Neural Network Based Control of Four-Bar Mechanism with Variable Input Velocity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Mathematical Model for a Motor-Driven Four-Bar Mechanism System
2.1. Dynamics of the Four-Bar Linkages
2.2. Mathematical Model of the Electric Motor and Transmission
2.3. Dynamic Model of the System
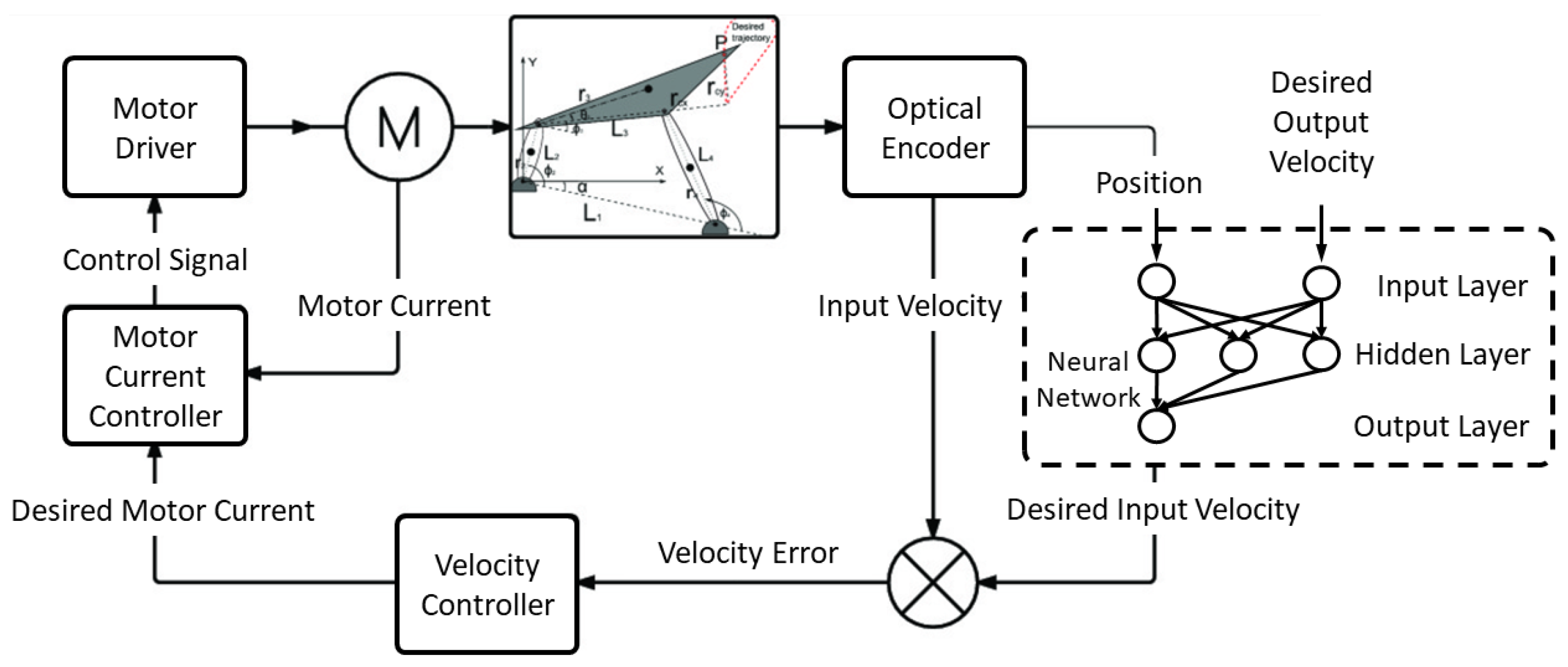
3. ANN-Based PID Control Scheme
3.1. Current Control Loop
3.2. Velocity Control Loop
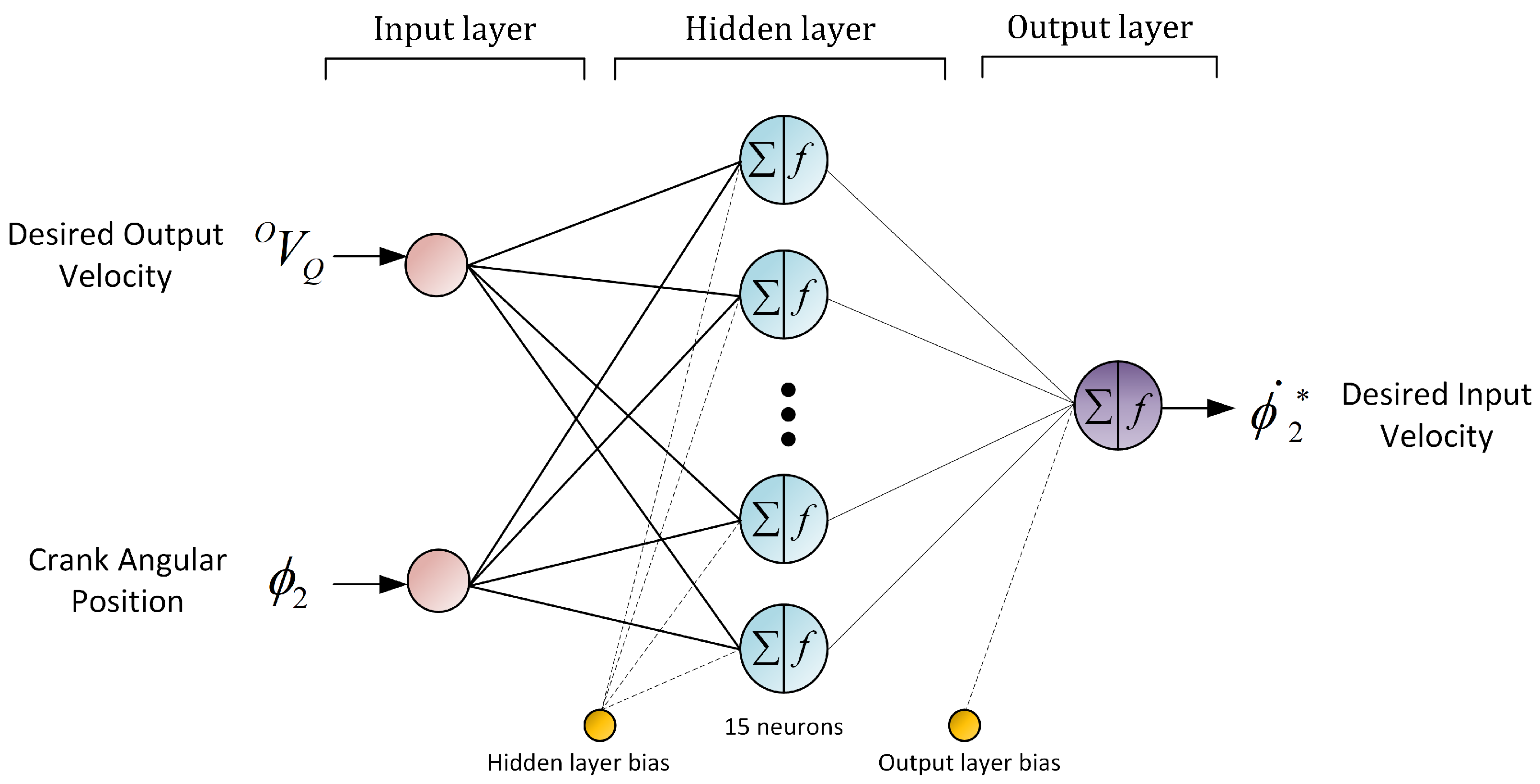
3.3. Variable Input Velocity Generator with Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs)
4. Simulation Results and Discussion
4.1. Servo-Controlled Four-Bar Mechanism Simulation Parameters
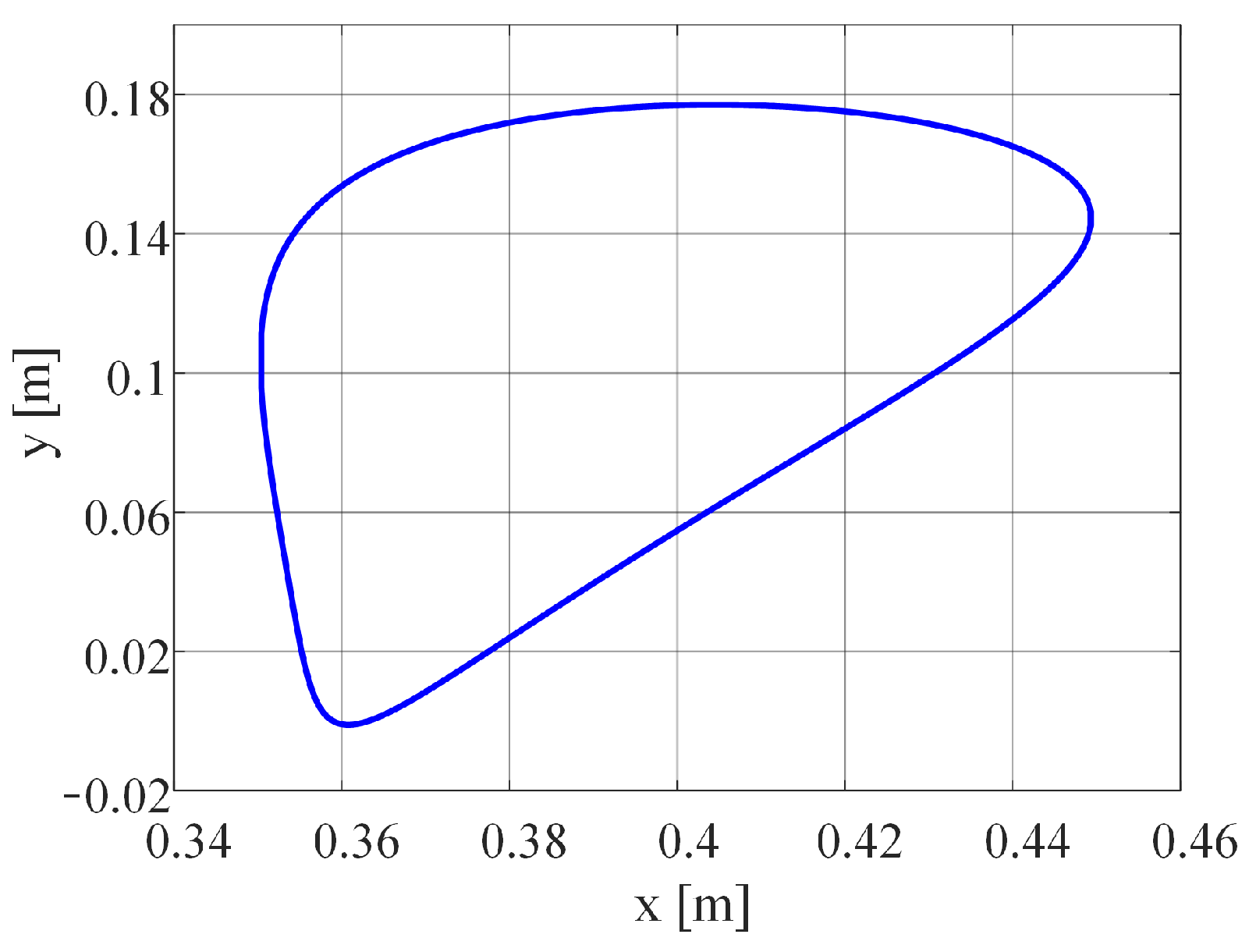
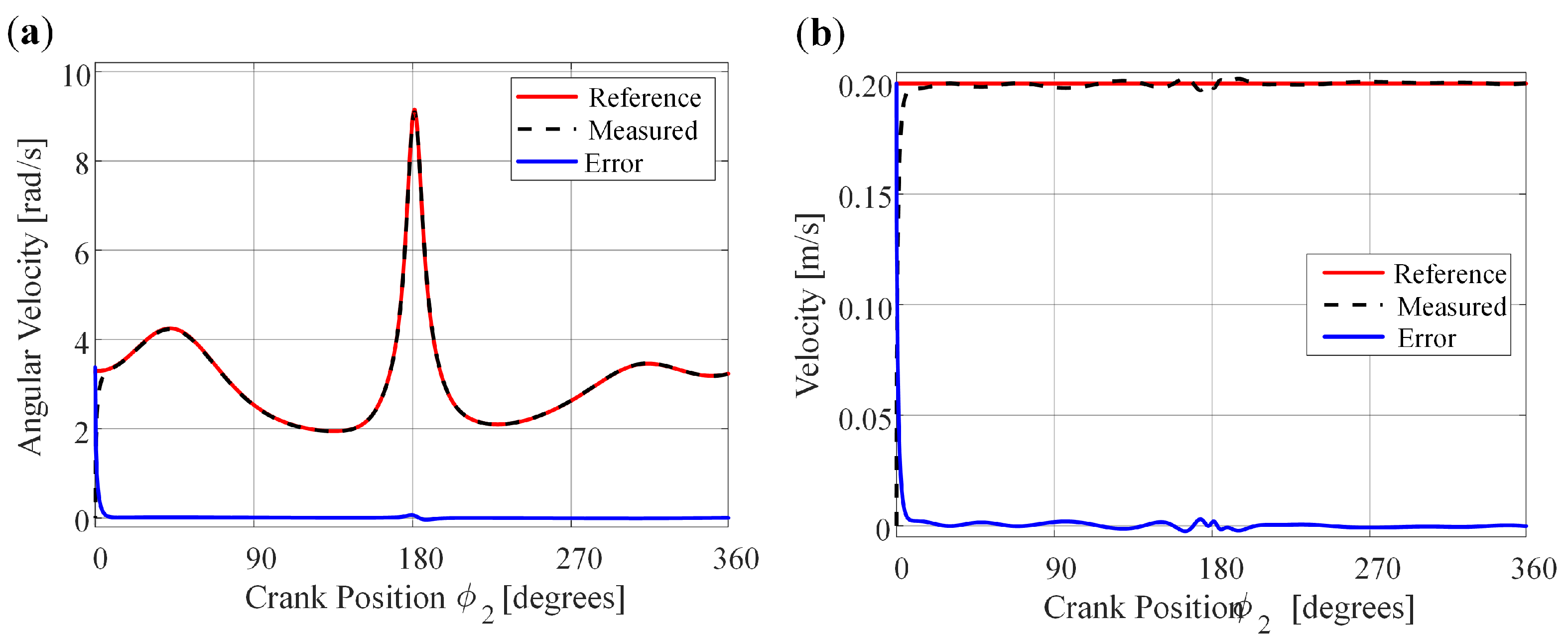
4.2. Constant Crank Velocity
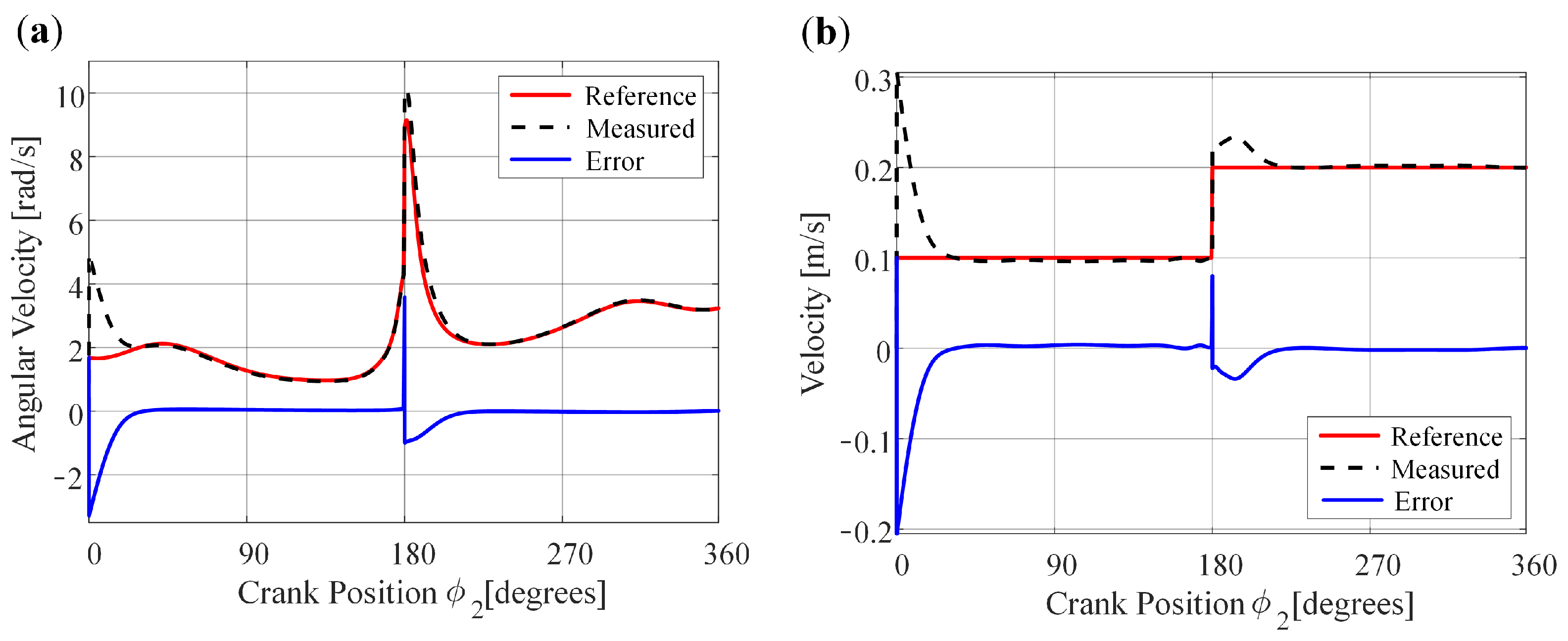
4.3. Variable Input Velocity for Obtaining a Constant Output Velocity at the Coupler Point
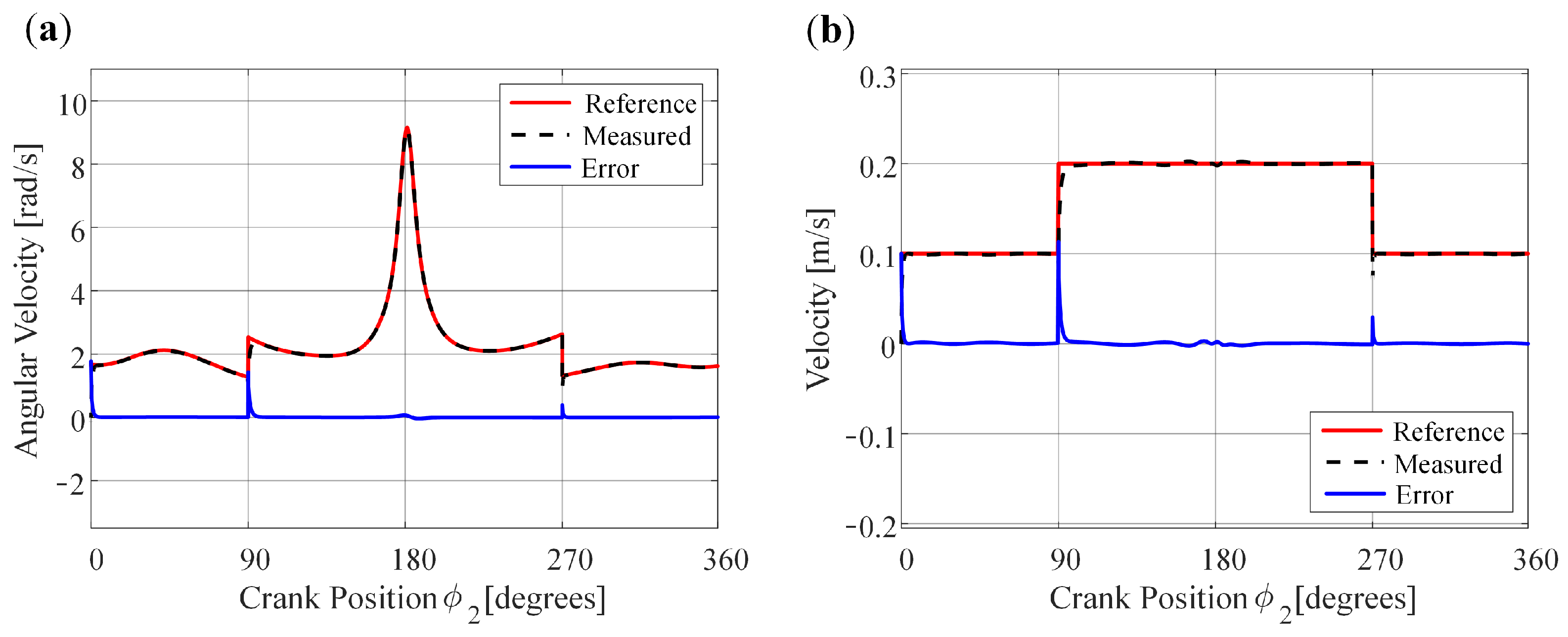
4.4. Variable Input Velocity for Generating Two Different Output Velocities at the Coupler Point
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tao, J.; Sadler, J. Constant speed control of a motor driven mechanism system. Mech. Mach. Theory 1995, 30, 737–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dulger, L.; Uyan, S. Modelling, simulation and control of a four-bar mechanism with a brushless servo motor. Mechatronics 1997, 7, 369–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Tso, S.; Guo, L.; Zhang, W. Improving motion tracking of servomotor-driven closed-loop mechanisms using mass-redistribution. Mech. Mach. Theory 2000, 35, 1033–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.X.; Zhang, W.J.; Li, Q.; Ouyang, P.R. Integrated Design and PD Control of High-Speed Closed-loop Mechanisms. J. Dyn. Syst. Meas. Control 2002, 124, 522–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Sun, D.; Zheng, C. Nonlinear trajectory tracking control of a closed-chain manipulator. In Proceedings of the Fifth World Congress on Intelligent Control and Automation (IEEE Cat. No. 04EX788), Hangzhou, China, 15–19 June 2004; Volume 6, pp. 5012–5016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.C.; Chen, J.S. Experiments toward MRAC design for linkage system. Mechatronics 1996, 6, 933–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gündoğdu, Ö.; Erentürk, K. Fuzzy control of a dc motor driven four-bar mechanism. Mechatronics 2005, 15, 423–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koca, G.O.; Akpolat, Z.H.; Özdemir, M. Type-2 Fuzzy Sliding Mode Control of A Four-Bar Mechanism. Int. J. Model. Simul. 2011, 31, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, C.L.; Kuo, C.Y. A stable adaptive fuzzy sliding-mode control for affine nonlinear systems with application to four-bar linkage systems. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2001, 9, 238–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koca, G.O.; Akpolat, Z.H.; Özdemir, M. Development of robust fuzzy control methods and their applications to a mechanical system. Turk. J. Sci. Technol. 2014, 9, 47–56. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, Q.; Bigras, P. Design and implementation of model-free PID fuzzy logic control on a 4-bar parallel mechanism. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Advanced Intelligent Mechatronics (AIM), Busan, Republic of Korea, 7–11 July 2015; pp. 1647–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Feng, C.; Li, B. PID Control of Nonlinear Motor-Mechanism Coupling System Using Artificial Neural Network. In Advances in Neural Networks—ISNN 2006, Proceedings of the Third International Symposium on Neural Networks, Chengdu, China, 28 May–1 June 2006; Wang, J., Yi, Z., Zurada, J.M., Lu, B.L., Yin, H., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; pp. 1096–1103. [Google Scholar]
- Lungu, R.; Sepcu, L.; Lungu, M. Four-Bar Mechanism’s Proportional-Derivative and Neural Adaptive Control for the Thorax of the Micromechanical Flying Insects. J. Dyn. Syst. Meas. Control 2015, 137, 051005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çakar, O.; Tanyıldızı, A.K. Application of moving sliding mode control for a DC motor driven four-bar mechanism. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2018, 10, 1687814018762184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salah, M.; Al-Jarrah, A.; Tatlicioglu, E.; Banihani, S. Robust Backstepping Control for a Four-Bar Linkage Mechanism Driven by a DC Motor. J. Intell. Robot. Syst. 2019, 94, 327–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erenturk, K. Hybrid Control of a Mechatronic System: Fuzzy Logic and Grey System Modeling Approach. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatronics 2007, 12, 703–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Jarrah, A.; Salah, M.; Banihani, S.; Al-Widyan, K.; Ahmad, A. Applications of Various Control Schemes on a Four-Bar Linkage Mechanism Driven by a Geared DC Motor. WSEAS Trans. Syst. Control 2015, 10, 584–597. [Google Scholar]
- Tutunji, T.A.; Salah, M.; Al-Jarrah, A.; Ahmad, A.; Alhamdan, R. Modeling and Identification of a Four-Bar Linkage Mechanism Driven by a Geared DC Motor. Int. Rev. Mech. Eng. 2015, 9, 296–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- İşbitirici, A.; Altuğ, E. Design and Control of a Mini Aerial Vehicle that has Four Flapping-Wings. J. Intell. Robot. Syst. 2017, 88, 247–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohseni, S.A.; Duchaine, V.; Wong, T. A comparative study of the optimal control design using evolutionary algorithms: Application on a close-loop system. In Proceedings of the 2017 Intelligent Systems Conference (IntelliSys), London, UK, 7–8 September 2017; pp. 942–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Molina, A.; Villarreal-Cervantes, M.G.; Aldape-Pérez, M. Indirect adaptive control using the novel online hypervolume-based differential evolution for the four-bar mechanism. Mechatronics 2020, 69, 102384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.; Liu, C.; Sun, Z.; Yue, X. Coupled orbit-attitude dynamics and trajectory tracking control for spacecraft electromagnetic docking. Appl. Math. Model. 2022, 101, 553–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Yue, X.; Shi, K.; Sun, Z. Spacecraft Attitude Control: A Linear Matrix Inequality Approach; Elsevier: London, UK, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrusquía, A.; Flores-Campos, J.A.; Yu, W. Optimal sliding mode control for cutting tasks of quick-return mechanisms. ISA Trans. 2022, 122, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, G.; Wang, F.; Zhang, J.; Alattas, K.A.; Mohammadzadeh, A.; The Vu, M. A New Type-3 Fuzzy Predictive Approach for Mobile Robots. Mathematics 2022, 10, 3186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Zhang, C.; Mohammadzadeh, A. Type-3 Fuzzy Control of Robotic Manipulators. Symmetry 2023, 15, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadzadeh, A.; Sabzalian, M.H.; Ahmadian, A.; Nabipour, N. A dynamic general type-2 fuzzy system with optimized secondary membership for online frequency regulation. ISA Trans. 2021, 112, 150–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.S.; Yan, G.J. Integrated control and mechanism design for the variable input-speed servo four-bar linkages. Mechatronics 2009, 19, 274–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peón-Escalante, R.; Flota-Bañuelos, M.; Ricalde, L.J.; Acosta, C.; Perales, G.S. On the coupler point velocity control of variable input speed servo-controlled four-bar mechanism. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2016, 8, 1687814016678356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flota-Bañuelos, M.; Peón-Escalante, R.; Ricalde, L.J.; Cruz, B.J.; Quintal-Palomo, R.; Medina, J. Vision-based control for trajectory tracking of four-bar linkage. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 2021, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, H.; Poole, C.; Safko, J. Classical Mechanics; Pearson Education: London, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Haykin, S.S. Neural Networks and Learning Machines; Prentice Hall: London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
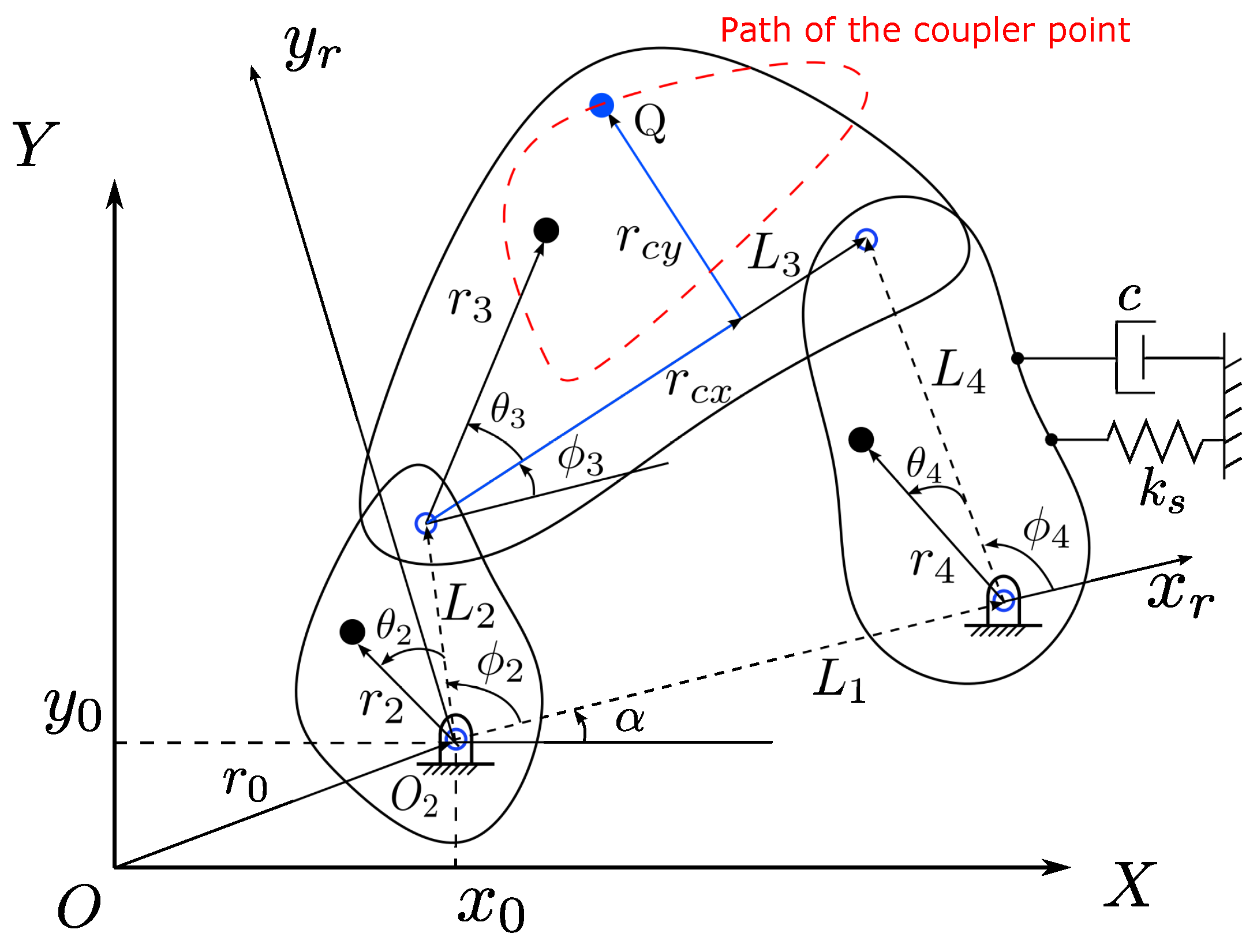
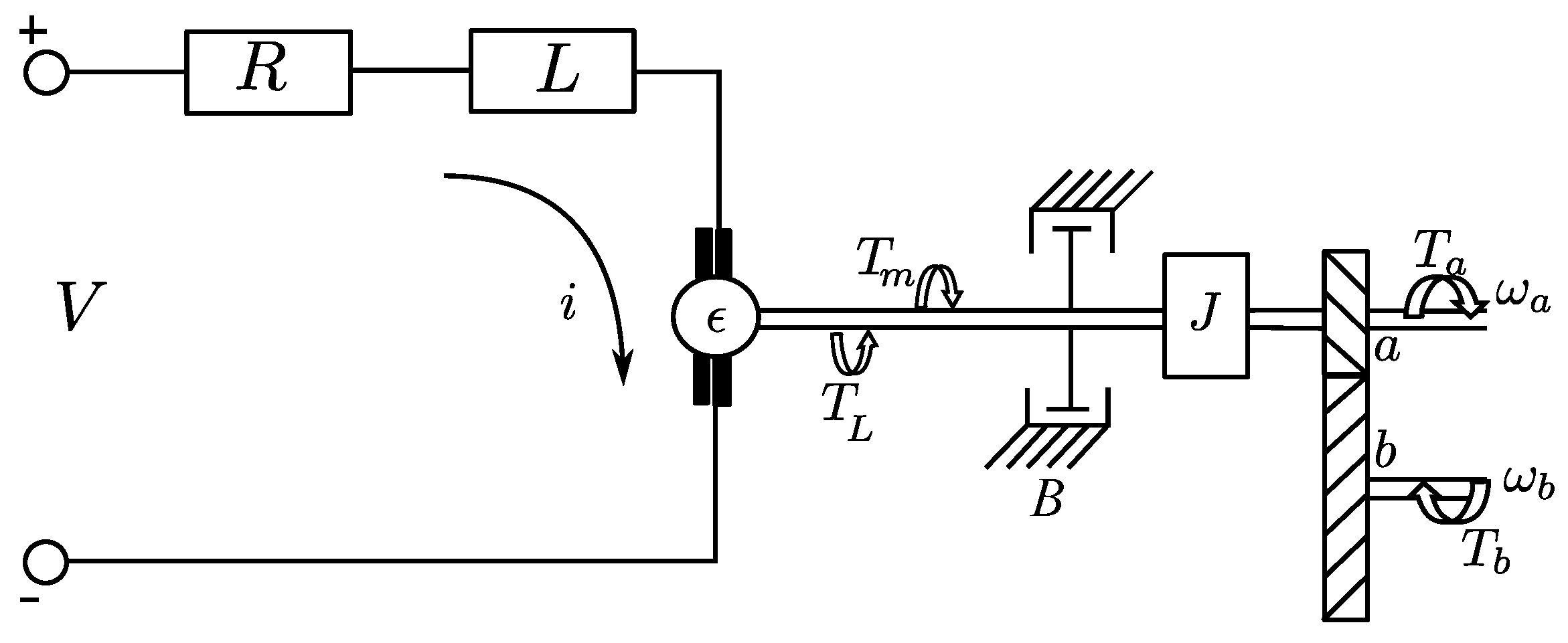


| Parameter | Description for Each Link |
|---|---|
| length of the link i | |
| angular position for link i with respect to the axis | |
| mass of link i | |
| mass moment of inertia | |
| and | location of the center of mass for each link i |
| and | location of point Q on link 3 |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| (m) | 0.3972 |
| (m) | 0.0588 |
| (m) | 0.2351 |
| (m) | 0.22716 |
| (m) | 0.403779 |
| (m) | 0.093921 |
| (kg·m) | |
| (kg·m) | |
| (kg·m) | |
| m (kg) | 0.04234 |
| m (kg) | 0.2586 |
| m (kg) | 0.08156 |
| (rad) | 5.83047 |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| R () | 2 |
| L(H) | 1 |
| (N·m/A) | 0.260 |
| (V·s) | 0.260 |
| J (kg·m) | 0.011 |
| (N·m) | 0.28 |
| B (N·m·s) | 0 |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| 3000 | |
| 200 | |
| 50 | |
| 10.8 | |
| 0 | |
| 100 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Peón-Escalante, R.; Flota-Bañuelos, M.; Quintal-Palomo, R.; Ricalde, L.J.; Peñuñuri, F.; Jiménez, B.C.; Viñas, J.A. Neural Network Based Control of Four-Bar Mechanism with Variable Input Velocity. Mathematics 2023, 11, 2148. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11092148
Peón-Escalante R, Flota-Bañuelos M, Quintal-Palomo R, Ricalde LJ, Peñuñuri F, Jiménez BC, Viñas JA. Neural Network Based Control of Four-Bar Mechanism with Variable Input Velocity. Mathematics. 2023; 11(9):2148. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11092148
Chicago/Turabian StylePeón-Escalante, R., Manuel Flota-Bañuelos, Roberto Quintal-Palomo, Luis J. Ricalde, F. Peñuñuri, B. Cruz Jiménez, and J. Avilés Viñas. 2023. "Neural Network Based Control of Four-Bar Mechanism with Variable Input Velocity" Mathematics 11, no. 9: 2148. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11092148
APA StylePeón-Escalante, R., Flota-Bañuelos, M., Quintal-Palomo, R., Ricalde, L. J., Peñuñuri, F., Jiménez, B. C., & Viñas, J. A. (2023). Neural Network Based Control of Four-Bar Mechanism with Variable Input Velocity. Mathematics, 11(9), 2148. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11092148







