A Survey on Isogeometric Collocation Methods with Applications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- Higher-order continuity across elements;
- Higher accuracy without mesh generation;
- Fewer degrees of freedom (DoFs).
2. Methods and Comparisons
2.1. NURBS Basis Function
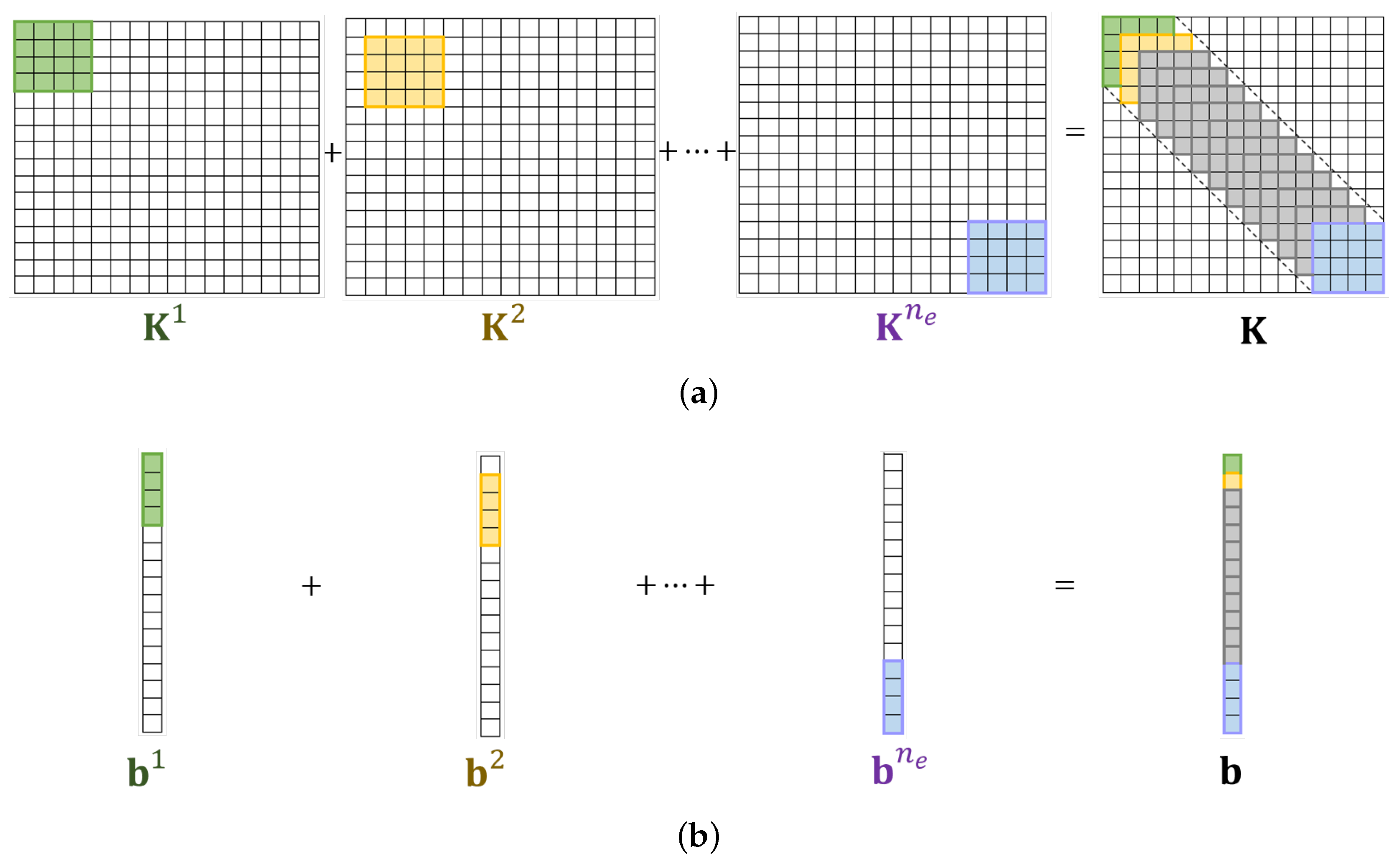
2.2. IGA Galerkin Method
2.3. Isogeometric Collocation Method
2.4. Comparison of IGA Galerkin and IGA-C
- Numerical quadrature rules in the assembly;
- High-quality parameterization for IGA-suitable analysis;
- Construction of alternative basis functions for particular cases.
- Clarification of the consistency and convergence conditions;
- Design of efficient collocation schemes;
- Improvement of calculation accuracy and speed.
2.5. IGA-CL and IGA-GL Methods
3. Collocation Schemes and Convergence
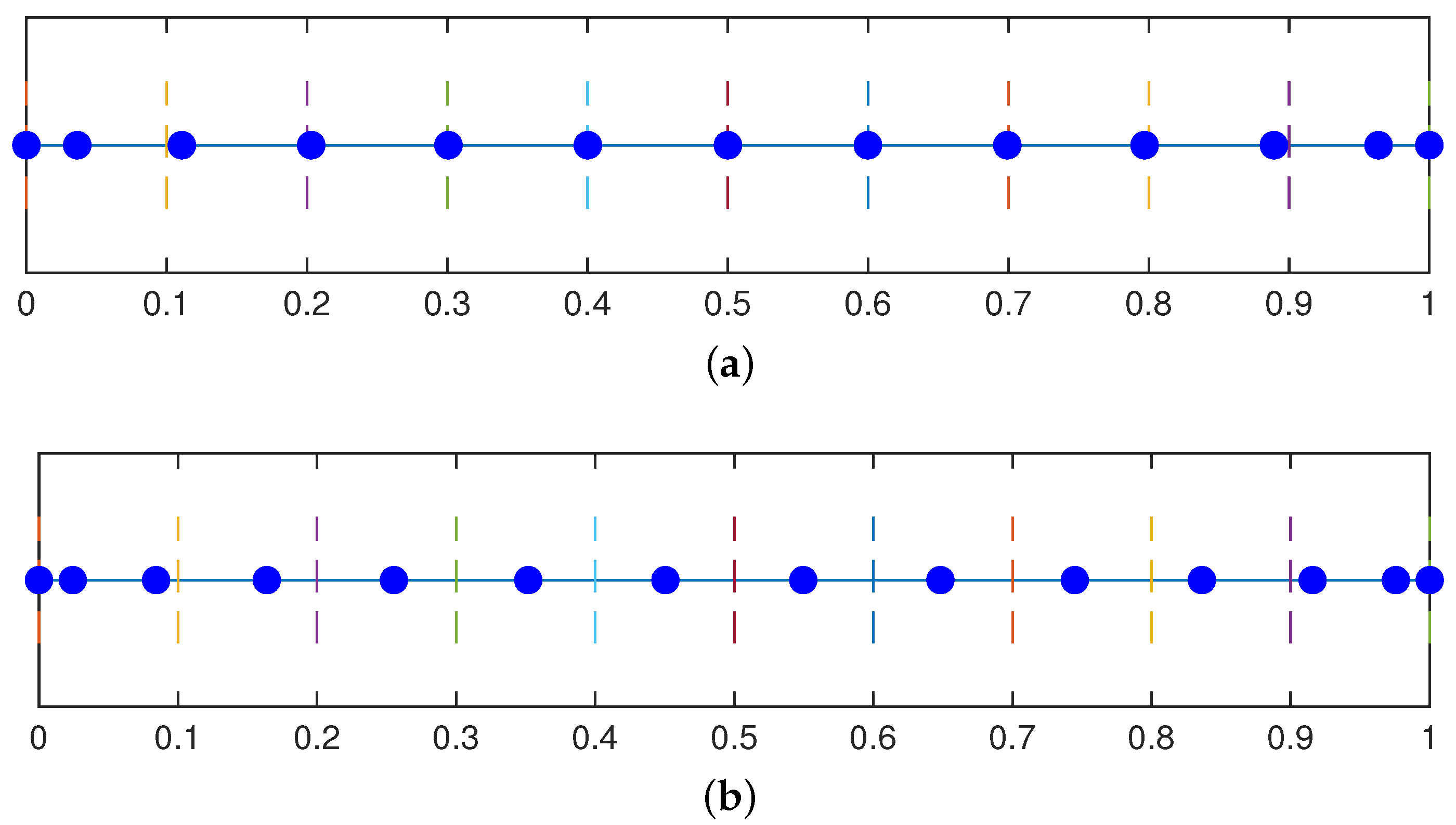
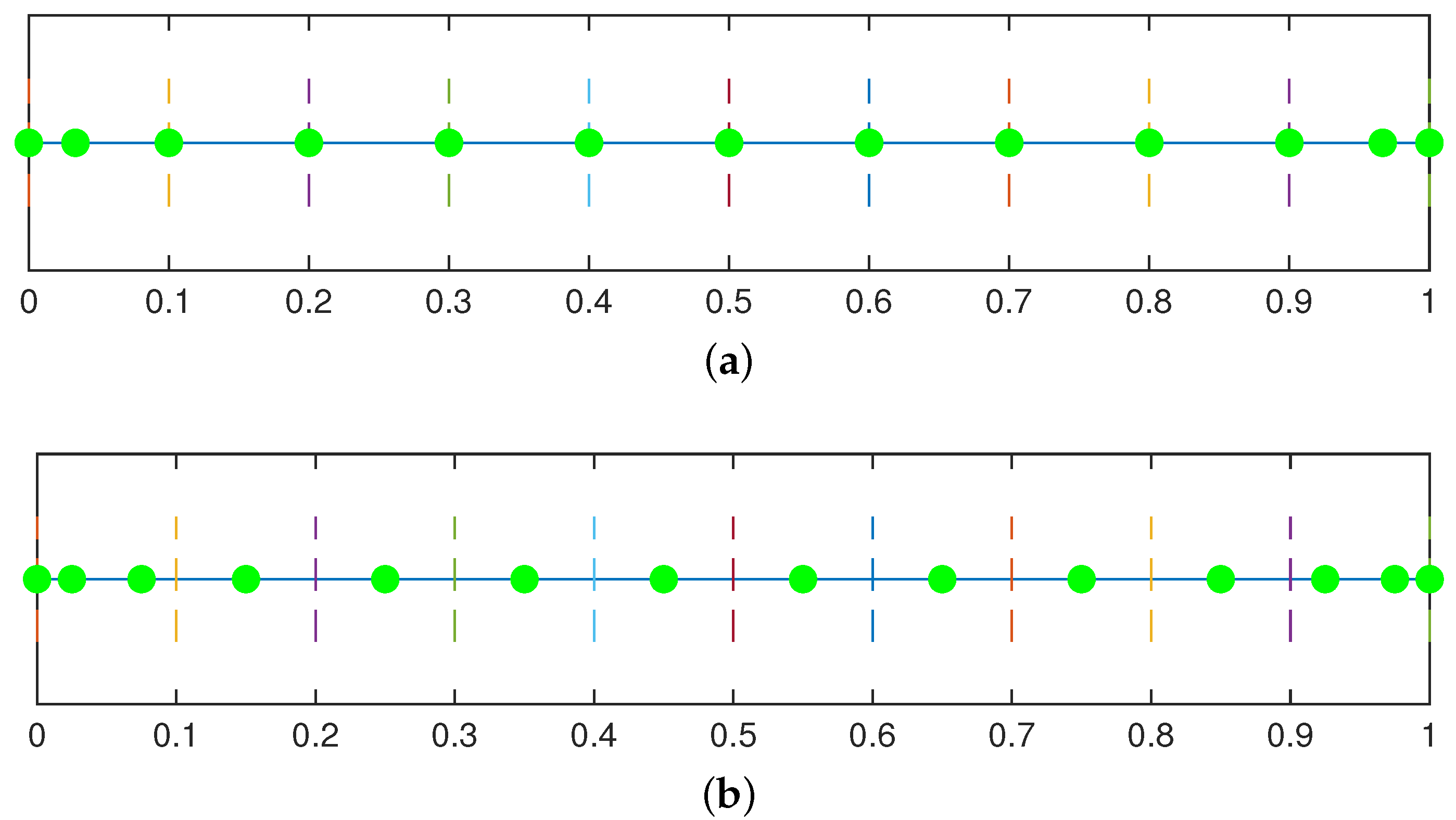
3.1. Demko and Greville Abscissae
3.2. Superconvergent Points
3.3. Cauchy–Galerkin Points
3.4. Alternating/Clustered Superconvergent Points
3.5. Other Collocation Schemes and Open Problems
- How can a new collocation scheme be designed to improve the computational accuracy and convergence rate of the IGA-C method even for even-degree bases?
- How can boundary conditions (Dirichlet, Neumann, mixed boundary conditions) be dealt with in the new collocation scheme?
- How can a collocation selection method with the same convergence rate as the IGA Galerkin method be designed?
- How can a collocation scheme in the presence of singular points in the parameterization of the computational domain be designed such that the IGA-C method can perform an effective calculation with the highest possible calculation accuracy?
4. Applications
4.1. Structural Mechanics
4.2. Elastic Mechanics
4.3. Fluid Mechanics and Mixed Problems
4.4. Shape and Topology Optimization
5. Discussion and Conclusions
- Quality optimization for computational domain parameterization.
- Design of the collocation scheme.
- Consistency, convergence, and convergence rate of the IGA-C method.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| IGA | Isogeometric analysis |
| IGA Galerkin | Isogeometric analysis with Galerkin |
| IGA-C | Isogeometric analysis with collocation |
| IGA-GL | Isogeometric analysis with Galerkin by fitting load function |
| IGA-CL | Isogeometric analysis with collocation by fitting load function |
| SC | Superconvergent |
| CG | Cauchy–Galerkin |
| ASC | Alternating superconvergent |
| CSC | Clustered superconvergent |
References
- Hughes, T.J.R.; Cottrell, J.A.; Bazilevs, Y. Isogeometric analysis: CAD, finite elements, NURBS, exact geometry and mesh refinement. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2005, 194, 4135–4195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Piegl, L.; Tiller, W. The NURBS Book, 2nd ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Zienkiewicz, O.C.; Taylor, R.L. The Finite Element Method: Its Basis and Fundamentals, 7th ed.; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Bern, M.; Eppstein, D. Mesh Generation And Optimal Triangulation. In Computing in Euclidean Geometry; World Scientific: Singapore, 1992; pp. 1–78. [Google Scholar]
- Cottrell, J.A.; Hughes, T.J.R.; Bazilevs, Y. Isogeometric Analysis: Toward Integration of CAD and FEA; John Wiley & Sons: Chichester, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Auricchio, F.; Beirão da Veiga, L.; Hughes, T.J.R.; Reali, A.; Sangalli, G. Isogeometric Collocation Methods. Math. Model. Methods Appl. Sci. 2010, 20, 2075–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hong, Q.; Terzopoulos, D. Dynamic NURBS swung surfaces for physics-based shape design. Comput.-Aided Des. 1995, 27, 111–127. [Google Scholar]
- Terzopoulos, D.; Hong, Q. Dynamic NURBS with Geometric Constraints for Interactive Sculpting. ACM Trans. Graph. 1996, 13, 103–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Q.; Terzopoulos, D. D-NURBS: A physics-based geometric design framework. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 1996, 2, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Veiga, L.; Cho, D.; Pavarino, L.F.; Scacchi, S. Overlapping Schwarz Methods for Isogeometric Analysis. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 2012, 3, 1394–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veiga, L.B.D.; Cho, D.; Pavarino, L.F.; Scacchi, S. Isogeometric Schwarz preconditioners for linear elasticity systems. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2013, 253, 439–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prenter, F.D.; Verhoosel, C.V.; Brummelen, H.V.; Evans, J.A.; Maute, K. Multigrid solvers for immersed finite element methods and immersed isogeometric analysis. Comput. Mech. 2020, 65, 807–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Diwan, G.; Mohamed, M.S. Iterative solution with shifted Laplace preconditioner for plane wave enriched isogeometric analysis and finite element discretization for high-frequency acoustics. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2021, 384, 114006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Mourrain, B.; Duvigneau, R.; Galligo, A. Constructing analysis-suitable parameterization of computational domain from CAD boundary by variational harmonic method. J. Comput. Phys. 2013, 252, 275–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nian, X.; Chen, F. Planar domain parameterization for isogeometric analysis based on Teichmüller mapping. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2016, 311, 41–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchegger, F.; Juttler, B. Planar multi-patch domain parameterizaton via patch adjacency graphs. Comput. Aided Des. 2017, 82, 2–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Yu, Y.; Wang, M.; Zhu, C. Constructing high-quality planar NURBS parameterization for isogeometric analysis by adjustment control points and weights. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 2021, 396, 113615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Cao, J.; Wei, X.; Zhang, Y.J. TCB-spline-based isogeometric analysis method with high-quality parameterizations. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2022, 393, 114771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Ren, J.; Fang, X.; Lin, H.; Xu, G.; Bao, H.; Huang, J. IGA-suitable planar parameterization with patch structure simplification of closed-form polysquare. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2022, 392, 114678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Jin, S.; Hu, Q.; Liu, Z. Constructing B-spline solids from tetrahedral meshes for isogeometric analysis. Comput. Aided Geom. Des. 2015, 35–36, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Mourrain, B.; Duvigneau, R.; Galligo, A. Analysis-suitable volume parameterization of multi-block computational domain in isogeometric applications. Comput. Aided Des. 2013, 45, 395–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, G.; Kwok, T.; Wang, C. Isogeometric computation reuse method for complex objects with topology-consistent volumetric parameterization. Comput. Aided Des. 2017, 91, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pan, M.; Chen, F.; Tong, W. Volumetric spline parameterization for isogeometric analysis. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2020, 359, 112769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, Y.; Chen, F. Volumetric parameterization with truncated hierarchical B-splines for isogeometric analysis. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2022, 401, 115662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Hu, Q.; Xiong, Y. Consistency and convergence properties of the isogeometric collocation method. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2013, 267, 471–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Xiong, Y.; Hu, H.; Yan, J.; Hu, Q. The convergence rate and necessary-and-sufficient condition for the consistency of isogeometric collocation method. Appl.-Math.- J. Chin. Univ. 2022, 37, 272–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Xiong, Y.; Wang, X.; Hu, Q.; Ren, J. Isogeometric Least-Squares Collocation Method with Consistency and Convergence Analysis. J. Syst. Sci. Complex. 2020, 33, 1656–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anitescu, C.; Yue, J.; Zhang, Y.J.; Rabczuk, T. An isogeometric collocation method using superconvergent points. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2015, 284, 1073–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, T.J.R.; Reali, A.; Sangalli, G. Efficient quadrature for NURBS-based isogeometric analysis. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2015, 199, 301–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barton, M.; Calo, V. Gauss-Galerkin quadrature rules for quadratic and cubic spline spaces and their application to isogeometric analysis. Comput.-Aided Des. 2016, 82, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hiemstra, R.R.; Calabrò, F.; Schillinger, D.; Hughes, T.J.R. Optimal and reduced quadrature rules for tensor product and hierarchically refined splines in isogeometric analysis. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2017, 316, 966–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, Z.; Wang, S.; Shao, W.; Yu, L. Reusing the evaluations of basis functions in the integration for isogeometric analysis. Comput. Model. Eng. Sci. 2020, 316, 459–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazilevs, Y.; Calo, V.; Cottrell, J.; Evans, J.; Hughes, T.; Lipton, S.; Scott, M.; Sederberg, T. Isogeometric analysis using T-splines. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2010, 199, 229–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Habib, S.; Kezrane, C.; Hachi, B. Moving local mesh based on analysis-suitable T-splines and Bézier extraction for extended isogeometric finite element analysis—Application to two-dimensional crack propagation. Finite Elem. Anal. Des. 2023, 213, 103854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuong, A.; Giannelli, C.; Jüttler, B.; Simeon, B. A hierarchical approach to adaptive local refinement in isogeometric analysis. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2011, 200, 3554–3567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schillinger, D.; Evans, J.; Reali, A.; Scott, M.; Hughes, T. Isogeometric collocation: Cost comparison with Galerkin methods and extension to adaptive hierarchical NURBS discretizations. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2013, 267, 170–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, M.; Jüttler, B.; Giust, A. Fast Formation of Isogeometric Galerkin Matrices via Integration by Interpolation and Look-up. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2020, 366, 113005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, M.; Jüttler, B.; Scholz, F. Efficient matrix computation for isogeometric discretizations with hierarchical B-splines in any dimension. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2022, 388, 114210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atri, H.; Shojaee, S. Truncated hierarchical B-splines in isogeometric analysis of thin shell structures. Steel Compos. Struct. Int. J. 2018, 26, 171–182. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen-Thanh, N.; Nguyen-Xuan, H.; Rabczuk, T. Isogeometric analysis using polynomial splines over hierarchical T-meshes for two-dimensional elastic solids. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2011, 200, 1892–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen-Thanh, N.; Kiendl, J.; Nguyen-Xuan, H.; Wuchner, R.; Bletzinger, K.; Bazilevs, Y.; Rabczuk, T. Rotation free isogeometric thin shell analysis using PHT-splines. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2011, 200, 3410–3424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen-Thanh, N.; Zhou, K. Extended isogeometric analysis based on PHT-splines for crack propagation near inclusions. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 2017, 112, 1777–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johannessen, K.A.; Kvamsdal, T.; Dokken, T. Isogeometric analysis using LR B-splines. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2014, 269, 471–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Evans, E.; Scott, M.; Li, X.; Thomas, D. Hierarchical T-splines: Analysis-suitability, Bézier extraction, and application as an adaptive basis for isogeometric analysis. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2015, 284, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Constantini, P.; Manni, C.; Pelosi, F.; Sampoli, M. Quasi-interpolation in isogeometric analysis based on generalized B-splines. Comput. Aided Geom. Des. 2010, 27, 656–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manni, C.; Pelosi, F.; Sampoli, M. Generalized B-splines as a tool in isogeometric analysis. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2011, 200, 867–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bracco, C.; Berdinsky, D.; Cho, D.; Oh, M.j.; Kim, T.w. Trigonometric generalized T-splines. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2014, 268, 540–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babuška, I.; Melenk, J. The partition of unity method. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 1997, 40, 727–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorashi, S.; Valizadeh, N.; Mohammadi, S. Extended isogeometric analysis for simulation of stationary and propagating cracks. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 2012, 89, 1069–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen-Thanh, N.; Valizadeh, N.; Nguyen, M.; Nguyen-Xuan, H.; Zhuang, X.; Areias, P.; Zi, G.; Bazilevs, Y.; De Lorenzis, L.; Rabczuk, T. An extended isogeometric thin shell analysis based on Kirchhoff–Love theory. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2015, 284, 265–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.G.; Lee, C.O. Splitting basis techniques in cloth simulation by isogeometric analysis. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2020, 362, 112871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.P.; Anitescu, C.; Bordas, S.P.; Rabczuk, T. Isogeometric analysis: An overview and computer implementation aspects. Math. Comput. Simul. 2015, 117, 89–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cohen, E.; Martin, T.; Kirby, R.; Lyche, T.; Riesenfeld, R.F. Analysis-aware modeling: Understanding quality considerations in modeling for isogeometric analysis. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2010, 199, 334–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Mourrain, B.; Duvigneau, R.; Galligo, A. Optimal analysis-aware parameterization of computational domain in 3D isogeometric analysis. Comput. Aided Des. 2013, 45, 812–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pilgerstorfer, E.; Jüttler, B. Bounding the influence of domain parameterization and knot spacing on numerical stability in isogeometric analysis. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2014, 268, 589–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Atroshchenko, E.; Gang, X.; Tomar, S.; Bordas, S.P.A. Weakening the tight coupling between geometry and simulation in isogeometric analysis: From sub-and super-geometric analysis to Geometry Independent Field approximaTion (GIFT). Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 2018, 114, 1131–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demko, S. On the existence of interpolating projections onto spline spaces. J. Approx. Theory 1985, 43, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gomez, H.; Lorenzis, L.D. The variational collocation method. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2016, 309, 152–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montardini, M.; Sangalli, G.; Tamellini, L. Optimal-order isogeometric collocation at Galerkin superconvergent points. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2017, 316, 741–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, D.; Qi, D.; Li, X. Superconvergent isogeometric collocation method with Greville points. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2021, 377, 113689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marino, E.; Hosseini, S.F.; Hashemian, A.; Reali, A. Effects of parameterization and knot placement techniques on primal and mixed isogeometric collocation formulations of spatial shear-deformable beams with varying curvature and torsion. Comput. Math. Appl. 2020, 80, 2563–2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, Z.; Ma, W. Isogeometric collocation method with intuitive derivative constraints for PDE-based analysis-suitable parameterizations. Comput. Aided Geom. Des. 2021, 87, 101994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, D. Optimal multilevel preconditioners for isogeometric collocation methods. Math. Comput. Simul. 2020, 168, 76–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, D.; Pavarino, L.; Scacchi, S. Overlapping Additive Schwarz preconditioners for isogeometric collocation discretizations of linear elasticity. Comput. Math. Appl. 2021, 93, 66–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Lin, H. New perspective to isogeometric analysis: Solving isogeometric analysis problem by fitting load function. Comput. Model. Eng. Sci. 2022, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Boor, C. A Practical Guide to Splines; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1978; Volume 27. [Google Scholar]
- Reali, A.; Gomez, H. An isogeometric collocation approach for Bernoulli–Euler beams and Kirchhoff plates. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2015, 284, 623–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weeger, O.; Yeung, S.K.; Dunn, M.L. Isogeometric collocation methods for Cosserat rods and rod structures. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2017, 316, 100–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marino, E. Locking-free isogeometric collocation formulation for three-dimensional geometrically exact shear-deformable beams with arbitrary initial curvature. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2017, 324, 546–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beirão da Veiga, L.; Lovadina, C.; Reali, A. Avoiding shear locking for the Timoshenko beam problem via isogeometric collocation methods. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2012, 241–244, 38–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auricchio, F.; Beirão da Veiga, L.; Kiendl, J.; Lovadina, C.; Reali, A. Locking-free isogeometric collocation methods for spatial Timoshenko rods. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2013, 263, 113–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, J.; Hiemstra, R.; Hughes, T.; Reali, A. Explicit higher-order accurate isogeometric collocation methods for structural dynamics. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2018, 338, 208–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marino, E.; Kiendl, J.; De Lorenzis, L. Isogeometric collocation for implicit dynamics of three-dimensional beams undergoing finite motions. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2019, 356, 548–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavan, G.; Muppidi, H.; Dixit, J. Static, free vibrational and buckling analysis of laminated composite beams using isogeometric collocation method. Eur. J. Mech. A/Solids 2022, 96, 104758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weeger, O.; Schillinger, D.; Müller, R. Mixed isogeometric collocation for geometrically exact 3D beams with elasto-visco-plastic material behavior and softening effects. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2022, 399, 115456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavan, G.; Nanjunda Rao, K. Bending analysis of laminated composite plates using isogeometric collocation method. Compos. Struct. 2017, 176, 715–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurin, F.; Greco, F.; Coox, L.; Vandepitte, D.; Desmet, W. Isogeometric collocation for Kirchhoff-Love plates and shells. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2018, 329, 396–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahrendorf, F.; Morganti, S.; Reali, A.; Hughes, T.; De Lorenzis, L. Mixed stress-displacement isogeometric collocation for nearly incompressible elasticity and elastoplasticity. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2020, 369, 113112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morganti, S.; Fahrendorf, F.; Lorenzis, L.D.; Evans, J.A.; Hughes, T.; Reali, A. Isogeometric Collocation: A Mixed Displacement-Pressure Method for Nearly Incompressible Elasticity. Comput. Model. Eng. Sci. 2021, 129, 1125–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elguedj, T.; Bazilevs, Y.; Calo, V.M.; Hughes, T.J.R. B- and F- projection methods for nearly incompressible linear and non-linear elasticity and plasticity using higher-order NURBS elements. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2010, 197, 2732–2762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, W.; Nguyen-Thanh, N.; Zhou, K. An isogeometric-meshfree collocation approach for two-dimensional elastic fracture problems with contact loading. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2020, 223, 106779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayala, T.; Videla, J.; Anitescu, C.; Atroshchenko, E. Enriched Isogeometric Collocation for two-dimensional time-harmonic acoustics. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2020, 365, 113033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zampieri, E.; Pavarino, L.F. Isogeometric collocation discretizations for acoustic wave problems. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2021, 385, 114047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atroshchenko, E.; Calderon Hurtado, A.; Anitescu, C.; Khajah, T. Isogeometric collocation for acoustic problems with higher-order boundary conditions. Wave Motion 2022, 110, 102861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casquero, H.; Liu, L.; Bona-Casas, C.; Zhang, Y.; Gomez, H. A hybrid variational-collocation immersed method for fluid-structure interaction using unstructured T-splines. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 2016, 105, 855–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morganti, S.; Callari, C.; Auricchio, F.; Reali, A. Mixed isogeometric collocation methods for the simulation of poromechanics problems in 1D. Meccanica 2018, 53, 1441–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Darve, E. Isogeometric collocation method for the fractional Laplacian in the 2D bounded domain. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2020, 364, 112936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostas, K.; Ginnis, A.; Politis, C.; Kaklis, P. Shape-optimization of 2D hydrofoils using an Isogeometric BEM solver. Comput.-Aided Des. 2017, 82, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gillebaart, E.; De Breuker, R. Low-fidelity 2D isogeometric aeroelastic analysis and optimization method with application to a morphing airfoil. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2016, 305, 512–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, J.; Xue, H.; Gao, L.; Luo, Z. Topology optimization for auxetic metamaterials based on isogeometric analysis. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2019, 352, 211–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Ren, J.; Hu, H.; Lin, H. Topology optimization for parametric porous structure based on isogeometric analysis. J. Jilin Univ. (Sci. Ed.) 2021, 59, 65–76. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, C.; Hu, H.; Lin, H.; Yan, J. Isogeometric Analysis-Based Topological Optimization for Heterogeneous Parametric Porous Structures. J. Syst. Sci. Complex. 2022, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Lian, H.; Liu, Z.; Gong, Y.; Zheng, C.; Bordas, S. Bi-material topology optimization for fully coupled structural-acoustic systems with isogeometric FEM–BEM. Eng. Anal. Bound. Elem. 2022, 135, 182–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Lian, H.; Natarajan, S.; Zhao, W.; Chen, X.; Bordas, S. Multi-frequency acoustic topology optimization of sound-absorption materials with isogeometric boundary element methods accelerated by frequency-decoupling and model order reduction techniques. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2022, 395, 114997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostas, K.; Ginnis, A.; Politis, C.; Kaklis, P. Ship-hull shape optimization with a T-spline based BEM–isogeometric solver. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2015, 284, 611–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xie, X.; Wang, S.; Xu, M.; Wang, Y. A new isogeometric topology optimization using moving morphable components based on R-functions and collocation schemes. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2018, 339, 61–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weeger, O.; Narayanan, B.; Dunn, M.L. Isogeometric shape optimization of nonlinear, curved 3D beams and beam structures. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2019, 345, 26–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
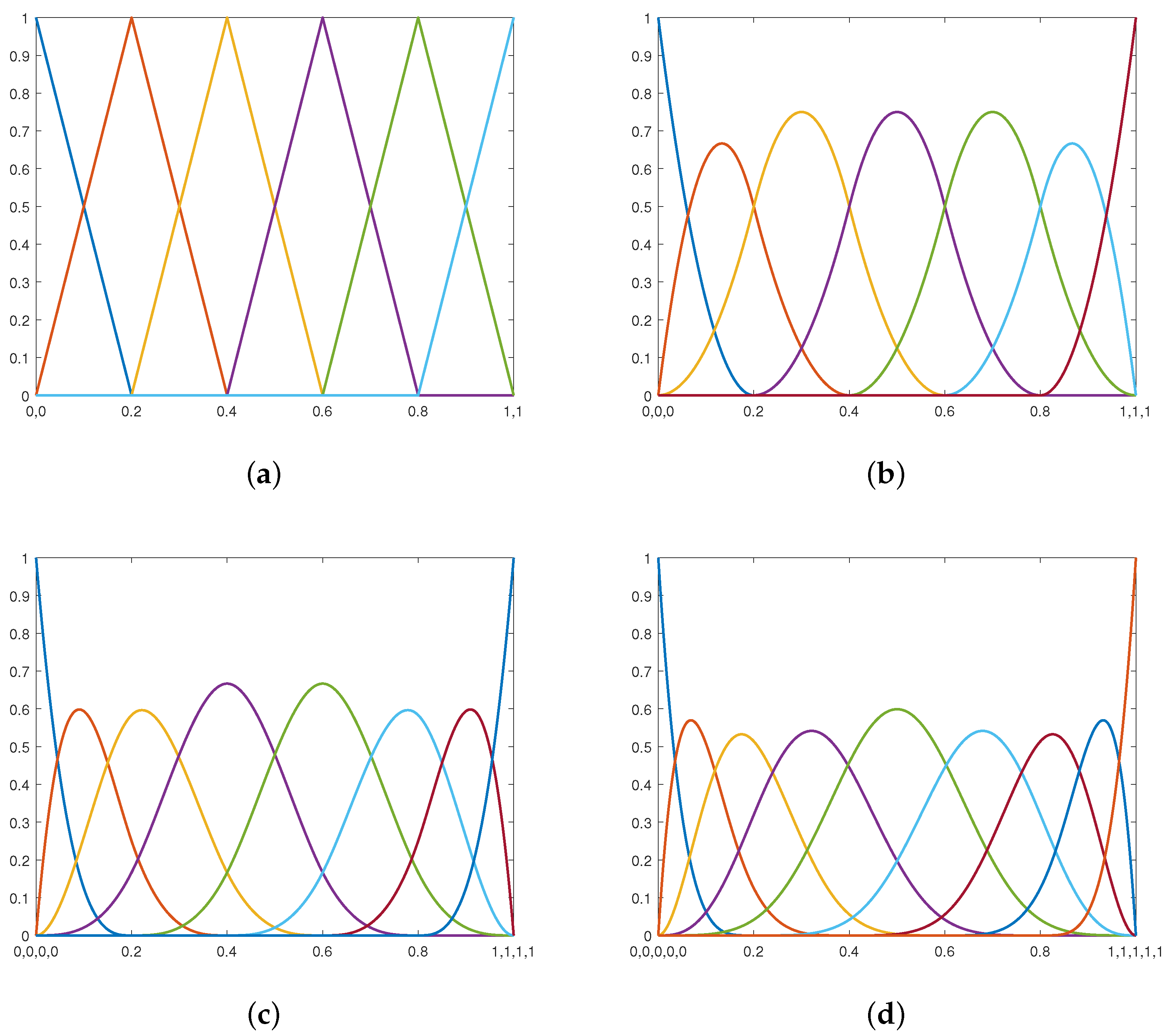
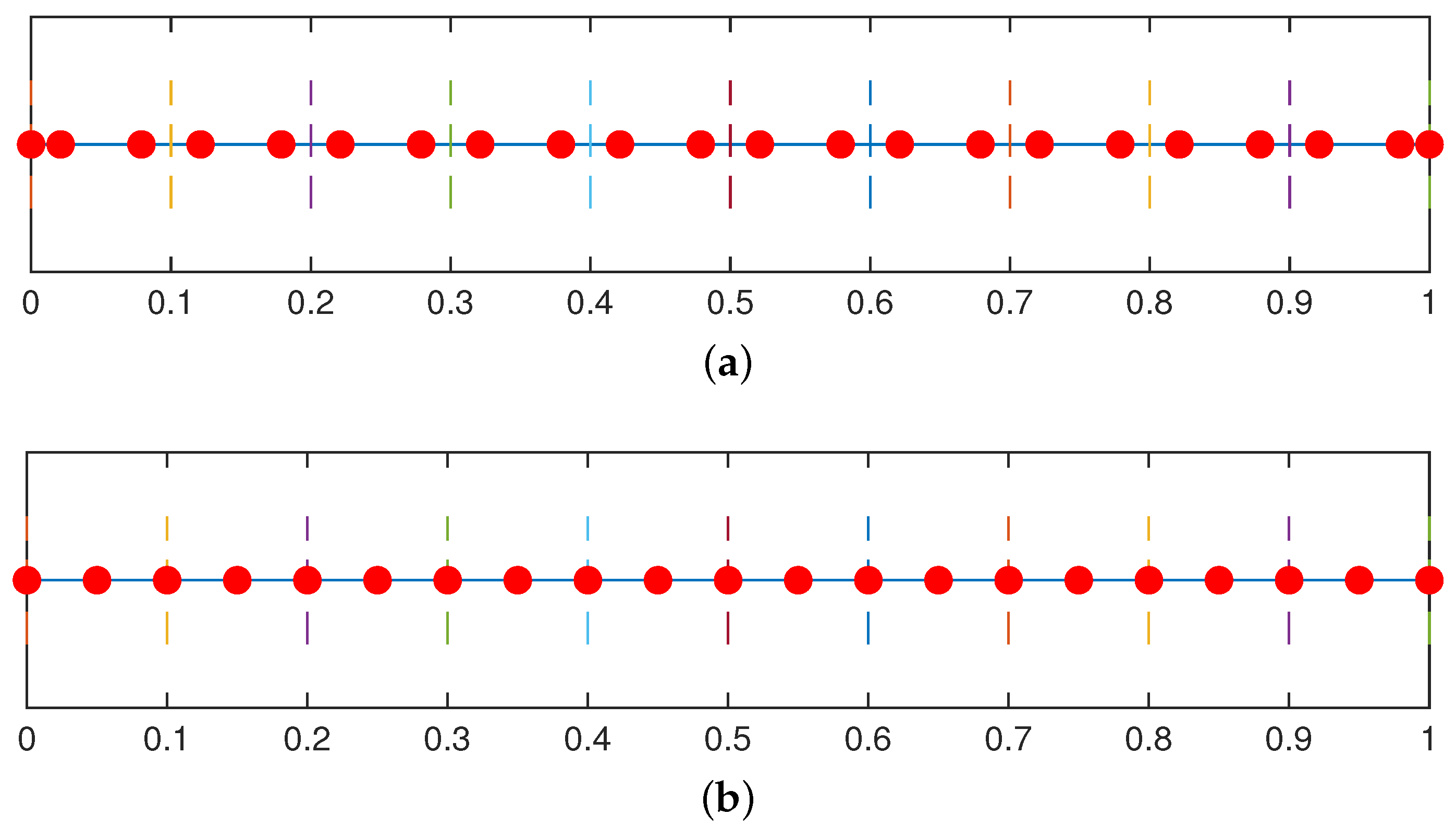
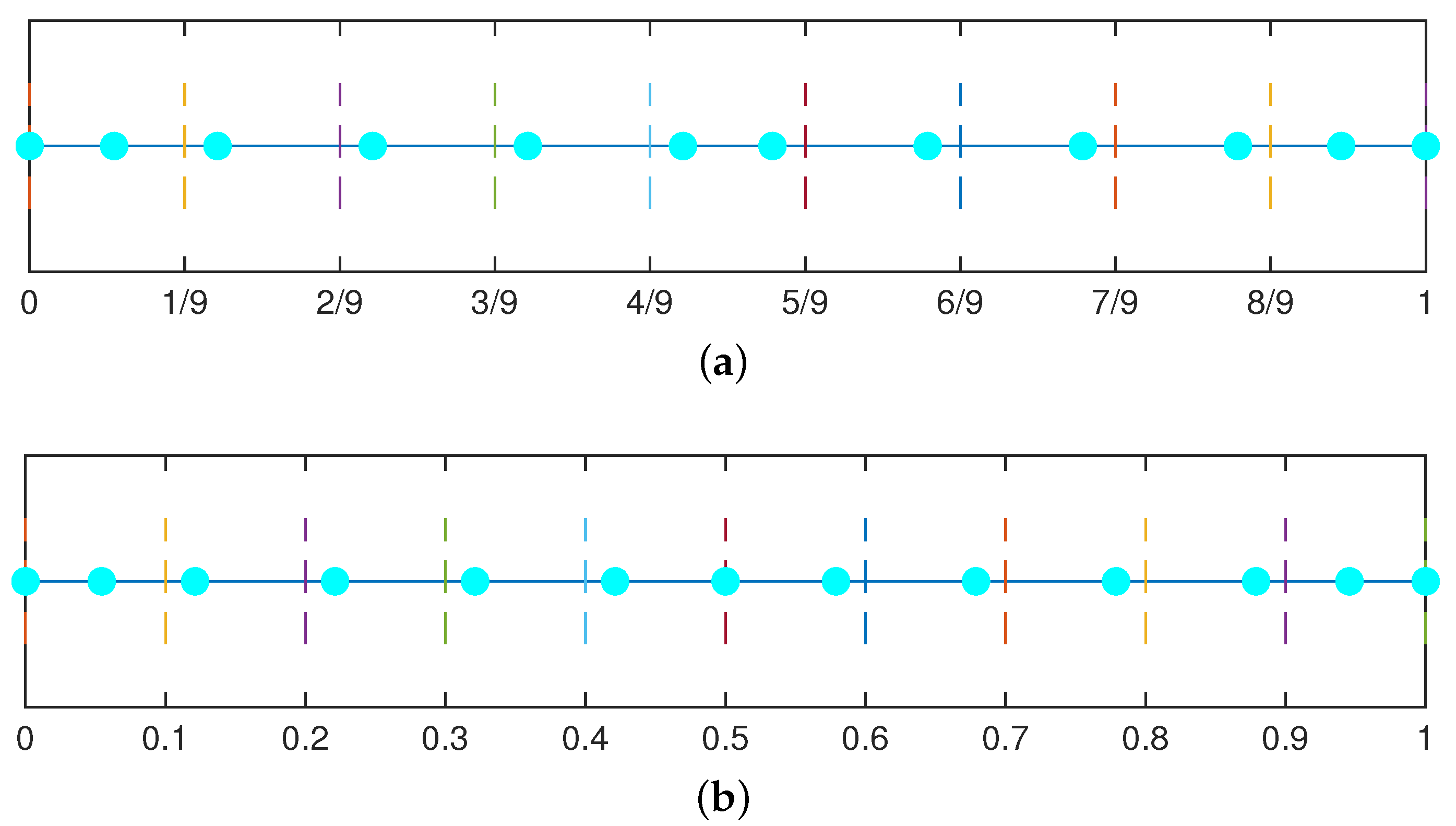
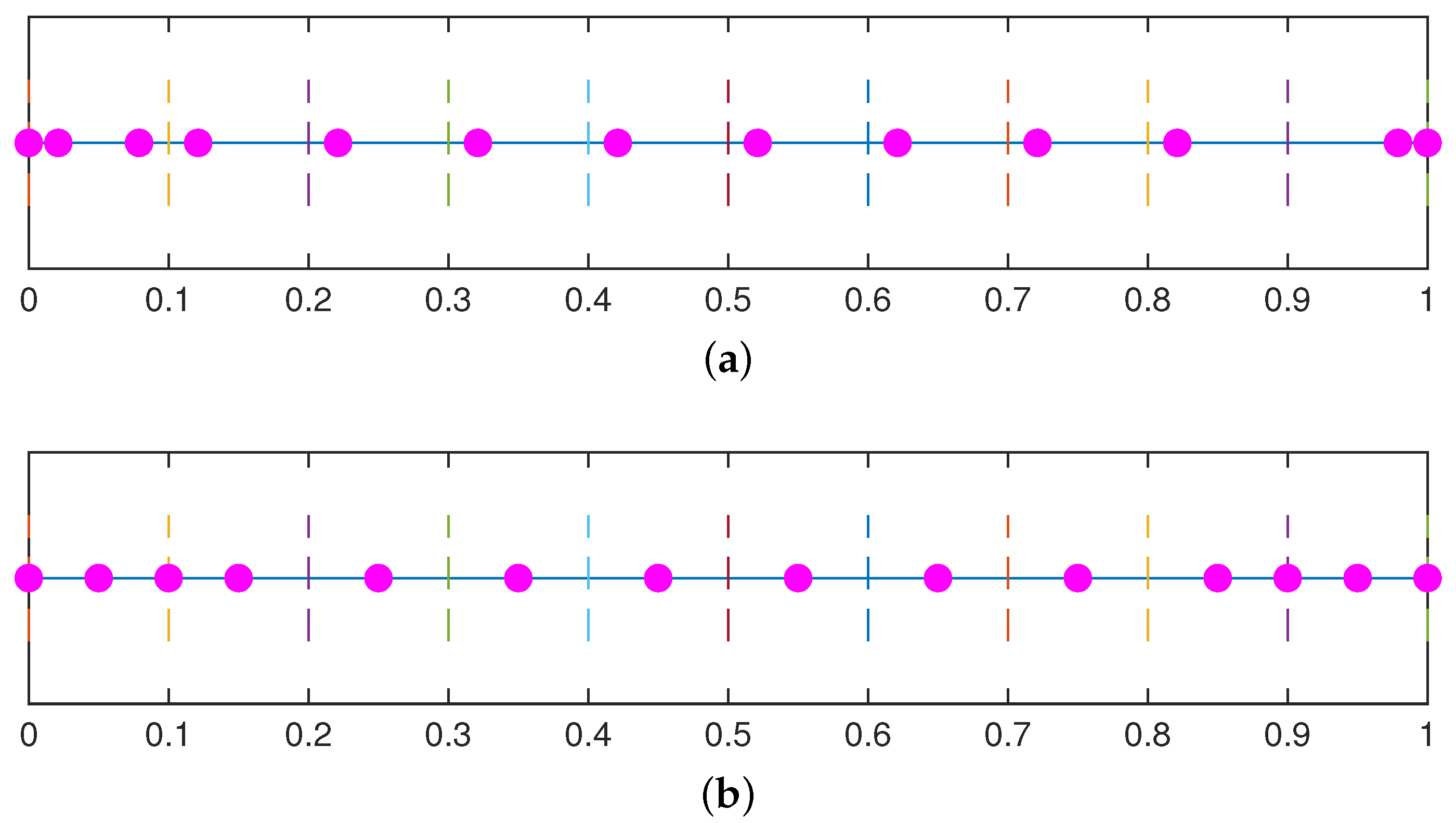
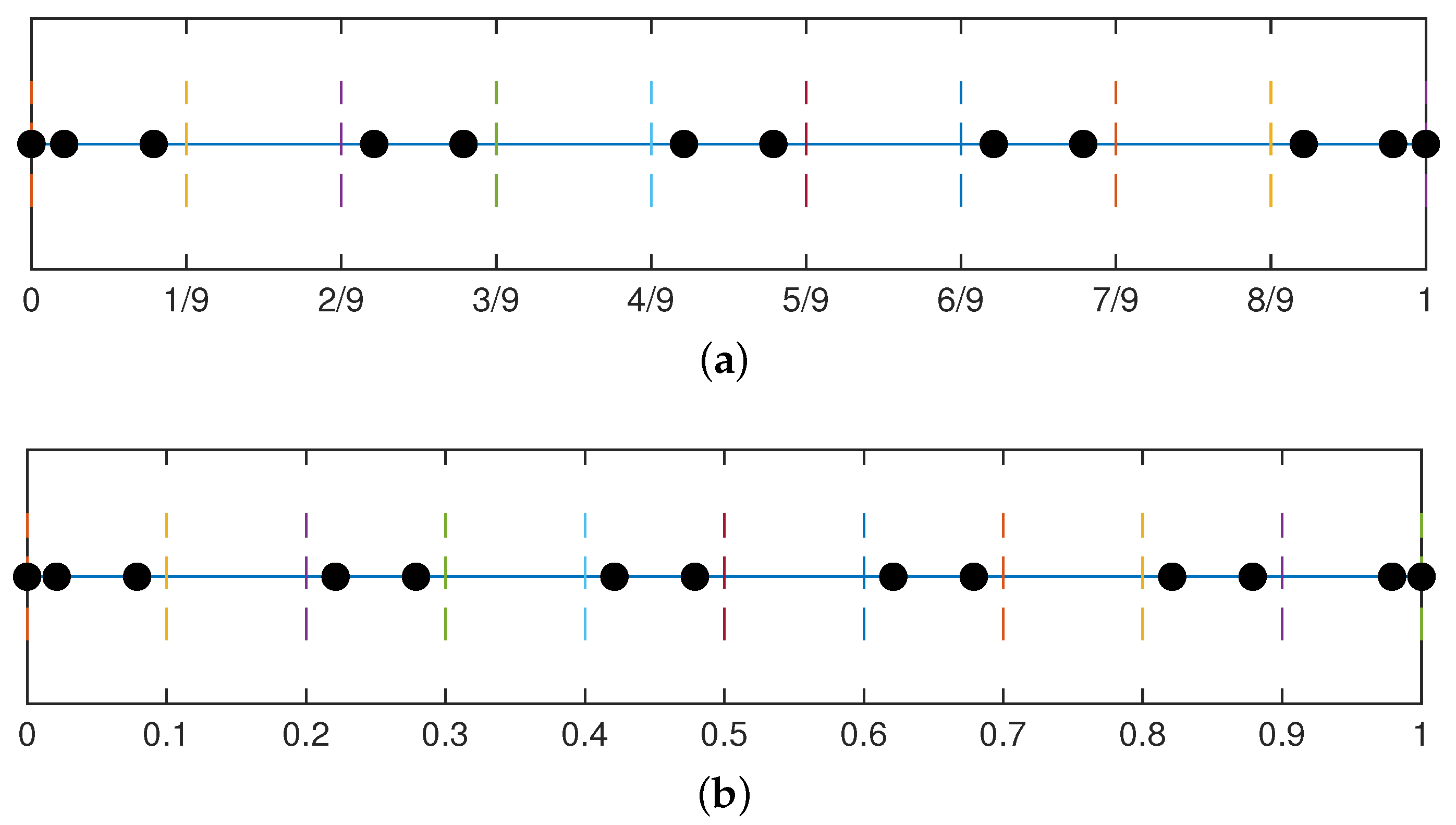

| Degree | Second Derivative Superconvergent Points |
|---|---|
| IGA-C Methods | 169 DoFs | 529 DoFs | 1849 DoFs |
|---|---|---|---|
| Greville | |||
| Demko | |||
| SC | |||
| CG | |||
| ASC | |||
| CSC |
| Galerkin | Demko | Greville | SC | CG | ASC | CSC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| odd p | p | p | |||||
| even p | p | p | p | p | p | p |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ren, J.; Lin, H. A Survey on Isogeometric Collocation Methods with Applications. Mathematics 2023, 11, 469. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11020469
Ren J, Lin H. A Survey on Isogeometric Collocation Methods with Applications. Mathematics. 2023; 11(2):469. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11020469
Chicago/Turabian StyleRen, Jingwen, and Hongwei Lin. 2023. "A Survey on Isogeometric Collocation Methods with Applications" Mathematics 11, no. 2: 469. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11020469
APA StyleRen, J., & Lin, H. (2023). A Survey on Isogeometric Collocation Methods with Applications. Mathematics, 11(2), 469. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11020469





