An MM Algorithm for the Frailty-Based Illness Death Model with Semi-Competing Risks Data
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. The Semi-Competing Risk Model with Gamma Frailty
3. The Estimation via MM Method
3.1. Philosophy of the MM Principle
3.2. The Estimation Procedure
| Algorithm 1 The estimation procedures via MM method. |
| Input: (, , ) |
| whiledo |
| S1. Update and via Equation (3.6) given |
| S2. Estimate using (3.2)–(3.4) given and |
| S3. |
| end while |
| Output: |
4. Simulation Study
5. Real Data Analysis
6. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fine, J.P.; Jiang, H.; Chappell, R. On semi-competing risks data. Biometrika 2001, 88, 907–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W. Estimating the association parameter for copula models under dependent censoring. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B (Stat. Methodol.) 2003, 65, 257–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakhal, L.; Rivest, L.P.; Abdous, B. Estimating survival and association in a semicompeting risks model. Biometrics 2008, 64, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Kalbfleisch, J.D.; Tai, B. Statistical analysis of illness–death processes and semicompeting risks data. Biometrics 2010, 66, 716–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, M.H.; Ibrahim, J.G.; Zeng, D.; Chen, Q.; Pan, Z.; Xue, X. Bayesian gamma frailty models for survival data with semi-competing risks and treatment switching. Lifetime Data Anal. 2014, 20, 76–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, K.H.; Haneuse, S.; Schrag, D.; Dominici, F. Bayesian semiparametric analysis of semicompeting risks data: Investigating hospital readmission after a pancreatic cancer diagnosis. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. C (Appl. Stat.) 2015, 64, 253–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ha, I.D.; Xiang, L.; Peng, M.; Jeong, J.H.; Lee, Y. Frailty modelling approaches for semi-competing risks data. Lifetime Data Anal. 2020, 26, 109–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.; Haneuse, S. A semi-parametric transformation frailty model for semi-competing risks survival data. Scand. J. Stat. 2017, 44, 112–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y.H. Maximum likelihood analysis of semicompeting risks data with semiparametric regression models. Lifetime Data Anal. 2012, 18, 36–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, M.P.; Yang, I.; Lange, K. EM algorithms without missing data. Stat. Methods Med Res. 1997, 6, 38–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.H.; Michimae, H.; Emura, T. Meta-analysis of individual patient data with semi-competing risks under the Weibull joint frailty–copula model. Comput. Stat. 2020, 35, 1525–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, D.; Lin, D. Semiparametric transformation models with random effects for joint analysis of recurrent and terminal events. Biometrics 2009, 65, 746–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, R.; Zhu, H.; Bondy, M.; Ning, J. Semiparametric model for semi-competing risks data with application to breast cancer study. Lifetime Data Anal. 2016, 22, 456–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hsieh, J.J.; Huang, Y.T. Regression analysis based on conditional likelihood approach under semi-competing risks data. Lifetime Data Anal. 2012, 18, 302–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.; Fine, J.P. Regression modeling of semicompeting risks data. Biometrics 2007, 63, 96–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvares, D.; Haneuse, S.; Lee, C.; Lee, K.H. SemiCompRisks: An R package for the analysis of independent and cluster-correlated semi-competing risks data. R J. 2019, 11, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chapple, A.G.; Vannucci, M.; Thall, P.F.; Lin, S. Bayesian variable selection for a semi-competing risks model with three hazard functions. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 2017, 112, 170–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeder, H.T.; Lu, J.; Haneuse, S. Penalized estimation of frailty-based illness-death models for semi-competing risks. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2202.00618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, M.; Xiang, L.; Wang, S. Semiparametric regression analysis of clustered survival data with semi-competing risks. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 2018, 124, 53–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, D.R.; Lange, K. Computing estimates in the proportional odds model. Ann. Inst. Stat. Math. 2002, 54, 155–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Xu, J.; Tian, G. On profile MM algorithms for gamma frailty survival models. Stat. Sin. 2019, 29, 895–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hunter, D.R.; Lange, K. Quantile regression via an MM algorithm. J. Comput. Graph. Stat. 2000, 9, 60–77. [Google Scholar]
- Johansen, S. An extension of Cox’s regression model. Int. Stat. Rev. Int. Stat. 1983, 51, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, J.P. Semiparametric estimation of random effects using the Cox model based on the EM algorithm. Biometrics 1992, 48, 795–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moertel, C.G.; Fleming, T.R.; Macdonald, J.S.; Haller, D.G.; Laurie, J.A.; Goodman, P.J.; Ungerleider, J.S.; Emerson, W.A.; Tormey, D.C.; Glick, J.H.; et al. Levamisole and fluorouracil for adjuvant therapy of resected colon carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 1990, 322, 352–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurie, J.A.; Moertel, C.G.; Fleming, T.R.; Wieand, H.S.; Leigh, J.E.; Rubin, J.; McCormack, G.W.; Gerstner, J.B.; Krook, J.E.; Malliard, J. Surgical adjuvant therapy of large-bowel carcinoma: An evaluation of levamisole and the combination of levamisole and fluorouracil. The North Central Cancer Treatment Group and the Mayo Clinic. J. Clin. Oncol. 1989, 7, 1447–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
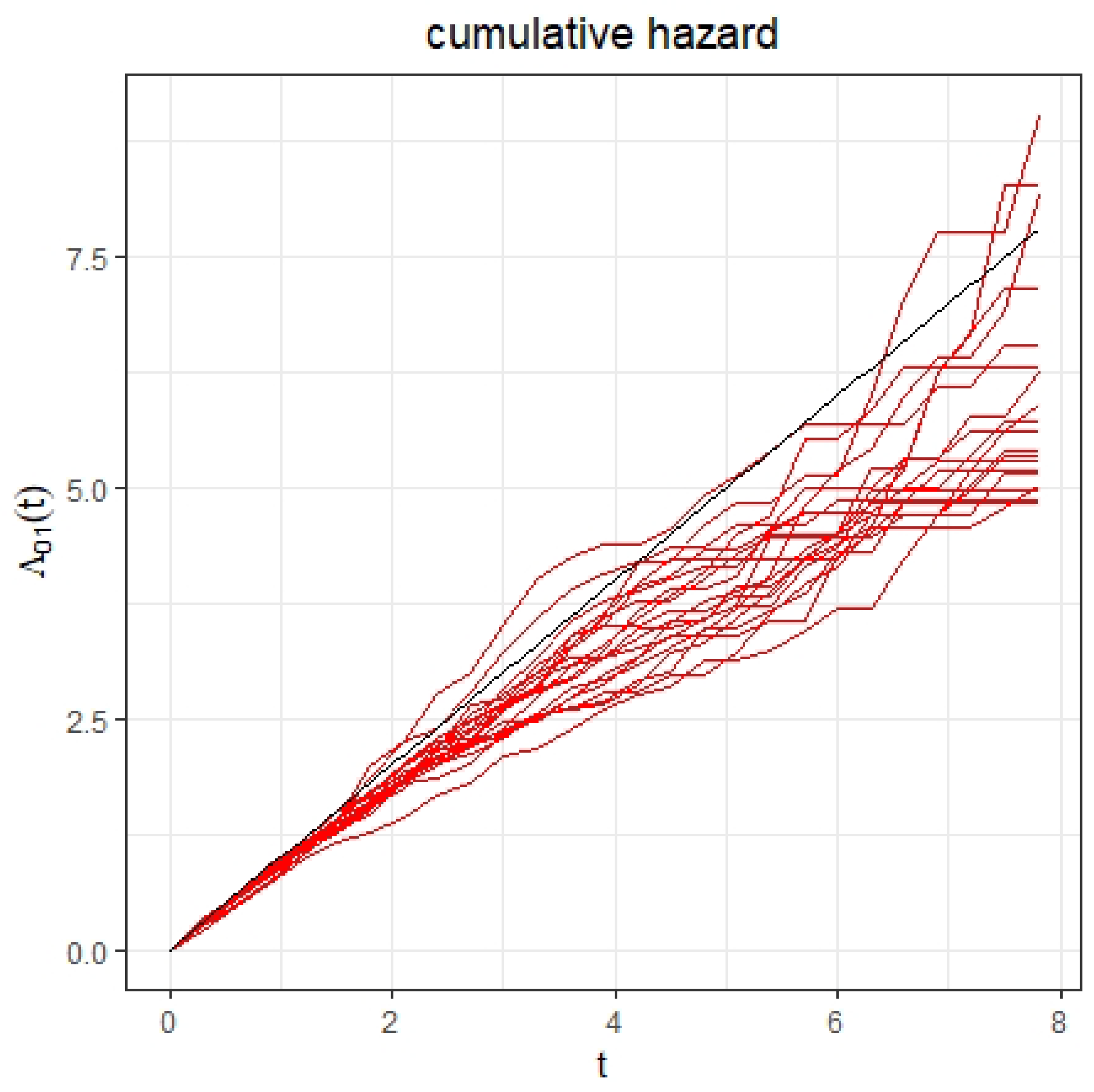
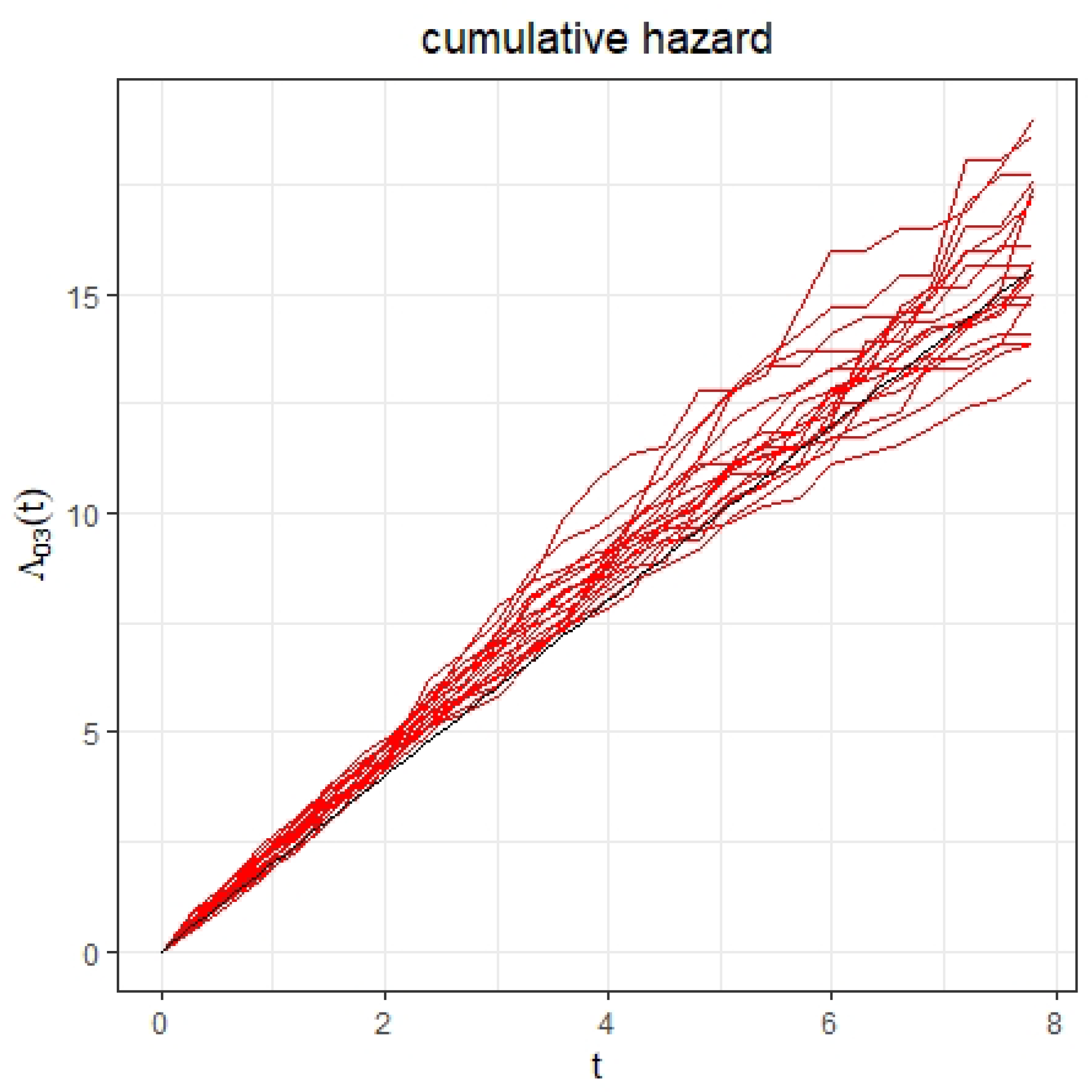
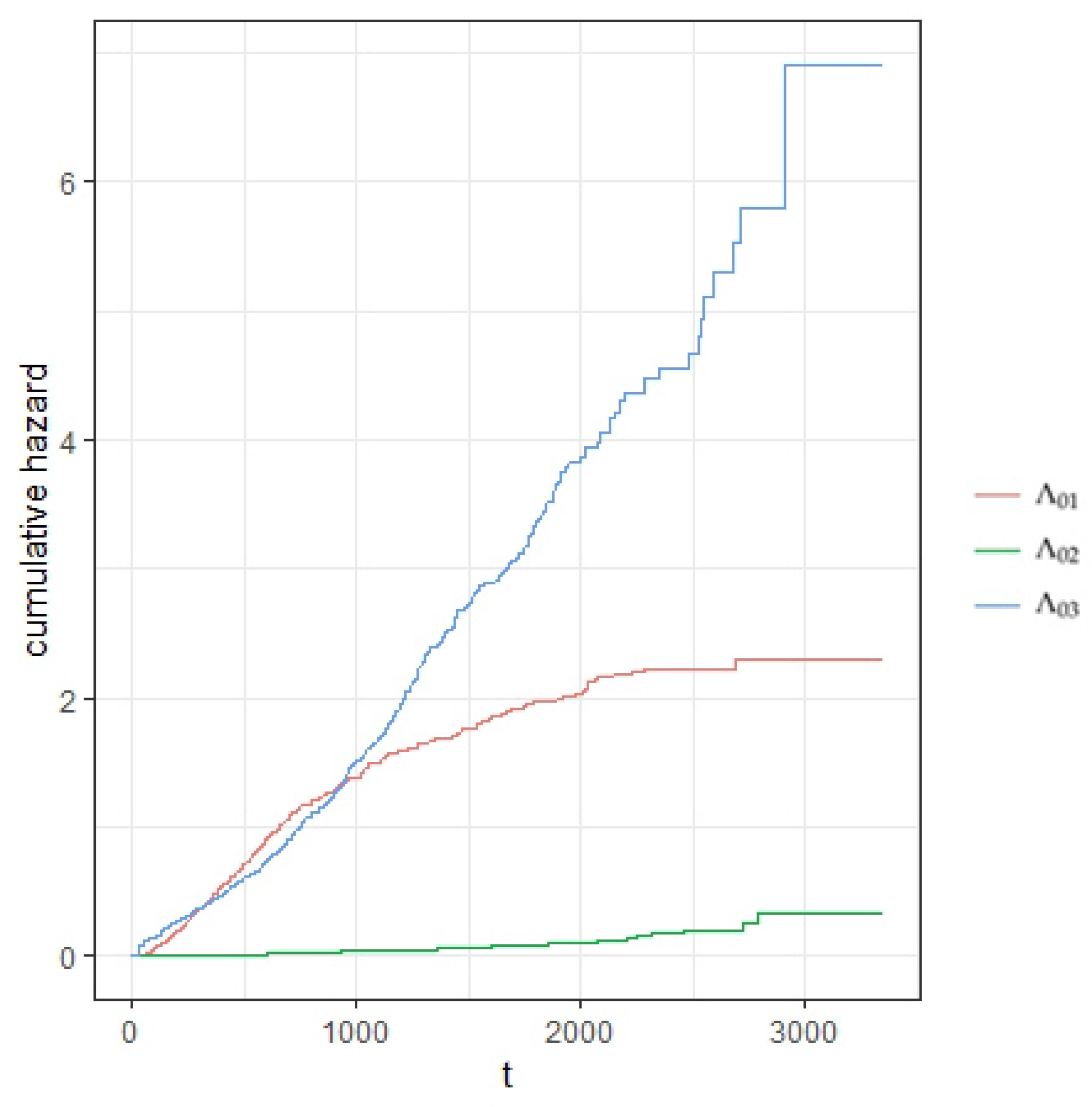
| Parameter | Parameter | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bias | SD | Bias | SD | |||
| 0.5 | T = 0.1957 | T = 0.6736 | ||||
| −0.088 | 0.128 | −0.072 | 0.091 | |||
| 0.045 | 0.173 | −0.032 | 0.066 | |||
| 0.032 | 0.196 | −0.021 | 0.077 | |||
| 0.044 | 0.118 | −0.023 | 0.087 | |||
| −0.036 | 0.080 | −0.024 | 0.063 | |||
| 0.023 | 0.061 | −0.013 | 0.044 | |||
| 0.045 | 0.302 | −0.038 | 0.227 | |||
| 1 | T = 0.2576 | T = 0.8667 | ||||
| 0.098 | 0.173 | 0.088 | 0.135 | |||
| −0.058 | 0.096 | −0.032 | 0.089 | |||
| 0.045 | 0.094 | 0.025 | 0.073 | |||
| −0.043 | 0.133 | −0.022 | 0.084 | |||
| −0.031 | 0.067 | −0.022 | 0.045 | |||
| 0.029 | 0.058 | −0.021 | 0.034 | |||
| 0.051 | 0.336 | 0.031 | 0.284 | |||
| 2 | T = 0.3157 | T = 1.1273 | ||||
| 0.101 | 0.184 | 0.098 | 0.171 | |||
| 0.075 | 0.097 | −0.045 | 0.073 | |||
| 0.056 | 0.107 | −0.042 | 0.069 | |||
| 0.061 | 0.137 | 0.051 | 0.086 | |||
| −0.033 | 0.062 | −0.029 | 0.05 | |||
| −0.028 | 0.055 | −0.024 | 0.04 | |||
| −0.054 | 0.341 | −0.045 | 0.246 | |||
| Parameter | Parameter | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bias | SD | Bias | SD | |||
| 0.5 | T = 0.2250 | T = 0.7070 | ||||
| −0.148 | 0.132 | −0.114 | 0.104 | |||
| −0.029 | 0.107 | −0.024 | 0.078 | |||
| −0.036 | 0.116 | −0.031 | 0.083 | |||
| −0.016 | 0.175 | −0.014 | 0.113 | |||
| −0.031 | 0.08 | 0.029 | 0.055 | |||
| 0.021 | 0.055 | 0.022 | 0.039 | |||
| 0.053 | 0.232 | −0.048 | 0.173 | |||
| 1 | T = 0.2966 | T = 1.0153 | ||||
| −0.161 | 0.176 | −0.143 | 0.147 | |||
| −0.032 | 0.120 | −0.028 | 0.083 | |||
| 0.033 | 0.129 | −0.027 | 0.088 | |||
| 0.02 | 0.187 | 0.018 | 0.126 | |||
| −0.037 | 0.066 | −0.034 | 0.048 | |||
| 0.028 | 0.051 | −0.025 | 0.035 | |||
| 0.061 | 0.297 | −0.055 | 0.201 | |||
| 2 | T = 0.3883 | T = 1.2907 | ||||
| 0.173 | 0.194 | −0.161 | 0.172 | |||
| 0.041 | 0.119 | −0.034 | 0.083 | |||
| −0.036 | 0.119 | −0.031 | 0.086 | |||
| 0.025 | 0.184 | 0.022 | 0.138 | |||
| −0.041 | 0.063 | −0.038 | 0.044 | |||
| −0.032 | 0.047 | −0.029 | 0.038 | |||
| −0.068 | 0.293 | −0.060 | 0.232 | |||
| Parameter | Parameter | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bias | SD | Bias | SD | |||
| 0.1 | T = 0.4923 | T = 1.3003 | ||||
| −0.139 | 0.106 | −0.131 | 0.098 | |||
| 0.030 | 0.114 | 0.030 | 0.088 | |||
| 0.035 | 0.084 | 0.024 | 0.064 | |||
| 0.075 | 0.143 | 0.075 | 0.120 | |||
| 0.004 | 0.067 | 0.015 | 0.054 | |||
| −0.104 | 0.084 | −0.112 | 0.066 | |||
| −0.050 | 0.489 | −0.043 | 0.350 | |||
| 0.5 | T = 0.9377 | T = 2.6653 | ||||
| −0.163 | 0.147 | −0.159 | 0.144 | |||
| −0.050 | 0.110 | −0.038 | 0.091 | |||
| −0.049 | 0.076 | −0.026 | 0.062 | |||
| −0.157 | 0.142 | −0.101 | 0.107 | |||
| −0.028 | 0.058 | −0.024 | 0.050 | |||
| −0.155 | 0.071 | −0.151 | 0.054 | |||
| 0.262 | 0.569 | 0.262 | 0.382 | |||
| 1 | T = 1.2817 | T = 3.6046 | ||||
| −0.178 | 0.145 | −0.160 | 0.145 | |||
| −0.072 | 0.109 | −0.064 | 0.088 | |||
| −0.065 | 0.081 | −0.063 | 0.064 | |||
| −0.225 | 0.136 | −0.179 | 0.105 | |||
| −0.072 | 0.060 | −0.050 | 0.046 | |||
| −0.227 | 0.072 | −0.166 | 0.056 | |||
| 0.619 | 0.694 | 0.484 | 0.514 | |||
| Parameter | Est. | SE | p-Value | 95% Bootstrap CI |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 71.56 | 3.50 | [66.97, 75.62] | ||
| −0.735 | 0.180 | [−1.038, −0.473] | ||
| −0.036 | 0.373 | 0.397 | [−0.696, 0.532] | |
| 0.054 | 0.167 | 0.378 | [−0.220, 0.313] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, X.; Xu, J.; Guo, H.; Shi, J.; Zhao, W. An MM Algorithm for the Frailty-Based Illness Death Model with Semi-Competing Risks Data. Mathematics 2022, 10, 3702. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10193702
Huang X, Xu J, Guo H, Shi J, Zhao W. An MM Algorithm for the Frailty-Based Illness Death Model with Semi-Competing Risks Data. Mathematics. 2022; 10(19):3702. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10193702
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Xifen, Jinfeng Xu, Hao Guo, Jianhua Shi, and Wenjie Zhao. 2022. "An MM Algorithm for the Frailty-Based Illness Death Model with Semi-Competing Risks Data" Mathematics 10, no. 19: 3702. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10193702
APA StyleHuang, X., Xu, J., Guo, H., Shi, J., & Zhao, W. (2022). An MM Algorithm for the Frailty-Based Illness Death Model with Semi-Competing Risks Data. Mathematics, 10(19), 3702. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10193702






