Utilization of Improved Machine Learning Method Based on Artificial Hummingbird Algorithm to Predict the Tribological Behavior of Cu-Al2O3 Nanocomposites Synthesized by In Situ Method
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experiments
- Cu (NO3)2. 3H2O and Al (NO3)3. 9H2O were dissolved in water using a magnetic stirrer at 70 °C for 30 min. The salt concentrations were chosen to produce a Cu-Al2O3 nanocomposite system with 2.5, 7.5, and 12.5 wt.% Al2O3.
- To obtain nitrate salt powder precursor particles, dry spraying was performed with a sprayer at 180 °C. Copper oxide (CuO) and aluminum oxide (Al2O3) phases were obtained by oxidation of the powder at 850 °C for 1 h in an air atmosphere.
- The powders were reduced in hydrogen for 30 min at 500 °C, resulting in copper oxide being reduced to its metallic state and Al2O3 remaining as the scattered ceramic phase.
3. Machine Learning Models
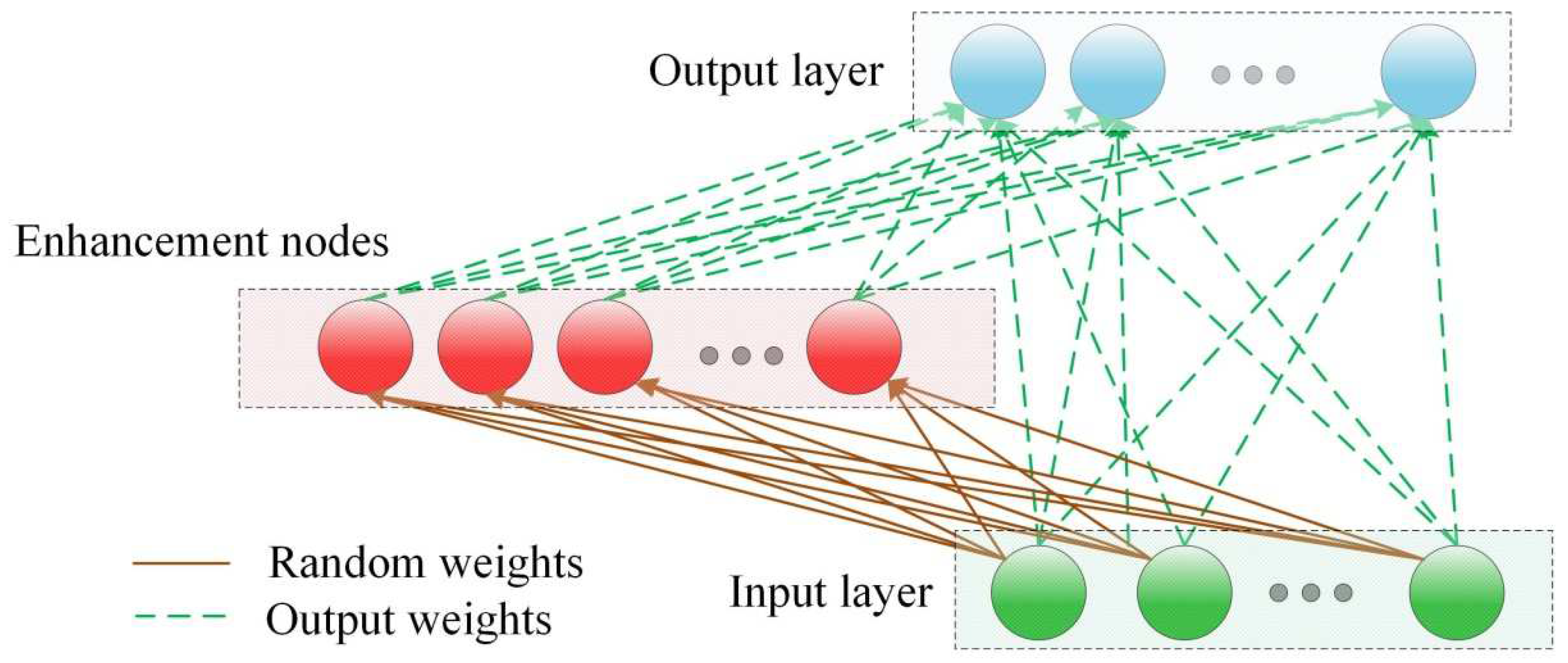
3.1. Random Vector Functional Link
3.2. Artificial Hummingbird Algorithm (AHA)
3.2.1. Guided Foraging
3.2.2. Territorial Foraging
3.2.3. Migration Foraging
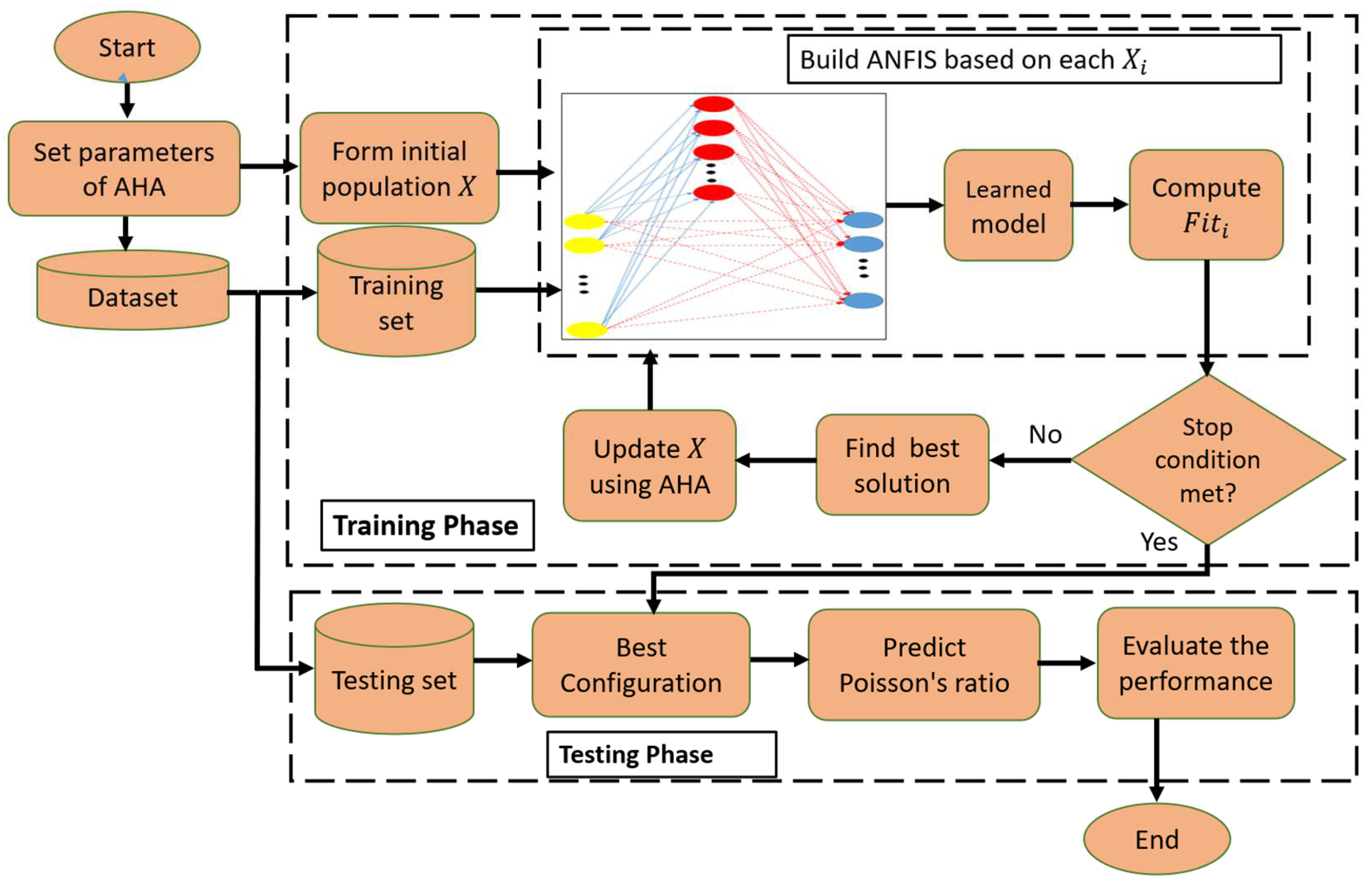
3.3. Proposed Model
4. Results and Discussion
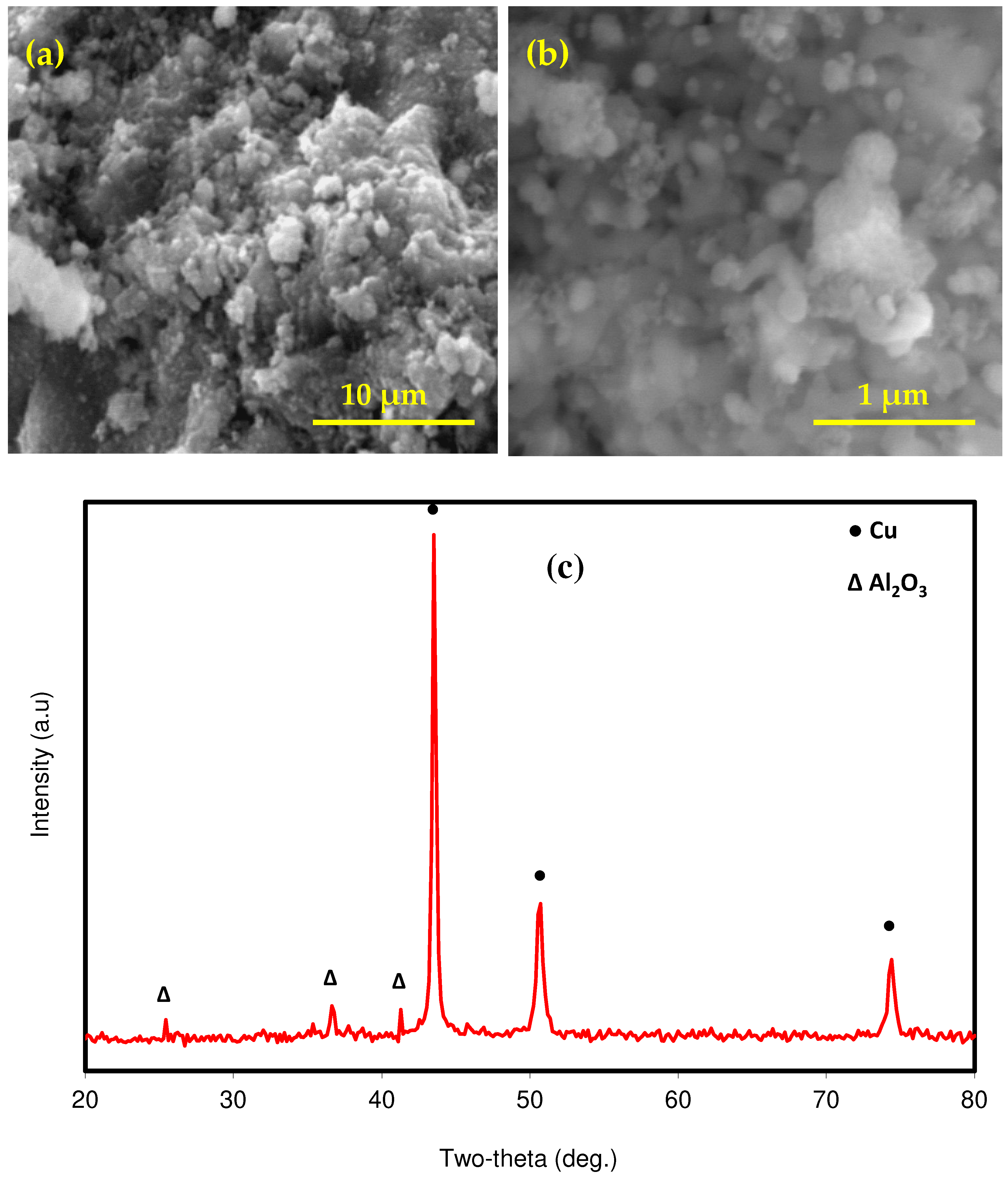
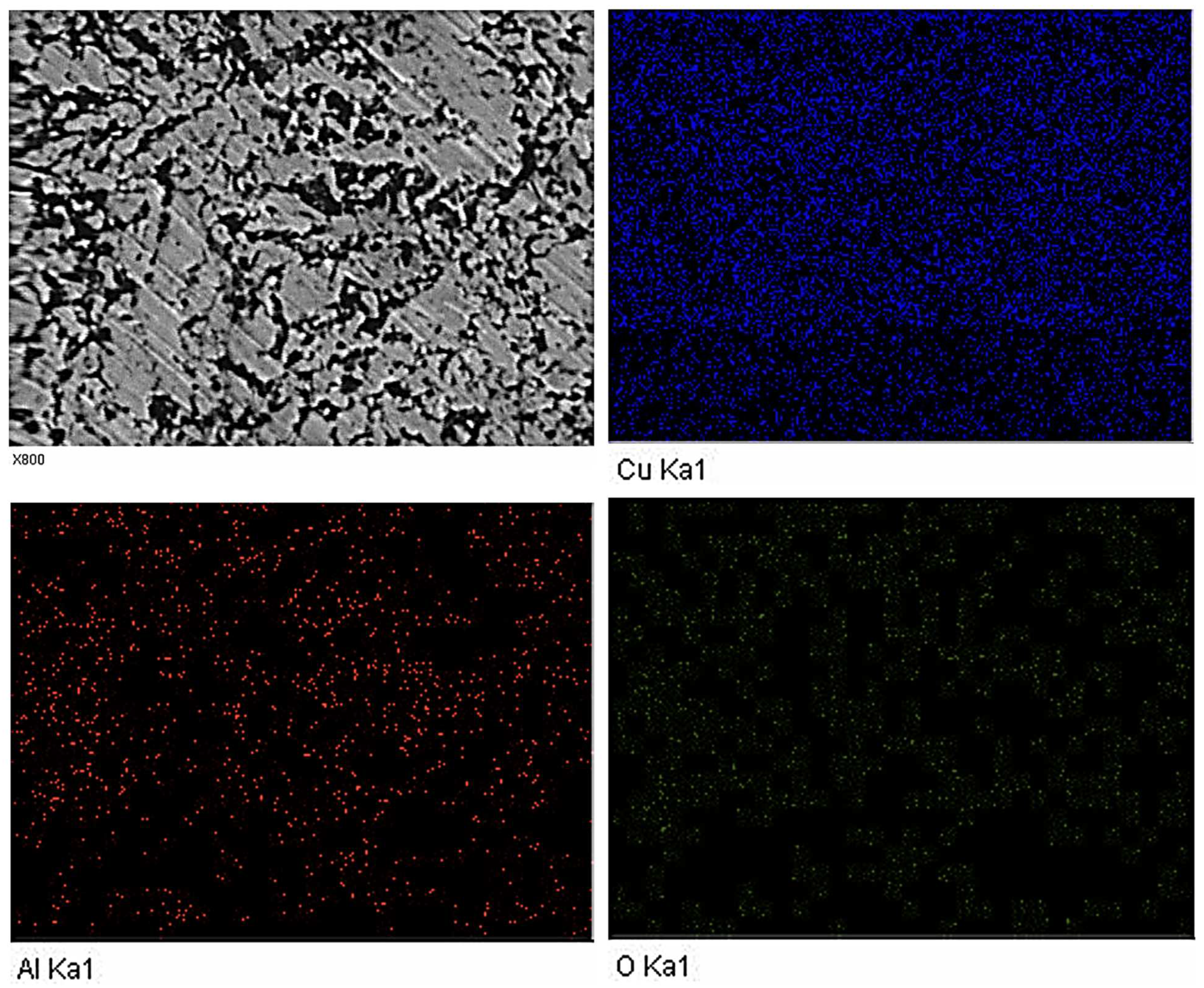
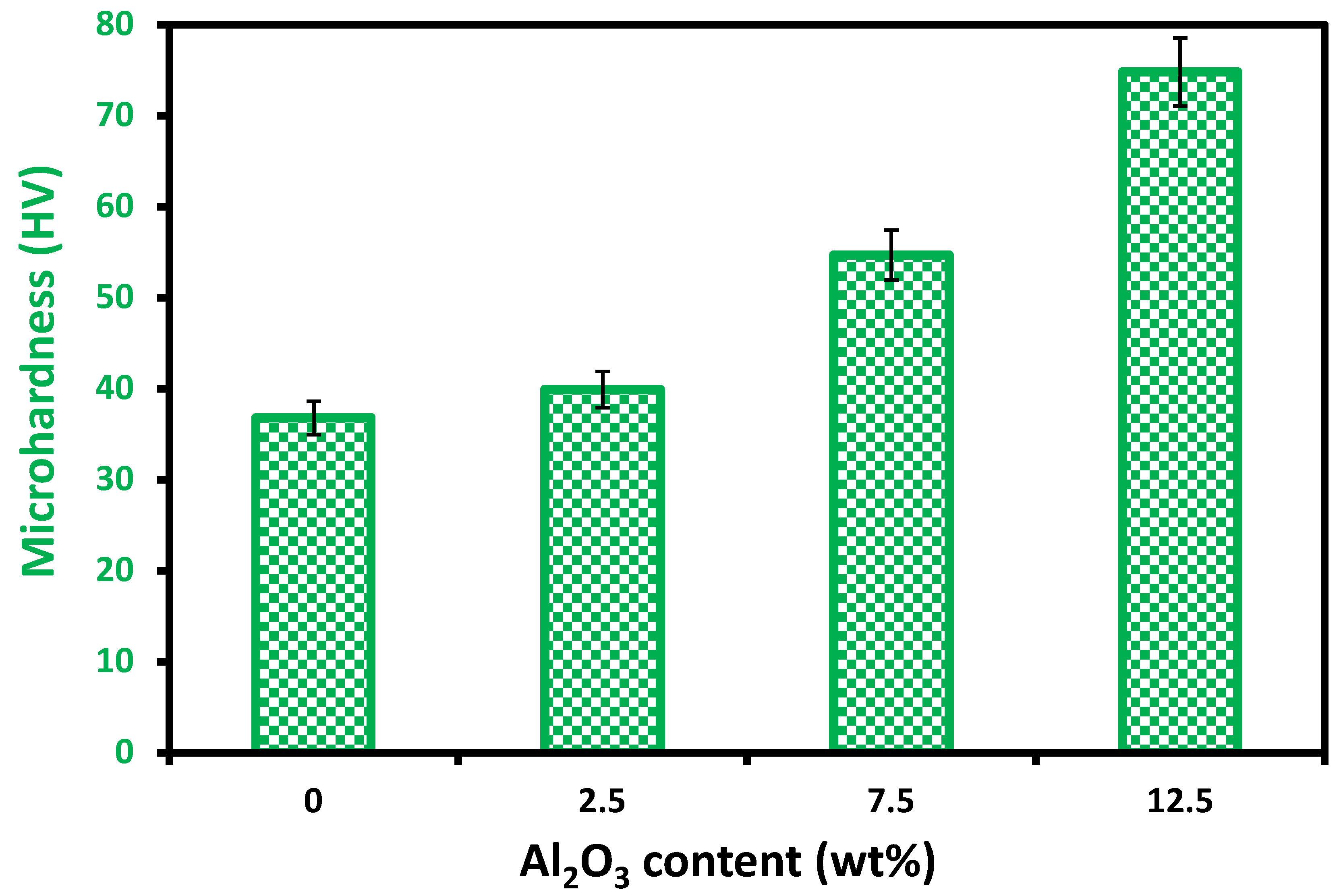
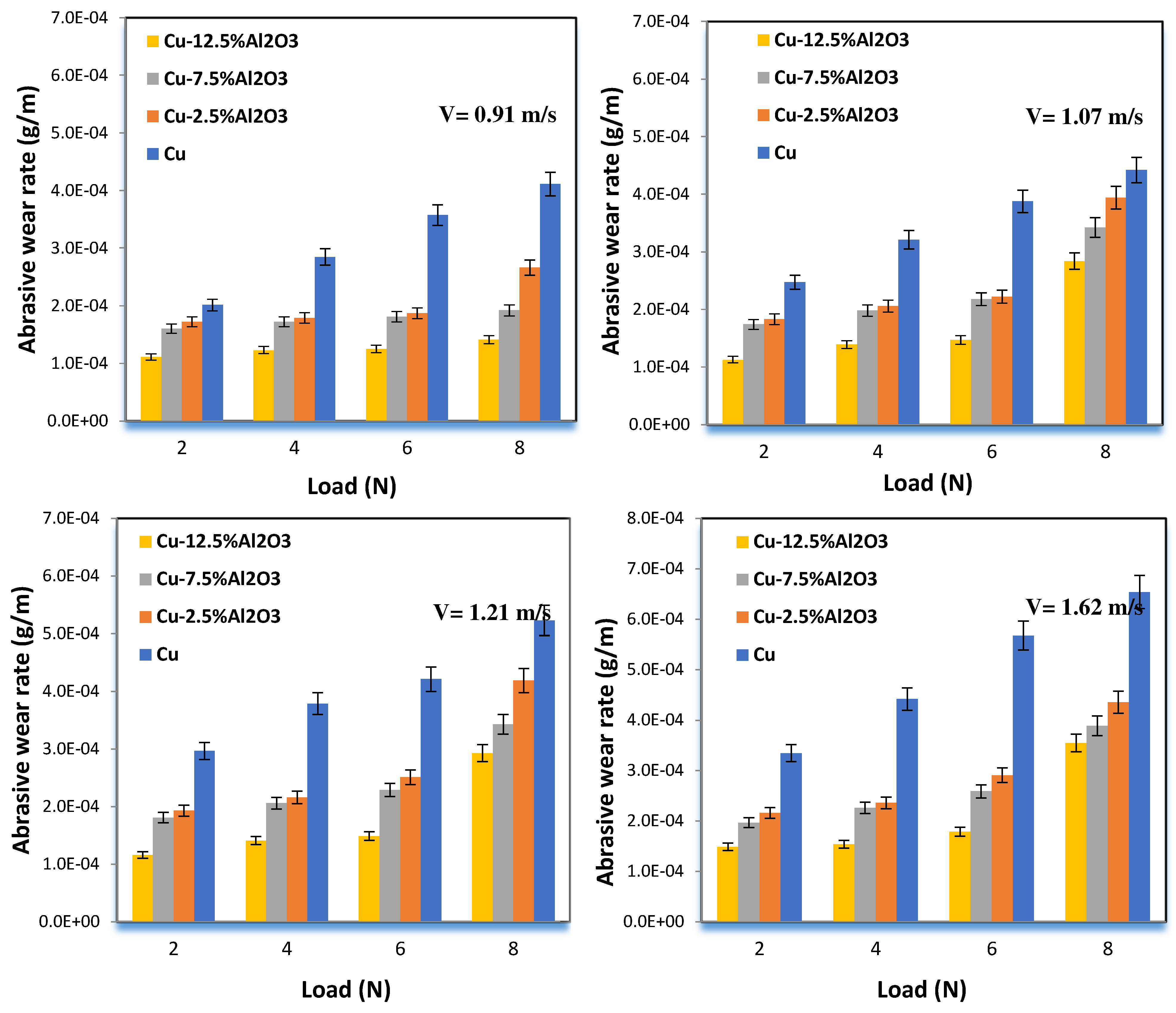
4.1. Structural and Tribological Properties
4.2. Prediction of Wear Rates Using the Improved RVFL Model
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rajkovic, V.; Bozic, D.; Jovanovic, M.T. Effects of copper and Al2O3 particles on characteristics of Cu–Al2O3 composites. Mater. Des. 2010, 31, 1962–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casati, R.; Vedani, M. Metal Matrix Composites Reinforced by Nano-Particles—A Review. Metals 2014, 4, 65–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagih, A.; Fathy, A.; Sebaey, T.A. Experimental investigation on the compressibility of Al/Al2O3 nanocomposites. Int. J. Mater. Prod. Technol. 2016, 52, 312–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tjong, S.C.; Lau, K.C. Tribological behaviour of SiC particle-reinforced copper matrix composites. Mater. Lett. 2000, 43, 274–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadoun, A.M.; Abd El-Wadoud, F.; Fathy, A.; Kabeel, A.M.; Megahed, A.A. Effect of through-the-thickness position of aluminum wire mesh on the mechanical properties of GFRP/Al hybrid composites. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 15, 500–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vettivel, S.; Selvakumar, N.; Leema, N.; Lenin, A. Electrical resistivity, wear map and modeling of extruded tungsten reinforced copper composite. J. Mater. Des. 2014, 56, 791–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadoun, A.M.; Meselhy, A.F.; Deabs, A.W. Improved strength and ductility of friction stir tailor-welded blanks of base metal AA2024 reinforced with interlayer strip of AA7075. Results Phys. 2020, 16, 102911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaat, M.; Fathy, A.; Wagih, A. Correlation between grain boundary evolution and mechanical properties of ultrafine-grained metals. Mech. Mater. 2020, 143, 103321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadoun, A.M.; Wagih, A.; Fathy, A.; Essa, A.R.S. Effect of tool pin side area ratio on temperature distribution in friction stir welding. Results Phys. 2019, 15, 102814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varol, T.; Canakci, A. Microstructure, electrical conductivity and hardness of multilayer graphene/Copper nanocomposites synthesized by flake powder metallurgy. Met. Mater. Int. 2015, 21, 704–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samal, C.; Parihar, J.; Chaira, D. The effect of milling and sintering techniques on mechanical properties of Cu–graphite metal matrix composite prepared by powder metallurgy route. J. Alloy. Compd. 2013, 569, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saber, D.; El-Aziz, K.A.; Fathy, A. Corrosion behavior of copper—Alumina nanocomposites in different corrosive media. Int. J. Mech. Eng. 2016, 5, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Elmahdy, M.; Abouelmagd, G.; Mazen, A.A.E. Microstructure and properties of Cu-ZrO2 nanocomposites synthesized by in situ processing. Mater. Res. 2018, 21, 1103–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Elmahdy, M.; Abouelmagd, G.; Mazen, A.A. Investigation on microstructure and thermal properties of in-situ synthesized Cu–ZrO2 nanocomposites. Int. J. Mater. Res. 2017, 108, 1103–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, K.; Wang, X. Microscratch behavior of copper–Graphite composites. J. Tribol. Int. 2013, 57, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, I.; Guedes, M.; Ferro, A. Processing of Copper-Graphite-Alumina Powders by High-Energy Milling. In Proceedings of the PM2014 World Congress-Proceedings of the 2014 World Conference on Powder Metallurgy, Orlando, FL, USA, 18–22 May 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Khamaj, A.; Farouk, W.M.; Shewakh, W.M.; Abu-Oqail AM, I.; Wagih, A.; Abu-Okail, M. Effect of lattice structure evolution on the thermal and mechanical properties of Cu–Al2O3/GNPs nanocomposites. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 16511–16520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Yue, H.; Guo, E.; Zhang, H.; Lin, X.; Yao, L.; Wang, B. Preparation and tensile properties of homogeneously dispersed graphene reinforced aluminum matrix composites. Mater. Des. 2016, 94, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadoun, A.M.; Najjar, I.M.R.; Abd-Elwahed, M.S.; Meselhy, A. Experimental study on properties of Al–Al2O3 nanocomposite hybridized by graphene nanosheets. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 14708–14717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd-Elwahed, M.S.; Wagih, A.; Najjar, I.M.R. Correlation between micro/nano-structure, mechanical and tribological properties of copper-zirconia nanocomposites. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathy, A. Investigation on microstructure and properties of Cu-ZrO2 nanocomposites synthesized by in situ processing. Mater. Lett. 2018, 213, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd-Elwahed, M.S.; Ibrahim, A.F.; Reda, M.M. Effects of ZrO2 nanoparticle content on microstructure and wear behavior of titanium matrix composite. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 8528–8534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torabi, H.; Arghavanian, R. Investigations on the corrosion resistance and microhardness of Cu–10Sn/SiC composite manufactured by powder metallurgy process. J. Alloy. Compd. 2019, 806, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meselhy, A.F.; Reda, M.M. Investigation of mechanical properties of nanostructured Al-SiC composite manufactured by accumulative roll bonding. J. Compos. Mater. 2019, 53, 3951–3961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagih, A.; Abu-Oqail, A.; Fathy, A. Effect of GNPs content on thermal and mechanical properties of a novel hybrid Cu-Al2O3/GNPs coated Ag nanocomposite. J. Ceram. Intern. 2019, 45, 1115–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadoun, A.M.; Fathy, A.; Abu-Oqail, A.; Elmetwaly, H.T.; Wagih, A. Structural, mechanical and tribological properties of Cu–ZrO2/GNPs hybrid nanocomposites. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 7586–7594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramkumar, K.R.; Sivasankaran, S.; Alaboodi, A.S. Effect of alumina content on microstructures, mechanical, wear and machining behavior of Cu-10Zn nanocomposite prepared by mechanical alloying and hot-pressing. J. Alloy. Compd. 2017, 709, 129–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, R.S.; Yadava, V. Experimental investigations on electrical discharge diamond peripheral surface grinding (EDDPSG) of hybrid metal matrix composite. J. Manuf. Process. 2017, 27, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadoun, A.; Ibrahim, A.; Abdallah, A.W. Fabrication and evaluation of tribological properties of Al2O3 coated Ag reinforced copper matrix nanocomposite by mechanical alloying. J. Asian Ceram. Soc. 2020, 8, 1228–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barakat, W.S.; Wagih, A.; Elkady, O.A.; Abu-Oqail, A.; Fathy, A.; EL-Nikhaily, A. Effect of Al2O3 nanoparticles content and compaction temperature on properties of Al–Al2O3 coated Cu nanocomposites. Compos. Part B Eng. 2019, 175, 107140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadoun, A.M.; Meselhy, A.F.; Abdallah, A.W. Microstructural, mechanical and wear behavior of electroless assisted silver coated Al2O3–Cu nanocomposites. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2021, 266, 124562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Megahed, M.; Fathy, A.; Morsy, D.; Shehata, F. Mechanical Performance of glass/epoxy composites enhanced by micro-and nanosized aluminum particles. J. Ind. Text. 2021, 51, 68–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güler, O.; Cuvalci, H.; Canakci, A.; Celebi, M. The Effect of Nano Graphite Particle Content on the Wear Behaviour of ZA27 Based Hybrid Composites. Adv. Compos. Lett. 2017, 26, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wagih, A. Mechanical properties of Al–Mg/Al2O3 nanocomposite powder produced by mechanical alloying. Adv. Powder Technol. 2015, 26, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, R.; Thakur, D.G. Qualitative and Quantitative Assessment of Microstructure in Al-B4C Metal Matrix Composite Processed by Modified Stir Casting Technique. Arch. Civ. Mech. Eng. 2016, 16, 949–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatt, J.; Balachander, N.; Shekher, S.; Karthikeyan, R.; Peshwe, D.R.; Murty, B.S. Synthesis of Nanostructured Al-Mg-SiO2 Metal Matrix Composites Using High- Energy Ball Milling and Spark Plasma Sintering. J. Alloy. Compd. 2012, 536, S35–S40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagih, A. Synthesis of nanocrystalline Al2O3 reinforced Al nanocomposites by high-energy mechanical alloying: Microstructural evolution and mechanical properties. Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 2016, 69, 851–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canakci, A.; Varol, T.; Cuvalci, H.; Erdemir, F.; Ozkaya, S. Development and Characterization of Bronze-Cr-Ni Composites Produced by Powder Metallurgy. Sci. Eng. Compos. Mater. 2015, 22, 425–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagih, A.; Fathy, A. Improving compressibility and thermal properties of Al–Al2O3 nanocomposites using Mg particles. J. Mater. Sci. 2018, 53, 11393–11402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, A.; Mohammed, M.M.; Ibrahim, A.F.; El-Kady, O.A. Effect of nano Al2O3 coated Ag reinforced Cu matrix nanocomposites on mechanical and tribological behavior synthesis by P/M technique. J. Compos. Mater. 2020, 54, 4921–4928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagih, A. Effect of Mg addition on mechanical and thermoelectrical properties of Al–Al2O3 nanocomposite. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2016, 26, 2810–2817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagih, A. Effect of milling time on morphology and microstructure of Al-Mg/Al2O3 nanocomposite powder produced by mechanical alloying. Int. J. Adv. Eng. Sci. 2014, 4, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Cipolloni, G.; Menapace, C.; Pellizzari, M.; Ischia, G. Differences of the microstructural evolution of Cu powder during continuous and interrupted mechanical milling. Powder Metall. 2017, 60, 232–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatir, S.; Boutchicha, D.; le Thanh, C.; Tran-Ngoc, H.; Nguyen, T.N.; Abdel-Wahab, M. Improved ANN technique combined with Jaya algorithm for crack identification in plates using XIGA and experimental analysis. Theor. Appl. Fract. Mech. 2020, 107, 102554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zenzen, R.; Khatir, S.; Belaidi, I.; le Thanh, C.; Wahab, M.A. A modified transmissibility indicator and Artificial Neural Network for damage identification and quantification in laminated composite structures. Compos. Struct. 2020, 248, 112497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wang, H.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, J.; Dai, P.; Du, X.; Wahab, M.A. Automatic laser profile recognition and fast tracking for structured light measurement using deep learning and template matching. Measurement 2021, 169, 108362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Wang, L.; Mirjalili, S. Artificial hummingbird algorithm: A new bio-inspired optimizer with its engineering applications. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2022, 388, 114194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasheminejad, N.; Pipintakos, G.; Vuye, C.; De Kerf, T.; Ghalandari, T.; Blom, J. Utilizing deep learning and advanced image processing techniques to investigate the microstructure of a waxy bitumen. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 313, 125481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobbelaere, M.R.; Plehiers, P.P.; Van de Vijver, R.; Stevens, C.V.; Van Geem, K.M. Machine learning in chemical engineering: Strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. Engineering 2021, 7, 1201–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, S.; Zhang, K.; Bagheri, M.; Burken, J.G.; Gu, A.; Li, B.; Ma, X.; Marrone, B.L.; Ren, Z.J.; Schrier, J.; et al. Machine Learning: New Ideas and Tools in Environmental Science and Engineering. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 12741–12754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadoun, A.M.; Najjar, I.R.; Alsoruji, G.S.; Wagih, A.; Elaziz, M.A. Utilizing a Long Short-Term Memory Algorithm Modified by Dwarf Mongoose Optimization to Predict Thermal Expansion of Cu-Al2O3 Nanocomposites. Mathematics 2022, 10, 1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najjar IM, R.; Sadoun, A.M.; Alsoruji, G.S.; Abd Elaziz, M.; Wagih, A. Predicting the mechanical properties of Cu–Al2O3 nanocomposites using machine learning and finite element simulation of indentation experiments. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 7748–7758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmaadawy, K.; Elaziz, M.A.; Elsheikh, A.H.; Moawad, A.; Liu, B.; Lu, S. Utilization of random vector functional link integrated with manta ray foraging optimization for effluent prediction of wastewater treatment plant. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 298, 113520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khoshaim, A.B.; Moustafa, E.B.; Bafakeeh, O.T.; Elsheikh, A.H. An Optimized Multilayer Perceptrons Model Using Grey Wolf Optimizer to Predict Mechanical and Microstructural Properties of Friction Stir Processed Aluminum Alloy Reinforced by Nanoparticles. Coatings 2021, 11, 1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zayed, M.E.; Zhao, J.; Li, W.; Elsheikh, A.H.; Elaziz, M.A. A hybrid adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system integrated with equilibrium optimizer algorithm for predicting the energetic performance of solar dish collector. Energy 2021, 235, 121289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadoun, A.M.; Mohammed, M.M.; Fathy, A.; El-Kady, O.A. Effect of Al2O3 addition on hardness and wear behavior of Cu–Al2O3 electro-less coated Ag nanocomposite. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 5024–5033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd-Elwahed, M.S.; Meselhy, A.F. Experimental investigation on the mechanical, structural and thermal properties of Cu–ZrO2 nanocomposites hybridized by graphene nanoplatelets. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 9198–9206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asiri, S.; Wagih, A.; Eltaher, M.A. Predictive model for spherical indentation on elastoplastic nanocomposites: Loading and unloading behavior. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 3088–3100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagih, A.; Shaat, M. The dependence of accumulative roll bonded copper mechanical properties on grain sub-division, stacking faults, and lattice strains. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 756, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadoun, A.M.; Mohammed, M.M.; Elsayed, E.M.; Meselhy, A.F.; El-Kady, O.A. Effect of nano Al2O3 coated Ag addition on the corrosion resistance and electrochemical behavior of Cu-Al2O3 nanocomposites. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 4485–4493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elwan, M.; Fathy, A.; Wagih, A.; Essa AR, S.; Abu-Oqail, A.; EL-Nikhaily, A.E. Fabrication and investigation on the properties of ilmenite (FeTiO3)-based Al composite by accumulative roll bonding. J. Compos. Mater. 2020, 54, 1259–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omer, G.L.; Ertan, E. The investigation of contact performance of oxide reinforced copper composite via mechanical alloying. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2009, 209, 1286–1290. [Google Scholar]

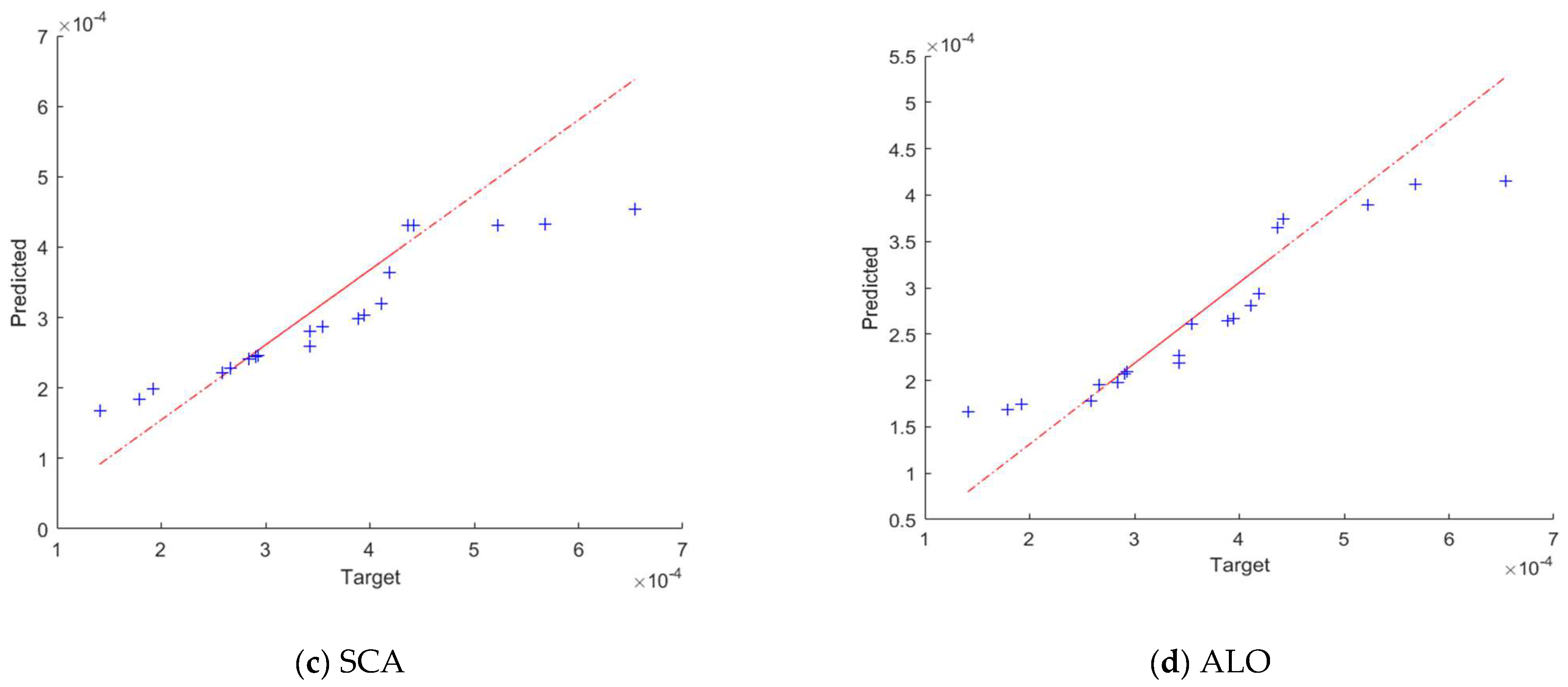
| Training Set | Testing Set | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AHA | SSA | SCA | ALO | AHA | SSA | SCA | ALO | |
| R2 | 1 | 0.9985 | 0.9986 | 0.9998 | 0.9554 | 0.9195 | 0.9294 | 0.9034 |
| RMSE | 1.27 × 1018 | 8.92 × 106 | 8.65 × 106 | 2.79 × 106 | 8.04 × 105 | 0.000108 | 0.000101 | 0.000118 |
| MAE | 1.14 × 1018 | 6.61 × 106 | 6.19 × 106 | 1.25 × 106 | 6.1 × 105 | 8.8 × 105 | 8.84 × 105 | 9.9 × 105 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sadoun, A.M.; Najjar, I.R.; Alsoruji, G.S.; Abd-Elwahed, M.S.; Elaziz, M.A.; Fathy, A. Utilization of Improved Machine Learning Method Based on Artificial Hummingbird Algorithm to Predict the Tribological Behavior of Cu-Al2O3 Nanocomposites Synthesized by In Situ Method. Mathematics 2022, 10, 1266. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10081266
Sadoun AM, Najjar IR, Alsoruji GS, Abd-Elwahed MS, Elaziz MA, Fathy A. Utilization of Improved Machine Learning Method Based on Artificial Hummingbird Algorithm to Predict the Tribological Behavior of Cu-Al2O3 Nanocomposites Synthesized by In Situ Method. Mathematics. 2022; 10(8):1266. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10081266
Chicago/Turabian StyleSadoun, Ayman M., Ismail R. Najjar, Ghazi S. Alsoruji, M. S. Abd-Elwahed, Mohamed Abd Elaziz, and Adel Fathy. 2022. "Utilization of Improved Machine Learning Method Based on Artificial Hummingbird Algorithm to Predict the Tribological Behavior of Cu-Al2O3 Nanocomposites Synthesized by In Situ Method" Mathematics 10, no. 8: 1266. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10081266
APA StyleSadoun, A. M., Najjar, I. R., Alsoruji, G. S., Abd-Elwahed, M. S., Elaziz, M. A., & Fathy, A. (2022). Utilization of Improved Machine Learning Method Based on Artificial Hummingbird Algorithm to Predict the Tribological Behavior of Cu-Al2O3 Nanocomposites Synthesized by In Situ Method. Mathematics, 10(8), 1266. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10081266







