Calculation Method and Application of Time-Varying Transmission Rate via Data-Driven Approach
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
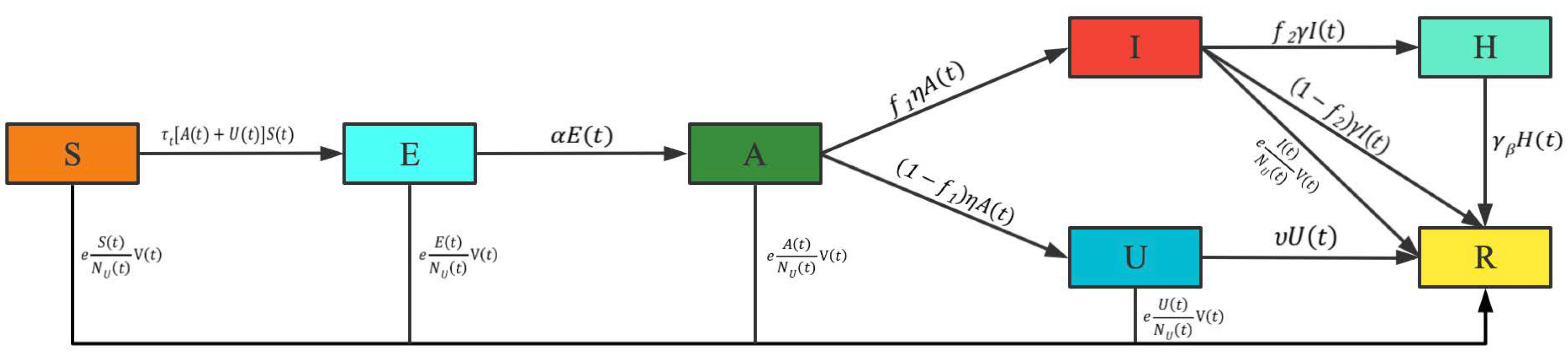
2.1. Epidemic Model
2.2. Transformation of the System (4)
2.3. Method of Calculating the Time-Varying Transmission Rate
3. Application
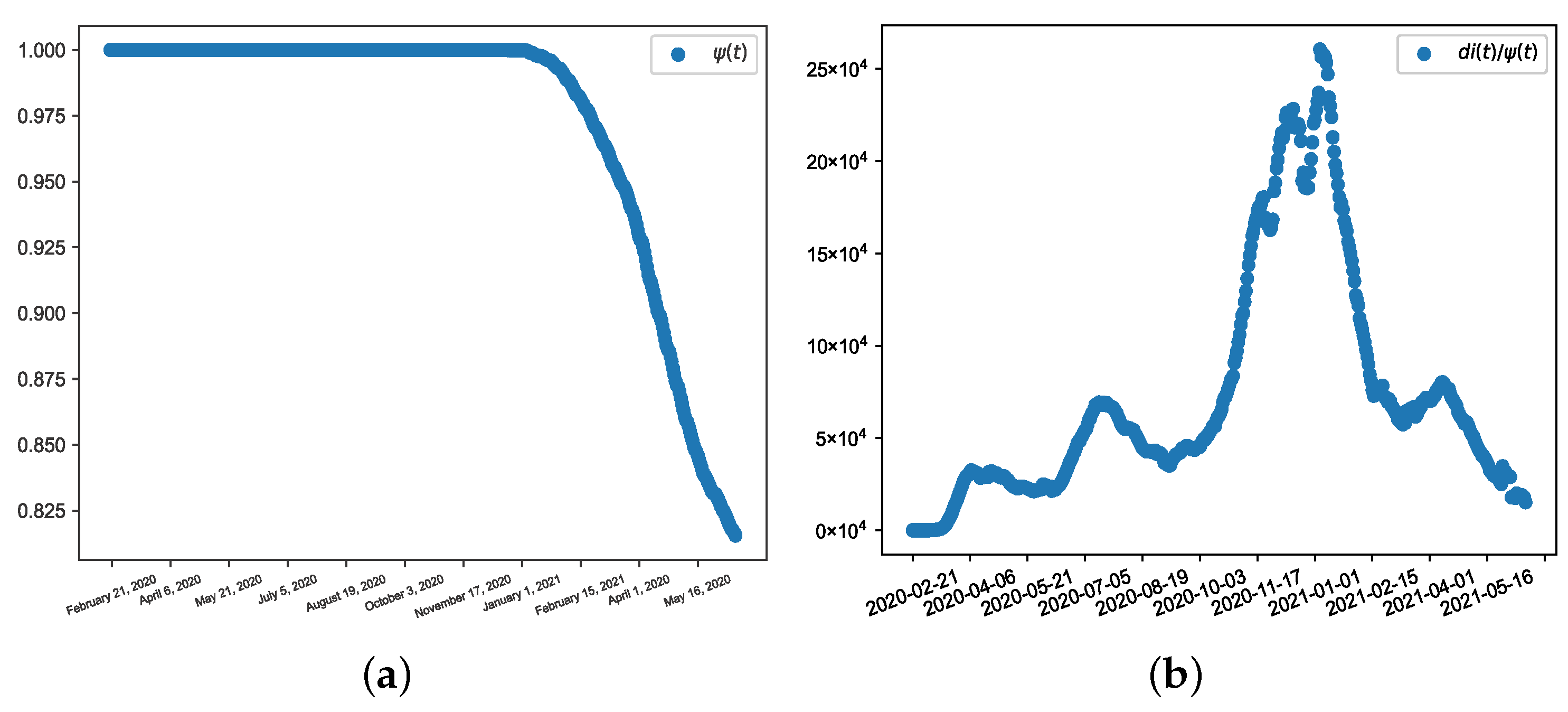
3.1. Data Preparation
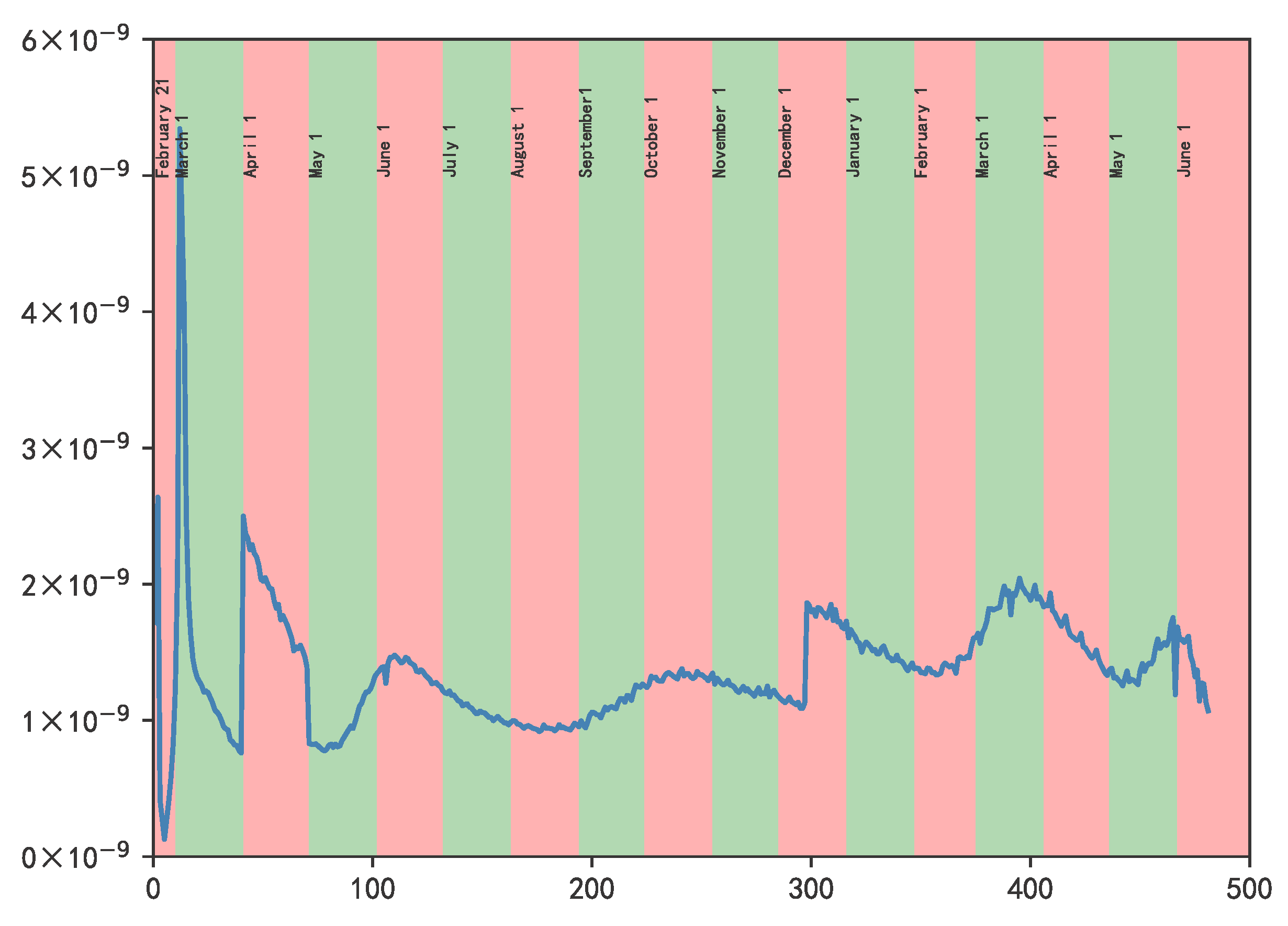
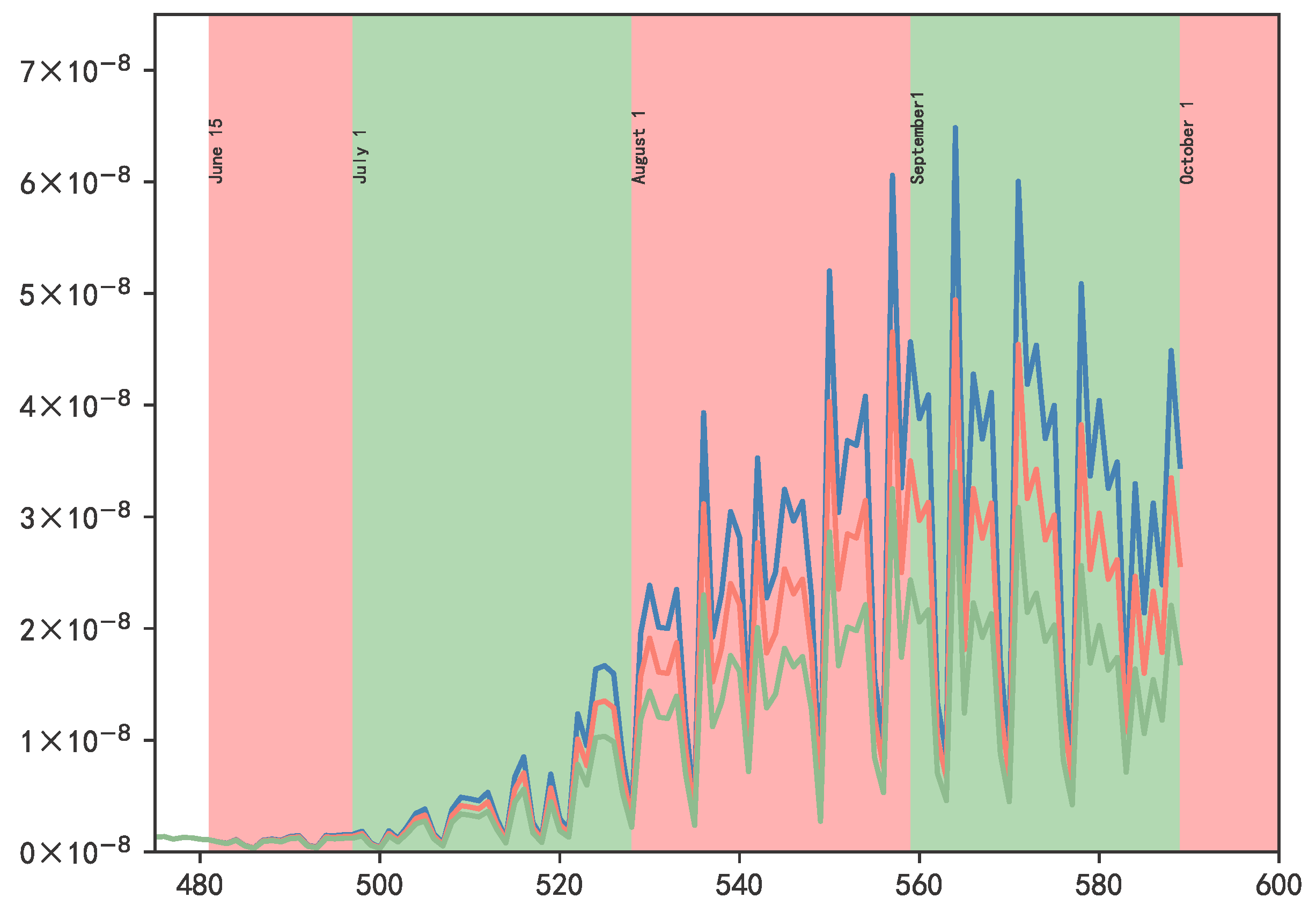
3.2. Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Michelsen, C. Mathematical modeling is also physics—Interdisciplinary teaching between mathematics and physics in Danish upper secondary education. Phys. Educ. 2015, 50, 489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, K.T.; Rajamani, R.K. Mathematical model of the hydrocyclone based on physics of fluid flow. AIChE J. 1991, 37, 735–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johns, P.B. A new mathematical model to the physics of propagation. Radio Electron. Eng. 1974, 44, 657–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borodin, A.I.; Tatuev, A.A.; Shash, N.N.; Lyapuntsova, E.V.; Rokotyanskaya, V.V. Economic-mathematical model of building a company’s potential. Asian Soc. Sci. 2015, 11, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shaimardanovich, D.A.; Rustamovich, U.S. Economic-mathematical modeling of optimization production of agricultural production. Asia Pac. J. Res. Bus. Manag. 2018, 9, 10–21. [Google Scholar]
- Vovk, O.; Tulchynska, S.; Popelo, O.; Tulchinskiy, R.; Tkachenko, T. Economic and Mathematical Modeling of the Integration Impact of Modernization on Increasing the Enterprise Competitiveness. Manag. Theory Stud. Rural Bus. Infrastruct. Dev. 2021, 43, 383–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, S.; Xing, J.; Levine, H.; Jolly, M.K. Mathematical modeling of plasticity and heterogeneity in EMT. Methods Mol. Biol. 2021, 2179, 385–413. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, S.; Panda, P.K.; Luo, W.; Hashimoto, R.F.; Ahuja, R. Network analysis reveals that the tumor suppressor lncRNA GAS5 acts as a double-edged sword in response to DNA damage in gastric cancer. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 18312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.A.; Economou, T.; Lowe, R. A Bayesian modelling framework to quantify multiple sources of spatial variation for disease mapping. J. R. Soc. Interface 2022, 19, 20220440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heesterbeek, H.; Anderson, R.M.; Andreasen, V.; Bansal, S.; De Angelis, D.; Dye, C.; Eames, K.T.; Edmunds, W.J.; Frost, S.D.; Funk, S.; et al. Modeling infectious disease dynamics in the complex landscape of global health. Science 2015, 347, aaa4339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Osemwinyen, A.C.; Diakhaby, A. Mathematical modelling of the transmission dynamics of ebola virus. Appl. Comput. Math. 2015, 4, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rachah, A. Analysis, simulation and optimal control of a SEIR model for Ebola virus with demographic effects. Commun. Fac. Sci. Univ. Ank. Ser. A1 Math. Stat. 2018, 67, 179–197. [Google Scholar]
- Ngeleja, R.C.; Luboobi, L.S.; Nkansah-Gyekye, Y. Modelling the dynamics of bubonic plague with yersinia pestis in the environment. Commun. Math. Biol. Neurosci. 2016, 2016, 10. [Google Scholar]
- Foley, J.E.; Zipser, J.; Chomel, B.; Girvetz, E.; Foley, P. Modeling plague persistence in host-vector communities in California. J. Wildl. Dis. 2007, 43, 408–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hidayati, N.; Sari, E.R.; Waryanto, N.H. Mathematical model of Cholera spread based on SIR: Optimal control. Pythagoras J. Pendidik. Mat. 2021, 16, 70–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fung, I.C.H. Cholera transmission dynamic models for public health practitioners. Emerg. Themes Epidemiol. 2014, 11, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zakary, O.; Larrache, A.; Rachik, M.; Elmouki, I. Effect of awareness programs and travel-blocking operations in the control of HIV/AIDS outbreaks: A multi-domains SIR model. Adv. Differ. Equ. 2016, 2016, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mwalili, S.; Kimathi, M.; Ojiambo, V.; Gathungu, D.; Mbogo, R. SEIR model for COVID-19 dynamics incorporating the environment and social distancing. BMC Res. Notes 2020, 13, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, I.; Mondal, A.; Antonopoulos, C.G. A SIR model assumption for the spread of COVID-19 in different communities. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2020, 139, 110057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, D.E.; Welch, G.; Peck, J.S. A modified SIR model equivalent to a generalized logistic model, with standard logistic or log-logistic approximations. IISE Trans. Healthc. Syst. Eng. 2022, 12, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, M.; Ng, K.Y.; Mac Namee, B.; Biglarbeigi, P.; Brisk, R.; Bond, R.; Finlay, D.; McLaughlin, J. COVID-19 modelling by time-varying transmission rate associated with mobility trend of driving via Apple Maps. J. Biomed. Inform. 2021, 122, 103905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wintachai, P.; Prathom, K. Stability analysis of SEIR model related to efficiency of vaccines for COVID-19 situation. Heliyon 2021, 7, e06812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghostine, R.; Gharamti, M.; Hassrouny, S.; Hoteit, I. An extended SEIR model with vaccination for forecasting the COVID-19 pandemic in Saudi Arabia using an ensemble Kalman filter. Mathematics 2021, 9, 636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capaldi, A.; Behrend, S.; Berman, B.; Smith, J.; Wright, J.; Lloyd, A.L. Parameter estimation and uncertainty quantication for an epidemic model. Math. Biosci. Eng. 2012, 553–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdy, M.; Side, S.; Annas, S.; Nur, W.; Sanusi, W. An SIR epidemic model for COVID-19 spread with fuzzy parameter: The case of Indonesia. Adv. Differ. Equ. 2021, 2021, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Magal, P.; Webb, G. Predicting the number of reported and unreported cases for the COVID-19 epidemics in China, South Korea, Italy, France, Germany and United Kingdom. J. Theor. Biol 2021, 509, 110501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Villaverde, J.; Jones, C.I. Estimating and simulating a SIRD model of COVID-19 for many countries, states, and cities. J. Econ. Dyn. Control 2022, 140, 104318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowell, G.; Hengartner, N.W.; Castillo-Chavez, C.; Fenimore, P.W.; Hyman, J.M. The basic reproductive number of Ebola and the effects of public health measures: The cases of Congo and Uganda. J. Theor. Biol. 2004, 229, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chowell, G.; Viboud, C.; Hyman, J.M. The Western Africa ebola virus disease epidemic exhibits both global exponential and local polynomial growth rates. PLoS Curr. 2015, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viboud, C.; Simonsen, L.; Chowell, G.; Simonsen, L. A generalized-growth model to characterize the early ascending phase of infectious disease outbreaks. Epidemics 2016, 15, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Johns Hopkins Coronavirus Resource Center. Available online: https://coronavirus.jhu.edu/map.html (accessed on 28 February 2023).
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Available online: https://covid.cdc.gov/covid-data-tracker/#vaccinations_vacc-people-booster-percent-total (accessed on 28 February 2023).
- United States Census. Available online: https://ballotpedia.org/United_States_census,_2020#cite_note-1 (accessed on 6 March 2023).
- Britton, A.; Slifka, K.M.J.; Edens, C.; Nanduri, S.A.; Bart, S.M.; Shang, N.; Harizaj, A.; Armstrong, J.; Xu, K.; Ehrlich, H.Y.; et al. Effectiveness of the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine among residents of two skilled nursing facilities experiencing COVID-19 outbreaks—Connecticut, December 2020–February 2021. Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2021, 70, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/cases-updates/burden.html (accessed on 6 March 2023).
- Demongeot, J.; Griette, Q.; Magal, P.; Webb, G. Modeling vaccine efficacy for COVID-19 outbreak in New York city. Biology 2022, 11, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Guan, X.; Wu, P.; Wang, X.; Zhou, L.; Tong, Y.; Ren, R.; Leung, K.S.M.; Lau, E.H.Y.; Wong, J.Y.; et al. Early transmission dynamics in Wuhan, China, of novel coronavirus—Infected pneumonia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1199–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, H.; Tao, J.; McHugo, G.J.; Drake, R.E. Comparing statistical methods for analyzing skewed longitudinal count data with many zeros: An example of smoking cessation. J. Subst. Abuse Treat. 2013, 45, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Data | 03/08 | 03/09 | 03/10 | 03/11 | 03/12 | 03/13 | 03/14 | 03/15 | 03/16 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cases | 213 | 472 | 696 | 987 | 1264 | 1678 | 2995 | 3782 | 4661 |
| Parameter | Value | Source |
|---|---|---|
| N | 331,108,434 | [33] |
| e | [34] | |
| [35] | ||
| 3 | [36] | |
| 5 | [37] | |
| 7 | [38] |
| Time | Peak Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| First stage | 3 March 2020 | ||
| Second stage | |||
| 6 September 2021 | |||
| Third stage | |||
| 3 January 2022 | |||
| Time | Peak Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| First stage | 3 March 2020 | ||
| Second stage | |||
| 6 September 2021 | |||
| Third stage | |||
| 3 January 2022 | |||
| Time | Peak Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| First stage | 3 March 2020 | ||
| Second stage | |||
| 6 September 2021 | |||
| Third stage | |||
| 3 January 2022 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Sun, Y. Calculation Method and Application of Time-Varying Transmission Rate via Data-Driven Approach. Mathematics 2023, 11, 2955. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11132955
Sun Y, Zhang Z, Sun Y. Calculation Method and Application of Time-Varying Transmission Rate via Data-Driven Approach. Mathematics. 2023; 11(13):2955. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11132955
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Yuqing, Zhonghua Zhang, and Yulin Sun. 2023. "Calculation Method and Application of Time-Varying Transmission Rate via Data-Driven Approach" Mathematics 11, no. 13: 2955. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11132955
APA StyleSun, Y., Zhang, Z., & Sun, Y. (2023). Calculation Method and Application of Time-Varying Transmission Rate via Data-Driven Approach. Mathematics, 11(13), 2955. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11132955




