RanKer: An AI-Based Employee-Performance Classification Scheme to Rank and Identify Low Performers
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Motivation
1.2. Research Contributions
- A comparative analysis of various existing classification approaches such as RF, ANN, DT, XGBoost, has been conducted with the proposed approach, i.e., RanKer, to address the employee-performance classification problem.
- A novel ensemble-learning approach named RanKer combines with standard classifiers such as RF, ANN, DT, and XGBoost to predict an employee’s performance rating.
- Finally, the proposed model is analyzed for its performance using various AI-based evaluation metrics, such as ROC curve, confusion matrix, precision, recall, F1-score.
2. State-of-the-Art
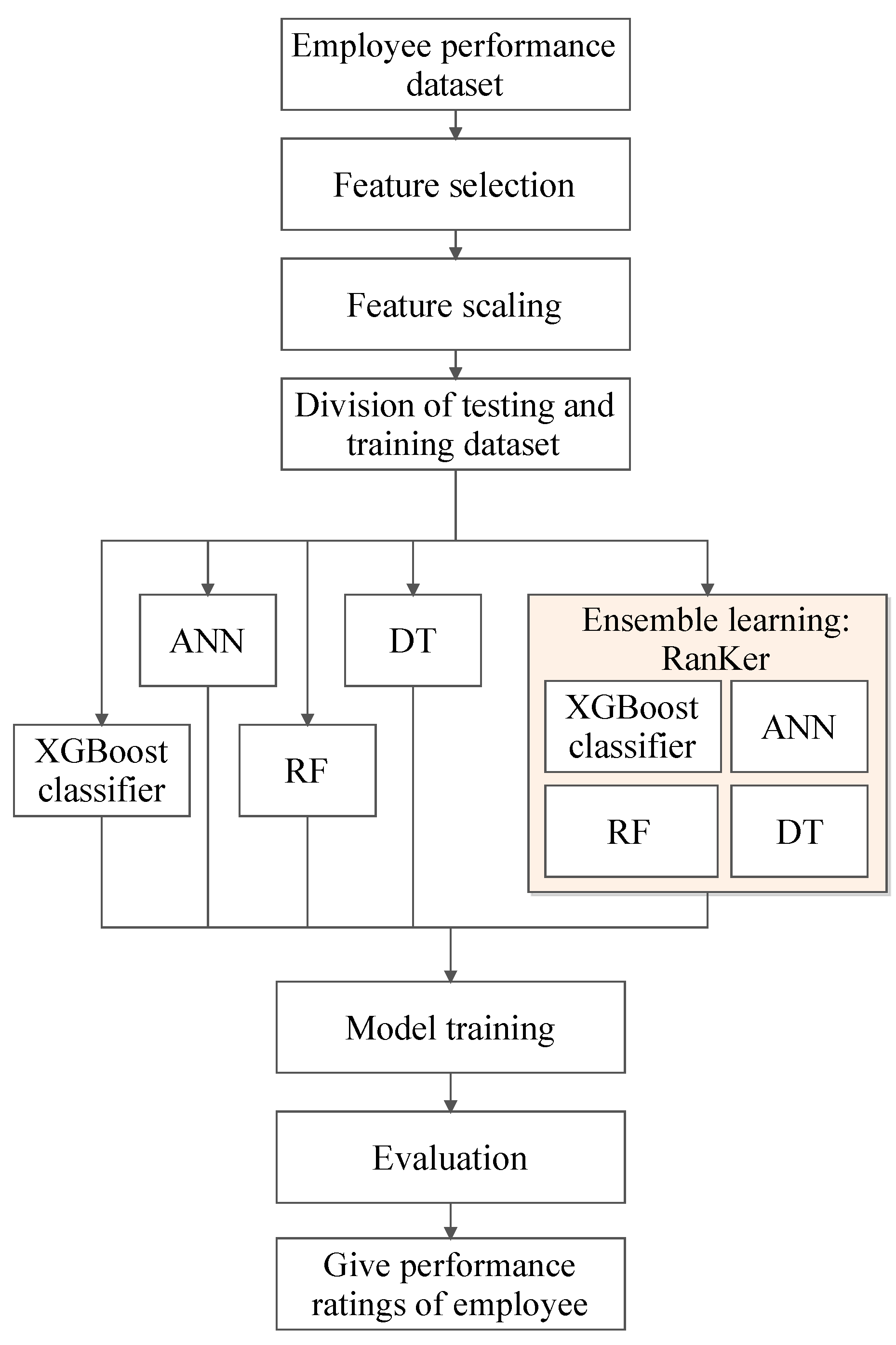
3. Proposed Approach
3.1. System Architecture
3.2. ML Classification Algorithms
3.2.1. Decision Tree (DT)
3.2.2. Random Forest Classifier (RF)
3.2.3. Artificial Neural Networks (ANN)
3.2.4. XGBoost Classifier
| Algorithm 1 XGBoost Classifier |
| Input: X, Employee Performance data. Input: r, Constrained DT Ratio. Input: K, The number of intervals according to feature sets. Output: Performance Rating P, . Procedure: Calculating the degree of coorelation between the features in the data set which divides the feature interval. while i < 100 do using bootstrap to randomly select part of the sample data. if then generation of candidate feature sets According to split node criteria, construction of DT else Random selection process to generate candidate features. Generation of DT with the help of traditional RF algorithm. end if end while Prediction: for to do Predict target for 100 created DT. Consider final prediction of XGBoost Algorithm. end for |
3.3. RanKer: An Ensemble Learning Approach
3.3.1. Ensemble Learning
- Averaging methods: In this method, all the estimators are built differently and predictions of all of them are averaged [31]. This combined estimator is different than any other single estimator. The bagging method is an averaging method and it helps increase the accuracy.
- Boosting methods: Boosting tries to combine the weak models to make a powerful ensemble. This method focuses on the errors made by previous classifiers and tries to minimize these errors as in gradient boosting [32].
3.3.2. Implementation of RanKer Approach
| Algorithm 2RanKer: ensemble-learning approach |
| Input: X, Employee Performance dataset. Input: L, Learning Algorithm Utilized for RanKer. Input: W, Labels of the training dataset utilized. Input: N, Number of L used. Output: Performance Rating P, . Procedure: ⟹ SET 4, i.e., number of L (DT, RF, ANN, and XGBoost learning algorithms). ⟹ SET 3, i.e., classes in the training dataset. for to N do (1) Call L with and stores the classifier . (2) , where was generated from . (3) Update the vote according to the comparison results. (4) Aggregate votes of the to the ensemble approach RanKer. end for Prediction: for to do (1) Predict target for all created for RanKer and voting approach was utilized for finalizing the prediction. (2) Consider final prediction of RanKer as output . end for |
4. Result Analysis of RanKer
4.1. Dataset Description
4.2. Feature Selection
| Listing 1. Mann–Whitney U Test. |
  |
4.3. Feature Scaling
4.4. Evaluation Metrics
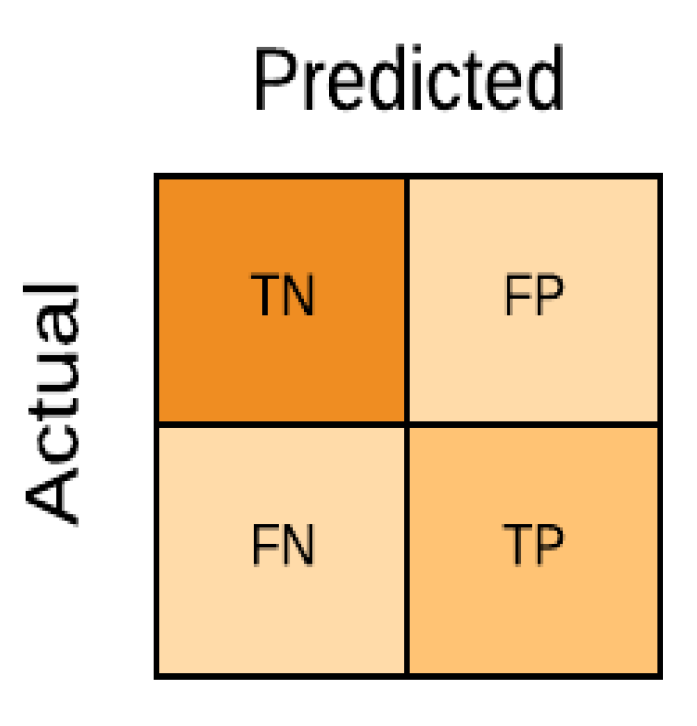
4.4.1. Confusion Matrix
- True positive (TP): this is an outcome metric that aims to correctly predict the positive class, i.e., an employee performing well.
- True negative (TN): this is an outcome metric that aims to correctly predict the negative class, i.e., an employee not performing well.
- False positive (FP): this is an outcome metric that shows the model inaccuracy, i.e., the classifier model inaccurately predicts the positive class (employee performing well).
- False negative (FN): this is an outcome metric that shows the model inaccuracy, i.e., the classifier model inaccurately predicts the negative class (employee not performing well).
4.4.2. Recall
4.4.3. Precision
4.4.4. F1-Score
4.4.5. Regional Operating Characteristic Curve (ROC)
4.4.6. Area Under the Curve (AUC)
4.5. Performance Evaluation of the Ranker
4.5.1. Decision Tree
4.5.2. Random Forest Classifier (RF)
4.5.3. Artificial Neural Network
4.5.4. XGBoost Classifier
4.6. Ensemble Approach: RanKer
4.7. Performance Comparison of RanKer with Other Methods
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lather, A.S.; Malhotra, R.; Saloni, P.; Singh, P.; Mittal, S. Prediction of Employee Performance Using Machine Learning Techniques. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Advanced Information Science and System, Singapore, 15–17 November 2019; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, G.S.; Gupta, A.; Gupta, S. Data Mining for Prediction of Human Performance Capability in the Software-Industry. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1504.01934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasikumar, R.; Alekhya, B.; Harshita, K.; Sree, O.H.; Pravallika, I.K. Employee Performance Evaluation Using Sentiment Analysis. Rev.-Geintec-Gest. Inov. Tecnol. 2021, 11, 2086–2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alduayj, S.S.; Rajpoot, K. Predicting Employee Attrition using Machine Learning. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Innovations in Information Technology (IIT), Al Ain, United Arab Emirates, 18–19 November 2018; pp. 93–98. [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava, D.K.; Nair, P. Employee attrition analysis using predictive techniques. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Information and Communication Technology for Intelligent Systems, Ahmedabad, India, 25–26 March 2017; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 293–300. [Google Scholar]
- Punnoose, R.; Ajit, P. Prediction of Employee Turnover in Organizations using Machine Learning Algorithms. Int. J. Adv. Res. Artif. Intell. 2016, 4, C5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Long, Y.; Fang, M.; He, R.; Wang, T.; Chen, G. Analyzing Employee Turnover Based on Job Skills. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Data Processing and Applications, Guangzhou, China, 12–14 May 2018; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamtar, P.; Jitkongchuen, D.; Pacharawongsakda, E. Multi-Label Classification of Employee Job Performance Prediction by DISC Personality. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Computing and Big Data, Taichung, Taiwan, 18–20 October 2019; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayadi, R.; Firmantyo, H.M.; Dzaka, M.T.J.; Suaidy, M.F.; Putra, A.M. Employee performance prediction using naïve bayes. Int. J. Adv. Trends Comput. Sci. Eng. 2019, 8, 3031–3035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallucchi, F.; Coladangelo, M.; Giuliano, R.; William De Luca, E. Predicting Employee Attrition Using Machine Learning Techniques. Computers 2020, 9, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juvitayapun, T. Employee Turnover Prediction: The impact of employee event features on interpretable machine learning methods. In Proceedings of the 2021 13th International Conference on Knowledge and Smart Technology (KST), Chonburi, Thailand, 21–24 January 2021; pp. 181–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y. Statistical Analysis and Prediction of Employee Turnover Propensity Based on Data Mining. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on Big Data, Information and Computer Network (BDICN), Sanya, China, 20–22 January 2022; pp. 235–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sujatha, P.; Dhivya, R. Ensemble Learning Framework to Predict the Employee Performance. In Proceedings of the 2022 Second International Conference on Power, Control and Computing Technologies (ICPC2T), Raipur, India, 1–3 March 2022; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obiedat, R.; Toubasi, S.A. A Combined Approach for Predicting Employees’ Productivity based on Ensemble Machine Learning Methods. Informatica 2022, 46, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jay, P.; Kalariya, V.; Parmar, P.; Tanwar, S.; Kumar, N.; Alazab, M. Stochastic Neural Networks for Cryptocurrency Price Prediction. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 82804–82818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, C.; Stoffová, V.; Illés, Z.; Tanwar, S.; Kumar, N. Machine Learning-Based Student’s Native Place Identification for Real-Time. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 130840–130854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negnevitsky, M. Artificial Intelligence: A Guide to Intelligent Systems; Pearson Education: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Russell, S.; Norvig, P. Artificial Intelligence: A Modern Approach; Pearson Education: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Shah, H.; Shah, S.; Tanwar, S.; Gupta, R.; Kumar, N. Fusion of AI Techniques to Tackle COVID-19 Pandemic: Models, Incidence Rates, and Future Trends. Multimed. Syst. 2021, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safavian, S.R.; Landgrebe, D. A survey of decision tree classifier methodology. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 1991, 21, 660–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, T.K. Random decision forests. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Document Analysis and Recognition, Montreal, QC, Canada, 14–16 August 1995; Volume 1, pp. 278–282. [Google Scholar]
- Mistry, C.; Thakker, U.; Gupta, R.; Obaidat, M.S.; Tanwar, S.; Kumar, N.; Rodrigues, J.J.P.C. MedBlock: An AI-enabled and Blockchain-driven Medical Healthcare System for COVID-19. In Proceedings of the ICC 2021-IEEE International Conference on Communications, Montreal, QC, Canada, 14–23 June 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, M. Random forest classifier for remote sensing classification. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2005, 26, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random Forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCulloch, W.S.; Pitts, W. A logical calculus of the ideas immanent in nervous activity. Bull. Math. Biophys. 1943, 5, 115–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, K.; Mehta, D.; Mistry, C.; Gupta, R.; Tanwar, S.; Kumar, N.; Alazab, M. Facial Sentiment Analysis Using AI Techniques: State-of-the-Art, Taxonomies, and Challenges. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 90495–90519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.P. Neural networks for classification: A survey. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man, Cybern. Part C Appl. Rev. 2000, 30, 451–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Qian, L.; Mao, B.; Huang, C.; Huang, B.; Si, Y. A Data-Driven Design for Fault Detection of Wind Turbines Using Random Forests and XGboost. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 21020–21031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, J.H. Greedy function approximation: A gradient boosting machine. Ann. Stat. 2001, 29, 1189–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polikar, R. Ensemble learning. In Ensemble Machine Learning; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 1–34. [Google Scholar]
- Dietterich, T.G. Ensemble learning. Handb. Brain Theory Neural Netw. 2002, 2, 110–125. [Google Scholar]
- Sewell, M. Ensemble learning. RN 2008, 11, 1–34. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Yang, Y.; Wang, H.; Chen, D. Soft-Voting Clustering Ensemble. In Proceedings of the Multiple Classifier Systems, Nanjing, China, 15–17 May 2013; Zhou, Z.H., Roli, F., Kittler, J., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 307–318. [Google Scholar]
- Juszczak, P.; Tax, D.; Duin, R.P. Feature scaling in support vector data description. In Proceedings of the Proc. ASCI, Lochem, NL, USA, 19–21 June 2002; Citeseer: University Park, PA, USA, 2002; pp. 95–102. [Google Scholar]
- Gareth, J.; Daniela, W.; Trevor, H.; Robert, T. An Introduction to Statistical Learning: With Applications in R; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Muhammad, Y.; Alshehri, M.; Alenazy, W.; Hoang, T.; Alturki, R. Identification of Pneumonia Disease Applying an Intelligent Computational Framework Based on Deep Learning and Machine Learning Techniques. Mob. Inf. Syst. 2021, 2021, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahir, M.; Khan, F.; Hayat, M.; Alshehri, M. An effective machine learning-based model for the prediction of protein–protein interaction sites in health systems. Neural Comput. Appl. 2022, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Author | Year | Approach | Results | Key Contributions | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ajit et al. [6] | 2016 | XGBoost Classifier | 86% (AUC) | Utilized XGBoost Classifier for predicting performance turnover of employees and concluded that XGBoost classifier is a superior algorithm for predicting turnover | They have not considered the scalability. |
| Liu et al. [7] | 2018 | RF, SVM, LR and AdaBoost | 86.3% (Accuracy) | Various AI-based prediction models are used to forecast staff turnover. Results show that expertise is the most influencing factor while predicting. | The proposed approach only focuses on one organization; they have not considered employee datasets from different organizations |
| Lather et al. [1] | 2019 | RF, SVM, ANN, LR and NB | 85.3% (Accuracy) | Proposed a system after conducting standard tests for better prediction of employee performance and performed various ML algorithms for the same. | They have not considered feature’s correlation matrix. |
| Kamtar et al. [8] | 2019 | SVM, KNN, RF, DT, NB, Cascading Classifier and LR | 90% (Recall) 80% (Precision) | Applied ML algorithms for employee performance prediction using DISC personality.Performance of Employee was predicted with the help of ensemble model. | They have not performed any statistical tests for the verification of their results. |
| Jayadi et al. [9] | 2019 | NB | 95.48% (Accuracy) | Authors implemented NB for dataset of 310 employees and obtained significant results. | Not compared the results with other ML-algorithms. |
| Fallucchi et al. [10] | 2020 | Gaussian Naive Bayes, NB, LR, KNN, DT, SVM, Linear SVM | 54.1 % (Recall) | Utilised various ML techniques to predict employee attrition. Models were trained and tested on a standard real-time dataset (given by IBM). | Adopted traditional ML algorithms; did not propose a novel approach. |
| Juvitayapun et al. [11] | 2021 | LR, RF, gradient boosting tree, extreme gradient boosting tree | 98.03% (accuracy), 97.18% (precision), 90.79% (F1-score), and 85.19% (recall) | Extreme gradient-boosting algorithm gives best results that detect worker’s likelihood to leave an organization. | They have not discussed statistical tests. |
| Duan et al. [12] | 2022 | LR and XGBoost | 98.17% (accuracy) | They involved Ml classifiers that predict employees’ tendency to leave enterprises. | No discussion on different performance evaluation metrics such as precision, recall, F1-score. |
| Sujatha et al. [13] | 2022 | XGBoost and gradient boosting | 92.20% (accuracy) | The proposed scheme predicts employee performance in an MNC company. | They have performed statistical test and not calculated a correlation matrix. |
| Obiedat et al. [14] | 2022 | J48, RF, RBF, MLP, NB, and SVM | 98.3% (Accuracy) | The proposed scheme predicts the productivity performance of garment workers. | They have not performed statistical tests. |
| Proposed approach RanKer | 2022 | Ensemble Learning (DT, RF, ANN, XGBoost) | 96.25% (Accuracy) | Proposed an ensemble-learning approach for employee performance classification based on ratings by combining individual approaches such as DT, ANN, RF and XGBoost. | - |
| Sr No. | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Not included Features | ||
| 1 | EmpNumber | Unique id for every employee |
| 2 | Gender | (Male = 1, Female = 0) |
| 3 | Education Background | (Human Resources = 0, Life Sciences = 1, Marketing = 2, Medical = 3, Techincal Degree = 4, Other = 5) |
| 4 | MaritalStatus | (Divorced = 0, Married = 1, Single = 2) |
| 5 | BusinessTravelFrequency | (Non-Travel = 0, Travel_Frequently = 1, Travel_Rarely = 2) |
| 6 | EmpEducationLevel | (Below College = 1, College = 2, Bachelor = 3, Master = 4, Doctor = 5) Employee education level from 1 to 5 |
| 7 | EmpJobInvolvement | (Very Low = 1, Low = 2, Medium = 3, High = 4, Very High = 5) Employee involvement level in job |
| 8 | EmpJobLevel | Employee job level in the current company |
| 9 | EmpJobSatisfaction | (Very Low = 1, Low = 2, Medium = 3, High = 4, Very High = 5) Employee job satisfaction |
| 10 | NumCompaniesWorked | Total number of companies employee has worked in |
| 11 | OverTime | NO = 0—not doing overtime YES = 1 Doing overtime |
| 12 | EmpRelationshipSatisfaction | (Very Low = 1, Low = 2, Medium = 3, High = 4, Very High = 5) Employee Relationship satisfaction |
| 13 | TotalWorkExperienceInYears | Total years of experience employee has |
| 14 | TrainingTimesLastYear | Number of times employee has completed training |
| 15 | ExperienceYearsInCurrentRole | Number of years in the current role |
| 16 | YearsSinceLastPromotion | Number of years since employee got last promotion |
| 17 | YearsWithCurrManager | Number of years the employee worked under the current manager |
| 18 | Attrition | (No = 0, Yes = 1) |
| Included Features | ||
| 1 | EmpDepartment | (Data Science = 0, Development = 1, Finance = 2, Human Resources = 3, Research & Development = 4, Sales = 5) |
| 2 | EmpJobRole | (Business Analyst = 0, Data Scientist = 1, Delivery Manager = 2, Developer = 3, Finance Manager = 4, Healthcare Representative = 5, Human Resources = 6, Laboratory Technician = 7, Manager = 8, Manager = 9 R&D, Manufacturing Director = 10, Research Director = 11, Research Scientist = 12, Sales Executive = 13, Sales Representative = 14, Senior Developer = 15, Senior Manager = 16 R&D, Technical Architect = 17, Technical Lead = 18) |
| 3 | DistanceFromHome | Distance from home to work |
| 4 | EmpLastSalaryHikePercent | Last percentage increase in salary (in %) |
| 5 | EmpWorkLifeBalance | Time spent by the employee between work and outside |
| 6 | EmpHourlyRate | Number of hours per week employee is working |
| 7 | ExperienceYearsAtThisCompany | Total number of years completed working at the company. |
| 8 | Age | Age of an employee = N |
| 9 | EmpEnvironmentSatisfaction | (Very Low = 1, Low = 2, Medium = 3, High = 4, Very High = 5) Employee environment satisfaction |
| 10 | Performance Rating | (Low = 1, Good = 2, Better = 3, Excellent = 4, Outstanding = 5) Employee performance in the company |
| Classifier | Classes | Precision | Recall | F1-Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Decision Tree | 0 | 71% | 82% | 76% |
| 1 | 95% | 94% | 94% | |
| 2 | 96% | 86% | 91% | |
| Random Forest | 0 | 94% | 94% | 94% |
| 1 | 98% | 98% | 98% | |
| 2 | 92% | 86% | 89% | |
| ANN | 0 | 71% | 76% | 74% |
| 1 | 93% | 93% | 93% | |
| 2 | 75% | 75% | 75% | |
| XGBoost | 0 | 91% | 97% | 94% |
| 1 | 98% | 98% | 98% | |
| 2 | 96% | 86% | 91% | |
| Ranker | 0 | 91% | 97% | 94% |
| 1 | 98% | 97% | 97% | |
| 2 | 93% | 89% | 91% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Patel, K.; Sheth, K.; Mehta, D.; Tanwar, S.; Florea, B.C.; Taralunga, D.D.; Altameem, A.; Altameem, T.; Sharma, R. RanKer: An AI-Based Employee-Performance Classification Scheme to Rank and Identify Low Performers. Mathematics 2022, 10, 3714. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10193714
Patel K, Sheth K, Mehta D, Tanwar S, Florea BC, Taralunga DD, Altameem A, Altameem T, Sharma R. RanKer: An AI-Based Employee-Performance Classification Scheme to Rank and Identify Low Performers. Mathematics. 2022; 10(19):3714. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10193714
Chicago/Turabian StylePatel, Keyur, Karan Sheth, Dev Mehta, Sudeep Tanwar, Bogdan Cristian Florea, Dragos Daniel Taralunga, Ahmed Altameem, Torki Altameem, and Ravi Sharma. 2022. "RanKer: An AI-Based Employee-Performance Classification Scheme to Rank and Identify Low Performers" Mathematics 10, no. 19: 3714. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10193714
APA StylePatel, K., Sheth, K., Mehta, D., Tanwar, S., Florea, B. C., Taralunga, D. D., Altameem, A., Altameem, T., & Sharma, R. (2022). RanKer: An AI-Based Employee-Performance Classification Scheme to Rank and Identify Low Performers. Mathematics, 10(19), 3714. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10193714









