Abstract
IoT-Edge-Fog Computing presents a trio-logical model for decentralized computing in a time-sensitive manner. However, to address the rising need for real-time information processing and decision modeling, task allocation among dispersed Edge Computing nodes has been a major challenge. State-of-the-art task allocation techniques such as Min–Max, Minimum Completion time, and Round Robin perform task allocation, butv several limitations persist including large energy consumption, delay, and error rate. Henceforth, the current work provides a Quantum Computing-inspired optimization technique for efficient task allocation in an Edge Computing environment for real-time IoT applications. Furthermore, the QC-Neural Network Model is employed for predicting optimal computing nodes for delivering real-time services. To acquire the performance enhancement, simulations were performed by employing 6, 10, 14, and 20 Edge nodes at different times to schedule more than 600 heterogeneous tasks. Empirical results show that an average improvement of 5.02% was registered for prediction efficiency. Similarly, the error reduction of 2.03% was acquired in comparison to state-of-the-art techniques.
MSC:
68T01
1. Introduction
Internet of Things (IoT) technology has profoundly altered industrial sectors, resulting in the concept of Industry 4.0 [1]. Intelligent Healthcare, Smart Academics, and Self-Aware Transportation are some of the vital domains where IoT is significantly beneficial [2]. According to research, the worldwide industrial IoT market is estimated to reach 30.9 billion units by 2025 (source: https://www.statista.com/statistics/668996/worldwide-expenditures-for-the-internet-of-things/, accessed on 28 September 2022). As a result, ubiquitous service delivery and decision-modeling automation have become key study subjects in the modern day. The increased use of IoT devices has elevated the requirement of computational resources to do effective data analysis with the least amount of delay [3]. However, because of current constraints in the energy computing bandwidth, traditional approaches are not sufficient to meet the increased demands of Fog-Cloud Computing applications. Edge Computing is a novel concept presented by the upcoming internet revolution [4,5]. Edge-based resource allocation entails deploying networked compute nodes to efficiently deliver real-time services [6]. Edge Computing is a logical paradigm for supplying time-sensitive Computation, Storing Capability, and Services over the internet between consumers and Fog-Cloud database [7,8]. The use of an Edge layer for industrial IoT services is depicted in Figure 1 as a general 3-tier model of IoT-Fog-Edge-Cloud Computing.
Figure 1.
IoT-Edge-Fog-Cloud Architecture: Resource Capability Analysis.
1.1. Application-Oriented Research Motivation
In virtually all industrial areas, Edge Computing plays a key role in dynamically allocating heterogeneous resources [9]. Smart industry is divided into three categories including Extraction-related, Manufacturing-related, and Service-related. Edge Computing has shown new avenues to meet the aims of a futuristic smart industry with the capability of becoming a vital component of the next-generation smart industry vision. The following are some of the key industrial domains where Edge-based computing has improved services:
- 1.
- Smart Mining Industry: The use of smart devices to collect ubiquitous information on chemical emissions in the mining industry such as coal and mineral has enabled real-time preventative measures. Furthermore, because substantial data processing may be conducted utilizing co-located Edge nodes, Edge Computing can considerably enhance accuracy.
- 2.
- Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITS) are a subset of the Internet of Things (IoT)-enabled transportation business. To allow ITS, a roadside mobility vehicle can be outfitted with Edge Computing nodes. Edge Computing, for example, can lead to Support for in-vehicle Entertainment Systems (SivES) and Intelligent Vehicles (IV) that can provide contextual data collection, GPS-based service delivery, and intelligent traffic management that control signal-based on traffic volume and emergency. Additionally, Edge-based ITS includes providing required information to drivers and commuters regarding traffic volume and road conditions.
- 3.
- Smart Waste Management Industry (SWMI): One of the primary goals of SWMI is to automate the waste management process. Edge-enabled SWMI monitors toxic and non-toxic waste disposal in the industrial sector.
Other industry domains where Edge Computing has been successful in meeting service expectations are Advertising Industry, Smart Parking, and Third-Party Service Delivery.
1.2. Technical Research Motivation
Edge Computing has been shown to be a powerful paradigm for achieving a decentralized computing platform over the network. Despite the multiple industrial utilization, task allocation between Edge nodes is a crucial component. With the smooth development of heterogeneous IoT activities, it is necessary to schedule tasks appropriately among diverse processing nodes to provide efficient IoT services with low latency. Indeed, to improve system performance, reliability, and efficiency, scheduling diverse tasks among Edge nodes remains a major hindrance. Moreover, lowering total energy usage and minimizing temporal delay for completing numerous activities are essential indications for distributed systems. Traditional allocation algorithms are unable to meet the seamless need for delivering real-time services in complex environments with a high number of IoT devices with unpredictable resource requirements. Furthermore, for optimal performance in an Edge Computing environment, improved task routing models are required. As a result, Edge-based allocation has been a popular study topic in recent years. Figure 2 depicts the resource constraints analysis for IoT-Edge-Fog-Cloud architecture.
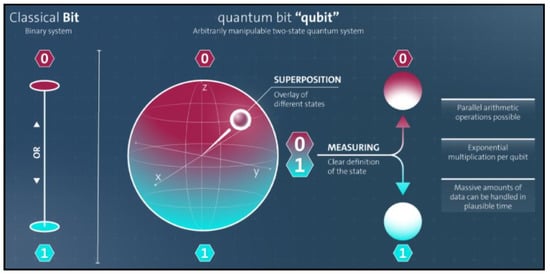
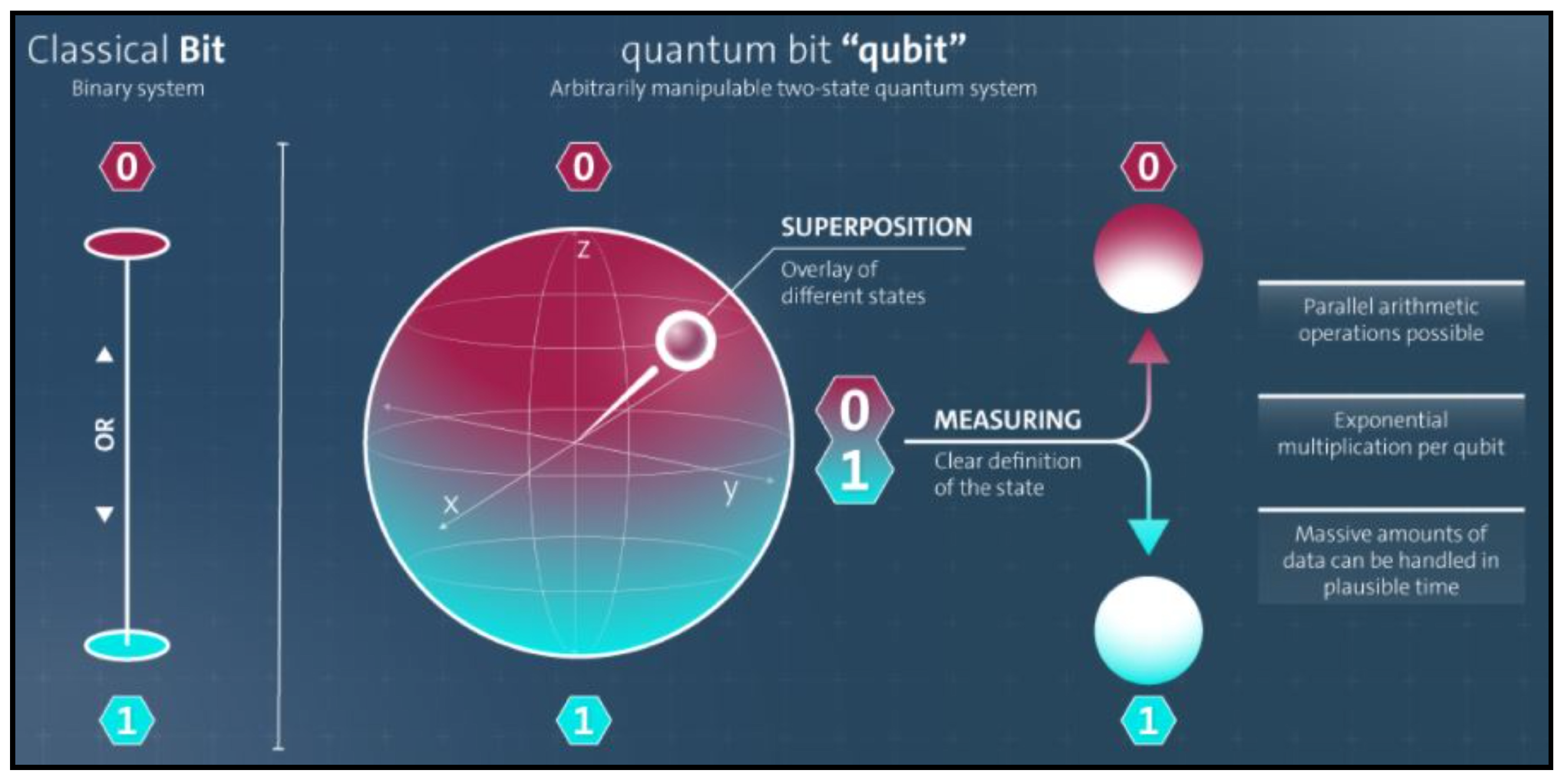
Figure 2.
Classical Bit vs. Quantum Bit.
1.3. Edge-Related Quantum-Inspired Computing
Even with Edge Computing’s broad industrial use, dynamic resource distribution for ubiquitous service delivery persists as a key challenge in IoT systems [10]. Because Edge node capacity is limited, the allocation of IoT-specific tasks necessitates novel strategies and processes to fulfill the growing need for real-time applications [11,12]. The allocation of Edge resources including processing ability, processor cycle-time, and main memory are key attributes to be monitored in an effective manner [13]. Furthermore, the temporal efficacy with which an Edge node can execute the tasks assigned to it is an issue that must be addressed [14]. As a result, an effective real-time task allocation technique is indispensable in the Edge computational environment to achieve optimal system performance. Quantum Computing-inspired (Qci) Optimization is a strategy that has emerged from its infancy in recent years [15]. QCi is a type of computing that is based on quantum theory and physical events. By the virtualization of network nodes in the Edge Computing platform, QC-inspired task allocation allows maximal scalability, availability, and feasibility [13]. QCi tackles critical challenges such as traffic management for Edge-inspired applications.
1.4. Novel Contribution
The broad adoption of IoT technology by many enterprises has led to the development of petabytes and exabytes of internet data, necessitating efficient data allocation and node-specific computation for ubiquitous services. Based on the aforementioned aspects, some of the novel contributions are as follows;
- 1.
- Utilizing QCi allocates IoT tasks across an Edge Computing platform in real time.
- 2.
- Allocating diverse resources over Edge nodes using a QCO technique to achieve maximal performance.
- 3.
- A novel QCO technique has been proposed for mapping IoT-task to the best Edge node for processing. This mapping is achieved in terms of the Usability Index Measure (UIM), a probabilistic measure that represents a unifying factor for analyzing an Edge-computational node’s availability for managing current demand.
- 4.
- Proposing a QC-Neural Network Model for predicting optimum node-based specifications.
Paper Organization
The remainder of this paper is organized into different sections. Section 2 gives a review of QC-specific fundamental principles and related mathematical functions. In Section 3, state-of-the-art relevant studies in QCi applications are depicted. Section 4 describes the proposed QC-based task allocation approach. Experimental simulations are carried out in Section 5 for validation purposes. Finally, Section 6 concludes the paper by outlining several future research areas.
2. Fundamental Concept
2.1. Task Allocation
The distribution of IoT tasks across distinct Edge computation nodes for the aim of service delivery to the IoT services is referred to as task allocation. Task allocation has been a vital research topic, whether applied to local multiprocessor systems or distributed computing paradigms such as Fog-Cloud Computing. The revolutionary technique of Edge computation has developed an efficient way to handle heterogeneous resource requirements for real-time services, focusing on current developments in Fog-Cloud Computing. Moreover, task allocation among multiple Edge nodes, platform independence, and the challenge of varied resource needs have been successfully addressed. Furthermore, task allocation may remap Edge Computing nodes and physically assign resources in response to the dynamic task, resulting in optimal resource utilization in the entire system. Edge-based task schedulers, on the other hand, require modification for adapting to deliver time-sensitive services, and optimal performance due to the dynamic resource request in IoT applications. Furthermore, IoT tasks must be effectively allocated to ensure optimal system performance. As a result, task allocation in Edge Computing platforms for time-sensitive analysis and resource utilization has become a focus of research. Specifically, numerous task allocation techniques for distributed computing systems have been proposed by scholars all around the world. However, resource needs and node availability are crucial variables to consider during task transmission in the current scenario of dynamic task allocation via Edge nodes. The current study provides an effective task allocation strategy in an Edge Computing environment by exploiting the analytical capabilities of the QCi approach. Before diving into the details, a quick overview of the QCO approach has been presented.
2.2. QC-Inspired Optimization (QCO) Technique
QC-inspired Optimization (QCO) technique has been around for a while. However, with recent advancements in distributed platforms such as Edge Computing, its utilization in task allocation has become a pivotal aspect. QCO has been studied extensively in several application areas by researchers all over the world. Before delving into the application of the QCi approach, it is crucial to understand the basics of the QCi technique. QCi is formulated over quantum computer-inspired techniques, where binary datum is represented in indefinite and definite forms at the same time. The status of the entire system is determined by the data representation format.
- 1.
- Qubit: A qubit is the fundamental unit of the data held in a 2-state QC. A qubit can be in one of three states: 0|state, 1|state, or superposition-state. A qubit is expressed assuch that and are complex integers describing the probabilistic measures of states. indicates the likelihood of 0|state, and gives the likelihood of 1|state. The difference between a conventional bit and a qubit is seen in Figure 3. The following relationship is guaranteed when the state is normalized to unity.
 Figure 3. Proposed Approach.
Figure 3. Proposed Approach. - 2.
- Qubit Individual: It is a string that contains numerous qubits at the same time. It is notated assuch that n is the qubit number that formulates the qubit individual. The ability to express different states via linear superposition is one of the advantages of qubit individuals. For example, the following is a 3-bit qubit individual.The aforementioned representation concurrently indicates information from eight separate states. Specifically, the above equation represents the full state of the system with appropriate probability asTable 1 shows the probability of each state based on the supplied linear superposition of system states. In general, 2n states may be expressed simultaneously with n qubits.
 Table 1. Qubit State Probability.
Table 1. Qubit State Probability. - 3.
- Qubit Population: It is a group of qubit individuals. It is represented by m + 1 separate qubit individuals, each of length n.
- 4.
- Q-gate: It is a variability operation that updates the qubit individual to fulfill the normalization requirement, where the updated qubits are and . The operation using a Q-gate can modify the state of a qubit. It is described as a urinary operator Z working on the quantum-state to meet the condition ZTZ = ZZT. The Hermitian Adjoint of Z is denoted by ZT. The Rotation gate, Hadamard gate, and controlled-NOT gate are examples of quantum gates. Observing a quantum state, on the other hand, compresses it into a single state. For a better understanding, a general rotating gate is given below.
3. Literature Review
In distributed computing, task allocation has been a major research domain. Task allocation benefits significantly from the addition of QC, particularly in IoT-inspired platforms that demand optimal computational services. The current section summaries a brief review of significant contributions in decentralized computing-based task allocation. Additionally, a portion is devoted to a study of several significant contributions to the QCi approach.
3.1. Dynamic Task Allocation Techniques
Task allocation is a technique for efficiently dividing incoming user-generated requests among numerous geographically dispersed server nodes. Over the last few years, academics all over the world have proposed a variety of task allocation approaches for achieving optimal system performance. Table 2 lists many state-of-the-art task allocation strategies with respective parameters. For allocating tasks in remote computing systems, Kaur et al. [16] suggested a task-specific approach. To improve the entire system’s efficiency, the authors used genetic algorithms to analyze parameters and time-sensitive user demands for computing resource distribution. When compared to alternative methodologies, experimental implementations on the proposed model produced better performance metrics in terms of delay (56.26 s), and specificity (78.25%). In a Cloud Computing context, Chawla and Ghumman [17] offered a unique technique for task allocation. If the needed data package is not accessible, the suggested solution is inspired by data aggregation and executing virtual machine cloning. The suggested technique proved to be very efficient in allocating data among dispersed servers with 90.01% accuracy. By describing the standard mixed-criticality task model in the context of cyber physical systems, analysing and proposing the most suitable scheduling algorithms to be implemented in cyber physical systems, and identifying the particularities of the latter and their influence on scheduling mechanisms, Capota et al. [18] aims to facilitate the integration of mixed criticality systems-based strategy in cyber physical systems. New research opportunities are opened up by the combination of cyber and physical systems, and this article explores the implications for the future of this field. Burns et al. [19] published studies on mixed criticality systems. For real-time allocation, Belgaum et al. [20] presented a log-based task allocation approach. To provide time-sensitive service delivery, the provided solutions combine a rank-based idea for ranking various incoming user requests. Furthermore, for better overall service allocation, the request-specific rank is forecasted utilizing multiple approaches. The authors reported efficient outcomes with 89.25% precision in numerous experimental implementations of the suggested approach. Srivastava and Singh [21] provided a fascinating paper on task allocation using the Cloud segregation approach. The authors have combined the Cloud partition state mechanism and several task allocation methods in the proposed model to improve task distribution efficiency. The authors used the CloudSim simulator to implement the suggested approach and were able to obtain the best results in terms of f-measure (88.48%) when compared to other strategies. For the Cloud conceptualization of infrastructure as a service (Iaas), Adhikari and Amgoth [22] devised a unique task allocation technique. A technique is being developed to set up different Cloud databases based on the magnitude of resource demands. To maximize resource efficiency, appropriate virtual machines are set up for task assignments. Results were reported with good efficacy (90.15%) when compared to other methodologies based on the authors’ experimental simulation. Tang et al. [23] proposed a dynamic task allocation solution for reducing task imbalance in the spark framework for containers. Furthermore, a task allocation strategy based on aggregation is suggested for data blocks. A sampling technique of the reservoir approach is presented for finding the key distribution of interim data. Text searching, sorting, and word counting were three benchmark datasets for which the suggested method was implemented in Spark 1.1. The given approach was able to produce greater overall task allocation performance while reducing task execution time, according to experimental data. Shahdi-Pashaki et al. [24] proposed Group Technology, a unique technique in cellular manufacturing technology. Furthermore, a mathematical model has been established to handle task migration and server task variation concerns by consolidating virtual machines, Cloud servers, and tasks at the same time. The authors used the LINGO 9 program to run multiple simulations to validate the concept. The obtained results were contrasted with state-of-the-art allocation strategies such as First Come First Serve (FCFS), and Round Robin (RR) depicting that the suggested technique is more accurate with 3.02% enhancement.

Table 2.
Survey of Task allocation Algorithms For Distributed Computing Environments.
3.2. QCi Optimization (QCO) Research
One of the significant techniques for decision-optimization in real-time is QCO. QCO is a futuristic paradigm that presents novel directions for improved IoT applications by allowing complicated massive data to be evaluated in milliseconds. As a result, various academics throughout the world have effectively used the procedure for optimization and computational reasons. Spector et al. [41] suggested a Genetic Quantum Computing-based evolutionary computational approach (GQA). The linear superposition of solutions and relative probabilities are represented using qubits. In addition, quantum gates have been added to produce real-time optimum solutions in a vast solution space. In experimental implementations of the knapsack problem, the validation of the provided approach was assessed. Results depicted that the presented approach was stable (80.25%) and efficient (83.26% precision). Henderson et al. [42] proposed a quantum-inspired adaptive technique to improve the temporal efficacy in the multi-Cloud Computing platforms. For real-time task allocation with optimal space occupation, a predictive technique of kernel-inspired extreme learning approach is presented. When compared to previous task allocation methods, the authors were able to achieve a gain of about 26.6 percent when using different datasets. Li et al. [43] proposed the Quantum Inspired Particle Swarm Optimization (QPSO) approach for enabling parallel processing in a complicated environment in the Map-Reduce paradigm of large data. To describe the solution space of Map-Reduce functions, the proposed model integrates many QCi concepts such as qubits and q-gates. In comparative analysis with existing state-of-the-art optimization techniques, the provided methodology produced optimum outcomes in terms of average delay (29.36 s) during simulations.
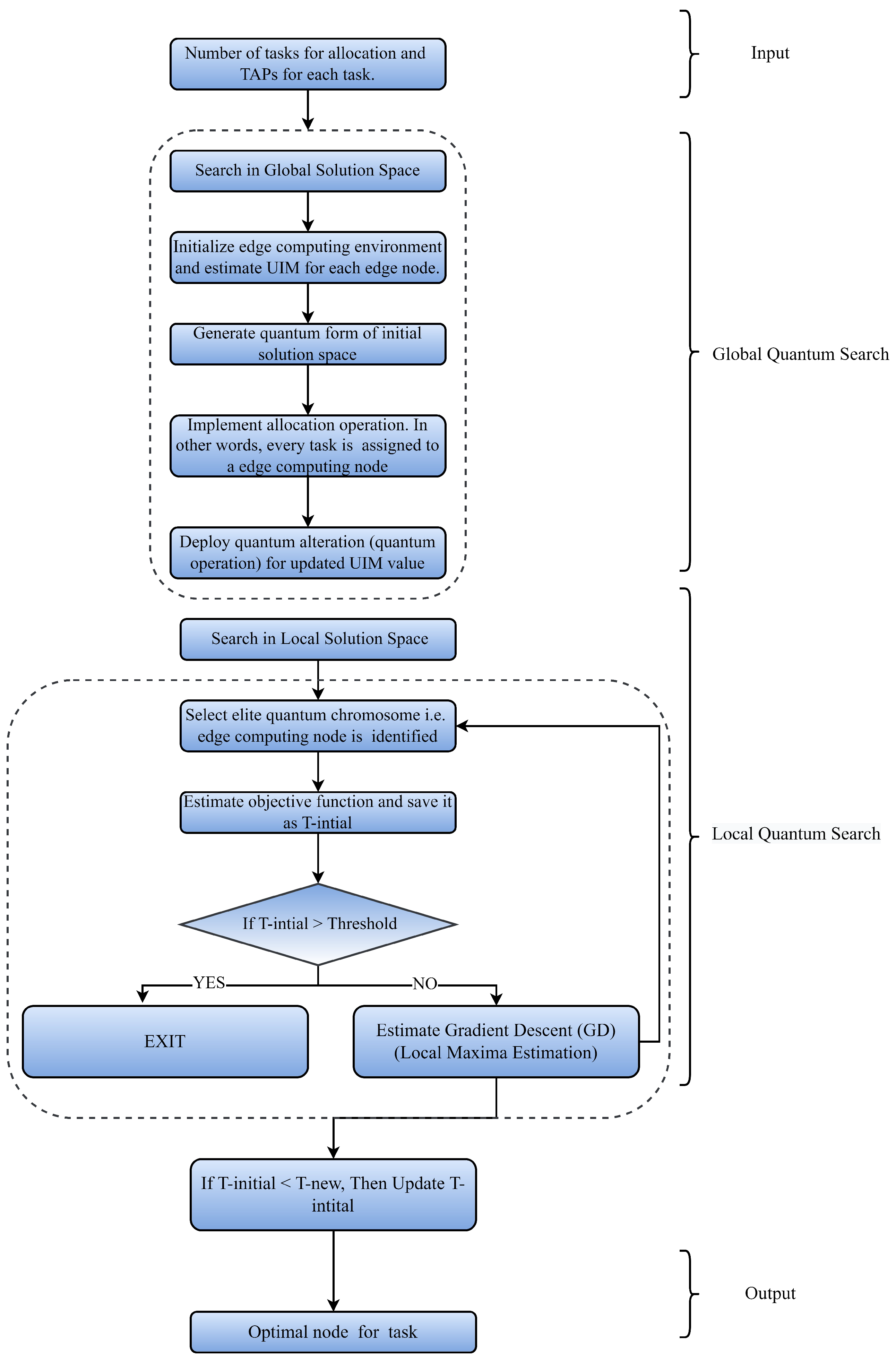
4. Proposed Technique
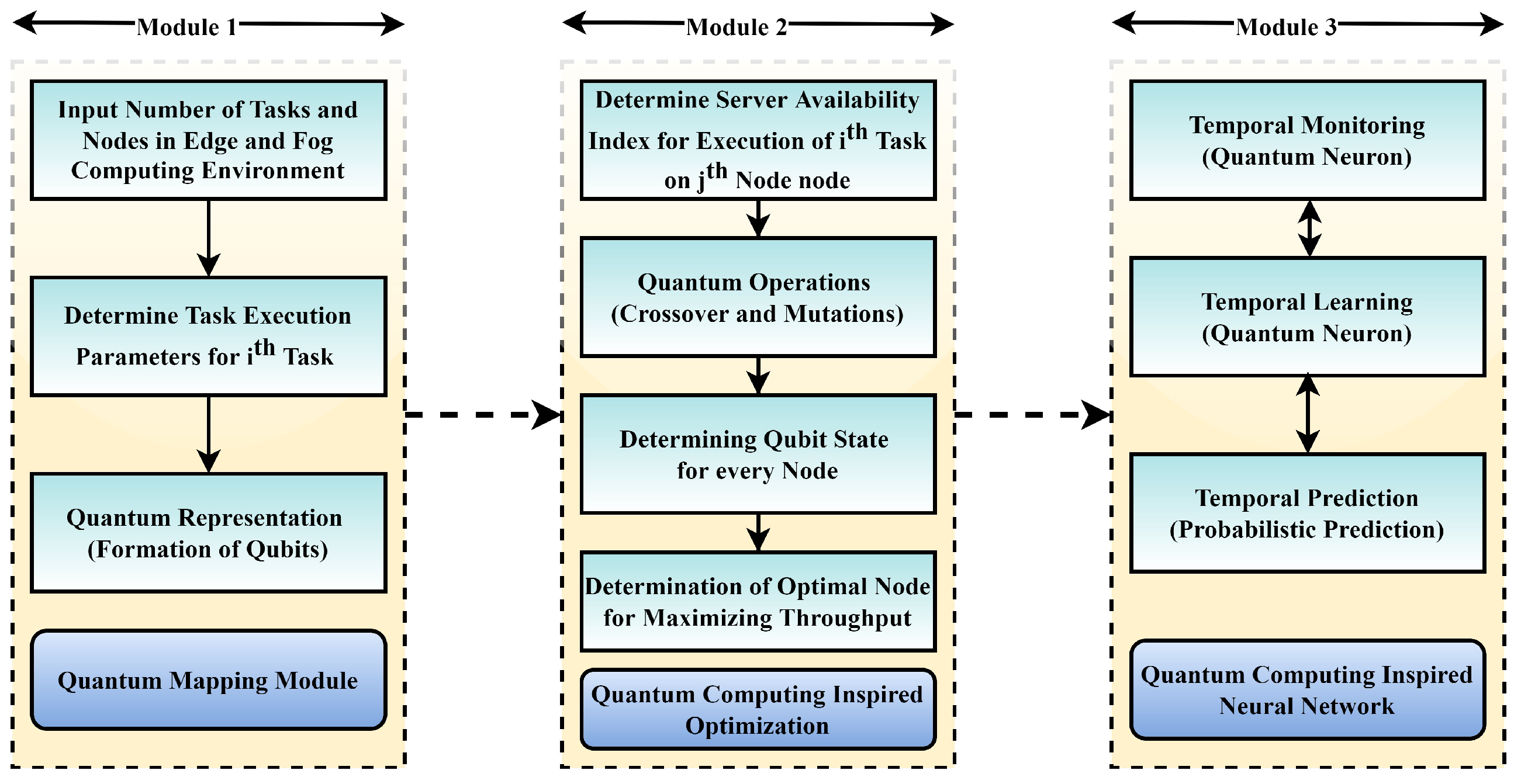
The presented technique is formulated in three modules as shown in Figure 4. Every module is responsible for completing certain tasks to achieve the overall goals of the proposed model. Numerous task allocation and Edge-oriented characteristics are described in quantum representations in the first module to determine respective computing capacities. Because Edge nodes are decentralized and have varied infrastructures such as processor speed, and memory, it is critical to find a metric that can be used to gauge an Edge node’s total computing capacity. Each Edge node is defined by a probabilistic parameter called Usability Index Measure (UIM) based on its computational capability. The second module introduces a unique QCO Algorithm for the allocation of IoT tasks among optimum Edge nodes using a novel QCO Algorithm. The final module introduces a QC-Neural Network (QNN) that uses a probabilistic element called Task Execution Index (TEI) to forecast the best Edge Computing node for managing current demand. Each of the modules is discussed in detail ahead.
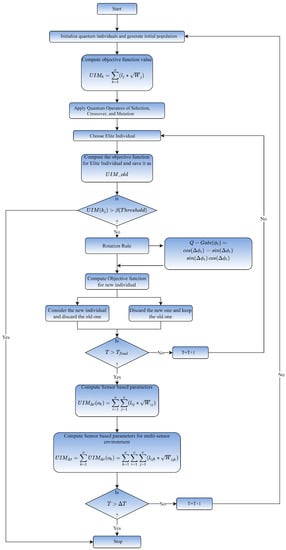
Figure 4.
Local Search procedure.
4.1. Quantum Formulation
This module focuses on the QCi approach for mapping different task allocation characteristics and Edge node requirements. As previously stated, appropriate task distribution over numerous computing nodes necessitates fast computation of the number of available resources, computing capabilities, and an accurate assessment of resource requirements for handling tasks, particularly in cases of dynamic task production. As a result, acquiring such knowlEdge and quantifying it together is now required to distribute tasks efficiently.
4.1.1. Task Allocation Parameter (TAP)
The Task Allocation Parameter (TAP) deals with an Edge node’s computing power and task parameters. Because each Edge node is scattered, it may or may not have comparable processing resources such as RAM capacity, CPU speed, and storage memory. Furthermore, there is a substantial risk of not having enough resources to handle the current task load. Furthermore, because user demand for resources varies over time, an effective assessment of the computing node is essential to ensure that it has sufficient resources throughout the task execution process. Edge-nodes in smart power supply systems, for example, can be of various computational specifications for Home Area Networks (HAN), Industrial Area Networks (IAN), Building Area Networks (BAN), and Smart Factory. To address these issues, a probabilistic measure called Usability Index Measure (UIM) is formulated concerning an Edge node.
Definition 1.
Usability Index Measure (UIM) is a probabilistic parameter that is utilized to acquire TAP extensively in a unifying parameter for Edge node availability determination in real time to supply dynamic resource requests required by IoT task.
Several characteristics may be used to determine a computational node’s availability at any given time. RAM availability, processor speed, the number of tasks previously allocated, and network latency are just a few examples. Each parameter is now compared to a predetermined threshold value to determine the node’s immediate availability.
Let there are o parameters to consider while assessing the availability of an Edge node at time u, where k represents the parameter-specific threshold and UIMk signifies the UIM due to the kth parameter. Then
4.1.2. Practical Considerations
Considering practical aspects, the entire task allocation technique involves a diverse set of parameters. Furthermore, it is worth noting that these factors are both static and dynamic. Static parameters have a fixed behavior and are computed in advance, whereas dynamic parameters are computed in real-time. Table 3 lists the many factors that are taken into account while allocating QCi tasks. The optimization issue of task allocation is expressed in the following fashion based on these parameters:

Table 3.
Task Allocation Parameters.
4.1.3. TAP: Qubits Representation
Several characteristics relating to the availability of an Edge node were explored in the preceding section. However, to use the QCi approach to schedule the optimal task, TAP must be represented in terms of qubits. A qubit is a probabilistic parameter that meets the normalization criterion, as explained in the previous section. Each parameter corresponds to a qubit, and if a probabilistic parameter value is larger than a certain threshold, it represents or state-1, and if it is less than that threshold, it represents or state-0. For instance, if the value of a jth parameter is larger than the predetermined threshold , then the state of an Edge node corresponding to jth parameter is represented as
The square root is used in the preceding equation to meet the QC-normalizing approach criteria. Every TAP is effectively represented in terms of qubits as a result. However, it is worth noting that state-0 implies the node’s low availability for handling IoT traffic, but state-1 denotes the Edge node’s high availability for computing.
4.1.4. Quantifying TAP
Edge-node-based quantum behavior gives information on the distributed computing environment. TAP is represented in terms of qubits, as indicated in the preceding section. The Edge-node availability is then expressed in terms of different TAP, resulting in the formation of a qubit individual. For example, if there are O parameters involved in determining the availability of an Edge node at time u, the state value of UIM for that node is given as follows with supplied parametric values.
In terms of TAP, the qubit individual exactly specifies the state of an Edge node. As stated above, the UIM value of an Edge node UIMk is calculated from a qubit individual. The related weight for the kth parameter is denoted by lk. However, a qubit population is defined to obtain information on the complete architecture, which consists of multiple Edge Computing nodes. UIM measure of kth Edge node is computed as
where lk is the weight for Wj parameter. With several Edge nodes and computing parameters, the above equation concurrently calculates the full state of Edge Computing architecture. Let N Edge nodes are engaging in real-time computation, with O TAP indicating each Edge node’s computing power. The total Edge-computing architecture’s qubit population is then codified in the following way.
4.2. Task Allocation-Specific QCO Algorithm
The processing capabilities of an Edge Computing environment are determined by the use of the QCi technique for the allocation of real-time tasks. The task scheduler’s time-sensitive allocation of IoT tasks across multiple Edge nodes is an essential feature. For example, in the Edge-equipped smart traffic management described by [44], the primary issues in the Edge environment are determining real-time traffic volume and recommending the best approach in emergency scenarios. For mobile health and early warning healthcare systems, distributed Edge-driven smart healthcare necessitates real-time tailored data analysis [45]. Energy efficiency, in addition to temporal delay, is a significant performance measure in task allocation. Using the QCi approach will address these concerns to achieve the necessary optimality. Various TAPs are expressed in qubit notational form, as previously mentioned. Furthermore, simultaneous TAP analysis for Edge Computing architecture is a difficult task that is well solved by qubit representation. As a result, an optimal task allocation technique for Edge Computing may be designed. However, before going through the suggested task allocation technique, it is vital to explore quantum operations that are implied over a single qubit to achieve optimization. The QC-inspired operations are detailed ahead.
4.2.1. Quantum Operations
Quantum operations are essential techniques for carrying out predetermined tasks. These procedures play a significant role in finding the best solution in a large number of solution spaces for a particular issue. The goal, of the current study, is to distribute tasks across distinct Edge nodes in real-time depending on respective UIM values. In addition, task prioritization is a significant difficulty that must be solved to achieve the present goal. Crossover and Mutation are two basic procedures explored in the current study. These procedures give both solution space variety and prioritizing, as well as time sensitivity to find the best solution.
- 1.
- Mutation: As a quantum mutation operator, the NOT gate is utilized. The mutation procedure is employed to expand the quantum individual’s variety. Furthermore, the total likelihood of immature convergence is reduced. Furthermore, the improved solution’s searching capability has been much enhanced. The NOT gate is being utilized to reverse the potential probabilities of formalized qubits and the related population in the current study. In each generation, a random qubit, also known as a gene, is chosen for mutation from the preceding qubit individual, and a value is created in its place. NOT gate is used to determine the updated qubit if the probability is greater than the prefixed mutation probability.
- 2.
- Crossover: Another significant functional feature of the QCi approach is crossover. It improves solution space efficiency on a temporal scale, allowing for the development of time-sensitive outcomes. Individual qubits can crossover in this procedure to assess and identify the fittest potential individual among qubit populations. As a result, only the fittest qubits can repeat and deliver the best outcomes. In the current case, crossover operations are used to examine the solution space to determine the best Edge node. The following manner depicts the crossover operation on qubit individuals.Assume that the qubit population is made up of 2-qubit individuals, each with n qubits. After that, the crossover operation is carried out as follows:Qubit1 = Qubit2 = .If Qubit1 is fitter than Qubit2, new chromosome population will beQubit’1 = Qubit’2 =As it can be seen that Qubit’1 and Qubit’2 have been changed except the initial value of ’1 and ’1. This diversification enables rapid analysis of a wide number of solution spaces. In the current situation, these two procedures, crossover and mutation, are used to cover the largest possible solution space for ideal Edge nodes and, as a result, to provide overall accuracy in the suggested task allocation method.
4.2.2. Algorithm for QC-Task Allocation
Quantum bits, as previously stated, are a linear superposition of solutions depending on acquired probability. It is utilized to analyze node-specific UIM values for optimizing functions such as task allocation because of its effective representation technique. The existing task allocation problem can be mapped to a quantum scale using a qubit encoding and decoding approach. Assume that the individual qubit of jth task is represented by Q(j). The total number of Edge nodes determines the size of the qubit population. The jth task is mapped to the kth Edge node using the UIM value. The respected probability based on available TAP and task requirements is related to Q(i). In other words, with the restriction 2o = l, if the number of computing nodes is l, each qubit must have o bits to represent the kth node. The approach described in Figure 5 is used to allocate each Edge node to the IoT task. When it comes to Key Performance Indicators (KPI), temporal delay and energy usage are taken into account.
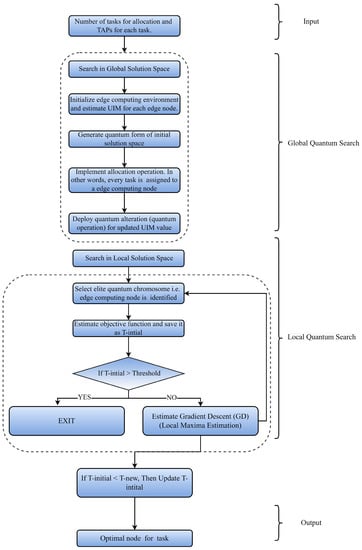
Figure 5.
QCi-Algorithm for Task Allocation.
4.2.3. Numerical Analysis
A numerical example for optimal task allocation based on the suggested approach is presented, utilizing temporal delay or execution time as a performance indicator. However, for the sake of clarity, quantum processes such as crossover and mutations are ignored in the current scenario. Let O be the number of tasks at a given point in time, and N be the number of Edge nodes that are accessible with the given execution settings. Task set may be expressed mathematically as (u1, u2, u3, …, uo) and node-set as (o1, o2, o3, …, on).
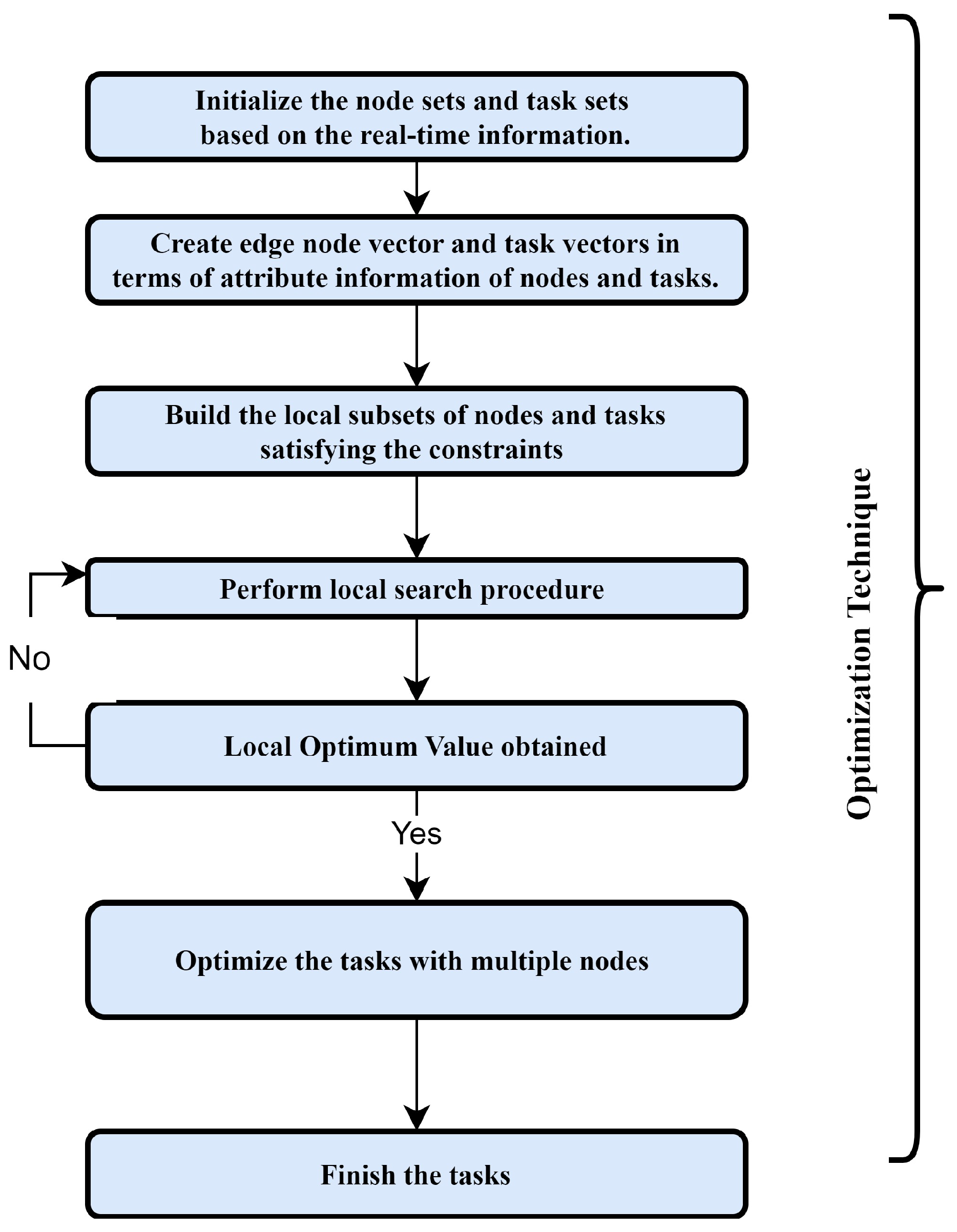
Local Search Procedure
In the local search method, a task with specific execution requirements is assigned to node ok based on the UIM value. It is worth noting that, if necessary, this approach may also be used to accomplish temporal task ranking by giving priority values to tasks. To put it another way, tasks with greater priority are assigned to Edge nodes first, while those with lower priority are assigned later. Figure 5 shows the procedure of local search in the quantum domain for the current study. Formally, the jth task will be allocated and the execution time will be computed with n computational Edge nodes.
∀ l ∈ 1 to o,
Repeat
uk → Map(ol)
Evaluate Completion Time (ol)
Assign uk → Minimum( Completion Time(ol))
Global Search Procedure
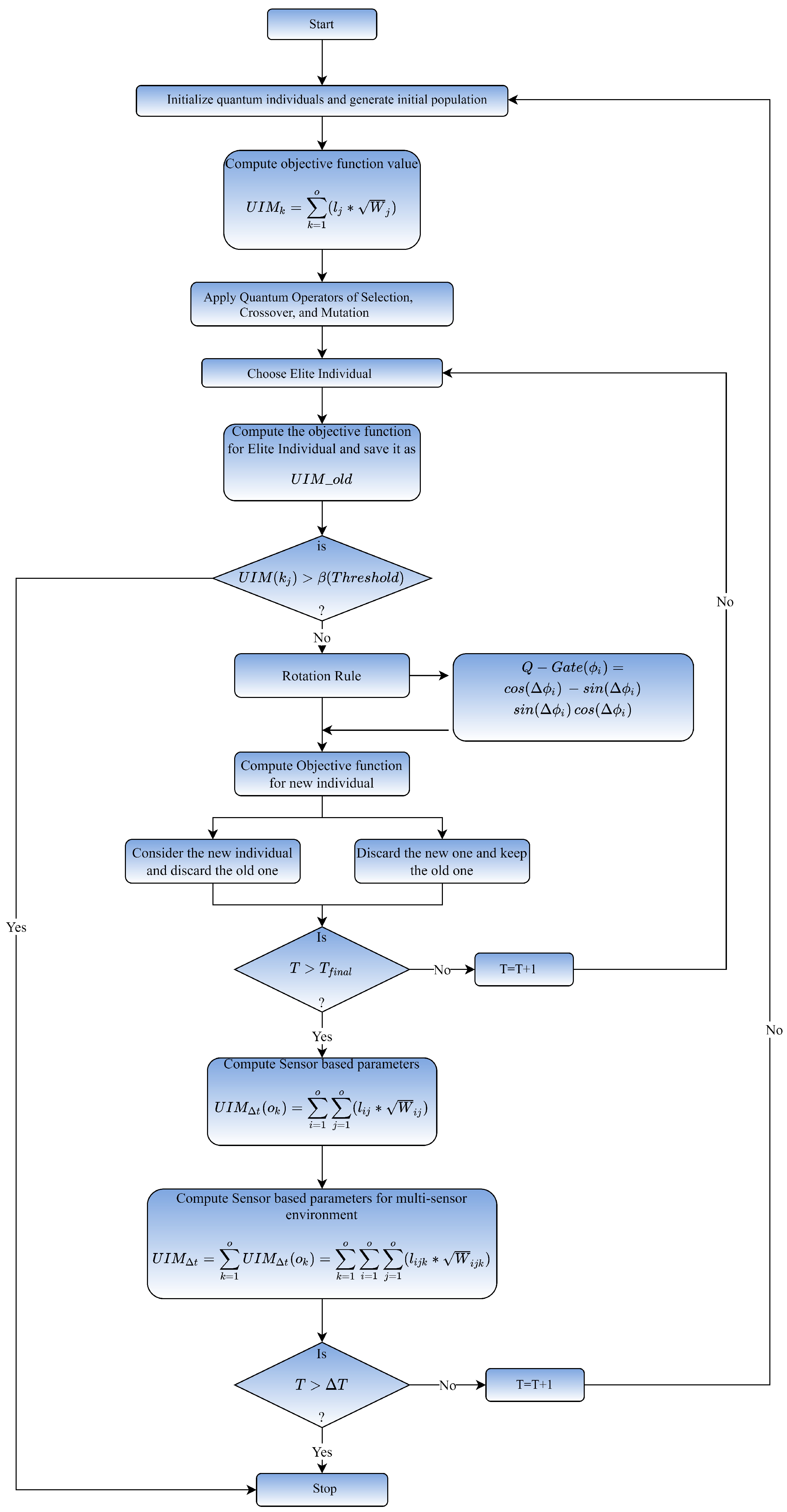
It selects the ideal computational Edge node for a jth task with the shortest execution time, i.e., TD value. Because there are o tasks in the queue for execution, a global search technique is employed to choose the best node for each task so that the overall TD is reduced. TD is inversely connected to the TQ value, as shown in the preceding sections. As a result, the total TS value is maximized at the same time as the overall minimal total TS value is reached. Furthermore, the best execution time for n Edge nodes will be determined. A comprehensive technique of QCO is depicted in Figure 6. Figure 7 shows the comprehensive flowchart of the proposed technique.
Local and global search can determine the TQ of distributed Edge Computing environments in a specific temporal frame t based on overall execution time. Furthermore, a mathematical illustration based on the suggested mechanism is presented ahead to explain the deployment of the QCi procedure.
∀ l = 1 to o,
∀ k = 1 to o,
Repeat
For Minimal Completion Time (ol),
uk → Map(ol)
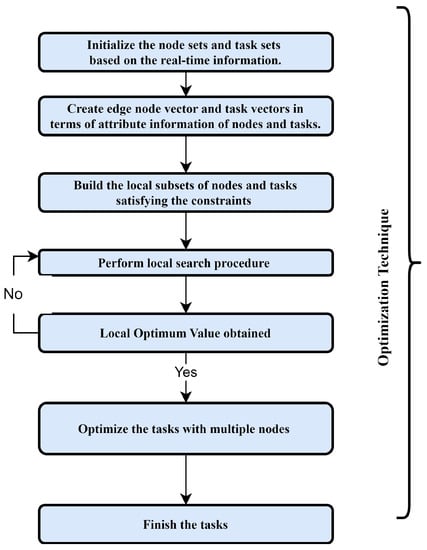
Figure 6.
Flowchart of the proposed technique.
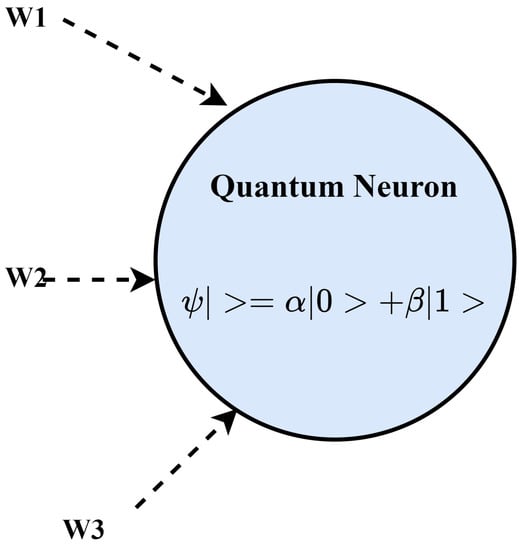
Figure 7.
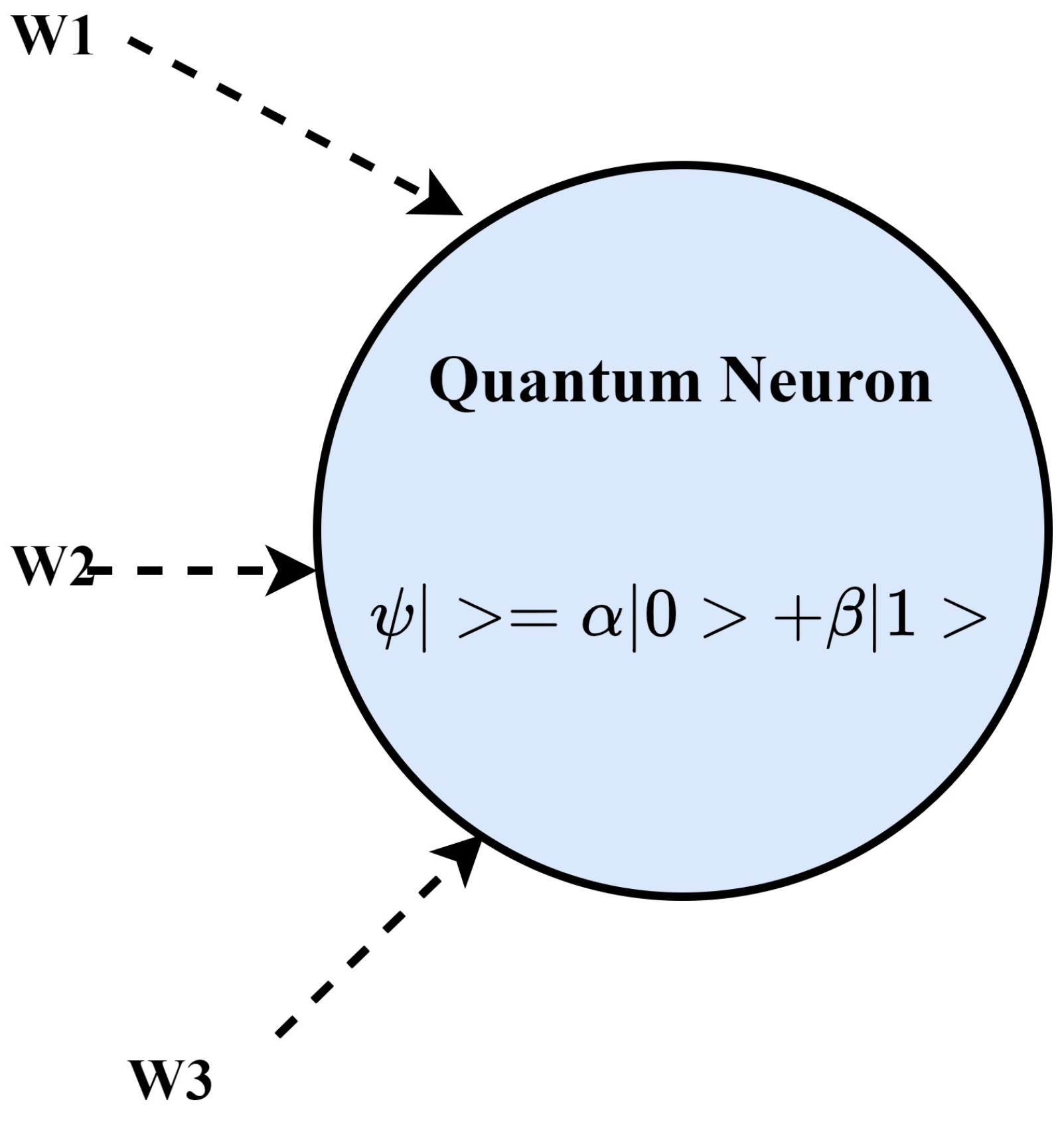
Quantum Neuron (W1, W2, W3 are the input weights).
4.2.4. Mathematical Example
Three computational nodes P(a), P(b), and P(c) are evaluated with hardware settings as presented in Table 4. As indicated in Table 5, three tasks X, Y, and Z are selected for the task set, each with different execution requirements. These tasks are considered to be created independently by scattered IoT devices with varying execution requirements. It is worth noting that just the hardware requirements are taken in this example. Other execution characteristics such as network slowness and regional topology are not considered. The general goal is to assign these three tasks (X, Y, and Z) to specific computing nodes in such a way that overall execution time is reduced while throughput is increased. In other words, a given problem is converted to a classical optimization problem, and each task is mapped to a specific Edge node using the QCi procedure. Formulation of Qubit Individual for computational node P(a) is first accomplished with specified heterogeneous task execution parameter values. Mathematically,

Table 4.
Computation Node Parameters (mParameter = ).

Table 5.
Task Parameters(mParameter = ).
The qubit population for TAP is formed and expressed as follows based on qubit people.
Qubit Population = Qubit Individual (O(a)), Qubit Individual (O(b)), Qubit Individual (O(c))
The Computation Index Measure (CIM) is calculated based on the time it takes for each task to complete. In other words, the higher a task’s CIM value is concerning a computational node, the more probable it is that is becomes allocated to that node. Each task’s qubit representation is developed and presented ahead, based on the task execution requirements listed in Table 5.
In quantum format, the aforementioned depiction efficiently displays various task requirements. As a result, the CIM value is optimally assessed for each of the three tasks. Each task is compared to the qubit population of Edge nodes in the local process. The calculation of CIM values for all Edge nodes is critical since the qubit population reflects the full computational state of the Edge Computing architecture. It is worth noting, however, that in the current example, only one task may be assigned to each node. CIM for task X with computational nodes P(a), P(b), and P(c) may be calculated as follows.
where indicates the probability of assigning a task to a specific computing node. Similarly, CIM values for tasks Y and Z are evaluated.
The following equation will be used to schedule Task X to an Edge node j.
L is the normalization constant, with L equal to +1 if UIM > 1 and L equal to −1 if UIM <1. Allocation will be conducted in the same way for Task Y and Task Z. UIM ∗ CIM values for Node P(a) are calculated based on these assessments for various tasks. Node P(a) will be allocated to a certain task for maximum value. Similarly, values for Node P(b) and Node P(c) are calculated, and tasks are assigned accordingly. For P(a), the CIM value is given by 0.19, and values corresponding to UIMxa are given by −0.51, UIMya is given by −0.31 and UIMza is given by 0.11. Let’s suppose, at time instance t2, the Edge node P(a) has modified RAM to 300 MB. Henceforth, at t2 time instance, the modified quantum bit is estimated by implementing mutation and crossover operation. Therefore, modified P(a) (depicted by P’(a)) can be represented as (0.22, 0.31, 0.59). Henceforth, updated P’(a) is presented in quantum formulation as
Moreover, modified UIM will be utilized in temporal instance t2 for allocating tasks. Furthermore, based on the aforementioned computations, UIM ∗ CIM values are obtained for P(a) concerning task(X), task(Y), and task(X). For the maximum value, P’(a) will be assigned to the corresponding task. Likewise, P(b) and P(c) are computed and allocations of tasks are performed.
Maximum (UIMj ∗ (CIMX)L)
4.3. Quantum Neural Network (QNN)
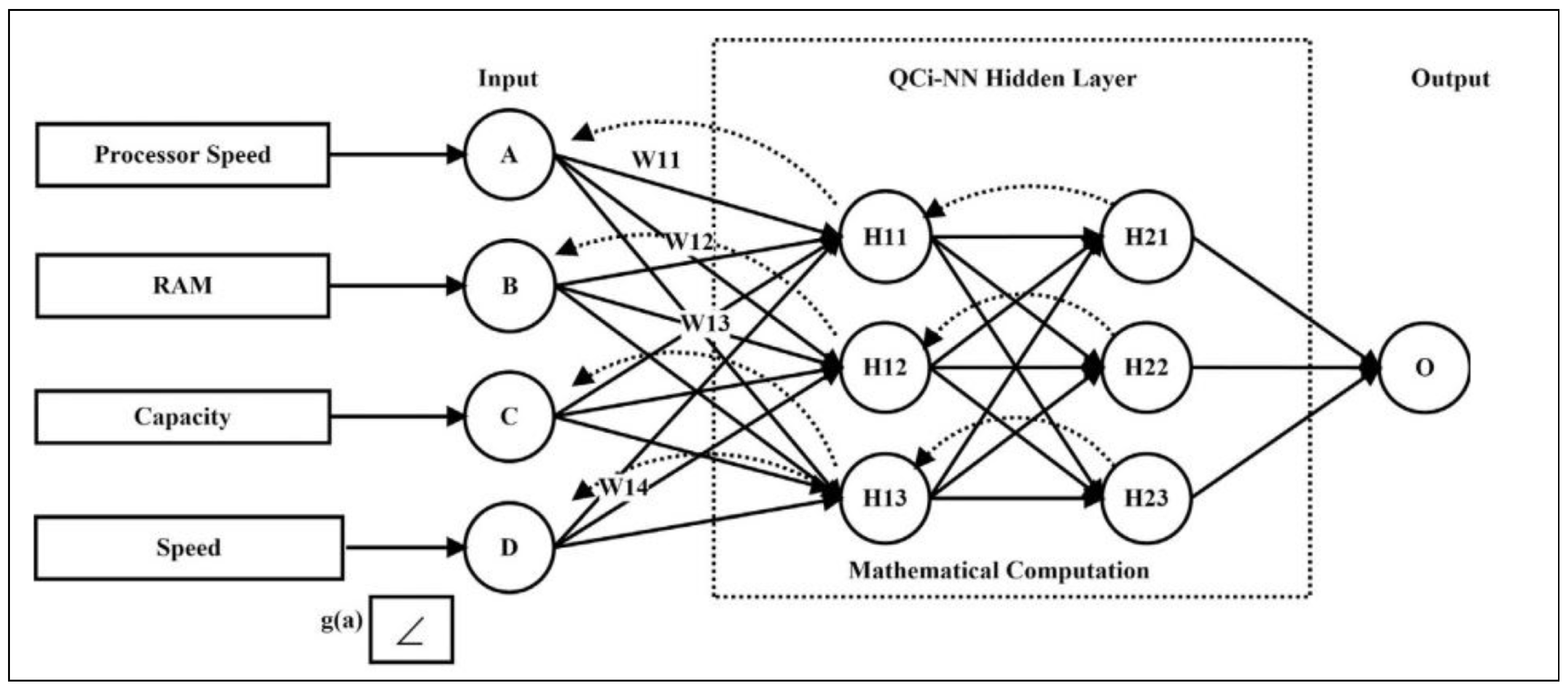
A novel QC-Neural Network (QNN) model for Task Allocation Prediction is provided in the current section. Neural Network Models are predictive techniques that are utilized in a variety of IoT applications to enable predictive decision-making. These probabilistic models are made up of neurons and associated weights, which are computed using sophisticated mathematical computations. The current study focuses on using a quantized version of NN known as a quantum NN. The [46] presents an in-depth analysis of the quantum neuron. W1, W2, and W3 are the corresponding weights applied to each parameter by a domain expert in Figure 8, which shows an overview of the quantum neuron. QNN is employed in the current scenario to forecast the best computational Edge node for task assignment based on probabilistic data. In applications with a dynamic task in a dispersed context, such prediction enhances dependability and precision [47]. For instance, in the e-commerce business, internet traffic might be directed to a specialized Edge-node server for efficient analysis and service provisioning. Monitoring, Learning, and Predicting are the three steps of QNN. The task execution requirements are saved in the temporal database during the Monitoring step. The learning step specifies how the current task will behave based on previous data. Finally, the QNN model and temporal database are used to predict the suitable computational Edge node. Each of the 3 steps has been thoroughly specified ahead.
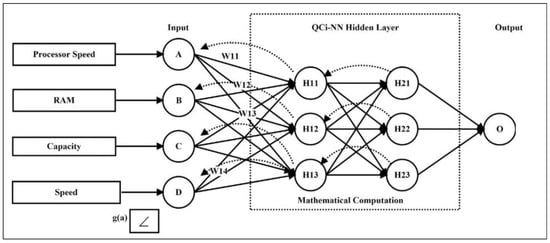
Figure 8.
QNN Model.
4.3.1. Monitoring
QNN monitors the job assignment technique and keeps the outcomes in a temporal database. Each parameter is given probability weights in the present situation. QNN is illustrated in great detail in Figure 9. Depending on the weights you supply, various jobs will be allocated to the specified computational node (pre-fixed by domain experts). These assignments are monitored and kept using a temporal database.
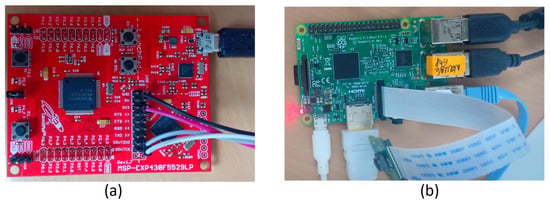
Figure 9.
(a) MSP-EXP430F5529LP; (b) Raspberry Piv3.
4.3.2. Learning
Probabilistic values of quantum states are used at this stage in the supplied system to assess the performance of tasks given to computing nodes. Task behavior incorporates TAP-related data such as arrival time, capacity requirements, and execution time. In addition, for the sake of uniformity, some standards are set up as well. When a job is given to a certain server, that server’s information about the job is kept in the temporal database. Moreover, the back propagation technique is used in the proposed model to enhance overall accuracy [47]. Probabilistic prediction functions are used to accurately forecast a future Edge node based on existing allocations. The learning rule is as follows;
4.3.3. Prediction
The final level of QNN is temporal prediction. This stage involves determining the computing node based on probabilistic quantum values, temporal behavior, and database information. When a task is issued by an IoT device after the system has stabilized, the Edge node is automatically anticipated and assigned using probabilistic predictive values. Let the frequency of Task X, Task Y, and Task Z be o1, o2, and o3, respectively, in the context of the previous scenario. Then, for Task X, let the temporal database contain the frequency of Task X’s allocation information as o1a (X is assigned to node a), o1b (X is assigned to node b), and o1c (X is assigned to node c). The likelihood of Task X being assigned to nodes a, b, and c will then be expressed as P(task(x)/a), P(task(x)/b), and P(task(x)/c).
Similarly, P(task(y)/a) = , P(task(y)/b) = , P(task(y)/c) = , P(task(z)/a) = , P(task(z)/b) = , P(task(z)/c) =
5. Implementation Analysis
The current section presents a statistical examination of the proposed system by distributing it across a large number of tasks. There are two basic phases in the mechanism depicted. The suggested system can calculate the temporal delay for task assignment to the best Edge node in the first stage. In the second stage, QNN is utilized to forecast the most likely Edge node for task allocation to attain the best results. The experimental simulation is used to identify the following elements based on these factors.
- 1.
- In the simulation environment, assess the temporal delay for task execution.
- 2.
- Determine the suggested QNN model’s prediction efficiency statistically.
- 3.
- Determine the overall system’s stability for a varying number of tasks.
5.1. Simulation Environment
iFogSim (Source:https://github.com/Cloudslab/iFogSim, accessed on 28 September 2022) provides the simulator toolbox for experimental implementation. It allows for accurate modeling of Edge nodes and IoT devices by fine-tuning computation, communication, and data storage capabilities. Specifically, it includes;
- 1.
- The number of computer cores and respective CPU speeds.
- 2.
- Bandwidth on the network for the matching transmission rate.
- 3.
- The amount of RAM available for task storage. The simulation environment for heterogeneous Edge nodes is created in the following ways
- (a)
- The Edge Computing nodes are linked by a high-speed, dependable inter-network.
- (b)
- Each Edge node does the operation in a parallel manner.
- (c)
- Each Edge node is capable of flawless inter-node communication.
- (d)
- On the Edge node, task execution is non-preemptive.
Intel Core-i7 computer with 3.25 GHz dual-core CPU and 32 GB RAM was utilized for experimental simulation. Edge nodes are made up of several Raspberry Pi modules, a task allocation module called the MSP-EXP430F5529LP, and a network connection module of ZigBee. Raspberry Pi has been used in the experimental simulation as it is one of the most effective hardware for simulation [48]. Edge nodes come in groups of 10, each having a processing capacity of 3–4 G cycles/s and computational intensity of 400 cycles/bit. The link bandwidth is around 200 MHz. Edge nodes are set up identically to test the performance of the proposed method. The hardware used for task allocation and execution is shown in Figure 10. Video recording (mp4 format), Textual data (text format), Image capture (jpeg and jpg forms), and audio recording (mp3 format) are all part of the task set for environmental monitoring. Each task’s data size varies between 4 and 41 MB. 3 separate task allocation methods are explored for reference models: Round Robin (RR), Minimal Completion Time (MCT), and Min–Max (MM). It is crucial to notice that just the allocation technique is changed, while the rest of the model remains the same.
Figure 10.
(a) iFogSim Header Files (b) Execution Time Calculation.
5.2. Temporal Delay
As previously stated, the tasks created are diverse because of the varied data sizes. For successful real-time execution, these diverse tasks are distributed to Edge nodes using a task allocator. The current study assesses the temporal delay for overall execution time to estimate the efficiency of the suggested model. In particular, temporal efficacy is concerned with determining the time delay between task initiation and task execution. Temporal Delay is calculated using the following formula.
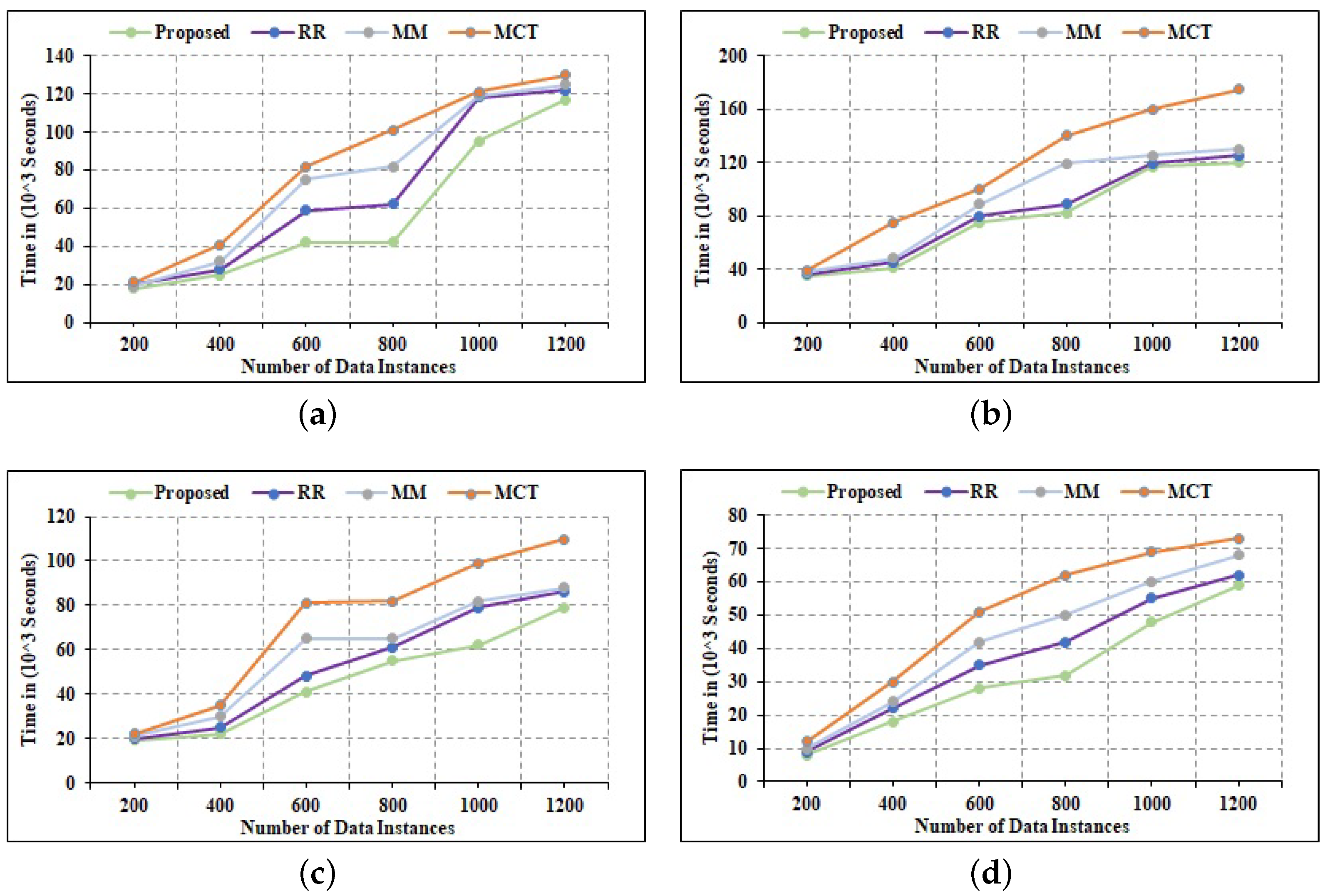
where Delay is the task execution delay for the task, Texecuted is the time when the computing node has completed the task, and Toriginated is the time when the task was created. The source code for the vital temporal delay computation is depicted in Figure 11. The number of tasks for each simulation was set to 200, 400, 600, 800, 1000, and 1200, correspondingly. Each simulation was run 20 times and the results were averaged. As can be observed from the findings in Figure 12, the suggested allocation approach is capable of completing all tasks in the shortest amount of time when compared to existing task allocation algorithms. Furthermore, when the number of heterogeneous tasks created grows, the suggested approach can successfully outperform previous allocation techniques. A comprehensive examination of the results is discussed ahead.
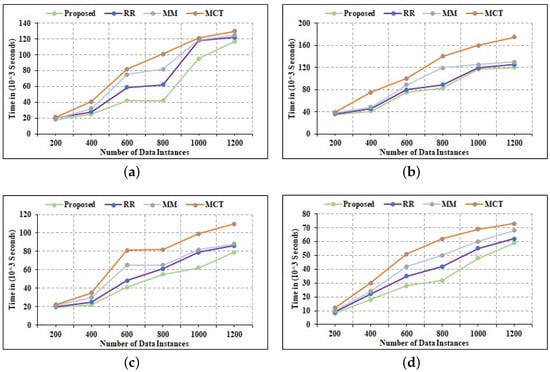
Figure 11.
Comparative Analysis of Temporal Delay Efficiency. (a) 6 Edge Nodes; (b) 10 Edge Nodes; (c) 14 Edge Nodes; (d) 20 Edge Nodes.
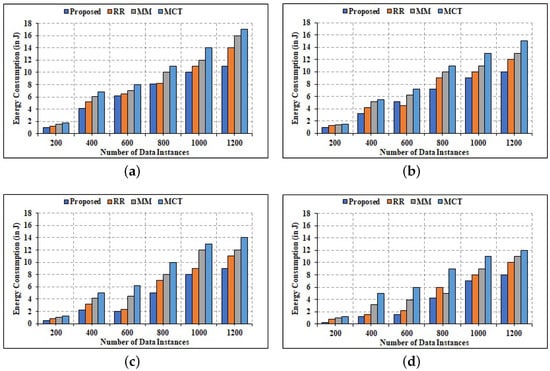
Figure 12.
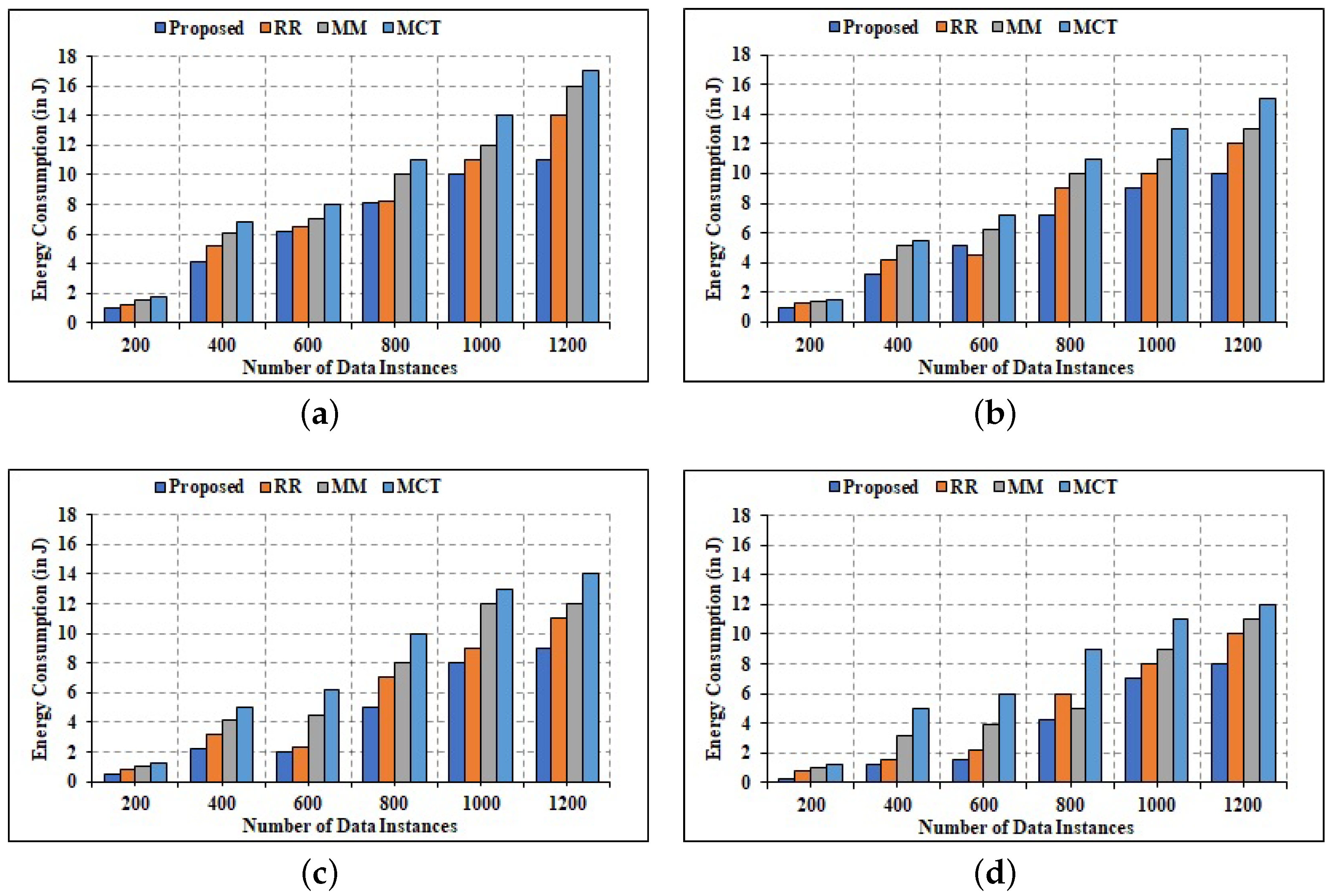
Comparative Analysis of Energy Efficiency. (a) 6 Edge Nodes; (b) 10 Edge Nodes; (c) 14 Edge Nodes; (d) 20 Edge Nodes.
Results
- 1.
- The findings with 6 Edge nodes are shown in Figure 12a. When averaging across a large number of tasks, the suggested approach can complete tasks in 96.24 s, compared to 105.36 s for RR, 122.36 s for MM, and 141.56 s for MCT.
- 2.
- When the number of Edge nodes is raised to 10, as shown in Figure 12b, the average temporal delay for the proposed strategy approaches 52.23 s, compared to 70.34 s for RR, 85.23 s for MM, and 90.25 s for MCT.
- 3.
- When the number of Edge nodes is raised to 14, Figure 12c displays the mean execution time for the suggested approach. It reveals that the overall execution latency is 39.12 s, which is better than 44.81 s for RR, 47.20 s for MM, and 49.26 s for MCT.
- 4.
- The results of a simulation with 20 Edge nodes are shown in Figure 12d. The average execution latency in this scenario is 20.15 s, which is better than the 30.15 s of RR, 36.78 s of MM, and 39.14 s of MCT. As a result, it can be inferred that, based on comparative analysis with state-of-the-art allocation strategies, the suggested algorithm is very efficient on a temporal scale.
5.3. Utilization of Energy
Figure 12 compares the results of energy consumption simulations for several allocation categories. Because Edge nodes are taken into account during computing, the aggregation of all Edge nodes is shown. The energy usage of 6 Edge nodes is shown in Figure 13a. Moreover, the energy consumption of 10, 14, and 20 Edge nodes is depicted in Figure 13b–d. It is apparent that as the number of tasks grows, so does the amount of energy consumed. It is because as the number of tasks rises, so does the execution delay, causing Edge nodes to use increased energy receiving, and executing tasks. Because each Edge node’s power is fixed at 2.1 W, the energy consumption is solely determined by the task completion. As shown in Figure 13, the suggested allocation criterion consumes the least amount of energy when compared to other allocation strategies since all tasks are completed in less time. It can be deduced with an increased number of tasks to 1200, the energy utilization increases at the same time. In addition, when the number of Edge nodes increases from 6 to 20, the amount of energy consumed decreases. This is because the time it takes to complete a task is reduced. As a result, it can be inferred that the suggested allocation criterion uses the least amount of energy when compared to other methods.
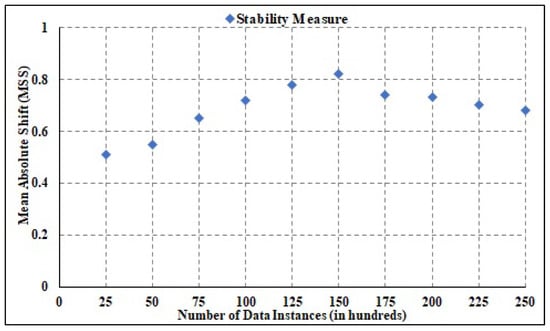
Figure 13.
Stability Analysis.
5.4. Prediction Efficacy
Prediction efficiency is concerned with the real-time analysis of tasks for Edge node allocation. Because heterogeneous tasks are created in varying numbers of 200, 400, 600, 800, 1000, and 1200, determining the accuracy of the suggested prediction model is critical. Furthermore, when a probabilistic model-based prediction is used, the confidence level is set at 98% with a normalizing constant of 1.92. The statistical range of probabilistic certainty is defined by the confidence interval, which is a statistic interval. Furthermore, because the number of actions varies, only the end outcomes are presented for prediction. It is crucial to note, however, that these tasks are created before the prediction analysis. In the current, a comparative examination of the suggested model’s prediction efficiency is presented. Numerous performance factors are analyzed to determine the statistical analysis including Sensitivity, Coverage, Specificity, Precision, Root Mean Square Error, Mean Absolute Error, Relative Absolute Error, and Root Relative Squared Error.
Results
Table 6 shows the computed findings based on the experimental simulations. Because the confidence interval is linked to error rates, the relevant range of errors is shown. These findings are compared to existing state-of-the-art prediction models, such as Support Vector Machine (SVM), Bayesian Belief Networks (BBN), and conventional Artificial Neural Networks (cANN), to assess the usefulness of the proposed model. However, it should be noted that just the prediction model is updated during the assessment, and the rest of the system stays unchanged. Sensitivity (89.48%), Specificity (90.78%), Precision (94.25%), and Coverage (96.66%) are all enhanced performance measures registered for the proposed QNN approach. Moreover, low error rates of Mean Absolute Error (2.23%), Root Mean Square Error (1.23%), Relative Absolute Error (3.34%), and Root Relative Squared Error (2.56%) were registered. In comparison to these results, SVM, BBN, and cANN had lower performance values for Sensitivity (80.23%, 85.31%, 84.51%), Specificity (89.12%, 88.12%, 89.21%), Precision (87.25%, 90.12%, 89.01%), Coverage (90.55%, 90.25%, 91.54%), Mean Absolute Error (3.55%, 3.85%, 3.59%). Based on these findings, it can be stated that the proposed system is very effective at predicting the best Edge node for a given task based on node availability.

Table 6.
Statistical Results for Prediction Efficacy.
5.5. System Stability
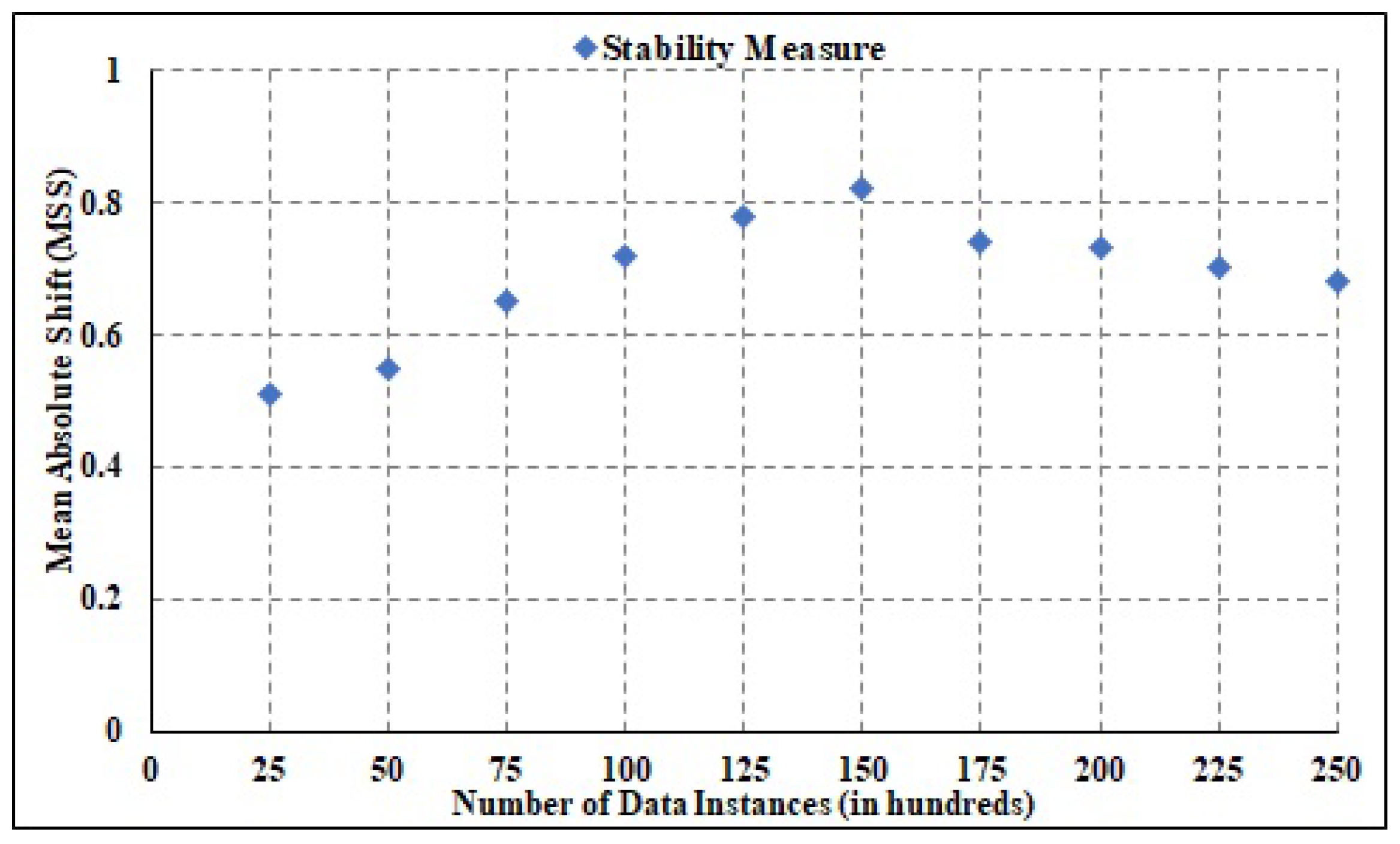
The overall stability for the presented approach across heterogeneous tasks is determined by Overall System Stability (OSS). Specifically, OSS gives an estimate for overall system stability estimation. Mean Absolute Shift (MAS) is the unit of measurement for OSS. The value of MAS is estimated in (0,1), with 0 indicating reduced system stability and 1 indicating elevated system stability. The graphical depiction of the OSS values for various numbers of tasks is shown in Figure 13. In addition, to ensure system stability, tasks were raised to 25,000. The MAS value ranges from 0.51 to 0.82 for a diverse set of tasks, with an average of 0.61. It shows that the suggested approach is extremely stable and effective in allocating resources. Moreover, it is inferred that the described approach is extremely stable.
5.6. Comparative Analysis
The current section compares and contrasts the proposed QCi predictive task allocation model with existing research in the QCi domain. For the comparison analysis, four state-of-the-art research works are studied including [23,49,50,51]. Table 7 shows a summary of the unique traits that the presented work shares with the comparative works. For the sake of comparison, 7 important parameters are chosen. Furthermore, these parameters indicate innovation in the proposed QNN model in terms of QC-Approach, Major Contribution, Domain of Research, Mathematical Assessment, Suitability for Edge Computing, Temporal Assessment, and Predictive Behavior. Each parameter has been thoroughly discussed ahead.

Table 7.
State-of-the-Art Comparison Analysis (1 Yes, 0 No).
- 1.
- Domain of Research (DoR): DoR specifies the research domain in which the authors conducted their respective research. In other words, it gives a high-level summary of the study model.
- 2.
- Significant contribution It establishes the unique contribution made by the authors in the comparative research. Furthermore, it gives a quick review of the performance assessment.
- 3.
- QC-Approach: It establishes the QCi technique’s suitability for the optimal scheduler. Specifically, the use of QCO in the given research of task allocation in distributed architectures such as Edge-Cloud Computing is a unique technique and hence an important parameter for comparison analysis.
- 4.
- Temporal Assessment: It describes the suggested research’s behavior in terms of optimal task distribution across distributed Edge nodes in real-time. Specifically, it represents the use of specific features for resource allocation to provide outcomes with the least amount of delay.
- 5.
- Mathematical Assessment: The numerical analysis of the suggested approach for prediction purposes is provided through mathematical assessment. Because the current QCO approach is based on probability, numerical analysis is required.
- 6.
- Edge Computing: It establishes the use of Edge Computing-based applications. Specifically, the usefulness of task allocation in settings based on the Edge Computing platform is indicated by the attribute.
- 7.
- Prediction: It is a vital factor to consider when comparing two studies. It specifically gives information on the prediction features of numerous studies that are being compared.
6. Conclusions
The current research addresses issues that must be overcome to achieve effective Edge-based task allocation in real time. Specifically, (a) an Edge-based model that combines Task Allocation Parameters (TAPs) of IoT tasks is presented in the current study; (b) In an Edge Computing environment, a QCi technique is provided for provisioning optimum task allocation; (c) Qubit format of TAPs allows for the most accurate evaluation of the Edge node’s probabilistic Utilization Index Measure (UIM) and Computation Index Measure (CIM); (d) QNN is shown to identify the Edge node for task execution with the least amount of time delay, energy consumption, and throughput. Different simulations were run utilizing the ifogSim simulation toolbox for validation reasons, and the results were compared to state-of-the-art task allocation strategies. Based on the obtained findings, it can be stated that the provided system is extremely efficient and successful at predicting the best node for Edge Computing platforms. Specifically, improvement of 5.02% was registered for prediction efficiency. Similarly, an error reduction of 2.03% was acquired in comparison to state-of-the-art techniques. Several tangential works can be found for futuristic study directions. Because Edge Computing is elevating, concerns such as network protection, particularly in dispersed systems can be a major challenge. Furthermore, network bandwidth and resource allocation are two major areas of open research for Edge Computing.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, T.A.A. and U.T.; methodology, T.A.A. and I.U.; software, T.A.A. and F.D.; validation, T.A.A., U.T., F.D. and I.U.; formal analysis, T.A.A. and F.D.; investigation, U.T. and I.U.; resources, I.U.; data curation, T.A.A.; writing—original draft preparation, T.A.A., U.T., F.D. and I.U.; writing—review and editing, T.A.A., U.T., F.D. and I.U.; visualization, I.U.; supervision, T.A.A.; project administration, U.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The authors extend their appreciation to the Deputyship for Research and Innovation, Ministry of Education in Saudi Arabia for funding this research work through the project number (IF2-PSAU-2022/01/22636).
Data Availability Statement
Data sharing does not apply to this article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest in this area.
References
- Chegini, H.; Naha, R.K.; Mahanti, A.; Thulasiraman, P. Process Automation in an IoT–Fog–Cloud Ecosystem: A Survey and Taxonomy. IoT 2021, 2, 92–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghazal, T.M.; Hasan, M.K.; Alshurideh, M.T.; Alzoubi, H.M.; Ahmad, M.; Akbar, S.S.; Al Kurdi, B.; Akour, I.A. IoT for smart cities: Machine learning approaches in smart healthcare—A review. Future Internet 2021, 13, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajjaji, Y.; Boulila, W.; Farah, I.R.; Romdhani, I.; Hussain, A. Big data and IoT-based applications in smart environments: A systematic review. Comput. Sci. Rev. 2021, 39, 100318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Ran, X. Deep Learning With Edge Computing: A Review. Proc. IEEE 2019, 107, 1655–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakarami, A.; Ghobaei-Arani, M.; Shahidinejad, A. A survey on the computation offloading approaches in mobile Edge computing: A machine learning-based perspective. Comput. Netw. 2020, 182, 107496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, N.; Yau, K.L.A.; Wu, C. Edge Computing in 5G: A review. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 127276–127289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siriwardhana, Y.; Porambage, P.; Liyanage, M.; Ylianttila, M. A survey on mobile augmented reality with 5G mobile Edge Computing: Architectures, applications, and technical aspects. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2021, 23, 1160–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portilla, J.; Mujica, G.; Lee, J.S.; Riesgo, T. The extreme Edge at the bottom of the Internet of Things: A review. IEEE Sens. J. 2019, 19, 3179–3190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Zhang, D.; He, S.; Zhang, Y.; Li, T. A survey on end-Edge-Cloud orchestrated network computing paradigms: Transparent computing, mobile Edge Computing, fog computing, and Cloudlet. ACM Comput. Surv. (CSUR) 2019, 52, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyongyosi, L.; Imre, S. A survey on quantum computing technology. Comput. Sci. Rev. 2019, 31, 51–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatia, M.; Sood, S.K. Quantum computing-inspired network optimization for IoT applications. IEEE Internet Things J. 2020, 7, 5590–5598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manocha, A.; Bhatia, M.; Kumar, G. Dew computing-inspired health-meteorological factor analysis for early prediction of bronchial asthma. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 2021, 179, 102995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatia, M.; Sood, S.K.; Kaur, S. Quantum-based predictive fog scheduler for IoT applications. Comput. Ind. 2019, 111, 51–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatia, M.; Sood, S.K.; Kaur, S. Quantumized approach of load scheduling in fog computing environment for IoT applications. Computing 2020, 102, 1097–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manocha, A.; Bhatia, M. A novel deep fusion strategy for COVID-19 prediction using multimodality approach. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2022, 103, 108274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, K.; Kaur, N.; Kaur, K. A novel context and load-aware family genetic algorithm based task scheduling in Cloud Computing. In Data Engineering and Intelligent Computing; Springer: Singapore, 2018; pp. 521–531. [Google Scholar]
- Chawla, A.; Ghumman, N.S. Package-based approach for load balancing in Cloud Computing. In Big Data Analytics; Springer: Singapore, 2018; pp. 71–77. [Google Scholar]
- Capota, E.A.; Stangaciu, C.S.; Micea, M.V.; Curiac, D.I. Towards mixed criticality task scheduling in cyber physical systems: Challenges and perspectives. J. Syst. Softw. 2019, 156, 204–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, A.; Davis, R. Mixed Criticality Systems—A Review; Tech. Rep.; Department of Computer Science, University of York: York, UK, 2013; pp. 1–69. [Google Scholar]
- Belgaum, M.R.; Soomro, S.; Alansari, Z.; Alam, M. Cloud service ranking using checkpoint-based load balancing in real-time scheduling of Cloud Computing. In Progress in Advanced Computing and Intelligent Engineering; Springer: Singapore, 2018; pp. 667–676. [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava, S.; Singh, S. Performance optimization in Cloud Computing through Cloud partitioning-based load balancing. In Advances in Computer and Computational Sciences; Springer: Singapore, 2018; pp. 301–311. [Google Scholar]
- Adhikari, M.; Amgoth, T. Heuristic-based load-balancing algorithm for IaaS Cloud. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2018, 81, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Li, K.; Li, K. An intermediate data placement algorithm for load balancing in spark computing environment. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2018, 78, 287–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahdi-Pashaki, S.; Teymourian, E.; Tavakkoli-Moghaddam, R. New approach based on group technology for the consolidation problem in Cloud Computing-mathematical model and genetic algorithm. Comput. Appl. Math. 2018, 37, 693–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, A.; Wüstefeld, K.; Weichert, F. A Data-Centric Augmentation Approach for Disturbed Sensor Image Segmentation. J. Imaging 2021, 7, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamali, A.J.U.; Mondal, R.R. Modified Dynamically-updated Weighted Opportunity Cost Based Algorithm for Unbalanced Transportation Problem. J. Eng. Sci. 2021, 12, 119–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mala, K.; Priyadharshini, S.; Madhumathi, R. Resource Allocation in Cloud Using Enhanced Max–Min Algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2021 12th International Conference on Computing Communication and Networking Technologies (ICCCNT), Kharagpur, India, 6–8 July 2021; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Ajmal, M.S.; Iqbal, Z.; Khan, F.Z.; Ahmad, M.; Ahmad, I.; Gupta, B.B. Hybrid ant genetic algorithm for efficient task scheduling in Cloud data centers. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2021, 95, 107419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gershengorn, H.B.; Holt, G.E.; Rezk, A.; Delgado, S.; Shah, N.; Arora, A.; Colucci, L.B.; Mora, B.; Iyengar, R.S.; Lopez, A.; et al. Assessment of disparities associated with a crisis standards of care resource allocation algorithm for patients in 2 US hospitals during the COVID-19 pandemic. JAMA Netw. Open 2021, 4, e214149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Suo, K.; Hodge, J.; Mohandoss, D.P.; Kemp, S. Towards Optimizing Task Scheduling Process in Cloud Environment. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 11th Annual Computing and Communication Workshop and Conference (CCWC), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 January 2021; pp. 0081–0087. [Google Scholar]
- Weiqing, G.; Yanru, C. Task-scheduling algorithm based on improved genetic algorithm in Cloud Computing environment. Recent Adv. Electr. Electron. Eng. (Former. Recent Patents Electr. Electron. Eng. 2021, 14, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Li, K.; Liu, C.; Li, K. Are task mappings with the highest frequency of servers so good A case study on Heterogeneous Earliest Finish Time (HEFT) algorithm. J. Syst. Archit. 2021, 121, 102311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhadi Zavleh, A.; Bakhshi, H. Resource allocation in sparse code multiple access-based systems for Cloud-radio access network in 5G networks. Trans. Emerg. Telecommun. Technol. 2021, 32, e4153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran-Dang, H.; Kim, D.S. FRATO: Fog resource based adaptive task offloading for delay-minimizing IoT service provisioning. IEEE Trans. Parallel Distrib. Syst. 2021, 32, 2491–2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centorrino, V.; Bilotta, G.; Cappello, A.; Ganci, G.; Corradino, C.; Del Negro, C. A particle swarm optimization–based heuristic to optimize the configuration of artificial barriers for the mitigation of lava flow risk. Environ. Model. Softw. 2021, 139, 105023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.H.; Ali, M.H. A Priority-Based Deficit Weighted Round Robin Queuing for Dynamic Bandwidth Allocation Algorithm in Gigabit Passive Optical Network. In Intelligent Energy Management Technologies; Springer: Singapore, 2021; pp. 65–71. [Google Scholar]
- Truong, T.Q.; Zhang, J.; Li, Z.; Wang, L. Integrated Herfindahl–Hirschman Index, Compromise Programming, and ε-Constraint Method For Multicriteria Performance-Based Transportation Budget Allocation. Transp. Res. Rec. 2021, 2675, 468–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giuliari, G.; Wyss, M.; Legner, M.; Perrig, A. GMA: A Pareto Optimal Distributed Resource-Allocation Algorithm. In Proceedings of the International Colloquium on Structural Information and Communication Complexity; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 243–261. [Google Scholar]
- Hosseini Shirvani, M.; Noorian Talouki, R. Bi-objective scheduling algorithm for scientific workflows on Cloud computing platform with makespan and monetary cost minimization approach. Complex Intell. Syst. 2021, 8, 1085–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; He, H.; Yan, H.; Gao, S.; Liu, X.; Zheng, X. Lr-Stream: Using latency and resource aware scheduling to improve latency and throughput for streaming applications. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2021, 114, 243–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spector, L.; Barnum, H.; Bernstein, H.J.; Swamy, N. Quantum computing applications of genetic programming. Adv. Genet. Program. 1999, 3, 135–160. [Google Scholar]
- Henderson, L.J.; Belenchia, A.; Castro-Ruiz, E.; Budroni, C.; Zych, M.; Brukner, Č.; Mann, R.B. Quantum temporal superposition: The case of quantum field theory. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2020, 125, 131602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Chen, Z.; Wang, Y.; Jiao, L.; Xue, Y. A novel distributed quantum-behaved particle swarm optimization. J. Optim. 2017, 2017, 4685923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.; Xia, S.; Li, Q.; Chen, W.; Fang, W. Resource pooling in vehicular fog computing. J. Cloud Comput. 2021, 10, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiswarya, S.; Ramesh, K.; Prabha, B.; Sasikumar, S.; Vijayakumar, K. A time optimization model for the Internet of Things-based Healthcare system using Fog computing. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on Innovative Computing, Intelligent Communication and Smart Electrical Systems (ICSES), Chennai, India, 24–25 September 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.Y.; Chen, C.; Chang, C.T.; Shih, L.M. Single-hidden-layer feed-forward quantum neural network based on Grover learning. Neural Netw. 2013, 45, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, T.; Marelli, D.E.; Fu, M.; Lu, R. Accuracy analysis for distributed weighted least-squares estimation in finite steps and loopy networks. Automatica 2018, 97, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatia, M.; Sood, S.K. A comprehensive health assessment framework to facilitate IoT-assisted smart workouts: A predictive healthcare perspective. Comput. Ind. 2017, 92, 50–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghu, G.; Sharma, N.K.; Domanal, S.G.; Reddy, G.R.M. Memory-based load balancing algorithm in structured peer-to-peer system. In Progress in Intelligent Computing Techniques: Theory, Practice, and Applications; Springer: Singapore, 2018; pp. 431–439. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, N.; Shukla, D. Load balancing mechanism using fuzzy row penalty method in Cloud computing environment. In Information and Communication Technology for Sustainable Development; Springer: Singapore, 2018; pp. 365–373. [Google Scholar]
- Puthal, D.; Obaidat, M.S.; Nanda, P.; Prasad, M.; Mohanty, S.P.; Zomaya, A.Y. Secure and sustainable load balancing of Edge data centers in fog computing. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2018, 56, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).