The Influence of Service Quality on User’s Perceived Satisfaction with Light Rail Transit Service in Klang Valley, Malaysia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Users’ Satisfaction with the Service Quality Attributes
2.2. Artificial Neural Network Model
3. Research Methodology
4. Results
4.1. Respondent Characteristics
4.2. Exploratory Factor Analysis
4.3. Correlation Analysis
4.4. Artificial Neural Network Model
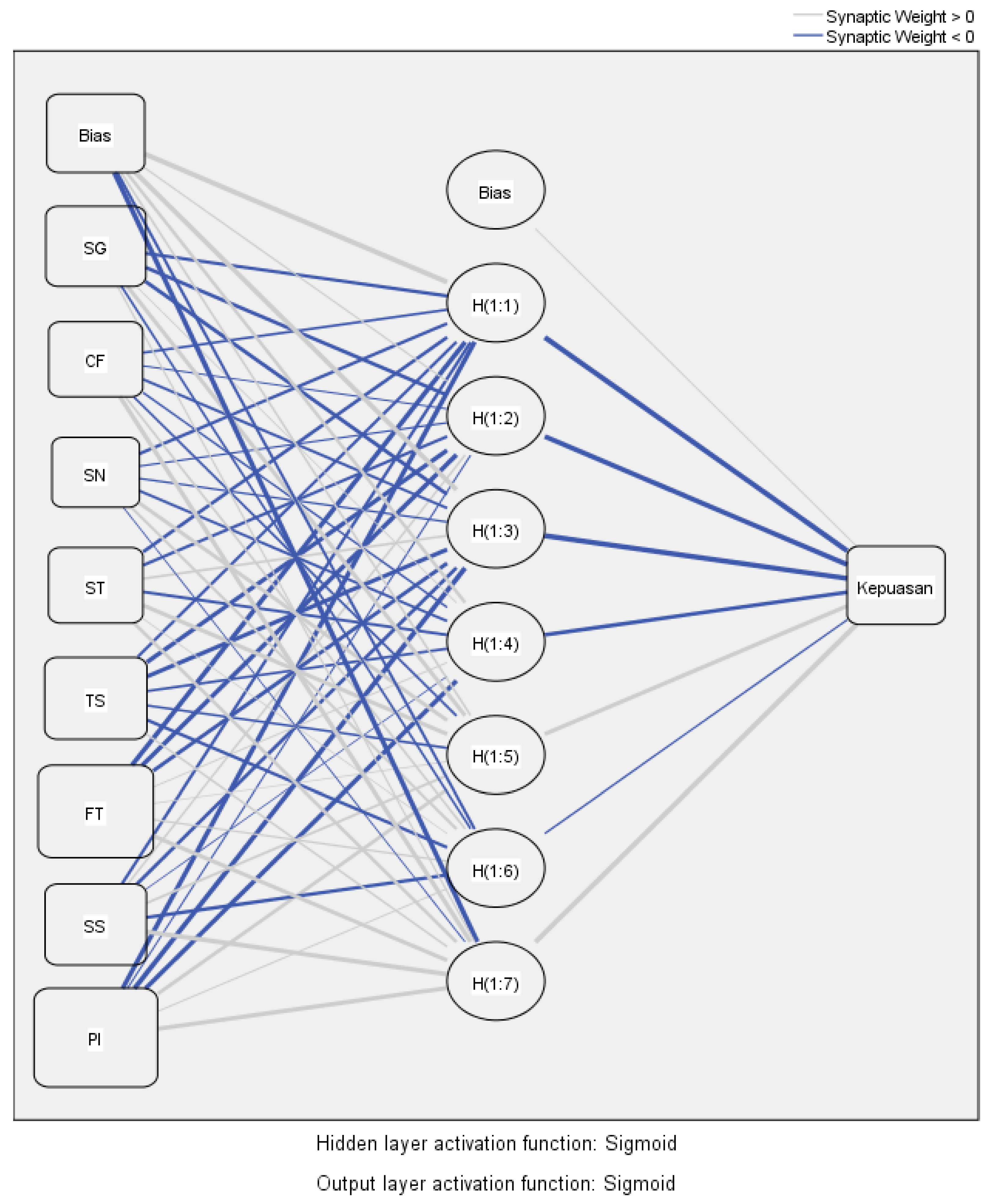
4.4.1. Artificial Neural Network Architecture
4.4.2. Assessment of Model Performance
4.4.3. Sensitivity Analysis
5. Discussions of the Results
5.1. Theoretical Implication
5.2. Practical Implication
6. Conclusions and Suggestion for Further Study
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| No. | Quality of Service Attributes | References |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Frequency | [3,6,8,100,105,110,111,112,113,114] |
| 2 | Network coverage | [104,105,112,115,116] |
| 3 | Service provision hours | [3,6,105,117] |
| 4 | Station parking | [100,104,114,118] |
| 5 | Accessibility | [8,104,105,111,113,117] |
| 6 | Easy of transfer/Distance | [105,112,117] |
| 7 | Ticket price | [3,6,8,104,105,110,111,115,116,118,119] |
| 8 | Ticket selling network | [3,6,8,104,105,120] |
| 9 | Type of tickets/Passes | [3,110,117] |
| 10 | On board information | [3,6,8,104,105,111,117,118,119] |
| 11 | Information at station | [3,6,8,105,117,118,119] |
| 12 | Punctuality | [3,6,8,104,105,110,111,115,117,118,119] |
| 13 | Access time | [3,8,105,111,112,113,117] |
| 14 | Travel speed | [3,8,105,111,117] |
| 15 | Waiting time | [105,113,115] |
| 16 | Driver and personnel’s behavior | [3,6,8,104,111,115,117,118,119] |
| 17 | Customer service | [6,105,110] |
| 18 | Cleanliness | [3,8,104,105,111,113,115,117,118,119] |
| 19 | Comfort | [3,8,104,105,110,111,112,113,117,118,119] |
| 20 | Seating capacity | [3,8,104,105,112,113,117] |
| 21 | Quality of vehicles | [105,113,117,118,119] |
| 22 | Temperature | [3,105,111,115] |
| 23 | Waiting condition | [104,110,112,113] |
| 24 | On board safety | [3,6,8,104,105,110,111,117,118,119] |
| 25 | Safety at station | [3,6,8,105,112,117] |
Appendix B
| Signage | SG |
|---|---|
| Signage for station’s location | SG1 |
| Provision of instructions at the station | SG2 |
| Automatic gate signs at the station | SG3 |
| Clear signs showing directions | SG4 |
| Train departure/arrival signal at the station | SG5 |
| Comfort | CF |
| The level of illumination at the station | CF1 |
| Appropriate ventilation and temperature at the station | CF2 |
| Cleanliness at the station | CF3 |
| Ventilation and suitable temperature in the carriage | CF4 |
| Hygiene in the carriage | CF5 |
| Facilities | FT |
| Suitable location for self-service machines | FT1 |
| The location of the waiting area seats at the appropriate station | FT2 |
| The distortion of the sound level for announcements | FT3 |
| Comfortable handrails in carriages for standing passengers | FT4 |
| Mobile signal strength level at the station | FT5 |
| Mobile signal strength level in the carriage | FT6 |
| Speediness | SN |
| Exact train arrival time | SN1 |
| Acceptable stopping time at the station | SN2 |
| Acceptable departure time interval | SN3 |
| Acceptable length of service time | SN4 |
| Ticketing service | TS |
| Types of tickets offered | TS1 |
| Quantity of self-service ticket machines | TS2 |
| Clear instructions for using a self-service ticket machine | TS3 |
| Self-service ticket machine functions well | TS4 |
| Staff service | SS |
| Staff appearance | SS1 |
| Staff attitude | SS2 |
| Staff efficiency in resolving passenger problems | SS3 |
| Call centre response time during service hours | SS4 |
| Safety | ST |
| Security level at the station | ST1 |
| The level of safety in the carriage | ST2 |
| Safety during travel | ST3 |
| Other passengers’ behaviour | ST4 |
| Early signalling of closure of the carriage doors before departure | ST5 |
| Provision of Information | PI |
| Announcements related to the services provided | PI1 |
| The efficiency of announcements related to service disruption | PI2 |
| Provision of information related to services at the station | PI3 |
| Provision of information related to services in the mass media | PI4 |
| Perceived Satisfaction | Kepuasan |
| Overall satisfaction with the services provided | Kepuasan 1 |
| My perception of the level of service provided exceeded my expectations | Kepuasan 2 |
| My perception of the excellence of the services provided exceeded my expectations | Kepuasan 3 |
| I believe I benefitted from using this service | Kepuasan 4 |
References
- Murakami, A.; Zain, A.M.; Takeuchi, K.; Tsunekawa, A.; Yokota, S. Trends in urbanization and patterns of land use in the Asian mega cities Jakarta, Bangkok, and Metro Manila. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2005, 70, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borhan, M.N.; Ibrahim, A.N.H.; Syamsunur, D.; Rahmat, R.A. Why Public Bus is a Less Attractive Mode of Transport: A Case Study of Putrajaya, Malaysia. Period. Polytech. Transp. Eng. 2019, 47, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shen, W.; Xiao, W.; Wang, X. Passenger satisfaction evaluation model for Urban rail transit: A structural equation modeling based on partial least squares. Transp. Policy 2016, 46, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwan, S.C.; Sutan, R.; Hashim, J.H. Trip characteristics as the determinants of intention to shift to rail transport among private motor vehicle users in Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2018, 36, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hussain, B.; Zefreh, M.M.; Torok, A. Designing the Appropriate Data Collection Method for Public Transport Passenger Satisfaction Analysis. Int. J. Traffic Transp. Eng. 2018, 8, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irtema, H.I.M.; Ismail, A.; Borhan, M.N.; Das, A.M.; Alshetwi, A.B.Z. Case study of the behavioural intentions of public transportation passengers in Kuala Lumpur. Case Stud. Transp. Policy 2018, 6, 462–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redman, L.; Friman, M.; Gärling, T.; Hartig, T. Quality attributes of public transport that attract car users—A research review. Transp. Policy J. 2013, 25, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouwen, A. Drivers of customer satisfaction with public transport services. Transp. Res. Part A Policy Pract. 2015, 78, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, A.N.H.; Borhan, M.N.; Yazid, M.R.M.; Rahmat, R.A.; Yukawa, S. Factors influencing passengers’ satisfaction with the light rail transit service in alpha cities: Evidence from Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia using structural equation modelling. Mathematics 2021, 9, 1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beirão, G.; Cabral, J.A.S. Understanding attitudes towards public transport and private car: A qualitative study. Transp. Policy 2007, 14, 478–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wall, G.; Olaniyan, B.; Woods, L.; Musselwhite, C. Encouraging sustainable modal shift—An evaluation of the Portsmouth Big Green Commuter Challenge. Case Stud. Transp. Policy 2017, 5, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ibrahim, A.N.H.; Borhan, M.N.; Darus, N.S.; Yunin, N.A.M.; Ismail, R. Understanding the Willingness of Students to Use Bicycles for Sustainable Commuting in a University Setting: A Structural Equation Modelling Approach. Mathematics 2022, 10, 861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Replogle, M.; Fulton, L. A Global High Shift Scenario: Impacts and Potential for More Public Transport, Walking, And Cycling with Lower Car Use; Institute for Transportation and Development Policy: New York, NY, USA; University of California, Davis: Davis, CA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Lai, W.T.; Chen, C.F. Behavioral intentions of public transit passengers—The roles of service quality, perceived value, satisfaction and involvement. Transp. Policy 2011, 18, 318–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, S. Users’ willingness to ride an integrated public-transport service: A literature review. Transp. Policy 2016, 48, 183–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thøgersen, J. Promoting public transport as a subscription service: Effects of a free month travel card. Transp. Policy 2009, 16, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, S.; Aggarwal, P.; Kumar, P.; Singhal, S.; Sharma, P. Identifying public preferences using multi-criteria decision making for assessing the shift of urban commuters from private to public transport: A case study of Delhi. Transp. Res. Part F Traffic Psychol. Behav. 2014, 24, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.H.; Chung, J.H.; Park, S.; Choi, K. Analysis of user satisfaction to promote public transportation: A pattern-recognition approach focusing on out-of-vehicle time. Int. J. Sustain. Transp. 2017, 11, 582–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Lierop, D.; Badami, M.G.; El-Geneidy, A.M. What influences satisfaction and loyalty in public transport? A review of the literature. Transp. Rev. 2018, 38, 52–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zulkifli, S.N.A.M.; Hamsa, A.A.K.; Noor, N.M.; Ibrahim, M. Evaluation of land use density, diversity and ridership of Rail Based Public Transportation System. Transp. Res. Procedia 2017, 25, 5266–5281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belwal, R. Public transportation in Oman: A strategic analysis. Adv. Transp. Stud. 2017, 42, 99–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, A.N.H.; Borhan, M.N.; Yusoff, N.I.; Ismail, A. Rail-based Public Transport Service Quality and User Satisfaction—A Literature Review. Promet-Traffic Transp. 2020, 32, 423–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, V.; Ari, E. The effects of service quality, image, and customer satisfaction on customer complaints and loyalty in high-speed rail service in Turkey: A proposal of the structural equation model. Transp. A Transp. Sci. 2017, 13, 67–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Yang, M.; Wu, J.; Rasouli, S.; Lei, D. Assessing bus transit service from the perspective of elderly passengers in Harbin, China. Int. J. Sustain. Transp. 2019, 13, 761–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, A.; Borhan, M.; Yusoff, N.; Ismail, A.; Yazid, M.M.; Yunin, N.M.; Sotaro, Y. Gender and Age Do Matter: Exploring the Effect of Passengers’ Gender and Age on the Perception of Light Rail Transit Service Quality in Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia. Sustainability 2021, 13, 990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngah, R.; Putit, L.; Mat, A.; Abdullah, J.; Ab Majid, R. Moderating effect of service quality on public transport travel behaviour and antecedents. Plan. Malays. J. 2020, 18, 80–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiglao, N.C.C.; De Veyra, J.M.; Tolentino, N.J.Y.; Tacderas, M.A.Y. The perception of service quality among paratransit users in Metro Manila using structural equations modelling (SEM) approach. Res. Transp. Econ. 2020, 83, 100955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuenyindee, T.; Ong, A.K.S.; Ramos, J.P.; Prasetyo, Y.T.; Nadlifatin, R.; Kurata, Y.B.; Sittiwatethanasiri, T. Public utility vehicle service quality and customer satisfaction in the Philippines during the COVID-19 pandemic. Util. Policy 2022, 75, 101336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joewono, T.B.; Kubota, H. Paratransit service in Indonesia: User satisfaction and future choice. Transp. Plan. Technol. 2008, 31, 325–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jannah, E.N.; Ibrahim, A.N.H.; Borhan, M.N. Public transportation in Jabodetabek: Performance satisfaction analysis. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 930, 012069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wonglakorn, N.; Ratanavaraha, V.; Karoonsoontawong, A.; Jomnonkwao, S. Exploring passenger loyalty and related factors for urban railways in Thailand. Sustainability 2021, 13, 5517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jomnonkwao, S.; Champahom, T.; Ratanavaraha, V. Methodologies for determining the service quality of the intercity rail service based on users’ perceptions and expectations in Thailand. Sustainability 2020, 12, 4259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díez-Mesa, F.; de Oña, R.; de Oña, J. Bayesian networks and structural equation modelling to develop service quality models: Metro of Seville case study. Transp. Res. Part A Policy Pract. 2018, 118, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Liu, Y.; Lu, W.; Xiao, G. Evaluating passenger satisfaction index based on PLS-SEM model: Evidence from Chinese public transport service. Transp. Res. Part A Policy Pract. 2019, 120, 149–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oña, J.; Estévez, E.; de Oña, R. Public transport users versus private vehicle users: Differences about quality of service, satisfaction and attitudes toward public transport in Madrid (Spain). Travel Behav. Soc. 2021, 23, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oña, J.; Estévez, E.; de Oña, R. Perception of Public Transport Quality of Service among Regular Private Vehicle Users in Madrid, Spain. Transp. Res. Rec. 2020, 2674, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, B.; Barreda, R.; Dell’Olio, L.; Ibeas, A. Modelling user perception of taxi service quality. Transp. Policy 2018, 63, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dell’Olio, L.; Ibeas, A.; Cecín, P. Modelling user perception of bus transit quality. Transp. Policy 2010, 17, 388–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, J.; Eboli, L.; Mazzulla, G.; Ortúzar, J.d.D. Effect of critical incidents on public transport satisfaction and loyalty: An Ordinal Probit SEM-MIMIC approach. Transportation 2020, 47, 827–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garver, M.S. Best practices in identifying customer-driven improvement opportunities. Ind. Mark. Manag. 2003, 32, 455–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, M.; Avineri, E.; Fries, R.; Ishak, S.; Jha, M.; Kikuchi, S.; Liu, F.; Praveen, E.; Qi, Y.; Sanford-Bernhardt, K.; et al. Thoughts on the future of artificial intelligence and transportation. Transp. Res. Circ. 2012, E-C168, 137–144. [Google Scholar]
- Chong, A.Y.L. Predicting m-commerce adoption determinants: A neural network approach. Expert Syst. Appl. 2013, 40, 523–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrido, C.; de Oña, R.; de Oña, J. Neural networks for analyzing service quality in public transportation. Expert Syst. Appl. 2014, 41, 6830–6838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, A.N.H.; Borhan, M.N.; Osman, M.H.; Khairuddin, F.H.; Zakaria, N.M. An Empirical Study of Passengers’ Perceived Satisfaction with Monorail Service Quality: Case of Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia. Sustainability 2022, 14, 6496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leong, L.; Hew, T.; Ooi, K.; Tan, G.W. Predicting actual spending in online group buying—An artificial neural network approach. Electron. Commer. Res. Appl. 2019, 38, 100898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leong, L.; Hew, T.; Ooi, K.; Dwivedi, Y.K. Predicting trust in online advertising with an SEM-artificial neural network approach. Expert Syst. Appl. 2020, 162, 113849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larasati, A.; DeYong, C.; Slevitch, L. The Application of Neural Network and Logistics Regression Models on Predicting Customer Satisfaction in a Student-Operated Restaurant. Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 2012, 65, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mahapatra, S.S.; Khan, M.S. A Methodology for Evaluation of Service Quality Using Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Global Manufacturing and Innovation, Coimbatore, India, 27–29 July 2006; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Lien, C.H.; Wu, J.J.; Chen, Y.H.; Wang, C.J. Trust transfer and the effect of service quality on trust in the healthcare industry. Manag. Serv. Qual. 2014, 24, 399–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lien, C.H.; Cao, Y.; Zhou, X. Service quality, satisfaction, stickiness, and usage intentions: An exploratory evaluation in the context of WeChat services. Comput. Human Behav. 2017, 68, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Lu, X.; Tan, Y. Impact of product attributes on customer satisfaction: An analysis of online reviews for washing machines. Electron. Commer. Res. Appl. 2018, 29, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wikhamn, W. Innovation, sustainable HRM and customer satisfaction. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 2019, 76, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadic-Maglajlic, S.; Boso, N.; Micevski, M. How internal marketing drive customer satisfaction in matured and maturing European markets? J. Bus. Res. 2018, 86, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radojevic, T.; Stanisic, N.; Stanic, N.; Davidson, R. The effects of traveling for business on customer satisfaction with hotel services. Tour. Manag. 2018, 67, 326–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homburg, C.; Rudolph, B. Customer satisfaction in industrial markets: Dimensional and multiple role issues. J. Bus. Res. 2001, 52, 15–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouhna, L.; Mekkaoui, S. The Effect of Relationship Satisfaction in Customer Loyalty: Case Study of Moroccan Agri-Food Industries. Int. J. Bus. Soc. Sci. 2013, 4, 279–286. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.C. The customer satisfaction-loyalty relation in an interactive e-service setting: The mediators. J. Retail. Consum. Serv. 2012, 19, 202–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suki, N.M. Passenger satisfaction with airline service quality in Malaysia: A structural equation modeling approach. Res. Transp. Bus. Manag. 2014, 10, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadiuzzman, M.; Das, T.; Hasnat, M.M.; Hossain, S.; Musabbir, S.R. Structural equation modeling of user satisfaction of bus transit service quality based on stated preferences and latent variables. Transp. Plan. Technol. 2017, 40, 257–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchinson, T.P. Classification of reasons for poor customer experiences in service industries: The case of public transport. Transp. Plan. Technol. 2011, 34, 747–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, A.N.H.; Borhan, M.N. Sex Disparity in Satisfaction and Loyalty Towards Urban Rail Transit: A Survey of Light Rail Transit (LRT) Passengers in Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia. Int. J. Integr. Eng. 2021, 13, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morfoulaki, M.; Tyrinopoulos, Y.; Aifadopoulou, G. Estimation of Satisfied Customers in Public Transport Systems: A New Methodological Approach. J. Transp. Res. Forum 2007, 46, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, J.S.; Kim, C. A structural equation analysis of the QSL relationship with passenger riding experience on high speed rail: An empirical study of Taiwan and Korea. Expert Syst. Appl. 2009, 36, 6945–6955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, C.W.; Tang, M.L. Relationship among service quality, corporate image, customer satisfaction and behaviroal intention for the elderly in high speed rail service. J. Adv. Transp. 2013, 47, 512–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, A.N.H.; Borhan, M.N. The Interrelationship Between Perceived Quality, Perceived Value and User Satisfaction Towards Behavioral Intention in Public Transportation: A Review of the Evidence. Int. J. Adv. Sci. Eng. Inf. Technol. 2020, 10, 2048–2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zefreh, M.M.; Hussain, B.; Sipos, T. In-Depth Analysis and Model Development of Passenger Satisfaction with Public Transportation. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2020, 24, 3064–3073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srisaeng, P.; Baxter, G.S.; Wild, G. Forecasting demand for low cost carriers in Australia using an artificial neural network approach. Aviation 2015, 19, 90–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Srisaeng, P.; Baxter, G.; Wild, G. Using an artificial neural network approach to forecast Australia’s domestic passenger air travel demand. World Rev. Intermodal Transp. Res. 2015, 5, 281–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Curcio, S.; Iorio, G. Models of membrane reactors based on artificial neural networks and hybrid approaches. In Handbook of Membrane Reactors; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2013; ISBN 9780857097330. [Google Scholar]
- Watts, M.J.; Worner, S.P. Using artificial neural networks to determine the relative contribution of abiotic factors influencing the establishment of insect pest species. Ecol. Inform. 2008, 3, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunt, M.M.; Aghayan, I.; Noii, N. Prediction for traffic accident severity: Comparing the artificial neural network, genetic algorithm, combined genetic algorithm and pattern search methods. Transport 2011, 26, 353–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sineglazov, V.; Chumachenko, E.; Gorbatyuk, V. An algorithm for solving the problem of forecasting. Aviation 2013, 17, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ba-fail, A.O.; Abed, S.Y.; Jasimuddin, S.M. The determinants of domestic air travel demand in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. J. Air Transp. World Wide 2000, 5, 72–86. [Google Scholar]
- Tiryaki, S.; Aydin, A. An artificial neural network model for predicting compression strength of heat treated woods and comparison with a multiple linear regression model. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 62, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claveria, O.; Torra, S. Forecasting tourism demand to Catalonia: Neural networks vs. time series models. Econ. Model. 2014, 36, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arif, M.I.M.; Hamim, A.; Ibrahim, A.N.H.; Khairuddin, F.H.; Jamaludin, N.A.A.; Yusoff, N.I. Kajian perbandingan penggunaan model rangkaian saraf tiruan dan model penyesuaian logik kabur untuk meramal modulus elastik turapan boleh lentur. J. Kejuruter. 2019, 31, 357–366. [Google Scholar]
- Masirin, M.I.M.; Salin, A.M.; Zainorabidin, A.; Martin, D.; Samsuddin, N. Review on Malaysian Rail Transit Operation and Management System: Issues and Solution in Integration. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 226, 012029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ibrahim, A.N.H.; Borhan, M.N.; Rahmat, R.A.O.K. Understanding users’ intention to use park-and-ride facilities in malaysia: The role of trust as a novel construct in the theory of planned behaviour. Sustainability 2020, 12, 2484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Borhan, M.N.; Ibrahim, A.N.H.; Aziz, A.; Yazid, M.R.M. The relationship between the demographic, personal, and social factors of Malaysian motorcyclists and risk taking behavior at signalized intersections. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2018, 121, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krejcie, R.V.; Morgan, D.W. Determining Sample Size for Research Activities. Educ. Psychol. Meas. 1970, 38, 607–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ooi, K.B.; Foo, F.E.; Tan, G.W.H.; Hew, J.J.; Leong, L.Y. Taxi within a grab? A gender-invariant model of mobile taxi adoption. Ind. Manag. Data Syst. 2020, 121, 312–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkawsi, G.A.; Ali, N.; Mustafa, A.S.; Baashar, Y.; Alhussian, H.; Alkahtani, A.; Tiong, S.K.; Ekanayake, J. A hybrid SEM-neural network method for identifying acceptance factors of the smart meters in Malaysia: Challenges perspective. Alex. Eng. J. 2021, 60, 227–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamim, A.; Hardwiyono, S.; El-Shafie, A.; Yusoff, N.I.M.; Hainin, M.R. Ramalan Cirian Reologi Campuran Berasfalt Menggunakan Rangkaian. J. Teknol. 2013, 65, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen-Phuoc, D.Q.; Su, D.N.; Tran, P.T.K.; Le, D.T.T.; Johnson, L.W. Factors influencing customer’s loyalty towards ride-hailing taxi services—A case study of Vietnam. Transp. Res. Part A Policy Pract. 2020, 134, 96–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolaou, P.; Basbas, S.; Politis, I.; Borg, G. Trip and personal characteristics towards the intention to cycle in Larnaca, Cyprus: An EFA-SEM approach. Sustainability 2020, 12, 4250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morton, C.; Caulfield, B.; Anable, J. Customer perceptions of quality of service in public transport: Evidence for bus transit in Scotland. Case Stud. Transp. Policy 2016, 4, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obsie, A.; Woldeamanuel, M.; Woldetensae, B. Service Quality of Addis Ababa Light Rail Transit: Passengers’ Views and Perspectives. Urban Rail Transit 2020, 6, 231–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, H.F. The Application of Electronic Computers to Factor Analysis. Educ. Psychol. Meas. 1960, 20, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maskey, R.; Fei, J.; Nguyen, H.O. Use of exploratory factor analysis in maritime research. Asian J. Shipp. Logist. 2018, 34, 91–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uca, S.; Altintas, V.; Tuzunkan, D.; Toanoglou, M. A study on the effects of demographic factors on hotel selection process. Int. J. Tour. Sci. 2017, 17, 231–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Field, A. Discovering Statistics using SPSS Statistics, 3rd ed.; SAGE Publications Ltd.: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2009; ISBN 9781847879073. [Google Scholar]
- Hair, J.F.; Hult, G.T.M.; Ringle, C.M.; Sarstedt, M. A Primer on Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modeling (PLS-SEM); SAGE Publications, Inc.: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Leong, L.; Hew, T.; Lee, V.; Ooi, K. An SEM—artificial-neural-network analysis of the relationships between SERVPERF, customer satisfaction and loyalty among low-cost and full-service airline. Expert Syst. Appl. 2015, 42, 6620–6634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leong, L.; Hew, T.; Ooi, K.; Chong, A.Y. Predicting the antecedents of trust in social commerce—A hybrid structural equation modeling with neural network approach. J. Bus. Res. 2020, 110, 24–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahzad, F.; Xiu, G.; Aamir, M.; Khan, S.; Shahbaz, M. Predicting the adoption of a mobile government security response system from the user’ s perspective: An application of the artificial neural network approach. Technol. Soc. 2020, 62, 101278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.K.; Gaur, A.; Saddikuti, V.; Rastogi, A. Structural equation model (SEM)-neural network (NN) model for predicting quality determinants of e-learning management systems. Behav. Inf. Technol. 2017, 36, 1053–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veerasamy, R.; Rajak, H.; Jain, A.; Sivadasan, S.; Varghese, C.P.; Agrawal, R.K. Validation of QSAR Models—Strategies and Importance. Int. J. Drug Des. Disocovery 2011, 2, 511–519. [Google Scholar]
- Chong, A.Y.L. A two-staged SEM-neural network approach for understanding and predicting the determinants of m-commerce adoption. Expert Syst. Appl. 2013, 40, 1240–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sim, J.J.; Tan, G.W.H.; Wong, J.C.J.; Ooi, K.B.; Hew, T.S. Understanding and predicting the motivators of mobile music acceptance—A multi-stage MRA-artificial neural network approach. Telemat. Inform. 2014, 31, 569–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oña, R.; Machado, J.L.; de Oña, J. Perceived Service Quality, Customer Satisfaction, and Behavioral Intentions. Transp. Res. Rec. J. Transp. Res. Board 2015, 2538, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanık, S.; Aktas, E.; Topcu, Y.I. Traveler satisfaction in rapid rail systems: The case of Istanbul metro. Int. J. Sustain. Transp. 2017, 11, 642–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- de Oña, J.; de Oña, R.; Calvo, F.J. A classification tree approach to identify key factors of transit service quality. Expert Syst. Appl. 2012, 39, 11164–11171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Cao, M.; Bai, Y.; Song, Z. Analysis of Public Transportation Competitiveness Based on Potential Passenger Travel Intentions: Case Study in Shanghai, China. Transp. Res. Rec. 2019, 2673, 823–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.M.; Ladin, M.A.; Ismail, A.; Rahmat, R.O.K. Consumers satisfaction of public transport monorail user in Kuala Lumpur. J. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2013, 8, 272–283. [Google Scholar]
- Machado-Leóna, J.L.; de Oñaa, R.; Baounib, T.; de Oñaa, J. Railway transit services in Algiers: Priority improvement actions based on users perceptions. Transp. Policy 2017, 53, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Yu, Y.; Liang, W. Public Transit Customer Satisfaction Dimensions Discovery from Online Reviews. Urban Rail Transit 2016, 2, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Geetika, S.N. Determinants of Customer Satisfaction on Service Quality: A Study of Railway Platforms in India. J. Public Transp. 2010, 13, 97–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Borhan, M.N.; Akhir, N.M.; Ismail, A.; Rahmat, R.A.A.O. Pemodelan Hubungan Antara Kualiti Perkhidmatan, Kesan Alam Sekitar, Sikap dan Keinginan untuk Menggunakan Park-and-Ride. J. Kejuruter. 2015, 27, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borhan, M.N.; Ibrahim, A.N.H.; Miskeen, M.A.A. Extending the theory of planned behaviour to predict the intention to take the new high-speed rail for intercity travel in Libya: Assessment of the influence of novelty seeking, trust and external influence. Transp. Res. Part A Policy Pract. 2019, 130, 373–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Githui, J.N.; Okamura, T.; Nakamura, F. The Structure of Users’ Satisfaction on Urban Public Transport Service in Developing Country: The Case of Nairobi. J. East. Asia Soc. Transp. Stud. 2010, 8, 1288–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oña, J.; de Oña, R.; Eboli, L.; Mazzulla, G. Perceived service quality in bus transit service: A structural equation approach. Transp. Policy 2013, 29, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Susilo, Y.O.; Cats, O. Exploring key determinants of travel satisfaction for multi-modal trips by different traveler groups. Transp. Res. Part A Policy Pract. 2014, 67, 366–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nwachukwu, A.A. Assessment of Passenger Satisfaction with Intra-City Public Bus Transport Services in Abuja, Nigeria. J. Public Transp. 2014, 17, 99–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oña, J.; de Oña, R. Quality of service in public transport based on customer satisfaction surveys: A review and assessment of methodological approaches. Transp. Sci. 2015, 49, 605–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grujičić, D.; Ivanović, I.; Jović, J.; Đorić, V. Customer perception of service quality in public transport. Transport 2014, 29, 285–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eboli, L.; Forciniti, C.; Mazzulla, G.; Calvo, F.J. Exploring the Factors that Impact on Transit Use through an Ordered Probit Model: The Case of Metro of Madrid. In Proceedings of the Transportation Research Pro, Valencia, Spain, 7–9 June 2016; pp. 35–43. [Google Scholar]
- Eboli, L.; Fu, Y.; Mazzulla, G. Multilevel Comprehensive Evaluation of the Railway Service Quality. Procedia Eng. 2016, 137, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- de Oña, R.; Eboli, L.; Mazzulla, G. Key factors affecting rail service quality in the Northern Italy: A decision tree approach. Transport 2014, 29, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- de Oña, J.; de Oña, R.; Eboli, L.; Mazzulla, G. Heterogeneity in Perceptions of Service Quality among Groups of Railway Passengers. Int. J. Sustain. Transp. 2015, 9, 612–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oña, J.; de Oña, R.; Eboli, L.; Forciniti, C.; Mazzulla, G. Transit passengers’ behavioural intentions: The influence of service quality and customer satisfaction. Transp. A Transp. Sci. 2016, 12, 385–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Factor/Item | Exploratory Factor Analysis (EFA) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Loading Factor | Eigenvalue | Explained Variance | Cronbach Alpha | |
| Signage (SG)/ SG1-SG5 | 0.639–0.698 | 14.839 | 34.509 | 0.903 |
| Comfort (CF)/ CF1-CF5 | 0.599–0.692 | 7.419 | 17.254 | 0.912 |
| Facilities (FT)/ FT1-FT6 | 0.667–0.808 | 2.212 | 5.145 | 0.947 |
| Speediness (SN)/ SN1-SN6 | 0.639–0.712 | 1.707 | 3.910 | 0.904 |
| Ticketing service (TS)/ TS1-TS4 | 0.611–0.672 | 1.471 | 3.421 | 0.908 |
| Staff service (SS)/ SS1-SS4 | 0.738–0.784 | 1.231 | 2.877 | 0.897 |
| Safety (ST)/ ST1-ST5 | 0.506–0.836 | 1.148 | 2.670 | 0.912 |
| Provision of Information (PI)/ PI1-PI4 | 0.515–0.552 | 1.017 | 2.366 | 0.929 |
| Factor | SG | CF | SN | ST | TS | FT | SS | PI | PS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SG | 1.000 | ||||||||
| CF | 0.757 ** | 1.000 | |||||||
| SN | 0.683 ** | 0.710 ** | 1.000 | ||||||
| ST | 0.605 ** | 0.649 ** | 0.679 ** | 1.000 | |||||
| TS | 0.707 ** | 0.706 ** | 0.680 ** | 0.714 ** | 1.000 | ||||
| FT | 0.649 ** | 0.676 ** | 0.648 ** | 0.558 ** | 0.680 ** | 1.000 | |||
| SS | 0.566 ** | 0.601 ** | 0.564 ** | 0.575 ** | 0.628 ** | 0.615 ** | 1.000 | ||
| PI | 0.663 ** | 0.677 ** | 0.631 ** | 0.586 ** | 0.685 ** | 0.738 ** | 0.643 ** | 1.000 | |
| PS | 0.696 ** | 0.719 ** | 0.684 ** | 0.597 ** | 0.725 ** | 0.722 ** | 0.650 ** | 0.740 ** | 1.000 |
| ANN Network | Training | Testing | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | SSE | MSE | RMSE | N | SSE | MSE | RMSE | |
| ANN1 | 372 | 4.457 | 0.012 | 0.109 | 45 | 0.833 | 0.019 | 0.136 |
| ANN2 | 375 | 3.932 | 0.010 | 0.102 | 42 | 0.644 | 0.015 | 0.124 |
| ANN3 | 372 | 4.215 | 0.011 | 0.106 | 45 | 0.317 | 0.007 | 0.084 |
| ANN4 | 369 | 4.326 | 0.012 | 0.108 | 48 | 0.585 | 0.012 | 0.110 |
| ANN5 | 368 | 4.252 | 0.012 | 0.107 | 49 | 0.458 | 0.009 | 0.097 |
| ANN6 | 380 | 4.130 | 0.011 | 0.104 | 37 | 0.589 | 0.016 | 0.126 |
| ANN7 | 375 | 4.436 | 0.012 | 0.109 | 42 | 0.469 | 0.011 | 0.106 |
| ANN8 | 364 | 3.905 | 0.011 | 0.104 | 53 | 0.608 | 0.011 | 0.107 |
| ANN9 | 382 | 5.041 | 0.013 | 0.115 | 35 | 0.260 | 0.007 | 0.086 |
| ANN10 | 365 | 4.515 | 0.012 | 0.111 | 52 | 0.508 | 0.010 | 0.099 |
| 4.321 | 0.012 | 0.108 | 0.527 | 0.012 | 0.107 | |||
| SD | 0.327 | 0.001 | 0.004 | SD | 0.165 | 0.004 | 0.017 | |
| ANN Network | Relative Importance | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SG | CF | SN | ST | TS | FT | SS | PI | |
| ANN1 | 0.116 | 0.090 | 0.064 | 0.092 | 0.125 | 0.179 | 0.121 | 0.213 |
| ANN2 | 0.149 | 0.045 | 0.051 | 0.030 | 0.141 | 0.218 | 0.086 | 0.280 |
| ANN3 | 0.128 | 0.095 | 0.068 | 0.030 | 0.091 | 0.216 | 0.138 | 0.234 |
| ANN4 | 0.181 | 0.092 | 0.117 | 0.020 | 0.200 | 0.189 | 0.045 | 0.155 |
| ANN5 | 0.067 | 0.076 | 0.091 | 0.016 | 0.224 | 0.225 | 0.081 | 0.220 |
| ANN6 | 0.158 | 0.090 | 0.049 | 0.077 | 0.028 | 0.222 | 0.122 | 0.254 |
| ANN7 | 0.149 | 0.093 | 0.103 | 0.048 | 0.171 | 0.219 | 0.077 | 0.141 |
| ANN8 | 0.176 | 0.024 | 0.088 | 0.010 | 0.092 | 0.155 | 0.167 | 0.289 |
| ANN9 | 0.189 | 0.048 | 0.059 | 0.080 | 0.123 | 0.116 | 0.128 | 0.258 |
| ANN10 | 0.144 | 0.110 | 0.093 | 0.164 | 0.129 | 0.156 | 0.114 | 0.091 |
| Average of relative importance | 0.146 | 0.077 | 0.078 | 0.057 | 0.132 | 0.189 | 0.108 | 0.213 |
| Normalised relative importance (%) | 68.2 | 35.8 | 36.5 | 26.6 | 62.0 | 88.8 | 50.5 | 100.0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ibrahim, A.N.H.; Borhan, M.N.; Osman, M.H.; Mat Yazid, M.R.; Md. Rohani, M. The Influence of Service Quality on User’s Perceived Satisfaction with Light Rail Transit Service in Klang Valley, Malaysia. Mathematics 2022, 10, 2213. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10132213
Ibrahim ANH, Borhan MN, Osman MH, Mat Yazid MR, Md. Rohani M. The Influence of Service Quality on User’s Perceived Satisfaction with Light Rail Transit Service in Klang Valley, Malaysia. Mathematics. 2022; 10(13):2213. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10132213
Chicago/Turabian StyleIbrahim, Ahmad Nazrul Hakimi, Muhamad Nazri Borhan, Mohd Haniff Osman, Muhamad Razuhanafi Mat Yazid, and Munzilah Md. Rohani. 2022. "The Influence of Service Quality on User’s Perceived Satisfaction with Light Rail Transit Service in Klang Valley, Malaysia" Mathematics 10, no. 13: 2213. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10132213
APA StyleIbrahim, A. N. H., Borhan, M. N., Osman, M. H., Mat Yazid, M. R., & Md. Rohani, M. (2022). The Influence of Service Quality on User’s Perceived Satisfaction with Light Rail Transit Service in Klang Valley, Malaysia. Mathematics, 10(13), 2213. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10132213








