Abstract
As AI coding tools become more prevalent in programming, it is essential to understand how they influence programming education. This study, conducted in a first-semester Introduction to Programming course, aimed to determine the positive and negative effects of these tools on students’ learning experiences and their ability to develop essential programming skills. Using a mixed-methods approach, we collected data from 73 teams of engineering students over a 12-week period. Students completed surveys and reported on their AI tool usage. We analyzed this data quantitatively to identify trends in tool familiarity, usage, and student satisfaction. Additionally, qualitative analysis of student reports provided insights into the specific ways AI tools were used and their perceived benefits and drawbacks. The findings revealed a significant increase in AI tool familiarity (from 28% to 100%) and usage among students. Students’ satisfaction with AI tools improved over time. The most prevalent tasks for which novice programmers used AI tools included creating comments (91.7%), identifying and correcting bugs (80.2%), and seeking information (68.5%), while other tasks were less common. While these tools offered benefits like assisting in learning and enhancing real-world relevance, they also raised concerns about cheating, over-reliance on AI tools, and a limited understanding of core programming concepts.
1. Introduction
The integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and AI-driven coding tools in programming education has opened new avenues for enhancing both the teaching and learning experience. These tools, while offering significant benefits, can also be a double-edged sword. Our study raises important questions about the AI tools’ long-term impact on students’ understanding and proficiency. The potential of AI tools to transform education is undeniable. They can automate routine coding tasks, provide instant feedback, improve debugging and troubleshooting, and offer personalized, student-centered learning experiences. However, their use also introduces challenges, particularly regarding the balance between automation and preserving essential programming skills [1,2,3,4,5].
AI in education is rapidly emerging as a key area of focus in educational technology, yet its broader pedagogical implications remain a subject of ongoing debate. The uncertainty about how educators can effectively harness AI to create meaningful learning experiences in higher education is a major concern [3,6,7]. Educators are tasked with the crucial role of preparing students for a future where AI will be ubiquitous, not only in technology-driven industries but across various sectors. To achieve this, educators must equip students with a comprehensive skill set that includes traditional programming principles and knowledge in addition to the ability to leverage cutting-edge AI tools.
Teaching students to use AI tools in programming education aligns with the current demands of the high-tech industry and enhances their readiness for the workplace. By training students to effectively utilize AI tools, educators can improve their efficiency and productivity, allowing them to focus on more complex and creative aspects of software development [8,9]. These tools can automate tedious and repetitive tasks, thereby freeing up cognitive resources for higher-order problem-solving and innovation [10,11]. However, the integration of AI tools in programming education must be approached with caution. Over-reliance on AI-driven solutions can result in a superficial understanding of programming concepts, where students may become adept at using tools without fully grasping the underlying logic and principles that drive software development [12,13].
A balanced approach is essential, where AI tools are used to complement, rather than replace, traditional coding practices and teaching methods [4,14]. This balance ensures that students develop a deep understanding of programming fundamentals while also learning to use AI to enhance their work. The primary objective of the current study is to investigate how college students use these tools in a first-semester introductory programming course and to explore how educators can achieve this balance, ensuring that AI tools are used to augment learning without diminishing the importance of manual coding and critical thinking [15]. The study also seeks to address the potential risks associated with AI tools, such as the risk of fostering surface-level learning and the possible erosion of essential problem-solving skills.
Ultimately, while AI tools offer significant potential for transforming programming education, their integration must be thoughtfully managed to ensure that they contribute positively to the educational process. By striking the right balance, educators can harness the power of AI to create more dynamic and effective learning environments that prepare students for the challenges of the future.
1.1. Literature Review
Code-generation tools powered by large language models can correctly and reliably solve most of programming problems that are typical in introductory courses. It is therefore unsurprising that Finnie-Ansley et al. [10] showed that AI tools could solve programming assignments and exam problems that are typically given in CS1 (computer science) and CS2 more effectively than most students. The implications of this capability extend beyond mere performance; they challenge the traditional approaches to teaching introductory programming.
Lau and Guo [13], in their semi-structured interviews with introductory programming instructors, revealed a range of perspectives on the integration of AI tools into education. While short-term concerns focused heavily on the potential for cheating, long-term perspectives were more varied. Some educators expressed a desire to resist the use of AI tools in introductory programming courses, concerned that such tools might undermine the development of fundamental skills. On the other hand, others advocated for embracing AI, suggesting that these tools could be integrated into the curriculum to enhance learning and better prepare students for a future where AI is ubiquitous in software development.
The debate about how to manage the influence of AI tools in education is further complicated by the issues of academic integrity and the assessment of student learning. Bommasani et al. [6] emphasized the increasing difficulty educators face in determining the extent of a student’s individual contribution. The challenge of preventing ineffective collaborations and detecting plagiarism has become more pronounced as AI tools become more capable. This raises significant questions about the validity of traditional assessment methods and the need for new approaches that can accurately measure a student’s understanding and effort in an environment where AI-generated code is easily accessible.
Becker et al. [1] argued in their position paper that AI-generated code presents both opportunities and challenges for students and educators alike. On the one hand, these tools could serve as powerful aids, helping students overcome obstacles in their coding tasks and providing instant feedback that can enhance learning. On the other hand, they pose significant risks, such as the potential for students to become overly reliant on AI-generated solutions, which may hinder the development of critical thinking and problem-solving skills that are central to programming education.
Denny et al. [3] further argued that generative AI brings both challenges and opportunities to computing education, calling for updated pedagogical strategies that focus on new skill sets. The ability of generative AI models to generate solutions to problems typical of introductory programming courses raises concerns about student overreliance and misuse. However, this also opens the door for reimagining the educational landscape, where the focus shifts from rote learning and simple problem-solving to more complex tasks that require higher-order thinking and a deeper understanding of underlying concepts.
In a study conducted by Yilmaz and Yilmaz [11] on undergraduate students, it was found that tools like ChatGPT could enhance students’ programming self-efficacy and motivation. The study suggested that ChatGPT could be a valuable tool for teaching computational thinking, providing students with a supportive environment where they can explore programming concepts with instant feedback. This potential for AI tools to positively influence student learning underscores the need for educators to consider how these tools can be integrated into the curriculum in a way that maximizes their benefits while mitigating their risks.
Several studies showed that ChatGPT could provide users with explanations, examples, and guidance to help them understand complex concepts and technologies. It could be used to assist with debugging by analyzing data on the programming language, code structure, error messages, and code documentation, and even assist with code review [16,17,18,19].
Vukojičić’s and Krstić’s [20] study found that using ChatGPT as a programming assistant resulted in better outcomes than working without external assistance. Students who used ChatGPT demonstrated improved coding proficiency, wrote higher-quality explanations, and gained a deeper understanding of standard solution methods.
Zhai [21] examined ChatGPT from the perspective of educators, asserting that the AI tool holds significant potential for offering specific and personalized guidance to both teachers and student teachers. The study found ChatGPT highly effective in automating essential tasks such as assessment development, grading, learning guidance, and recommending learning materials. This automation can greatly reduce the time and effort required for creating educational materials, enabling educators to dedicate more time to direct teaching and student engagement. However, to fully leverage these benefits, educators must possess the necessary technological, content, and professional expertise to access and evaluate the quality and relevance of the materials provided by ChatGPT.
Malinka et al. [22] studied the impact of ChatGPT on higher education, focusing primarily on computer security-oriented specializations. The study demonstrated the effectiveness and usability of ChatGPT for handling programming assignments, completing exams, and writing term papers. Various levels of tool misuse were evaluated, ranging from using it as a consultant to simply copying its outputs. The benefits of ChatGPT for computer science education were also highlighted.
Rudolph et al. [23] examined the relevance of ChatGPT in the context of higher education, with a particular focus on its impact on assessment, learning, and teaching. Following an overview of ChatGPT’s functionality and a summary of its strengths and limitations, the study delved into the broader implications of this technology for the future of higher education. The potential of AI chatbots like ChatGPT to reshape learning, teaching, and assessment practices was explored. ChatGPT was positioned within the current landscape of AI in education research, with its applications for students, educators, and educational systems discussed. The analysis highlighted both the opportunities and challenges presented by AI integration in education. Practical recommendations were proposed for students, educators, and higher education institutions on how to effectively navigate and leverage these emerging technologies.
Finnie-Ansley et al. [10] likened the introduction of Codex into students’ hands to giving a power tool to an amateur—a tool with the potential to either construct or destruct, depending on how it is used. While the presence of AI tools in educational settings presents clear threats to student learning and academic integrity, it also offers fantastic opportunities to refactor existing curricula. By leveraging these tools appropriately, educators can design learning experiences that not only impart essential programming skills but also prepare students for a future where collaboration with AI is an integral part of the software development process.
Traditional teaching methods often suffer from low student participation, lack of personalized instruction, and insufficient motivation [24,25]. Modern approaches in education enhance active learning approaches [26]. Traditional education often relies on theory-based materials, but the integration of ChatGPT can foster personalized learning experiences tailored to individual needs and preferences. Students can leverage ChatGPT to outsource certain knowledge tasks, allowing them to concentrate on ‘hands-on’ learning and gain practical experience in their chosen fields. Additionally, ChatGPT could also create adaptive learning environments that respond to individual learner progress and performance [14,27,28].
Constructivist theory emphasizes that students construct knowledge through their own experience and participation. Integrating AI tools into a constructivist framework can significantly enhance educational experiences by encouraging students to take charge of their educational journeys through real-time assistance like clarification of concepts, answering questions, and offering tailored guidance based on individual learning needs and styles. With AI tools, educators can create environments that emphasize active learning. Students can engage in inquiry-based activities, utilizing AI as a resource for exploration and problem-solving [29,30,31,32,33]. AI integration may transform educators from content providers to facilitators, emphasizing mentorship and the development of soft skills [4,5,23,27].
Cognitive load theory posits that learning is most effective when cognitive load is managed, helping students focus on essential concepts without being overwhelmed [34,35]. AI tools can reduce extraneous cognitive load by automating routine tasks, allowing students to concentrate on understanding core programming principles. This can be particularly useful for novice programmers who may struggle with complex concepts.
Mandai and co-authors [36], in their opinion paper, discussed the potential impacts of ChatGPT on higher education through the lens of educational theories by John Dewey’s Reflective Thought and Action model and the revised Bloom’s taxonomy. The analysis was based on a review of existing literature on ChatGPT and educational theories. The key points mentioned positive expectations: ChatGPT could enhance personalized learning, shift education towards more practical, hands-on learning by reducing the need for memorizing information, and lead to assessment reforms. They also mentioned negative expectations, like over-reliance on ChatGPT, failing to acquire necessary skills, diminished student creativity and originality, and they raised concerns about the authenticity and accuracy of sources.
Lo [32], in a literature review, provided an analysis of the implications of ChatGPT in educational contexts. The review assessed ChatGPT’s capabilities across various subject domains, its potential applications in education, and the challenges it poses. ChatGPT’s performance varied significantly across different subjects, demonstrating outstanding results in critical thinking and economics but showing unsatisfactory performance in mathematics and medical education. Potential applications in education include serving as an assistant for instructors or as a virtual tutor for students. Several challenges were identified, such as accuracy issues, plagiarism concerns, and the need for updated institutional policies to address these issues. The conclusion emphasized that while ChatGPT holds significant promise for enhancing educational practices, careful consideration must be given to its limitations and the ethical implications of its use.
1.2. Aims and Research Questions
As we see, the central question is that of finding the right balance between the different aspects of the use of the tools. To determine the most effective approach, we need a clear understanding of how these tools are actually used in practice, particularly: how students perceive them and how they apply them in real-life programming courses. Especially interesting is observing students’ first encounters with these tools, such as during their initial programming course in the first semester of their studies.
In this study, we aim to analyze novice programmers’ attitudes toward AI tools. We seek to understand the dynamics of AI tool usage and changes in behavior over time. Additionally, we want to uncover patterns of AI usage and explore students’ sentiments about these tools. Essentially, our goal is to identify the ‘Good’ and the ‘Bad’ aspects of AI tool usage in novice programming education. To achieve this, we have formulated the following research questions:
RQ1. How familiar are novice programmers with AI tools during their programming education?
RQ2. Does the usage of AI tools evolve over time in an introductory programming course?
RQ3. Are students satisfied with the results provided by AI tools, and does this satisfaction improve over time?
RQ4. What common tasks do novice programming teams use AI tools for, and how prevalent are these tasks among the teams?
RQ5. What are the common benefits and concerns students have about using AI tools in their studies?
2. Methodology
The primary aims of this study are to understand the dynamics of AI tools usage, uncover patterns in their application, and explore students’ sentiments regarding these tools. Data from students’ reports and questionnaires on AI tool usage during the Introduction to Programming course are analyzed in this paper. The course spans a period of 12 weeks, with an instructional format consisting of 2 h of lectures and 4 h of lab sessions each week. A pragmatic mixed-methods study was undertaken to explore potential global patterns based on quantitative data, enriched with qualitative data. Students completed surveys and reported on their AI tool usage. The analytical framework of the study is presented in Figure 1.
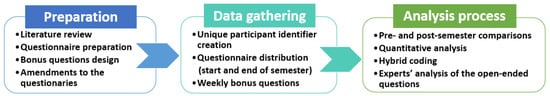
Figure 1.
Analytical framework of the study.
2.1. Participants
The participants in this study were first-semester, first-year undergraduate students, who were novice programmers enrolled in the Introduction to Programming course. A total of 73 teams, each comprising two students from the Faculty of Engineering at Ruppin Academic Center in Israel, took part in the study. Students joined a team of their choice and remained with the same team until the end of the semester. Among the participants, 53% were male (78) and 47% were female (68). The median age was 24, with the range between 18 and 29 years. Only teams that submitted all required data items were included in this report. The data from these teams were used for the majority of the analysis in this study.
2.2. Procedure and Data Analysis
All procedures performed in this study were in accordance with APA ethical guidelines and the ethical standards of the institutional research committee. Prior to conducting the research, the requirements of the institutional ethics committee were complied with. At the beginning of the semester, before starting the experimental process, the students were informed about the aims and procedures of the research. The tasks the students would undertake during the experimental process were explained. Each participant was instructed on how to create a unique identifier using a combination of personal but non-identifiable information. This identifier was used in all surveys and bonus questions throughout the semester. Team members merged the two personal, unique identifiers together.
Before the course started, participants completed a pre-semester questionnaire that included questions on students’ personal information and basic knowledge of AI. At the end of the course, participants completed a post-semester questionnaire that assessed their perceptions of their AI knowledge, as well as their views on the benefits and concerns related to using AI tools in their studies.
Believing in the importance of incorporating AI tools into classrooms from the very beginning, specific assignment questions were designed where students were tasked with using AI tools to generate or explain portions of code, as well as to explore or learn about particular modules, concepts, or functions. Since these tasks required students to have a basic understanding of AI and the ability to effectively interact with AI tools, several examples were provided to demonstrate how these tools could be used in the context of their assignments. Although no specific AI tool was mandated, students were encouraged to explore different options to find what best suited their needs. As the formulation of the question of the student to the AI tool (usually called the prompt) could be important, in addition to these examples, prompt-writing tips were shared to help students craft more effective queries, enabling them to maximize the potential of the AI tools they chose to work with.
Furthermore, on a weekly basis, students worked on home assignments. A 5-point bonus question related to the usage of AI tools and students’ feelings about them was added to some assignments. A bonus question is an additional question or set of questions included in an assignment that offers students the opportunity to earn extra points beyond the regular scoring criteria. To enable continuous data collection throughout the semester and gain insights into how teams interacted with AI tools as they progressed through the course, weekly multipart bonus questions were included in each assignment for the teams to answer. Detailed, ongoing data was gathered, mapping the progression of AI tool integration into their work and providing a nuanced understanding of how their usage evolved.
The course spanned 12 weeks, with weekly assignments categorized into two groups: those requiring the use of AI tools (assignments 3, 7, and 10) and those that did not (assignments 2, 6, 9, and 11). Bonus questions were incorporated into assignments 2, 3, 6, 7, 9, and 11, each having a slightly different structure based on whether AI tools were used. A sample of the bonus question questionnaires can be found in Appendix A. No bonus questions were included in the remaining weeks.
2.3. Data Analysis
The impact of AI tools was measured using several indicators: familiarity with AI tools was assessed through pre- and post-semester questionnaires that captured students’ self-reported familiarity levels; the frequency of AI tool usage in assignments was evaluated with a dichotomous (yes/no) statement, “I used AI tools during this assignment”, focusing on weeks where usage was not explicitly required to identify trends in voluntary adoption; students’ comfort levels with AI tools were tracked during weeks 3, 7, and 10 using a 5-point Likert scale, allowing for the assessment of how comfort evolved as they became more accustomed to the tools; satisfaction with AI tools was measured through survey questions asking students to rate their satisfaction with the results provided by the tools on a Likert scale, offering insights into their perceptions of the quality of outcomes from AI tool usage.
IBM SPSS Statistics 28 software was applied for quantitative data analysis. Several statistical tests were used in this study: the Wilcoxon signed ranks test for two related samples, the Friedman test for several related samples, and Cohran’s Q test. Cronbach’s alpha coefficients, showing the internal consistency reliability, were computed. The values were acceptable: 0.935 for feeling comfortable with usage of AI tools in the assignment on weeks 3, 7, 10; 0.924 for using AI tools during the assignment on weeks 2, 6, 9; 0.758 for being happy with the results provided by AI tools on weeks 3, 7, 10.
For the qualitative data, participants’ responses to the open-ended questions included in the bonus tasks were analyzed using content analysis. Prior to analyzing the data, two sets of categories based on prior research and literature were designed. The first set of categories was designed for responses to the statement, “I used AI tools during this assignment for the following tasks”, and the second set was for responses to the direction, “Describe the benefits and concerns about using AI tools in your studies, personally”.
We initially employed a deductive coding approach to categorize the data based on these predefined categories. However, several new categories emerged during the analysis, which were subsequently added to the pre-existing codes. Thus, a hybrid coding approach was adopted: the deductive coding provided a structured framework, while the inductive coding allowed for the discovery of additional categories, adding depth and nuance to the findings.
3. Results
Based on the responses received, we analyzed the results to address our research questions. We did not specify the use of particular tools. The majority of students utilized tools designed to understand and generate human-quality text in response to a variety of prompts and questions. Most of these tools are user-friendly, featuring simple interfaces that allow users to input prompts and receive responses easily.
3.1. Familiarity with AI Tools
To answer the first research question about the familiarity of novice programmers with AI tools during their programming education, the level of agreement of the students to the following statement, “I feel familiar with AI tools usage”, was analyzed at the beginning and at the end of the course. The descriptive frequency and percentage of responses can be found in Table 1. The analysis of survey responses indicated that, initially, only 28% of the teams reported feeling familiar with the usage of AI tools. However, by the end of the course, this familiarity had increased to 100%.

Table 1.
Frequency and percent of responses to the statement, “I feel familiar with AI tools usage”, at the beginning and at the end of the semester (n = 73).
Wilcoxon signed ranks test for two related samples was used to compare the responses at the beginning and at the end of the semester to the statement, “I feel familiar with AI tools usage”, measured on a Likert 1–5 scale. This test revealed significant differences between the responses at the beginning and at the end: Z = −6.085, p < 0.001.
3.2. Dynamics of AI Tool Integration
To address the second research question—whether the usage of AI tools evolves over time in an introductory programming course—the level of agreement with the statement, “I feel comfortable using AI tools in this assignment”, was analyzed on a Likert scale from 1 to 5 during weeks 3, 7, and 10. During these weeks, the use of AI tools was required to complete the assignments. The descriptive frequencies and percentages of responses are presented in Table 2.

Table 2.
Frequency and percentage of responses to the statement, “I feel comfortable using AI tools in this assignment”, during weeks 3, 7, and 10 (n = 73).
The Friedman test for several related samples was applied, comparing the responses to the item, “I feel comfortable with usage of AI tools in this assignment”, on weeks 3, 7, and 10. The differences in medians were significant: χ2 (2) = 9.8, p = 0.007.
Additionally, to answer the second research question, we analyzed the level of agreement to the dichotomous (yes, no) statement, “I used AI tools during this assignment”, on weeks 2, 6, 9 and 11. Those weeks did not require the use of AI tools. The descriptive frequency and percentage of responses to the statement can be found in Table 3.

Table 3.
Frequency and percentage of responses to the statement, “I used AI tools during this assignment”, during weeks 2, 6, 9, and 11 (n = 73).
Non-parametric Cohran’s Q test was used to compare the response to the item, “I used AI tools during this assignment”, on weeks 2, 6, 9, and 11 (yes, no). Cohran’s Q = 34.839, p < 0.001, meaning that there were significant differences on the response between weeks 2, 6, 9, and 11, indicating that students used more AI tools.
3.3. Student Satisfaction with AI Tools
To address the third research question, “Are students satisfied with the results provided by AI tools, and does this satisfaction improve over time?”, we analyzed students’ level of agreement with the statement, “I was happy with the results provided by AI tools”, using a Likert scale of 1 to 5 during weeks 3, 7, and 10. During these specific weeks, the use of AI tools was mandatory for completing an assignment. The descriptive frequency and percentage of responses can be found in Table 4.

Table 4.
Frequency and percentage of responses to the statement, “I was happy with the results provided by AI tools”, during weeks 3, 7, 10 (n = 73).
The Friedman test for several related samples was applied comparing the responses to the item, “I was happy with the results provided by AI tools”, on weeks 3, 7, and 10. The differences in medians were significant: χ2 (2) = 11.594, p = 0.003, meaning that the answers were better. However, since students used the same language model, this result suggests that they improved their prompt-engineering skills over time.
3.4. Common AI Tool Tasks and Prevalence
To address the fourth research question, “What common tasks do novice programming teams use AI tools for, and how prevalent are these tasks among the teams?”, we analyzed the responses to the statement, “I used AI tools during this assignment for the following tasks”. Each team was allowed to provide as many responses as they wished. Given that the quality of the code and its accompanying description becomes more demanding toward the end of the course, we focused on the teams’ responses from weeks 9 and 11. We combined the responses from each team across these two weeks, and if the same category was mentioned more than once, it was counted only once.
Categories that emerged from the analysis of the responses in the qualitative stage of the research and the percentage of the teams that expressed them were as follows: creation of comments mentioned by 67 teams (91.7%), bugs identification and correction—59 teams (80.2%), information seeking—50 teams (68.5%), code comparisons—33 teams (45.21%), creating some part of the code—25 teams (34.2%), debugging assistance—25 teams (34.2%), code simplification—14 teams (19.2%), translation of exercise from Hebrew (the original language) to another language (for example, Arabic or Russian)—12 teams (16.4%), algorithm selection—11 teams (15.1%). Translation of exercise from the original language to another language was a category that was added as a result of the inductive coding approach.
3.5. Benefits and Concerns of AI Tool Usage
To address the fifth research question about the common benefits and concerns students have regarding the use of AI tools in their studies, responses to the open-ended direction, “Describe the benefits and concerns you personally have about using AI tools in your studies”, during the last week of the course were analyzed. Common benefit categories emerged from the analysis of the responses, and the percentage of the teams that expressed them were as follows: instant help or quick answers and explanations mentioned by 58 teams (79.4%), assistance with repetitive tasks (like writing comments)—55 teams (75.3%), immediate response/feedback—42 teams (57.5%), help with identification and correction of errors—40 teams (54.8%), access to diverse resources/providing additional examples—33 teams (45.21%), spelling correction—17 teams (23.3%), translation from one language to another—14 teams (19.2%). Once again, translation from one language to another was added during the inductive coding process.
Common concern categories that emerged from the analysis of the responses and the percentage of the teams that expressed them were as follows: inaccurate or misleading information/answers mentioned by 65 teams (89.0%), over-reliance on AI tools/becoming too dependent on AI tools—55 teams (75.3%), identification of advanced functions and structures that were not learned in class—33 teams (45.21%), incorrect explanations which appear believable to novices—27 teams (36.9%), low code quality—25 teams (34.2%), wasting too much time on unsuccessful bug identification and error fixing—12 teams (16.4%), inconsistency/producing different outputs, even when given the same prompt—10 teams (13.6%). This last category was added as a result of the inductive coding approach.
4. Discussion
4.1. General Discussion
This study uniquely combines quantitative and qualitative methods to examine novice programmers’ interactions with AI tools. The findings illustrate a progression in usage patterns, suggesting that, as students became more familiar with AI tools, they were more inclined to use them voluntarily, even in assignments where they were not explicitly required. Notably, we achieved an impressive 98.5% response rate for the bonus question, generating substantial and valuable information.
We will focus on identifying the ‘Good’ and ‘Bad’ aspects of AI tool usage in novice programming education.
The results of the first research question revealed that, at the beginning of the course, only 28% of the teams reported feeling familiar with the use of AI tools. However, by the end of the course, this familiarity had significantly increased, with all teams (100%) expressing confidence in their ability to use these tools. This dramatic rise in familiarity underscores the effectiveness of integrating AI tools into the curriculum, allowing students to gradually build their skills and comfort levels as they progressed through the course. The initial hesitation gave way to a comprehensive understanding of AI tools, suggesting that consistent exposure and practical application were key factors in fostering this growth. The analysis of the second research question reveals a progression in students’ confidence and usage of AI tools over time in an introductory programming course. Initially, a significant portion of students felt uncomfortable using AI tools, as indicated by the low agreement to the statement, “I feel comfortable with usage of AI tools in this assignment”, in Week 3. However, by Weeks 7 and 10, there was a marked increase in comfort levels, with all students either agreeing or strongly agreeing with the statement, as demonstrated by the significant results of the Friedman test.
Moreover, additional evidence for this trend comes from the results of the Cochrane’s Q test, which analyzed AI tool usage in assignments where their use was not explicitly required (Weeks 2, 6, 9, and 11). The significant increase in the number of students using AI tools on their own initiative over time suggests that as students became more familiar and comfortable with these tools, they became more inclined to integrate them into their work, even when not mandated. This indicates a positive shift in both the acceptance and practical application of AI tools as the course progressed.
These findings are consistent with the principles of constructivist theory, which emphasizes that students construct knowledge through active participation and hands-on experiences. The gradual increase in students’ confidence and voluntary usage of AI tools suggests that they were actively engaging with these technologies as they constructed their understanding of programming concepts. Furthermore, the shift in students’ usage patterns, from initial hesitation to confident application, reflects their growing autonomy in learning, a key goal in a constructivist educational framework.
The results of the third research question, “Are students satisfied with the results provided by AI tools, and does this satisfaction improve over time?”, reveal a significant increase in student satisfaction as the course progressed. In Week 3, a substantial proportion of students expressed dissatisfaction with the results provided by AI tools, as reflected in the higher percentages of “disagree” and “strongly disagree” responses. However, by Weeks 7 and 10, the majority of students reported either “agree” or “strongly agree” with the statement, indicating a marked improvement in their satisfaction levels.
The significant findings from the Friedman test suggest that not only did students’ satisfaction improve over time, but the quality of their interactions with AI tools also likely improved. Since the same AI model was used throughout the course, this trend indicates that students became more adept at prompt engineering, enabling them to extract better results from the AI tools for any topic, not only programming. Additionally, a majority of students reported switching to English as their prompt language, which could also provide better results. These findings open up several areas for further discussion. First, the improvement in satisfaction over time underscores the importance of practice and experience when using AI tools. As students became more proficient with the capabilities and limitations of these tools, they were able to craft better prompts, leading to more satisfactory outcomes. This suggests that prompt engineering is a critical skill that can be developed over time and should be an integral part of AI education. Therefore, teaching students how to effectively interact with AI tools can enhance their learning experiences, a point that has not been extensively addressed in the prior literature.
The analysis of the fourth research question reveals a diverse range of applications for AI tools in an introductory programming course. These findings suggest that novice programming teams are leveraging AI tools primarily to optimize and enhance their coding processes, particularly in areas that require repetitive or detailed work, such as commenting and debugging. The varied use of AI tools across different tasks also highlights their versatility and the teams’ growing confidence in incorporating these tools into various aspects of their assignments as the course progresses.
The data indicates that, as the course demands increased, so did the reliance on AI tools for more complex tasks, reflecting a deeper integration of these tools into the programming workflow. This underscores the importance of AI tools as a valuable resource in programming education, particularly for tasks that can support learning and improve code quality. However, it also raises questions about the potential for over-reliance and the need to balance AI tool usage with the development of fundamental programming skills.
The analysis of the fifth research question, which explored the common benefits and concerns students have regarding the use of AI tools in their studies, revealed a complex interplay of advantages and challenges experienced by novice programmers. The most frequently cited benefit was the provision of instant help and quick answers or explanations, mentioned by 79.4% of teams (58 teams). This was closely followed by assistance with repetitive tasks, such as writing comments, reported by 75.3% of teams (55 teams). This means that AI tools can minimize extraneous cognitive load by automating routine tasks, thereby enabling students to focus more effectively on mastering core programming principles. Immediate response and feedback from AI tools were valued by 57.5% of teams (42 teams), while help with identifying and correcting errors was acknowledged by 54.8% of teams (40 teams). Other notable benefits included access to diverse resources and additional examples (45.21%), spelling correction (23.3%), and translation between languages (19.2%). These findings are in line with Malinka et al. [22], who suggested that ChatGPT could serve as a valuable aid in discussing challenges encountered during assignments or speed up the learning process. These results are consistent with the findings of Biswas [16], Haleem et al. [17], Jalil et al. [18], and Surameery and Shakor [19], which indicated that ChatGPT could provide users with explanations, examples, and guidance, assist with debugging by analyzing data on the programming language, code structure, and error messages, code documentation and even assist with code review.
The significant role of AI tools in reducing cognitive load is evident from our findings. As cognitive load theory posits, learning is optimized when extraneous cognitive load is minimized, allowing students to focus on essential concepts. The automation of routine tasks, such as debugging and commenting, by AI tools reduced the cognitive demands on students, thereby enabling them to concentrate on mastering core programming principles. This is particularly beneficial for novice programmers, who often struggle with the dual challenge of learning programming concepts and managing complex coding tasks. By offloading repetitive and time-consuming activities to AI, students could devote more cognitive resources to understanding and applying programming logic, which likely contributed to the observed increase in their satisfaction and comfort with AI tools over time.
On the other hand, several significant concerns emerged from the analysis. The most prevalent issue was the provision of inaccurate or misleading information, reported by 89.0% of teams (65 teams). Over-reliance on AI tools and the risk of becoming too dependent on them was a concern for 75.3% of teams (55 teams). Additionally, 45.21% of teams (33 teams) expressed frustration with AI tools identifying advanced functions or structures that were not covered in class, potentially confusing students. Incorrect but seemingly believable explanations were another concern, mentioned by 36.9% of teams (27 teams). Issues related to low code quality (34.2%), wasted time on unsuccessful bug identification and error fixing (16.4%), and inconsistency in outputs, even when the same prompt was used (13.6%), were also highlighted. These findings, particularly the concerns about inaccurate information and over-reliance on AI tools, align with challenges identified in Lo’s literature review [32], which highlighted similar issues in the use of AI in educational settings. Lo’s work emphasized the potential for AI to provide misleading information and the risk of students becoming overly dependent on AI tools, mirroring our observations in this study.
The finding that nearly 90% of students perceived AI as inaccurate has significant implications for the integration of AI into education. It underscores a critical challenge that must be addressed to ensure AI is used effectively and responsibly in learning environments. Repeated inaccuracies can erode students’ trust in AI tools, potentially hindering their willingness to use these tools in the future, even when they could be beneficial. Additionally, if students rely on inaccurate information from AI tools, they may struggle to achieve desired learning outcomes. This finding emphasizes the crucial role of teachers in equipping students with the skills to evaluate the quality of information generated by AI and guiding them in using these tools effectively.
A third of the students reported issues related to low code quality, which was surprising, keeping in mind that studies showed that AI tools could solve programming assignments and exam problems that are typically given in introduction to programming courses more effectively than most students [10,37].
These findings underscore the dual nature of AI tools in programming education. While they offer substantial benefits, such as speeding up the learning process and providing immediate assistance, they also present challenges that can hinder learning and foster dependency. The balance between leveraging the strengths of AI tools and mitigating their drawbacks is crucial for maximizing their effectiveness in educational settings. Educators must be aware of these benefits and concerns to better support students in using AI tools effectively while also encouraging the development of independent problem-solving skills. Rahman and Watanobe [38] explored how ChatGPT helps students improve their programming skills. They claimed that ChatGPT could generate nearly accurate answers to technical questions from a wide range of topics and correct or partially correct programming code based on problem descriptions, algorithm and problem names, etc. However, simply acquiring answers and code from ChatGPT can be a barrier to improving learners’ critical thinking and problem-solving skills.
4.2. The Good
The positive (‘Good’) aspects can be summarized as follows: AI tools significantly enhanced participants’ learning experiences by assisting with information retrieval, bug identification, and writing comments. Participants felt that the use of AI tools brought real-world relevance to the course, fostering essential literacies and skills that are crucial for understanding technology and preparing them for the future. Additionally, some participants noted that receiving feedback from AI tools when they were stuck boosted their self-efficacy and motivation to learn. This finding aligns with Yilmaz and Yilmaz [11], who demonstrated that ChatGPT enhances student programming self-efficacy and motivation. Similarly, Yin et al. [15] found that chatbot-based learning effectively increases college students’ motivation in basic computer science courses.
Another advantage (‘Good’) of incorporating AI tools (beyond just programming courses) is their role in shaping learners’ mindsets and skills related to AI, fostering their understanding and application of these technologies. Usage of these tools will help students in their future endeavors to understand the principles of AI, experience AI achievements, and implement AI applications effectively.
4.3. The Bad
On the negative (‘Bad’) side, challenges emerged, including instances of cheating, where students relied on AI tools to generate entire solutions, particularly under time pressure towards the end of the semester or when facing difficulties with certain learning topics. The efficiency of AI tools also led to the over-automation of some programming tasks, such as generating comments, with 92% of teams fully outsourcing this task to AI. Additionally, there were occasional issues with the quality of produced code, unsuccessful bug identification and error fixing, and the use of incorrect or non-existent functions and packages. AI can generate inaccurate outputs, inaccurate code, or incorrect explanations which appear believable to novices.
The generation of solutions (creating some part of the code) was mentioned only by a third of the teams, possibly because students perceive it as a violation of academic integrity. Despite this, the literature indicates that a high percentage of computer science students engage in some form of plagiarism, with some studies reporting the percentage being nearly 80% [39,40]. Sheard et al. [40] argued that when students are given tasks with readily available solutions in textbooks or lecture notes, they may be tempted to take shortcuts, thus bypassing the intended learning experience. In contrast, Albluwi [41], in his systematic review, noted that research on the relationship between pressure in computing courses and plagiarism is limited and does not adequately reflect the significant impact this factor has on academic dishonesty.
The ‘Bad’ side of AI tool usage highlighted several significant concerns. One of the primary issues is the risk of students developing an excessive or even blind reliance on these tools, which can lead to a superficial understanding of programming concepts and a diminished ability to solve problems independently. This reliance also opens the door to potential misuse, where the ease of accessibility and inclusion of these tools can tempt students to shortcut their learning process rather than engaging deeply with the material. As Chen et al. [42] mentioned, the value of a tool depends on its use, and there is the potential for Codex to be used in ways that limit learning, or ways that make the work of educators difficult. Actually, the developers of Codex mentioned one such challenge: possible over-reliance on Codex by novice programmers.
Furthermore, the overuse of code generation tools was found to result in a limited grasp of fundamental programming principles and concepts. This not only undermines students’ ability to write and understand code on their own but also makes them more vulnerable to technical issues and algorithmic errors. Such errors often arise from the AI’s misinterpretation of tasks or from poorly formulated queries, leading to incorrect or suboptimal solutions.
Moreover, instead of fostering a collaborative learning environment where students work alongside AI to enhance their understanding, the AI is often doing most of the work. This dynamic can erode the learning experience, as students become passive recipients rather than active participants in the problem-solving process. The result is a concerning shift away from critical engagement with programming tasks towards a more superficial reliance on AI-generated solutions.
5. Conclusions
So, do advantage overweigh the disadvantages of these tools? Despite many difficulties and challenges, integration of AI coding tools in programming courses will bring benefits to most of the students and increase the number of participants. Discovering patterns in the AI tool usage of novel programmers can enhance students’ learning. Identifying trends can help in tailoring future educational strategies and interventions based on observed patterns of engagement. We agree with Finnie-Ansley and co-authors [10] that, whatever we do, it is certain that the AI revolution has arrived at the door of our classrooms, and we must consider how we adapt to it. Keeping it out is not an option.
Incorporating AI tools into courses represents a new essential form of digital literacy in modern education. As technology becomes integral to various aspects of life and work, proficiency in AI tools is as crucial as traditional digital skills. This new literacy involves not only effectively using AI but also critically assessing its outputs and understanding its ethical implications. By integrating AI tools into curricula, educators equip students with the skills needed to navigate an increasingly automated future, fostering creativity and innovation. Ultimately, teaching students how to leverage AI thoughtfully prepares them to thrive in evolving job markets while enhancing their problem-solving abilities.
As educators, we believe it is crucial to integrate AI tools into our classrooms from the beginning, and to teach students how to use them responsibly. In our forward-thinking approach to programming education, we acknowledge the importance of equipping students with AI skills that will be essential for their future careers. The learning of AI, and learning with AI, has the potential to significantly enhance students’ critical thinking skills as they engage with AI applications, analyze their real-world implications, and rigorously test the code generated by these tools. When faced with incorrect or suboptimal solutions, students are required to reconsider and refine their prompts, rephrase their initial queries, and develop a deeper understanding of what went wrong in their previous attempts. This process not only sharpens their problem-solving abilities but also fosters a more nuanced comprehension of AI interactions and the logic behind coding.
By balancing the integration of AI, addressing ethical considerations, and fostering adaptability, educators can play a crucial role in preparing a workforce that is well-equipped to navigate the challenges and opportunities presented by AI in the programming field.
6. Limitations
This study has some limitations. First, the experimental process was conducted with 73 teams, which introduces the possibility that one team member may have been more dominant in the decision-making process. As a result, the outcomes and responses may reflect the perspectives or actions of that single dominant member, rather than representing the collective input of the entire team. In addition, the sample consists of a specific group of students from one course; therefore, the results might not be representative of all student populations. In further research, the number of participants can be increased, students from additional courses or institutions can join this study, and the wider results can be compared to current ones.
Additionally, a limitation of this study was the lack of direct measures of critical thinking skills. Future research incorporating such measures would provide a more comprehensive understanding of the impact of AI tools on student development. This addition would allow for a more precise evaluation of how AI tools affect students’ critical thinking abilities, rather than relying solely on indirect indicators or self-reported data.
Also, much of the data relies on self-reported measures, such as students’ comfort levels or perceived improvements. This could introduce biases, as students might overestimate or underestimate their abilities or comfort with AI tools.
7. Future Research
In our future research, we plan to further investigate the characteristics of effective and ineffective prompts, explore the impact of AI tools on individual versus team-based learning, and compare different AI tools in programming education. Additionally, we will examine how AI-enhanced learning affects critical thinking skills and conduct a comparative study between traditional and AI-enhanced teaching methods across various courses. This research aims to provide valuable insights into the effective integration of AI in education and its potential to improve student learning outcomes.
Funding
This research was funded by Ruppin Academic Center grant number 33139.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the guidelines of the Ruppin Academic Center, and approved by the Institutional Review Board under approval number 208, Approval Date: 20 March 2024.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The data supporting the reported results in this study are available on request from the corresponding author. Due to privacy and ethical restrictions, the data are not publicly available.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the internal project of Ruppin Academic Center.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Appendix A
The bonus questionnaire structure:
- I feel familiar with AI tools usage (Likert scale from 1 to 5). (This question was given at the beginning of the course and was given again at the end of the course.)
- I feel comfortable with usage of AI tools in this assignment (Likert scale from 1 to 5). (This question was given only for assignments that required the use of AI tools.)
- Which tools did you use: ____________________
- I used AI tools during this assignment (yes/no). (This question was given only for assignments that do not require the use of AI tools.)
- Query language: I used only English, only Hebrew, both English and Hebrew, other language ____
- I was happy with the results provided by AI tools (Likert scale from 1 to 5).
- I am concerned that I may not have enough time to complete the assignment without the help of AI tools (Likert scale from 1 to 5).
- I used AI tools during this assignment for the following tasks ____________________ (Note: In the analysis of this question, we did not analyze the specific tasks required by the assignment itself.)
- Provide a screenshot of the good prompt (a compulsory question in all assignments where students were asked to use AI tools).
- Provide a screenshot of the bad prompt (a compulsory question in all assignments where students were asked to use AI tools).
- Describe the benefits and concerns about using AI tools in your studies, personally. (This question was given in the middle of the course and was given again at the end of the course.)
References
- Becker, B.A.; Denny, P.; Finnie-Ansley, J.; Luxton-Reilly, A.; Prather, J.; Santos, E.A. Programming is hard-or at least it used to be: Educational opportunities and challenges of ai code generation. In Proceedings of the 54th ACM Technical Symposium on Computer Science Education V. 1; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2023; pp. 500–506. [Google Scholar]
- Cotton, D.R.E.; Cotton, P.A.; Shipway, J.R. Chatting and cheating: Ensuring academic integrity in the era of ChatGPT. Innov. Educ. Teach. Int. 2023, 61, 228–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denny, P.; Prather, J.; Becker, B.A.; Finnie-Ansley, J.; Hellas, A.; Leinonen, J.; Luxton-Reilly, A.; Reeves, B.N.; Santos, E.A.; Sarsa, S. Computing Education in the Era of Generative AI. Commun. ACM 2024, 67, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firat, M. What ChatGPT means for universities: Perceptions of scholars and students. J. Appl. Learn. Teach. 2023, 6, 57–63. [Google Scholar]
- Tlili, A.; Shehata, B.; Adarkwah, M.A.; Bozkurt, A.; Hickey, D.T.; Huang, R.; Agyemang, B. What if the devil is my guardian angel: ChatGPT as a case study of using chatbots in education. Smart Learn. Environ. 2023, 10, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bommasani, R.; Hudson, D.A.; Adeli, E.; Altman, R.; Arora, S.; von Arx, S.; Bernstein, M.S.; Bohg, J.; Bosselut, A.; Brunskill, E.; et al. On the opportunities and risks of foundation models. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2108.07258. [Google Scholar]
- Zawacki-Richter, O.; Marín, V.I.; Bond, M.; Gouverneur, F. Systematic review of research on artificial intelligence applications in higher education–where are the educators? Int. J. Educ. Technol. High. Educ. 2019, 16, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalliamvakou, E. Research: Quantifying GitHub Copilot’s Impact on Developer Productivity and Happiness. GitHub Blog 2022. Available online: https://github.blog/news-insights/research/research-quantifying-github-copilots-impact-on-developer-productivity-and-happiness/ (accessed on 1 May 2024).
- Peng, S.; Kalliamvakou, E.; Cihon, P.; Demirer, M. The impact of ai on developer productivity: Evidence from github copilot. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2302.06590. [Google Scholar]
- Finnie-Ansley, J.; Denny, P.; Becker, B.A.; Luxton-Reilly, A.; Prather, J. The robots are coming: Exploring the implications of OpenAI Codex on introductory programming. In Proceedings of the 24th Australasian Computing Education Conference, Virtual Event, 14–18 February 2022; pp. 10–19. [Google Scholar]
- Yilmaz, R.; Yilmaz, F.G.K. The effect of generative artificial intelligence (AI)-based tool use on students’ computational thinking skills, programming self-efficacy and motivation. Comput. Educ. Artif. Intell. 2023, 4, 100147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bird, C.; Ford, D.; Zimmermann, T.; Forsgren, N.; Kalliamvakou, E.; Lowdermilk, T.; Gazit, I. Taking Flight with Copilot: Early insights and opportunities of AI-powered pair-programming tools. Queue 2022, 20, 35–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, S.; Guo, P. From “Ban it till we understand it” to “Resistance is futile”: How university programming instructors plan to adapt as more students use AI code generation and explanation tools such as ChatGPT and GitHub Copilot. In Proceedings of the 2023 ACM Conference on International Computing Education Research-Volume 1; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2023; pp. 106–121. [Google Scholar]
- Ray, P.P. ChatGPT: A comprehensive review on background, applications, key challenges, bias, ethics, limitations and future scope. Internet Things Cyber-Phys. Syst. 2023, 3, 121–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Goh, T.T.; Yang, B.; Xiaobin, Y. Conversation technology with micro-learning: The impact of chatbot-based learning on students’ learning motivation and performance. J. Educ. Comput. Res. 2021, 59, 154–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, S. Role of ChatGPT in Computer Programming. Mesopotamian J. Comput. Sci. 2023, 2023, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haleem, A.; Javaid, M.; Singh, R.P. An era of ChatGPT as a significant futuristic support tool: A study on features, abilities, and challenges. BenchCouncil Trans. Benchmarks Stand. Eval. 2022, 2, 100089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalil, S.; Rafi, S.; LaToza, T.D.; Moran, K.; Lam, W. Chatgpt and software testing education: Promises & perils. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Conference on Software Testing, Verification and Validation Workshops (ICSTW), Dublin, Ireland, 16–20 April 2023; pp. 4130–4137. [Google Scholar]
- Surameery, N.M.S.; Shakor, M.Y. Use chat gpt to solve programming bugs. Int. J. Inf. Technol. Comput. Eng. 2023, 3, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vukojičić, M.; Krstić, J. ChatGPT in programming education: ChatGPT as a programming assistant. InspirED Teach. Voice 2023, 2023, 7–13. [Google Scholar]
- Zhai, X. ChatGPT for next generation science learning. XRDS Crossroads ACM Mag. Stud. 2023, 29, 42–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malinka, K.; Peresíni, M.; Firc, A.; Hujnák, O.; Janus, F. On the educational impact of chatgpt: Is artificial intelligence ready to obtain a university degree? In Proceedings of the 2023 Conference on Innovation and Technology in Computer Science Education V. 1; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2023; pp. 47–53. [Google Scholar]
- Rudolph, J.; Tan, S.; Tan, S. ChatGPT: Bullshit spewer or the end of traditional assessments in higher education? J. Appl. Learn. Teach. 2023, 6, 342–363. [Google Scholar]
- Covill, A.E. College students’ perceptions of the traditional lecture method. Coll. Stud. J. 2011, 45, 92–102. [Google Scholar]
- Yue, S. The Evolution of Pedagogical Theory: From Traditional to Modern Approaches and Their Impact on Student Engagement and Success. J. Educ. Educ. Res. 2024, 7, 226–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stukalenko, N.M.; Zhakhina, B.B.; Kukubaeva, A.K.; Smagulova, N.K.; Kazhibaeva, G.K. Studying innovation technologies in modern education. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Educ. 2016, 11, 7297–7308. [Google Scholar]
- Baidoo-Anu, D.; Ansah, L.O. Education in the era of generative artificial intelligence (AI): Understanding the potential benefits of ChatGPT in promoting teaching and learning. J. AI 2023, 7, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardos, Z.A.; Bhandari, S. Learning gain differences between ChatGPT and human tutor generated algebra hints. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2302.06871. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, R.; Zhao, H. ChatGPT in Creative Writing Courses in Chinese Universities: Application and Research. In Proceedings of the 2024 12th International Conference on Information and Education Technology (ICIET), Yamaguchi, Japan, 18–20 March 2024; pp. 243–247. [Google Scholar]
- Fischer, R.; Luczak-Roesch, M.; Karl, J.A. What does chatgpt return about human values? exploring value bias in chatgpt using a descriptive value theory. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2304.03612. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Z.; Mao, Y.; Zhang, J. The Influence of Artificial Intelligence Technology on College Students’ Learning Effectiveness from the Perspective of Constructivism—Taking ChatGPT as an Example. J. Educ. Humanit. Soc. Sci. 2024, 30, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, C.K. What is the impact of ChatGPT on education? A rapid review of the literature. Educ. Sci. 2023, 13, 410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, P.; Warr, M.; Islam, R. TPACK in the age of ChatGPT and Generative AI. J. Digit. Learn. Teach. Educ. 2023, 39, 235–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koć-Januchta, M.M.; Schönborn, K.J.; Roehrig, C.; Chaudhri, V.K.; Tibell, L.A.; Heller, H.C. “Connecting concepts helps put main ideas together”: Cognitive load and usability in learning biology with an AI-enriched textbook. Int. J. Educ. Technol. High. Educ. 2022, 19, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandoval-Medina, C.; Arévalo-Mercado, C.A.; Muñoz-Andrade, E.L.; Muñoz-Arteaga, J. Self-Explanation Effect of Cognitive Load Theory in Teaching Basic Programming. J. Inf. Syst. Educ. 2024, 35, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandai, K.; Tan, M.J.H.; Padhi, S.; Pang, K.T. A Cross-Era Discourse on ChatGPT’s Influence in Higher Education through the Lens of John Dewey and Benjamin Bloom. Educ. Sci. 2024, 14, 614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhail, M.A.; Mathew, S.S.; Khalil, A.; Berengueres, J.; Shah, S.J.H. “Will I be replaced?” Assessing ChatGPT’s effect on software development and programmer perceptions of AI tools. Sci. Comput. Program. 2024, 235, 103111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Watanobe, Y. ChatGPT for education and research: Opportunities, threats, and strategies. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 5783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dick, M.; Sheard, J.; Bareiss, C.; Carter, J.; Joyce, D.; Harding, T.; Laxer, C. Addressing student cheating: Definitions and solutions. ACM SigCSE Bull. 2002, 35, 172–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheard, J.; Simon Butler, M.; Falkner, K.; Morgan, M.; Weerasinghe, A. Strategies for maintaining academic integrity in first-year computing courses. In Proceedings of the 2017 ACM Conference on Innovation and Technology in Computer Science Education, Bologna, Italy, 3–5 July 2017; pp. 244–249. [Google Scholar]
- Albluwi, I. Plagiarism in programming assessments: A systematic review. ACM Trans. Comput. Educ. (TOCE) 2019, 20, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Tworek, J.; Jun, H.; Yuan, Q.; de Oliveira Pinto, H.P.; Kaplan, J.; Edwards, H.; Burda, Y.; Joseph, N.; Brockman, G.; et al. Evaluating large language models trained on code. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2107.03374. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).