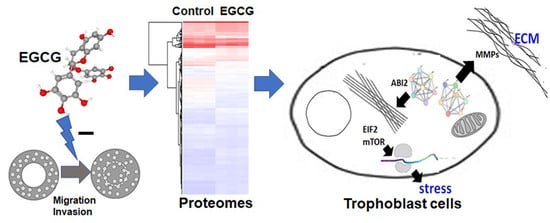
A Proteomics-Based Identification of the Biological Networks Mediating the Impact of Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate on Trophoblast Cell Migration and Invasion, with Potential Implications for Maternal and Fetal Health
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemical Reagents
2.2. Cell Culture
2.3. Zone Closure Assay for Cell Migration and Invasion
2.4. Proteomics Comparison of EGCG-Treated and Control Trophoblast Cells
2.4.1. Preparation and Digestion of Protein Samples
2.4.2. Analysis of Protein Samples Using Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry
2.4.3. Identification and Quantification of Proteins
2.5. Bioinformatics Analysis and Data Visualization
2.5.1. IPA Network Analysis
2.5.2. KEGG Enrichment Analysis Using the ShinyGO Web Tool
2.5.3. GSEA Analysis
2.6. Quantitative Real-Time PCR
2.7. Western Blot Analysis
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. EGCG Inhibits Migration and Invasion of Trophoblast Cells at a Non-Cytotoxic Concentration
3.2. Proteomics Analysis Reveals Significant Differences in Protein Expression between EGCG-Treated and Control Groups
3.3. Downregulation of EIF2, mTOR, and Estrogen Response Signaling Pathways and Protein Translation Processes in EGCG-Treated Trophoblast Cells
3.4. Upregulation of Lipid Degradation, Oxidative Metabolism, and in EGCG-Treated Trophoblast Cells
3.5. EGCG Modulated Protein Expression in Trophoblast Cells by Regulating Gene Transcription
3.6. EGCG Suppresses Cytoskeletal and Extracellular Matrix Reorganization Proteins
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wolfram, S. Effects of green tea and EGCG on cardiovascular and metabolic health. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2007, 26, 373S–388S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohishi, T.; Goto, S.; Monira, P.; Isemura, M.; Nakamura, Y. Anti-inflammatory Action of Green Tea. Anti-Inflamm. Anti-Allergy Agents Med. Chem. 2016, 15, 27634207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menegazzi, M.; Campagnari, R.; Bertoldi, M.; Crupi, R.; Paola, D.; Cuzzocrea, R.S. Protective Effect of Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate (EGCG) in Diseases with Uncontrolled Immune Activation: Could Such a Scenario Be Helpful to Counteract COVID-19? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higdon, J.V.; Frei, B. Tea catechins and polyphenols: Health effects, metabolism, and antioxidant functions. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2003, 43, 89–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negri, A.; Naponelli, V.; Rizzi, F.; Bettuzzi, S. Molecular Targets of Epigallocatechin-Gallate (EGCG): A Special Focus on Signal Transduction and Cancer. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, K.W.; Xia, J.; Cheng, B.H.; Gao, H.C.; Fu, L.W.; Luo, X.L. Tea polyphenol EGCG inhibited colorectal-cancer-cell proliferation and migration via downregulation of STAT3. Gastroenterol. Rep. 2020, 9, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.H.; Hsieh, C.H.; Tsai, S.Y.; Wang, C.Y.; Wang, C.C. Anticancer effects of epigallocatechin-3-gallate nanoemulsion on lung cancer cells through the activation of AMP-activated protein kinase signaling pathway. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 5163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barenys, M.; Gassmann, K.; Baksmeier, C.; Heinz, S.; Reverte, I.; Schmuck, M.; Temme, T.; Bendt, F.; Zschauer, T.C.; Rockel, T.D.; et al. Epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) inhibits adhesion and migration of neural progenitor cells in vitro. Arch. Toxicol. 2016, 91, 27116294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Borm, H.T.; El-Gaber, A.S.A. Effect of prenatal exposure of green tea extract on the developing central nervous system of rat fetuses; histological, immune-histochemical and ultrastructural studies. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 28, 4704–4716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.C.; Chan, W.H. Epigallocatechin gallate induces embryonic toxicity in mouse blastocysts through apoptosis. Drug Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 37, 24164432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burrows, T.D.; King, A.; Loke, Y.W. Trophoblast migration during human placental implantation. Hum. Reprod. Update 1996, 2, 307–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, C.; Gleeson, L.M.; Mckinnon, T.; Lala, P.K. Regulation of human trophoblast migration and invasiveness. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2002, 80, 116–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naicker, T.; Khedun, S.M.; Moodley, J.; Pijnenborg, R. Quantitative analysis of trophoblast invasion in preeclampsia. Acta Obstet. Gynecol. Scand. 2003, 82, 722–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazurakova, A.; Koklesova, L.; Samec, M.; Kudela, E.; Sivakova, J.; Pribulova, T.; Pec, M.J.; Pec, M.; Kello, M.; Büsselberg, D.; et al. Flavonoids exert potential in the management of hypertensive disorders in pregnancy. Pregnancy Hypertens. 2022, 29, 35803199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zulliati, Z.; Hidayah, N. Green Tea and The Preeclampsia in Intra Partum. In Proceedings of the First National Seminar Universitas Sari Mulia, NS-UNISM 2019, Banjarmasin, Indonesia, 23 November 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Tan, J.; Dai, W.; Wang, B.; Bai, Y.; Ren, Y.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, Y. The association between maternal tea consumption and the risk of pregnancy induced hypertension: A retrospective cohort study in Lanzhou, China. Pregnancy Hypertens. 2022, 30, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.Q.; Xu, H.; Xiong, X.; Luo, Z.C.; Audibert, F.; Fraser, W.D. Tea Consumption During Pregnancy and the Risk of Pre-Eclampsia. Int. J. Gynecol. Obstet. 2009, 105, 123–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Williams, K.E.; Kwan, E.Y.; Kapidzic, M.; Puckett, K.A.; Aburajab, R.K.; Robinson, J.F.; Fisher, S.J. Global proteomic analyses of human cytotrophoblast differentiation/invasion. Development 2021, 148, 199561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.G.; Lu, C.C.; Lin, Y.H.; Shen, W.C.; Lai, C.H.; Ho, Y.J.; Chung, J.G.; Lin, T.H.; Lin, Y.C.; Yang, J.S. Proteomic approaches to study epigallocatechin gallate-provoked apoptosis of TSGH-8301 human urinary bladder carcinoma cells: Roles of AKT and heat shock protein 27-modulated intrinsic apoptotic pathways. Oncol. Rep. 2011, 26, 939–947. [Google Scholar]
- Flores-Pérez, A.; Marchat, L.A.; Sánchez, L.L.; Romero-Zamora, D.; Arechaga-Ocampo, E.; Ramírez-Torres, N.; Chávez, J.D.; Carlos-Reyes, A.; La, A.D.; Vega, H.; et al. Differential proteomic analysis reveals that EGCG inhibits HDGF and activates apoptosis to increase the sensitivity of non-small cells lung cancer to chemotherapy. Proteom. Clin. Appl. 2016, 10, 172–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Li, Q.; Huang, J.; Liang, Q.; Yan, Y.; Lin, H.; Xiao, W.; Lin, Y.; Zhang, S.; Tan, B.; et al. Proteomic analysis of the inhibitory effect of epigallocatechin gallate on lipid accumulation in human HepG2 cells. Proteome Sci. 2013, 11, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aplin, J.D.; Charlton, A.K. The Role of Matrix Macromolecules in the Invasion of Decidua by Trophoblast: Model Studies Using BeWo Cells. In Trophoblast Invasion and Endometrial Receptivity; Denker, H.W., Aplin, J.D., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1990; pp. 139–158. [Google Scholar]
- Orendi, K.; Kivity, V.; Sammar, M.; Grimpel, Y.; Gonen, R.; Meiri, H.; Lubzens, E.; Huppertz, B. Placental and Trophoblastic In Vitro Models to Study Preventive and Therapeutic Agents for Preeclampsia. Placenta 2011, 32, S49–S54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bralewska, M.; Pietrucha, T.; Sakowicz, A. Reduction in CgA-Derived CST Protein Level in HTR-8/SVneo and BeWo Trophoblastic Cell Lines Caused by the Preeclamptic Environment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 7124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, C.C.; Chen, Y.W.; Jeng, T.L.; Li, C.R.; Kuo, C.F. Consumption of purple sweet potato affects post-translational modification of plasma proteins in hamsters. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 12450–12458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Liao, C.C.; Han, Y.; Lv, J.; Lei, M.; Li, Y.; Lv, Q.; Dong, D.; Zhang, S.; Pan, Y.H.; et al. Co-activation of Akt, Nrf2, and NF-κB signals under UPRER in torpid Myotis ricketti bats for survival. Commun. Biol. 2020, 3, 7658203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, S.X.; Jung, D.; Yao, R. ShinyGO: A graphical gene-set enrichment tool for animals and plants. Bioinformatics 2020, 36, 2628–2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subramanian, A.; Tamayo, P.; Mootha, V.K.; Mukherjee, S.; Ebert, B.L.; Gillette, M.A.; Paulovich, A.; Pomeroy, S.L.; Golub, T.R.; Lander, E.S.; et al. Gene set enrichment analysis: A knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 1239896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shih, L.J.; Chen, T.F.; Lin, C.K.; Liu, H.S.; Kao, Y.H. Green tea (-)-epigallocatechin gallate inhibits the growth of human villous trophoblasts via the ERK, p38, AMP-activated protein kinase, and protein kinase B pathways. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2016, 311, 27147558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanselow, S.; Neumann-Arnold, L.; Wojciech-Moock, F.; Seufert, W. Stepwise assembly of the eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2 complex. J. Biol. Chem. 2022, 298, 8844851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxton, R.A.; Sabatini, D.M. mTOR Signaling in Growth, Metabolism, and Disease. PMID 2017, 168, 5394987. [Google Scholar]
- Wahl, P.W.; Walden, C.E.; Knopp, R.H.; Warnick, G.R.; Hoover, J.J.; Hazzard, W.R.; Albers, J.J. Lipid and lipoprotein triglyceride and cholesterol interrelationships: Effects of sex, hormone use, and hyperlipidemia. Metabolism 1984, 33, 6727651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohmann, T.; Dehghani, F. The Cytoskeleton-A Complex Interacting Meshwork. Cells 2019, 8, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baryla, M.; Kaczynski, P.; Goryszewska, E.; Riley, S.C.; Waclawik, A. Prostaglandin F2α stimulates adhesion, migration, invasion and proliferation of the human trophoblast cell line HTR-8/SVneo. Placenta 2019, 77, 30827352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Q.; Chen, Y.; Yin, N.; Shan, N.; Luo, X.; Tong, C.; Zhang, H.; Baker, P.N.; Liu, X.; Qi, H. N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase V inhibits the invasion of trophoblast cells by attenuating MMP2/9 activity in early human pregnancy. Placenta 2015, 36, 26349781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradley, W.D.; Koleske, A.J. Regulation of cell migration and morphogenesis by Abl-family kinases: Emerging mechanisms and physiological contexts. J. Cell Sci. 2009, 122, 3441–3454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Borek, D.; Padrick, S.B.; Gomez, T.S.; Metlagel, Z.; Ismail, A.M.; Umetani, J.; Billadeau, D.D.; Otwinowski, Z.; Rosen, M.K. Structure and control of the actin regulatory WAVE complex. Nature 2010, 468, 533–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, J.; Guo, W.; Zhang, H.; Wang, J. Enhanced Rb/E2F and TSC/mTOR Pathways Induce Synergistic Inhibition in PDGF-Induced Proliferation in Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, 5226788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentilella, A.; Kozma, S.C.; Thomas, G. A liaison between mTOR signaling, ribosome biogenesis and cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1849, 4766360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosario, F.J.; Powell, T.L.; Gupta, M.B.; Cox, L.; Jansson, T. mTORC1 Transcriptional Regulation of Ribosome Subunits, Protein Synthesis, and Molecular Transport in Primary Human Trophoblast Cells. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 583801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnelly, N.; Gorman, A.M.; Gupta, S.; Samali, A. The eIF2α kinases: Their structures and functions. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2013, 70, 23354059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Moustaid-Moussa, N.; Chen, L.; Mo, H.; Shastri, A.; Su, R.; Bapat, P.; Kwun, I.; Shen, C.L. Novel insights of dietary polyphenols and obesity. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2014, 25, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenti, D.; De Rasmo, D.; Signorile, A.; Rossi, L.; De Bari, L.; Scala, I.; Granese, B.; Papa, S.; Vacca, R.A. Epigallocatechin-3-gallate prevents oxidative phosphorylation deficit and promotes mitochondrial biogenesis in human cells from subjects with Down’s syndrome. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1832, 23291000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, L.M.; Kelleher, N.L. Proteoform: A single term describing protein complexity. Consort. Top Down Proteom. 2013, 10, 186–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, L.M.; Kelleher, N.L. Proteoforms as the next proteomics currency. Science 2018, 359, 5944612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Y.-C.; Liao, C.-C.; Shui, H.-A.; Huang, P.-H.; Shih, L.-J. A Proteomics-Based Identification of the Biological Networks Mediating the Impact of Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate on Trophoblast Cell Migration and Invasion, with Potential Implications for Maternal and Fetal Health. Proteomes 2023, 11, 31. https://doi.org/10.3390/proteomes11040031
Chen Y-C, Liao C-C, Shui H-A, Huang P-H, Shih L-J. A Proteomics-Based Identification of the Biological Networks Mediating the Impact of Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate on Trophoblast Cell Migration and Invasion, with Potential Implications for Maternal and Fetal Health. Proteomes. 2023; 11(4):31. https://doi.org/10.3390/proteomes11040031
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Yueh-Chung, Chen-Chung Liao, Hao-Ai Shui, Pei-Hsuan Huang, and Li-Jane Shih. 2023. "A Proteomics-Based Identification of the Biological Networks Mediating the Impact of Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate on Trophoblast Cell Migration and Invasion, with Potential Implications for Maternal and Fetal Health" Proteomes 11, no. 4: 31. https://doi.org/10.3390/proteomes11040031
APA StyleChen, Y. -C., Liao, C. -C., Shui, H. -A., Huang, P. -H., & Shih, L. -J. (2023). A Proteomics-Based Identification of the Biological Networks Mediating the Impact of Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate on Trophoblast Cell Migration and Invasion, with Potential Implications for Maternal and Fetal Health. Proteomes, 11(4), 31. https://doi.org/10.3390/proteomes11040031