A Kind of Water Surface Multi-Scale Object Detection Method Based on Improved YOLOv5 Network
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Related Work
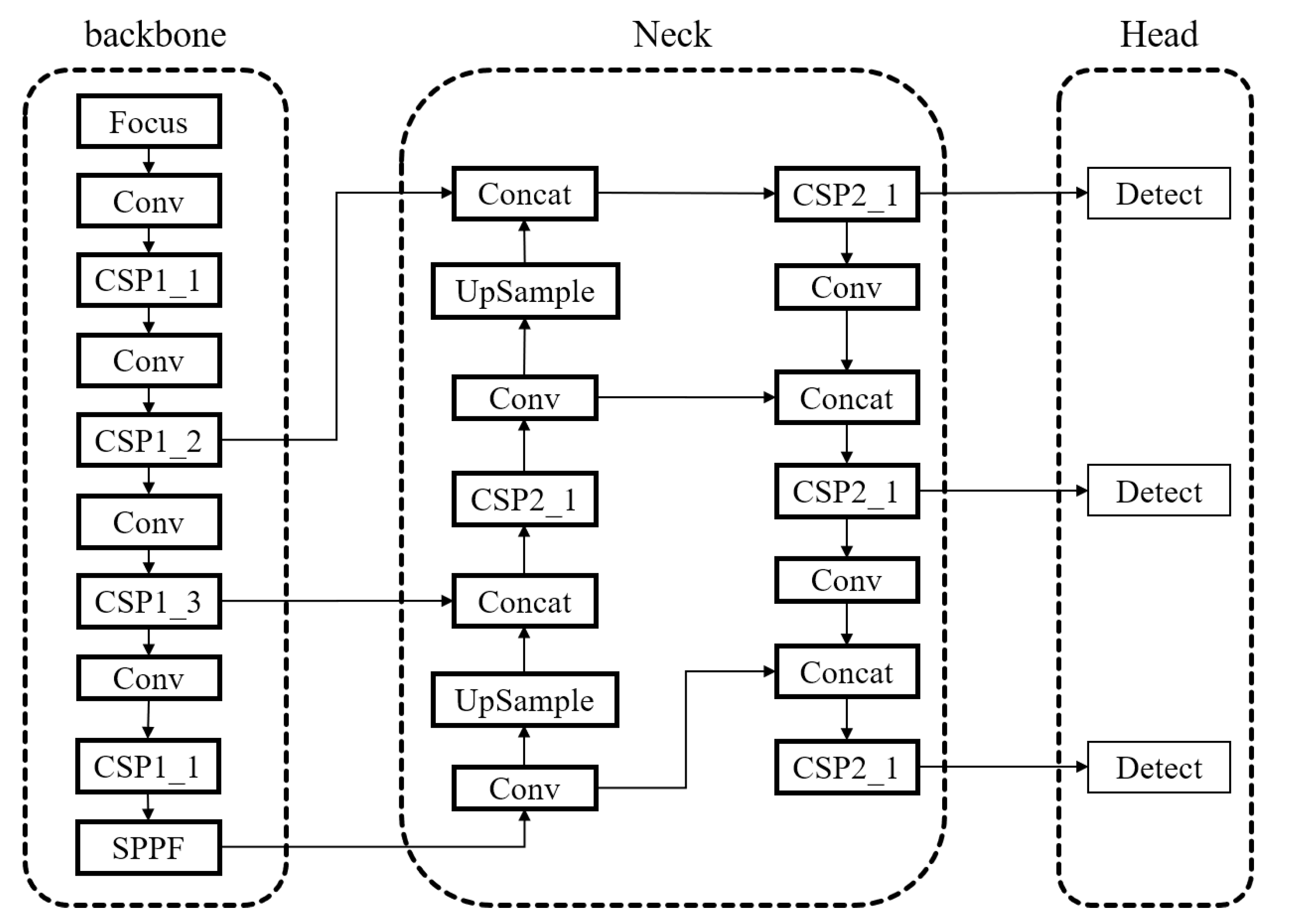
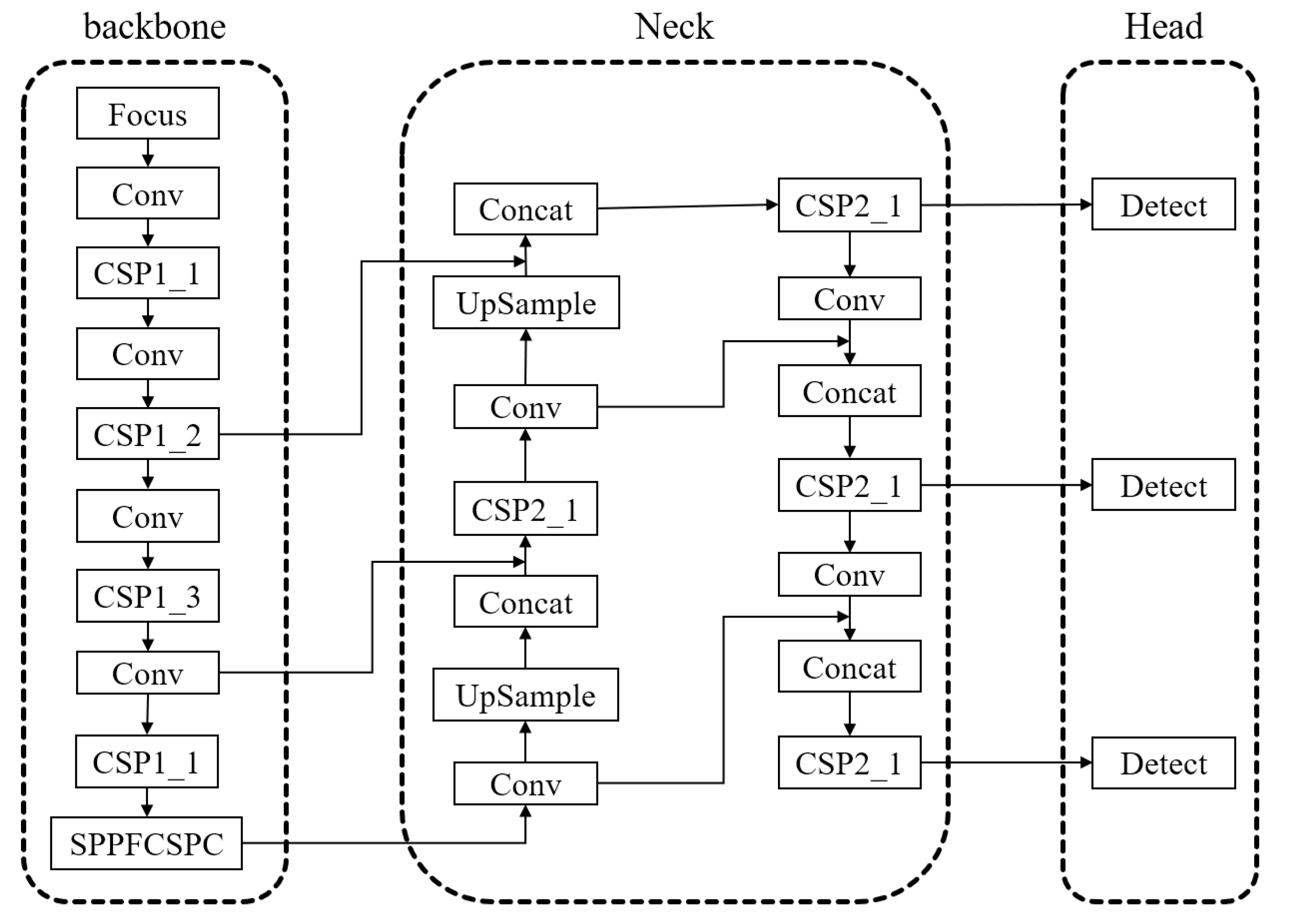
2.1. YOLOv5 Model Analysis
- Focus Structure and CSPNet-inspired Backbone: The model employs the Focus structure in the backbone network and draws inspiration from the CSPNet [20] architecture. It uses the ReLU activation function [21], which enhances the gradient flow within the network, improves computational speed, and facilitates better extraction of depth information.
- GIOU loss and Anchor-based Detection: The YOLOv5 model employs the GIOU loss as the loss function at the output end. It utilizes anchor boxes to predict target boxes [24].
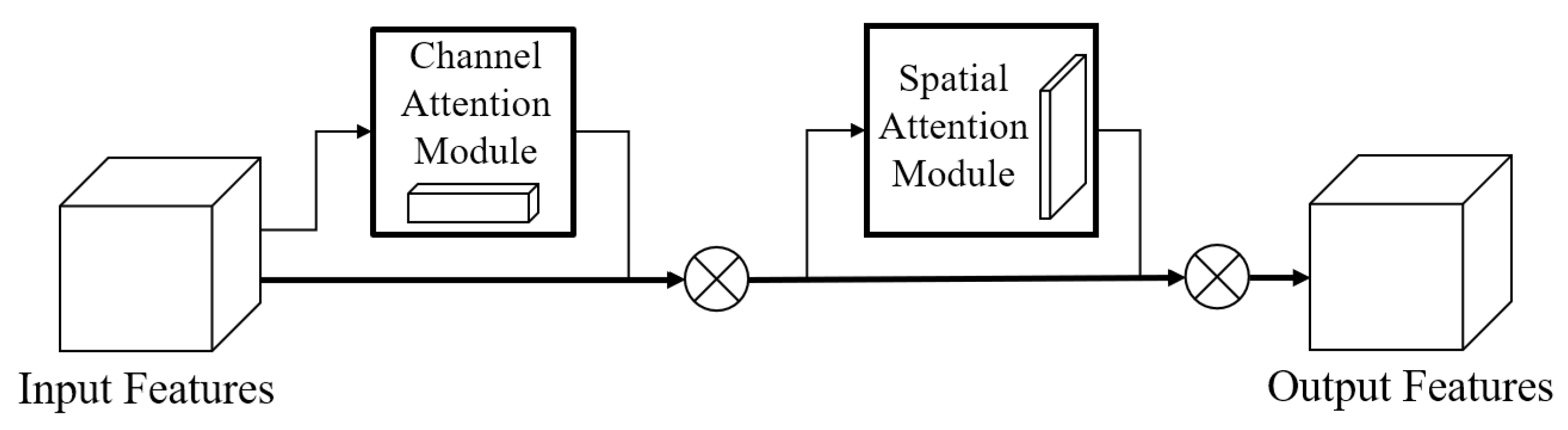
2.2. GAMAttention Attention Mechanism
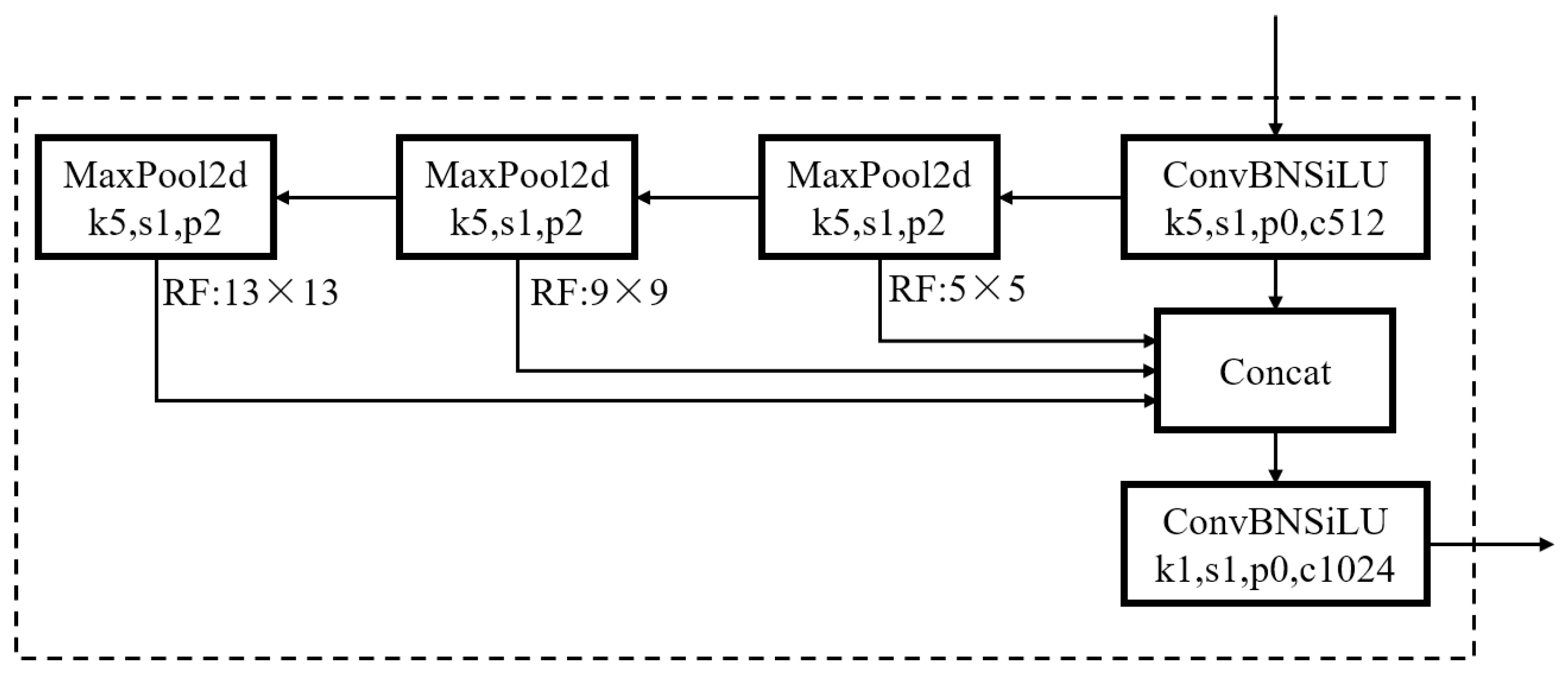
2.3. SPPFCSPC Spatial Pyramid Pooling Module
2.4. Focal Loss Classified Loss Function
3. Improvement of YOLOv5 Network Model
3.1. Basic Idea of Improving YOLOv5 Model
3.2. Optimization of Target Box Based on K-Means++
- Initialize the cluster centers by randomly selecting the bounding box regions of certain samples.
- Calculate the distances from the initial cluster centers to each data sample.
- Compute the probability for each sample to become the next cluster center using Equation (3).
- Compare the probabilities and select the next cluster center using the roulette wheel selection method.
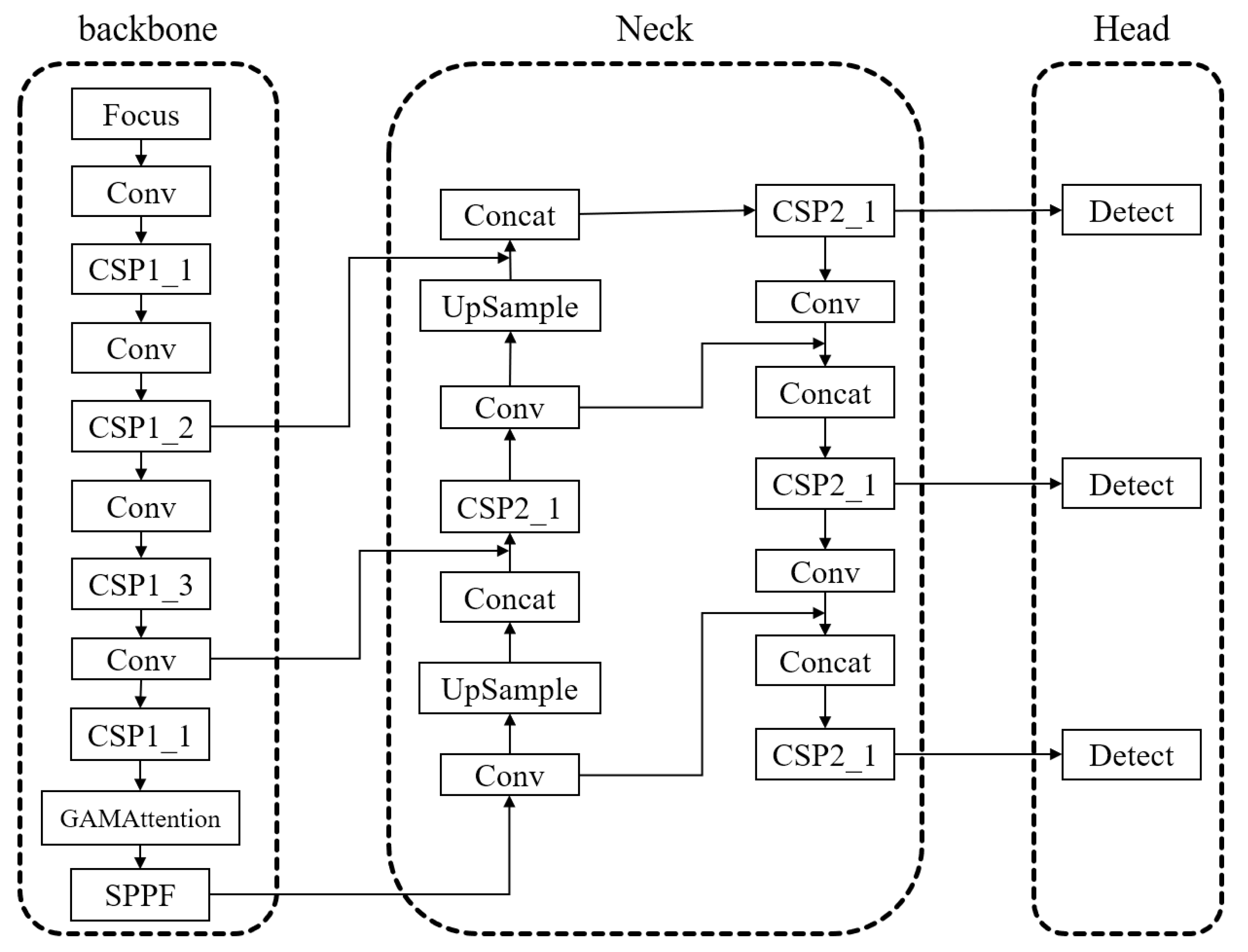
3.3. Embedding GAMAttention and SPPFCSPC Modules
- (1)
- Embedding of GAMAttention module
- (2)
- Embedding of SPPFCSPC module
- (3)
- GAMAttention and SPPFCSPC module are embedded at the same time
3.4. Loss Function Optimization
3.5. Pseudocode of the Improved Model
4. Experimental Research and Result Analysis
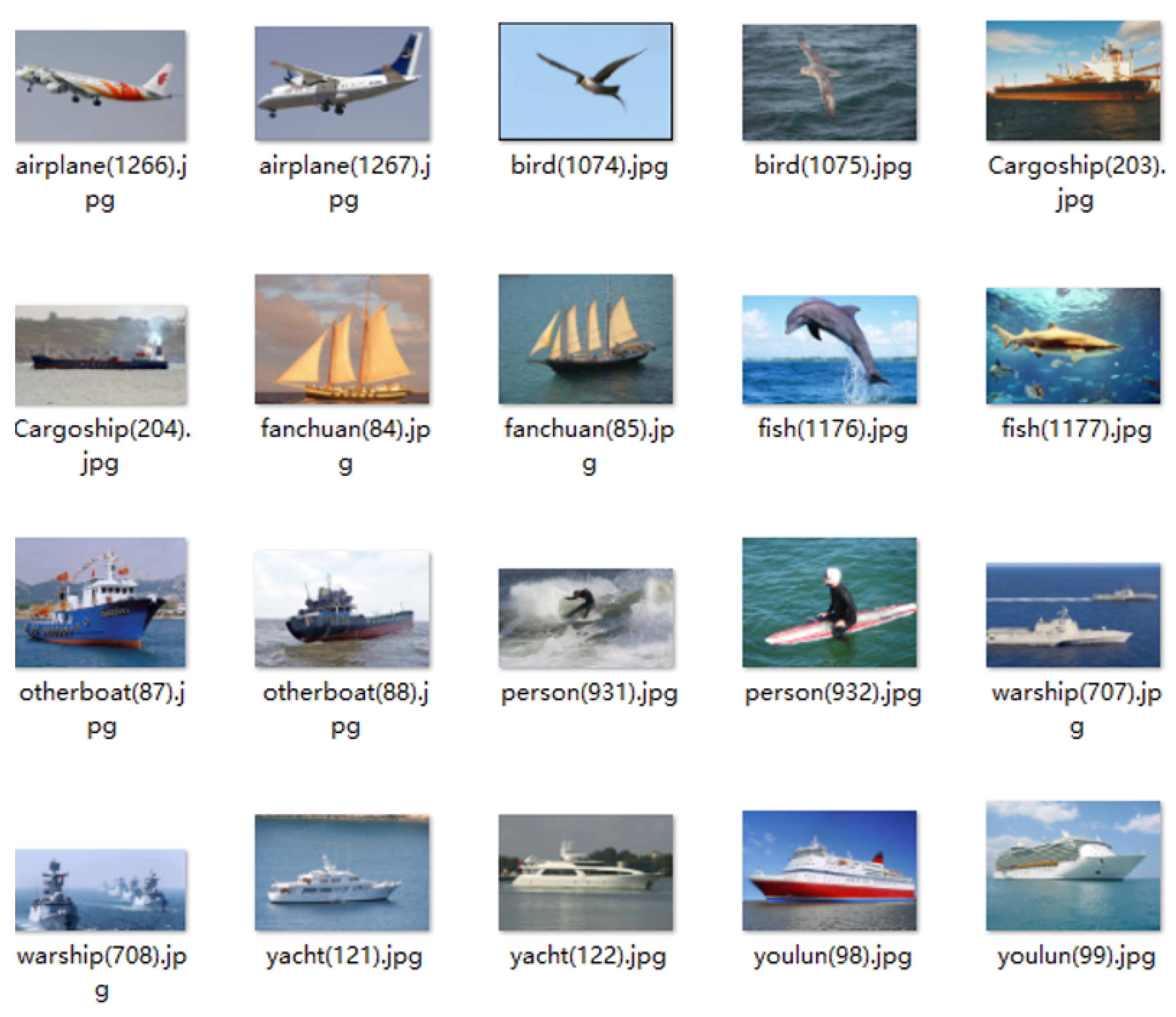
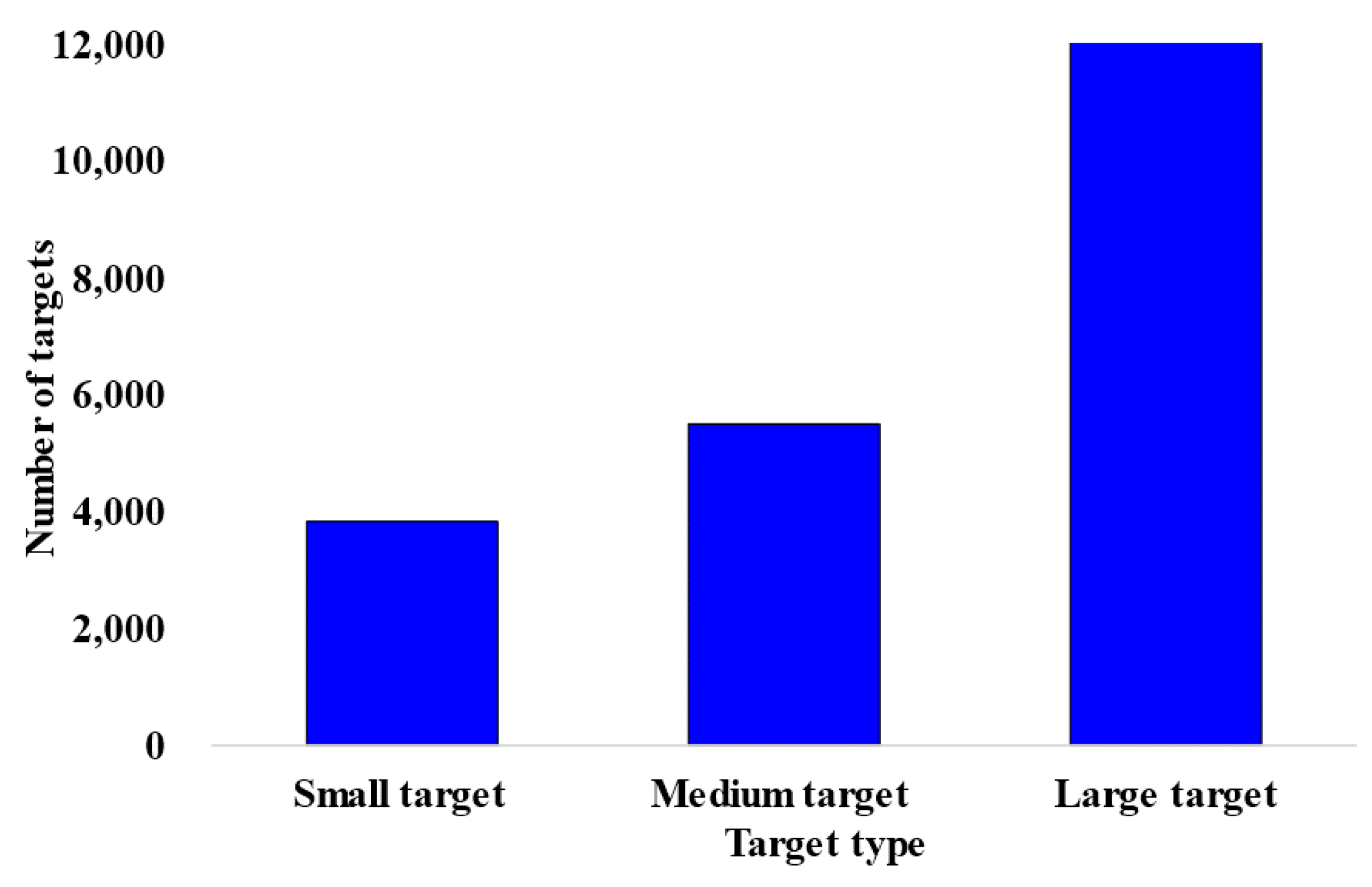
4.1. Establishment of Water Surface Target Data Set
4.2. Target Detection Evaluation Index
4.3. Classification and Comparison Experiment
- (1)
- Comparative experiment of target box optimization
- (2)
- Comparative experiment of GAMAttention embedded in backbone network
- (3)
- Comparative experiment of replacing SPPFCSPC module with backbone network
- (4)
- Comparative experiment before and after adding the loss function Focal loss
4.4. Comparative Experiment of Improved YOLOv5 Model
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, H. Research on Multi-Target Recognition and Tracking Technology of Ship Vision System for Sea-Air Targets. Master’s Thesis, Harbin Engineering University, Harbin, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, K.; Wang, X.; Wu, Y.; Qin, M.; Zhang, J.; Chu, Z. Water Surface Garbage Detection Based on YOLOv5. Comput. Knowl. Technol. 2022, 18, 28–30. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, K.; Zhu, Z.; Deng, X.; Ma, C.; Wang, H. A Survey on Deep Learning for Multi-Scale Object Detection. J. Softw. 2021, 32, 1201–1227. [Google Scholar]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Commun. ACM 2017, 60, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Russakovsky, O.; Deng, J.; Su, H.; Krause, J.; Satheesh, S.; Ma, S.; Huang, Z.; Karpathy, A.; Khosla, A.; Bernstein, M.; et al. ImageNet large scale visual recognition challenge. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2015, 115, 211–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zuo, J.; Wu, Y. Intelligent Monitoring Technology of Water Floating Objects. Softw. Guide 2013, 12, 150–152. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, P. Research on Dynamic Obstacle Detection Technology of Water Surface Unmanned Vessels. Master’s Thesis, Shenyang Li Gong University, Shenyang, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.; Zhang, M.; Gong, L. A Rapid Detection Algorithm for Surface Ships Based on Geometric Features. J. Nav. Univ. Eng. 2016, 28, 57–63. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, L. Research on Image-Based Object Detection of Unmanned Surface Vehicles. Master’s Thesis, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H. Research on Detection of Water Surface Target Images Based on SSD Algorithm. Master’s Thesis, Dalian Maritime University, Dalian, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, Y.; Feng, H.; Xu, H. Fine-grained Detection of Ship Visible Light Images Based on YOLOv3-tiny. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol. (Transp. Sci. Eng.) 2020, 44, 1041–1045+1051. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.L.; Ma, J.; Luo, X.; Wang, S. Surface garbage target detection based on SPMYOLOv3. Comput. Syst. Appl. 2023, 32, 163–170. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Tan, X.; Zhang, H. Rapid Detection of Water Surface Targets Based on YOLOv4. Ship Electron. Eng. 2022, 42, 110–113. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Fan, Y.; Wang, S.; Bai, J.; Li, K. Application of YOLOv5 Based on Attention Mechanism and Receptive Field in Identifying Defects of Thangka Images. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 81597–81611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chen, Y.; Dong, Z.; Gao, M. Improved YOLOv5 network for real-time multi-scale traffic sign detection. Neural Comput. Appl. 2023, 35, 7853–7865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Lyu, S.; Wang, X.; Zhao, Q. TPH-YOLOv5: Improved YOLOv5 Based on Transformer Prediction Head for Object Detection on Drone-captured Scenarios. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops (ICCVW), Montreal, BC, Canada, 24 October 2022; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 2778–2788. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.Y.; Goyal, P.; Girshick, R.; He, K.; Dollár, P. Focal loss for dense object detection. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2999–3007. [Google Scholar]
- Yun, S.; Han, D.; Oh, S.J.; Chun, S.; Choe, J.; Yoo, Y. Cutmix: Regularization strategy to train strong classifiers with localizable features. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 6023–6032. [Google Scholar]
- Dulal, R.; Zheng, L.; Kabir, M.A.; McGrath, S.; Medway, J.; Swain, D.; Swain, W. Automatic Cattle Identification using YOLOv5 and Mosaic Augmentation: A Comparative Analysis. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2210.11939. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.Y.; Liao, H.Y.; Wu, Y.H.; Chen, P.Y.; Hsieh, J.W.; Yeh, I.H. CSPNet: A new backbone that can enhance learning capability of CNN. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1911.11929. [Google Scholar]
- Glorot, X.; Bordes, A.; Bengio, Y. Deep Sparse Rectifier Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the Fourteenth International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics, Lauderdale, FL, USA, 14 June 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.Y.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R.; He, K.; Hariharan, B.; Belongie, S. Feature Pyramid Networks for Object Detection. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1612.03144. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Qi, L.; Qin, H.; Shi, J.; Jia, J. Path Aggregation Network for Instance Segmentation. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1803.01534. [Google Scholar]
- Rezatofighi, H.; Tsoi, N.; Gwak, J. Generalized Intersection over Union: A Metric and A Loss for Bounding Box Regression. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1902.09630. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Sun, C.; Han, H.; Wang, H.; Sun, H.; Zheng, N. Object-fabrication Targeted Attack for Object Detection. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2212.06431. [Google Scholar]
- Woo, S.; Park, J.; Lee, J.Y.; Kweon, I.S. Cbam: Convolutional block attention module. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 3–19. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Shao, Z.; Hoffmann, N. Global Attention Mechanism: Retain Information to Enhance Channel-Spatial Interactions. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2112.05561. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Spatial Pyramid Pooling in Deep Convolutional Networks for Visual Recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2014, 37, 1904–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Q.; Zhang, C.; He, Q.; Wang, H. Research Progress on Loss Functions for Object Detection. Comput. Sci. Appl. 2021, 11, 2836–2844. [Google Scholar]
- MacQueen, J. Some methods for classification and analysis of multivariate observations. In Proceedings of the Fifth Berkeley Symposium on Mathematical Statistics and Probability, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 21 June 1967; Volume 1, pp. 281–297. [Google Scholar]
- Arthur, D.; Vassilvitskii, S. k-means++: The advantages of careful seeding. In Proceedings of the Eighteenth annual ACM-SIAM Symposium on Discrete Algorithms, New Orleans, LA, USA, 7 January 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Everingham, M.; Van Gool, L.; Williams, C.K.; Winn, J.; Zisserman, A. The pascal visual object classes challenge. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2010, 88, 303–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Everingham, M.; Eslami, S.A.; Van Gool, L.; Williams, C.K.; Winn, J.; Zisserman, A. The pascal visual object classes challenge: A retrospective. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2015, 111, 98–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.Y.; Maire, M.; Belongie, S.; Hays, J.; Perona, P.; Ramanan, D.; Dollár, P.; Zitnick, C.L. Microsoft coco: Common objects in context. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision—ECCV 2014: 13th European Conference, Zurich, Switzerland, 6–12 September 2014; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; pp. 740–755. [Google Scholar]
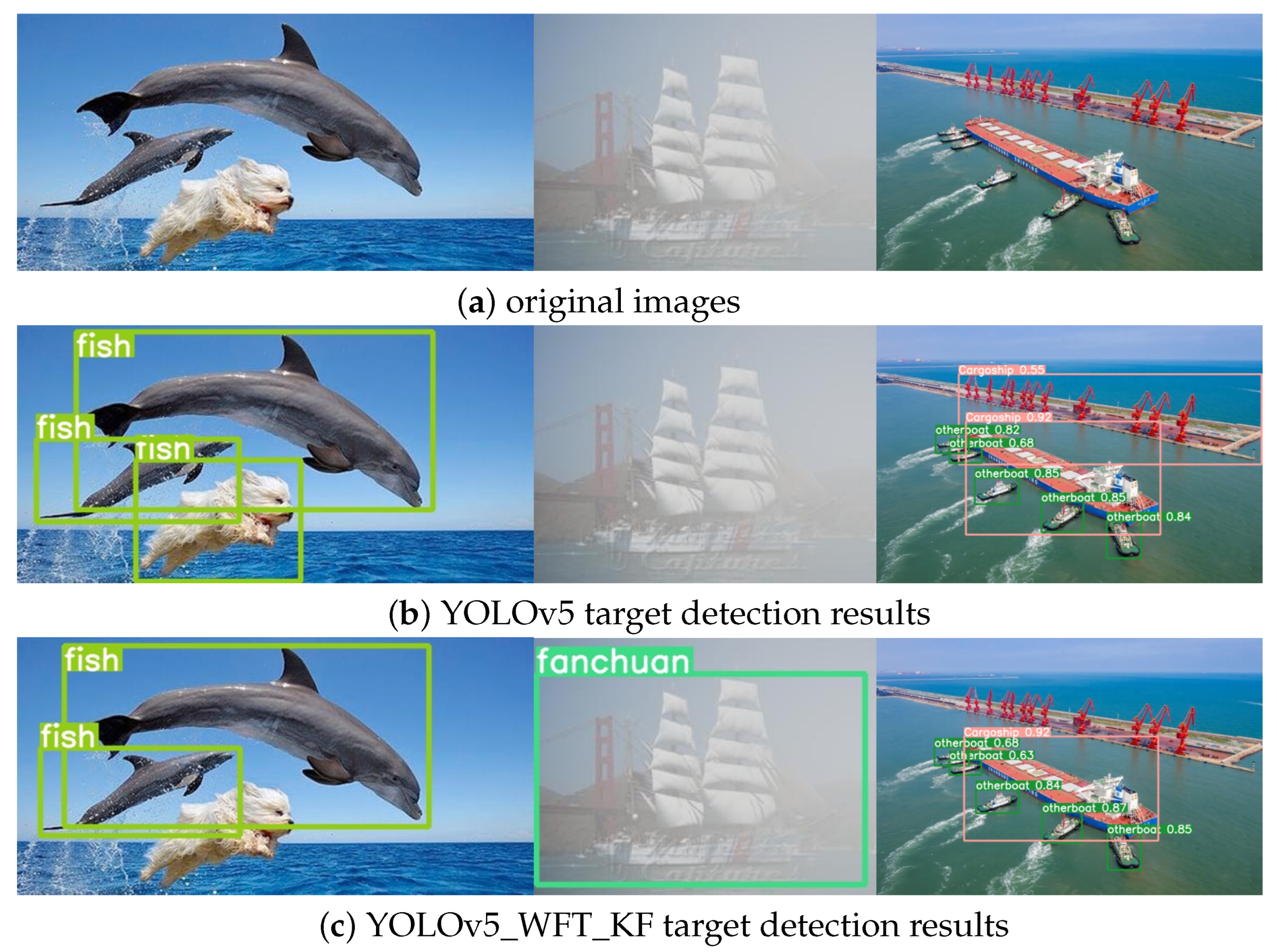






| Argument | Value |
|---|---|
| batch_size | −1 |
| Imgsz | 640 |
| epochs | 100 |
| loss | Focal_loss |
| classes | 10 |
| Network Model | P/IOU0.5 | R/IOU0.5 | [email protected] |
|---|---|---|---|
| YOLOv5 | 89.7% | 81.6% | 86.5% |
| YKmeans++ | 90.60% | 82.42% | 87.37% |
| Network Model | P/IOU0.5 | R/IOU0.5 | [email protected] |
|---|---|---|---|
| YOLOv5 | 89.7% | 81.6% | 86.5% |
| YWFA_B | 83.2% | 92.5% | 92.2% |
| Network Model | P/IOU0.5 | R/IOU0.5 | [email protected] |
|---|---|---|---|
| YOLOv5 | 89.7% | 81.6% | 86.5% |
| YWFS_B | 90.4% | 85.5% | 93.4% |
| Network Model | P/IOU0.5 | R/IOU0.5 | [email protected] |
|---|---|---|---|
| YOLOv5 | 89.7% | 81.6% | 86.5% |
| YWFS_BF | 92.3% | 88.2% | 93.7% |
| Network Model | P/IOU0.5 | R/IOU0.5 | [email protected] |
|---|---|---|---|
| YOLOv5 | 89.7% | 81.6% | 86.5% |
| YOLOv5_WFT | 93.6% | 86.4% | 94% |
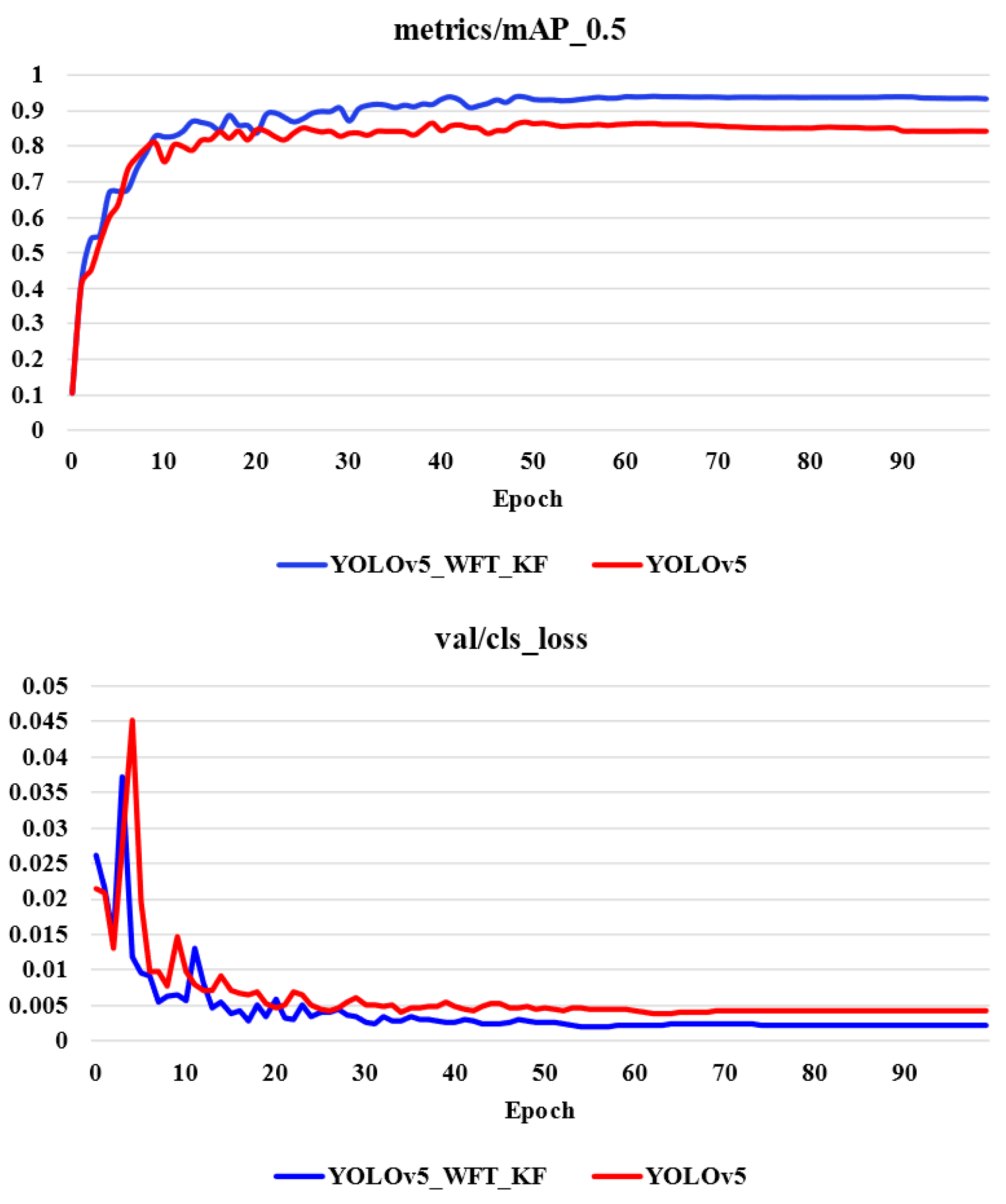
| YOLOv5_WFT_KF | 93.8% | 87.2% | 94.6% |
| Algorithm Model | Airplane (%) | Bird (%) | Cargoship (%) | Fanchuan (%) | Fish (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Faster R-CNN | 81.16 | 88.99 | 81.09 | 80.66 | 60.38 |
| YOLOv4 | 94.34 | 80.31 | 83.10 | 88.92 | 35.03 |
| YOLOv5 | 99.1 | 95.7 | 93.9 | 94.7 | 85.4 |
| YOLOv5_WFT_KF | 95.2 | 94.4 | 93.8 | 98.4 | 93.9 |
| Otherboat (%) | Person (%) | Youlun (%) | Warship (%) | Yacht (%) | [email protected] (%) |
| 57.51 | 52.70 | 90.61 | 80.84 | 71.13 | 74.51 |
| 81.79 | 65.81 | 85.14 | 95.99 | 95.24 | 80.57 |
| 59.3 | 66.6 | 91.8 | 91.4 | 86.8 | 86.5 |
| 89.9 | 83.7 | 99.5 | 94.3 | 97.3 | 94.6 |
| Network Model | Layers | Parameters | Flops | FPS |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| YOLOv5 | 213 | 7 M | 15.8 G | 203.415 |
| YOLOv5_WFT_KF | 239 | 15.2 M | 22.4 G | 172.015 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, Z.; Wan, Y.; Liu, J.; An, R.; Wu, L. A Kind of Water Surface Multi-Scale Object Detection Method Based on Improved YOLOv5 Network. Mathematics 2023, 11, 2936. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11132936
Ma Z, Wan Y, Liu J, An R, Wu L. A Kind of Water Surface Multi-Scale Object Detection Method Based on Improved YOLOv5 Network. Mathematics. 2023; 11(13):2936. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11132936
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Zhongli, Yi Wan, Jiajia Liu, Ruojin An, and Lili Wu. 2023. "A Kind of Water Surface Multi-Scale Object Detection Method Based on Improved YOLOv5 Network" Mathematics 11, no. 13: 2936. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11132936
APA StyleMa, Z., Wan, Y., Liu, J., An, R., & Wu, L. (2023). A Kind of Water Surface Multi-Scale Object Detection Method Based on Improved YOLOv5 Network. Mathematics, 11(13), 2936. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11132936






