Fuzzy-Based Fixed-Time Nonsingular Tracker of Exoskeleton Robots for Disabilities Using Sliding Mode State Observer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- −
- Presentation of free and typical types of the dynamical robot system for describing a dynamical model of the upper-limb exoskeleton robot system;
- −
- Design of the fixed-time convergence rate state observer for compensation of the uncertainty in the states of the upper-limb exoskeleton robot system;
- −
- Proposition of the nonsingular terminal sliding mode control method with the target of the fixed-time convergence of position tracking error of the exoskeleton robot system;
- −
- Suggestion of fuzzy control procedure for improvement of the control input performance.
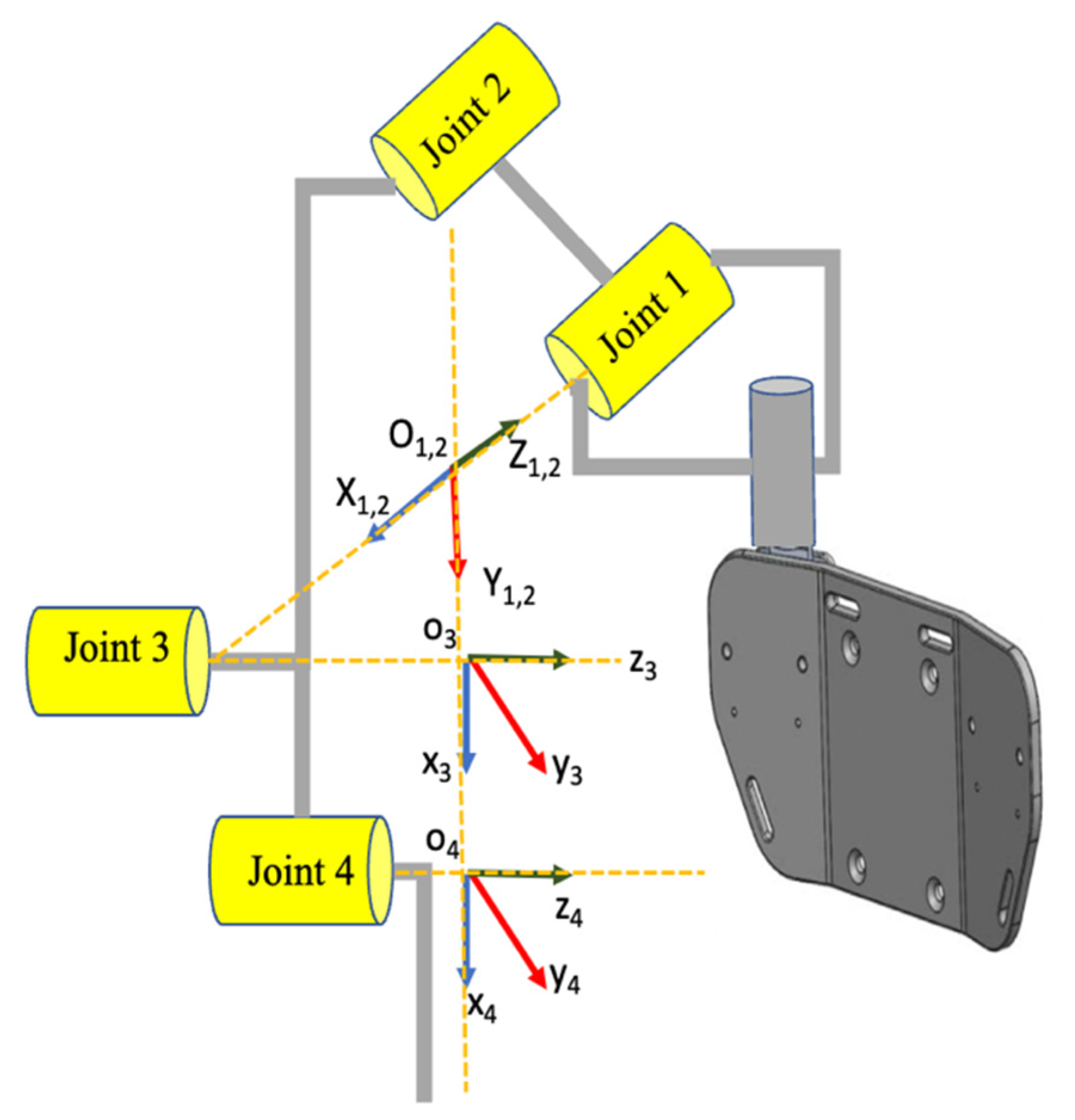
2. Description of Mechanical Model of Upper-Exoskeleton Robot
3. Preliminaries
4. Main Results
4.1. Design of the State Observer
4.2. Fast Non-Singular Terminal Sliding Mode Control
4.3. Fuzzy Nonsingular Terminal Sliding Mode Control
5. Simulation Results
- A.
- Example 1
- B.
- Example 2
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, B.; Xi, L. Development of an Omni-Directional Wheelchair Robot. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Engineering Simulation and Intelligent Control (ESAIC), Changsha, China, 10–11 August 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Fehr, L.; Langbein, W.E.; Skaar, S.B. Adequacy of power wheelchair control interfaces for persons with severe disabilities: A clinical survey. J. Rehabil. Res. Dev. 2000, 37, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pazzaglia, M.; Molinari, M. The embodiment of assistive devices—From wheelchair to exoskeleton. Phys. Life Rev. 2016, 16, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schabron, B.; Desai, J.; Yihun, Y. Wheelchair-Mounted Upper Limb Robotic Exoskeleton with Adaptive Controller for Activities of Daily Living. Sensors 2021, 21, 5738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gagnon, D.H.; Vermette, M.; Duclos, C.; Aubertin-Leheudre, M.; Ahmed, S.; Kairy, D. Satisfaction and perceptions of long-term manual wheelchair users with a spinal cord injury upon completion of a locomotor training program with an overground robotic exoskeleton. Disabil. Rehabil. Assist. Technol. 2019, 14, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, H.; Tohyama, T.; Maki, D.; Sato, K.; Nakano, E. Autonomous Step Climbing Strategy Using a Wheelchair and Care Robot. In Proceedings of the 2019 4th International Conference on Control, Robotics and Cybernetics (CRC), Tokyo, Japan, 27–30 September 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escobedo, A.; Spalanzani, A.; Laugier, C. Multimodal control of a robotic wheelchair: Using contextual in-formation for usability improvement. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Tokyo, Japan, 3–7 November 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Z.; Tian, C.; Dai, J.S. Mechanism design and analysis of a proposed wheelchair-exoskeleton hybrid robot for assisting human movement. Mech. Sci. 2019, 10, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiguchi, K.; Rahman, M.H.; Sasaki, M.; Teramoto, K. Development of a 3DOF mobile exoskeleton robot for human upper-limb motion assist. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2008, 56, 678–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Rosen, J. Neural PID Control of Robot Manipulators with Application to an Upper Limb Exoskeleton. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2013, 43, 673–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, L.; Gull, M.A.; Bai, S. PD-Based Fuzzy Sliding Mode Control of a Wheelchair Exoskeleton Robot. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2020, 25, 2546–2555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gull, M.A.; Thoegersen, M.; Bengtson, S.; Mohammadi, M.; Struijk, L.A.; Moeslund, T.; Bak, T.; Bai, S. A 4-DOF Upper Limb Exoskeleton for Physical Assistance: Design, Modeling, Control and Performance Evaluation. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 5865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razzaghian, A. A fuzzy neural network-based fractional-order Lyapunov-based robust control strategy for exoskeleton robots: Application in upper-limb rehabilitation. Math. Comput. Simul. 2022, 193, 567–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Rosen, J. A novel linear PID controller for an upper limb exoskeleton. In Proceedings of the 49th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control (CDC), Atlanta, GA, USA, 15–17 December 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Li, X.; Yu, H. Efficient PID Tracking Control of Robotic Manipulators Driven by Compliant Actuators. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2018, 27, 915–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W. PID Control with Intelligent Compensation for Exoskeleton Robots; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alattas, K.A.; Vu, M.T.; Mofid, O.; El-Sousy, F.F.; Fekih, A.; Mobayen, S. Barrier Function-Based Nonsingular Finite-Time Tracker for Quadrotor UAVs Subject to Uncertainties and Input Constraints. Mathematics 2022, 10, 1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alattas, K.A.; Mofid, O.; El-Sousy, F.F.; Alanazi, A.K.; Awrejcewicz, J.; Mobayen, S. Adaptive Nonsingular Terminal Sliding Mode Control for Performance Improvement of Perturbed Nonlinear Systems. Mathematics 2022, 10, 1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Guo, Q.; Li, T.; Yan, Y.; Jiang, D. Gait Prediction and Variable Admittance Control for Lower Limb Exoskeleton With Measurement Delay and Extended-State-Observer. IEEE Trans. Neural Networks Learn. Syst. 2022, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanesar, M.A.; Branson, D. Robust Sliding Mode Fuzzy Control of Industrial Robots Using an Extended Kalman Filter Inverse Kinematic Solver. Energies 2022, 15, 1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, M.T.; Alattas, K.A.; Bouteraa, Y.; Rahmani, R.; Fekih, A.; Mobayen, S.; Assawinchaichote, W. Optimized Fuzzy Enhanced Robust Control Design for a Stewart Parallel Robot. Mathematics 2022, 10, 1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Su, C.-Y.; Li, G.; Su, H. Fuzzy Approximation-Based Adaptive Backstepping Control of an Exoskeleton for Human Upper Limbs. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2014, 23, 555–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riani, A.; Madani, T.; Benallegue, A.; Djouani, K. Adaptive integral terminal sliding mode control for upper-limb rehabilitation exoskeleton. Control Eng. Pract. 2018, 75, 108–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Wang, X.; Chen, B.; Wu, H. Design and fuzzy sliding mode admittance control of a soft wearable exoskeleton for elbow rehabilitation. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 60249–60263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmani, M.; Rahman, M.H. An upper-limb exoskeleton robot control using a novel fast fuzzy sliding mode control. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2019, 36, 2581–2592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Precup, R.-E.; Preitl, S. Stability and sensitivity analysis of fuzzy control systems. Mechatronics applications. Acta Polytech. Hung. 2006, 3, 61–76. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, T.; Babanin, A.; Muhammad, A.; Chapron, B.; Chen, C. Modified evolved bat algorithm of fuzzy optimal control for complex nonlinear systems. Rom. J. Inf. Sci. Technol. 2020, 23, T28–T40. [Google Scholar]
- Precup, R.-E.; Roman, R.-C.; Hedrea, E.-L.; Petriu, E.M.; Bojan-Dragos, C.-A. Data-Driven Model-Free Sliding Mode and Fuzzy Control with Experimental Validation. Int. J. Comput. Commun. Control 2021, 16, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preitl, Z.; Precup, R.E.; Tar, J.K.; Takács, M. Use of multi-parametric quadratic programming in fuzzy control systems. Acta Polytech. Hung. 2006, 3, 29–43. [Google Scholar]
- Zeinali, M.; Notash, L. Adaptive sliding mode control with uncertainty estimator for robot manipulators. Mech. Mach. Theory 2010, 45, 80–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polyakov, A. Nonlinear Feedback Design for Fixed-Time Stabilization of Linear Control Systems. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2011, 57, 2106–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Z. Nonsingular fixed-time consensus tracking for second-order multi-agent networks. Automatica 2015, 54, 305–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mobayen, S.; Majd, V.J.; Sojoodi, M. An LMI-based composite nonlinear feedback terminal sliding-mode controller design for disturbed MIMO systems. Math. Comput. Simul. 2012, 85, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
















| Reference | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Li et al. [22] | The backstepping control technique is an iterative controller which leads to complexity in the control process, so it is not preferred for exoskeleton system owing complicated motion. |
| Riani et al. [23] | Whereas exoskeleton robot is located near the human body which its impression has to be considered in the design of the controller. |
| Wu et al. [24] | Although, this method relays on the exact dynamical model of the exoskeleton robot system which is not possible due to existence of modeling error. |
| Rahmani and Rahman [25] | The removal of the singularity problem which is realized by NSSMC method has not been investigated in this paper. |
| Parameter | Value | Parameter | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number | Initial Condition |
|---|---|
| Number | Initial Condition |
|---|---|
| Parameter | Value | Parameter | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Example | Initial Condition | NTSMC | Fuzzy-NTSMC |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.27 | 0.18 | |
| 0.98 | 0.79 | ||
| 0.37 | 0.25 | ||
| 2 | 0.15 | 0.1 | |
| 0.45 | 0.33 | ||
| 1.21 | 0.92 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aly, A.A.; The Vu, M.; El-Sousy, F.F.M.; Alotaibi, A.; Mousa, G.; Le, D.-N.; Mobayen, S. Fuzzy-Based Fixed-Time Nonsingular Tracker of Exoskeleton Robots for Disabilities Using Sliding Mode State Observer. Mathematics 2022, 10, 3147. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10173147
Aly AA, The Vu M, El-Sousy FFM, Alotaibi A, Mousa G, Le D-N, Mobayen S. Fuzzy-Based Fixed-Time Nonsingular Tracker of Exoskeleton Robots for Disabilities Using Sliding Mode State Observer. Mathematics. 2022; 10(17):3147. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10173147
Chicago/Turabian StyleAly, Ayman A., Mai The Vu, Fayez F. M. El-Sousy, Ahmed Alotaibi, Ghassan Mousa, Dac-Nhuong Le, and Saleh Mobayen. 2022. "Fuzzy-Based Fixed-Time Nonsingular Tracker of Exoskeleton Robots for Disabilities Using Sliding Mode State Observer" Mathematics 10, no. 17: 3147. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10173147
APA StyleAly, A. A., The Vu, M., El-Sousy, F. F. M., Alotaibi, A., Mousa, G., Le, D.-N., & Mobayen, S. (2022). Fuzzy-Based Fixed-Time Nonsingular Tracker of Exoskeleton Robots for Disabilities Using Sliding Mode State Observer. Mathematics, 10(17), 3147. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10173147










