CSF Proteomic Alzheimer’s Disease-Predictive Subtypes in Cognitively Intact Amyloid Negative Individuals
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participant Description
2.2. Cerebrospinal Fluid Data
2.3. APOE e4 Genotyping
2.4. Cluster Analyses with Non-Negative Matrix Factorization
2.5. Post-Hoc Subtype Comparisons Statistical Procedures
3. Results
3.1. Sample Description
3.2. Three CSF Proteomic Subtypes
3.3. Longitudinal Comparisons of CSF Proteomic Subtypes on Amyloid and p-Tau Levels, and Delayed Memory Functioning
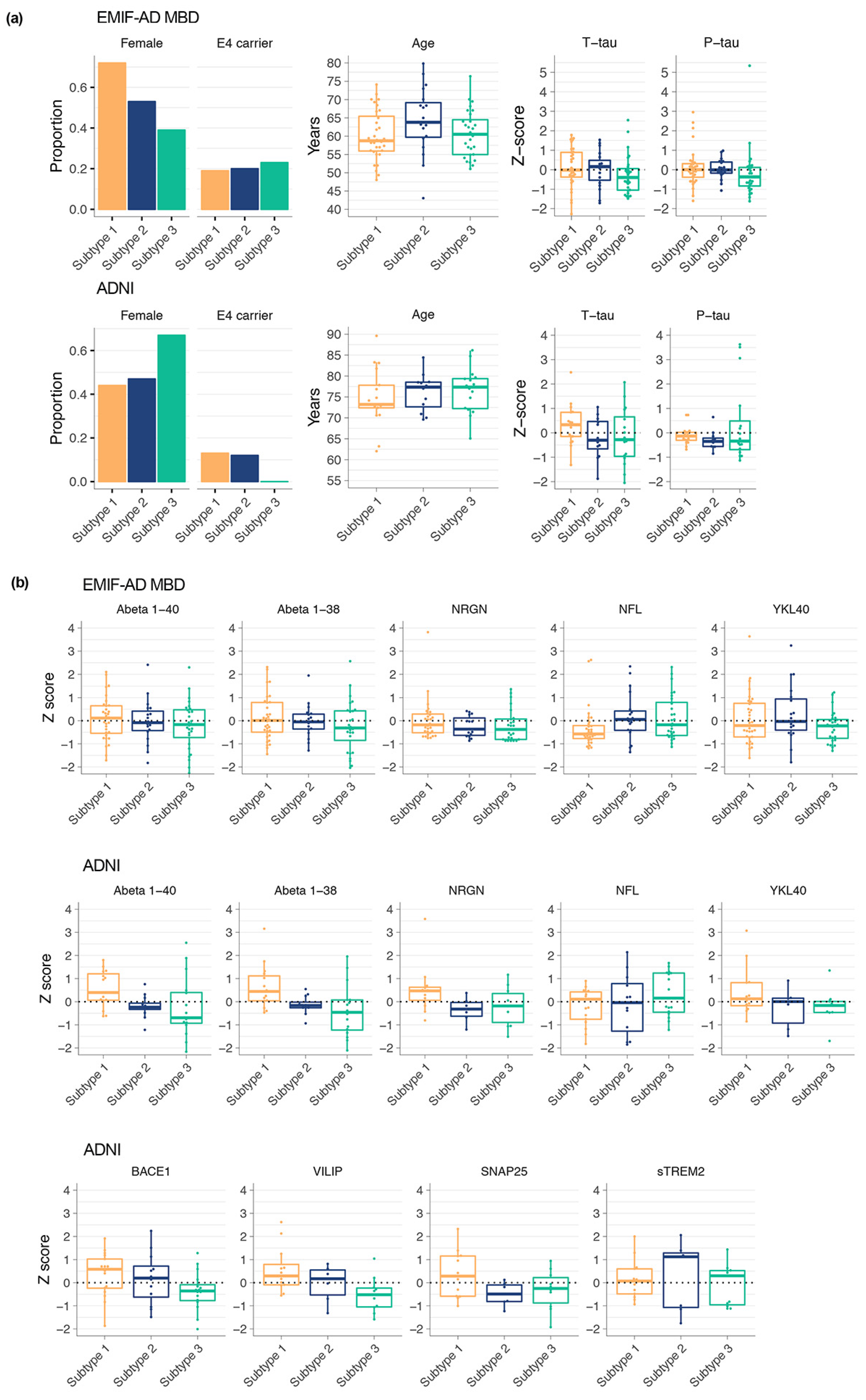
3.4. CSF Proteomic Subtypes Comparisons on Other Biological Characteristics
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Albert, M.S.; DeKosky, S.; Dickson, D.W.; Dubois, B.; Feldman, H.; Fox, N.; Gamst, A.; Holtzman, D.M.; Jagust, W.J.; Petersen, R.C.; et al. The diagnosis of mild cognitive impairment due to Alzheimer’s disease: Recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer’s Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2011, 7, 270–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dubois, B.; Feldman, H.H.; Jacova, C.; DeKosky, S.T.; Barberger-Gateau, P.; Cummings, J.L.; Delacourte, A.; Galasko, D.; Gauthier, S.; Jicha, G.A.; et al. Research criteria for the diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease: Revising the NINCDS–ADRDA criteria. Lancet Neurol. 2007, 6, 734–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois, B.; Feldman, H.; Jacova, C.; Hampel, H.; Molinuevo, J.L.; Blennow, K.; DeKosky, S.; Gauthier, S.; Selkoe, D.; Bateman, R.; et al. Advancing research diagnostic criteria for Alzheimer’s disease: The IWG-2 criteria. Lancet Neurol. 2014, 13, 614–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jack, C.R., Jr.; Albert, M.S.; Knopman, D.S.; McKhann, G.M.; Sperling, R.A.; Carrillo, M.C.; Thies, W.; Phelps, C.H. Introduction to the recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer’s Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2011, 7, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jack, C.R., Jr.; Bennett, D.A.; Blennow, K.; Carrillo, M.C.; Dunn, B.; Haeberlein, S.B.; Holtzman, D.M.; Jagust, W.; Jessen, F.; Karlawish, J.; et al. NIA-AA Research Framework: Toward a biological definition of Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2018, 14, 535–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sperling, R.A.; Aisen, P.S.; Beckett, L.A.; Bennett, D.A.; Craft, S.; Fagan, A.M.; Iwatsubo, T.; Jack, C.R., Jr.; Kaye, J.; Montine, T.J.; et al. Toward defining the preclinical stages of Alzheimer’s disease: Recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer’s Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2011, 7, 280–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Higginbotham, L.; Ping, L.; Dammer, E.B.; Duong, D.M.; Zhou, M.; Gearing, M.; Hurst, C.; Glass, J.D.; Factor, S.A.; Johnson, E.C.B.; et al. Integrated proteomics reveals brain-based cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers in asymptomatic and symptomatic Alzheimer’s disease. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaaz9360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, E.C.B.; Dammer, E.B.; Duong, D.; Ping, L.; Zhou, M.; Yin, L.; Higginbotham, L.A.; Guajardo, A.; White, B.; Troncoso, J.C.; et al. Large-scale proteomic analysis of Alzheimer’s disease brain and cerebrospinal fluid reveals early changes in energy metabolism associated with microglia and astrocyte activation. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 769–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drummond, E.; Nayak, S.; Faustin, A.; Pires, G.; Hickman, R.A.; Askenazi, M.; Cohen, M.; Haldiman, T.; Kim, C.; Han, X.; et al. Proteomic differences in amyloid plaques in rapidly progressive and sporadic Alzheimer’s disease. Acta Neuropathol. 2017, 133, 933–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drummond, E.; Pires, G.; MacMurray, C.; Askenazi, M.; Nayak, S.; Bourdon, M.; Safar, J.; Ueberheide, B.; Wisniewski, T. Phosphorylated tau interactome in the human Alzheimer’s disease brain. Brain 2020, 143, 2803–2817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vassar, R. BACE1: The β-Secretase Enzyme in Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2004, 23, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konijnenberg, E.; Tomassen, J.; Braber, A.D.; Kate, M.T.; Yaqub, M.M.; Mulder, S.D.; Nivard, M.G.; Vanderstichele, H.; Lammertsma, A.A.; Teunissen, C.E.; et al. Onset of Preclinical Alzheimer Disease in Monozygotic Twins. Ann. Neurol. 2021, 89, 987–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bateman, R.J.; Xiong, C.; Benzinger, T.L.S.; Fagan, A.M.; Goate, A.; Fox, N.C.; Marcus, D.S.; Cairns, N.J.; Xie, X.; Blazey, T.M.; et al. Clinical and Biomarker Changes in Dominantly Inherited Alzheimer’s Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 367, 795–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Donohue, M.C.; Sperling, R.A.; Petersen, R.; Sun, C.-K.; Weiner, M.W.; Aisen, P.S.; Initiative, F.T.A.D.N. Association Between Elevated Brain Amyloid and Subsequent Cognitive Decline Among Cognitively Normal Persons. JAMA 2017, 317, 2305–2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tijms, B.M.; Vermunt, L.; Zwan, M.D.; Van Harten, A.C.; van der Flier, W.; Teunissen, C.E.; Scheltens, P.; Visser, P.J.; Adni, F. Pre-amyloid stage of Alzheimer’s disease in cognitively normal individuals. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2018, 5, 1037–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vos, S.J.; Visser, P.J. Preclinical Alzheimer’s Disease: Implications for Refinement of the Concept. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2018, 64, S213–S227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tijms, B.M.; Gobom, J.; Reus, L.; Jansen, I.; Hong, S.; Dobricic, V.; Kilpert, F.; Kate, M.T.; Barkhof, F.; Tsolaki, M.; et al. Pathophysiological subtypes of Alzheimer’s disease based on cerebrospinal fluid proteomics. Brain 2020, 143, 3776–3792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bos, I.; Vos, S.; Vandenberghe, R.; Scheltens, P.; Engelborghs, S.; Frisoni, G.; Molinuevo, J.L.; Wallin, A.; Lleó, A.; Popp, J.; et al. The EMIF-AD Multimodal Biomarker Discovery study: Design, methods and cohort characteristics. Alzheimer’s Res. Ther. 2018, 10, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McKhann, G.; Drachman, D.; Folstein, M.; Katzman, R.; Price, D.; Stadlan, E.M. Clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease: Report of the NINCDS-ADRDA Work Group* under the auspices of Department of Health and Human Services Task Force on Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurology 1984, 34, 939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McKhann, G.M.; Knopman, D.S.; Chertkow, H.; Hyman, B.T.; Jack, C.R., Jr.; Kawas, C.H.; Klunk, W.E.; Koroshetz, W.J.; Manly, J.J.; Mayeux, R.; et al. The diagnosis of dementia due to Alzheimer’s disease: Recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer’s Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2011, 7, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Winblad, B.; Palmer, K.; Kivipelto, M.; Jelic, V.; Fratiglioni, L.; Wahlund, L.-O.; Nordberg, A.; Backman, L.J.; Albert, M.S.; Almkvist, O.; et al. Mild cognitive impairment - beyond controversies, towards a consensus: Report of the International Working Group on Mild Cognitive Impairment. J. Intern. Med. 2004, 256, 240–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, R.C.; Smith, G.E.; Waring, S.C.; Ivnik, R.J.; Tangalos, E.G.; Kokmen, E. Mild Cognitive Impairment: Clinical Characterization and Outcome. Arch. Neurol. 1999, 56, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, L.M.; Vanderstichele, H.; Knapik-Czajka, M.; Clark, C.M.; Aisen, P.S.; Petersen, R.C.; Blennow, K.; Soares, H.; Simon, A.; Lewczuk, P.; et al. Cerebrospinal fluid biomarker signature in Alzheimer’s disease neuroimaging initiative subjects. Ann. Neurol. 2009, 65, 403–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Toledo, J.; Xie, S.X.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Shaw, L.M. Longitudinal change in CSF Tau and Aβ biomarkers for up to 48 months in ADNI. Acta Neuropathol. 2013, 126, 659–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Batth, T.S.; Francavilla, C.; Olsen, J.V. Off-Line High-pH Reversed-Phase Fractionation for In-Depth Phosphoproteomics. J. Proteome Res. 2014, 13, 6176–6186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magdalinou, N.; Noyce, A.; Pinto, R.; Lindstrom, E.; Holmén-Larsson, J.; Hölttä, M.; Blennow, K.; Morris, H.; Skillbäck, T.; Warner, T.; et al. Identification of candidate cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers in parkinsonism using quantitative proteomics. Park. Relat. Disord. 2017, 37, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perez-Riverol, Y.; Csordas, A.; Bai, J.; Bernal-Llinares, M.; Hewapathirana, S.; Kundu, D.J.; Inuganti, A.; Griss, J.; Mayer, G.; Eisenacher, M.; et al. The PRIDE database and related tools and resources in 2019: Improving support for quantification data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D442–D450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spellman, D.S.; Wildsmith, K.R.; Honigberg, L.A.; Tuefferd, M.; Baker, D.; Raghavan, N.; Nairn, A.; Croteau, P.; Schirm, M.; Allard, R.; et al. Development and evaluation of a multiplexed mass spectrometry based assay for measuring candidate peptide biomarkers in Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (ADNI) CSF. Proteom. Clin. Appl. 2015, 9, 715–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, S.; Prokopenko, D.; Dobricic, V.; Kilpert, F.; Bos, I.; Vos, S.J.B.; Tijms, B.M.; Andreasson, U.; Blennow, K.; Vandenberghe, R.; et al. Genome-wide association study of Alzheimer’s disease CSF biomarkers in the EMIF-AD Multimodal Biomarker Discovery dataset. Transl. Psychiatry 2020, 10, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.D.; Seung, H.S. Learning the parts of objects by non-negative matrix factorization. Nature 1999, 401, 788–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaujoux, R.; Seoighe, C. A flexible R package for nonnegative matrix factorization. BMC Bioinform. 2010, 11, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brunet, J.-P.; Tamayo, P.; Golub, T.R.; Mesirov, J.P. Metagenes and molecular pattern discovery using matrix factorization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 4164–4169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mi, H.; Muruganujan, A.; Casagrande, J.T.; Thomas, P.D. Large-scale gene function analysis with the PANTHER classification system. Nat. Protoc. 2013, 8, 1551–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuleshov, M.V.; Jones, M.R.; Rouillard, A.D.; Fernandez, N.F.; Duan, Q.; Wang, Z.; Koplev, S.; Jenkins, S.L.; Jagodnik, K.M.; Lachmann, A.; et al. Enrichr: A comprehensive gene set enrichment analysis web server 2016 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, W90–W97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, E.Y.; Tan, C.M.; Kou, Y.; Duan, Q.; Wang, Z.; Meirelles, G.V.; Clark, N.R.; Ma’Ayan, A. Enrichr: Interactive and collaborative HTML5 gene list enrichment analysis tool. BMC Bioinform. 2013, 14, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, K.; Sloan, S.A.; Bennett, M.L.; Scholze, A.R.; O’Keeffe, S.; Phatnani, H.P.; Guarnieri, P.; Caneda, C.; Ruderisch, N.; et al. An RNA-Sequencing Transcriptome and Splicing Database of Glia, Neurons, and Vascular Cells of the Cerebral Cortex. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 11929–11947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijaymeena, M.K.; Kavitha, K. A Survey on Similarity Measures in Text Mining. Mach. Learn. Appl. Int. J. 2016, 3, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dayon, L.; Cominetti, O.; Wojcik, J.; Galindo, A.N.; Oikonomidi, A.; Henry, H.; Migliavacca, E.; Kussmann, M.; Bowman, G.; Popp, J. Proteomes of Paired Human Cerebrospinal Fluid and Plasma: Relation to Blood–Brain Barrier Permeability in Older Adults. J. Proteome Res. 2019, 18, 1162–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wesenhagen, K.E.J.; Teunissen, C.E.; Visser, P.J.; Tijms, B.M. Cerebrospinal fluid proteomics and biological heterogeneity in Alzheimer’s disease: A literature review. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2019, 57, 86–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pedrero-Prieto, C.M.; García-Carpintero, S.; Frontiñan, J.; Llanos-González, E.; García, C.A.; Alcain, F.J.; Lindberg, I.; Durán-Prado, M.; Peinado, J.R.; Ruiz, Y.R. A comprehensive systematic review of CSF proteins and peptides that define Alzheimer’s disease. Clin. Proteom. 2020, 17, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konijnenberg, E.; Tomassen, J.; Braber, A.D.; ten Kate, M.; Yaqub, M.; Mulder, S.D.; Nivard, M.G.; Vanderstichele, H.; Lammertsma, A.A.; Teunissen, C.E.; et al. Contribution of Genetic and Environmental Factors to the Onset of Preclinical Alzheimer’s Disease—A Monozygotic Twin Study. MedRxiv 2020, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.-Y.; Zukin, R.S. REST, a master transcriptional regulator in neurodegenerative disease. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2018, 48, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodenas-Ruano, A.; Chávez, A.E.; Cossio, M.J.; Castillo, P.E.; Zukin, R.S. REST-dependent epigenetic remodeling promotes the developmental switch in synaptic NMDA receptors. Nat. Neurosci. 2012, 15, 1382–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, K.; Feldman, H.M.; Lu, T.; Drake, D.; Lim, T.T.; Ling, K.H.; Bishop, N.A.; Pan, Y.; Seo, J.; Lin, Y.-T.; et al. REST and Neural Gene Network Dysregulation in iPSC Models of Alzheimer’s Disease. Cell Rep. 2019, 26, 1112–1127.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nation, D.A.; Sweeney, M.D.; Montagne, A.; Sagare, A.P.; D’Orazio, L.M.; Pachicano, M.; Sepehrband, F.; Nelson, A.R.; Buennagel, D.P.; Harrington, M.G.; et al. Blood–brain barrier breakdown is an early biomarker of human cognitive dysfunction. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 270–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, A.R.; Sweeney, M.; Sagare, A.P.; Zlokovic, B.V. Neurovascular dysfunction and neurodegeneration in dementia and Alzheimer’s disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2016, 1862, 887–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montagne, A.; Barnes, S.R.; Sweeney, M.D.; Halliday, M.R.; Sagare, A.P.; Zhao, Z.; Toga, A.W.; Jacobs, R.E.; Liu, C.Y.; Amezcua, L.; et al. Blood-Brain Barrier Breakdown in the Aging Human Hippocampus. Neuron 2015, 85, 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bowman, G.L.; Dayon, L.; Kirkland, R.; Wojcik, J.; Peyratout, G.; Severin, I.C.; Henry, H.; Oikonomidi, A.; Migliavacca, E.; Bacher, M.; et al. Blood-brain barrier breakdown, neuroinflammation, and cognitive decline in older adults. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2018, 14, 1640–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soto-Rojas, L.; Pacheco-Herrero, M.; Martínez-Gómez, P.; Campa-Córdoba, B.; Apátiga-Pérez, R.; Villegas-Rojas, M.; Harrington, C.; de la Cruz, F.; Garcés-Ramírez, L.; Luna-Muñoz, J. The Neurovascular Unit Dysfunction in Alzheimer’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderone, A.; Jover, T.; Noh, K.-M.; Tanaka, H.; Yokota, H.; Lin, Y.; Grooms, S.Y.; Regis, R.; Bennett, M.V.L.; Zukin, R.S. Ischemic Insults Derepress the Gene Silencer REST in Neurons Destined to Die. J. Neurosci. 2003, 23, 2112–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nixon, R.A.; Yang, D.-S.; Lee, J.-H. Neurodegenerative lysosomal disorders: A continuum from development to late age. Autophagy 2008, 4, 590–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Donati, A. The involvement of macroautophagy in aging and anti-aging interventions. Mol. Asp. Med. 2006, 27, 455–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nilsson, P.; Loganathan, K.; Sekiguchi, M.; Matsuba, Y.; Hui, K.; Tsubuki, S.; Tanaka, M.; Iwata, N.; Saito, T.; Saido, T.C. Aβ Secretion and Plaque Formation Depend on Autophagy. Cell Rep. 2013, 5, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bourdenx, M.; Martín-Segura, A.; Scrivo, A.; Rodriguez-Navarro, J.A.; Kaushik, S.; Tasset, I.; Diaz, A.; Storm, N.J.; Xin, Q.; Juste, Y.R.; et al. Chaperone-mediated autophagy prevents collapse of the neuronal metastable proteome. Cell 2021, 184, 2696–2714.e25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Characteristic | EMIF-AD MBD (n = 82) | ADNI (n = 45) |
|---|---|---|
| Age in years, mean (SD) | 61.1 (7) | 75.8 (6) * |
| Female, n (%) | 47 (57) | 23 (51) |
| Years of education, mean (SD) | 11.9 (3.5) | 15.6 (3) * |
| MMSE, mean (SD) | 28.6 (1.3) | 29.2 (0.6) * |
| ≥1 APOE ε4 allele, n (%) | 14 (22) | 4 (8) * |
| Amyloid β 1–42, mean (SD) ‘ | 0 (1) | 247.5 (29.2) |
| P181-tau, mean (SD) ‘ | 0 (1) | 20.3 (9.4) |
| T-tau, mean (SD) ‘ | 0 (1) | 57.1 (13.1) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tijms, B.M.; Gobom, J.; Teunissen, C.; Dobricic, V.; Tsolaki, M.; Verhey, F.; Popp, J.; Martinez-Lage, P.; Vandenberghe, R.; Lleó, A.; et al. CSF Proteomic Alzheimer’s Disease-Predictive Subtypes in Cognitively Intact Amyloid Negative Individuals. Proteomes 2021, 9, 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/proteomes9030036
Tijms BM, Gobom J, Teunissen C, Dobricic V, Tsolaki M, Verhey F, Popp J, Martinez-Lage P, Vandenberghe R, Lleó A, et al. CSF Proteomic Alzheimer’s Disease-Predictive Subtypes in Cognitively Intact Amyloid Negative Individuals. Proteomes. 2021; 9(3):36. https://doi.org/10.3390/proteomes9030036
Chicago/Turabian StyleTijms, Betty Marije, Johan Gobom, Charlotte Teunissen, Valerija Dobricic, Magda Tsolaki, Frans Verhey, Julius Popp, Pablo Martinez-Lage, Rik Vandenberghe, Alberto Lleó, and et al. 2021. "CSF Proteomic Alzheimer’s Disease-Predictive Subtypes in Cognitively Intact Amyloid Negative Individuals" Proteomes 9, no. 3: 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/proteomes9030036
APA StyleTijms, B. M., Gobom, J., Teunissen, C., Dobricic, V., Tsolaki, M., Verhey, F., Popp, J., Martinez-Lage, P., Vandenberghe, R., Lleó, A., Molinuévo, J. L., Engelborghs, S., Freund-Levi, Y., Froelich, L., Bertram, L., Lovestone, S., Streffer, J., Vos, S., ADNI, ... Visser, P. J. (2021). CSF Proteomic Alzheimer’s Disease-Predictive Subtypes in Cognitively Intact Amyloid Negative Individuals. Proteomes, 9(3), 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/proteomes9030036








