Stochastic Finite Element Analysis of Plate Structures Considering Spatial Parameter Random Fields
Abstract
:1. Introduction
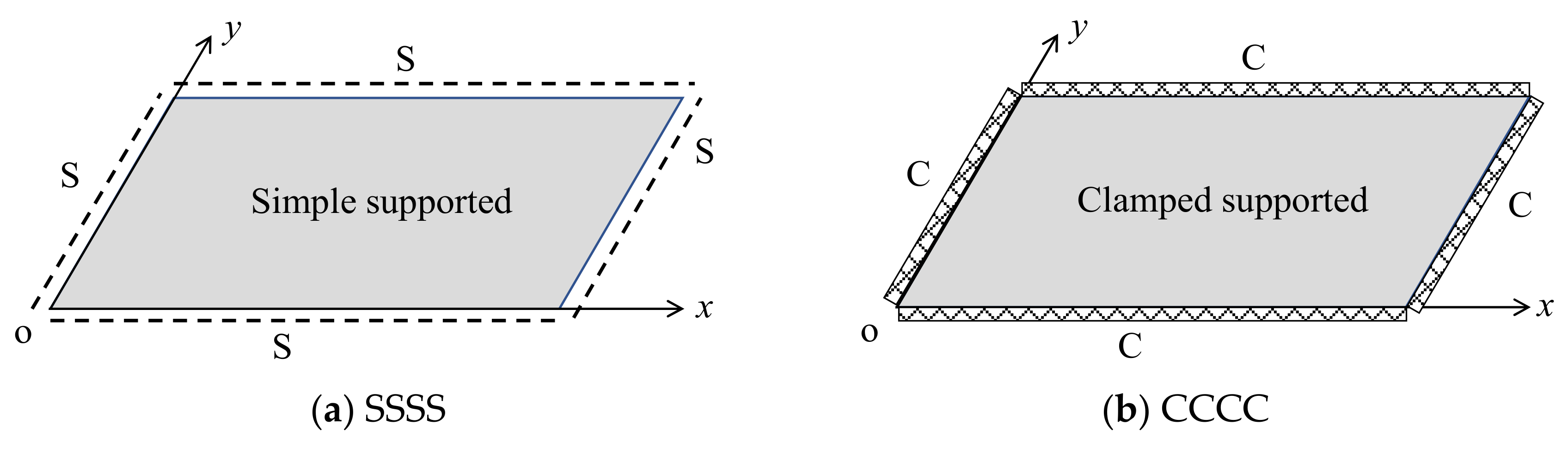
2. FEM of Plate Considering Spatial Parameters
2.1. FEM of Plate Structure
2.2. Mathematical Expression of a Random Field
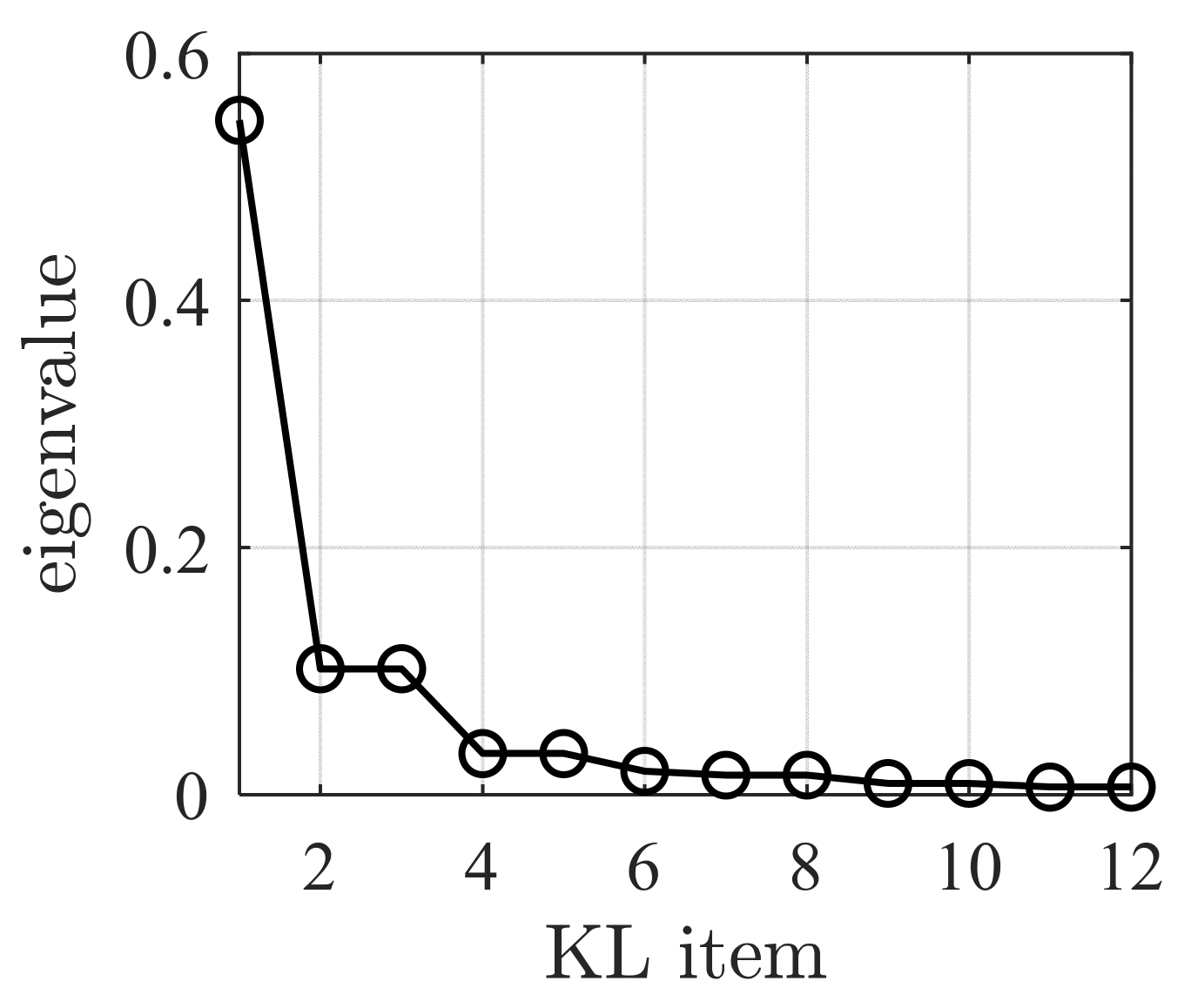
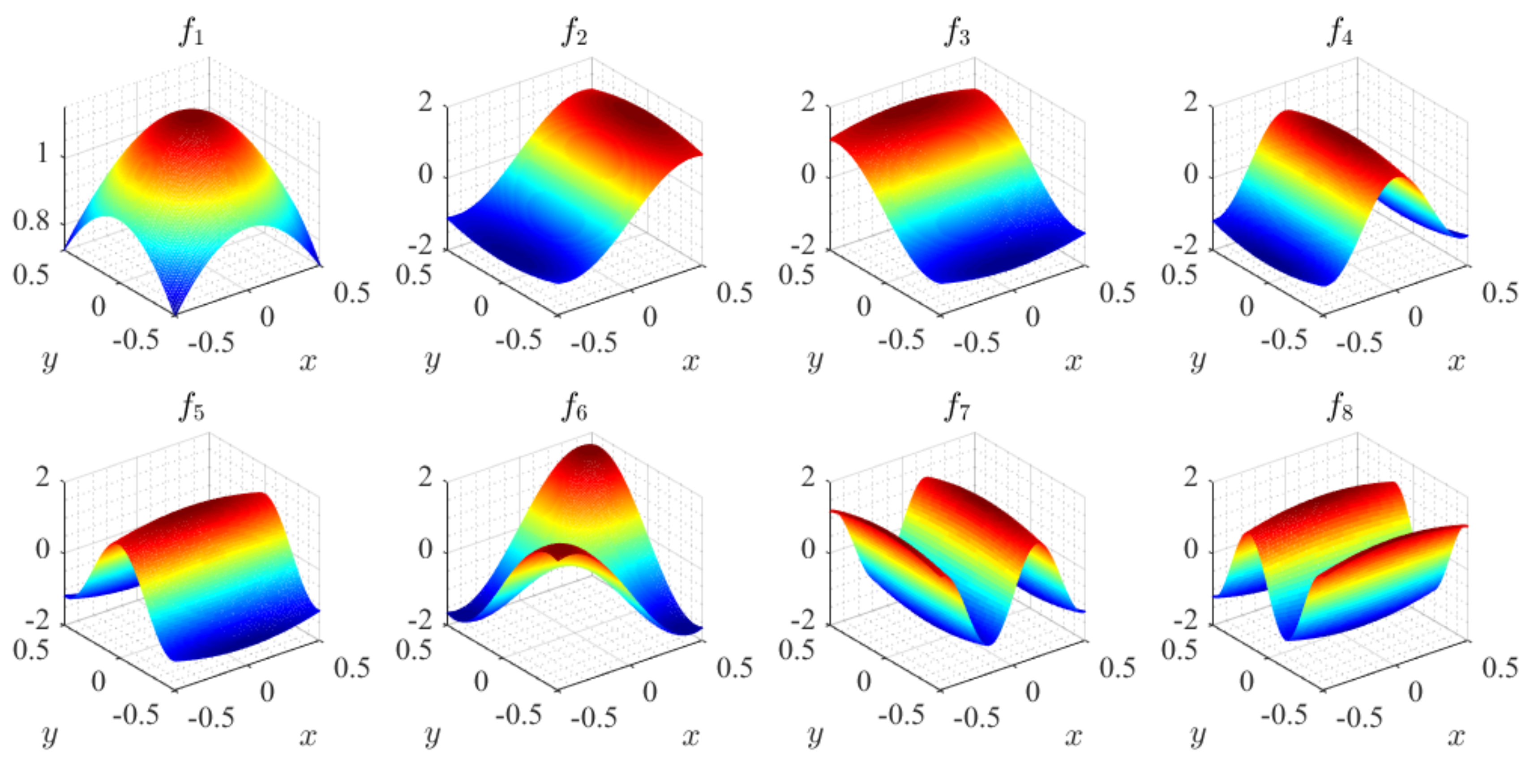
3. Solution Strategy of SFEM
4. Discussions
4.1. Validation
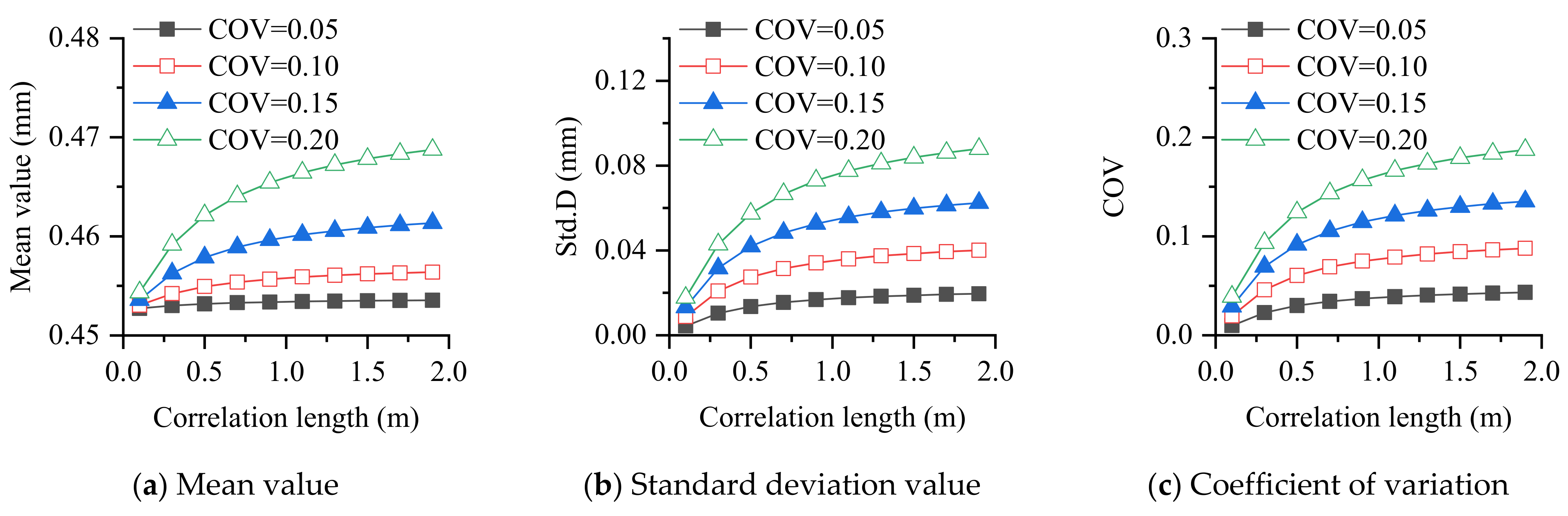
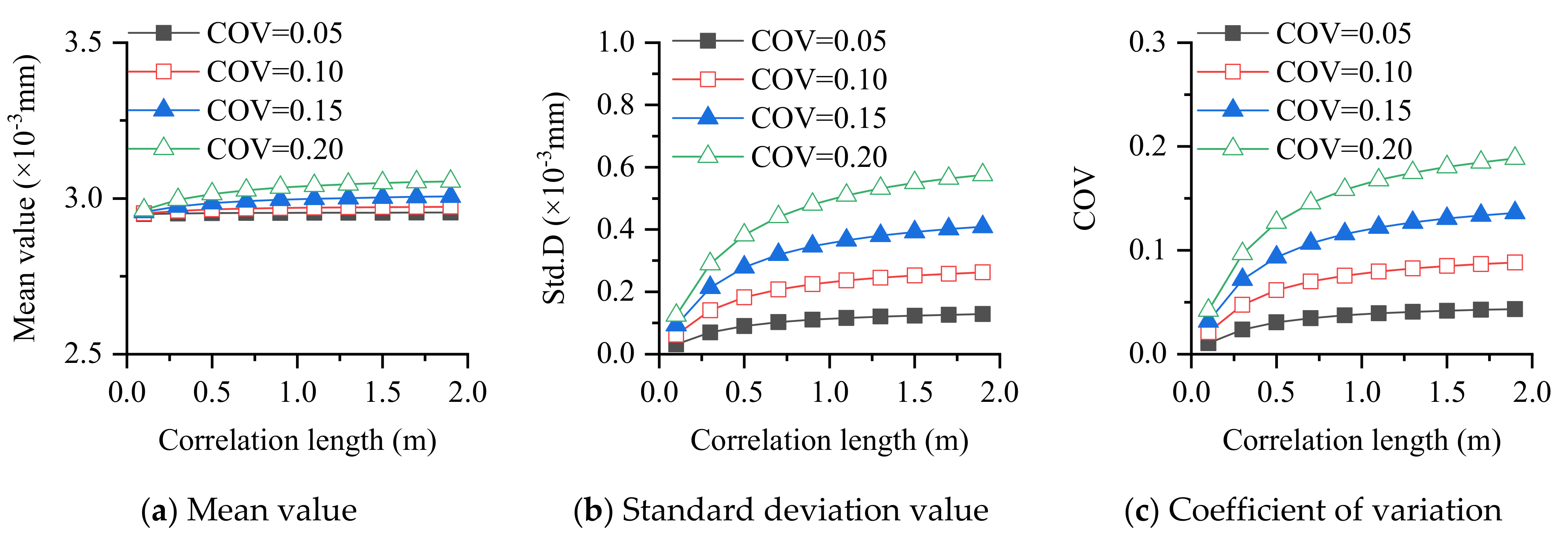
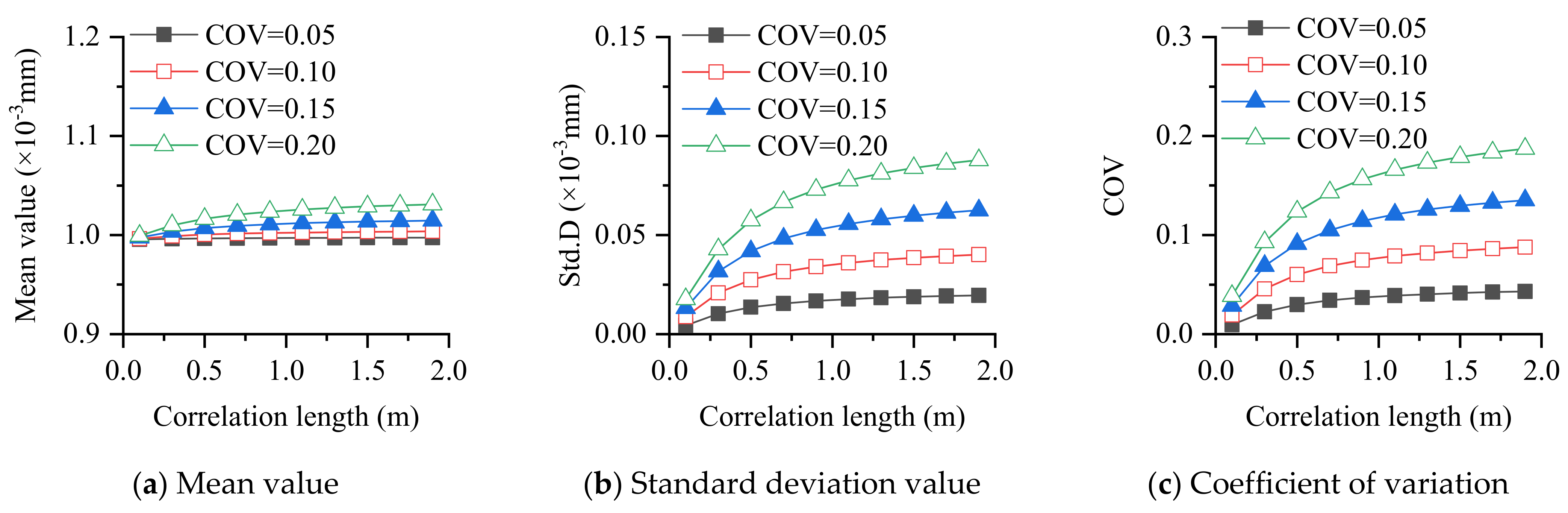
4.2. Parameter Analysis
4.2.1. Example 1
4.2.2. Example 2
4.2.3. Example 3
4.2.4. Example 4
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- The calculation strategy of setting the reference point to zero can greatly improve computational efficiency. Compared with the Monte Carlo simulation and the results from other literature, the KLE-PEM-based stochastic finite element method has been shown to have extremely high computational efficiency and accuracy.
- (2)
- The boundary conditions and types of the plate have a significant impact on the mean and standard deviation of the plate responses; however, the impact on the coefficient of variation of the response is minimal.
- (3)
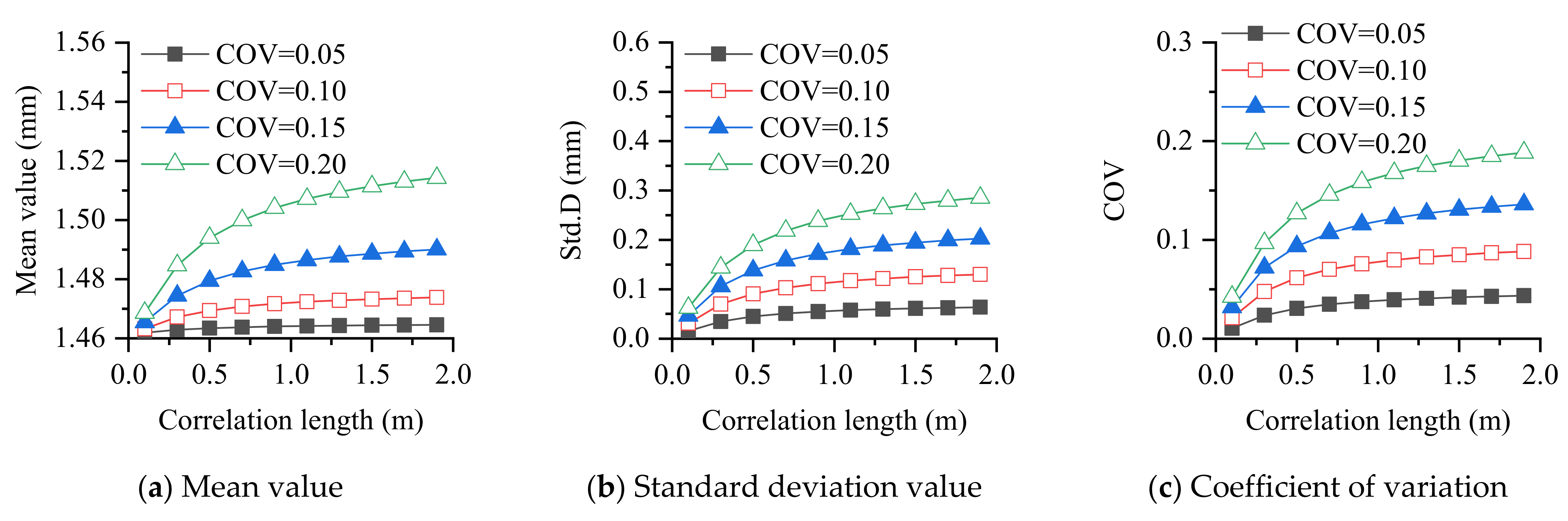
- For different boundary conditions and plate types, the mean value of response is not sensitive to parameter changes, while the sensitivity of the standard deviation and coefficient of variation, in response to parameter changes, is much greater than that of the mean value.
- (4)
- The larger the coefficient of variation of the parameter, the larger the statistical response, which is in line with common sense. The larger the correlation length, the larger the standard deviation and coefficient of variation of the response, which indicates that the correlation length of the random field should be properly considered in the analysis of plate structures.
- (5)
- This study provides a new approach for the SFEM solution of plate structures. Because of its efficiency and accuracy, it can be used to solve some plate structure problems considering spatial random fields, such as track slab deformation, floor slab deformation, etc. However, the plate structure problems considering the spatial random field include not only static behaviors, but also dynamic behaviors, nonlinear behaviors, and temperature transmission behaviors, which are the directions that can be considered in future work.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, X.; Jiang, L.; Xiang, P.; Lai, Z.; Liu, L.; Cao, S.; Zhou, W. Probability Analysis of Train-Bridge Coupled System Considering Track Irregularities and Parameter Uncertainty. Mech. Based Des. Struct. Mach. 2021, 51, 2918–2935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Jiang, L.; Lai, Z.; Xiang, P.; Chen, Y. Sensitivity and Dynamic Analysis of Train-Bridge Coupled System with Multiple Random Factors. Eng. Struct. 2020, 221, 111083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Jiang, L.; Xiang, P.; Jiang, L.; Lai, Z. Safety and Comfort Assessment of a Train Passing over an Earthquake-Damaged Bridge Based on a Probability Model. Struct. Infrastruct. Eng. 2021, 19, 525–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Sett, K. Time Domain Stochastic Finite Element Simulation towards Probabilistic Seismic Soil-Structure Interaction Analysis. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2019, 116, 460–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanem, R.G.; Spanos, P.D. Stochastic Finite Elements: A Spectral Approach; Dover Publications Inc.: Mineola, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Du, W.; Ma, J.; Zhou, C.; Yan, Y.; Wriggers, P. Uncertain Dynamic Characteristic Analysis for Structures with Spatially Dependent Random System Parameters. Materials 2023, 16, 1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nastos, C.; Komninos, P.; Zarouchas, D. Non-Destructive Strength Prediction of Composite Laminates Utilizing Deep Learning and the Stochastic Finite Element Methods. Compos. Struct. 2023, 311, 116815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nastos, C.; Zarouchas, D. Probabilistic Failure Analysis of Quasi-Isotropic CFRP Structures Utilizing the Stochastic Finite Element and the Karhunen–Loève Expansion Methods. Compos. Part B Eng. 2022, 235, 109742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Dai, H.; Beer, M. Efficient Structural Reliability Analysis via a Weak-Intrusive Stochastic Finite Element Method. Probabilistic Eng. Mech. 2023, 71, 103414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Beer, M.; Dai, H.; Nackenhorst, U. A Weak-Intrusive Stochastic Finite Element Method for Stochastic Structural Dynamics Analysis. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2022, 399, 115360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pokusiński, B.; Kamiński, M. Numerical Convergence and Error Analysis for the Truncated Iterative Generalized Stochastic Perturbation-Based Finite Element Method. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2023, 410, 115993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepahvand, K. Stochastic Finite Element Method for Random Harmonic Analysis of Composite Plates with Uncertain Modal Damping Parameters. J. Sound Vib. 2017, 400, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daneshvar, K.; Moradi, M.J.; Ahmadi, K.; Mahdavi, G.; Hariri-Ardebili, M.A. Dynamic Behavior of Corroded RC Slabs with Macro-Level Stochastic Finite Element Simulations. Eng. Struct. 2021, 239, 112056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, H.; Xu, W.; Wang, W.; Chen, G.; Yang, D. New Non-Intrusive Stochastic Finite Element Method for Plate Structures. Comput. Struct. 2022, 268, 106812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Jiang, L.; Xiang, P.; Zhou, W.; Lai, Z.; Feng, Y. Stochastic Finite Element Method Based on Point Estimate and Karhunen–Loéve Expansion. Arch. Appl. Mech. 2021, 91, 1257–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; Tian, Y.; Sheng, X. Simulation of a Non-Gaussian Stochastic Process Based on a Combined Distribution of the UHPM and the GBD. Probabilistic Eng. Mech. 2023, 72, 103438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Liu, Z.; Peng, Y. Dimension Reduction of Karhunen-Loeve Expansion for Simulation of Stochastic Processes. J. Sound Vib. 2017, 408, 168–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, A.J.M.; Fantuzzi, N. MATLAB Codes for Finite Element Analysis: Solids and Structures; Solid Mechanics and Its Applications; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; Volume 157, ISBN 978-3-030-47951-0. [Google Scholar]
- Noh, H.-C. A Formulation for Stochastic Finite Element Analysis of Plate Structures with Uncertain Poisson’s Ratio. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2004, 193, 4857–4873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudret, B. Stochastic Finite Element Methods and Reliability a State-of-the-Art Report. 190; Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, University of California: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
| 0 | ±1.22474 | 0 | ±0.958572 | ±2.02018 | 0 | ±0.816288 | ±1.67355 | ±2.65196 | |
| 1.18164 | 0.295409 | 0.945309 | 0.393619 | 0.019953 | 0.810265 | 0.425607 | 0.054516 | 9.72 × 10−4 |
| Method | Correlation Lengths (m) | 0.2 | 0.6 | 1.0 | 1.4 | 1.8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MCS-based | Mean (10−5 m) | 5.0536 | 5.0682 | 5.0764 | 5.0875 | 5.0844 |
| Std.D (10−6 m) | 1.6161 | 3.0745 | 3.7574 | 4.0770 | 4.2780 | |
| COV | 0.0320 | 0.0607 | 0.0740 | 0.0801 | 0.0841 | |
| KLE-PEM-based | Mean (10−5 m) | 5.0545 | 5.0693 | 5.0772 | 5.0818 | 5.0849 |
| Std.D (10−6 m) | 1.6116 | 3.0748 | 3.7174 | 4.0743 | 4.3012 | |
| COV | 0.0319 | 0.0607 | 0.0732 | 0.0802 | 0.0846 | |
| Ref. [14] | Mean (10−5 m) | 5.0678 | 5.0832 | 5.0914 | 5.0955 | 5.0957 |
| Std.D (10−6 m) | 1.5957 | 3.0649 | 3.7591 | 4.1063 | 4.3332 | |
| COV | 0.0315 | 0.0603 | 0.0738 | 0.0806 | 0.0850 |
| Method | Correlation Lengths (m) | 0.2 | 0.6 | 1.0 | 1.4 | 1.8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MCS | Mean (10−5 m) | 1.2698 | 1.2735 | 1.2746 | 1.2769 | 1.2786 |
| Std.D (10−6 m) | 0.3863 | 0.7664 | 0.9399 | 1.0210 | 1.0774 | |
| COV | 0.0304 | 0.0602 | 0.0737 | 0.0800 | 0.0843 | |
| KLE-PEM | Mean (10−5 m) | 1.2698 | 1.2736 | 1.2757 | 1.2768 | 1.2776 |
| Std.D (10−6 m) | 0.3856 | 0.7646 | 0.9282 | 1.0179 | 1.0744 | |
| COV | 0.0304 | 0.0600 | 0.0728 | 0.0797 | 0.0841 | |
| Ref. [14] | Mean (10−5 m) | 1.2703 | 1.2743 | 1.2765 | 1.2776 | 1.2780 |
| Std.D (10−6 m) | 0.3829 | 0.7697 | 0.9491 | 1.0378 | 1.0778 | |
| COV | 0.0301 | 0.0301 | 0.0744 | 0.0812 | 0.0843 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, Y.; Ge, F.-W.; Liu, X. Stochastic Finite Element Analysis of Plate Structures Considering Spatial Parameter Random Fields. Mathematics 2023, 11, 2535. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11112535
Yang Y, Ge F-W, Liu X. Stochastic Finite Element Analysis of Plate Structures Considering Spatial Parameter Random Fields. Mathematics. 2023; 11(11):2535. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11112535
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Yan, Fang-Wen Ge, and Xiang Liu. 2023. "Stochastic Finite Element Analysis of Plate Structures Considering Spatial Parameter Random Fields" Mathematics 11, no. 11: 2535. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11112535
APA StyleYang, Y., Ge, F.-W., & Liu, X. (2023). Stochastic Finite Element Analysis of Plate Structures Considering Spatial Parameter Random Fields. Mathematics, 11(11), 2535. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11112535






