Extracellular Matrix Proteome and Phosphoproteome of Potato Reveals Functionally Distinct and Diverse Canonical and Non-Canonical Proteoforms
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Plant Material and Growth Condition
2.2. Isolation of Pure ECM
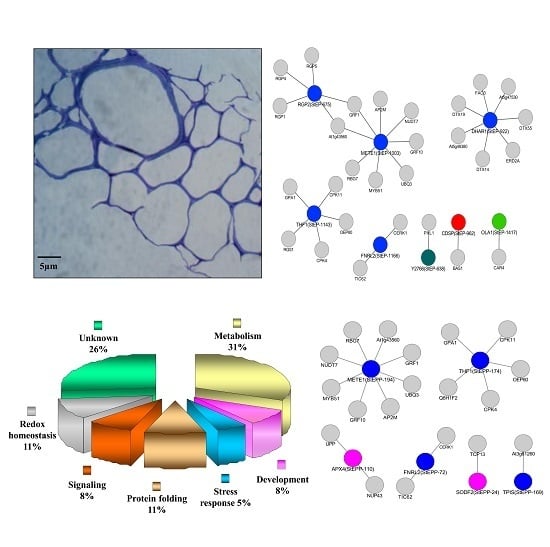
2.3. Light Microscopy
2.4. ECM Protein Extraction and Quantification
2.5. Isolation of Plasma Membrane Proteins
2.6. Isolation of Cytosolic Proteins
2.7. Enzyme Assay
2.8. Two-Dimensional Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis
2.9. Detection of ECM Phosphoproteins and Proteins
2.10. Image Acquisition and in Silico Analysis
2.11. Peptide Preparation for Tandem Mass-Spectrometry
2.12. Protein Identification Using LC-MS/MS
2.13. Network Visualization
2.14. Bioinformatic Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Evaluation of Potato ECM Integrity and Purity Assessment
3.2. Construction of 2-DE ECM Proteome and Phosphoproteome Map
3.3. Distribution Pattern and Physicochemical Characteristics of ECM Proteins and Phosphoproteins
3.4. Functional Categorization of ECM Proteins
3.5. Functional Categorization of ECM Phosphoproteins
3.6. Identification of Non-Canonical Proteins and Phosphoproteins in ECM
3.7. Cellular ECM Proteome and Phosphoproteome Network
4. Discussion
4.1. ECM Proteoform Homeostasis Regulates Wall Architecture and Mechanics
4.2. ECM Proteoforms Mediate Semantics, Wall Signaling, and Metabolism
4.3. Comparison of Extracellular Matrix Proteomes
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DTT | Dithiothreitol |
| PMSF | Phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride |
| ACN | Acetonitrile |
| SDS | Sodium dodecyl sulfate |
| ATP | Adenosine Triphosphate |
| SDS PAGE | Sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis |
| LC-MS/MS | Liquid Chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry |
References
- Wolf, S.; Hematy, K.; Hofte, H. Growth control and cell wall signaling in plants. Ann. Rev. Plant Biol. 2012, 63, 381–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fry, S.C. The Growing Plant Cell Wall: Chemical and Metabolic Analysis; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1988; p. 333. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.J.; Saravanan, R.S.; Damasceno, C.M.B.; Yamane, H.; Kim, B.D.; Rose, J.K.C. Digging deeper into the plant cell wall proteome. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2004, 42, 979–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamet, E.; Canut, H.; Boudart, G.; Pont-Lezica, R.F. Cell wall proteins: A new insight through proteomics. Trends Plant Sci. 2006, 11, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamet, E.; Albenne, C.; Boudart, G.; Irshad, M.; Canut, H.; Pont-Lezica, R.F. Recent advances in plant cell wall proteomics. Proteomics 2008, 8, 893–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rose, J.K.C.; Lee, S.J. Straying off the highway: Trafficking of secreted plant proteins and complexity in the plant cell wall proteome. Plant Physiol. 2010, 153, 433–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narula, K.; Elagamey, E.; Datta, A.; Chakraborty, N.; Chakraborty, S. Comparative Analyses of Extracellular Matrix Proteome: An Under-Explored Area in Plant Research; Goyal, A., Ed.; Crop Plants. InTech: Janeza Tradine, Croatia, 2012; pp. 145–166. [Google Scholar]
- Feiz, L.; Irshad, M.; Pont-Lezica, R.F.; Canut, H.; Jamet, E. Evaluation of cell wall preparations for purifying cell walls from Arabidopsis hypocotyls. Plant Methods 2006, 2, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watson, B.S.; Sumner, L.W. Isolation of Cell Wall Proteins from Medicago Sativa Stems. In Plant Proteomics: Methods and Protocols, Methods in Molecular Biology; Thiellement, H., Zivy, M., Damerval, C., Me´chin, V., Eds.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2007; Volume 355, pp. 79–92. [Google Scholar]
- Jamet, E.; Boudart, G.; Borderies, G.; Charmont, S.; Lafitte, C.; Rossignol, M.; Canut, H.; Pont-Lezica, R.F. Isolation of plant cell wall proteins. Methods Mol Biol. 2008, 425, 187–201. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gebicki, S.; Gebicki, J.M. Formation of peroxides in amino acids and proteins exposed to oxygen free radicals. Biochem. J. 1993, 289, 743–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehesranta, S.J.; Davies, H.V.; Shepherd, L.V.T.; Nunan, N.; McNicol, J.W.; Auriola, S.; Koistinen, K.M.; Suomalainen, S.; Kokko, H.I.; Kärenlampi, S.O. Comparison of tuber proteomes of potato varieties, landraces, and genetically modified lines. Plant Physiol. 2005, 138, 1690–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murashige, T.; Skoog, F. A revised medium for rapid growth and bio assays with tobacco tissue culture. Physiol. Plant. 1962, 15, 473–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Averyhart-Fullard, V.; Datta, K.; Marcus, A. A hydroxyproline-rich protein in the soybean cell wall. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1988, 85, 1082–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhushan, D.; Pandey, A.; Chattopadhyay, A.; Choudhary, M.K.; Chakraborty, S.; Datta, A.; Chakraborty, N. Extracellular matrix proteome of chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) illustrates pathway abundance, novel protein functions and evolutionary perspect. J. Proteome Res. 2006, 5, 1711–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bessire, M.; Chassot, C.; Jacquat, A.C.; Humphry, M.; Borel, S.; Petétot, J.M.; Métraux, J.P.; Nawrath, C. A permeable cuticle in Arabidopsis leads to a strong resistance to Botrytis cinerea. EMBO J. 2007, 26, 2158–2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santoni, V. Plant Plasma Membrane Protein Extraction and Solubilization for Proteomic Analysis. Plant Proteom. 2007, 93–109. [Google Scholar]
- Schiltz, S.; Gallardo, K.; Huart, M.; Negroni, L.; Sommerer, N.; Burstin, J. Proteome reference maps of vegetative tissues in pea. An investigation of nitrogen mobilization from leaves during seed filling. Plant Physiol. 2004, 135, 2241–2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsson, C.; Sommarin, M.; Widell, S. Isolation of highly purified plasma membranes and the separation of inside-out and right-side-out vesicles. Method Enzymol. 1994, 228, 451–469. [Google Scholar]
- Ames, B.N. Assay of inorganic phosphate, total phosphate, and phosphatases. Methods Enzymol. 1966, 8, 113–114. [Google Scholar]
- Ruebelt, M.C.; Leimgruber, N.K.; Lipp, M.; Reynolds, T.L.; Nemeth, M.A.; Astwood, J.D.; Engel, K.H.; Jany, K.D. Application of two-dimensional gel electrophoresis to interrogate alterations in the proteome of genetically modified crops. 1. Assessing analytical validation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 2154–2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakraborty, N.; Ghosh, R.; Ghosh, S.; Narula, K.; Tayal, R.; Datta, A.; Chakraborty, S. Reduction of oxalate levels in tomato fruit and consequent metabolic remodeling following overexpression of a fungal oxalate decarboxylase. Plant Physiol. 2013, 162, 364–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GeneMANIA. Available online: http://genemania.org (accessed on 17 March 2016).
- The Bio-Analytic Resource for Plant Biology. Available online: http://bar.utoronto.ca (accessed on 17 March 2016).
- STRING. Available online: http://string-db.org (accessed on 17 March 2016).
- Mentha the interactome browser. Available online: http://mentha.uniroma2.it (accessed on 17 March 2016).
- InteroPorc automatic molecular interaction predictions. Available online: http://biodev.extra.cea.fr/interoporc/Default.aspx (accessed on 17 March 2016).
- IntAct. Available online: http://www.ebi.ac.uk/intact/ (accessed on 17 March 2016).
- Database of Interacting Proteins. Available online: http://dip.doe-mbi.ucla.edu/dip/Main.cgi (accessed on 17 March 2016).
- Agile Protein Interactomes DataServer. Available online: http://bioinfow.dep.usal.es/apid/index.html (accessed on 17 March 2016).
- The Molecular INTeraction Database. Available online: http://mint.bio.uniroma2.it/mint/Welcome.do (accessed on 17 March 2016).
- BIND. Available online: http://bind.ca (accessed on 17 March 2016).
- Cytoscape. Available online: http://www.cytoscape.org (accessed on 17 March 2016).
- Shannon, P.; Markiel, A.; Ozier, O.; Baliga, N.S.; Wang, J.T.; Ramage, D.; Amin, N.; Schwikowski, B.; Ideker, T. Cytoscape: A software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res. 2003, 1, 2498–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conesa, A.; Gotz, S.; Garcia-Gomez, J.M.; Terol, J.; Talon, M.; Robles, M. Blast2GO: A universal tool for annotation, visualization and analysis in functional genomics research. Bioinformatics 2005, 21, 3674–3676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- InterPro. Available online: http://www.ebi.ac.uk/interpro/ (accessed on 17 March 2016).
- TargetP. Available online: http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/TargetP/ (accessed on 17 March 2016).
- PSORT. Available online: http://www.psort.org/ (accessed on 17 March 2016).
- Unituebingen.de. Available online: http://abi.inf.unituebingen.de/Services/YLoc/webloc.cgi (accessed on 17 March 2016).
- NetPhos 2.0 Server. Available online: http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/NetPhos/ (accessed on 17 March 2016).
- Horvath, B.M.; Magyar, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Hamburger, A.W.; Bako, L.; Visser, R.G.; Bachem, C.W.; Bogre, L. EBP1 regulates organ size through cell growth and proliferation in plants. Embo. J. 2006, 25, 4909–4920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandelc, S.; Javornik, B. The secretome of vascular wilt pathogen Verticillium albo-atrum in simulated xylem fluid. Proteomics 2015, 15, 787–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baskin, T.I.; Meekes, H.T.; Liang, B.M.; Sharp, R.E. Regulation of growth anisotropy in well-watered and water-stressed maize roots. II. Role of cortical microtubules and cellulose microfibrils. Plant Physiol. 1999, 119, 681–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, M.; Meng, Y.; Yang, C.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, Y.; Chen, B. Protein expression changes during cotton fiber elongation in response to drought stress and recovery. Proteomics 2014, 14, 1776–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.Y.; Bahn, S.C.; Kang, Y.M.; Lee, K.H.; Kim, H.J.; Noh, E.K.; Palta, J.P.; Shin, J.S.; Ryu, S.B. Secretory low molecular weight phospholipase A2 plays important roles in cell elongation and shoot gravitropism in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2003, 15, 1990–2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valentin, C.; Banerjee, R. Novel B12-dependent Acyl-CoA Mutases and their Biotechnological Potential. Biochemistry 2012, 51, 6039–6046. [Google Scholar]
- Hepler, P.K.; Rounds, C.M.; Winship, L.J. Control of cell wall extensibility during pollen tube growth. Mol. Plant. 2013, 6, 998–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ray, P.M.; Green, P.B.; Cleland, R. Role of turgor in plant cell growth. Nature 1972, 239, 163–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosgrove, D.J. Enzymes and other agents that enhance cell wall extensibility. Ann. Rev. Plant Biol. 1999, 50, 391–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talbott, L.D.; Ray, P.M. Changes in molecular size of previously deposited and newly synthesized pea cell wall matrix polysaccharides: Effects of auxin and turgor. Plant Physiol. 1992, 98, 369–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minic, Z.; Jamet, E.; San-Clemente, H.; Pelletier, S.; Renou, J.P.; Rihouey, C.; Okinyo, D.P.; Proux, C.; Lerouge, P.; Jouanin, L. Transcriptomic analysis of Arabidopsis developing stems: A close-up on cell wall genes. BMC Plant Biol. 2009, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monshausen, G.B.; Bibikova, T.N.; Weisenseel, M.H.; Gilroy, S. Ca2+ regulates reactive oxygen species production and pH during mechano sensing in Arabidopsis roots. Plant Cell 2009, 21, 2341–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bischoff, V.; Nita, S.; Neumetzler, L.; Schindelasch, D.; Urbain, A.; Eshed, R.; Persson, S.; Delmer, D.; Scheible, W.R. TRICHOME BIREFRINGENCE and its homolog AT5G01360 encode plant-specific DUF231 proteins required for cellulose biosynthesis in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2010, 153, 590–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miernyk, J.A. Protein folding in the plant cell. Plant Physiol. 1999, 121, 695–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veronica, M.; Santos, J.J.; Tacchi, J.L.; Raymond, B.B.A.; Deutscher, A.T.; Jenkins, C.; Padula, M.P.; Djordjevic, S.P. MHJ_0461 is a multifunctional leucine aminopeptidase on the surface of Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae. Open Biol. 2015, 5, 140–175. [Google Scholar]
- Irshad, M.; Canut, H.; Borderies, G.; Pont-Lezica, R.; Jamet, E. A new picture of cell wall protein dynamics in elongating cells of Arabidopsis thaliana: Confirmed actors and newcomers. BMC Plant Biol. 2008, 8, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayer, E.M.; Bottrill, A.R.; Walshaw, J.; Vigouroux, M.; Naldrett, M.J.; Thomas, C.L.; Maule, A.J. Arabidopsis cell wall proteome defined using multidimensional protein identification technology. Proteomics 2006, 6, 301–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basu, U.; Francis, J.L.; Whittal, R.M.; Stephens, J.L.; Wang, Y.; Zaiane, O.R.; Goebel, R.; Muench, D.G.; Taylor, G.J. Extracellular proteomes of Arabidopsis thaliana and Brassica napus roots: Analysis and comparison by MudPIT and LC-MS/MS. Plant Soil. 2006, 286, 357–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Functional Category | Spot ID a. | Protein Name | Species | Protein ID b | Score | NP c | % coverage | Thr. Mw/pI | Exp. Mw/pI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metabolism | StEP-840 | Enolase | Lycopersicon esculentum | 119354 | 88 | 3 | 10 | 47.768/5.68 | 60.334/5.49 |
| StEP-1003 | 5-ethyltetrahyd ropteroyltriglutamate-homocysteine | Solanum tuberosum | XP_002328083.1 | 198 | 5 | 6 | 84.54/6.26 | 53.065/5.82 | |
| StEP-1166 | Ferredoxin-NADP(H) oxidoreductase | Oryza sativa (japonica cultivar-group) | 41052915 | 57 | 2 | 5 | 40.638/7.98 | 40.844/6.22 | |
| StEP-1418 | Glutamate dehydrogenase | Lycopersicon esculentum | 12229803 | 441 | 9 | 26 | 44.78/6.68 | 53.599/6.94 | |
| StEP-675 | Alpha-1,4-glucan-protein synthase | Solanum tuberosum | 34582499 | 216 | 8 | 22 | 41.57/5.71 | 51.107/5.29 | |
| StEP-529 | RGP3 (Reversibly glycosylated polypeptide 3) | Arabidopsis thaliana | 30680679 | 69 | 2 | 4 | 41.25/5.39 | 50.666/4.94 | |
| StEP-376 | Transaldolase | Unknown species | 85112172 | 78 | 2 | 6 | 35.20/5.38 | 45.309/4.62 | |
| StEP-1143 | Protein thylakoid formation1 | Solanum tuberosum | 75140959 | 140 | 5 | 20 | 33.34/8.69 | 28.646/5.89 | |
| StEP-1213 | ErbB-3 binding protein1 | Solanum tuberosum | 116292768 | 320 | 7 | 21 | 42.79/6.25 | 58.028/6.37 | |
| StEP-1005 | ErbB-3 binding protein1 | Solanum tuberosum | 116292768 | 147 | 5 | 13 | 42.79/6.25 | 58.891/5.87 | |
| StEP-893 | DH putative beta-hydroxyacyl-ACP dehydratase | Capsicum annuum | 193290688 | 138 | 4 | 14 | 23.966/9.35 | 22.904/5.64 | |
| Development | StEP-1333 | Germin-like protein 1 | Nicotiana tabacum | 1169944 | 58 | 1 | 4 | 21.98/6.27 | 26.698/6.75 |
| StEP-1122 | 24K germin like protein | Nicotiana tabacum | 31711507 | 67 | 2 | 15 | 21.954/5.82 | 26.698/6.75 | |
| StEP-656 | Chain A, The Crystal Structure Of Semet Patatin | Solanum tuberosum | 31615943 | 72 | 2 | 4 | 40.93/5.17 | 39.366/5.25 | |
| Stress Response | StEP-962 | Chloroplast Drought-induced Stress Protein of 32 kDa | Solanum tuberosum | 2582822 | 221 | 7 | 20 | 33.436/8.07 | 37.4815.64 |
| StEP-965 | Chloroplast Drought-induced Stress Protein of 32 kDa | Solanum tuberosum | 2582822 | 179 | 7 | 20 | 33.436/8,07 | 37.525/5.83 | |
| Protein Folding | StEP-567 | Chaperonin-60 beta subunit | Solanum tuberosum | 1762130 | 275 | 7 | 17 | 62.98/5.72 | 76.934/4.85 |
| StEP-405 | Chaperonin hsp60 | Arabidopsis thaliana | 16221 | 279 | 7 | 12 | 61.31/5.66 | 70.819/5.12 | |
| StEP-402 | Heat shock protein 70 | Nicotiana tabacum | 30025966 | 457 | 8 | 13 | 70.83/5.17 | 76.624/5.06 | |
| StEP-1024 | Leucine aminopeptidase 2 | Lycopersicon esculentum | 2492530 | 191 | 5 | 11 | 59.512/8.18 | 69.045/5.67 | |
| Signaling | StEP-1417 | GTP-binding protein | Capsicum annuum | 7643796 | 433 | 12 | 38 | 44.37/6.45 | 57.878/6.88 |
| StEP-1001 | Glucose-regulated protein 78 | Lycopersicon esculentum | 170386 | 177 | 5 | 12 | 41.15/8.51 | 55.669/5.78 | |
| StEP-810 | Endoplasmin homolog | Hordeum vulgare | 544242 | 52 | 1 | 1 | 92.859/4.86 | 41.936/5.47 | |
| Redox Homeostasis | StEP-1137 | Dehydroascorbate reductase-like protein | Solanum tuberosum | 76160951 | 62 | 2 | 9 | 23.425/6.09 | 28.647/5.99 |
| StEP-922 | Dehydroascorbate reductase | Lycopersicon esculentum | 66475036 | 61 | 2 | 9 | 23.523/6.32 | 28.508/5.79 | |
| StEP-615 | Thioredoxin peroxidase 1 | Lycopersicon esculentum | 30841938 | 57 | 2 | 11 | 17.426/5.18 | 20.169/5.68 | |
| StEP-765 | Peroxiredoxin | Ricinus communis | 223543823 | 55 | 1 | 5 | 21.82/8.74 | 22.953/5.42 | |
| StEP-530 | Lactoylglutathione lyase | Ricinus communis | 223542315 | 249 | 4 | 16 | 31.52/7.63 | 42.983/4.98 | |
| Unknown | StEP-848 | Unknown protein 18 | Pseudotsuga menziesii | 205830697 | 63 | 1 | 91 | 1.393/5.80 | 70.364/5.37 |
| StEP-853 | Unknown protein 18 | Pseudotsuga menziesii | 205830697 | 50 | 2 | 100 | 1.393/5.80 | 79.178/5.508 | |
| StEP-1004 | Unknown protein 18 | Pseudotsuga menziesii | 205830697 | 83 | 2 | 100 | 1.39/5.80 | 58.661/5.83 | |
| StEP-352 | Unknown protein 18 | Pseudotsuga menziesii | 205830697 | 99 | 2 | 100 | 1.39/5.80 | 40.823/4.82 | |
| StEP-879 | Unknown protein 19 | Pseudotsuga menziesii | 205830698 | 54 | 1 | 91 | 1.393/5.80 | 13.226/5.69 | |
| StEP-1180 | Unknown | Solanum tuberosum | 77745483 | 281 | 7 | 20 | 37.64/7.70 | 45.963/6.01 | |
| StEP-354 | Unknown | Populus trichocarpa | 118486367 | 71 | 3 | 8 | 44.55/8.48 | 41.326/4.72 | |
| StEP-963 | Hypothetical protein | Pseudotsuga menziesii | 83649448 | 55 | 2 | 2 | 36.547/6.47 | 37.799/5.78 | |
| StEP-346 | Predicted protein | Populus trichocarpa | 224103823 | 113 | 2 | 7 | 33.55/6.85 | 38.700/5.02 | |
| StEP-638 | Os03g0822200 | Oryza sativa (japonica cultivar-group) | 115456265 | 57 | 1 | 6 | 27.89/6.34 | 33.319/5.17 |
| Functional Category | Spot ID a. | Protein Name | Species | Protein ID b | Score | NP c | % coverage | Thr. Mw/pI | Exp. Mw/pI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metabolism | StEPP-48 | Enolase | Lycopersicon esculentum | 119354 | 176 | 5 | 15 | 47.76/ 5.68 | 61.074/5.05 |
| StEPP- 93 | Enolase | Lycopersicon esculentum | 119354 | 812 | 16 | 48 | 47.768/5.68 | 60.703/5.18 | |
| StEPP-138 | Enolase | Lycopersicon esculentum | 119354 | 522 | 12 | 38 | 47.76/5.68 | 55.289/5.47 | |
| StEPP-137 | Enolase | Lycopersicon esculentum | 119354 | 818 | 19 | 51 | 47.76/5.68 | 55.058/5.64 | |
| StEPP-82 | Enolase | Lycopersicon esculentum | 3023685 | 104 | 2 | 6 | 47.56/5.41 | 53.226/5.53 | |
| StEPP-94 | Enolase-like | Solanum tuberosum | 82623425 | 487 | 12 | 37 | 48.002/7.53 | 60.888/5.32 | |
| StEPP-194 | Methionine synthase | Solanum tuberosum | 8439545 | 557 | 12 | 18 | 84.61/5.93 | 56.404/5.84 | |
| StEPP-135 | Cobalamine-independent methionine synthase | Solenostemon scutellarioides | 974782 | 161 | 3 | 4 | 86.71/6.17 | 51.932/5.49 | |
| StEPP-72 | Ferredoxin-NADP reductase | Nicotiana tabacum | 3913651 | 216 | 9 | 29 | 40.41/8.37 | 41.686/5.28 | |
| StEPP-179 | Ferredoxin-NADP reductase | Nicotiana tabacum | 3913651 | 584 | 14 | 48 | 40.419/8.37 | 41.408/5.79 | |
| StEPP-43 | Ferredoxin-NADP reductase | Nicotiana tabacum | 3913651 | 55 | 3 | 11 | 40.419/8.37 | 59.082/5.21 | |
| StEPP-122 | Ferredoxin-NADP reductase | Nicotiana tabacum | 3913651 | 238 | 8 | 18 | 40.419/8.37 | 41.962/5.54 | |
| StEPP-191 | Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase | Solanum tuberosum | 22094840 | 319 | 7 | 31 | 26.62/6.34 | 48.900/6.38 | |
| StEPP-241 | Glutamate dehydrogenase | Lycopersicon esculentum | 12229803 | 688 | 15 | 39 | 44.78/6.68 | 54.134/6.79 | |
| StEPP-251 | Glutamate dehydrogenase | Lycopersicon esculentum | 12229803 | 99 | 3 | 8 | 44.785/6.68 | 58.542/6.61 | |
| StEPP-169 | Triose phosphate isomerase cytosolic isoform-like | Solanum tuberosum | 77745458 | 171 | 6 | 33 | 26.99/5.73 | 27.782/5.85 | |
| StEPP-233 | Succinic semialdehyde reductase isoform1 | Solanum lycopersicum | 171854589 | 247 | 6 | 31 | 30.428/6.60 | 35.085/6.44 | |
| StEPP-174 | Protein Thylakoid formation1 | Solanum tuberosum | 75140959 | 74 | 2 | 9 | 33.34/8.69 | 29.287/5.89 | |
| StEPP-64 | Soluble inorganic pyrophosphatase | Arabidopsis thaliana | 2500047 | 163 | 5 | 28 | 24.24/5.59 | 28.967/5.28 | |
| StEPP-202 | ErbB-3 binding protein | Solanum tuberosum | 116292768 | 346 | 9 | 27 | 42.79/6.25 | 59.333/5.94 | |
| StEPP-231 | Endolysin | Vitis vinifera | 220928911 | 57 | 1 | 3 | 26.76/8.90 | 41.559/6.13 | |
| Development | StEPP-167 | Germin-like protein | Capsicum chinense | 123965222 | 51 | 2 | 7 | 21.03/7.74 | 27.647/5.77 |
| StEPP-166 | Germin-like protein | Capsicum chinense | 123965222 | 101 | 2 | 7 | 21.03/7.74 | 26.158/5.75 | |
| StEPP-80 | Patatin | Solanum tuberosum | 129640 | 55 | 1 | 3 | 42.463/5.34 | 51.770/5.47 | |
| StEPP-38 | Patatin-11 | Solanum tuberosum | 122201875 | 270 | 6 | 18 | 42.47/5.58 | 51.132/5.23 | |
| Redox Homeostasis | StEPP-110 | Putative l-ascorbate peroxidase | Lycopersicon esculentum | 11387206 | 467 | 9 | 21 | 37.72/8.27 | 32.795/5.94 |
| StEPP-171 | Putative l-ascorbate peroxidase | Lycopersicon esculentum | 11387206 | 295 | 8 | 34 | 37.72/8.27 | 31.295/5.96 | |
| StEPP-111 | Iron superoxide dismutase | Solanum tuberosum | 170675264 | 114 | 3 | 25 | 16.246/5.69 | 27.594/5.67 | |
| StEPP-225 | Iron superoxide dismutase | Solanum tuberosum | 170675264 | 64 | 2 | 12 | 16.24/5.69 | 27.375/6.03 | |
| StEPP-24 | Superoxide dismutase | Solanum lycopersicum | 33413303 | 120 | 3 | 15 | 27.893/6.60 | 27.456/5.19 | |
| StEPP-67 | Iron superoxide dismutase | Solanum tuberosum | 27543371 | 255 | 6 | 33 | 21.31/5.87 | 26.943/5.27 | |
| Transcriptiom regulator | StEPP-136 | Eukaryotic translation elongation factor | Ricinus communis | 223547312 | 314 | 7 | 9 | 93.99/5.87 | 44.550/5.58 |
| Unknown | StEPP-221 | Unknown | Solanum tuberosum | 81076617 | 72 | 4 | 18 | 24.95/7.77 | 28.551/6.12 |
| StEPP-180 | Unknown | Medicago truncatula | 217072754 | 54 | 2 | 7 | 27.84/5.51 | 33.564/5.88 | |
| StEPP-160 | Predicted protein | Populus trichocarpa | 224091917 | 86 | 3 | 26 | 16.610/6.20 | 20.264/6.25 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Elagamey, E.; Narula, K.; Sinha, A.; Aggarwal, P.R.; Ghosh, S.; Chakraborty, N.; Chakraborty, S. Extracellular Matrix Proteome and Phosphoproteome of Potato Reveals Functionally Distinct and Diverse Canonical and Non-Canonical Proteoforms. Proteomes 2016, 4, 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/proteomes4030020
Elagamey E, Narula K, Sinha A, Aggarwal PR, Ghosh S, Chakraborty N, Chakraborty S. Extracellular Matrix Proteome and Phosphoproteome of Potato Reveals Functionally Distinct and Diverse Canonical and Non-Canonical Proteoforms. Proteomes. 2016; 4(3):20. https://doi.org/10.3390/proteomes4030020
Chicago/Turabian StyleElagamey, Eman, Kanika Narula, Arunima Sinha, Pooja Rani Aggarwal, Sudip Ghosh, Niranjan Chakraborty, and Subhra Chakraborty. 2016. "Extracellular Matrix Proteome and Phosphoproteome of Potato Reveals Functionally Distinct and Diverse Canonical and Non-Canonical Proteoforms" Proteomes 4, no. 3: 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/proteomes4030020
APA StyleElagamey, E., Narula, K., Sinha, A., Aggarwal, P. R., Ghosh, S., Chakraborty, N., & Chakraborty, S. (2016). Extracellular Matrix Proteome and Phosphoproteome of Potato Reveals Functionally Distinct and Diverse Canonical and Non-Canonical Proteoforms. Proteomes, 4(3), 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/proteomes4030020