Abstract
In this paper, we study the regularized Huber regression algorithm in a reproducing kernel Hilbert space (RKHS), which is applicable to both fully supervised and semi-supervised learning schemes. Our focus in the work is two-fold: first, we provide the convergence properties of the algorithm with fully supervised data. We establish optimal convergence rates in the minimax sense when the regression function lies in RKHSs. Second, we improve the learning performance of the Huber regression algorithm by a semi-supervised method. We show that, with sufficient unlabeled data, the minimax optimal rates can be retained if the regression function is out of RKHSs.
Keywords:
robust regression; Huber loss function; reproducing kernel Hilbert space; semi-supervised data MSC:
62J02
1. Introduction
The ordinary least squares (OLS) is an important statistical tool applied in regression analysis. However, OLS does not perform well when the data are contaminated by the occurrence of outliers or heavy-tailed noise. Thus, OLS is suboptimal in the robust regression analysis and a variety of robust loss functions have been developed that are not so easily affected by noises. Among them, Huber loss function is usually a popular choice in the fields of statistics, machine learning and optimization since it is less sensitive to outliers and can address the issue of heavy-tailed errors effectively. Huber regression was initiated by Peter Huber in his seminal work [1,2]. Statistical bounds and convergence properties for Huber estimation and inference have been further investigated in the subsequent works. See, e.g., [3,4,5,6,7,8,9].
Semi-supervised learning has been gaining increased attention as an active research area in the fields of science and engineering. The original idea of semi-supervised method can date back to self-learning in the context of classification [10] and then is well developed in decision-directed learning, co-training in text classification, and manifold learning [11,12,13]. Most existing research on Huber regression work is in the supervised framework. Unlabeled data had been deemed useless and thus thrown away in the design of algorithms. Recently, it has been shown in vast literature that utilizing the additional information in unlabeled data can effectively improve the learning performance of algorithms. See, e.g., [14,15,16,17,18]. In this paper, we focus on the Huber regression algorithm performance with unlabeled data. By the semi-supervised method, we find that optimal learning rates are available if sufficient unlabeled data are added in the Huber regression analysis.
In the standard framework of statistical learning, we let the explanatory variable X take values in a compact domain in a Euclidean space, and the response variable Y takes values in the output space This work investigates the application of the Huber loss that is linked to the following regression model:
where is the regression function and is the noise in the regression model. Let be a Borel probability measure on the product space . Let and and denote the marginal distribution of on , and the conditional distribution on given , respectively. In the supervised learning setting, is assumed to be unknown and the purpose of regression is to estimate according to a sample drawn independently from , where N is the sample size, the cardinality of D. The Huber loss function is defined as
where is a robustification parameter. Given the prediction function , Huber regression searches for a good approximation of by minimizing the empirical prediction error with the Huber loss
over a suitable hypothesis space.
In this work, we study the kernel based Huber regression algorithm and the minimization of (1) performs in a reproducing kernel Hilbert space (RKHS) [19]. Recall that is a Mercer kernel if it is continuous, symmetric, and positive semidefinite. The RKHS is the completion of the linear span of the function set with the inner product induced by . The reproducing property is given by . Note that, by Cauchy–Schwarz inequality and [19],
To avoid overfitting, the regularized Huber regression algorithm in the RKHS is given as
where is a regularization parameter.
In this paper, we derive the explicit learning rate of Algorithm (2) in the supervised learning, which is comparable to the minimax optimal rate of OLS. By a semi-supervised method, we show that utilizing unlabeled data can conquer the bottleneck that optimal learning rates for algorithm (2) are only achievable when lies in
2. Assumptions and Main Results
To present our main results, we introduce some necessary assumptions. In this section, we study the convergence of to in the square integrable space (, ).
Below, we elaborate on three important assumptions to carry out the analysis. The first assumption (3) is about the regularity of the regression function Define the integral operator associated with the kernel K by
Since K is a Mercer kernel on the compact domain , is compact and positive. Thus, as the r-th power of for is well defined [20]. Our error bounds are stated in terms of the regularity of , given by
The condition (3) characterizes the regularity of and is directly related to the smoothness of when is a Sobolev space. If (3) holds with , lies in the space [21].
The second assumption (4) is about the capacity of , measured by the effective dimension [22,23,24]
where I is the identity operator on . In this paper, we assume that
This condition measures the complexity of with respect to the marginal distribution It is typical in the analysis of the performances of kernel methods’ estimators. It is always satisfied with by taking the constant When is a Sobolev space with all derivatives of an order up to then (4) is satisfied with [25]. When , (4) is weaker than the eigenvalue decaying assumption in the literature [17,23].
The third assumption is about the conditional probability distribution on the output space . We assume that the output variable Y satisfies the moment condition when there exist two positive numbers such that, for any integer ,
The assumption (5) covers many common distributions, for example, Gaussian, sub-Gaussian, and the distributions with compact support [26].
Now, we are ready to present the main results of this paper. Without loss of generality, we assume
2.1. Convergence in the Supervised Learning
The following error estimate for Algorithm (2) is the first result of this section, which presents the convergence of Huber regression with fully supervised data and will be proved in Section 3.
Theorem 1.
The above theorem shows that the parameter in the Huber loss balances the robustness of Algorithm (2) and its convergence rates. We can see that, when the Huber loss function is employed in nonparametric regression problems, the enhancement of robustness occurs with the sacrifice of the convergence rate of Algorithm (2). Thus, what one needs to do is to find a trade-off. It is then direct to obtain the following corollary that provides the explicit learning rates for (2) with a suitable choice of .
Corollary 1.
Under the same conditions of Theorem 1, if , then with probability at least ,
Remark 1.
The above corollary tells us that, when Algorithm (2) achieves the error rate , which coincides with the minimax lower bound proved in [23,25], and is optimal. We also notice that the convergence rate can not improve when . It is referred to as the saturation phenomenon, which has been found in a vast amount of literature [20,22,25].
2.2. Convergence in the Semi-Supervised Learning
Although optimal convergence rates of the Algorithm (2) were deduced when lies in () in the previous subsection, the error rate for the case needs improvements. In this subsection, we study the influence of unlabeled data on the convergence of (2) by using semi-supervised data.
Let an unlabeled data set be drawn independently according to the marginal distribution , where is the cardinality of . With the fully supervised data set , we then introduce the supervised data set associated with Huber regression problems as , given by
By replacing D with in Algorithm (2), we then obtain the output function with semi-supervised data . The enhanced convergence results are as follows.
Theorem 2.
Based on the theorem above, we can obtain the improved convergence rate as follows.
Corollary 2.
Under the same conditions of Theorem 2, if
then, with probability ,
Remark 2.
Corollary 1 shows that, provided no unlabeled data are involved, the minimax optimal convergence rate for (2) is obtained only in the situation . When , the rate reduces to . It implies that the regression function is assumed to belong to for achieving the optimal rate, which is difficult to verify in practice. In contrast, Corollary 2 tells us that, with sufficient unlabeled data engaged in Algorithm (2), the minimax optimal rate is retained for This removes the strict regularity condition on
3. Proofs
Now, we are in a position of proving results stated in Section 2.
3.1. Useful Estimates
First, we will estimate the bound of defined by (2). In the sequel, for notational simplicity, let and define the empirical operator by
so, for any , . Then, we have the following representation for .
Lemma 1.
Proof.
Note that . Since is the minimizer of Algorithm (2), we take the gradient of the regularized functional on to give
With the fact , it yields
which is .
The proof is complete. □
Based on the above lemma, we can obtain the bound of
Lemma 2.
Under the moment condition (5), with a probability at least , there holds
Proof.
Under the moment condition (5), it has been proven in [27] that, with a probability of at least , there holds
By the definition of , we have that . Thus,
It follows that
This together with (15) yields the desired conclusion. □
Furthermore, we see that
3.2. Error Decomposition
To derive the explicit convergence rate of Algorithm (2), we introduce the regularization function in , defined by
where is the expected risk associated with the least squares loss. It is direct to verify that
so . By the work in [20], we know that under the regularity assumption (3) with ,
and
Now, we state two error decompositions for . By (19), we have
In the sequel, we denote
Noting that, for any ,
by the fact [21], one obtains a bound for the sample error by the decomposition (23) above.
Proposition 1.
Define by (2). Then, there holds
3.3. Deriving Main Results
To prove our main results, we need to bound the quantities by the following probability estimates.
Lemma 3.
With a confidence of at least there holds
where
These inequalities are well studied in the literature and can be found in [17,18].
Proof of Theorem 1.
We can decompose as the sample error and the approximation error . As stated in (20), for . Thus, we just estimate by Proposition 1.
By Lemma 3 and the bound (18), with probability at least , the following bounds hold simultaneously:
and
Scaling to by (20) and the estimates above, we have with confidence at least
By (4),
Collecting the above estimates,
and
The proof is complete. □
Proof of Theorem 2.
Similar as the proof of (25), there holds
Note that, by (9),
It means Furthermore, similar to (16), we have
In addition, by (17),
Then, by (15), with confidence at least
This together with Lemma 3 yields that, with a confidence of at least
and
Thus, to prove Theorem 2, we need the estimates as follows:
Since and ,
Thus,
Furthermore, by (21),
By the restriction , we conclude that
The proof is finished. □
4. Numerical Simulation
In this part, we carry out simulations to verify our theoretical statements. We employ the mean squared error of a testing set for the comparison. We generate labeled data by the regression model , where , and the random inputs ’s are independently drawn according to the Normal distribution , and is the independent Gaussian noise . We also generate unlabeled data with ’s drawn independently according to the uniform distribution on . We choose the Gaussian kernel , and regularization parameter . Algorithm 1 shows the mean squared error of Algorithm (1) with the training data set Algorithm 2 shows the mean squared error of Algorithm (2) with the semi-supervised data set by (9). Algorithm (2)’ s error is obviously smaller than Algorithm (1) if 20 unlabeled data are added into the training data. When we add more unlabeled data from 20 to 200, Algorithm (2)’ s curve decreases continuously. These experimental results coincide with our theoretical analysis through the following Figure 1.
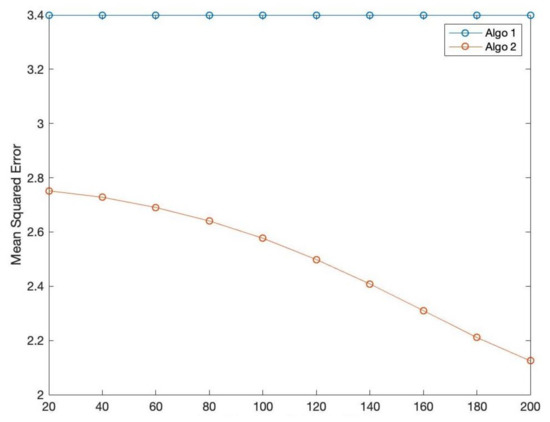
Figure 1.
The number of unlabeled data.
5. Discussion
Unlabeled data are ubiquitous in a variety of fields including signal processing, privacy concerns, feature selection, and data clustering. For the applications of Huber regression that have robustness, we adopted a semi-supervised learning method to our regularized Huber regression algorithm. We derived the explicit learning rate of algorithm (2) in the supervised learning, which was comparable to the minimax optimal rate of OLS. By a semi-supervised method, we showed that an inflation of unlabeled data could improve learning performance for Huber regression analysis. It suggested that using the additional information of unlabeled data could extend the application of Huber regression.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.W.; Funding acquisition, C.P.; Methodology, B.W. and X.L.; Project administration, B.W.; Resources, X.L.; Supervision, C.P. and H.Y.; Writing—original draft, Y.W.; Writing—review & editing, H.Y. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The work described in this paper is partially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Project 12071356).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Huber, P.J. Robust Estimation of a Location Parameter. Ann. Math. Stat. 1964, 35, 73–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, P.J. Robust Regression: Asymptotics, Conjectures and Monte Carlo. Ann. Stat. 1973, 1, 799–821. [Google Scholar]
- Christmann, A.; Steinwart, I. Consistency and robustness of kernel based regression. Bernoulli 2007, 13, 799–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Li, Q.; Wang, Y. Estimation of high dimensional mean regression in the absence of symmetry and light tail assumptions. J. R. Stat. Soc. 2017, 79, 247–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Wu, Q. A statistical learning assessment of Huber regression. J. Approx. Theory 2022, 273, 105660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loh, P.L. Statistical consistency and asymptotic normality for high-dimensional robust M-estimators. Statistics 2015, 45, 866–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, B. Asymptotic behavior of M-estimators for the linear model with dependent errors. Bull. Inst. Math. Acad. Sin. 1981, 9, 367–375. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Q.; Zhou, W.; Fan, J. Adaptive Huber Regression. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 2017, 115, 254–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, H.; Zhang, T. Optimal computational and statistical rates of convergence for sparse nonconvex learning problems. Ann. Stat. 2013, 42, 2164–2201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapelle, O.; Schölkopf, B.; Zien, A. Semi-Supervised Learning; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Belkin, M.; Niyogi, P. Semi-Supervised Learning on Riemannian Manifolds. Mach. Learn. 2004, 56, 209–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blum, A.; Mitchell, T. Combining Labeled and Unlabeled Data with Co-Training. In Proceedings of the 11th Annual Conference on Computational Learning Theory, Madison, WI, USA, 24–26 July 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Jebara, T.; Chang, S.F. Semi-Supervised Learning Using Greedy Max-Cut. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2013, 14, 771–800. [Google Scholar]
- Andrea Caponnetto, Y.Y. Cross-validation based adaptation for regularization operators in learning theory. Anal. Appl. 2010, 8, 161–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Hu, T.; Wu, Q. Distributed Minimum Error Entropy Algorithms. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2020, 21, 1–31. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, T.; Fan, J.; Xiang, D.H. Convergence Analysis of Distributed Multi-Penalty Regularized Pairwise Learning. Anal. Appl. 2019, 18, 109–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.B.; Guo, X.; Zhou, D.X. Distributed Learning with Regularized Least Squares. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2016, 18, 3202–3232. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, S.B.; Zhou, D.X. Distributed Kernel-Based Gradient Descent Algorithms. Constr. Approx. 2018, 47, 249–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aronszajn, N. Theory of reproducing kernels. Trans. Am. Math. Soc. 1950, 686, 337–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smale, S.; Zhou, D.X. Learning Theory Estimates via Integral Operators and Their Approximations. Constr. Approx. 2007, 26, 153–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cucker, F.; Ding, X.Z. Learning Theory: An Approximation Theory Viewpoint; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Bauer, F.; Pereverzev, S.; Rosasco, L. On regularization algorithms in learning theory. J. Complex. 2007, 23, 52–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caponnetto, A.; Vito, E.D. Optimal Rates for the Regularized Least-Squares Algorithm. Found. Comput. Math. 2007, 7, 331–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Z. Effective Dimension and Generalization of Kernel Learning. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 15, NIPS 2002, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 9–14 December 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Neeman, M.J. Regularization in kernel learning. Ann. Stat. 2010, 38, 526–565. [Google Scholar]
- Raskutti, G.; Wainwright, M.J.; Yu, B. Early stopping and non-parametric regression. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2014, 15, 335–366. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Hu, T. Online minimum error entropy algorithm with unbounded sampling. Anal. Appl. 2019, 17, 293–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).