscope and magnetometer |
| Lousado et al. [13] | 2021 | LoRaWAN | Accelerometer |
| Fan et al. [27] | 2022 | NB-IoT | Accelerometer and gyroscope |
| Li et al. [16] | 2022 | LoRaWAN | Accelerometer and gyroscope |
| Qian et al. [26] | 2022 | NB-IoT | Accelerometer and gyroscope |
| Salah et al. [36] | 2022 | LoRaWAN | Accelerometer |
| Wong et al. [33] | 2022 | LoRaWAN | Accelerometer, gyroscope and magnetometer |
| Wu et al. [34] | 2022 | NB-IoT | Accelerometer and gyroscope |
| Pierleoni et al. [66] | 2023 | NB-IoT | Accelerometer, gyroscope and magnetometer |
| Ref. | Contribution | Conclusions on LPWAN Technology | LPWAN Limitations | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Escriba et al. [20] | Development of a smart wearable active patch for elderly health prevention, utilizing Sigfox for fall detection and GPS tracking. | Sigfox is effective for low-power data transfer and suitable for fall detection and geolocation. | A low data rate limits the amount of information transmitted; communication is affected by environmental conditions and device location. | The system effectively used Sigfox for low-power data transfer, with the patch maintaining communication reliability in 67.92% of tested positions, validating its capability for fall detection and location tracking. |
| Patel et al. [14] | Development of a LoRaWAN-based system for real-time monitoring of vital signs and fall detection, with alerts sent via LINE application. | LoRaWAN can extract data from weak signals in noisy environments, which is useful for delivering critical medical data. | No specific limitations are commented. | The system demonstrated high performance with LoRaWAN, achieving 100% sensitivity, 96.93% accuracy, 94.25% specificity, and 91.38% predictability, ensuring reliable transmission of fall alerts. |
| Valach et al. [12] | Research on the feasibility of using LoRaWAN in healthcare IoT devices, focusing on energy optimization and transmission reliability. | LoRaWAN is suitable for long-distance data transmission with low power consumption and is useful for patient location and monitoring vital signs. | The LoRaWAN connection was unreliable when the end node was on the ground during tests. | LoRaWAN showed reliability issues in fall detection when the end node is near the ground; using Arduino Pro Mini is suggested to reduce energy consumption. |
| Manatarinat et al. [22] | Development of an NB-IoT-based system for elderly healthcare, enabling automatic fall detection and alerts via the LINE application. | NB-IoT is suitable for health monitoring applications, providing efficient low-power communication with wide coverage. | No specific limitations. | Reliable fall alert communication and patient location using NB-IoT, ensuring immediate medical response. Achieved low latency and dependable alert delivery, with reliance on an NB-IoT operator for network functionality. |
| Pena Queralta et al. [53] | Developed and technically validated the AIDE-MOI fall detection algorithm using real-life data from older adults, utilizing LoRaWAN for effective long-range, low-power communication. | LoRaWAN is a promising option to overcome the limitations of traditional network infrastructures in remote health settings, providing long-distance, low-power data transmission. | LoRaWAN cannot support high data rate applications due to limited transmission bandwidth. | The AIDE-MOI system demonstrated significant improvement with LoRaWAN, achieving a sensitivity of 80% and a specificity of 99.9978%, ensuring reliable and efficient fall detection and data transmission in real-life environments. |
| Scheurer et al. [65] | Developed and technically validated the AIDE-MOI fall detection algorithm using real-life data from older adults, utilizing LoRaWAN for effective long-range, low-power communication. | LoRaWAN is used for long-range, low-power communication, allowing data transmission over several kilometers. | No specific limitations are commented. | The AIDE-MOI system using LoRaWAN achieved 80% sensitivity and 99.9978% specificity, ensuring reliable fall detection and efficient data transmission. |
| Cai et al. [54] | Developed a GBDT-based fall detection system using comprehensive data from posture sensors and human skeleton extraction, utilizing NB-IoT for effective data transmission to a cloud server for analysis. | NB-IoT provides wide coverage, multiple connections, low speed, and low power consumption. | No specific limitations are commented. | The system, using NB-IoT, achieved an I2 score of 0.878 on a fused dataset and 95% accuracy, demonstrating reliable and low-latency data communication. |
| Chang et al. [8] | This study proposes an intelligent assistive system for visually impaired individuals using smart glasses and a smart cane connected via BLE, with LoRaWAN for reliable fall detection and alert transmission. | LoRaWAN-based intelligent assistive system for aerial obstacle avoidance and fall detection for visually impaired people shows high accuracy and long-range communication. | Dependence on public LoRaWAN network coverage, which can vary based on geographical location and network infrastructure availability. | The system effectively uses LoRaWAN to transmit fall alerts, achieving long-distance coverage and low latency. The integration of both devices reduced false alarms, achieving an overall accuracy rate of 94.56%. |
| Huynh et al. [6] | Develops a LoRaWAN-based system for activity assessment and fall detection at home, using low-cost inertial sensors and a cloud platform for data analysis and emergency notifications. | LoRaWAN technology advantages of long-range capabilities and low power consumption. Wearable devices can operate 2–10 km from a LoRaWAN base station with an optimized battery life of one week between charges. | No specific limitations. | The system demonstrated a high specificity of 100% in fall detection during approximately 200 h of normal activities, proving the effectiveness of using LoRaWAN for reliable data transmission and emergency alerts. |
| Lachtar et al. [11] | Proposes a monitoring architecture using LoRaWAN and MQTT * for fall detection in elderly people within a smart city environment. | LoRaWAN technology is used for long-range, low-power communication in a smart city environment, effectively robust and efficient for elderly monitoring. | Reliance on public LoRaWAN network coverage, which can fluctuate based on geographic location and available infrastructure. | The system demonstrated efficient long-range communication with LoRaWAN, covering an average area of 6 km2 with minimal packet loss, making it suitable for smart cities. |
| Zanaj et al. [7] | Proposes a wearable fall detection system integrated into shoes, using LoRaWAN for long-range, low-power communication and MQTT for alert notifications. | LoRaWAN is an attractive and promising technology for health and wellness monitoring, enabling long-range communication with low battery consumption. It has been demonstrated to be effective for long-term use and reliable coverage with a single gateway. | Packet loss can occur due to obstacles affecting the connection between the end node and gateway. | Demonstrated efficient data transmission with a 95% success rate in various environments. The system operates for approximately 23 h on a 500 mAh battery, proving LoRaWAN’s viability for fall detection. |
| Liu et al. [28] | Proposes a wearable fall detection system utilizing a 1D CNN deep learning model and NB-IoT communication to send alerts and GPS data to the cloud. | NB-IoT is key for data transmission and alerts in a successful fall detection system based on 1D CNN. | Lack of NB-IoT service coverage can cause interference and data loss due to variability in signal quality across different geographical environments and network conditions. | The system demonstrated a fall detection accuracy of 98.85%, with a sensitivity of 98.86% and specificity of 99.84%, highlighting the effectiveness of using NB-IoT for reliable data transmission and fall alerts. |
| Lousado et al. [13] | Proposes a cost-effective, energy-efficient monitoring system for elderly individuals using LoRaWAN and The Things Network (TTN) for long-range communication and data processing. | LoRaWAN offers an effective and low-cost solution for monitoring the health and home conditions of elderly people, especially in remote areas with limited mobile network coverage. | Variability in LoRaWAN public network coverage, which may be insufficient in certain geographical areas due to uneven infrastructure availability. | Demonstrated high predictive accuracy (99.73%) for detecting falls and other anomalies, showcasing the viability of using LoRaWAN for reliable and continuous monitoring of elderly individuals’ health and movement in areas with limited mobile network coverage. |
| Fan et al. [27] | Design and development of a low-power wearable fall detection device for the elderly using NB-IoT technology, capable of remote positioning, tracking, fall detection, and one-touch emergency calls. | NB-IoT communication is of paramount importance for the successful implementation of this fall detection device for the elderly, providing an effective solution for monitoring elderly safety and reducing caregiving pressure on family members. | No specific limitations. | The device demonstrated effective fall detection in different directions during simulated tests. GPS positioning accuracy showed that 94% of the time, the positioning error was within 20 m, validating the device’s capability for precise location tracking using NB-IoT technology. |
| Li et al. [16] | Design and development of an emergency communication system for elderly people living alone, using LoRaWAN technology for long-range, low-power communication, along with a fall detection algorithm based on the channel hopping strategy. | LoRaWAN, combined with channel hopping, enhances the communication quality and efficiency of emergency systems monitoring the elderly, facilitating remote monitoring. | Communication loss rate of 2% at distances up to 1800 m due to electronic interference, physical obstacles, and simulated environmental conditions. | The device achieved a fall detection rate of over 85% in simulated tests. The average communication latency was 9.5 s, and the effective communication distance reached 1800 m, validating the efficiency of LoRaWAN for emergency communication systems. |
| Qian et al. [26] | Design and development of a wearable fall detection system combining MEMS * sensors and NB-IoT, capable of integrating with public health systems for real-time monitoring and timely rescue. | NB-IoT, combined with MEMS sensors and a multilevel threshold algorithm, provides an efficient, low-power solution for real-time fall detection that is suitable for integration with public communication networks. | Signals are sensitive to the environment, and disturbances and noises can cause system faults. | The system demonstrated a fall detection accuracy of 94.88%, sensitivity of 95.25%, and specificity of 94.5% in experimental tests. This validates the effectiveness of the NB-IoT-based system for real-time fall detection and location tracking in elderly individuals. |
| Salah et al. [36] | Design of a fall detection system based on Edge artificial intelligence, combining a microcontroller and LoRaWAN communication. | LoRaWAN technology, used with edge AI, enables long-range, low-power communication, making it suitable for real-time fall detection systems with high accuracy and low latency. | Communication range decreases when moving from a direct line of sight to a non-line of sight due to obstacle interference, affecting system performance. | The device achieved a 95.55% accuracy in fall detection using a convolutional neural network (CNN). Local inference reduced latency and improved energy efficiency, with a battery life exceeding 53 h and a communication range of up to 180 m in line-of-sight using LoRaWAN. |
| Wong et al. [33] | Design of a fall detection system based on LoRaWAN communication, optimizing fall detection accuracy while reducing costs by eliminating the need for mobile phones. | LoRaWAN technology is highlighted for its low power consumption, reduced operational costs, and flexible data transmission rate, making it the best option for long-distance communication in emergency situations. | Communication can be affected by obstacles, electrical and magnetic interferences, leading to system instability and data transmission issues. | The system accurately detected falls in various scenarios with set thresholds, demonstrating reliable performance in both indoor and outdoor environments. The LoRaWAN protocol ensured stable signal transmission up to 318 m with minor obstructions, proving its effectiveness for long-range communication. |
| Wu et al. [34] | Design and development of a fall detection module based on NB-IoT technology and MEMS systems, capable of collecting acceleration and angle data and transmitting it for precise fall analysis. | NB-IoT, combined with MEMS sensors and a GRU-based algorithm, provides an effective, low-power solution for real-time fall detection, suitable for long-distance data transmission. | No specific limitations. | The module demonstrated an accuracy of 90.1% using the threshold method and 92.9% with GRU. Data was successfully transmitted via NB-IoT, enabling alerts to be sent to family members and rescue centers in the event of a detected fall. |
| Pierleoni et al. [66] | Design and development of a comprehensive architecture for Ambient Assisted Living (AAL) scenarios, incorporating a cross-protocol proxy for seamless communication between different IoT protocols and a wireless wearable fall detection device based on LPWAN technologies such as NB-IoT. | NB-IoT, used in combination with CoAP * and MQTT, provides an efficient and reliable communication solution for wearable fall detection devices, ensuring low latency and high throughput. | Latency issues due to network congestion and packet loss requiring retransmissions, with latency averaging 0.4 s and occasional peaks up to 10 s. | The system demonstrated low latency (approx. 0.4 s) and high reliability in transmitting fall detection alerts using NB-IoT and MQTT. The proxy improved interoperability, and the wearable device showed a high success rate in fall detection and alerting in an AAL environment. The packet loss rate was slightly above 0.1%, with recovery through retransmissions. |
| Technology | Environmental Conditions | User Mobility Scenarios | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sigfox | Sensitive to environmental conditions; ideal for rural environments | Suitable for low mobility applications where data transmission is not continuous and can tolerate delays. | [20,71] |
| LoRaWAN | May face reliability issues in environments with physical obstacles; offers good interference resistance | Ideal for urban and rural applications with limited to moderate mobility due to its combination of long-range and low-power consumption. | [6,7,8,11,12,13,14,16,33,36,53,65,71] |
| NB-IoT | Can be affected by network coverage variability and environmental interference | Best for urban environments where support for mobile devices and high reliability in data transmission are required, making it ideal for critical applications such as fall detection. | [22,26,27,28,34,54,66,71] |
| Reference | Device Position |
|---|---|
| Huynh et al. [6] | Waist or wrist |
| Zanaj et al. [7] | Foot (shoes) |
| Lachtar et al. [11] | Cane |
| Lousado et al. [13] | Backpack |
| Escriba et al. [20] | Back |
| Qian et al. [26] | Wrist |
| Fan et al. [27] | Wrist |
| Wu et al. [34] | Waist |
| Liu et al. [28] | Waist |
| Wong et al. [33] | Chest |
| Scheurer et al. [65] | Back, abdomen, or chest |
| Pierleoni et al. [66] | Ankle or shoe |
| Reference | Algorithm Type * | Accuracy | Sensitivity | Specificity | Sensor | Sample Size (Number of Participants) | No. of Evaluated Falls |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Huynh et al. [6] | Thresholding policies | n.i. | 96.3% | 96.2% | Accelerometer, gyroscope and magnetometer | 10 | n.i. |
| Chang et al. [8] | 98.3% | n.i. | n.i. | Accelerometer, gyroscope and IR (Infrared) | 3 | 150 | |
| Li et al. [16] | 85% | n.i. | n.i. | Accelerometer and gyroscope | 6 | 500 | |
| Wu et al. [34] | 90.1% | n.i. | n.i. | Accelerometer and gyroscope | n.i. | n.i. | |
| Qian et al. [26] | 94.88% | 95.25% | 94.5% | Accelerometer and gyroscope | 20 | 400 | |
| Salah et al. [36] | K-NN (15 neighbors) | 78.64% | 81.07% | 76.57% | Accelerometer | 24 | 1798 |
| Salah et al. [36] | K-NN (5 neighbors) | 79.11% | 80.06% | 78.21% | Accelerometer | 24 | 1798 |
| Salah et al. [36] | CNN | 95.55% | 95.1% | 94.86 | Accelerometer | 24 | 1798 |
| Liu et al. [28] | 98.85% | 98.86% | 99.84% | Accelerometer, gyroscope and magnetometer | 35 | 1798 and 288 | |
| Salah et al. [36] | LSTM | 96.78% | 97.87% | 95.21% | Accelerometer | 24 | 1798 |
| Pena Queralta et al. [53] | 91.90% | 95.3% | n.i. | Accelerometer, gyroscope and magnetometer | 54 | 647 | |
| Salah et al. [36] | SVM | 82.27% | 87.21% | 78.48% | Accelerometer | 24 | 1798 |
| Wu et al. [34] | GRU | 92.9% | n.i. | n.i. | Accelerometer and gyroscope | n.i. | n.i. |
| Cai et al. [54] | GBDT (Acceleration Dataset) | 89.2% | n.i. | n.i. | Accelerometer and gyroscope | 10 | n.i. |
| Reference | Battery Life * | Battery Capacity ** | Algorithm Type | LPWAN Technology | Employed Sensor |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Huynh et al. [6] | 1 week–1 month | Not specified | Thresholding | LoRaWAN | Accelerometer, gyroscope and magnetometer |
| Zanaj et al. [7] | 23 h (500 mA/h), 36 h (800 mA/h) | 500 mAh 800 mAh | Thresholding | LoRaWAN | Accelerometer, gyroscope and magnetometer |
| Salah et al. [36] | More than 53 h | 2000 mAh | CNN | LoRaWAN | Accelerometer |
| Escriba et al. [20] | 3 days (low-power mode)–13 h (GPS tracking) | 30 mAh | Not indicated | Sigfox | Accelerometer |
| Reference | Transceiver | LPWAN Technology * |
|---|---|---|
| Zanaj et al. [7] | SX1257 | LoRaWAN |
| Salah et al. [36] | RFM95W | LoRaWAN |
| Lachtar et al. [11] | RFM95/96/97/98(W) | LoRaWAN |
| Valach et al. [12] | RFM95W | LoRaWAN |
| Lousado et al. [13] | SX1276 | LoRaWAN |
| Qian et al. [26] | BC-95 | NB-IoT |
| Fan et al. [27] | M5310A | NB-IoT |
| Wong et al. [33] | SX1278 RA-02 | LoRaWAN |
| Pierleoni et al. [66] | nRF9160 | NB-IoT |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Villa, M.; Casilari, E. Wearable Fall Detectors Based on Low Power Transmission Systems: A Systematic Review. Technologies 2024, 12, 166. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies12090166
Villa M, Casilari E. Wearable Fall Detectors Based on Low Power Transmission Systems: A Systematic Review. Technologies. 2024; 12(9):166. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies12090166
Chicago/Turabian StyleVilla, Manny, and Eduardo Casilari. 2024. "Wearable Fall Detectors Based on Low Power Transmission Systems: A Systematic Review" Technologies 12, no. 9: 166. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies12090166
APA StyleVilla, M., & Casilari, E. (2024). Wearable Fall Detectors Based on Low Power Transmission Systems: A Systematic Review. Technologies, 12(9), 166. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies12090166











