Abstract
Although cooperative learning is an effective instructional method, it cannot be taken for granted that students will gain new knowledge when engaging in a cooperative activity. Even if cooperative learning is effectively designed, problems might arise regarding cognitive, behavioral and motivational aspects of learning. For students to gain knowledge, cognition, metacognition, behavior and motivation should be collectively regulated by the group, which is called the socially shared regulation of learning (SSRL). However, up until now, there has been no consensus about how SSRL is manifested during cooperative learning. This study investigated how SSRL is manifested during cooperative learning by means of a grounded theory approach. This was done to identify what is necessary for effective SSRL and what its consequences are. A theoretical model was built based on the data in order to portray these prerequisites and consequences of SSRL. This study also investigated whether equal participation fostered SSRL. In this study, participants were students from the fourth, fifth and sixth grades of elementary school, working together in groups of four (n = 104). The data indicated that SSRL is a rare process, the absence of which caused less structured collaboration in groups who were not prompted to participate equally.
1. Introduction
Cooperative learning is an instructional method that is widely advocated in primary education [1]. In cooperative learning, students work together in small, most often heterogeneous, groups in which they help each other to complete a group task in order to achieve a shared goal [2,3]. When students engage in effective cooperative learning, their academic outcomes will be positively affected [4], and they will even outperform students who learn individually [5].
Yet, even if cooperative learning is carefully designed [6], problems can arise at the cognitive, motivational and socioemotional levels [7]. Challenges at the cognitive level might arise when students experience problems in understanding each other’s reasoning. Problems at the motivational level can arise when students have different learning goals and expectations [8]. Problems at the socioemotional level will occur when groups engage in dysfunctional communication, which decreases the likelihood of on-task behavior and diminishes task focus [9]. Subsequently, common group goals might not be reached [10]. As the extent to which students establish new knowledge depends on the quality of the aforementioned interactions [11], students should collectively regulate and adapt cognition, metacognition, behavior and motivation, which is called the socially shared regulation of learning (SSRL) [12]. This will guide the team towards better decision making and adaptation of the cooperative processes, progress, and products, which enhances learning [13]. However, research has shown that learners are often unsuccessful in regulating their collective learning process [14]. In comparison to individual self-regulation, already considered a difficult process for many students [15], engaging in SSRL calls for additional coordination and communication, which might burden working memory [16]. This is challenging, as each student is an individual self-regulating human being with personal learning goals, metacognitive strategies and emotions [8]. In fact, the few students who are capable of applying regulation strategies in a group work situation mostly only regulate their own work without aiming to influence the group [17]. As SSRL seems to be an essential skill for effective cooperative learning [18] and as students often fail to engage in SSRL [17], researchers have agreed that SSRL should be supported [10]. However, thus far, researchers have not yet found a clear-cut way to identify SSRL as a whole [12]. As not all aspects of SSRL have been sufficiently investigated, and it is unclear what aspects need (what kinds of) support, how important each of these skills are for effective cooperative learning and what conditions are necessary for particular SSRL skills to occur. Regarding these conditions, some studies have suggested that equal participation might lead to higher levels of regulation in the group [19] However, thus far the effects of equal participation on SSRL during cooperative learning have not yet been investigated in depth.
The aim of this study is, first, to create an all-encompassing theoretical framework for SSRL that identifies the prerequisites for, consequences of and relationships between SSRL (sub-)processes in both the social and task domains. These prerequisites and consequences will, in the end, underline the conditions that are necessary for SSRL skills to occur and how important the occurrence of these skills actually is. As engaging in SSRL puts a burden on working memory [16], it is necessary first to identify whether it is desirable for students to perform these skills so that it can be determined whether these skills should be supported. As well as determining how SSRL is manifested, the current study will investigate the effect on SSRL of supporting equal participation. As SSRL involves processes that concern the group as a whole [18], it is important to determine whether supporting the participation of all group members is necessary to evoke SSRL.
1.1. Socially Shared Regulation of Learning (SSRL)
When students carry out cooperative learning, just engaging in task-related activities is not enough for successful collaboration; the regulation of task-related activities is also necessary [20]. In studies about individual self-regulation, researchers have mostly distinguished between three phases of metacognitive self-regulation: planning, monitoring and evaluating, e.g., [21,22,23,24]. The learner should enact these phases before, during and after the task [25]. In the planning phase, students select appropriate strategies, set up learning goals, become oriented to the problem [26] and activate prior knowledge [27]. Next, in the monitoring phase, learners continually analyze information on their learning process and assess their progress [28]. Additionally, they assess comprehension and overall performance and make adaptations if necessary. In the evaluation phase, learners assess their learning outcome and the learning process [29]. With regard to the learning outcome, this typically involves appraising their learning gains [29], learning outcomes and learning goals [26]. For the learning process, generally, the quality of the planning and collaboration are evaluated. Students who have a higher level of self-regulation skills are (1) more skilled than novices in monitoring problem solving, (2) better in estimating the difficulty of tasks, (3) more aware of mistakes they make in their work and (4) better time estimators [30]. All in all, self-regulation seems to be an important facilitator of academic achievement.
However, apart from just performing regulatory strategies individually, regulatory strategies should be shared with group members in order to achieve the shared group goal, which is identified as SSRL [18]. What is essential in SSRL theory and different from theories focused on individual self-regulated learning is that it focuses not only on cognition and metacognition, but also on the reciprocal roles of motivation, behavior and emotion within the group [31], which are considered to be the more social aspects of learning. Whereas the previously described processes mainly concern students’ skills to regulate learning processes, learning outcomes and task engagement, and are therefore predominantly task focused [32], the regulation of social aspects is also required [26]. Social interactions between peers during cooperative learning such as giving each other compliments can increase the involvement and participation of group members [33]. What is more, social interactions can increase performance and learning satisfaction [34]. Yet, social activities can also be dysfunctional, which decreases on-task behavior and diminishes task focus [9]. Therefore, the regulation of the social aspects is crucial. As a result, groups will create or maintain a positive group atmosphere [35], which will thereby increase group members’ motivation to complete the task [36]. Although research by Panadero and Järvelä [12] mentioned that the regulation of these social aspects should be shared among group members, research on regulation in collaborative learning has predominantly focused on the regulation of task-related activities [20].
Thus, SSRL involves the regulation of the shared activity, which concerns collectively or interdependently shared regulatory processes, knowledge and beliefs in order to achieve a shared goal [18]. When groups engage in SSRL, they generally perceive the task as less difficult [37] and obtain better learning outcomes than when they do not engage in SSRL or when there are lower levels of shared regulation [38]. However, research by Järvelä et al. [10] indicated that SSRL is an implicit process. That is, group members are mostly unaware of each other’s goals, strategies and knowledge. Additionally, regulating the collaborative process calls for additional coordination and communication, which can overload working memory [16]. As students need support in their self-regulation process [14], it is useful to investigate the differences between students when they engage in SSRL and to adjust support to their needs. However, in order to do this, one should know how SSRL is manifested. Yet, research on how students share regulatory processes is scarce. A review by Panadero and Järvelä [12] pointed this out as well and named some features of SSRL that have not yet been sufficiently investigated. First, even though research aims to create encouraging methodological opportunities to measure SSRL, researchers have not yet found a clear-cut way to identify SSRL. This can be attributed to the fact that SSRL research has predominantly measured self-regulation in an individual context or in the context of collaborative and social activities. Second, a variety of studies have measured regulation on a general level and did not take account of the diversity of regulatory processes such as setting up goals and selecting learning strategies [18]. What is more, although SSRL concerns the regulation of both task-related and social activities, researchers often do not focus on the complete picture [39]. Therefore, an analysis of the complete construct of SSRL is called for [13]. The study by Hadwin et al. [13] indicated that, when creating a model of SSRL, the researcher should also take into consideration the interplay of the task-related and social activities. Therefore, one should not just focus on domain-related interactions, as shared task-regulation can be a consequence of social interactions. For example, if a student has task anxiety, students in a group can collectively make sure that everyone gets the chance to share their ideas.
Research by Panadero and Järvelä [12] added that it is important to take into consideration the difference between co-regulation and SSRL. Research sometimes uses the term co-regulation when in fact SSRL is described. Co-regulation is considered to be a process in which group members regulate each other’s learning, instead of sharing the regulatory process, which is what happens in SSRL. Panadero and Järvelä [12] stated that in future research, in which new categories for SSRL will be defined, it is important to take into consideration the difference between co-regulation and SSRL in order to develop an adequate view of what SSRL entails.
1.2. Equal Participation
To increase the likelihood of learning during cooperative learning, all students need to actively share their knowledge [40]. This can be achieved by ensuring equal participation of group members [41]. Equal participation might also be important for effective SSRL, because the extent to which groups collaborate may influence their construction of social regulation processes, as they have to co-construct shared understanding and work towards a shared goal [11] Alongside of that, when (some) students decide not to collaborate, these processes might not become shared processes. Research by Panadero and Järvela [12] adds that an important requirement for the occurrence of SSRL is to have more than just one expert learner in the group [12]. If just one student is perceived as the expert in the group, the other students will blindly follow the expert’s advice and regulatory strategies will not be shared among group members. Therefore, symmetrical cooperation in which group members are dependent on each other’s information (i.e., positive interdependence) and each individual has to bring information to the group process in order to achieve a shared outcome (i.e., individual accountability) might support SSRL during cooperative learning.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
A sample of 136 elementary school children in the fourth (9–10 years), fifth (10–11 years) and sixth grades (11 to 12 years) was recruited from 6 different elementary schools based in a medium-sized city in the Netherlands (60 males, 76 females; Mage = 10.95 years, SD = 0.86, range from 8 years and 9 months to 12 years and 8 months). Based on the CITO’s monitoring system, these children were categorized as low-ability, average-ability or high-ability learners [42]. Subsequently, students were assigned to heterogeneous groups of four students, which consisted of one high-ability student, two average-ability students and one low-ability student. Within these ability levels, children were randomly assigned to a group. These groups were then randomly assigned to the supported or unsupported condition. It turned out that not all video-recorded data were useable for analysis, as some videos were inaudible. This led to a final sample of 104 students (i.e., 26 groups) for this study (49 males, 55 females; Mage = 10.89, SD = 0.84, range from 8 to 12 years).
Before the start of the study, the children’s parents were informed about the aim of this study and gave active consent for their child to participate and for the usage of the data for future research purposes.
2.2. Worksheet
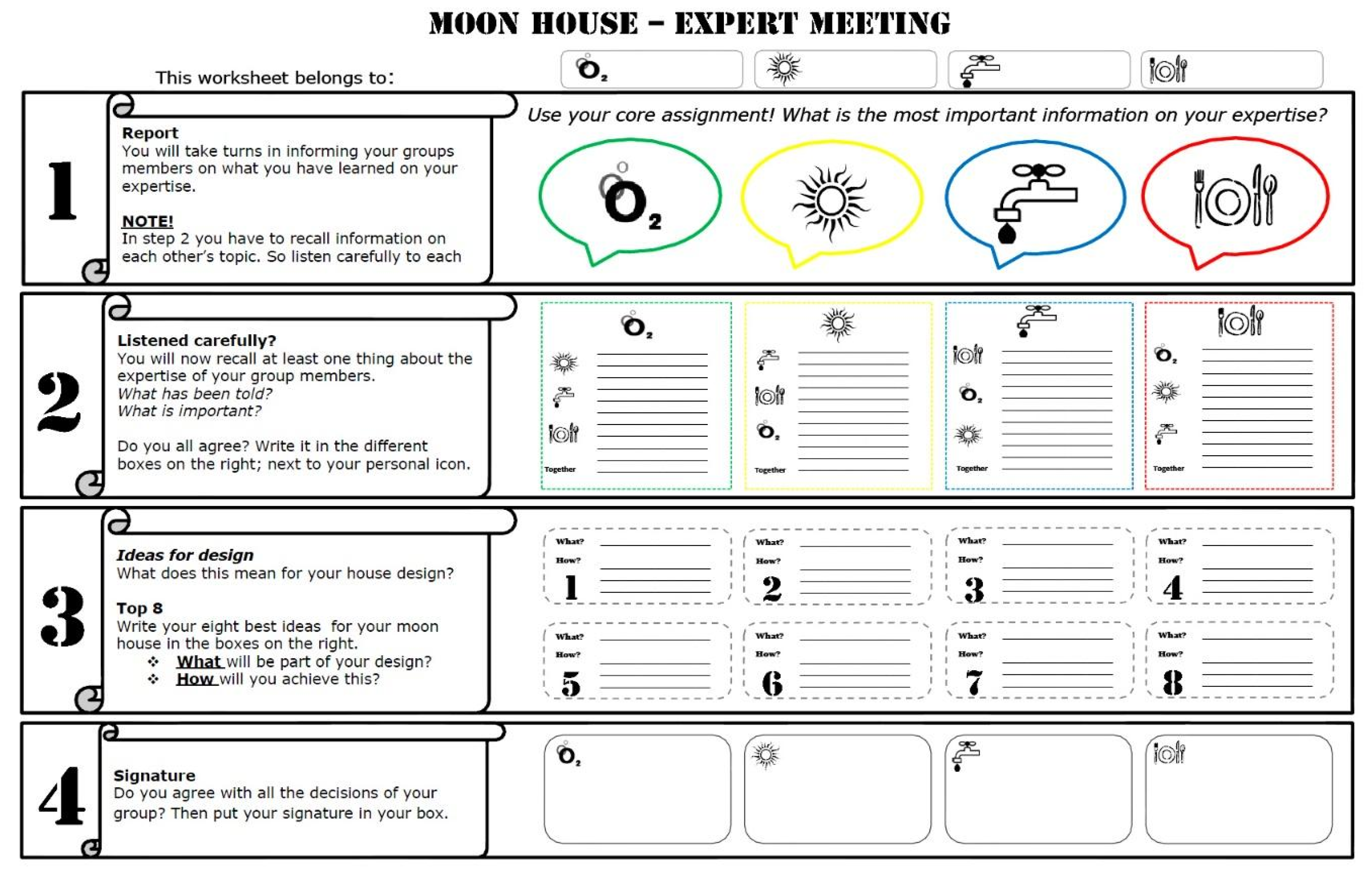
To structure information sharing by the group members in the heterogeneous design groups and to support equal participation, a worksheet was given to the students in the supported groups (see Appendix A) [43]. The worksheet consisted of four steps that were based on social interdependence theory [44], which holds that the accomplishment of goals is influenced by the acts of others.
In the first step, each student contributed to information sharing about the topics studied in the homogeneous expert groups. The aim of this step was to create a feeling of responsibility for the whole group’s performance (i.e., individual accountability). For this to happen, students should feel the need to participate in the group work [44]. As a result, the opportunity to engage in social loafing and free-riding should be reduced and equal participation by each student should be enhanced [45]. Creating individual accountability was done by giving a hint stating that children should recall each other’s information in the upcoming step.
In the second step, students had to identify two important concepts for each topic they were informed about by their group members. The aim of the second step was to make children aware of the assets provided by working together and that they are able to learn from each other (i.e., positive interdependence), which encompasses group members realizing that their success depends on the success of the other group members [44]. For this to happen, each child should have the opportunity to participate in the group work. If this occurs, helping each other, offering social support and information sharing will be enhanced [46].
In the third step, group members were stimulated to create a list of eight concepts that should be considered for inclusion in their moon house design.
In the fourth step, the cooperative process was evaluated. The aim of this step was to determine whether everyone agreed with what was written down on the worksheet and whether each topic had been adequately treated (i.e., group processing). This was done by making the students sign the worksheet, which indicated that they agreed on the design decisions that were made [44]. By engaging in group processing, groups can improve their learning for forthcoming learning situations.
Whereas most aspects of social interdependence theory were paired with one of the steps of the worksheet, face-to-face promotive interaction was encouraged throughout the whole worksheet. This encouragement was present as clear references in the worksheet representing the different topics by the use of different colors and symbols. The aim of doing this was to make children mindful about the topics that were to be discussed. Students could consult their group members who were representatives of a topic to be discussed. The fifth element of social interdependence theory, interpersonal and social skills, was not considered.
The study by van Dijk, Eysink and de Jong (2021) [43], in which the effectiveness of the worksheet was investigated, found that the students in the supported condition engaged in more equal participation in the domain-related discourse, gave more domain-related theoretical explanations, and spent more time on coordinating their cooperation than students in the unsupported condition.
2.3. Procedure
Elementary school students worked in small heterogeneous groups by means of the jigsaw method [47]. With the jigsaw method, students first worked together in homogeneous expert groups in which they gathered knowledge about one specific topic. In that study, students learned about the topics of Light and Heat, Oxygen, Water and Nutrition. Subsequently, students moved to a heterogeneous design group, which included one student per topic. Students’ work in their design groups was video-recorded, and those recordings supplied the data for the current study. In those groups, students discussed what they had all learned in their expert groups, with the aim of designing a house on the moon that could be inhabited by a family of four. Students in the supported condition were aided by a worksheet which aimed to stimulate equal participation in the group by means of social interdependence theory [44]. The unsupported condition did not have access to the worksheet.
2.4. Data Analysis
As the aim of the study is to actively develop theory about how SSRL during cooperative learning should be identified, a grounded theory approach was adopted: the constructivist approach of Charmaz [48]. Following Charmaz, we go through six phases while working with the data: (1) initial coding, (2) focused coding, (3) memo writing, (4) theoretical sampling (5) theoretical coding and, finally, (6) production of substantive theory by means of a theoretical model. It is important to mention that these phases are not followed synchronously but are considered iterative processes.
For the initial coding and focused coding phases, video recordings of the groups in the supported condition were coded using ELAN software [49]. During a former analysis of the data, which has been published in [43], the data had already been subdivided into segments in ELAN. Each segment represented a speaking turn of a specific student and started when a student started to speak and stopped when another student started to speak, when the student was interrupted or when a silence of more than two seconds occurred. Those segments were also used for the current data-analysis but were split up in multiple segments when two different patterns of SSRL were shown during a given segment. Use of segments is suitable for data that entail fundamental empirical problems (i.e., the measurement of SSRL), as this process allows the researcher to remain open to the data and to observe small nuances [48].
In total, 7066 segments were coded, which included the video data for 14 groups whose cooperative dialogue was supported and 11 groups whose cooperative dialogue was not supported. In order to determine interrater reliability, a second coder coded 8.1% (N = 572) of the segments using the codes found during the focused coding phase (Section 3.2). The interrater reliability (i.e., Cohen’s kappa) was considered to be acceptable (κ = 0.73). For the analyses, all segments that were not relevant (i.e., interruptions by the teacher, researcher, or other groups, silences and talk before the start of the assignment) or non-codable were left out, which left 6064 segments for the analysis.
3. Results
3.1. Initial Coding
The first phase, the initial coding process, entailed thoroughly studying the data and assigning codes to segments using open coding [48]. Sensitizing concepts, which are general concepts that provide suggestions about what directions to pay attention to, were created by filtering concepts related to self-regulation and SSRL from the literature. Based on the work of Hadwin et al. [13], SSRL encompasses the categories of metacognition, cognition, behavior and motivation and were therefore selected as sensitizing concepts. In addition, for the category of metacognition, the sensitizing concepts of planning, monitoring and evaluating were used to guide the researcher in developing the first codes regarding metacognition, e.g., [21]. For the categories of cognition, behavior and motivation, no lower-level sensitizing concepts were used. With these sensitizing concepts, the first five videos of the supported condition were analyzed. After analyzing the five videos, data saturation occurred and the second phase started.
Table 1 provides the codes that were found during the initial coding phase, and examples are provided of students who initiated a particular SSRL activity. The examples in the table were translated from Dutch.

Table 1.
Initial coding scheme including code descriptions and examples.
The data used for the initial coding phase consisted of the supported cooperative process of five groups of four students. In total, this sample provided 2258 segments that were coded with ELAN software [49]. After coding five videos, data saturation occurred and the initial coding phase was terminated.
3.2. Focused Coding
During the second phase, the focused coding phase, the researcher filtered out the codes that make the most analytical sense and uses these to code the rest of the data [48]. These are the codes that are the most significant and the most frequently occurring. The goal of the focused coding phase is to determine the adequacy of these codes by coding more data. Codes that were initially added to Table 1 were excluded from the analysis when they were only observed as co-regulation (i.e., code exclusion) and when the codes were considered as transactivity rather than SSRL (i.e., consensus building and asking for clarification). Codes that were considered similar to other codes were also removed (i.e., time management, which was similar to planning task). In this way, crucial concepts that define SSRL and can subsequently be used in order to measure this construct could be identified. As the phases of the grounded theory approach are iterative processes, new sensitizing concepts were added to the list throughout the whole study in order to create a more complete picture of what SSRL entailed during cooperative learning. The coding scheme that was developed in the focused coding phase can be found in Table 2.

Table 2.
Focused coding scheme including code descriptions and examples.
Initially, the data for the supported cooperative processes of 14 groups of four students were coded with the codes determined in the focused coding phase, which consisted of 5126 segments. During the theoretical sampling phase, it became clear that data for groups whose cooperative process was not supported would be useful as well. Therefore, the data for the unsupported groups, which consisted of 1940 segments, were also coded.
3.3. Memo Writing
In parallel with the initial and focused coding phases, the third phase, memo writing, represented the thoughts and annotations of the observations done by the researcher [48]. For each video, a memo was written in order to discover possible codes that could represent SSRL. In this way, categories were elaborated upon, relationships between categories were identified and gaps could be diagnosed. Possible connections with the theoretical model were also suggested.
3.4. Theoretical Sampling and Theoretical Coding
During phase four, the theoretical sampling phase, two processes were carried out. First, another sample of videos, namely, videos from the unsupported groups, was used to find possible additional codes and to substantiate the categories [48]. For the initial and open coding phases, only data from the supported condition were analyzed. However, it was believed that students might behave differently when they receive cooperative support versus when they do not. Support for equal participation in the group might lead to showing SSRL more often than when no support was given for equal participation [19]. Giving some sort of collaborative support that increases group awareness diminishes unproductive transactional activities and thereby students’ cognitive load [50]. Perhaps, students in the supported condition might therefore have more space left in working memory to engage in the transactive processes that involve SSRL. Therefore, data from the groups engaging in cooperative learning while their cooperative dialogue was not supported were analyzed as well. This involved data from 11 groups who engaged in cooperative learning without receiving support from the worksheet. In these groups, the children were given freedom as to how they wanted to discuss what they had learned and what they wanted to include in their moon house. When the additional sample had been selected, those data were used for the focused coding phase as well. Together, a complete list of concepts could be formulated (see Table 2).
Second, the data were used to substantiate the conceptual categories and to create subcategories [48]. After that, the properties of the category should be defined in order to create a clear definition of the category. Finally, the codes are sorted among the categories and subcategories can be created. This is done by searching for similarities between the codes and categories. In the case of the current study, it was investigated whether the categories that were provided in the definition of SSRL (i.e., metacognition, cognition, behavior and motivation) by Hadwin et al. [13] could fit the codes that were identified during the initial and focused coding phases. Therefore, each of these categories was described, and it was determined whether the codes that were found fit these descriptions. When similarities were found between the descriptions of codes, subcategories were created.
Every code suited one of the four categories Hadwin et al. [13] used to describe SSRL. Data analysis showed that some codes were related to the organization of the task, whilst other codes related to the organization of group processes. Therefore, the distinction was made between regulating task-related activities and social activities. In a similar matter, in research by [39], they also divided codes based on whether they belonged to task regulation or regulation of group processes. Within these two groups, subcategories could be created when processes were believed to have overlap or occurred together. In Table 3, the categories and subcategories are given. On top of that, codes belonging to these subcategories could be divided into even more concrete categories, while considering whether these codes belonged to task or group regulation.

Table 3.
The four categories of SSRL, their subcategories and their codes.
The theoretical sampling phase is followed by the theoretical coding phase, in which the codes and categories are related to each other can be determined [48] and to what extent they occurred. This is what is done in the theoretical coding phase, being the fifth phase of the research method. In order to determine relationships between categories, Charmaz [48] made use of analytic categories. As this study aims to explore how SSRL is manifested, how these behaviors relate to each other and under what circumstances they are performed, the analytic categories of conditions and consequences were used. For conditions, how codes were presented under several conditions and what processes were necessary for certain categories to occur was described. When a difference in the manifestation of a certain category between the unsupported and supported condition was observed, this was described. For consequences, what typically happened after a certain pattern of behavior was displayed was described. The importance of categories was also underlined by describing what happened when a certain category was not present in the group’s performance. Additionally, it was determined to what extent the SSRL and co-regulation codes (Table 4 and Table 5 respectively) and the SSRL subcategories (Table 6) occurred. Finally, it was determined how often the SSRL codes and subcategories were observed in relation to the other codes and categories (Table 7 and Table 8, respectively) in the supported and unsupported conditions. In the sections below, the results of the theoretical sampling and theoretical coding will be discussed.

Table 4.
Mean scores, percentages, standard deviations and minimum and maximum scores for SSRL.

Table 5.
Mean scores, percentages, standard deviations and minimum and maximum scores for co-regulation.

Table 6.
Mean scores, percentages, standard deviations and minimum and maximum scores for SSRL per subcategory.

Table 7.
Mean proportional contributions (%) to SSRL per code compared to the other codes.

Table 8.
Mean proportional contributions (%) to SSRL per subcategory compared to the other subcategories.
3.4.1. Metacognition
As already proposed in existing theory, metacognition is one of the categories that identifies SSRL [18] it involves metacognitive planning, monitoring, and evaluating, e.g., [21]. The codes that were discovered in the current study for the category of metacognition also belonged to one of these three subcategories. The aim of using metacognitive strategies is for students to understand, monitor and control what they are learning [51]. Overall, most of the groups applied metacognitive strategies such as planning, monitoring, or evaluating (88.5% of the groups, M = 7.31, SD = 10.00). The large standard deviation indicates large differences between groups. Some groups frequently enacted metacognitive strategies while other groups did not engage in any metacognitive strategy use.
Task Planning
The first code assigned to the task planning subcategory is goal setting. In the current study, this always entailed the group creating shared task goals together. According to Pintrich [52], goal setting is a process that occurs in the forethought phase of self-regulation. However, goal setting was occasionally observed throughout the course of the task. As the task for the supported group contained four steps, it also happened that goals were set when the students were about to start the upcoming step. Additionally, students discussed and created shared goals when the goal was unclear.
The second code for the task planning subcategory is also called task planning. This entails creating a shared plan for the task in which the group members agree on which tasks should be executed at a particular point of time.
More than half of the groups engaged in task planning (69.2% of the groups, M = 2.73, SD = 3.00). Despite the fact that no significant difference was observed between the supported and unsupported condition regarding the frequency of occurrence of SSRL [F(1, 24) = 0.798, p = 0.381], different patterns could be detected in the unsupported condition. When students in the supported condition created a shared plan, students adhered to this plan throughout the exercise. This could be attributed to the fact that the worksheet that was provided to the students in the supported condition already consisted of four steps in a specific order. Although it was not specifically mentioned that the students were obliged to work with this order, students always adhered to this structure. Students in the unsupported condition were not provided with the worksheet, and therefore had to make a plan themselves. What stood out was that students often did not adhere to this plan throughout the exercise. This might be explained by the fact that no suggestions for a complete shared plan were made in the unsupported condition. As a result, students were jumping from one step to another and had chaotic discussions. It was also observed more often in the unsupported condition than in the supported condition that the plan was not created at the beginning of the exercise. In those cases, the students just started mentioning ideas for their moon house without elaborating on them. Therefore, it might be concluded that the task planning in the supported condition was of higher quality than in the unsupported condition.
When task planning did not occur or was of low quality, this led to more off-task talk, which frequently entailed negative social interactions. Subsequently, students lost task focus and engaged in even more off-task talk. Research by Miller and Cohen [53] supports this pattern, by stating that planning is a necessary prerequisite for learners to diminish interference from possible distraction. Creating a shared task plan might, thus, help students to stay focused on the task. When students were not focused on the task and possibly even engaged in negative social interactions, this required even more shared regulation skills along the lines of motivational strategies or correcting behavior.
Group Planning
With regard to group regulation, coordinating collaboration is a code within the group planning subcategory. This process means that the group decides together who works on certain tasks and in which order. Throughout the exercise, students also occasionally realized that coordinating collaboration was necessary when they were not working in a specific order and chaos occurred.
A little more than half of the groups were involved in group planning (57.7% of the groups, M = 2.38, SD = 5.29). As shown by the large standard deviation, a large difference could be observed between groups who did and did not engage in group planning. This process was mostly co-regulated (2.81%) rather than socially shared (0.78%). To clarify, this process typically involves one student coordinating the collaboration (i.e., giving tasks to other students or monitoring whose turn it is).
For group planning to occur, some conditions should be met. First, as group planning occurred not only at the beginning but also throughout the assignment, task monitoring should take place. If students monitor the task progress, they might see which students still have to explain something. In addition to that, if students monitor their task progress, students will keep in mind that when they face a new step, discussing a new group plan might be necessary. Second, students should see the added value of every student contributing to the group work in order to create shared knowledge.
When collaboration was not coordinated, it could be observed that students became confused about the planning and division of labor later in the course of the assignment. This was manifested as discussions about whose turn it was, who would be next, and why. Especially in the unsupported condition, this led to a negative group atmosphere, as students would argue about whose turn it was about to be. In the supported condition, that pattern did not stand out. A reason for this could be that students in the supported condition had the worksheet which presented an order for the subjects to be discussed. When group planning was not discussed in the supported condition, groups relied on the order that was shown on the worksheet. This goes together with task monitoring, as students kept an eye on what information should still be shared and how many students still had to share information. However, this often did not entail shared task monitoring, but a lower level of regulation that involved one student monitoring who should share information next. Yet, as a result, negative interactions between group members were restricted. Furthermore, group planning is important to make sure everyone has the opportunity to share knowledge and learn from others; hence, shared knowledge could be created. When collaboration is not coordinated together and task division is unclear, some students do not get the chance to share what they have learned about their topic or to learn from others. Therefore, knowledge is divided among group members rather than shared.
Task Monitoring
Four codes were identified that fit the subcategory of task monitoring: monitoring task progress, monitoring task performance, monitoring comprehension and task perceptions. Research by Rogat and Linnenbrink-Garcia [54] who identified categories for socially shared regulation in collaborative mathematical problem solving, found three codes within the category of monitoring that are similar to monitoring progress, comprehension and task perceptions. In their article, these were called monitoring progress, content monitoring and monitoring plan, respectively. Monitoring performance was not observed in their study.
The first code within the task monitoring subcategory is monitoring task progress. This entails students monitoring together which (parts of the) tasks they have already performed and what still needs to be done.
The second code for the task monitoring subcategory is monitoring task performance. This entails students monitoring together how well they are handling the task or the quality of provided information.
The third code for the task monitoring subcategory is monitoring comprehension. This entails students monitoring together whether they understand the task or explanations given by other students.
The fourth code within the task monitoring subcategory is task perceptions. This entails students monitoring their shared attitudes towards the task.
In total, more than half of the groups monitored the task collectively (65.4% of the groups, M = 3.5, SD = 4.02) What stands out specifically is that task perceptions were shared by only 11.5% of the groups, and only 0.16% of the codes assigned in this study involved processes of building shared task perceptions. This pattern was also found in a study by Hadwin, Malmberg, Järvelä, Jarvenoja and Vainiopää [55], who indicated that students often failed to discuss their shared task perceptions and to understand the task completely.
The large standard deviation stands out in the current study, which indicates large differences between groups. This could be identified throughout the observations as well; some groups frequently monitored their shared performance, comprehension, progress and task perceptions, while other groups did not do this at all during their collaboration. It also stands out that some groups completely relied on monitoring by the teacher or researcher. Some groups did not spontaneously engage in task monitoring but did so when the teacher prompted the students to think about these processes. The teacher typically did this by posing questions such as “How are you keeping up with the task?”, “How are you doing?” or “Which step are you performing now?”. This is also what happened in the current study. When students lacked task understanding, typically no discussion about shared perceptions took place in order to create shared understanding. When groups did not monitor the task, the students also typically overlooked some of the steps that were necessary in order to complete the task successfully. These effects were more negative for the unsupported condition, as they did not possess the worksheet the supported condition could use in order to check their progress. In the supported condition, the students regularly checked the worksheet in order to monitor their progress and checked which steps should still be executed, which reduced the likelihood of missing steps or ignoring the contribution of certain group members to the task. On top of that, when certain group members did not fully understand the task or an explanation of a peer, but that situation was not recognized or responded to, knowledge would be divided rather than shared.
When the task was monitored, students kept an eye on whether their shared goal was about to be reached, which requires shared understanding. Furthermore, it could be observed that groups monitored the task in order to be on the same page with their ideas and hence create shared understanding. Additionally, the observations made it clear that task monitoring also involved including students in the group work when they had not shared information yet. When students monitored the task, sometimes they realized that not all information had been shared yet.
Group Monitoring
Monitoring group performance is a code falling under the group monitoring subcategory. This code entails assessing how well the group is functioning throughout the execution of the task.
Only one group (3.8%) monitored their group performance, which was coded for only 0.04% of the total number of segments. This pattern was also found in a study by Haataja, Malmberg and Järvelä [56], who observed that task-related behaviors are more often monitored, as students believe these are more task-related and therefore should be checked on more often. As group monitoring only happened on one occasion, it is difficult to determine what conditions are necessary for group monitoring to occur. Monitoring group performance can result in a communal awareness of positive and negative group patterns and will eventually lead to the adaptation of these patterns [57]. When a group did not monitor their group performance together, group members did not become aware of negative behavioral patterns and these might not be solved throughout the collaboration, which would result in more negative social interactions. When groups engaged in off-task behavior or negative behavior, this was mostly allowed by the group members.
Task Evaluation
For the task evaluation subcategory, only the code for evaluating the task outcome was identified. This code entails students evaluating at the end of the task whether they are satisfied with the outcome.
Only one group (3.8%) engaged in task evaluation, which was coded for 0.07% of the total number of segments. Therefore, when looking at metacognition, task evaluation occurs much less often than task planning and task monitoring. Nevertheless, the context of this assignment might have played a role here. When the students were done with the assignment, they were instructed to call the researcher, who subsequently turned off the camera and audio recording. Accordingly, it is possible that some groups engaged in task evaluation after the observation was terminated. However, other studies have also mentioned that task evaluation does not occur often and is of low quality when it happens [58].
As only one group evaluated their task outcome, it is impossible for now to identify conditions under which task evaluation occurs. However, all in all, it can be concluded that task evaluation is a scarce process and does not happen out of the blue. Research by Winne [59] identified that for task evaluation to occur, students should monitor whether the end product matches their standards. As setting up group standards (i.e., goal setting) was scarce in this study, it is not a surprise that task evaluation did not occur often. Students might not have evaluated the task outcome, as they were in most cases not aware of the standards held by their group members.
The group that evaluated the task outcome did this very superficially; namely, they discussed whether they agreed on what was written down on the worksheet. They did not argue about why they agreed on something, or what could be improved. In addition, they started the evaluation of the task outcome because the worksheet prompted them to do that at the final step. This makes it even more remarkable that only one of the groups engaged in task evaluation. As the evaluation was very superficial and did not entail any concrete statements about what could be improved in future collaboration, it seems likely that evaluating the task outcome would have few consequences for the performance of this group.
3.4.2. Cognition
The second category involved in SSRL is cognition. This category includes cognitive strategies that learners apply in order to develop shared knowledge and beliefs. The category of cognition has one cognitive task-related subcategory, containing two codes. No group-related subcategory was identified.
The aim of using cognitive strategies is to understand one another and, consequently, to build shared knowledge. Overall, just a little more than half of the groups enacted shared cognitive strategies (53.8% of the groups, M = 1.85). This low number is not a surprise, as research by Mercer, Dawes, Wegerif and Sams [60] indicated that children need to be supported in how to use language to reason, consider information together and negotiate in order to come to collective ideas. When groups adopted shared cognitive strategies more frequently, during the observation it was seen that students listened to each other more often and asked each other more questions in order to understand what someone was saying. It seems that this has a strong motivation component, as trying to understand what others mean and taking the perspective of another student require motivation.
Problem-Solving Strategies
The second task cognition-related code was problem-solving strategies. This entails learning strategies that students share in order to approach a shared problem and subsequently create shared beliefs. These learning strategies varied from getting additional materials such as extra sheets of paper to explain things better to their peers to a voting system to determine the best ideas for the moon house. Learning strategies were typically used as a form of problem-solving strategies, as learning strategies were negotiated when a group experienced difficulties or when they wanted to make the task easier for themselves.
A little less than half of the groups undertook shared problem-solving strategies (42.3% of the groups, M = 1.00, SD = 1.44). In order for students to come up with problem-solving strategies, they should acquire adequate metacognitive skills (e.g., monitoring one’s own knowledge) that help them to indicate how, why and under which circumstances a learning strategy should be implemented. So, it can be concluded that cognitive strategies and metacognition are connected to each other, as the ability to monitor is important to identify whether, and when, problems arise.
When students collectively applied problem-solving strategies to address their problem, the group was able to solve the problem and create shared understanding. This was, for example, shown in a situation in which a group decided to draw things on a sheet of paper in order to explain their ideas for the moon house. In that case, the group collectively arranged that every group member understood what was about to be organized for the moon house.
Verifying
The first code related to task cognition that was identified during the coding process was verifying. This entails discussing whether one’s provided information is correct and subsequently building shared knowledge and understanding.
A little less than half of the groups engaged in collective verifying (42.3% of the groups, M = 0.88, SD = 1.66). Verifying has been observed in multiple other SSRL studies, e.g., [37]. It emerged that more groups more often co-regulated verification rather than sharing it collectively (69.2% of the groups, M = 2.27, SD = 2.23).
Just as for problem-solving strategies, motivation seemed to play a part in the occurrence or absence of verification of thoughts. This is because students who engaged in verifying were willing to create shared knowledge, for which motivation is needed.
The consequence of verifying one’s thoughts is building shared knowledge. Namely, students check together whether they understand each other’s provided information.
3.4.3. Behavior
The third main category is behavior. This entails regulating the behavior of group members in order to create shared knowledge. However, for this category, it was difficult to find examples of shared regulation of behavior. The regulation of behavior was co-regulated rather than socially shared in almost every case. Therefore, we wondered whether, for example, regulation that involved including students in the group work together had added value over a situation in which one student included another student, as the effect in both situations would be the same: All students would be included in the groupwork again and they could continue working on their shared goals. However, in order to stay true to the definition of SSRL, which concerns shared regulatory strategies instead of one student regulating other students [12], only the regulation of behavior that was shared among group members was taken into consideration in this study.
All in all, the behavior category consists of four group-related codes. These codes are divided between two subcategories, positive social interactions and negative social interactions. Research by Rogat and Linnenbrink-Garcia [54] indicated that active listening and group cohesion are aspects of positive social interactions as well. However, in this study, we found that active listening was difficult to observe, and therefore, it was not included in the coding scheme. Rogat and Linnenbrink-Garcia [54] described group cohesion as “Conveying that the group functions as a team (rather than as individuals) by working together, referring to the group as ‘we’” (p. 384). As the current study deals with cooperative learning in which working together is necessary in order to achieve a shared goal [3] and non-cooperating groups were not observed, group cohesion was not included in the coding scheme.
The aim of controlling behavior during cooperative learning was to either create or maintain a positive group climate. Overall, it stood out that the regulation of behavior occurred much more often as co-regulation (92.3% of the groups, M = 9.29) than socially shared regulation (26.9% of the groups, M = 0.5). Yet, it was considered that groups are capable of regulating behavior collectively as well.
Positive Social Interactions
The code identified as positive social interaction is inclusion. This entails involving group members in the group process when group members are curious about the input of others, when a person does not engage in the task or when a group member has been excluded or disrespected by other group members.
In total, only 15.4% of the groups regulated positive social interactions (M = 0.23, SD = 0.59). Regarding positive social interactions, the group as a collective could ensure that everybody was included in the group work. However, inclusion was mostly a co-regulated process (65.4% of the groups, M = 1.58) rather than SSRL. Typically, one student included one other student who was not cooperating, ignored by group members or more aloof than the others. Subsequently, the whole group was involved in the group process again and shared knowledge could be built.
The regulation of positive behavior took place under several conditions. First, positive behavior was regulated when the group was engaging in off-task talk and told one another to participate in the groupwork again. Second, the regulation of positive social interactions occurred when a student seemed to be more aloof than the others. In this situation, the student was included in the groupwork and shared knowledge could be built. For that reason, positive social interactions can be connected to group planning. Namely, inclusion might be necessary for shared group planning to occur in cases in which not every student is participating in the group work.
Research by Rogat and Linnenbrink-Garcia [54] mentioned that groups with more positive socioemotional interactions engaged in higher quality planning, monitoring and behavioral interactions than groups with more negative socioemotional interactions. In the current study, positive social interactions did not seem to be a prerequisite for shared metacognition to occur. Shared metacognition also occurred in groups who did not have many positive social interactions and even when groups had some negative social interactions. However, groups who stand out for their negative social interactions also stood out for showing little SSRL. Therefore, it might be concluded that regulating a positive group atmosphere does not seem necessary for SSRL to occur, but it does seem to have a positive influence on its occurrence. However, as the only regulation of positive behavior was inclusion, it can be questioned what would have happened if more positive behaviors had been found. A student might feel more motivated when he or she sees that his or her opinion or contribution is valued by the group members. Although motivation was not measured in this study, it could be observed that when students’ contributions were valued by the rest of the group, they would engage with the task again.
Negative Social Interaction
The first code identified as negative social interaction is disrespect. This entails making negative comments about group members, bullying or annoying them. Disrespect occurred as negative remarks about a person, or as negative remarks about content-related issues. The latter does not involve substantiated disagreements, but attacking the input of others, which involves making fun of a student’s input or criticizing input by calling it, for example, ‘stupid’.
The last code identified as regulating negative social interaction was correcting behavior. This entails commenting on the inappropriate behavior of group members in order to make them stop that inappropriate behavior.
Just as for positive social interactions, 15.4% of the groups regulated negative social interactions (M = 0.27, SD = 0.67). The regulation of negative social interactions also occurred more often as co-regulation (92.3 % of the groups, M = 8.34) than as socially shared.
Negative social interactions occurred under several circumstances. Mostly, they occurred when group members were involved in off-task talk or off-task behavior. Additionally, they emerged when the group did not make a clear group and or task plan. In this particular situation, disrespect was manifested as arguments about who was allowed to tell something and what should happen at a specific point of time. The negative social interactions were regulated in situations in which the group was willing to continue with the task. This could be concluded from the fact that regulation of negative behavior always had the intention to get the student to stop acting off-task or in any other negative way and to engage with the task again. Yet, negative social interactions were not always regulated, as this off-task talk or behavior was mostly allowed by the group.
Interestingly, groups who stood out by their negative social interactions engaged very little in SSRL. This might be clarified by research by Rogat and Linnenbrink-Garcia [54], who stated that groups with more positive socioemotional interaction engage in higher quality planning, monitoring and behavioral interactions than groups with more negative socioemotional interactions. Therefore, groups who engage in more negative interactions might engage in lower quality planning, monitoring and behavioral interactions (i.e., less SSRL) than groups with more positive social interactions. However, when negative social interactions were regulated by the group, the group was able to continue with the task. Nevertheless, regulating negative social interactions was not always effective over time, as it could be observed that groups frequently kept on engaging in off-task talk or negative social interactions throughout the course of the task. In addition, when negative social interactions were not regulated, negative social interactions and off-task talk persisted.
3.4.4. Motivation
The last main category is motivation, which is a key factor in self-regulated learning according to many researchers, e.g., [61]. Throughout the coding process it became clear that in a cooperative setting, students find strategies to motivate group members together. Just as for the behavior category, for the motivation category, the distinction between co-regulation and SSRL was not clear for all codes.
In all, the motivation category consists of two task-related codes, which are clustered together under the task motivation subcategory. Group-related codes were not found for the motivation component.
The aim of using motivation strategies during cooperative learning was to maintain or foster the motivation of the group. Overall, less than half of the groups engaged in collective motivation strategies (30.8% of the groups, M = 0.5, SD = 0.86).
Task Motivation
The first code that could be classified under task motivation is stimulating task focus. This entails students motivating other students to engage with the task, mostly when they perform off-task behavior. This could involve verbally showing that a peer should engage with the task again, mentioning that a student should do his or her best or encouraging the student to tell the answer.
The second code for task motivation is praising. This involves giving positive remarks on the contribution of the group.
About a third of the groups regulated their task motivation collectively (30.8% of the groups, M = 0.50, SD = 0.86). Just as for behavior, it appeared that students mostly co-regulated their motivation (80.8% of the groups, M = 3.88) rather than collectively regulating it. In most cases, one student motivated one of the other students when he or she was engaging in off-task talk.
Group members should put effort into understanding other group members, for which intrinsic motivation is required. Thus, motivation is a prerequisite for SSRL to emerge [62]. Unfortunately, this study did not measure motivation with a questionnaire as was done in the study by Järvelä and Järvenoja [62], so therefore that claim cannot be made based on the current study. In addition, relating the frequency of shared motivational strategies to the frequencies of other areas does not give much information, as this does not indicate how motivated groups in fact are.
Although motivation and motivation regulation are conceptually different, in the current study, it appeared that when the group applied motivation strategies to motivate each other, the group member who initiated a motivational strategy was willing to create shared knowledge. This was manifested by mentioning that he or she believed it was important to stay focused and to share ideas with each other. This happened, for example, during situations in which stimulating task focus was enacted. Stimulating task focus always occurred when the group disengaged from the task due to diminishing motivation or interest for the task. Additionally, praising others is important in order to create a positive group atmosphere [35]. Subsequently, students feel more motivated to complete the task [36]. Regulation of positive social interactions is also important.
3.5. Theoretical Model
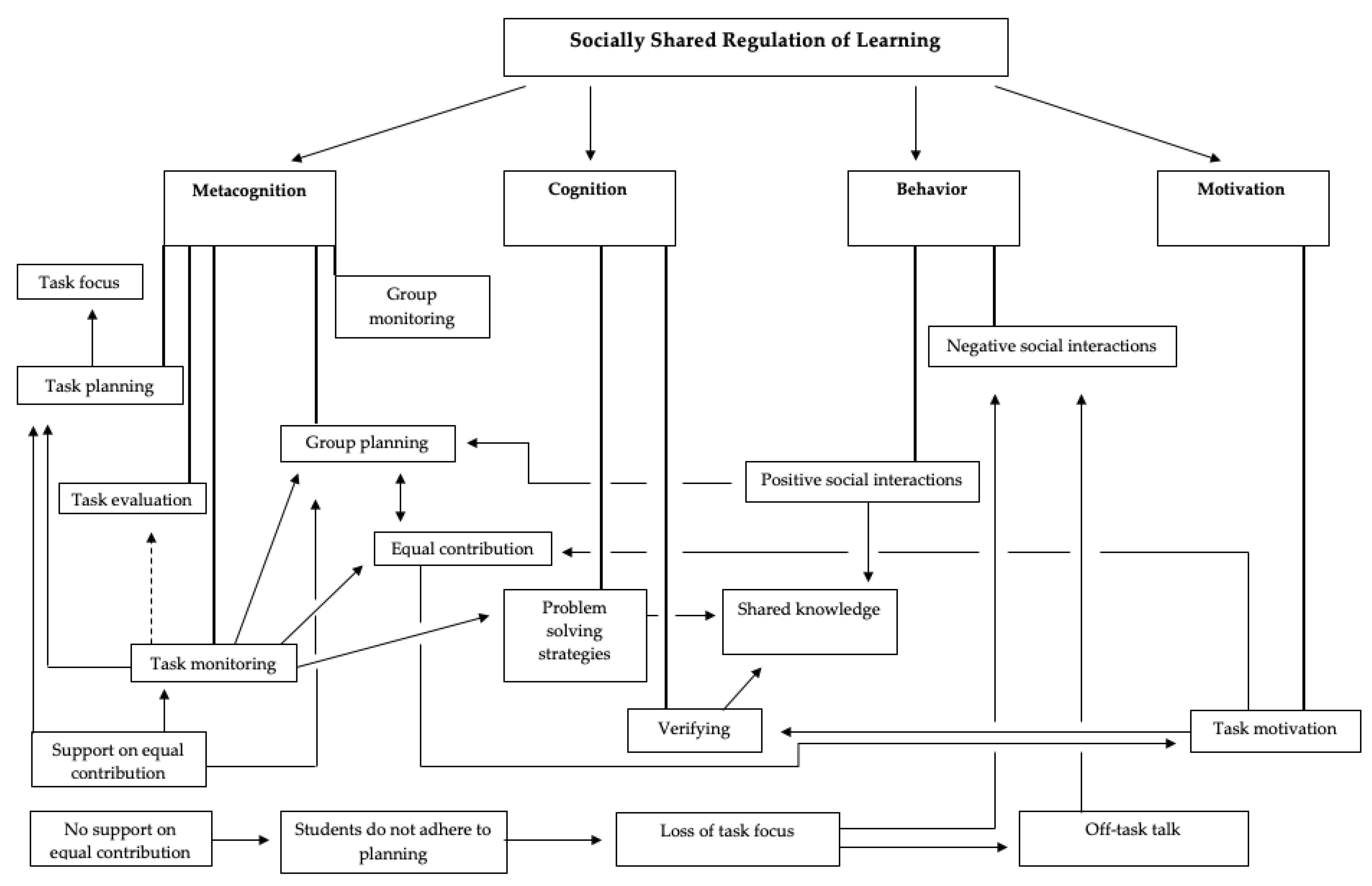
In Figure 1, the theoretical model (phase 6) of how SSRL is manifested during cooperative learning is shown. In grounded theory research, a model portrays a collection of concepts and their relationships integrated in a cohesive model [63]. The links that were discovered in the theoretical coding phase were used to create links in this model. First, in this theoretical model, it can be seen that SSRL consists of four categories: metacognition, cognition, behavior and motivation. The subcategories linked with these categories are identified with bold lines between the categories and subcategories. Links between subcategories were created by identifying the prerequisites and consequences of each of the subprocesses of SSRL. Continuous arrows were used to identify links that were observed in the current study. Intermittent arrows were used to identify links that were not observed in the current study but were observed in the literature (this refers only to the link between task monitoring and task evaluation).
Figure 1.
Theoretical model.
4. Discussion
The aim of the current study was to investigate how SSRL is manifested during cooperative learning. The effect of equal participation was also investigated by observing the SSRL processes in two conditions. The supported condition was assisted by a worksheet that fostered equal participation [43]. The unsupported condition did not have access to the worksheet. The results showed that SSRL is a scarce process which manifests itself differently when groups are not equally supported.
The first aim of the study was to identify SSRL by means of analysis of the video-data. According to the literature, SSRL involves collectively sharing metacognitive, cognitive, behavioral and motivational strategies in order to achieve a shared group goal [13,18]. The current study supported the fact that students are able to collectively set up strategies to regulate metacognition, cognition, behavior and motivation of the group as a whole. This study also supported the creation of subcategories within these categories. By means of information gathered through observations, this study led to the creation of a theoretical model of the manifestations of SSRL during cooperative learning. Although this study aimed to investigate SSRL as a whole, it especially underlines the importance of the regulation of social activities. Many studies have only focused on the task-related aspects of regulation [20]. The current study, however, points out that regulation of social aspects involves both the products and prerequisites of SSRL skills. This is in line with research by Hadwin et al. [13].
Additionally, the frequencies of the occurrence of SSRL were computed. First, it stood out that SSRL rarely occurred in the context of this study. In total, only 5.69% of the segments could be coded as manifestations of SSRL. Second, only three subcategories of SSRL processes were observed to be performed by more than half of the groups. All other subcategories were observed in less than half of the groups. This is in line with research by Järvelä et al. [14], who claimed that students often fail to regulate their learning process. Apart from SSRL being a scarce process, some subprocesses involved considerable between-group differences regarding the frequency of occurrence. It remains unclear what causes the difference between the occurrence of SSRL between groups and, more specifically, what individual differences might cause these differences [12]. Yet, it could be questioned whether the failure to use all of these skills was detrimental for the students’ learning processes. For some skills, it could be observed that when they were lacking, students fell into unproductive patterns of cooperative learning. When students did not create a shared plan or division of labor, this led to confusion among the students, which led to off-task talk and sometimes even negative social interactions. When negative social interactions were not regulated, this pattern of negative social interactions persisted. So, these skills could be considered effective for a productive cooperative learning process, as not engaging in these shared processes will lead to less time spent on the task. However, it is not known whether this would also negatively affect their learning performance.
For some SSRL skills, it can also be questioned whether it is important for them to be socially shared instead of co-regulated. For example, it could be observed that the codes that belonged to the categories of behavior and motivation, in particular, were more often co-regulated rather than socially shared (Table 4 and Table 5). Within these categories, behaviors that were socially shared were even more scarce. Some situations in which students collectively shared motivation strategies also seemed quite artificial. Therefore, it can be questioned whether collectively regulating behavior or motivation is a natural process for students to engage in and whether it has additional value over co-regulation. For example, one student correcting the behavior of one other student (i.e., the student co-regulates the other student) so that the whole group can work together to achieve the shared goal might promote the same outcome as multiple students correcting one another’s behavior (i.e., SSRL). Therefore, the fact that behavior and motivation were mostly not socially shared did not seem to be a problem in the current study. However, it should be mentioned that the importance of some skills was not easily determined. For instance, task evaluation that takes place after the execution of the task, so the exact effects of task evaluation could not be observed. However, as the students’ level of task performance was not investigated, it cannot be concluded whether the lack of some SSRL skills has negative effects on the task outcome.
The second aim of this study was to investigate whether groups who received collaborative support to increase equal participation would show more SSRL than groups who did not receive this support. This research demonstrates that no significant differences could be found regarding the frequency of occurrence of the SSRL subprocesses between the supported and unsupported condition. This seems to be in contrast to what was suggested by Volet et al. [19] who claimed that equal participation in groups leads to higher-level regulation (i.e., SSRL). This also contradicts the assumption that the collaborative support might increase group awareness and consequently diminish unproductive off-task talk, which decreases students’ cognitive load [50]. Yet the reason that the support did not cause significant differences between the unsupported and unsupported group may be that the support was mainly focused on equal sharing of task-related content [43]. Consequently, students were primarily occupied with sharing information rather than sharing regulatory strategies. On top of that, the fact that students in the supported condition received a worksheet might have taken away their freedom to engage in SSRL, as the worksheet slightly structured the assignment already. For example, the worksheet already presented an order for the topics that were about to be discussed. Although it was not stated explicitly that students were to work in this order, groups in the supported condition mostly relied on following that order, sometimes without discussing it. The planning of the task and collaboration was therefore more often monitored by one student, who kept an eye on the worksheet. Additionally, the worksheet also presented some steps that should be performed in specific order and hints were given about important points to discuss at particular moments. This might also have taken away the opportunity to regulate task or group planning or learning strategies collectively. With this line of reasoning, one could expect that these SSRL skills would have occurred even less often in the supported condition in comparison to the unsupported condition. However, as can be observed in Table 7 and Table 8, this was not the case. Therefore, it might be that equal participation, at some points, fostered higher levels of regulation (i.e., SSRL) but that this effect was cancelled out by the presence of the worksheet.
4.1. Implications
The outcomes of this study provide mainly theoretical implications rather than practical implications. This study presented a focused coding scheme (Table 2) that might benefit researchers in the field of SSRL when they wish to observe SSRL themselves. Furthermore, this study substantiates the existence of several SSRL processes that were not given sufficient attention in previous research. The theoretical model (Figure 1) provides a new basis for how SSRL is manifested during cooperative learning. More specifically, the current study gives an overview of SSRL skills that are hardly ever shown by students, but were considered as necessary for an effective cooperative learning process.
4.2. Limitations and Future Research
The first limitation of this research was that some subcategories were difficult to substantiate and link to the other subcategories, as they seemed to occur quite infrequently. This can be confirmed by the research of Volet et al. [38], who mentioned that it is difficult to distinguish between collaboration, knowledge co-construction and social regulation. Research by Malmberg, Haataja, Seppänen and Järvelä [64] added that some SSRL processes are difficult to measure by the unaided eye. They described an example of a group of three students in which two of the students verbally expressed that they were monitoring the task while the third student did not verbally express that he was monitoring. Does that mean this student was not monitoring the task? As SSRL is a result of individual self-regulation, it is difficult to determine whether the whole group of three students was mentally synchronized. Therefore, Malmberg et al. [64] measured students’ physiological synchrony by measuring electrodermal activity with wristbands during the collaborative process. Hence, it could be determined whether they monitored the task jointly. Physiological measurement instruments might therefore be something to consider in future research about SSRL.
A second limitation involves the specific context of the study. It might be the case that certain SSRL behaviors are just scarce and are not naturally displayed by student when they are not instructed to do so. However, this might also have happened because only the context of the Jigsaw method was investigated [43]. As the jigsaw method has quite a specific division of labor and group composition, it might be the case that SSRL plays a smaller role than in other forms of learning where students have to create their own roles. To obtain a better picture of the manifestation of SSRL, research should also investigate different cooperative learning contexts.
The third limitation concerned that students engaged very little in collective regulation of motivation and behavior. This might be explained by the fact that the element of appropriate use of social skills from social interdependence theory [44] was not incorporated in the collaborative support, which therefore is one of the limitations of this study. Young children often experience difficulties in using adequate social skills (e.g., decision making, conflict management) during cooperative learning, which could also refer to regulating social situations during cooperative learning. Using adequate social skills during cooperative learning requires extensive training [65]. The fact that the worksheet mostly prompted task-related behavior [43] can also explain why students were mainly occupied with task-related regulation rather than regulation of social aspects. Future research might investigate how these social skills can be taught in order to be effective for SSRL. Another limitation regarding the collaborative support for equal participation is that the worksheet might have cancelled out some of the effects of equal participation on SSRL. To test whether this is true, future research should investigate how to foster equal participation without giving the students a framework that takes away the opportunity to engage in SSRL.
Furthermore, this study observed large differences in the frequency of occurrence of SSRL between groups. This study was not able to identify why these differences occurred. However, during the observations, it stood out that some students came up with SSRL strategies but received no response from their group members. Research by Rogat and Linnenbrink-Garcia [54] observed the same phenomenon. Therefore, it might be useful to investigate whether individual differences play a role here, and if so, which ones. This is supported by Panadero and Järvelä [12], who mentioned that it is important to look not only at the group process, but also at the individual differences that students bring to the group. Then, one can better understand what is necessary for effective SSRL to occur.
5. Conclusions
The current study investigated how SSRL is manifested, what is necessary for the SSRL skills to emerge, and what the consequences of their occurrence are. This resulted in a theoretical model of SSRL, which can be the basis for further research on SSRL. Furthermore, the study indicated that equal contribution did not influence the frequency of occurrence of SSRL, but did influence the SSRL processes that were observed. Groups who do not equally contribute to the group process show dysfunctional group interactions to a higher extent than groups who do contribute equally. Appreciating each other’s contributions seems to be of importance for structured and effective group processes. Concludingly, SSRL is a scarce process, which should be carefully addressed in education to overcome unstructured collaborative processes when children learn together.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.H., A.M.v.D. and T.H.S.E.; methodology: L.H. and A.M.v.D.; Formal analysis: L.H. and A.M.v.D.; investigation: A.M.v.D.; resources: A.M.v.D. and T.H.S.E.; writing—original draft preparation: L.H.; writing—review and editing: A.M.v.D. and T.H.S.E.; supervision: A.M.v.D. and T.H.S.E.; project administration: T.H.S.E.; funding acquisition: T.H.S.E.; data Curation: L.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study was conducted according to the rules of the faculty of the department of Behavioural Management and Social Sciences (BMS) of the University of Twente and approved by the Ethics committee of the BMS (Project number 200295, date of approval: 3 April 2020).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in this study.
Data Availability Statement
The data of this study is not publicly available due to the privacy of respondents.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Appendix A
References
- Jolliffe, W. Bridging the gap: Teachers cooperating together to implement cooperative learning. Education 2015, 43, 3–13. [Google Scholar]
- Dyson, B.P.; Linehan, N.R.; Hastie, P.A. The Ecology of Cooperative Learning in Elementary Physical Education Classes. J. Teach. Phys. Educ. 2010, 29, 113–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Slavin, R.E. Co-operative learning: What makes group-work work? In The Nature of Learning: Using Research to Inspire Practice; Dumont, H., Istance, D., Benavides, F., Eds.; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2010; pp. 161–178. [Google Scholar]
- Slavin, R.E. Cooperative learning in elementary schools. Education 2014, 43, 5–14. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, D.W.; Johnson, R.T. Making cooperative learning work. Theory Pract. 1999, 38, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirschner, P.A.; Sweller, J.; Clark, R.E. Why minimal guidance during instruction does not work: An analysis of the failure of constructivist, discovery, problem-based experiential and inquiry-based teaching. Educ. Psychol. 2006, 41, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Bossche, P.; Gijselaers, W.H.; Segers, M.N.; Kirschner, P.A. Social and cognitive factors driving teamwork in collaborative learning environments: Team learning beliefs and behaviors. Small Group Res. 2006, 37, 490–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Järvelä, S.; Volet, S.; Järvenoja, H. Research on motivation in collaborative learning: Moving beyond the cognitive-situative divide and combining individual and social processes. Educ. Psychol. 2010, 45, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barron, B. When smart groups fail. J. Learn. Sci. 2003, 12, 307–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Järvelä, S.; Kirschner, P.A.; Hadwin, A.; Järvenoja, H.; Malmberg, J.; Miller, M.; Laru, J. Socially shared regulation of learning in CSCL: Understanding and prompting individual- and group-level shared regulatory activities. Int. J. Comput.-Support. Collab. Learn. 2016, 11, 263–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roschelle, J.; Teasely, S. The Construction of Shared Knowledge in Collaborative Problem Solving. In Computer Supported Collaborative Learning; O’Malley, C., Ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1995; Volume 128. [Google Scholar]
- Panadero, E.; Järvelä, S. Socially Shared Regulation of Learning: A Review. Eur. Psychol. 2015, 20, 190–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadwin, A.F.; Järvelä, S.; Miller, M. Self-regulation, co-regulation and shared regulation in collaborative learning environments. In Handbook of Self-regulation of Learning and Performance, 2nd ed.; Schunk, D., Greene, J., Eds.; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 83–106. [Google Scholar]
- Järvelä, S.; Kirschner, P.A.; Panadero, E.; Malmberg, J.; Phielix, C.; Jaspers, J.; Koivuniemi, M.; Järvenoja, H. Enhancing Socially Shared Regulation in Collaborative Learning Groups: Designing for CSCL Regulation Tools. Educ. Techol. Res. Dev. 2015, 63, 125–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Manlove, S.A. Regulative support during inquiry learning with simulations and modeling. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Twente, Enschede, The Netherlands, 25 October 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Kirschner, F.; Paas, F.; Kirschner, P.A. A cognitive-load approach to collaborative learning: United brains for complex tasks. Educ. Psychol. Rev. 2009, 21, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Rio, J.; Cecchini, J.A.; Méndez-Gimenez, A.; Mendez-Alonso, D.; Prieto, J. Self-Regulation, Cooperative Learning, and Academic Self-Efficacy: Interactions to Prevent School Failure. Front. Psychol. 2017, 8, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hadwin, A.F.; Järvelä, S.; Miller, M. Self-regulated, Co-regulated, and Socially Shared Regulation of Learning. In Handbook of Self-Regulation of Learning and Performance; Schunk, D., Greene, J., Eds.; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2011; pp. 65–82. [Google Scholar]
- Volet, S.; Vauras, M.; Salonen, P. Self- and social regulation in learning contexts: An integrative perspective. Educ. Psychol. 2009, 44, 215–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Meijden, H.; Veenman, S. Face-to-face versus computer-mediated communication in a primary school setting. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2005, 21, 831–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Jong, F.; Kollöffel, B.; van der Meijden, H.; Kleine Staarman, J.; Janssen, J. Regulative processes in individual, 3D and learning and computer supported cooperative learning contexts. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2005, 21, 645–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedaste, M.; Mäeotos, M.; Leijen, A.; Sarapuu, T. Improving Students’ Inquiry Skills through Reflection and Self-Regulation Scaffolds. Eur. Psychol. 2012, 9, 81–95. [Google Scholar]
- Schraw, G.; Moshman, D. Metacognitive theories. Educ. Psychol. Rev. 1995, 7, 351–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrance, M.; Fidalgo, R.; García, J. The teachability and effectiveness of cognitive self-regulation in sixth-grade writers. Learn. Instr. 2007, 17, 265–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, M.T. The Importance of Self-Regulation for College Student Learning. Coll. Stud. J. 2012, 46, 892–902. [Google Scholar]
- Manlove, S.A.; Lazonder, A.W.; de Jong, T. Regulative support for collaborative scientific inquiry learning. J. Comput. Assist. Learn. 2006, 22, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azevedo, R.; Cromly, J.G. Does Training on Self-Regulated Learning Facilitate Students’ Learning with Hypermedia? J. Educ. Psychol. 2004, 96, 523–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ertmer, P.A.; Newby, T.J. The expert learner: Strategic, self-regulated, and reflective. Instr. Sci. 1996, 24, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schraw, G.; Crippen, K.J.; Hartley, K. Promoting Self-Regulation in Science Education: Metacognition as Part of a Broader Perspective on Learning. Res. Sci. Educ. 2006, 36, 111–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matlin, M.W. Cognition, 3rd ed.; Harcource Brace Publishers: Orlando, FL, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman, B.J.; Schunk, D.H. Motivational sources and outcomes of self-regulated learningand performance. In Self-Regulated Learning and Academic Achievement; Zimmerman, B., Schunk, D., Eds.; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2011; pp. 49–64. [Google Scholar]
- Pintrich, P.R.; Wolters, C.A.; Baxter, G.P. Assessing metacognition and self-regulated learning. In Metacognitive Assessment; Schraw, G., Ed.; The University of Nebraska Press: Lincoln, NE, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Abedin, B.; Daneshgar, F.; D’Ambra, J. Do nontask interactions matter? The relationship between non-task sociability of computer supported collaborative learning and learning outcomes. Br. J. Educ. Technol. 2012, 43, 385–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muilenburga, L.Y.; Berge, Z.L. Student barriers to online learning: A factor analytic study. Distance Educ. 2005, 26, 29–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreijns, K. Sociable CSCL environments: Social affordances, sociability, and social presence. Ph.D. Thesis, Open Universiteit, Heerlen, The Netherlands, 7 May 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Jehn, K.A.; Shah, P.P. Interpersonal relationships and task performance: An examination of mediation processes in friendship and acquaintance groups. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 1997, 72, 775–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurme, T.; Merenluoto, K.; Järvelä, S. Socially shared metacognition of pre-service primary teachers in a computer supported mathematics course and their feelings of task difficulty: A case study. Educ. Res. Eval. 2009, 15, 503–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volet, S.; Summers, M.; Thurman, J. High-level co-regulation in collaborative learning: How does it emerge and how is it sustained? Learn. Inst. 2009, 19, 128–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, J.; Erkens, G.; Kirschner, P.A.; Kanselaar, G. Task-related and social regulation during online collaborative learning. Metacogn. Learn. 2012, 7, 25–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vuopala, E.; Naÿkki, P.; Isohätälä, J.; Järvelä, S. Knowledge co-construction activities and task-related monitoring in scripted collaborative learning. Learn. Cult. Soc. Interact. 2019, 21, 234–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinberger, A.; Fischer, F. A framework to analyse argumentative knowledge construction in computer-supported collaborative learning. Comput. Educ. 2006, 46, 71–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- CITO. Available online: https://www.cito.nl/-/media/files/ve-en-po/cito-flyer-toetsscore-vaardigheidsscore-en-dan.pdf (accessed on 20 July 2021).
- Van Dijk, A.M.; Eysink, T.H.S.; de Jong, T. Supporting Cooperative Dialogue in Heterogeneous Groups in Elementary Education. Small Group Res. 2020, 51, 464–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, D.W.; Johnson, R.T.; Smith, K. The state of cooperative learning in postsecondary and professional settings. Educ. Psychol. Rev. 2007, 19, 15–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laal, M.; Geranpaye, L.; Daemi, M. Individual accountability in collaborative learning. Soc. Behav. Sci. 2013, 93, 286–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roseth, C.J.; Lee, Y.; Saltarelli, W.A. Reconsidering jigsaw social psychology: Longitudinal effects on social interdependence, sociocognitive conflict regulation, motivation, and achievement. J. Educ. Psychol. 2019, 111, 149–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aronson, E.; Blaney, N.; Stephan, C.; Sikes, J.; Snapp, M. The Jigsaw Classroom; Sage: Beverly Hills, CA, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Charmaz, K. Constructing Grounded Theory: A Practical Guide Through Qualitative Analysis; Sage: London, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Sloetjes, H.; Wittenburg, P. Annotation by category—ELAN and ISO DCR. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Language Resources and Evaluation (LREC 2008), Marrakesh, Morroco, 26 May–1 June 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Kirschner, P.A.; Sweller, J.; Kirschner, F.; Zambrano, J.R. A cognitive-load approach to collaborative learning: United brains for complex tasks. Int. J. Comput.-Support. Collab. Learn. 2018, 13, 213–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wolters, C.A. Regulation of motivation: Evaluating an underemphasized aspect of self-regulated learning. Educ. Psychol. 2003, 38, 189–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pintrich, P.R. A conceptual framework for assessing motivation and self-regulated learning in college students. Educ. Psychol. Rev. 2004, 4, 385–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miller, E.K.; Cohen, J.D. An Integrative Theory of Prefrontal Cortex Function. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2001, 24, 167–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rogat, T.K.; Linnenbrink-Garcia, L. Socially shared regulation in collaborative groups: An analysis of the interplay between quality of social regulation and group processes. Cogn. Instr. 2011, 29, 375–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadwin, A.F.; Malmberg, J.; Järvelä, S.; Jarvenoja, H.; Vainiopää, M.V. Exploring Socially-Shared Metacognition in the Context of Shared Task Perceptions and Goals. In Proceedings of the 4th Biennial meeting of the European Association for Reasearch on Learning and Instruction SIG-16 Metacognition, Muenster, Germany, 3–6 September 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Haataja, E.; Malmberg, J.; Järvelä, S. Monitoring in collaborative learning: Co-occurrence of observed behavior and physiological synchrony explored. Comp. Hum. Behav. 2018, 87, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winne, P.H.; Hadwin, P.H.; Perry, N.E. The international handbook of collaborative learning. In The international Handbook of Collaborative Learning; Hmelo-Silver, C.E., Chinn, C.A., Chan, C.K.K., O’Donnel, A.M., Eds.; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 462–479. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, A. Socially shared regulation in computer-supported collaborative learning. Ph.D. Thesis, Graduate School New Brunswick, New Brunswick, NJ, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Winne, P.H. Issues in researching self-regulated learning as patterns of events. Metacogn. Learn. 2014, 9, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercer, N.; Dawes, L.; Wegerif, R.; Sams, C. Reasoning as a scientist: Ways of helping children to use language to learn science. Br. Educ. Res. J. 2004, 30, 359–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schunk, D.H. Self-Regulated Learning: The Educational Legacy of Paul, R. Pintrich. Educ. Psychol. 2005, 40, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Järvelä, S.; Järvenoja, H. Socially constructed self-regulated learning and motivation regulation in collaborative learning groups. Teach Coll. Rec. 2011, 113, 350–374. [Google Scholar]
- Sbaraini, A.; Carter, S.M.; Evans, R.W.; Blinkhorn, A. How to do a grounded theory study: A worked example of a study of dental practices. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2011, 11, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Malmberg, J.; Haataja, E.; Seppänen, T.; Järvelä, S. Are we together or not? The temporal interplay of monitoring, physiological arousal and physiological synchrony during a collaborative exam. Int. J. Comput.-Support. Collab. Learn. 2019, 14, 467–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gijlers, H.; Weinberger, A.; van Dijk, A.M.; Bollen, L.; van Joolingen, W. Collaborative drawing on a shared digital canvas in elementary science education: The effects of script and task awareness support. Int. J. Comput.-Support. Collab. Learn. 2013, 8, 427–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).