A Complete Procedure for a Constraint-Type Fictitious Time Integration Method to Solve Nonlinear Multi-Dimensional Elliptic Partial Differential Equations
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Nonlinear and Nonhomogeneous Elliptic Equation
2.1. Transformation into a New Evolutional PDE
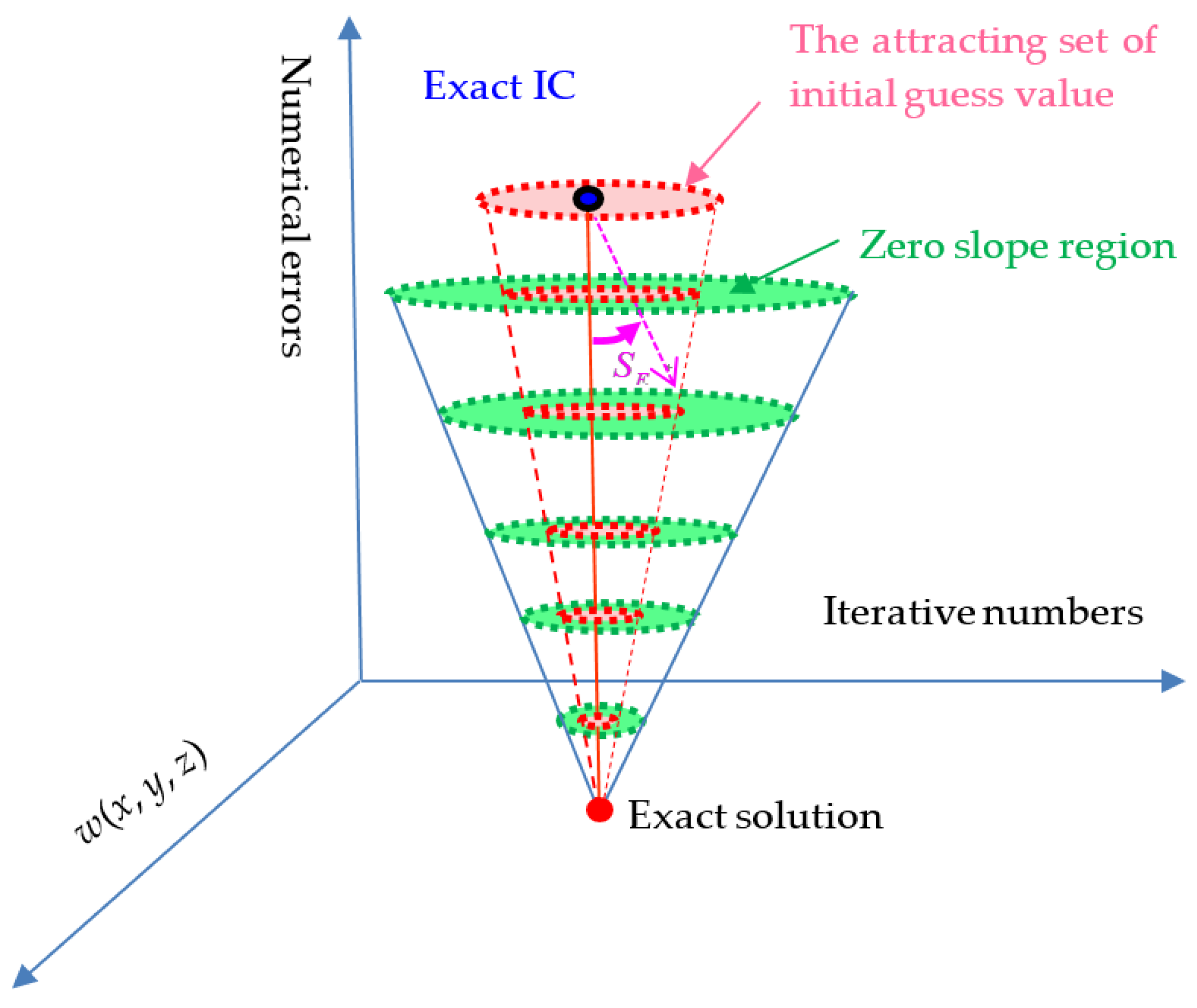
2.2. The Convergence Criterion
2.3. Normalized Initial Guess Value
3. Numerical Examples
3.1. Example 1
3.2. Example 2
3.3. Example 3
3.4. Example 4
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Atluri, S.N.; Zhu, T. A new meshless local Petrov-Galerkin (MLPG) approach in computational mechanics. Comput. Mech. 1998, 22, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, T.; Zhang, J.; Atluri, S.N. A meshless local boundary integral equation (LBIE) method for solving nonlinear problems. Comput. Mech. 1998, 22, 174–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, A.H.D.; Golberg, M.A.; Kansa, E.J.; Zammito, G. Exponential convergence and H-c multiquadric collocation method for partial differential equations. Numer. Meth. Part Differ. Equ. 2003, 19, 571–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.A.; Golberg, M.A.; Muleshkov, A.S.; Li, X. Trefftz methods for time dependent partial differential equations. Comput. Mat. Cont. 2004, 1, 1–38. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, B. A meshless method for the Laplace and biharmonic equations subjected to noisy boundary data. CMES-Comput. Model. Engrg. Sci. 2004, 6, 253–262. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, H.Y.; Li, Z.C.; Cheng, A.H.D. Radial basis collocation methods for elliptic boundary value problems. Comput. Math. Appl. 2005, 50, 289–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.Y.; Chen, J.S. Radial basis collocation method and quasi-Newton iteration for nonlinear elliptic problems. Numer. Meth. Part Differ. Equ. 2008, 24, 991–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.M.; Li, H.H.; Kuo, C.L. The modified collocation Trefftz method and Laplacian decomposition for solving two-dimensional Stokes problems. J. Mar. Sci. Technol.-Taiwan 2011, 19, 522–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.H.; Ouyang, J.; Zhang, L. Element-free characteristic Galerkin method for Burgers’ equation. Eng. Anal. Bound. Elem. 2009, 33, 356–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seydaoğlu, M. A meshless method for Burgers’ equation using multiquadric radial basis functions with a Lie-group integrator. Mathematics 2019, 7, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milewski, S. Combination of the meshless finite difference approach with the Monte Carlo random walk technique for solution of elliptic problems. Comput. Math. Appl. 2018, 76, 854–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colbrook, M.J.; Flyer, N.; Fornberg, B. On the Fokas method for the solution of elliptic problems in both convex and non-convex polygonal domains. J. Comput. Phys. 2018, 374, 996–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezeh, I.P.; Kamoh, N.M. On the numerical solution of second order two-dimensional Laplace equations using the alternating-direction implicit method. J. Phys. Commun. 2020, 4, 105004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.S.; Atluri, S.N. A novel time integration method for solving a large system of non-linear algebraic equations. CMES-Comp. Model. Eng. Sci. 2008, 31, 71–83. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.S. A fictitious time integration method for two-dimensional quasilinear elliptic boundary value problems. CMES-Comp. Model. Eng. Sci. 2008, 33, 179–198. [Google Scholar]
- Ku, C.Y.; Yeih, W.C.; Liu, C.S.; Chi, C.C. Applications of the fictitious time integration method using a new time-like function. CMES-Comp. Model. Eng. Sci. 2009, 43, 173–190. [Google Scholar]
- Tsai, C.C.; Liu, C.S.; Yeih, W.C. Fictitious time integration method of fundamental solutions with Chebyshev polynomials for solving Poisson-type nonlinear PDEs. CMES-Comp. Model. Eng. Sci. 2010, 56, 131–151. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, C.W. A fictitious time integration method for multi-dimensional backward heat conduction problems. CMES-Comp. Model. Eng. Sci. 2010, 19, 285–314. [Google Scholar]
- Ku, C.Y.; Yeih, W.C.; Liu, C.S. Solving non-linear algebraic equations by a scalar Newton-homotopy continuation method. Int. J. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2010, 11, 435–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.S.; Atluri, S.N. Simple “residual-norm” based algorithms, for the solution of a large system of non-linear algebraic equations, which converge faster than the Newton’s method. CMES-Comp. Model. Eng. Sci. 2011, 71, 279–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.W.; Chang, C.M.; Liu, C.S.; Chang, J.R. Application of a manifold-based exponentially convergent algorithm to solve elliptic boundary-value problems. IMA J. Numer. Anal. 2014, 34, 362–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ku, C.Y.; Kuo, C.L.; Fan, C.M.; Liu, C.S.; Guan, P.C. Numerical solution of three-dimensional Laplacian problems using the multiple scale Trefftz method. Eng. Anal. Bound. Elem. 2015, 50, 157–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.W. High order implicit and explicit Lie-group schemes for solving backward heat conduction problems. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2016, 101, 1016–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.W. A highly accurate backward-forward algorithm for multi-dimensional backward heat conduction problems in fictitious time domains. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2018, 120, 499–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.W. Simultaneous determination of the heat source and the initial data by using an explicit Lie-group shooting method. Numer. Heat Tranf. B-Fundam. 2019, 75, 239–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.W.; Liu, C.S.; Chang, Y.S.; Chang, J.R. Constraint type fictitious time integration method to solve non-linear multi-dimensional elliptic partial differential equations. J. Mar. Sci. Technol.-Taiwan 2020, 28, 168–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.S.; Chen, Y.W.; Liu, C.S.; Chang, J.R. A non-iteration solution for solving the backward-in-time two-dimensional Burgers’ equation with a large Reynolds number. J. Mar. Sci. Technol.-Taiwan 2022, 30, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

















Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Y.-W.; Shen, J.-H.; Chang, Y.-S.; Tan, C.-C. A Complete Procedure for a Constraint-Type Fictitious Time Integration Method to Solve Nonlinear Multi-Dimensional Elliptic Partial Differential Equations. Mathematics 2023, 11, 213. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11010213
Chen Y-W, Shen J-H, Chang Y-S, Tan C-C. A Complete Procedure for a Constraint-Type Fictitious Time Integration Method to Solve Nonlinear Multi-Dimensional Elliptic Partial Differential Equations. Mathematics. 2023; 11(1):213. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11010213
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Yung-Wei, Jian-Hung Shen, Yen-Shen Chang, and Ching-Chuan Tan. 2023. "A Complete Procedure for a Constraint-Type Fictitious Time Integration Method to Solve Nonlinear Multi-Dimensional Elliptic Partial Differential Equations" Mathematics 11, no. 1: 213. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11010213
APA StyleChen, Y.-W., Shen, J.-H., Chang, Y.-S., & Tan, C.-C. (2023). A Complete Procedure for a Constraint-Type Fictitious Time Integration Method to Solve Nonlinear Multi-Dimensional Elliptic Partial Differential Equations. Mathematics, 11(1), 213. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11010213






