When Less Is More: Understanding the Adoption of a Minimalist Lifestyle Using the Theory of Planned Behavior
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Data
3.2. Measurement
3.3. Method
4. Results
4.1. The Measurement (Outer) Model
4.2. The Inner Model
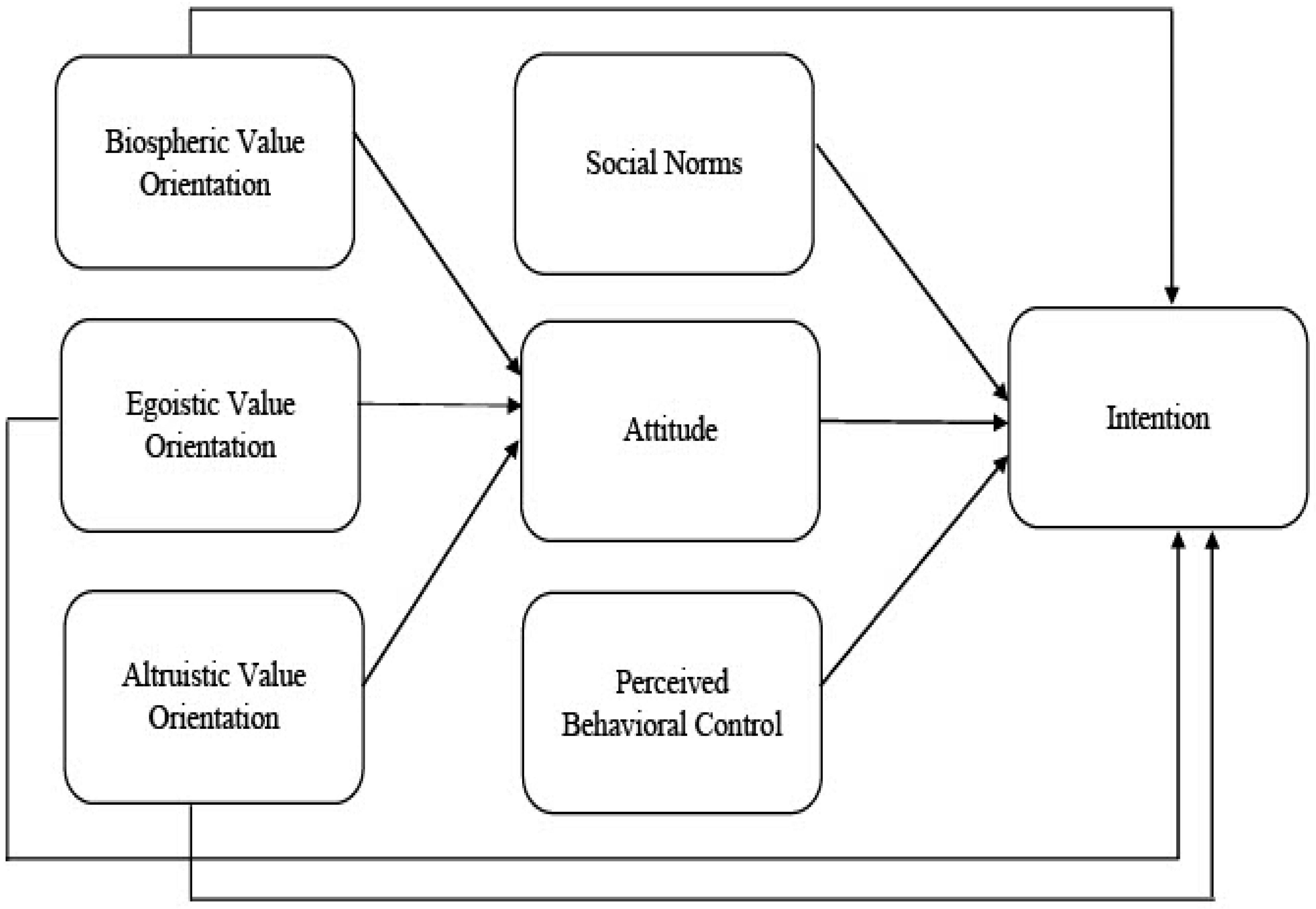
4.2.1. The TPB Dimensions
4.2.2. The Control Variables
4.2.3. The Mediation Effects
5. Discussion
5.1. Theoretical Implication
5.2. Practical Implications
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. The Measurement Items
| Latent Structure | Observed Variables |
| Intention to adopt a minimalist lifestyle (INT) [33,64] | Appoints an individual conscious decision to adopt or not a minimalist lifestyle; INT1–INT3; |
| Attitudes (ATT) [33,64] | Reflect the positive and negative features of adopting a minimalist lifestyle; ATT1–ATT6; |
| Subjective norms (SN) [33,64] | Refers to the perceived social pressure concerning the adoption of a minimalist lifestyle; SN1–SN4; |
| Perceived Behavioral Control (PBC) [33,64] | Refers to the perceived ease or difficulty to accede to a minimalist lifestyle; PBC1, PBC3; |
| Biospheric values (BIO) [43,65,66,68,97] | Concern about the environmental preservation and well-being of other species; BVO1–BVO3; |
| Egoistic values (EGO) [43,65,66,68] | Encompasses the tendency toward material wealth, desire for success and authority; EGO1–EGO3; |
| Altruistic values (ALT) [43,65,66,68] | Concern for the well-being of other individuals. AVO1–AVO4; |
| Dimensions | Item Abbreviation | Item |
| Intention | INT1 | I intend to adopt minimalism in consumption within the next month. |
| INT2 | I plan a minimalist consumption activity within the next month. | |
| INT3 | I will try minimalism in consumption within the next month. | |
| For me minimalism in consumption within the next month would be … | ||
| Attitude | ATT1 | 1 = Harmful/7 = beneficial |
| ATT2 | 1 = Good/7 = bad | |
| ATT3 | 1 = Worthless/7 = valuable | |
| ATT4 | 1= Unpleasant/7 = pleasant | |
| ATT5 | 1 = Dull/7 = exciting | |
| ATT6 | 1 = Unenjoyable/7 = enjoyable | |
| Social Norms | SN1 | Most people who are important to me think that I … 1 = should not adhere to minimalism in consumption within the next month/ 7 = should adhere to minimalism in consumption within the next month. |
| SN2 | The people in my life whose opinion I value would … 1 = disapprove minimalism in consumption within the next month/ 7 = approve minimalism in consumption within the next month | |
| SN3 | Most people who are important to me adopt minimalism in consumption. | |
| SN4 | Many people like me adhere to minimalism in consumption. | |
| Perceived Behavioral Control | PBC1 | If I wanted to, I could adhere to minimalism in consumption within the next month. 1 = definitely false/7 = true |
| dropped | For me adhere to minimalism in consumption within the next month would be … 1 = impossible/7 = possible | |
| PBC3 | How much control do you have over minimalism in consumption within the next month? 1 = not control/7 = full control | |
| How important or unimportant is … as a guiding principle in your life 1 = unimportant/7 = very important | ||
| Altruistic Value Orientation | AVO1 | … equality/equal opportunity for all |
| AVO2 | … helpful (working for the welfare of others) | |
| AVO3 | … social justice (correcting injustice, care for the weak) | |
| AVO4 | … a world at peace (free of war and conflict) | |
| Biospheric Value Orientation | BVO1 | … unity with nature (fitting into nature) |
| BVO2 | … protecting the environment (preserving nature) | |
| BVO3 | … respecting earth (harmony with other species) | |
| Egoistic Value Orientation | EVO1 | … successful (achieving goals) |
| EVO2 | … wealth (material possessions, money) | |
| EVO3 | … authority (the right to lead or command) | |
References
- Brown, P.M.; Cameron, L.D. What Can Be Done to Reduce Overconsumption? Ecol. Econ. 2000, 32, 27–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castano Garcia, A.; Ambrose, A.; Hawkins, A.; Parkes, S. High Consumption, an Unsustainable Habit That Needs More Attention. Energy Res. Soc. Sci. 2021, 80, 102241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Woodhead, A. Limited, Considered and Sustainable Consumption: The (Non) Consumption Practices of UK Minimalists. J. Consum. Cult. 2022, 22, 1012–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dopierała, R. Minimalism—A New Mode of Consumption? Przegląd Socjol. 2017, 66, 67–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd, K.; Pennington, W. Towards a Theory of Minimalism and Wellbeing. Int. J. Appl. Posit. Psychol. 2020, 5, 121–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, A.V.; Bellezza, S. Consumer Minimalism. J. Consum. Res. 2022, 48, 796–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zalewska, J.; Cobel-Tokarska, M. Rationalization of Pleasure and Emotions: The Analysis of the Blogs of Polish Minimalists. Pol. Sociol. Rev. 2016, 196, 495–512. [Google Scholar]
- Roster, C.A.; Ferrari, J.R. Having Less: A Personal Project Taxonomy of Consumers’ Decluttering Orientations, Motives and Emotions. J. Consum. Aff. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etzioni, A. Voluntary Simplicity: Characterization, Select Psychological Implications, and Societal Consequences. In Essays in Socio-Economics; Studies in Economic Ethics and Philosophy; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1999; pp. 1–26. ISBN 978-3-642-08415-7. [Google Scholar]
- Hook, J.N.; Hodge, A.S.; Zhang, H.; Van Tongeren, D.R.; Davis, D.E. Minimalism, Voluntary Simplicity, and Well-Being: A Systematic Review of the Empirical Literature. J. Posit. Psychol. 2021, 18, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matte, J.; Fachinelli, A.C.; De Toni, D.; Milan, G.S.; Olea, P.M. Relationship between Minimalism, Happiness, Life Satisfaction, and Experiential Consumption. SN Soc. Sci. 2021, 1, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Martinez, C.M.J.; Johnson, C. Minimalism as a Sustainable Lifestyle: Its Behavioral Representations and Contributions to Emotional Well-Being. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2021, 27, 802–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meissner, M. Against Accumulation: Lifestyle Minimalism, de-Growth and the Present Post-Ecological Condition. J. Cult. Econ. 2019, 12, 185–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloveras, J.; Quinn, L. Growth and Its Discontents: Paving the Way for a More Productive Engagement with Alternative Economic Practices. J. Macromarketing 2017, 37, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makri, K.; Schlegelmilch, B.B.; Mai, R.; Dinhof, K. What We Know about Anticonsumption: An Attempt to Nail Jelly to the Wall. Psychol. Mark. 2020, 37, 177–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorge, H.; Herbert, M.; Özçağlar-Toulouse, N.; Robert, I. What Do We Really Need? Questioning Consumption Through Sufficiency. J. Macromarketing 2015, 35, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palafox, C.L. When Less Is More: Minimalism and the Environment. Environ. Earth Law J. (EELJ) 2020, 10, 61. [Google Scholar]
- Roșu, M.-M.; Ianole-Călin, R.; Dinescu, R.; Bratu, A.; Papuc, R.-M.; Cosma, A. Understanding Consumer Stockpiling during the COVID-19 Outbreak through the Theory of Planned Behavior. Mathematics 2021, 9, 1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, T.; Pitafi, A.H.; Arya, V.; Wang, Y.; Akhtar, N.; Mubarik, S.; Xiaobei, L. Panic Buying in the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Multi-Country Examination. J. Retail. Consum. Serv. 2021, 59, 102357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheth, J. Impact of COVID-19 on Consumer Behavior: Will the Old Habits Return or Die? J. Bus. Res. 2020, 117, 280–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pangarkar, A.; Shukla, P.; Charles, R. Minimalism in Consumption: A Typology and Brand Engagement Strategies. J. Bus. Res. 2021, 127, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zavestoski, S. The Social–Psychological Bases of Anticonsumption Attitudes. Psychol. Mark. 2002, 19, 149–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fauzi, M.A.; Hanafiah, M.H.; Kunjuraman, V. Tourists’ Intention to Visit Green Hotels: Building on the Theory of Planned Behaviour and the Value-Belief-Norm Theory. J. Tour. Futur. 2022; ahead-of-print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gkargkavouzi, A.; Halkos, G.; Matsiori, S. Environmental Behavior in a Private-Sphere Context: Integrating Theories of Planned Behavior and Value Belief Norm, Self-Identity and Habit. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2019, 148, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajibade, I.; Boateng, G.O. Predicting Why People Engage in Pro-Sustainable Behaviors in Portland Oregon: The Role of Environmental Self-Identity, Personal Norm, and Socio-Demographics. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 289, 112538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, H. Travelers’ pro-Environmental Behavior in a Green Lodging Context: Converging Value-Belief-Norm Theory and the Theory of Planned Behavior. Tour. Manag. 2015, 47, 164–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ateş, H. Merging Theory of Planned Behavior and Value Identity Personal Norm Model to Explain Pro-Environmental Behaviors. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2020, 24, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valsan, C.; Druica, E.; Ianole, R. From Neo-Stalinism to Sluggish Markets: Transition in Romania. In Strategies Towards the New Sustainability Paradigm: Managing the Great Transition to Sustainable Global Democracy; Schwarz-Herion, O., Omran, A., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 35–48. ISBN 978-3-319-14699-7. [Google Scholar]
- Druică, E.; Cornescu, V.; Ianole, R. Consumerism and Hyperconsumerism in the Romanian Society. Glob. Bus. Manag. Res. Int. J. 2010, 2, 386–402. [Google Scholar]
- Ianole, R.; Druică, E.; Cornescu, V. Health Knowledge and Health Consumption in the Romanian Society. Procedia Econ. Financ. 2014, 8, 388–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ianole-Calin, R.; Hubona, G.; Druica, E.; Basu, C. Understanding Sources of Financial Well-Being in Romania: A Prerequisite for Transformative Financial Services. J. Serv. Mark. 2021, 35, 152–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ianole-Calin, R.; Druica, E.; Hubona, G.; Wu, B. What Drives Generations Y and Z towards Collaborative Consumption Adoption? Evidence from a Post-Communist Environment. Kybernetes 2020, 50, 1449–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajzen, I. The Theory of Planned Behavior. Organ. Behav. Hum. Decis. Process. 1991, 50, 179–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, D.; Johnson, K.K.P. Influences of Environmental and Hedonic Motivations on Intention to Purchase Green Products: An Extension of the Theory of Planned Behavior. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2019, 18, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, J.; Modi, A.; Patel, J. Predicting Green Product Consumption Using Theory of Planned Behavior and Reasoned Action. J. Retail. Consum. Serv. 2016, 29, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarimoglu, E.; Gunay, T. The Extended Theory of Planned Behavior in Turkish Customers’ Intentions to Visit Green Hotels. Bus. Strategy Environ. 2020, 29, 1097–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botetzagias, I.; Dima, A.-F.; Malesios, C. Extending the Theory of Planned Behavior in the Context of Recycling: The Role of Moral Norms and of Demographic Predictors. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2015, 95, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Wang, S.; Li, J.; Li, H. Application of the Extended Theory of Planned Behavior to Understand Individual’s Energy Saving Behavior in Workplaces. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2017, 127, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zuo, J.; Cai, H.; Zillante, G. Construction Waste Reduction Behavior of Contractor Employees: An Extended Theory of Planned Behavior Model Approach. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 172, 1399–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayar, I.; Gürbüz, A. Sustainable Consumption Intentions of Consumers in Turkey: A Research Within the Theory of Planned Behavior. SAGE Open 2021, 11, 21582440211047564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Li, L.; Zhang, J. Understanding Consumers’ Sustainable Consumption Intention at China’s Double-11 Online Shopping Festival: An Extended Theory of Planned Behavior Model. Sustainability 2018, 10, 1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ianole-Călin, R.; Francioni, B.; Masili, G.; Druică, E.; Goschin, Z. A Cross-Cultural Analysis of How Individualism and Collectivism Impact Collaborative Consumption. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2020, 157, 104762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roos, D.; Hahn, R. Understanding Collaborative Consumption: An Extension of the Theory of Planned Behavior with Value-Based Personal Norms. J. Bus. Ethics 2019, 158, 679–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotchen, M.J.; Reiling, S.D. Environmental Attitudes, Motivations, and Contingent Valuation of Nonuse Values: A Case Study Involving Endangered Species. Ecol. Econ. 2000, 32, 93–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woersdorfer, J.S. When Do Social Norms Replace Status-Seeking Consumption? An Application to the Consumption of Cleanliness. Metroeconomica 2010, 61, 35–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado, M.S.; Harriger-Lin, J.; Khanna, N. The Value of Environmental Status Signaling. Ecol. Econ. 2015, 111, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Ren, C.; Dong, X.; Zhang, B.; Wang, Z. Determinants Shaping Willingness towards On-Line Recycling Behaviour: An Empirical Study of Household e-Waste Recycling in China. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2019, 143, 218–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huneke, M.E. The Face of the Un-Consumer: An Empirical Examination of the Practice of Voluntary Simplicity in the United States. Psychol. Mark. 2005, 22, 527–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, S.; Ussher, S. The Voluntary Simplicity Movement: A Multi-National Survey Analysis in Theoretical Context. J. Consum. Cult. 2012, 12, 66–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbarossa, C.; De Pelsmacker, P. Positive and Negative Antecedents of Purchasing Eco-Friendly Products: A Comparison Between Green and Non-Green Consumers. J. Bus. Ethics 2016, 134, 229–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stern, P.C.; Dietz, T. The Value Basis of Environmental Concern. J. Soc. Issues 1994, 50, 65–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, S.H. Universals in the Content and Structure of Values: Theoretical Advances and Empirical Tests in 20 Countries. In Advances in Experimental Social Psychology; Zanna, M.P., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1992; Volume 25, pp. 1–65. [Google Scholar]
- Stern, P.C.; Dietz, T.; Kalof, L. Value Orientations, Gender, and Environmental Concern. Environ. Behav. 1993, 25, 322–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, N.T.; Lobo, A.; Greenland, S. Pro-Environmental Purchase Behaviour: The Role of Consumers’ Biospheric Values. J. Retail. Consum. Serv. 2016, 33, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perlaviciute, G.; Steg, L. The Influence of Values on Evaluations of Energy Alternatives. Renew. Energy 2015, 77, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steg, L.; de Groot, J.I.M. Environmental Values. In The Oxford Handbook of Environmental and Conservation Psychology; Clayton, S.D., Ed.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2012; ISBN 978-0-19-973302-6. [Google Scholar]
- Herziger, A.; Berkessel, J.B.; Steinnes, K.K. Wean off Green: On the (in) Effectiveness of Biospheric Appeals for Consumption Curtailment. J. Environ. Psychol. 2020, 69, 101415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolderdijk, J.W.; Steg, L.; Geller, E.S.; Lehman, P.K.; Postmes, T. Comparing the Effectiveness of Monetary versus Moral Motives in Environmental Campaigning. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2013, 3, 413–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griskevicius, V.; Tybur, J.M.; Van den Bergh, B. Going Green to Be Seen: Status, Reputation, and Conspicuous Conservation. J. Personal. Soc. Psychol. 2010, 98, 392–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gärling, T.; Fujii, S.; Gärling, A.; Jakobsson, C. Moderating Effects of Social Value Orientation on Determinants of Proenvironmental Behavior Intention. J. Environ. Psychol. 2003, 23, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, M.; Xu, L. Relationships between Personal Values, Micro-Contextual Factors and Residents’ pro-Environmental Behaviors: An Explorative Study. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2020, 156, 104697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Morais, L.H.L.; Pinto, D.C.; Cruz-Jesus, F. Circular Economy Engagement: Altruism, Status, and Cultural Orientation as Drivers for Sustainable Consumption. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2021, 27, 523–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baltar, F.; Brunet, I. Social Research 2.0: Virtual Snowball Sampling Method Using Facebook. Internet Res. 2012, 22, 57–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fishbein, M.; Ajzen, I. Predicting and Changing Behavior; Psychology Press: London, UK, 2011; ISBN 978-1-136-87473-4. [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz, S.H. Are There Universal Aspects in the Structure and Contents of Human Values? J. Soc. Issues 1994, 50, 19–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Groot, J.I.M.; Steg, L. Value Orientations and Environmental Beliefs in Five Countries: Validity of an Instrument to Measure Egoistic, Altruistic and Biospheric Value Orientations. J. Cross-Cult. Psychol. 2007, 38, 318–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojea, E.; Loureiro, M. Altruistic, Egoistic and Biospheric Values in Willingness to Pay (WTP) for Wildlife. Ecol. Econ. 2007, 63, 807–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stern, P.; Dietz, T.; Abel, T.; Guagnano, G.; Kalof, L. A Value-Belief-Norm Theory of Support for Social Movements: The Case of Environmentalism. Res. Hum. Ecol. 1999, 6, 81–97. [Google Scholar]
- Joreskog, K.G.; Wold, H. The ML and PLS Techniques for Modeling with Latent Variables: Historical and Comparative Aspects. In Systems under Indirect Observation: Causality, Structure, Prediction; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Nederlands, 1982; pp. 263–270. [Google Scholar]
- Hair, J.F.; Ringle, C.M.; Sarstedt, M. PLS-SEM: Indeed a Silver Bullet. J. Mark. Theory Pract. 2011, 19, 139–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hair, J.F.; Risher, J.J.; Sarstedt, M.; Ringle, C.M. When to Use and How to Report the Results of PLS-SEM. Eur. Bus. Rev. 2019, 31, 2–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravand, H.; Baghaei, P. Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modeling with R. Pract. Assess. Res. Eval. 2019, 21, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunnally, J.C.; Bernstein, I.H. Psychometric Theory, 3rd ed.; McGraw-Hill Series in Psychology; Tata McGraw Hill Education Private Ltd.: New Delhi, India, 2010; ISBN 978-0-07-107088-1. [Google Scholar]
- Cortina, J.M. What Is Coefficient Alpha? An Examination of Theory and Applications. J. Appl. Psychol. 1993, 78, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornell, C.; Larcker, D.F. Evaluating Structural Equation Models with Unobservable Variables and Measurement Error. J. Mark. Res. 1981, 18, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, P. A Guide to Econometrics, 6th ed.; Wiley-Blackwell: Malden, MA, USA, 2008; ISBN 978-1-4051-8257-7. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences; Routledge: Oxfordshire, UK, 2013; ISBN 978-1-134-74270-7. [Google Scholar]
- McGouran, C.; Prothero, A. Enacted Voluntary Simplicity—Exploring the Consequences of Requesting Consumers to Intentionally Consume Less. Eur. J. Mark. 2016, 50, 189–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stern, P.C. New Environmental Theories: Toward a Coherent Theory of Environmentally Significant Behavior. J. Soc. Issues 2000, 56, 407–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnould, E.J. Should Consumer Citizens Escape the Market? Ann. Am. Acad. Political Soc. Sci. 2007, 611, 96–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karg, C. New Fashion Minimalism in an Affluent Society: A Paradigm Shift? Ph.D. Thesis, Tese (Doutorado em Fashion Management)-The Swedish School of Textiles-University of Borås, Borås, Sweden, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Naderi, I.; Strutton, D. I Support Sustainability But Only When Doing So Reflects Fabulously on Me: Can Green Narcissists Be Cultivated? J. Macromarketing 2015, 35, 70–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuanr, A.; Pradhan, D.; Chaudhuri, H.R. I (Do Not) Consume; Therefore, I Am: Investigating Materialism and Voluntary Simplicity through a Moderated Mediation Model. Psychol. Mark. 2020, 37, 260–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gökşen, F.; Adaman, F.; Zenginobuz, Ü. On Environmental Concern, Willingness to Pay, and Postmaterialist Values: Evidence from Istanbul; University Library of Munich: Munich, Germany, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Strizhakova, Y.; Coulter, R.A. The “Green” Side of Materialism in Emerging BRIC and Developed Markets: The Moderating Role of Global Cultural Identity. Int. J. Res. Mark. 2013, 30, 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paijmans, H.; Pojani, D. Living Car-Free by Choice in a Sprawling City: Desirable and … Possible? Case Stud. Transp. Policy 2021, 9, 823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil-Giménez, D.; Rolo-González, G.; Suárez, E.; Muinos, G. The Influence of Environmental Self-Identity on the Relationship between Consumer Identities and Frugal Behavior. Sustainability 2021, 13, 9664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.N.; Lobo, A.; Greenland, S. The Influence of Vietnamese Consumers’ Altruistic Values on Their Purchase of Energy Efficient Appliances. Asia Pac. J. Mark. Logist. 2017, 29, 759–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zasuwa, G. Do the Ends Justify the Means? How Altruistic Values Moderate Consumer Responses to Corporate Social Initiatives. J. Bus. Res. 2016, 69, 3714–3719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocken, N.M.P.; Short, S.W. Towards a Sufficiency-Driven Business Model: Experiences and Opportunities. Environ. Innov. Soc. Transit. 2016, 18, 41–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozdamar Ertekin, Z.; Atik, D. Sustainable Markets: Motivating Factors, Barriers, and Remedies for Mobilization of Slow Fashion. J. Macromarketing 2015, 35, 53–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gossen, M.; Ziesemer, F.; Schrader, U. Why and How Commercial Marketing Should Promote Sufficient Consumption: A Systematic Literature Review. J. Macromarketing 2019, 39, 252–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khmara, Y.; Kronenberg, J. Degrowth in Business: An Oxymoron or a Viable Business Model for Sustainability? J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 177, 721–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ianole-Călin, R.; Rădulescu, M.; Druică, E. Sustainable Consumption Behavior Among Romanian Students. In Sustaining Our Environment for Better Future: Challenges and Opportunities; Omran, A., Schwarz-Herion, O., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 159–174. ISBN 9789811371585. [Google Scholar]
- Philip, H.E.; Ozanne, L.K.; Ballantine, P.W. Exploring Online Peer-to-Peer Swapping: A Social Practice Theory of Online Swapping. J. Mark. Theory Pract. 2019, 27, 413–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henninger, C.E.; Bürklin, N.; Niinimäki, K. The Clothes Swapping Phenomenon—When Consumers Become Suppliers. J. Fash. Mark. Manag. Int. J. 2019, 23, 327–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornara, F.; Molinario, E.; Scopelliti, M.; Bonnes, M.; Bonaiuto, F.; Cicero, L.; Admiraal, J.; Beringer, A.; Dedeurwaerdere, T.; de Groot, W.; et al. The Extended Value-Belief-Norm Theory Predicts Committed Action for Nature and Biodiversity in Europe. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2020, 81, 106338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Study Participants | Total N = 741 (100%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | ||||
| Male | Female | |||
| 177 (23.89%) | 564 (76.11%) | |||
| Age | 18–25 | 146 (19.70%) | 462 (62.35%) | 608 (82.05%) |
| 26–35 | 49 (6.61%) | 11 (1.48%) | 60 (8.09%) | |
| 36–45 | 12 (1.62%) | 36 (4.86%) | 48 (6.48%) | |
| 46–55 | 5 (0.67%) | 16 (2.16%) | 21 (2.83%) | |
| 56–65 | 3 (0.40%) | 1 (0.14%) | 4 (0.54%) | |
| Income | Under 500 RON | 45 (6.07%) | 146 (19.71%) | 191 (25.78%) |
| 500–999 RON | 26 (3.50%) | 93 (12.56%) | 119 (16.06%) | |
| 1000–1499 RON | 16 (2.16%) | 58 (7.83%) | 74 (9.99%) | |
| 1500–1999 RON | 13 (1.75%) | 53 (7.15%) | 66 (8.90%) | |
| 2000–2499 RON | 19 (2.56%) | 59 (7.96%) | 78 (10.52%) | |
| 2500–2999 RON | 10 (1.35%) | 38 (5.13%) | 48 (6.48%) | |
| Above 3000 RON | 48 (6.48%) | 117 (15.79%) | 165 (22.27%) | |
| Education | High school | 134 (18.08%) | 420 (56.69%) | 554 (74.77%) |
| Bachelor’s degree | 34 (4.59%) | 99 (13.36%) | 133 (17.95%) | |
| Master’s degree | 6 (0.80%) | 27 (3.65%) | 33 (4.45%) | |
| Doctoral degree | 3 (0.40%) | 18 (2.43%) | 21 (2.83%) | |
| Variable | Composite Reliability | Cronbach’s Alpha | Average Variance Extracted (AVE) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Intention to adopt a minimalist lifestyle (INT) | 0.963 | 0.943 | 0.897 |
| Attitudes (ATT) | 0.956 | 0.944 | 0.783 |
| Subjective norms (SN) | 0.948 | 0.926 | 0.819 |
| Perceived Behavioral control (PBC) | 0.883 | 0.735 | 0.790 |
| Biospheric values (BIO) | 0.944 | 0.911 | 0.849 |
| Egoistic values (EGO) | 0.828 | 0.686 | 0.618 |
| Altruistic values (ALT) | 0.872 | 0.804 | 0.630 |
| INT | ATT | SN | PBC | BIO | EGO | AVO | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| INT1 | 0.940 | −0.009 | −0.030 | −0.004 | 0.028 | 0.017 | −0.029 |
| INT2 | 0.947 | −0.053 | 0.066 | −0.024 | −0.021 | 0.010 | −0.019 |
| INT3 | 0.954 | 0.061 | −0.036 | 0.027 | −0.007 | −0.026 | 0.048 |
| ATT1 | 0.019 | 0.895 | −0.130 | −0.012 | 0.019 | −0.034 | −0.013 |
| ATT2 | −0.041 | 0.908 | −0.110 | 0.017 | 0.048 | −0.054 | 0.032 |
| ATT3 | 0.051 | 0.913 | −0.043 | −0.007 | 0.028 | −0.010 | −0.025 |
| ATT4 | 0.022 | 0.884 | 0.047 | −0.049 | −0.030 | 0.042 | 0.033 |
| ATT5 | −0.050 | 0.839 | 0.144 | 0.018 | −0.036 | 0.060 | −0.064 |
| ATT6 | −0.005 | 0.868 | 0.107 | 0.033 | −0.034 | 0.002 | 0.035 |
| SN1 | −0.030 | 0.005 | 0.892 | −0.039 | 0.042 | 0.067 | −0.042 |
| SN2 | 0.001 | 0.074 | 0.912 | 0.014 | −0.034 | −0.023 | 0.034 |
| SN3 | −0.043 | −0.046 | 0.930 | 0.022 | 0.021 | −0.009 | −0.020 |
| SN4 | 0.075 | −0.033 | 0.885 | 0.002 | −0.029 | −0.035 | 0.028 |
| PBC1 | 0.026 | 0.019 | 0.075 | 0.889 | 0.024 | −0.080 | 0.043 |
| PBC3 | −0.026 | −0.019 | −0.075 | 0.889 | −0.024 | 0.080 | −0.043 |
| BVO1 | −0.000 | 0.004 | 0.042 | 0.011 | 0.906 | −0.005 | 0.050 |
| BVO2 | 0.005 | 0.005 | −0.023 | −0.007 | 0.935 | −0.030 | 0.005 |
| BVO3 | −0.005 | −0.009 | −0.018 | −0.004 | 0.922 | 0.036 | −0.054 |
| EVO1 | −0.101 | 0.066 | −0.144 | 0.084 | 0.276 | 0.701 | 0.144 |
| EVO2 | 0.038 | −0.008 | −0.044 | −0.050 | −0.049 | 0.876 | 0.013 |
| EVO3 | 0.049 | −0.051 | 0.181 | −0.019 | −0.196 | 0.771 | −0.145 |
| AVO1 | 0.046 | −0.111 | 0.040 | −0.022 | −0.092 | −0.159 | 0.827 |
| AVO2 | 0.018 | −0.050 | 0.136 | 0.012 | −0.151 | −0.026 | 0.807 |
| AVO3 | −0.014 | 0.165 | −0.082 | 0.035 | −0.050 | 0.117 | 0.763 |
| AVO4 | −0.054 | 0.008 | −0.103 | −0.024 | 0.304 | 0.081 | 0.777 |
| INT | ATT | SN | PBC | BIO | EGO | AVO | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| INT | 0.947 | 0.745 | 0.573 | 0.567 | 0.312 | 0.097 | 0.383 |
| ATT | 0.745 | 0.885 | 0.486 | 0.618 | 0.418 | 0.139 | 0.481 |
| SN | 0.573 | 0.486 | 0.905 | 0.443 | 0.197 | 0.234 | 0.220 |
| PBC | 0.567 | 0.618 | 0.443 | 0.889 | 0.376 | 0.176 | 0.407 |
| BIO | 0.312 | 0.418 | 0.197 | 0.376 | 0.921 | 0.393 | 0.644 |
| EGO | 0.097 | 0.139 | 0.234 | 0.176 | 0.393 | 0.786 | 0.334 |
| AVO | 0.383 | 0.481 | 0.220 | 0.407 | 0.644 | 0.334 | 0.794 |
| Estimated Coefficients | Direct Effects | Indirect Effects via Mediator | Total Effects | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | Attitudes | Intention | Intention | Intention |
| Attitudes | - | 0.536 *** (p < 0.001) | - | 0.536 *** (p < 0.001) |
| Subjective norms | - | 0.265 *** (p < 0.001) | - | 0.265 *** (p < 0.001) |
| Perceived Behavioral Control | - | 0.106 ** (p = 0.002) | - | 0.106 ** (p = 0.002) |
| Biospheric values | 0.212 *** (p < 0.001) | 0.018 (p = 0.311) | 0.114 *** (p < 0.001) | 0.132 *** (p < 0.001) |
| Egoistic values | 0.065 * (p = 0.038) | 0.069 * (p = 0.029) | 0.035 * (p = 0.026) | 0.104 ** (p = 0.002) |
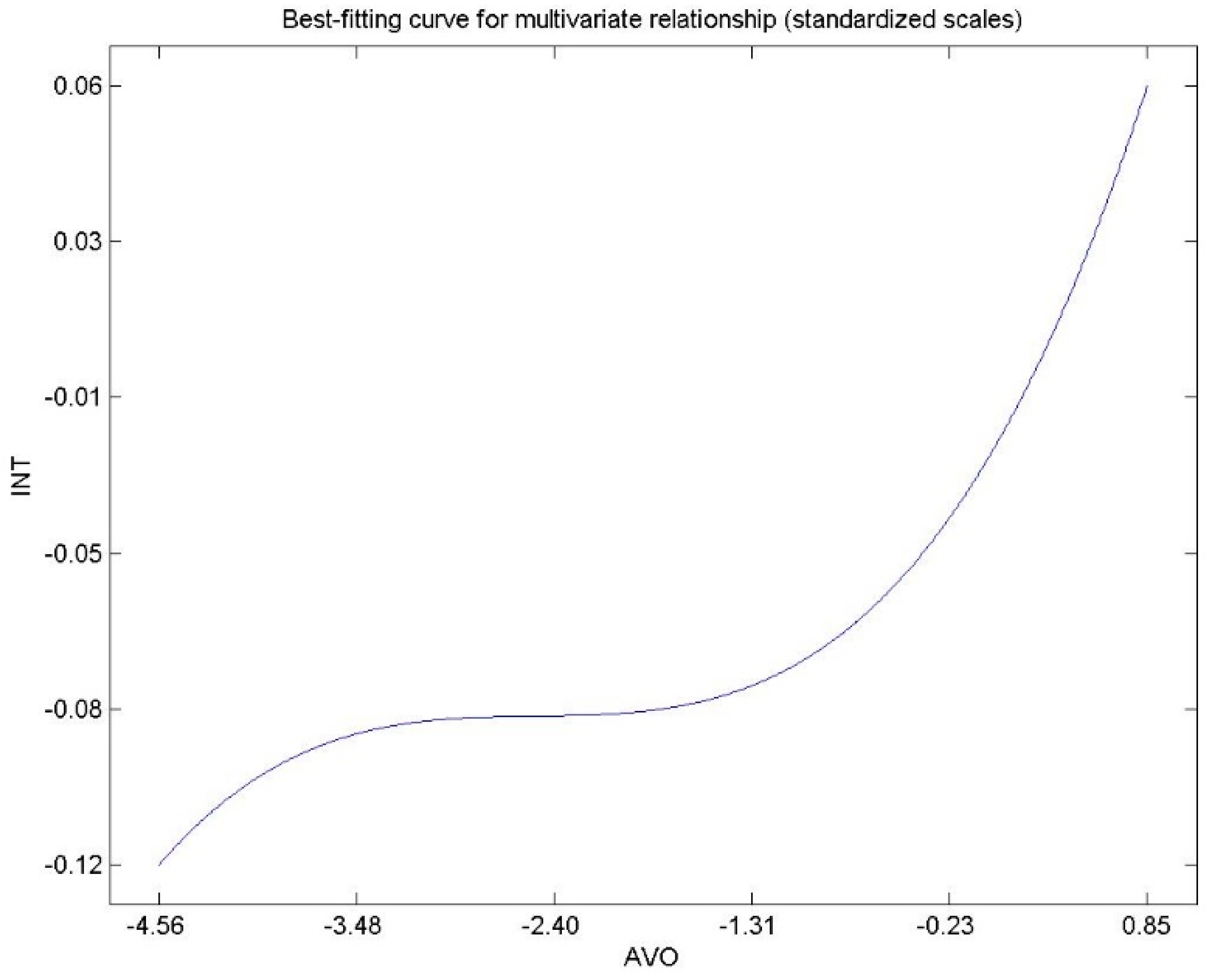
| Altruistic values | 0.393 *** (p < 0.001) | 0.056 (p = 0.064) | 0.211 *** (p < 0.001) | 0.267 *** (p < 0.001) |
| Age | - | 0.008 (p = 0.418) | - | 0.008 (p = 0.418) |
| R2/Adjusted R2 | 29.9%/29.6% | 65.4%/65.1% | - | - |
| Tenehaus GoF | 0.617 (large) | |||
| Estimated Coefficients | Direct Effects | Indirect Effects via Mediator | Total Effects | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | Attitudes | Intention | Intention | Intention |
| Attitudes | - | 0.401 | - | 0.401 |
| Subjective norms | - | 0.153 | - | 0.153 |
| Perceived Behavioral Control | - | 0.061 | - | 0.061 |
| Biospheric values | 0.092 | 0.006 | 0.037 | 0.043 |
| Egoistic values | 0.009 | 0.008 | 0.004 | 0.012 |
| Altruistic values | 0.198 | 0.023 | 0.088 | 0.111 |
| Age | - | 0.001 | - | 0.001 |
| Estimated Coefficients | Direct Effects | |
|---|---|---|
| Model | Attitudes | Intention |
| Attitudes | - | −0.133 * (p = 0.043) |
| Subjective norms | - | 0.045 (p = 0.294) |
| Perceived Behavioral control | - | 0.075 (p = 190) |
| Biospheric values | −0.143 * (p = 0.040) | −0.084 (p = 0.160) |
| Egoistic values | 0.049 (p = 0.284) | 0.006 (p = 0.473) |
| Altruistic values | −0.155 * (p = 0.029) | −0.132 (p = 0.058) |
| Age | - | −0.016 (p = 0.427) |
| Estimated Coefficients | Direct Effects | |
|---|---|---|
| Model | Attitudes | Intention |
| Attitudes | - | 0.175 * (p = 0.013) |
| Subjective norms | - | −0.047 (p = 0.278) |
| Perceived Behavioral control | - | −0.152 * (p = 0.031) |
| Biospheric values | 0.007 (p = 0.465) | −0.062 (p = 0.226) |
| Egoistic values | 0.037 (p = 0.329) | 0.055 (p = 255) |
| Altruistic values | −0.026 (p = 0.309) | 0.040 (p = 0.317) |
| Age | - | 0.042 (p = 0.309) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Druică, E.; Ianole-Călin, R.; Puiu, A.-I. When Less Is More: Understanding the Adoption of a Minimalist Lifestyle Using the Theory of Planned Behavior. Mathematics 2023, 11, 696. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11030696
Druică E, Ianole-Călin R, Puiu A-I. When Less Is More: Understanding the Adoption of a Minimalist Lifestyle Using the Theory of Planned Behavior. Mathematics. 2023; 11(3):696. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11030696
Chicago/Turabian StyleDruică, Elena, Rodica Ianole-Călin, and Andreea-Ionela Puiu. 2023. "When Less Is More: Understanding the Adoption of a Minimalist Lifestyle Using the Theory of Planned Behavior" Mathematics 11, no. 3: 696. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11030696
APA StyleDruică, E., Ianole-Călin, R., & Puiu, A.-I. (2023). When Less Is More: Understanding the Adoption of a Minimalist Lifestyle Using the Theory of Planned Behavior. Mathematics, 11(3), 696. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11030696






