Adaptive Mission Abort Planning Integrating Bayesian Parameter Learning
Abstract
1. Introduction
- A rigorous modeling approach has been employed to account for heterogeneity in the cumulative shock degradation process, a critical factor often overlooked in traditional models. Global Bayesian analysis has been leveraged to enhance the precision of estimating the unknown degradation parameter using real-time degradation signals.
- In order to mitigate the risk of system failure while maintaining mission reliability, an adaptive mission abort policy with integrated parameter learning is proposed, offering a significant advancement over static models. This strategy enables the dynamic adjustment of the abort decision based on the current state of the system.
- The optimal mission abort policy is characterized as an optimal control limit policy. The monotonicity of the value function is examined, and the existence and monotonicity of the optimal abort threshold are established.
2. Compound Poisson Process with Heterogeneity
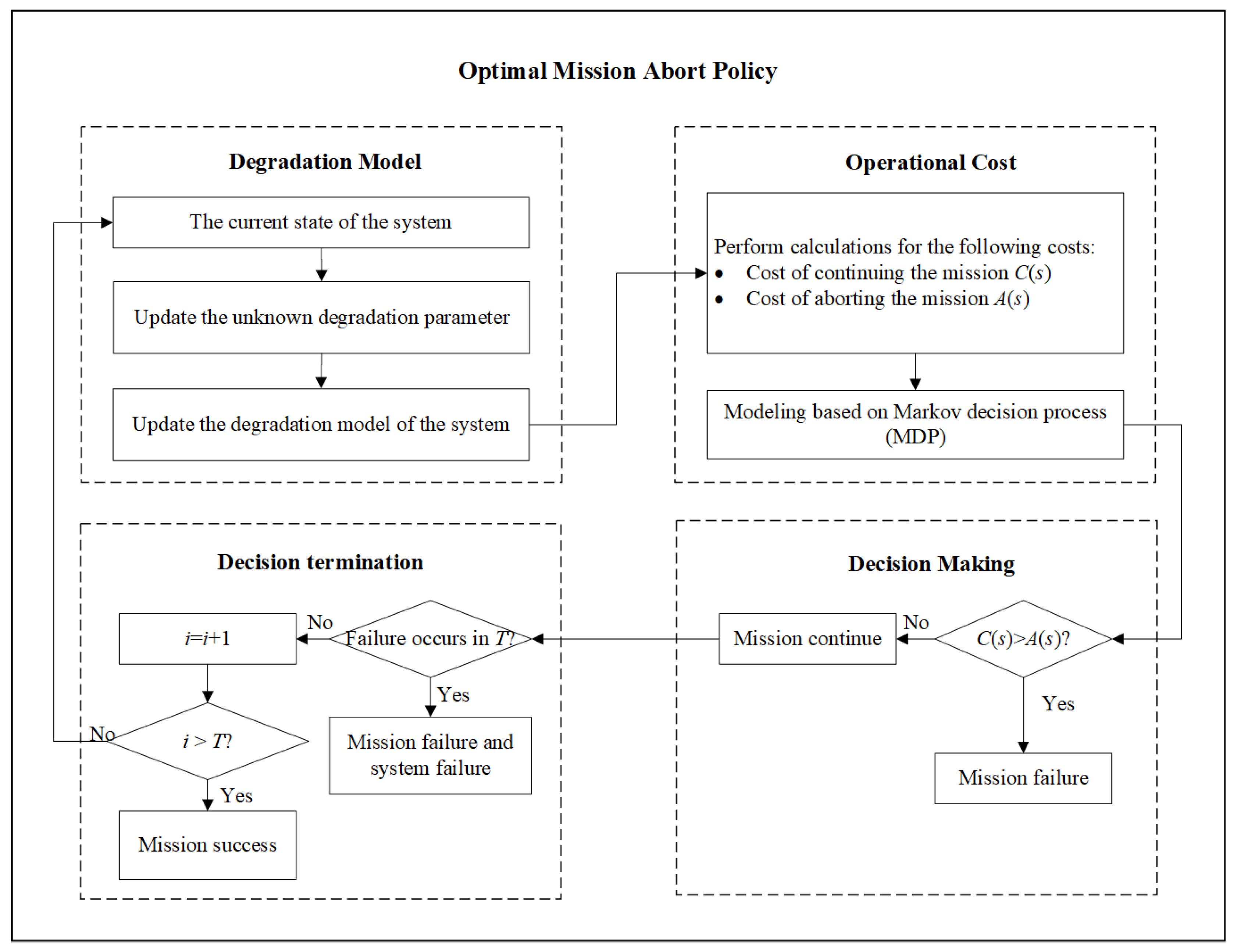
3. Mission Abort Problem for Heterogeneity Degradation
4. Structural Properties
5. Comparative Policies
5.1. Offline Parameter Learning Approach (Policy 1)
5.2. Fixed Abort Threshold (Policy 2)
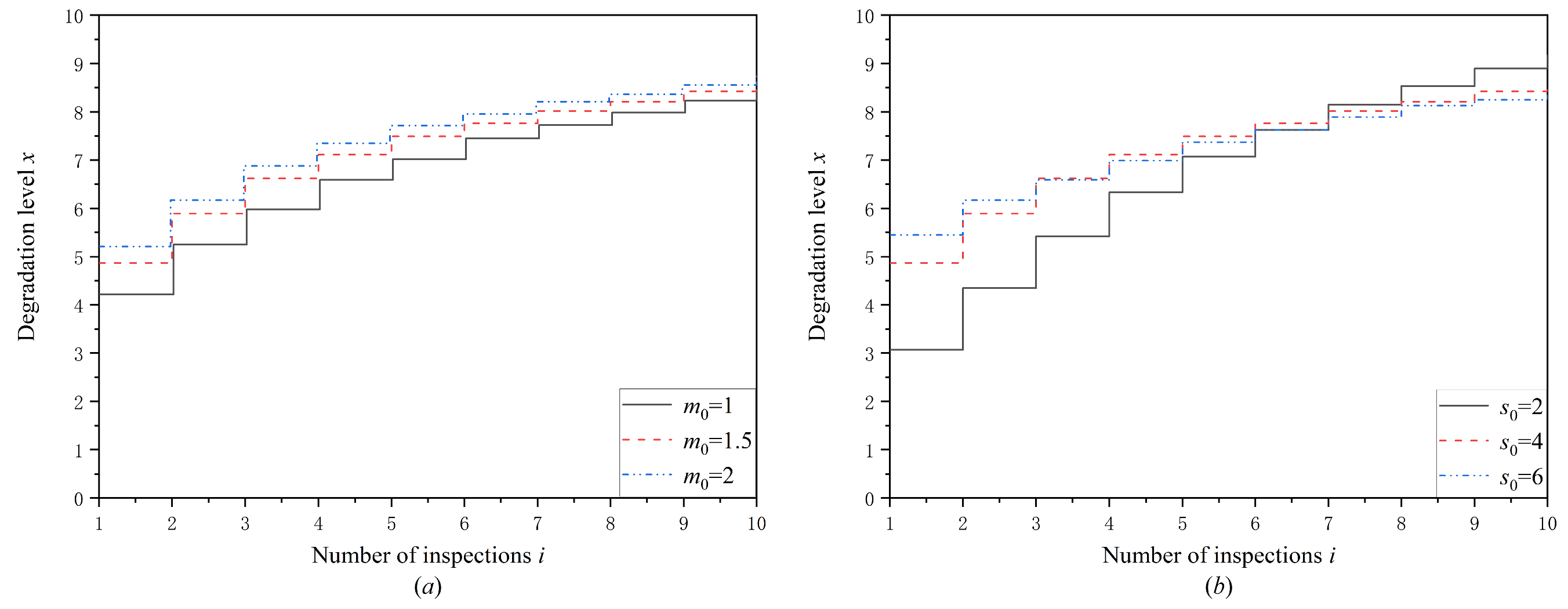
6. Numerical Experiment
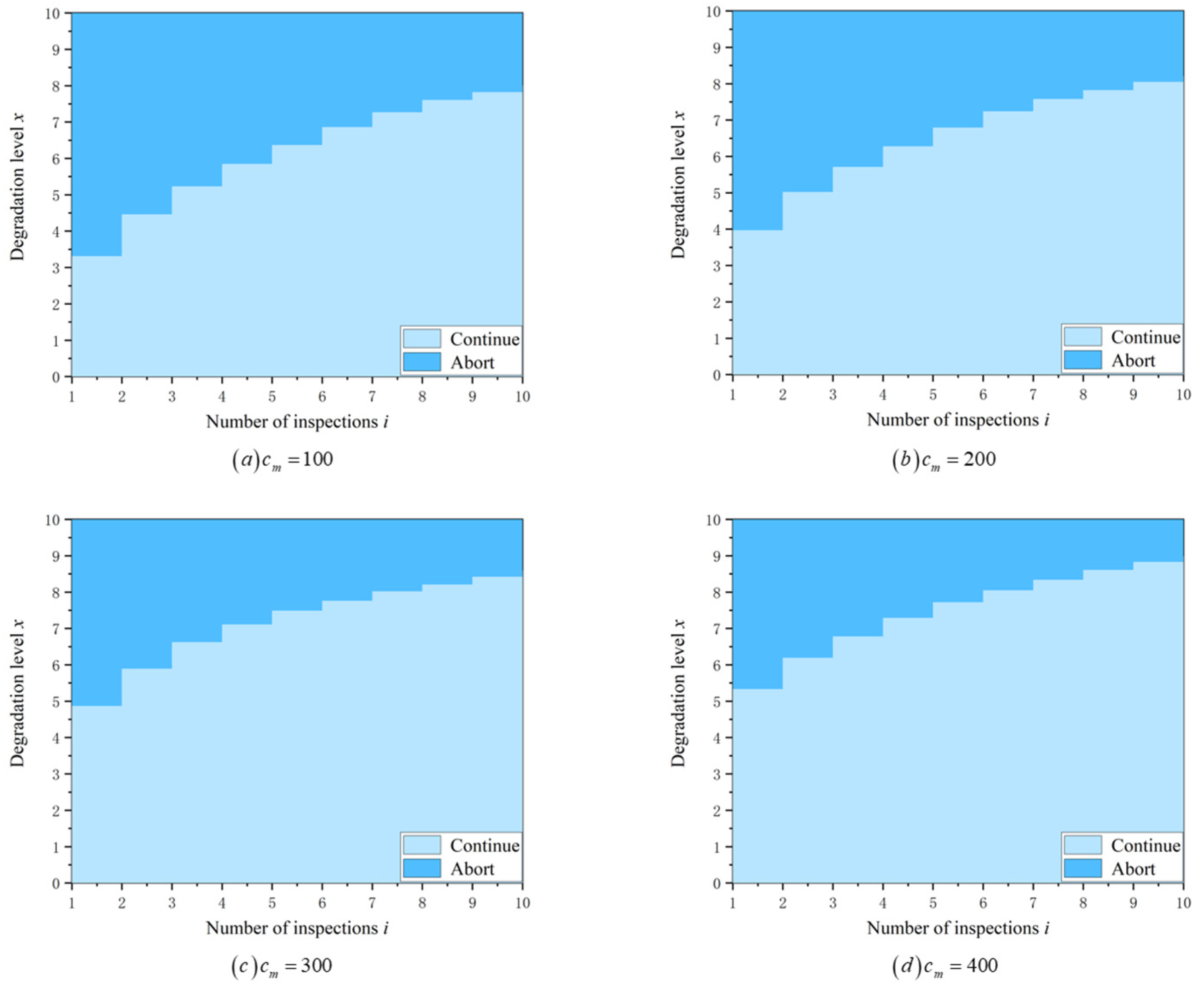
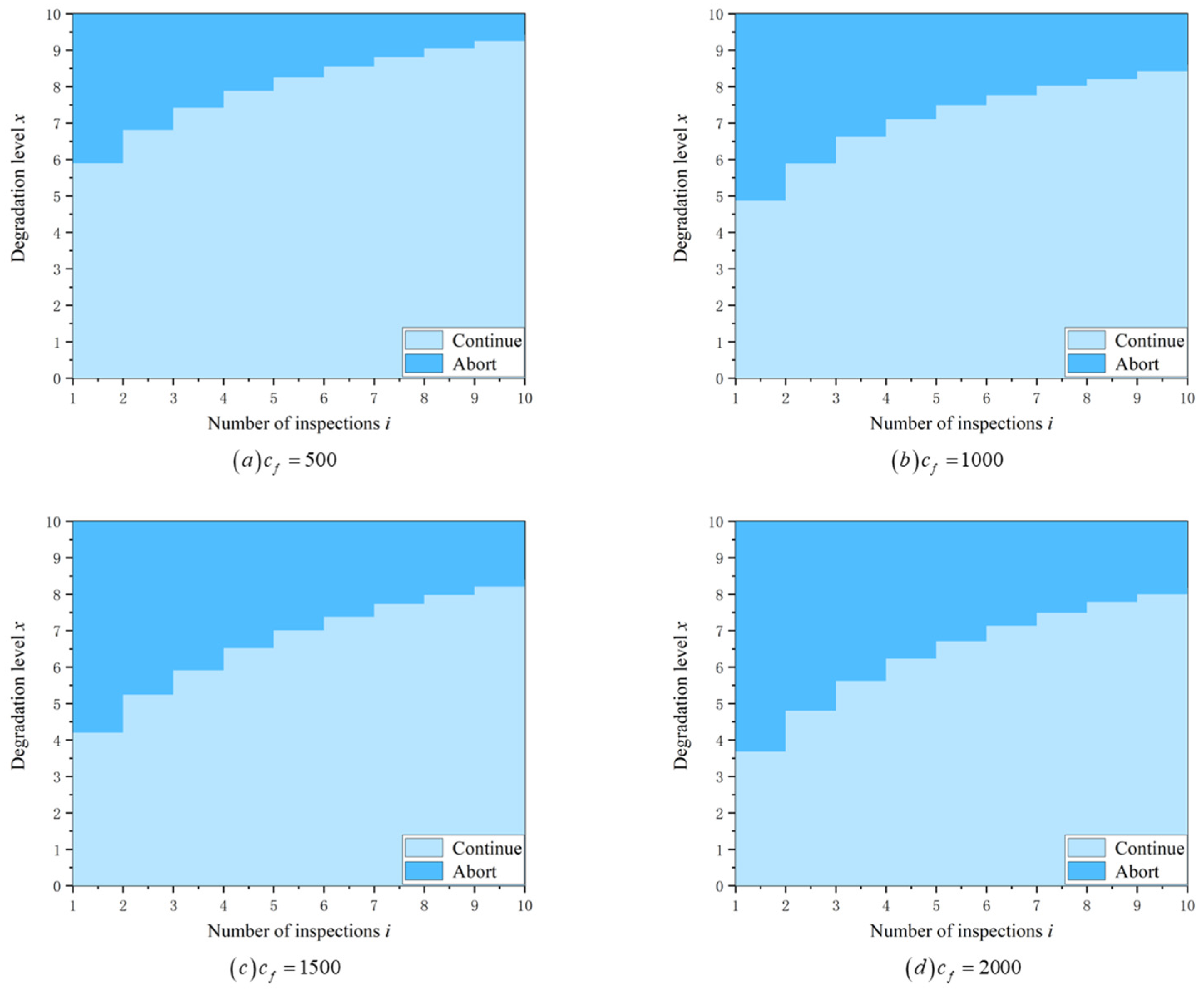
6.1. Optimal Mission Abort Policy
6.2. Comparison with Other Policies
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Appendix B
Appendix C
Appendix D
Appendix E
Appendix F
References
- Dui, H.; Xu, H.; Zhang, Y.-A. Reliability Analysis and Redundancy Optimization of a Command Post Phased-Mission System. Mathematics 2022, 10, 4180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Q.; Maillart, L.M.; Prokopyev, O.A.; Cui, L. Optimal condition-based mission abort decisions. IEEE Trans. Reliab. 2023, 72, 408–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, L.; Liu, B.; Gao, K.; Yang, L. Random Warranty and Replacement Models Customizing from the Perspective of Heterogeneity. Mathematics 2023, 11, 3330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, H.; Peng, R.; Yang, L.; Wu, T.; Liu, D.; Li, Y. Reliability evaluation of demand-based warm standby systems with capacity storage. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2022, 218, 108132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Li, B.; Mizutani, S.; Nakagawa, T. A Revisit of Age-Based Replacement Models With Exponential Failure Distributions. IEEE Trans. Reliab. 2022, 71, 1477–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.J.; Makis, V. Joint optimization of sampling and control of partially observable failing systems. Oper. Res. 2013, 61, 777–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Han, R.; Ma, Y.; Yang, L.; Wei, F.; Peng, R. A two-dimensional maintenance optimization framework balancing hazard risk and energy consumption rates. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2022, 169, 108193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Chen, Y.; Ma, X.; Qiu, Q.; Peng, R. A Prognosis-centered Intelligent Maintenance Optimization Framework under Uncertain Failure Threshold. IEEE Trans. Reliab. 2024, 73, 115–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, F.; Wang, J.; Ma, X.; Yang, L.; Qiu, Q. An Optimal Opportunistic Maintenance Planning Integrating Discrete- and Continuous-State Information. Mathematics 2023, 11, 3322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Ma, X.; Wei, F.; Yang, L.; Qiu, Q. Dynamic Scheduling of Intelligent Group Maintenance Planning under Usage Availability Constraint. Mathematics 2022, 10, 2730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levitin, G.; Xing, L.; Dai, Y. Optimal system loading and aborting in additive multi-attempt missions. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2024, 251, 110315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Zhao, X.; Qiu, Q. Optimal Task Abort and Maintenance Policies Considering Time Redundancy. Mathematics 2022, 10, 1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Yi, K.; Peng, R.; Kou, G. Reliability of a Distributed Computing System With Performance Sharing. IEEE Trans. Reliab. 2022, 71, 1555–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levitin, G.; Xing, L.; Dai, Y. Multi-attempt missions with multiple rescue options. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2024, 248, 110168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Q.; Li, R.; Zhao, X. Failure risk management: Adaptive performance control and mission abort decisions. Risk Anal. 2024, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Wei, F.; Qiu, Q. Mission Risk Control via Joint Optimization of Sampling and Abort Decisions. Risk Anal. 2024, 44, 666–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myers, A. Probability of loss assessment of critical k-out-of-n: G systems having a mission abort policy. IEEE Trans. Reliab. 2009, 58, 694–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levitin, G.; Xing, L.; Dai, Y. Mission Abort Policy in Heterogeneous Nonrepairable 1-Out-of-N Warm Standby Systems. IEEE Trans. Reliab. 2018, 67, 342–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levitin, G.; Xing, L.; Dai, Y. Co-optimization of state dependent loading and mission abort policy in heterogeneous warm standby systems. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2018, 172, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Ma, X.; Zhao, Y.; Gao, K.; Yang, L. Condition-based maintenance management for two-stage continuous deterioration with two-dimensional inspection errors. Qual. Reliab. Eng. Int. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Chai, X.; Sun, J.; Qiu, Q. Optimal bivariate mission abort policy for systems operate in random shock environment. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2021, 205, 107244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levitin, G.; Xing, L.; Xiang, Y.; Dai, Y. Mixed failure-driven and shock-driven mission aborts in heterogeneous systems with arbitrary structure. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2021, 212, 107581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Q.; Cui, L. Gamma process based optimal mission abort policy. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2019, 190, 106496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, G.; Li, L.; Zhang, L.; Yang, N.; Jiang, B.; Shangguan, C.; Su, Y. Optimal Joint Inspection and Mission Abort Policies for Degenerative Systems. IEEE Trans. Reliab. 2023, 72, 137–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Peng, R.; Qiu, Q.; Zhou, S.; Yang, L. An inspection-based replacement planning in consideration of state-driven imperfect inspections. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2023, 232, 109064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Chen, Y.; Qiu, Q.; Wang, J. Risk Control of Mission-Critical Systems: Abort Decision-Makings Integrating Health and Age Conditions. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2022, 18, 6887–6894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizutani, S.; Dong, W.; Zhao, X.; Nakagawa, T. Preventive replacement policies with products update announcements. Commun. Stat. -Theory Methods 2020, 49, 3821–3833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Q.; Kou, M.; Chen, K.; Deng, Q.; Kang, F.; Lin, C. Optimal stopping problems for mission oriented systems considering time redundancy. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2021, 205, 107226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Liu, B.; Yang, L.; Peng, R.; Zhang, X. Reliability analysis and condition-based maintenance optimization for a warm standby cooling system. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2020, 193, 106588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levitin, G.; Xing, L. Mission Aborting Policies and Multiattempt Missions. IEEE Trans. Reliab. 2024, 73, 51–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, S.; Xing, L.; Levitin, G. Activation delay and aborting policy minimizing expected losses in consecutive attempts having cumulative effect on mission success. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2024, 247, 110078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Tan, L.; Ma, X.; Gao, K.; Jia, H.; Yang, L. Prognosis-driven reliability analysis and replacement policy optimization for two-phase continuous degradation. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2023, 230, 108909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levitin, G.; Finkelstein, M.; Xiang, Y. Optimal mission abort policies for repairable multistate systems performing multi-attempt mission. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2021, 209, 107497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wu, T.; Ma, X.; Wang, J.; Peng, R.; Yang, L. System Maintenance Optimization Under Structural Dependency: A Dynamic Grouping Approach. IEEE Syst. J. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Ye, Z.S.; Lee, C.G.; Yang, S.F.; Peng, R. A two-phase preventive maintenance policy considering imperfect repair and postponed replacement. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2019, 274, 966–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, L.; Liu, B.; Qiu, Q.; Yang, L. Three-dimensional warranty and post-warranty maintenance of products with monitored mission cycles. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2023, 239, 109506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drent, C.; Drent, M.; Arts, J.; Kapodistria, S. Real-Time Integrated Learning and Decision Making for Cumulative Shock Degradation. Manuf. Serv. Oper. Manag. 2022, 25, 235–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Tsui, K.L. Condition monitoring and residual life prediction using degradation signals: Revisited. IIE Trans. 2013, 45, 939–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Peng, R.; Li, G.; Lee, C.G. Operations management of wind farms integrating multiple impacts of wind conditions and resource constraints. Energy Convers. Manag. 2020, 205, 112162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, L.; Liao, J.; Gao, K.; Yang, L. Joint Optimization of Production Lot Sizing and Preventive Maintenance Threshold Based on Nonlinear Degradation. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 8638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Chen, Y.; Ma, X. A State-age-dependent Opportunistic Intelligent Maintenance Framework for Wind Turbines under Dynamic Wind Conditions. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2023, 19, 10434–10443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Yang, L. Postponed maintenance scheduling integrating state variation and environmental impact. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2020, 202, 107065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, S.; Xing, L.; Levitin, G. Optimizing component activation and operation aborting in missions with consecutive attempts and common abort command. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2024, 243, 109842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Ma, X.; Qiu, Q.; Yang, L.; Shang, L.; Wang, J. A hybrid inspection-replacement policy for multi-stage degradation considering imperfect inspection with variable probabilities. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2023, 241, 109629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Yi, K.; Liu, H.; Kou, G. Reliability modeling and optimization of a two-dimensional sliding window system. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2021, 215, 107870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Li, G.; Zhang, Z.; Ma, X.; Zhao, Y. Operations & Maintenance Optimization of Wind Turbines Integrating Wind and Aging Information. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2021, 12, 211–221. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.; Qian, C.; Nakagawa, T. Comparisons of replacement policies with periodic times and repair numbers. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2017, 168, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yang, L.; Ma, X.; Peng, R. Joint optimization of multi-window maintenance and spare part provisioning policies for production systems. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2021, 216, 108006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levitin, G.; Xing, L.; Dai, Y. A new self-adaptive mission aborting policy for systems operating in uncertain random shock environment. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2024, 248, 110184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Q.; Cui, L. Optimal mission abort policy for systems subject to random shocks based on virtual age process. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2019, 189, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Yang, L. State-Based Opportunistic Maintenance with Multifunctional Maintenance Windows. IEEE Trans. Reliab. 2021, 70, 1481–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Song, Y.; Qiu, Q.; Yang, L. Warranty Cost Analysis for Multi-State Products Protected by Lemon Laws. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galiński, C.; Hajduk, J.; Kalinowski, M.; Wichulski, M.; Stefanek, L. Inverted joined wing scaled demonstrator programme. In Proceedings of the 29th Congress of the International Council of the Aeronautical Sciences (ICAS 2014), St. Petersburg, Russia, 7–12 September 2014. [Google Scholar]
| Cost | Increase (%) | Cost | Increase (%) | Cost | Increase (%) | Cost | Increase (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Optimal policy | 46 | - | 78 | - | 113 | - | 149 | - |
| Policy 1 | 55 | 19 | 96 | 23 | 136 | 20 | 194 | 30 |
| Policy 2 | 72 | 56 | 123 | 58 | 175 | 55 | 241 | 62 |
| Cost | Increase (%) | Cost | Increase (%) | Cost | Increase (%) | Cost | Increase (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Optimal policy | 72 | - | 113 | - | 141 | - | 168 | - |
| Policy 1 | 81 | 12 | 136 | 20 | 173 | 23 | 217 | 29 |
| Policy 2 | 104 | 44 | 175 | 55 | 223 | 58 | 272 | 62 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, Y.; Wei, F.; Ma, X.; Qiu, Q.; Yang, L. Adaptive Mission Abort Planning Integrating Bayesian Parameter Learning. Mathematics 2024, 12, 2461. https://doi.org/10.3390/math12162461
Ma Y, Wei F, Ma X, Qiu Q, Yang L. Adaptive Mission Abort Planning Integrating Bayesian Parameter Learning. Mathematics. 2024; 12(16):2461. https://doi.org/10.3390/math12162461
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Yuhan, Fanping Wei, Xiaobing Ma, Qingan Qiu, and Li Yang. 2024. "Adaptive Mission Abort Planning Integrating Bayesian Parameter Learning" Mathematics 12, no. 16: 2461. https://doi.org/10.3390/math12162461
APA StyleMa, Y., Wei, F., Ma, X., Qiu, Q., & Yang, L. (2024). Adaptive Mission Abort Planning Integrating Bayesian Parameter Learning. Mathematics, 12(16), 2461. https://doi.org/10.3390/math12162461








