Artificial Intelligence-Assisted Music Education: A Critical Synthesis of Challenges and Opportunities
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Defining Research Questions
- What is the state of the art regarding the involvement of AI in the field of music education?
- What are the most relevant application areas in the implementation of AI in music education ecosystems?
- What are the new possibilities offered by the integration of AI in schools from a pedagogical, organizational and curriculum development point of view?
- What are the challenges of the intersection of AI and digital didactics in the field of music education?
2.2. Formulation of the Search Equation
TOPIC: (“Artificial Intelligence” OR AI OR “machine learning” OR “deep learning”) AND TOPIC: music AND TOPIC: (education* OR teach* OR pedagog* OR didactics* OR “music curriculum”)
2.3. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.4. Qualitative Selection of the Final Sample
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Merchán-Sánchez-Jara, J.; Ramos-Ahijado, S.; Montoya-Rubio, J.C. Educational ecosystems for music practice in the Social Web environment: A systematic literature review. J. Educ. Res. 2022, 40, 565–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, C. Research on Human-centered Design in College Music Education to Improve Student Experience of Artificial Intelligence-based Information Systems. J. Inf. Syst. Eng. Manag. 2023, 8, 23761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, M.; Greer, R. Spectrogram-Based Deep Learning for Flute Audition Assessment and Intelligent Feedback. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Symposium on Multimedia (ISM), Laguna Hills, CA, USA, 11–13 December 2023; pp. 238–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, L.; Rolla, V.; Kestenberg, J.; Velho, L. Visual Representations for Music Understanding Improvement. In Music Technology with Swing; Aramaki, M., Davies, M., Kronland-Martinet, R., Ystad, S., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; Volume 11265, pp. 468–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, M. Design, Implementation, and Effects of Elementary Music Creation Class Using an AI-Based Music Program, Doodle Bach. Korean J. Res. Music Educ. 2023, 52, 211–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burrows, J.; Kumar, V.; Kinshuk; Dewan, A. Assessing a music student’s progress. In Proceedings of the IEEE 18th International Conference on Advanced Learning Technologies (ICALT), Mumbai, India, 9–13 July 2018; pp. 202–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giraldo, S.; Ortega, A.; Perez, A.; Ramirez, R.; Waddell, G.; Williamon, A. Automatic assessment of violin performance using dynamic time warping classification. In Proceedings of the 26th IEEE Signal Processing and Communications Applications Conference (SIU), Izmir, Turkey, 2–5 May 2018; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q. The Creation of Multi Intelligence Music Classroom in Children’s Enlightenment Stage Based on Virtual Reality Technology. In Proceedings of the 2021 2nd International Conference on Education, Knowledge and Information Management (ICEKIM), Xiamen, China, 29–31 January 2021; pp. 431–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, K. Artificial intelligence and creativity: Piano teaching with augmented reality applications. Interact. Learn. Environ. 2023, 31, 7017–7028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W. Research on the Design of Intelligent Music Teaching System Based on Virtual Reality Technology. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2022, 2022, 7832306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L. Fusion Artificial Intelligence Technology in Music Education Teaching. J. Electr. Syst. 2023, 19, 178–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B. Design and Development of Music Intelligent Education System Based on Artificial Intelligence. In Proceedings of the 2024 Third International Conference on Distributed Computing and Electrical Circuits and Electronics (ICDCECE), Ballari, India, 26–27 April 2024; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinze, V.; Dhami, J.; Desai, D.; Dalvi, H.; Raut, P. Application of AI as Singing Trainer. In Proceedings of the 7th IEEE International Conference on Advances in Computing, Communication and Control (ICAC3), Mumbai, India, 3–4 December 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y. E-learning and speech dynamic recognition based on network transmission in music interactive teaching experience. Entertain. Comput. 2024, 50, 100716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, D.; Xia, G. A Computer-aided Multimodal Music Learning System with Curriculum: A Pilot Study. In Proceedings of the International Conference on New Interfaces for Musical Expression (NIME), Online, 28 June–1 July 2022; pp. 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventura, M.D. A Self-adaptive Learning Music Composition Algorithm as Virtual Tutor. In Artificial Intelligence Applications and Innovations; Maglogiannis, I., Iliadis, L., Macintyre, J., Cortez, P., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; Volume 646, pp. 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.Z.A.; Hawthorne, C.; Roberts, A.; Dinculescu, M.; Wexler, J.; Hong, L.; Howcroft, J. The bach doodle: Approachable music composition with machine learning at scale. In Proceedings of the 20th International Society for Music Information Retrieval Conference (ISMIR), Delft, The Netherlands, 4–8 November 2019; pp. 793–800. [Google Scholar]
- Knapp, D.H.; Powell, B.; Smith, G.D.; Coggiola, J.C.; Kelsey, M. Soundtrap usage during COVID-19: A machine-learning approach to assess the effects of the pandemic on online music learning. Res. Stud. Music Educ. 2023, 45, 571–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, L. Research on Diversified Teaching Strategies for Music Courses in Colleges and Universities under the Background of Artificial Intelligence. Appl. Math. Nonlinear Sci. 2024, 9, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, H. Analysis and Innovation of Vocal Music Teaching Quality in Colleges and Universities Based on Artificial Intelligence. Appl. Math. Nonlinear Sci. 2024, 9, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, W. Evaluating the Vocal Music Teaching Using Backpropagation Neural Network. Mob. Inf. Syst. 2022, 2022, 3843726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solanskyi, S.; Zhmurkevych, Z.; Saldan, S.; Velychko, O.; Dyka, N. Innovative methods in modern piano pedagogy. Sci. Her. Uzhhorod. Univ. Ser. Phys. 2024, 55, 2978–2987. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W. Constructing a Theoretical Methodological System for Vocal Music Education in Colleges and Universities in the Context of Deep Learning Algorithms. Appl. Math. Nonlinear Sci. 2023, 9, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konecki, M. Adaptive Drum Kit Learning System: Impact on Students’ Learning Outcomes. Int. J. Inf. Educ. Technol. 2023, 13, 1534–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, A.-M.; Traube, C. Reports from the field: Learning to play the guitar with the novaxe online learning platform. In The Oxford Handbook of Social Media and Music Learning; Waldron, J.L., Horsley, S., Veblen, K.K., Eds.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2020; pp. 245–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Della Ventura, M. Exploring the Impact of Artificial Intelligence in Music Education to Enhance the Dyslexic Student’s Skills. In Learning Technology for Education Challenges; Uden, L., Liberona, D., Sánchez, G., Rodríguez-González, S., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; Volume 1011, pp. 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niediek, I.; Sieger, M.; Gerland, J. Music apps as inclusive engines?—A spotlight into practice. In Computers Helping People with Special Needs; Miesenberger, K., Kouroupetroglou, G., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; Volume 10896, pp. 159–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Jiang, C. On the Ethical Risks of Artificial Intelligence Applications in Education and Its Avoidance Strategies. J. Educ. Humanit. Soc. Sci. 2023, 14, 354–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Killian, L. Integrating Music Technology in the Classroom: Increasing Customization for Every Student; Carnegie Mellon University: Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 2019; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann-Wermser, A.; Weyel, B. [PosyMus]—The Music Education perspective. In Computer Based Assessment and Feedback in Music Education; Lehmann-Wermser, A., Breiter, A., Eds.; Institut für musikpädagogische Forschung, Hochschule für Musik, Theater und Medien Hannover: Hannover, Germany, 2021; pp. 29–50. [Google Scholar]
- Sturm, B.L.; Ben-Tal, O. Folk the algorithms: (Mis)Applying artificial intelligence to folk music. In Handbook of Artificial Intelligence for Music: Foundations, Advanced Approaches, and Developments for Creativity; Reck, E., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 423–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creely, E.; Henriksen, D.; Henderson, M. Artificial intelligence, creativity, and education: Critical questions for researchers and educators. In Proceedings of the Society for Information Technology & Teacher Education International Conference (SITE), New Orleans, LA, USA, 13–17 March 2023; pp. 1309–1317. Available online: https://www.learntechlib.org/primary/p/221998/ (accessed on 20 September 2024).
- Sun, H. The Research of Music AI in the Context of Information Security. In Intelligent Computing Methodologies, Proceedings of the Intelligent Computing Methodologies: 16th International Conference (ICIC 2020), Bari, Italy, 2–5 October 2020; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 593–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturm, B.L.; Iglesias, M.; Ben-Tal, O.; Miron, M.; Gómez, E. Artificial intelligence and music: Open questions of copyright law and engineering praxis. Arts 2019, 8, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akgun, S.; Greenhow, C. Artificial intelligence in education: Addressing ethical challenges in K-12 settings. AI Ethics 2022, 2, 431–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-González, C.S. The impact of artificial intelligence in education: Transforming the way we teach and learn. Qurriculum 2023, 36, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Gutiérrez, S.; Merchán-Sánchez-Jara, J. Digital humanities and educational ecosystem: Towards a new epistemic structure from digital didactics. Anu. ThinkEPI 2022, 16, e16a35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merchán-Sánchez-Jara, J. e-Score; impact, perception and uses in music educational institutions. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Technological Ecosystems for Enhancing Multiculturality (TEEM), Porto, Portugal, 7–9 October 2015; pp. 449–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
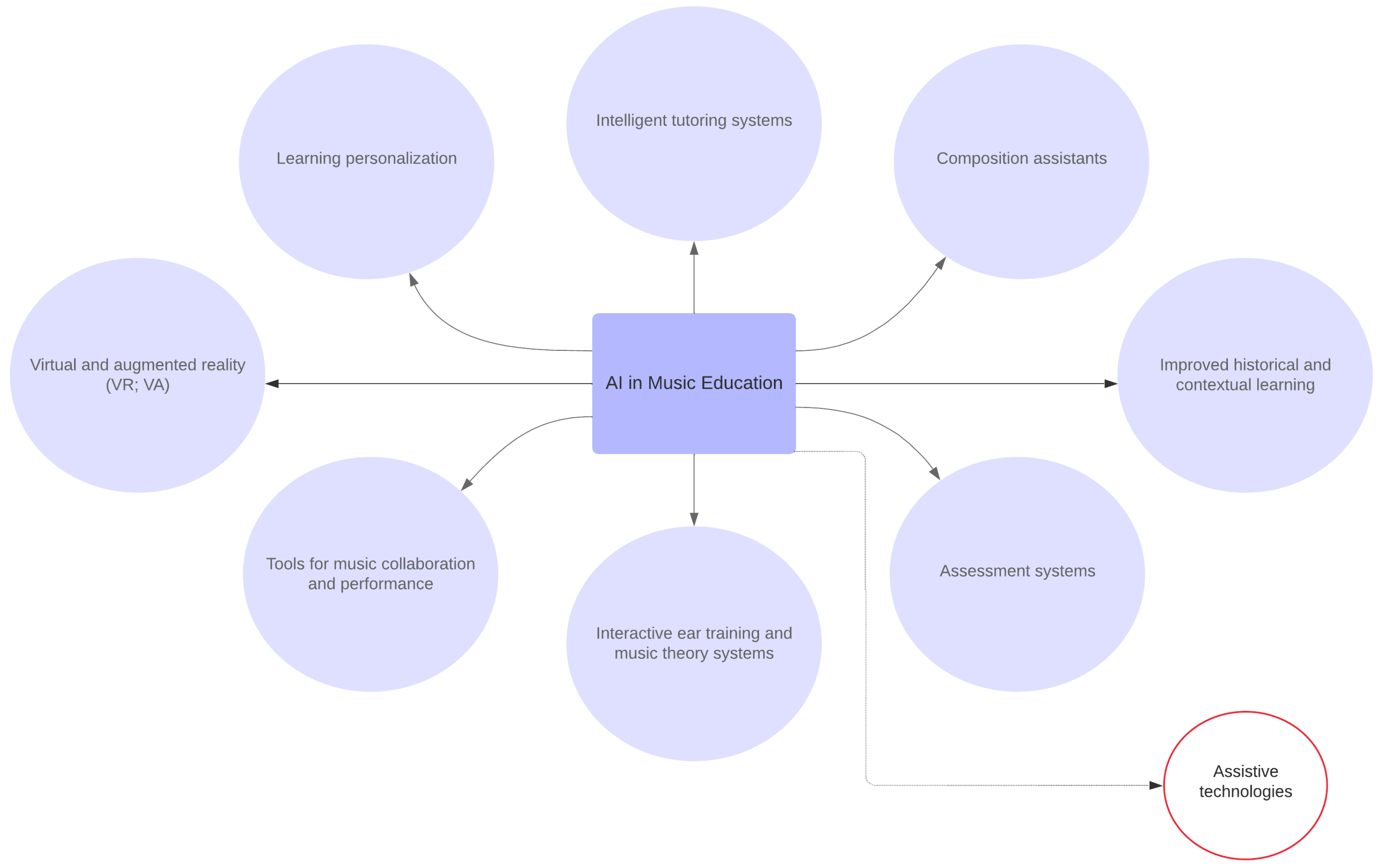
| Area | Authors | Educational Level | Didactic Potential of Generative AI |
|---|---|---|---|
| Virtual and augmented reality (VR; VA) 12% | Wang (2021) [9] | Early childhood education | Implementation of virtual reality in early childhood classrooms, as it maximizes children’s mental and thinking capacity by lowering the abstraction level of concepts, processes and ideas |
| Cui (2023) [10] | Basic musical skills | Analyzes the possibilities of augmented reality for first steps music performance instruction. Specifically, the acquisition of basic piano skills on mobile devices by means of augmented reality | |
| Chen (2022) [11] | All educational levels | Develops a music learning system based on virtual reality technology | |
| Learning personalization 12% | Zhang, L. (2023) [12] | All educational levels | Development of the innovative EFDfO (entropy features data fusion optimized) framework, a model that offers personalized musical education to students and improves their academic performance |
| Qian (2023) [2] | Higher music education | Personalization and multimodal methods will help increase engagement among college music students | |
| Xu (2024) [13] | Elementary school | AI-based education system that offers personalized guidance to enhance the interest of music students | |
| Intelligent tutoring systems 16% | Vinze et al., (2021) [14] | Basic musical skills | Assisted vocal music training |
| Zheng (2024) [15] | All educational levels | Interactive vocal music education | |
| Agarwal & Greer (2023) [3] | Conservatories | Flute performance improvement | |
| Chin & Xia (2022) [16] | Basic musical skills | AI-empowered music tutor with a systematic curriculum design and multimodal feedback | |
| Composition assistance 16% | Ventura (2022) [17] | Conservatories | Harmonization of music basslines |
| Huang et al. (2019) [18] | Elementary school | Approachable music composition with machine learning at scale | |
| Choi (2023) [5] | Elementary school | (Doodle Bach) music creation classes based on creative teaching design | |
| Knapp et al. (2023) [19] | All educational levels | (Soundtrap) web-based digital audio workstation | |
| Improved historical and contextual learning 4% | Wan (2024) [20] | Higher music education | Improved the effectiveness of music course resources |
| Automated assessment systems 12% | Hou (2024) [21] | Higher music education | Evaluation of the vocal music teaching process |
| Cao (2022) [22] | Basic musical skills | Evaluation of the vocal music teaching process | |
| Burrows et al. (2018) [6] | All educational levels | Objective evaluation of musical progress in musical performances | |
| Interactive ear training and music theory systems 8% | Cruz et al. (2018) [4] | Basic musical skills | Improved perception of musical structures |
| Solanskyi et al. (2024) [23] | Conservatories | Technological adaptation of piano pedagogy; individualized approach to musical learning with platforms such as MusicFlow | |
| Tools for music collaboration and performance 12% | Zhang, W. (2023) [24] | Higher music education | Improved performance of vocal music |
| Konecki (2023) [25] | Self-paced learning | Adaptive drum learning system | |
| Burns and Traube (2020) [26] | All educational levels | Improved the learning of musical instruments, specifically the guitar, and presented the Novaxe online learning platform (OLP) | |
| Assistive technologies 8% | Della Ventura (2019) [27] | Higher music education | Improved the learning of dyslexic students in music education |
| Niediek et al. (2018) [28] | Secondary education | Challenges of digital musical instruments and applications in inclusive music education environments |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Merchán Sánchez-Jara, J.F.; González Gutiérrez, S.; Cruz Rodríguez, J.; Syroyid Syroyid, B. Artificial Intelligence-Assisted Music Education: A Critical Synthesis of Challenges and Opportunities. Educ. Sci. 2024, 14, 1171. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci14111171
Merchán Sánchez-Jara JF, González Gutiérrez S, Cruz Rodríguez J, Syroyid Syroyid B. Artificial Intelligence-Assisted Music Education: A Critical Synthesis of Challenges and Opportunities. Education Sciences. 2024; 14(11):1171. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci14111171
Chicago/Turabian StyleMerchán Sánchez-Jara, Javier Félix, Sara González Gutiérrez, Javier Cruz Rodríguez, and Bohdan Syroyid Syroyid. 2024. "Artificial Intelligence-Assisted Music Education: A Critical Synthesis of Challenges and Opportunities" Education Sciences 14, no. 11: 1171. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci14111171
APA StyleMerchán Sánchez-Jara, J. F., González Gutiérrez, S., Cruz Rodríguez, J., & Syroyid Syroyid, B. (2024). Artificial Intelligence-Assisted Music Education: A Critical Synthesis of Challenges and Opportunities. Education Sciences, 14(11), 1171. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci14111171








