Abstract
The key problem to solving constrained multi-objective optimization problems (CMOPs) is how to achieve a balance between objectives and constraints. Unfortunately, most existing methods for CMOPs still cannot achieve the above balance. To this end, this paper proposes an adaptive constraint relaxation-based evolutionary algorithm (ACREA) for CMOPs. ACREA adaptively relaxes the constraints according to the iteration information of population, whose purpose is to induce infeasible solutions to transform into feasible ones and thus improve the ability to explore the unknown regions. Completely ignoring constraints can cause the population to waste significant resources searching for infeasible solutions, while excessively satisfying constraints can trap the population in local optima. Therefore, balancing constraints and objectives is a crucial approach to improving algorithm performance. By appropriately relaxing the constraints, it induces infeasible solutions to be transformed into feasible ones, thus obtaining more information from infeasible solutions. At the same time, it also establishes an archive for the storage and update of solutions. In the archive update process, a diversity-based ranking is proposed to improve the convergence speed of the algorithm. In the selection process of the mating pool, common density selection metrics are incorporated to enable the algorithm to obtain higher-quality solutions. The experimental results show that the proposed ACREA algorithm not only achieved the best Inverse Generation Distance (IGD) value in 54.6% of the 44 benchmark test problems and the best Hyper Volume (HV) value in 50% of them, but also obtained the best results in seven out of nine real-world problems. Clearly, CP-TSEA outperforms its competitors.
Keywords:
adaptive relaxation; archive; mating pool; diversity-based ranking; constrained multi-objective optimization MSC:
90C29; 68W50; 90C56
1. Introduction
Constrained multi-objective optimization problems (CMOPs) [1,2] refer to the optimization of multiple conflicting objective functions under constraints. In real life, constrained multi-objective optimization problems (CMOPs) manifest in many aspects, for example, as water resource management [3], robot manufacturing [4], and ICMES operation optimization [5]. The mathematical definition of a CMOP is as follows:
where denotes a objective vector including m conflicting objective functions, represents the ith inequality constraint, and represents the j-th equality constraints. p represents the number of inequality constraints, and represents the number of equality constraints. For a CMOP, the constraint violation degree on the jth constrinat of solution x is caluculated by
where is a small positive tolerance parameter set as . Based on (2), the total constraint violation degree of solution x is caluculated as follows:
when , it indicates that solution x is feasible. On the contrary, solution x is a infeasible solution.
At present, most researchers are focused on constrained multi-objective optimization problems, aiming to balance the constraints and objectives.
The unconstrained Pareto idea is to approximate the constrained Pareto front (CPF) [6] as the unconstrained Pareto front (UPF) [7]. This approach makes it difficult to obtain highly feasible solutions and indirectly reduces the convergence of the algorithm. Therefore, it is essential not to consider constraints in isolation but to maintain a balance between objectives and constraints. Due to the population-based search characteristics of constrained multi-objective evolutionary algorithms (CMOEAs) [8], they have significant advantages in solving constrained multi-objective optimization (CMOP). However, CMOEAs often do not achieve the desired results when dealing with discrete and large infeasible regions. When addressing these issues, most researchers lack the utilization of information from infeasible solutions, causing the algorithms to become trapped in local optima. Therefore, strengthening the mining of infeasible solution information is the most urgent means at the current stage.
To further expand the algorithm’s exploratory capabilities, researchers are dedicated to developing constraint-handling techniques (CHTs) [9]. At present, the methods for handling constraints mainly include constraint domination principle (CDP) [10], penalty functions, random ordering, and hybrid methods. The aforementioned methods have significant advantages in handling constrained single-objective optimization problems [11]. However, they often do not achieve the expected results when facing complex constrained multi-objective optimization problems (CMOPs). To address this issue and make full use of infeasible information, researchers have proposed dual-population-based methods [12,13,14,15]. The framework of dual population [13] aims to utilize information from infeasible solutions. To be specific, one population operating under unconstrained or relaxed constraints incorporates infeasible solutions into the candidate solution set, thus enhancing the population’s exploratory capabilities. On the contrary, the other population considers constraints to increase the algorithm’s convergence speed, prompting the population to obtain the complete Pareto front (PF). Although dual-population [16] algorithms have achieved promising results, most CMOEAs fail to promptly share information, the stagnation in population migration information. Wang et al. [17]. proposed an interaction method based on transfer information, which enhances the algorithm library and increases the feasibility of algorithms by solving the transfer probability of similar problems. However, it lacks the identification of transfer information.
For such issues, some researchers have proposed an archive mechanism [15] that updates throughout the algorithm’s evolution, preserving the highest-quality solutions to drive the population towards convergence on the CPF. However, updating the archive involves identifying a large number of solutions, which consumes a lot of algorithm resources and greatly deteriorates the algorithm performance.
Faced with the aforementioned issues, this paper proposes an adaptive constraint relaxation based evolutionary algorithm (ACREA) for CMOPs. The main contributions of this paper are as follows:
- (1)
- A novel archiving mechanism is designed, utilizing the constraint dominance principle (CDP) to filter and mine information on promising solutions, encouraging the population to explore more unknown areas. Additionally, as the algorithm evolves, the archive is updated based on diversity ranking.
- (2)
- An adaptive relaxation mechanism is designed to fully utilize information from infeasible solutions, facilitating the population’s ability to cross large and narrow infeasible regions in order to obtain a complete feasible area and prevent it from becoming trapped in local optima. This mechanism adaptively adjusts based on feedback from the proportion of feasible solutions, optimizing the search strategy to acquire more potentially valuable feasible solutions.
- (3)
- When selecting parents, a strict domination principle is proposed to ensure the feasibility of the algorithm, prompting the population to obtain higher-quality solutions, enhancing the diversity and convergence of the population.
- (4)
- In order to verify the effectiveness of the proposed ACREA algorithm, we compare the proposed ACREA algorithm with seven state-of-the-art algorithms on 44 test problems and 9 real-world problems. The experimental results show that the proposed algorithm (ACREA) significantly outperforms the competitors.
2. Related Work and Motivation
2.1. Related Work
In current CMOEAs, most researchers maintain a balance between objectives and constraints by improving various constraint handling techniques. These can generally be divided into the following four categories.
2.1.1. Penalty Function-Based CMOEA
These algorithms primarily use penalty factors to control the balance between objectives and constraints. Penalty factors can generally be classified into static [18] and dynamic [19] categories. Static penalty factors remain constant throughout the algorithm’s evolution process. However, determining an appropriate penalty factor throughout the algorithm’s entire process is extremely challenging because the penalty factor is not only influenced by the designed algorithm but also heavily dependent on different test problems. In contrast, dynamic penalty factors avoid this drawback. Researchers set up adaptive adjustment of penalty factors based on different penalty criteria. However, when setting up adaptive adjustment of penalty factors [20], the defined change rules greatly restrict the algorithm’s performance. It is precisely because of these limitations that the emergence of self-adaptive penalty (SP) functions [21] occurred, where penalty factors adaptively change based on feedback information during the evolutionary process.
2.1.2. CHT-Based CMOEA
Deb et al. [22] proposed a method called constraint dominance principle (CDP) to handle complex CMOPs. The core idea of CDP is the preferential selection, where feasible solutions always dominate infeasible solutions. Fan et al. [23] proposed an angle-based CDP, which incorporates angle information between population solutions into CDP to adjust the dominance relationship of solutions. For example, when two infeasible solutions exceed a specified threshold, they are non-dominated. Ma et al. [24] proposed a novel fitness function that weights the constraint dominance principle (CDP) and Pareto dominance ranking. Takahama et al. [25] proposed a concept of constraint relaxation, where the constraint values change adaptively based on their own specified rules. Fan et al. [26] dynamically adjusted the level based on changes in the population’s feasibility ratio, integrating the proposed constraint handling mechanism with MOEA/D to solve CMOPs. Peng et al. [27] set corresponding weights in the feasible and infeasible regions, respectively, prompting the algorithm to explore more of the objective space. Adel Younis et al. [28] explored promising regions using adaptive surrogate models to uncover more feasible domains, prompting the population to find a set of optimal solutions. Li et al. [14] proposed a dual-archive evolutionary algorithm called C-TAEA. One archive enhances the convergence of the population to obtain a complete PF, while the other archive only considers objectives, prompting the algorithm to obtain more information about solutions.
2.1.3. Multi-Stage Based CMOEA
Liu et al. [29] designed a novel two-stage framework. In the first stage, they transformed the constrained multi-objective problem into a constrained single-objective problem using weight vectors. In the second stage, they adopted the CMOEA/D [30] strategy to obtain a high-quality solution set. He et al. [31] proposed a parent crossover selection strategy to generate excellent offspring and improve the convergence speed of the population. Liu et al. [15] proposed a bi-directional cooperative evolution algorithm called BiCo, which utilizes feasible edges and infeasible edges to bound the boundaries of the feasible region. Ming et al. [13] proposed a multi-population multi-stage framework concept called CMOEMT. Zhou et al. [32] proposed a three-indicator evolutionary framework to balance convergence, diversity, and feasibility.
2.1.4. Based on Archive
Ming et al. [33] proposed a single-population archiving mechanism called C-TSEA. This algorithm stores the solutions of the Pareto front (PF) in an archive, which is continuously updated to encourage the population to obtain a set of evenly distributed high-quality solutions. Li et al. [34] proposed a dual-archived weakly cooperative evolutionary algorithm named CMOEA-TWC. This algorithm uses two archives: the driving archive and the ordinary archive. The driving archive only considers objectives, enhancing the algorithm’s exploration ability and prompting the population to obtain a complete PF, while the ordinary archive considers both objectives and constraints to ensure the feasibility of the algorithm. The archive plays an irreplaceable role in the evolutionary process of the algorithm, not only identifying regional solutions but also continuously updating and preserving them to enhance the population’s search capability. Therefore, selecting the archive to assist in population evolution is the most evident choice.
Based on the above discussion, we summarize the existing advantages and disadvantages of representative algorithms in Table 1. It is clear from the table that simultaneously improving both the diversity and convergence of algorithms is quite challenging. For example, CMOEA/D and CTAEA tend to favor diversity, which results in slower convergence, while the non-dominance principle of NSGA-II and the dynamic adaptive strategy of POCEA favor convergence, leading to poorer diversity. Therefore, to improve the overall performance of the algorithm, it is essential to overcome the challenges of balancing convergence and diversity.

Table 1.
Summary of existing CMOEA techniques.
2.2. Motivation
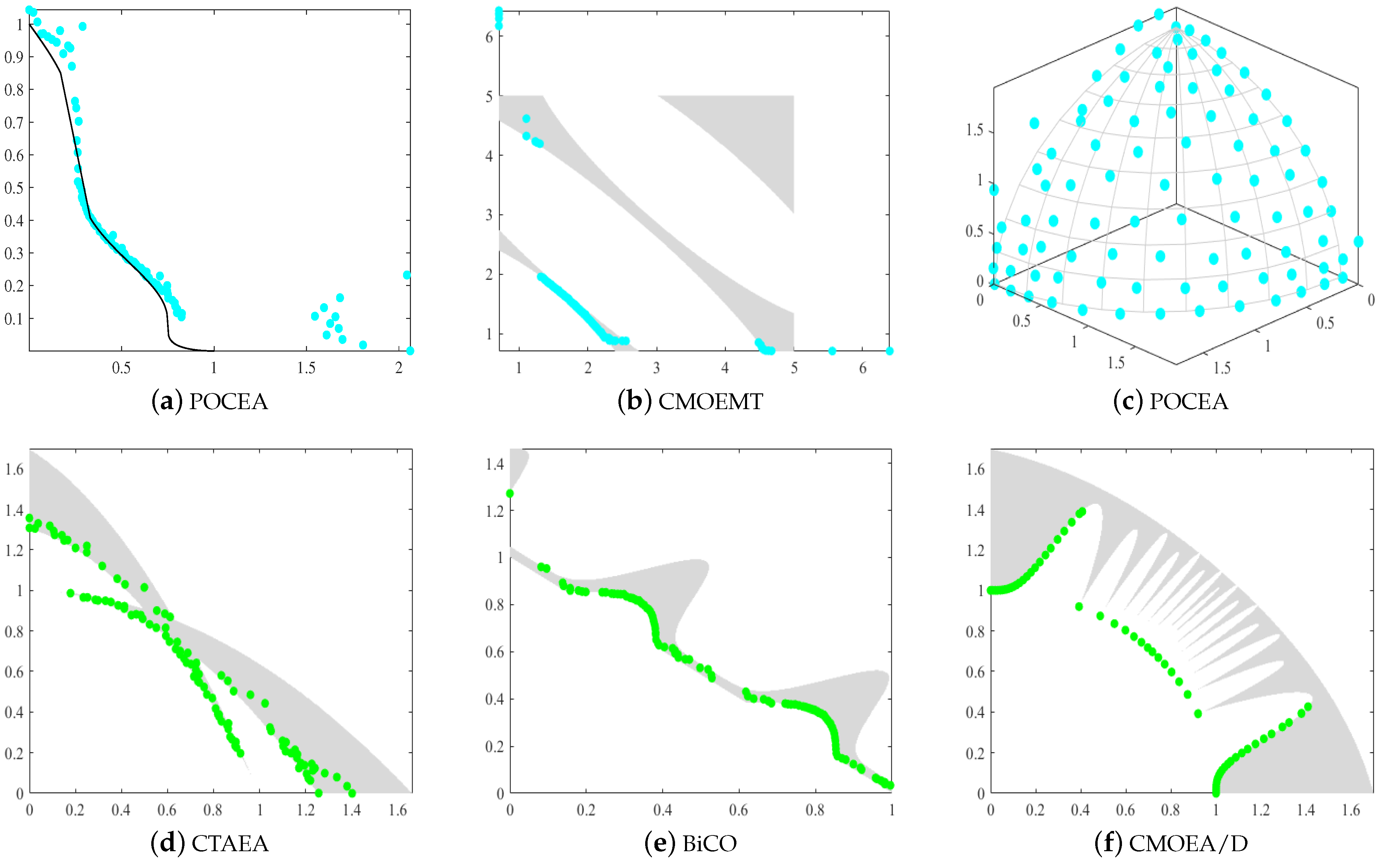
At the current stage of research, researchers often struggle to achieve optimal results when dealing with complex CMOPs. Therefore, there is still considerable room for improvement in algorithms that handle CMOPs. Some algorithms, even with the help of existing techniques, still struggle to converge to the approximate CPF, as shown in Figure 1a,d. For instance, in POCEA, part of the solution set found on the general PF fails to converge to the CPF. The fundamental reason is the lack of solution quality filtering, which prevents some inferior solutions from converging to the Pareto front. To enhance the convergence ability of solutions, researchers design various metrics to serve as selection criteria for candidate solutions. However, excessive convergence may cause the algorithm to fail to traverse larger infeasible regions, resulting in it becoming trapped in a local search loop. As shown in Figure 1b,e, certain feasible regions in CMOEAMT and BiCO were not explored. To address this limitation, researchers aim to enhance the exploration capabilities of the solutions while maintaining convergence, ensuring that the population fully covers the objective space. To further improve algorithm performance, the dimensionality of the objectives is increased to test the algorithm’s ability to handle complex CMOPs. For instance, Figure 1c shows the Pareto front of POCEA on the three-objective ZXH_CF15 test problem. POCEA successfully found the complete Pareto front, demonstrating its strong search performance. However, with increased search performance, the quality of solutions was overlooked, leading to some poor-quality solutions failing to converge to the Pareto front. Moreover, when exploring the objective space, the solution set often encounters many narrow and large infeasible regions. Many solutions are unable to traverse these narrow infeasible regions, causing the algorithm to become trapped in local optima, which severely affects its performance. As shown in Figure 1f, although the CMOEA/D algorithm has most of its solutions converging to the CPF, the population struggles to fully converge to the CPF when faced with narrow infeasible regions. To address this challenge, it is crucial not only to utilize the information from infeasible solutions to maintain diversity but also to rigorously design selection criteria for the solutions.
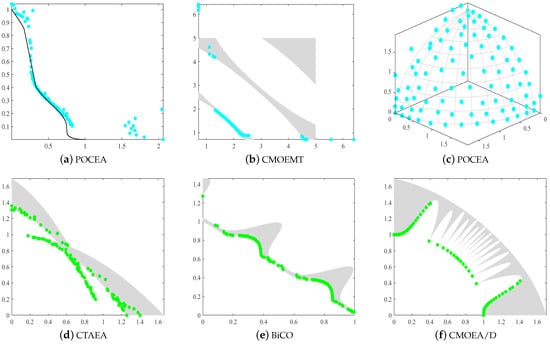
Figure 1.
The obtained feasible and non-dominated solutions of (a) POCEA on ZXH_CF15, (b) CMOEMT on LIRCMOP8, (c) POCEA on LIRCMOP14, (d) CTAEA on MW9, (e) BiCO on MW3, (f) CMOEA/D on MW5.
In summary, there is still significant room for expansion in current-stage algorithms. Faced with the aforementioned issues, we designed an adaptive constraint relaxation mechanim to encourage the algorithm to explore more of the objective space, thereby enhancing its diversity and convergence. To further maintain a balance between objectives and constraints, we adopted an archiving mechanism. Throughout the algorithm evolution, the archive is continuously updated, preserving high-quality solutions and encouraging population convergence to the PF, thereby obtaining the complete CPF. To maintain population diversity, it is crucial to strengthen the interaction between the archive and the population during the evolutionary process as well as to share information about infeasible solutions. Only when the population receives migration information from the archive can it further explore unknown regions, thus avoiding the algorithm becoming trapped in local optima. Therefore, this algorithm employs strict constraint dominance principles when selecting parents, further acquiring information about infeasible solutions, enhancing the population’s external search capability, and enabling the population to traverse narrow and extensive infeasible regions.
3. Framework of ACREA
This section provides an overview of the framework of ACREA and describes the steps involved in ACREA, with detailed explanations of important components.
3.1. Framework of ACREA
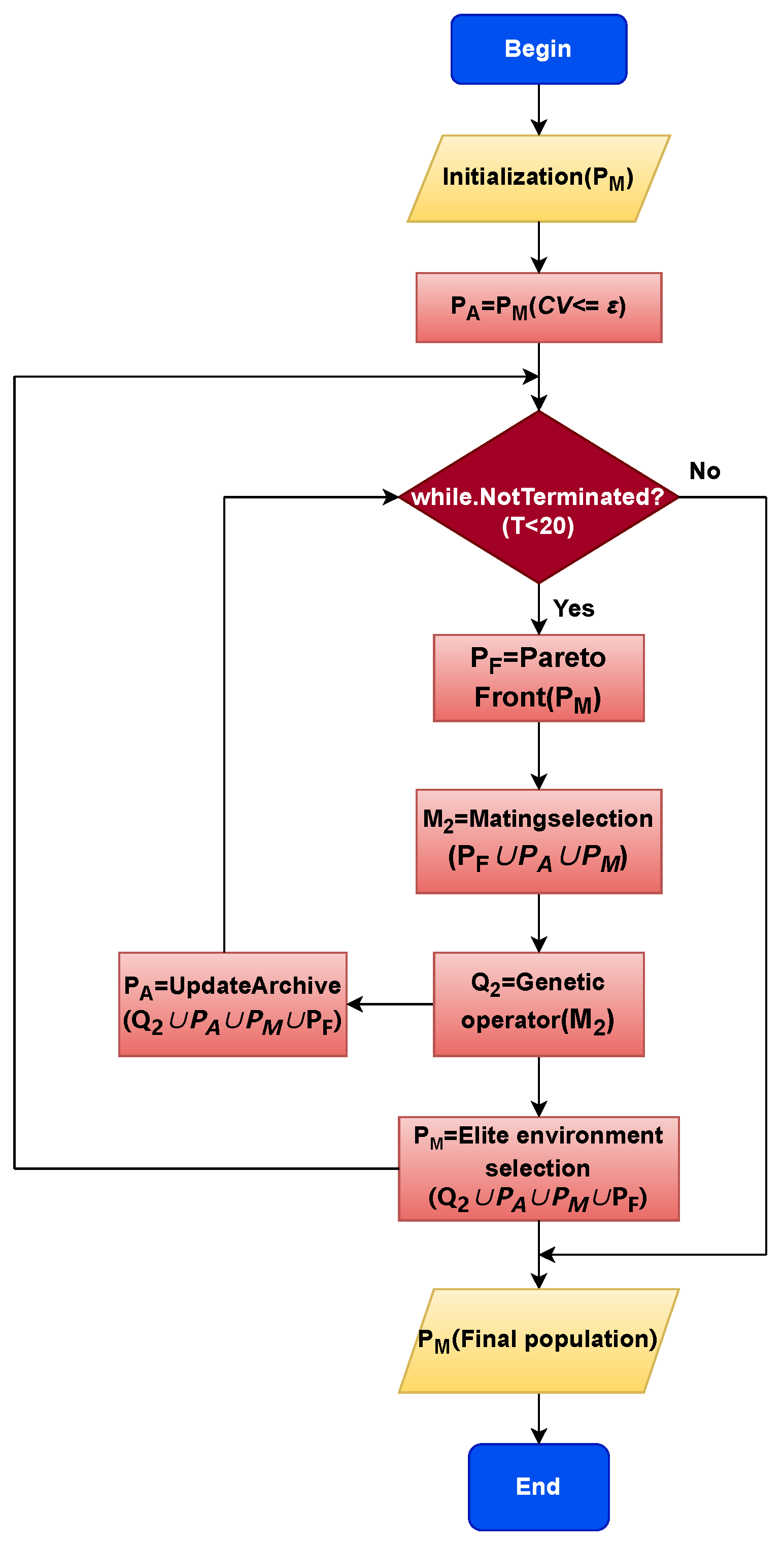
Algorithm 1 offers the framework of ACREA. As shown in Algorithm 1, a population is first initialized in the decision space. In Lines 2–3, the value is adaptively adjusted based on the proportion of feasible solutions, and solutions in population that satisfy () are stored in the archive. The calculation of is shown in Equation (5). controls the scaling of the boundaries and serves as a criterion for determining the entry of infeasible solutions into the population, thereby utilizing the information from high-quality infeasible solutions to enhance the diversity of the population. In the fifth line, the iteration of the algorithm is determined based on the maximum iteration count (). In Line 6, the Pareto front of is obtained, and in Line 7, and are combined to generate .
The main purpose is to increase the probability of selecting high-quality solutions, thereby enhancing the algorithm’s convergence capability and driving the population to converge to the forefront CPF. In Line 8, an elitist selection is performed on and the archive to generate parent . In Line 9, genetic operators are applied to to generate offspring . In Line 10, the Achieve is sorted and updated. In Line 11, we adopted the NRC’s IA [36] elite selection approach with the goal of finding as many high-quality solutions as possible to generate the final population . To better understand ARCEA, we also created a flowchart, as shown in Figure 2. The entire flowchart process of ARCEA corresponds to the description of Algorithm 1. Additionally, the total execution time for one invocation of ACREA is 0.02 s.
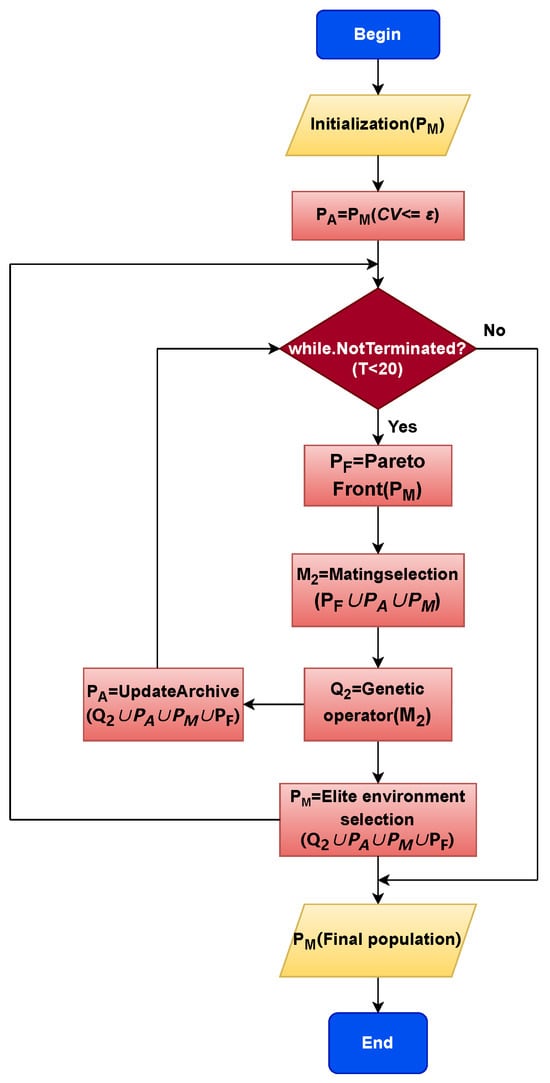
Figure 2.
Flowchart of ACREA.
| Algorithm 1 Framework of ACREA |
| Input: N (population size), T (max iterations) Output: P (final population)
|
3.2. Relaxed Constraint Learning Mechanism
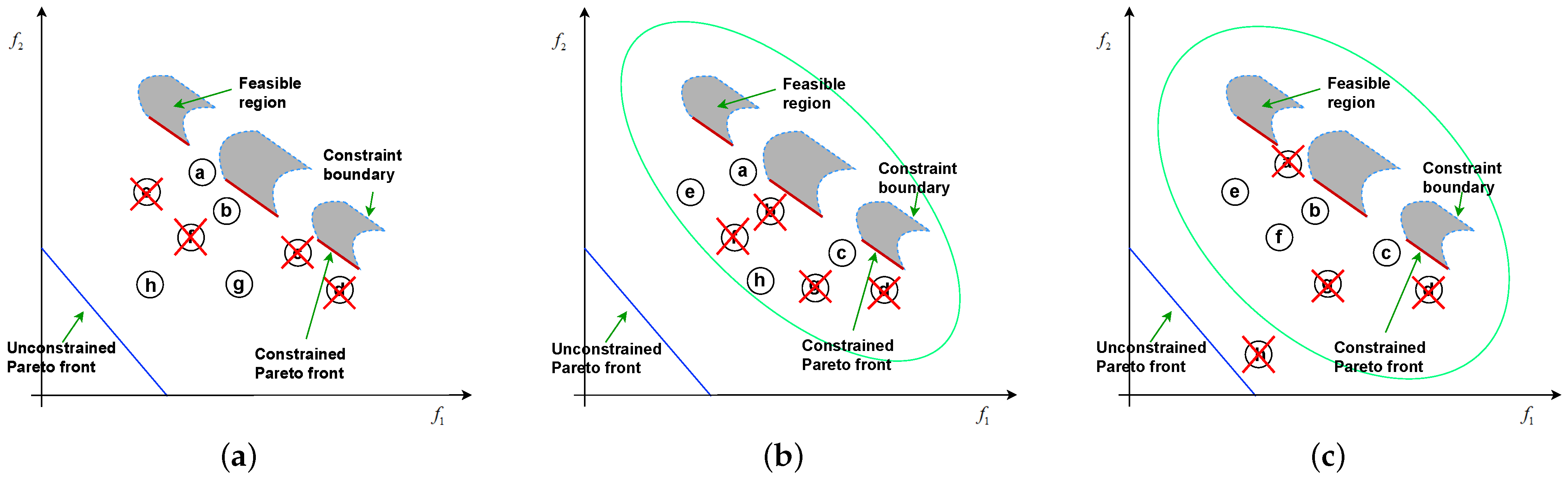
The primary goal of using the constraint relaxation learning mechanism is to fully leverage the information from infeasible solutions to drive the population towards a complete CPF. The boundary values are adjusted adaptively based on the proportion of feasible solutions, as shown in Equation (5). As the proportion of feasible solutions increases, the boundaries begin to gradually relax, allowing for more feasible solutions to reduce the proportion of infeasibility and control the boundary’s contraction capability, until the algorithm reaches its termination condition, at which point the constraint relaxation concludes. Figure 3 illustrates the entire constraint relaxation process. In Figure 3a, before constraint relaxation, infeasible solutions are ranked according to Equation (3) and poor solutions are removed. At this stage, many infeasible solutions are disregarded, significantly reducing the algorithm’s performance. In Figure 3b, the constraints begin to relax. It is evident that as the boundaries expand, many infeasible solutions are considered. Solutions within the boundaries are diversity-ranked according to Equation (5), with lower-ranked solutions being eliminated. For example, although solution b is close to the front and has low constraint violation, it is ranked lower when infeasible solutions are included within the boundary and is thus removed, while solution e, ranked higher, is retained. In Figure 3c, as the constraint relaxation completes, the boundary values are scaled, removing solution h from the boundary. Solutions within the boundary are preserved based on non-dominated sorting and diversity ranking, retaining those with higher rankings. The mathematical model for constraint relaxation is as follows:
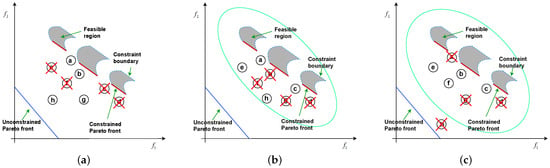
Figure 3.
The entire process of relaxing constraint boundaries. (a) Unrelaxed constraint boundaries; (b) start of relaxing constraint boundaries; and (c) finish of relaxing constraint boundaries.
t represents the current iteration number of the algorithm and T represents the maximum number of iterations. is a parameter threshold for relaxation, extending the constraint violation into the objective space. The motivation for the constraint relaxation mechanism is as follows: (1) To fully utilize information from infeasible solutions and encourage the population to traverse narrow infeasible regions, we appropriately relax the constraints, thereby enhancing the algorithm’s search capability in the objective space. (2) During the evolution process, the algorithm obtains more information from infeasible solutions by appropriately relaxing the constraints, encouraging the population to approximate the CPF from both the feasible and infeasible sides. The mathematical formula for the value of is as follows:
In the above formula, represents the proportion of feasible solutions, and indicates the rate of change set to 0.4. is adaptively adjusted based on the ratio of feasible solutions.
3.3. UpdatedArchive
Algorithm 2 describes the entire process of archive updating. When the number of solutions in the archive does not reach N, the solutions in the main population P are sorted in ascending order based on their values, and high-quality solutions are selected to supplement the archive. If the solution in the archive is greater than N, non-dominated sorting is applied on top of diversity sorting to remove redundant solutions. Diversity sorting is based on Equation (6), where each solution x is calculated and then sorted in descending order to remove redundant solutions. The main idea is to determine the quality of diversity by assessing whether the population solutions are evenly distributed. This promotes the convergence of the population towards the pareto front. The mathematical formula for diversity is as follows:
represents the distance from the ith solution x to k neighboring solutions depending solely on k. i indicates the index of the solution [37]. represents the crowding degree of solution x. The lower the crowding degree, the denser the solutions and the better the diversity; conversely, the higher the crowding degree, the worse the diversity.
| Algorithm 2 UpdatedArchive |
| Input: N (population size), U (combined population), (Archive population) Output: UpdatedArchive
|
3.4. Elite Mating Pool Selection
Algorithm 3 describes the entire process of elite parent selection. First, the number of feasible solutions in is calculated. If the number of feasible solutions is less than N or if the number of solutions in the is less than N, two solutions are randomly selected from the combined population U, and their density is calculated using Equation (7). The solution with the lower density is selected. The density calculation formula is shown below:
represents the density of the ith solution. represents the distance between the ith solution and the jth solution, and k represents the number of nearest neighbors.
Conversely, two solutions are randomly selected from and based on the probability function ratio, and the solution with stronger dominance is chosen. Under stricter constraint dominance principles, the selected solutions exhibit strong convergence capability, facilitating in obtaining a complete CPF. The constraint dominance formula is shown below:
| Algorithm 3 The elite mating selection |
| Input: (main population), (Archive population), N (population size) Output: (mating pool)
|
If the two solutions do not mutually dominate each other, the solution with higher density is selected using Equation (7). At this point, the supplementary solutions have strong dominance, which improves the population’s convergence speed toward the Pareto front (PF) and significantly enhances the convergence of the population. During the secondary selection, solutions with higher density are chosen to obtain a uniformly distributed set of solutions, thus maintaining the diversity of the population. The solutions selected under strict dominance principles and density support are of very high quality. This not only preserves the diversity of the population but also accelerates its convergence speed, indirectly maintaining a balance between diversity and convergence. This process continues until there are N remaining solutions in .
3.5. Elite Environment Selection
Algorithm 4 describes the process of elite environment selection. First, the combined population is layered based on non-dominated sorting, categorizing feasible solutions into different fronts (). If the number of feasible solutions in the combined population U exceeds N, layered sorting is performed for selection, as follows: if the number of feasible solutions in the first front exceeds N, non-dominated sorting based on reverse objectives and diversity sorting is applied to (), and the top N solutions are selected. If the number of feasible solutions in the first front is less than N, the process moves to the next front () and continues with the same sorting method until is filled to N solutions, and so on until () is reached, where () indicates that the number of feasible solutions only reaches N at layer l, thus ensuring meets the requirement of N solutions. Conversely, when the number of feasible solutions in the combined population U is less than N, the infeasible solutions are sorted based on diversity and supplemented into the population until it reaches N solutions.
| Algorithm 4 Cascading sorting-based environment selection |
| Input: U (combined population), N (population size) Output: (main population)
|
The cascading sorting used in elite environment selection ensures that the selected solutions not only possess strong dominance but also exhibit good diversity with the support of diversity metrics. This indirectly guarantees a balance between population diversity and convergence, preventing poor diversity from causing the population to become trapped in local optima.
4. Experiment Studies
This section discusses the experimental setup and algorithm comparison, concluding that ACREA significantly outperforms other competitors based on all the conclusions.
4.1. Experimental Setup
(1) Test problems: In this research work, we employ three sets of test instances: MW, LIRCMOP, and ZXH_CF, for comparative experiments. Among them, the decision space of MW is set to 15 for all instances. Except for MW4, MW8, and MW14, which are set to have 3 objectives, the rest are all set to have 2 objectives. The decision space of LIRCMOP is set to 30 for all instances. LIRCMOP13-14 instances are configured with 3 objectives, while LIRCMOP1-12 instances are configured with 2 objectives. ZXH_CF1-12 instances are configured with 3 objectives, and the decision space is set to 13. ZXH_CF13-16 instances are configured with 2 objectives, and the decision space is set to 12.
(2) Performance metrics: In this study, we employ the commonly used Inverted Generational Distance (IGD) [38] and Hypervolume (HV) [39] indicators to evaluate the diversity and convergence of algorithms. A smaller IGD value and a larger HV value indicate better overall performance of the algorithm. The settings for algorithm iterations are 20, evaluation counts are 100,000, and Wilcoxon’s rank is set to 0.05. “NaN” in the table indicates that no feasible solution is found. “+”, “−”, and “≈”, respectively, denote superior to, inferior to, and comparable to competitors. All experimenters in this study are conducted on Platform PlatEMO 4.3 [40].
(3) Genetic operators: The SBX and PM for all experimental algorithms in this article are set to 1 and , respectively. The distribution index is set to 20.
(4) Comparative algorithms: This paper compares with seven advanced algorithms, namely CMOEA/D, CTAEA, ToP, POCEA, CMOEMT [13], BiCo, and TiGE2. Both CMOEA/D and ToP adopt the decomposition approach. CMOEA/D decomposes the problem into weighted subproblems, while ToP decomposes the multi-objective into weighted single-objective. CTAEA applies an archive mechanism. BiCo employs a single-population archive framework. CMOEMT adopts a multi-population multi-stage approach. POCEA processes each problem with different weight vectors. TiGE2 employs a novel evaluation mechanism.
(5) Parameter settings for each algorithm: The population size of all algorithms in this paper is set to 100. The remaining settings are kept unchanged according to their respective papers to ensure fairness in experimental comparisons.
(6) Equipment requirements: In all experiments, the hardware used includes a processor model of i5-7300HQ (Intel, Santa Clara, CA, USA), with a system type based on a x64 processor and 8.00 GB of memory (RAM). On the software side, Windows 10 is used as the operating system, with MATLAB R2021a as the programming language. The toolbox utilized is the PlatEMO 4.6 toolbox in MATLAB.
4.2. Comparison Experiments with Seven Competitors
In this section, we assess ACREA’s performance by contrasting ACREA against its seven competitors across the MW, LIRCMOP, and ZXH_CF test suites. In the MW test problem, many narrow infeasible regions are set, as shown in Figure 1. Many algorithms struggle to overcome this difficulty, resulting in incomplete frontier surfaces. In the LIRCMOP test suite, large infeasible regions are set to test whether the algorithms could traverse these regions and find the complete feasible area. Many algorithms, due to a lack of external search capability, end up in local optima. In ZXH_CF, many three-objective test problems are set to evaluate whether the algorithms can address the conflicts between multiple objectives. Many algorithms when handling this issue fail to maintain a balance between constraints and multiple objectives, thus reducing their performance. Next, we conduct a comprehensive analysis of the IGD and HV indicators separately.
- (1)
- Comprehensive analysis of IGD indicators
As shown in Table 2, ToP did not find feasible solutions in the MW test suite for MW1 and MW10, primarily because it was unable to identify the true Pareto front in the face of narrow infeasible regions. To enhance ACREA’s exploration capabilities, an adaptive constraint relaxation strategy was implemented to utilize more information from infeasible solutions, helping the population to traverse larger infeasible areas. This is a key reason why ACREA achieved optimal solutions in 10 test problems, while CMOEA/D only found optimal solutions in MW9 and MW12, indicating that ACREA excels far beyond its competitors in exploration and expansion. ACREA outperformed CMOEA/D, CTAEA, ToP, POCEA, CMOEMT, BiCo, and TiGE2 in 12, 12, 9, 13, 13, 13, and 13 test problems, respectively. CMOEA/D, CTAEA, ToP, POCEA, CMOEMT, BiCo, and TiGE2 performed similarly to ACREA in 0, 0, 3, 0, 0, 0, and 1 test problems. Overall, considering the MW test suite, ACREA significantly outperforms these seven competitors.

Table 2.
The IGD results (mean and standard deviation) obtained by eight algorithms on the MW, LIRCMOP and ZXH_CF problems.
From Table 2, we can see the IGD metrics of the eight algorithms on the LIRCMOP test suite. With the support of strict dominance principles, the selected high-quality solutions are highly competitive, which contributes to ACREA’s strong exploration and handling capabilities when facing irregular Pareto fronts. This is why CMOEA/D, CTAEA, ToP, POCEA, CMOEMT, BiCo, and TiGE2 perform worse than ACREA in 12, 8, 8, 6, 11, 11, and 9 test problems, respectively. Although slightly inferior to competitors in some test problems, overall, considering the 14 test problems, ACREA significantly outperforms other competing methods. POCEA only performs similarly to ACREA in 8 test problems and does not surpass ACREA in any test problem. The main reason for this is that the adaptive constraint relaxation expands the population’s demand for solutions, while the strict dominance principle accelerates the population’s convergence ability. The LIRCMOP test suite features numerous discontinuous feasible regions, posing significant challenges for algorithms. Many algorithms tend to overlook the balance between diversity and convergence, resulting in suboptimal performance. For example, CTAEA’s dual-archive mechanism favors diversity, while POCEA’s dynamic adaptive evolution strategy favors convergence. Although the algorithms improve performance in one aspect, their overall performance declines significantly. In contrast, ACREA enhances algorithm diversity through the design of an adaptive constraint relaxation strategy and implements a strict dominance principle to ensure rapid convergence to optimal solutions. Therefore, we can conclude that ACREA outperforms its competitors both theoretically and experimentally.
The ZXH_CF test suite places significant demands on the search capabilities of algorithms. During the search for the Pareto front, there are many small independent feasible regions, making it difficult for most algorithms to find a complete feasible domain, often leading them to become stuck in local optima. The representative ToP algorithm frequently fails to cross larger infeasible areas to find new feasible domains, resulting in the algorithm remaining in a local optimum and unable to achieve a complete CPF. In contrast, ACREA exhibits strong exploration capabilities, continuously updating its archive with diverse, high-ranking solutions, which helps the population obtain a complete CPF. This is a key reason why ACREA performs well on the 16 ZXH_CF test problems, achieving the best results in seven of them. CTAEA, ToP, POCEA, and TiGE2 did not achieve the best results in any of these 16 test problems. CMOEA/D only outperformed ACREA in the ZXH_CF1 test problem. ACREA significantly outperformed these seven competitors in 12, 13, 16, 16, 12, 5, and 15 test problems, respectively.
For example, the similar BiCO algorithm updates its archive based on the degree of constraint violation. Although it explores many infeasible solutions, the quality of these solutions is inconsistent, leading to a significant waste of algorithmic resources. This results in BiCO’s inability to traverse infeasible areas on the ZXH_CF test problems, causing it to become stuck in local optima. In contrast, ACREA addresses this drawback by using diversity ranking as a criterion for solution selection, significantly enhancing the search capabilities of the population.
In summary, although ACREA did not perform well in some test problems, considering a total of 44 test problems, it significantly outperformed other competitors.
- (2)
- Comprehensive analysis of HV indicators
From Table 3, we can see the HV metrics of the eight algorithms across the three benchmark test suites. The HV metric is mainly used to assess the diversity of the algorithms, measuring whether the solutions are evenly distributed along the constrained Pareto front. On the MW test suite, ACREA achieved the best results on 11 test problems, significantly outperforming its competitors. The primary reason for this is that the archive update process uses diversity metrics as a criterion for selecting solutions, greatly improving the quality of the selected solutions and thus enhancing the diversity of the population. Due to the ToP algorithm’s lack of exploration capabilities, it is prone to becoming stuck in local optima when facing narrow Pareto fronts. For example, the reason ToP did not find feasible solutions in MW1 and MW10 is its poor exploration ability, which prevented it from finding the Pareto front. POCEA, CMOEMT, and BiCo achieved the best results in MW12, MW12, and MW9, respectively, indicating that their strategies favor handling diversity. CMOEA/D and CTAEA each obtained two best results in MW9 and MW12. ACREA significantly outperformed CMOEA/D, CTAEA, ToP, POCEA, CMOEMT, BiCo, and TiGE2 on 11, 12, 9, 12, 12, 12, and 13 test problems, respectively. This indirectly demonstrates that ACREA’s handling of diversity metrics in its archive is highly reliable.

Table 3.
The HV results (mean and standard deviation) obtained by eight algorithms on the MW, LIRCMOP and ZXH_CF problems.
The LIRCMOP test suite includes many large infeasible regions to evaluate the algorithms’ ability to traverse these areas. From the HV metrics of the LIRCMOP test suite, it is evident that most algorithms struggle to cross large infeasible regions in search of feasible solutions, significantly reducing their overall performance. For example, in the LIRCMOP6 test problem, there are extensive infeasible regions, and many algorithms, despite searching within the local space, fail to find suitable solutions, which greatly wastes algorithmic resources. To address this challenge, it is essential not only to enhance the algorithm’s exploration capabilities but also to strictly select high-quality solutions. With this approach in mind, ACREA relaxes constraints to gather more information from infeasible solutions, thereby increasing its ability to explore further. At the same time, it adopts a strict density dominance principle to select high-quality solutions, ensuring that the population obtains a set of optimal solutions. These two aspects are the primary reasons why ACREA outperforms the seven competitors in 9, 5, 7, 5, 9, 9, and 8 test problems.
In the ZXH_CF test suite, ToP, POCEA, CMOEMT, and TiGE2 did not achieve the best results on any test problems, indirectly indicating that this type of algorithm has poor exploration capabilities and fails to obtain the full feasible region, resulting in suboptimal solutions. In contrast, CMOEA/D and CTAEA achieved the best results on the ZXH_CF1 test problem, demonstrating that their algorithms perform well in terms of diversity. Compared to these, ACREA achieved the best results on six test problems, indirectly proving the effectiveness of its diversity metrics. The traditional exploration strategies fall short of enabling the algorithm to obtain better solutions. Although ACREA did not achieve the best performance on some test problems, considering the 16 ZXH_CF test problems and the seven comparative algorithms, ACREA outperforms its competitors.
From the above analysis, it can be seen that across 44 different test problems, ACREA’s overall performance far surpasses its competitors, fully demonstrating the superiority and competitiveness of ACREA.
4.3. The Validation of Parameter in ACREA
In this section, we validate parameter using an equidistant strategy and conduct comparative experiments on the LIRCMOP test suite with different settings of . From the IGD metric in Table 4, it can be seen that ACREA ( = 0.4) outperforms ACREA ( = 0, 0.2, 0.6, 0.8, and 1) on 2, 2, 1, 2, and 1 test problems, respectively. From the HV metric in Table 5, it can be seen that ACREA ( = 0, 0.2, 0.6, 0.8, and 1) performs worse than ACREA ( = 0.4) on 0, 2, 1, 1, and 1 test problems, respectively. Although ACREA ( = 0) achieves the same HV metric as ACREA ( = 0.4) on the LIRCMOP test suite, it performs worse on 2 test problems in the IGD metric compared to ACREA ( = 0.4). In summary, the results obtained by ACREA ( = 0.4) are the best. Therefore, setting to 0.4 is optimal.

Table 4.
The IGD results (mean and standard deviation) of ACREA ( = 0, 0.2, 0.4, 0.6, 0.8, and 1) on the LIRCMOP test suite.

Table 5.
The HV results (mean and standard deviation) of ACREA ( = 0, 0.2, 0.4, 0.6, 0.8, and 1) on the LIRCMOP test suite.
4.4. Performance Analysis
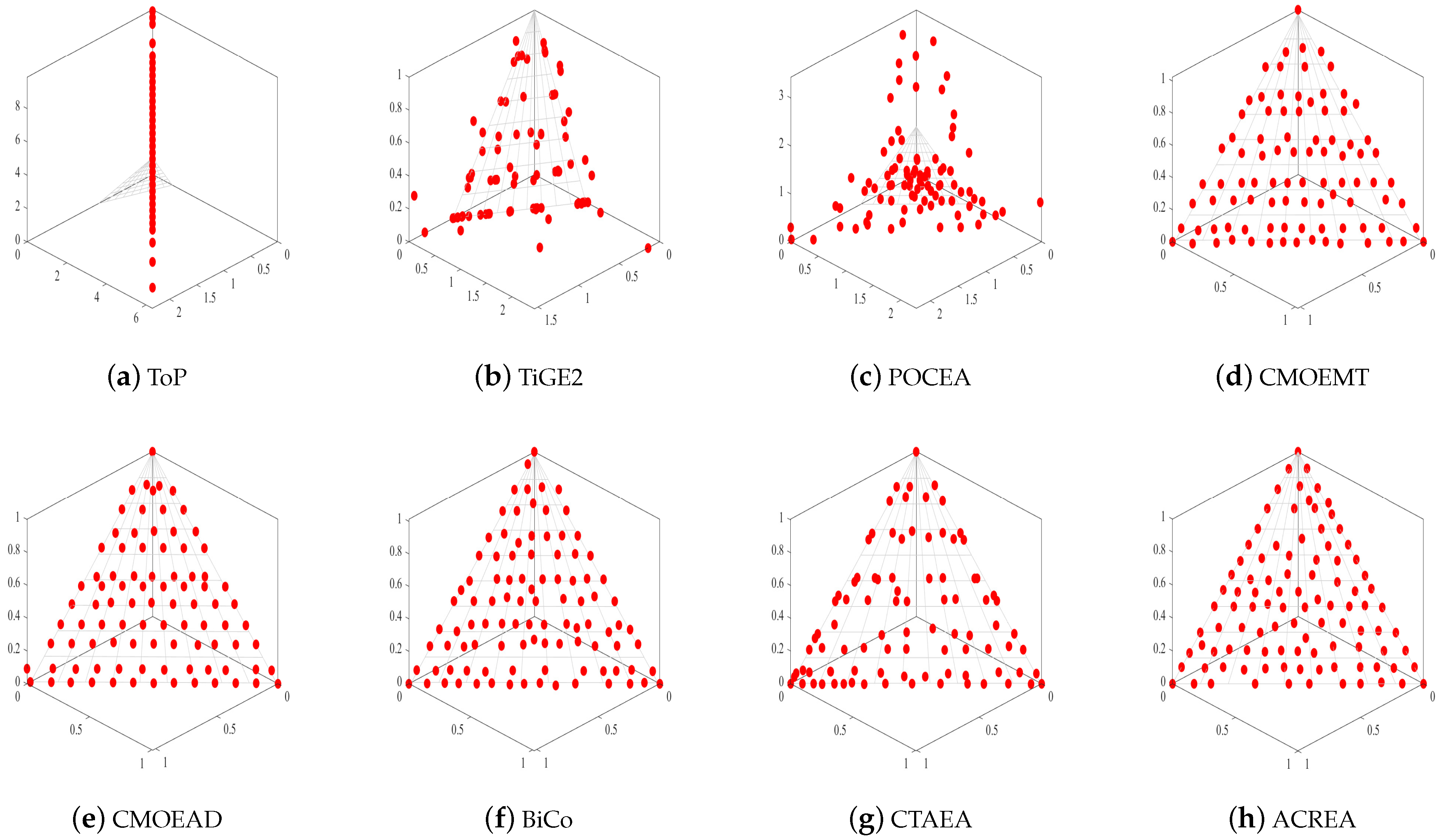
From Table 6, we can see the Wilcoxon rank analysis between ACREA and the comparative algorithms. , , and p-value, respectively, represent superior to, inferior to, and similar to values. In IGD’s , CMOEMT reached the highest at 187.0, while in HV’s , CTAEA achieved 257.0. However, in comparison to the values of competitors in , both for IGD and HV, they were all above 700, with the best reaching a peak value of 899.0. Therefore, overall, the performance of ACREA far surpasses that of its competitors. From Figure 4, we can see the PF of the 8 algorithms on MW4. ToP did not find the Pareto front, while TiGE2 and POCEA only found partial Pareto fronts. CTAEA, CMOEMT, and CMOEA/D have some missing solutions that are not on the Pareto front and are relatively sparse. Although all solutions of BiCo are on the Pareto front, they are not as uniformly distributed and dense as compared to ACREA.

Table 6.
Wilcoxon’s rank sum test results based on mean and HV values on the three test suite.
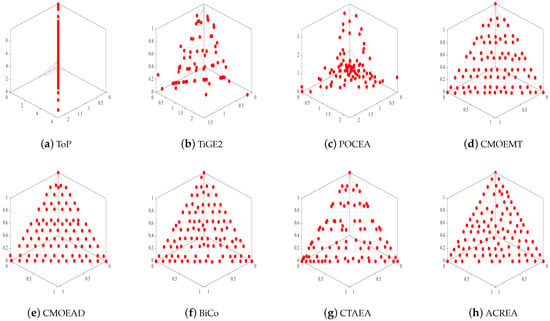
Figure 4.
The Pareto front (PF) plot obtained in MW4 test problem.
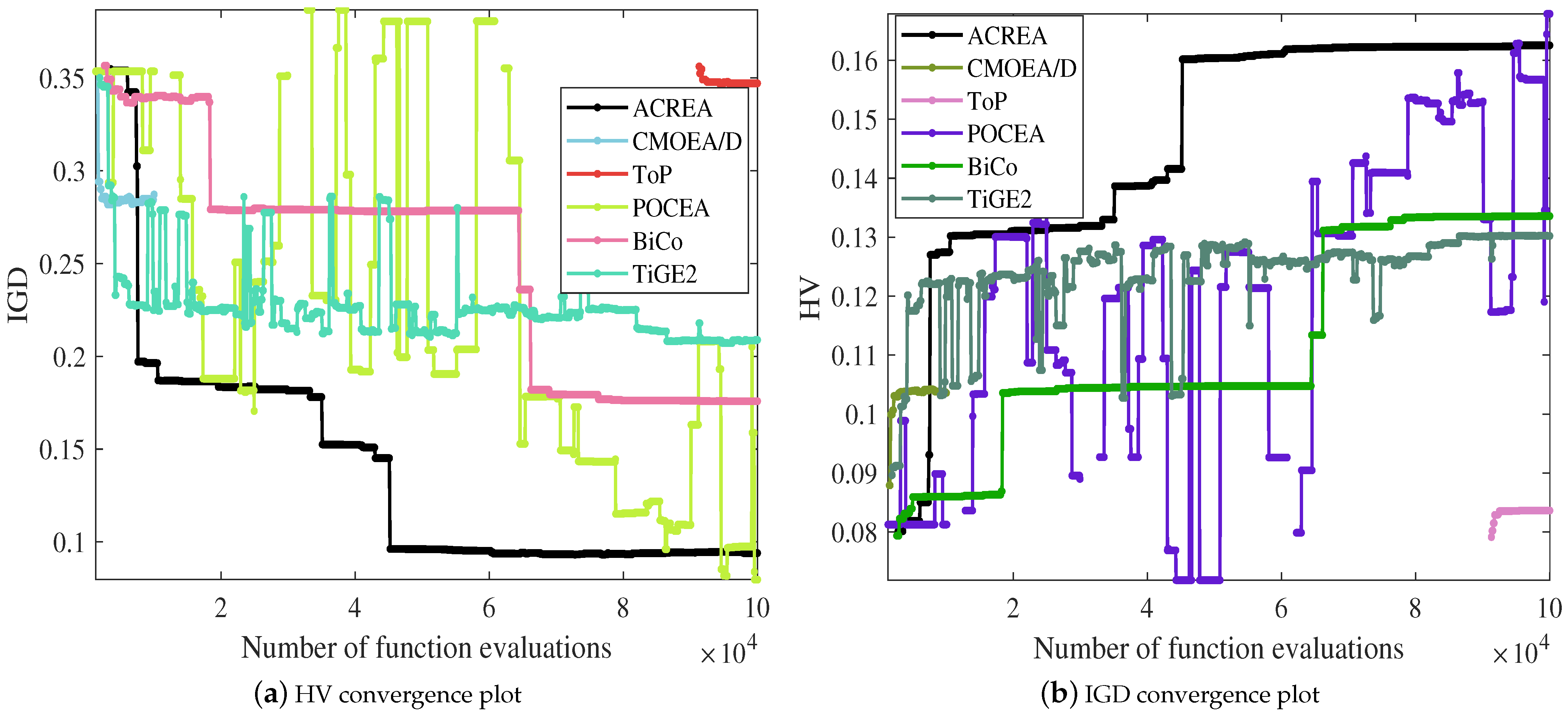
As shown in Figure 5, the convergence plots comparing ACREA with five representative algorithms clearly demonstrate the results. In Figure 4a, ACREA’s IGD metric remains at the lowest level as the evaluation count increases, indicating that lower IGD values reflect better algorithm performance. Conversely, in Figure 4b, ACREA’s HV metric consistently stays at a leading standard as the evaluation count increases, with higher HV values representing better algorithm performance. Therefore, considering the convergence plots of both IGD and HV metrics, ACREA outperforms its competitors.
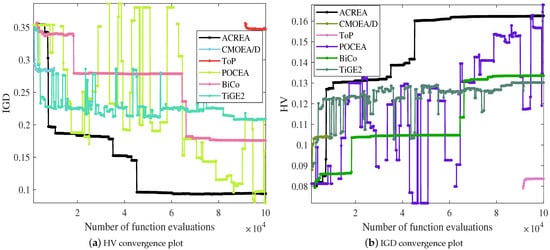
Figure 5.
HV and IGD convergence plots.
Analyzing from the perspective of time complexity, traditional CMOED algorithms such as CTAEA, ToP, POCEA, CMOEMT, BiCo, and TiGE2 have a time complexity of . However, ACREA also has a complexity of , but the experimental results of the seven competing algorithms are far inferior to those of ACREA. Additionally, the space complexity of eight CMOEAs is , indicating that the proposed ACREA algorithm not only significantly saves computational resources but also achieves ideal results.
In conclusion, ACREA achieved good performance in Wilcoxon rank-sum analysis, the Pareto front plot of MW4, time complexity, IGD convergence plots, and HV convergence plots, further demonstrating the superiority and competitiveness of ACREA.
4.5. Effectiveness of Core Components of ACREA
To further verify the effectiveness of ACREA, we conducted a comparative analysis of three variants and ACREA on the LIRCMOP test suite. The specific details are as follows:
- (1)
- ACREA1: Remove the boundary constraint learning mechanism and the corresponding constraint handling technique.
- (2)
- ACREA2: Remove the archive and replace it with the archive mechanism of CTSEA.
- (3)
- ACREA3: Remove the elite selection mechanism of the parent generation and replace it with binary tournament selection.
As shown in Table 7, the IGD metrics of the three variants and ACREA on LIRCMOP can be observed. When the boundary constraint mechanism and the corresponding constraint handling technique were removed, the performance of ACREA1 significantly decreased, further illustrating the importance of the boundary constraint handling mechanism. ACREA2 deleted the archive and performed worse than ACREA on eight test problems, indicating that the archiving mechanism significantly enhances the overall performance of the algorithm. ACREA outperformed ACREA3 on nine test problems, with only one test problem performing worse than ACREA3, thus fully validating the effectiveness of parent elite selection. ACREA outperforms the other three variants on 9, 8, and 9 test problems, respectively. As shown in Table 8, the three variants and ACREA in terms of the HV indicator in LIRCMOP. ACREA far outperforms the other three variants, once again validating the effectiveness of constraint boundary learning, archiving mechanism, and parent elite selection.

Table 7.
The IGD results (mean and standard deviation) of ACREA and three variants of it on LIRCMOP test suite.

Table 8.
The HV results (mean and standard deviation) of ACREA and three variants of it on LIRCMOP test suite.
In conclusion, the analysis of IGD and HV indicators on the LIRCMOP test suite for the three variants and ACREA further demonstrates the effectiveness of ACREA.
4.6. Real Case Problem Testing for ACREA
In this subsection, extending the application of ACREA to real-world problems, we select nine of the most common real-world problems to contrast the eight algorithms in our experiments. For example, the water resource management problem (WRM) [41] and the speed reducer design problem (SRD) [42], which are currently of most interest, have a WRM setup that includes 5 objectives and 7 constraints, and a SRD that has 2 objectives and 11 constraints. As shown in Table 9, ACREA outperforms 7 seven competitors in 8, 9, 9, 9, 9, 9, 7 and 9 real-world problems, which is enough to prove that ACREA is highly scalable in real-world applications.

Table 9.
The HV results (mean and standard deviation) of ACREA on the real-world case problem.
5. Conclusions
In this study, we cleverly designed a novel archiving mechanism to retain high-quality solutions, assisting the main population in approaching the CPF from both feasible and infeasible regions, in order to effectively address CMOPS. To further exploit information from infeasible solutions, a novel boundary relaxation constraint learning mechanism was established. The learning mechanism can adaptively relax the constraints according to the proportion of feasible solutions, enhance the search ability of the population, and promote the population to obtain a complete CPF. In terms of parent selection, strict constraint dominance principles and crowding distance definitions were established to drive competition between solutions. This approach helps select higher-quality solution sets, enabling the population to traverse large and narrow infeasible regions.
Comprehensive analysis of the experimental data shows that ACREA achieved 54.6% of the best values in the IGD metric across 44 benchmark test problems and 50% of the best values in the HV metric while obtaining seven best values among nine real-world problems. This once again verifies that ACREA not only outperforms its competitors but also demonstrates strong scalability in practical problems. Although ACREA achieved good results, there are still some areas for improvement. For example, the lack of interaction between the population and the archive not only leads to the mishandling of important information but also greatly reduces the speed of convergence to the Pareto front. Additionally, the threshold settings for parameters () in real-world problems are not precise enough, hindering the algorithm from truly achieving optimality in practical applications. In future research, we will enhance the information transfer between the population and the archive and optimize the precision of the threshold, embedding these improvements into a large-scale model for evaluation.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.C. and K.Z.; Methodology, J.C.; Software, J.C.; Validation, J.C. and Z.D.; Formal analysis, J.C.; Investigation, J.C.; Resources, J.D. and Z.D.; Data curation, J.C. and K.Z.; Writing—original draft, J.C., K.Z., H.Z., J.Y. and J.D.; Writing—review & editing, J.C., K.Z. and J.Y.; Visualization, J.C.; Supervision, J.D. and Z.D.; Project administration, Z.D.; Funding acquisition, Z.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Dataset available on request from the authors.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Prasanthi, A.; Shareef, H.; Errouissi, R.; Asna, M.; Wahyudie, A. Quantum chaotic butterfly optimization algorithm with ranking strategy for constrained optimization problems. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 114587–114608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Fan, N.; Wei, S.; Tong, W. A convergence-diversity balanced fitness evaluation mechanism for decomposition-based many-objective optimization algorithm. Integr. Comput.-Aided Eng. 2019, 26, 159–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Sun, K.; Men, R.; Wang, F.; Li, D.; Han, Y.; Qu, Y. Study on the Optimization of Multi-Objective Water Resources Allocation in the Henan Yellow River Water Supply Zone. Water 2023, 15, 4009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Zhou, Q.; Mo, Q.; Gan, L.; Hu, R. Using an Improved Artificial Hummingbird Algorithm for Vision-Guided Optimization And Grasping of Multi-Objective Robots. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2022, 2365, 012052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Sun, X.; Zhang, Y.; Gong, D.; Hu, H.; Zuo, M. Linear Regression-based Autonomous Intelligent Optimization for Constrained Multi-objective Problems. IEEE Trans. Artif. Intell. 2024, 5, 4620–4634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavankumar, Y.; Debnath, S.; Paul, S. Multi-objective pareto optimal unbalance voltage compensation in the microgrid. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2023, 217, 109104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, W. Adaptive multi-objective particle swarm optimization based on virtual Pareto front. Inf. Sci. 2023, 625, 206–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Chen, Z.; Wang, Y.; Ban, X.; Qiao, K.; Yu, K. A dual-population constrained multi-objective evolutionary algorithm with variable auxiliary population size. Complex Intell. Syst. 2023, 9, 5907–5922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Luo, K. Differential evolution improvement by adaptive ranking-based constraint handling technique. Soft Comput. 2023, 27, 11485–11504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alofairi, A.A.; Mabrouk, E.; Elsemman, I.E. Constraint-based models for dominating protein interaction networks. IET Syst. Biol. 2021, 15, 148–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Yang, J.; Huang, Z. Research and Analysis of Vegetable Pricing Strategy Model Based on Single Objective Optimization Algorithm. Inf. Syst. Econ. 2023, 4, 116–126. [Google Scholar]
- Vallerio, M.; Hufkens, J.; Van Impe, J.; Logist, F. An interactive decision-support system for multi-objective optimization of nonlinear dynamic processes with uncertainty. Expert Syst. Appl. 2015, 42, 7710–7731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ming, F.; Gong, W.; Wang, L.; Gao, L. Constrained multi-objective optimization via multitasking and knowledge transfer. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2022, 28, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Chen, R.; Fu, G.; Yao, X. Two-archive evolutionary algorithm for constrained multiobjective optimization. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2018, 23, 303–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.Z.; Wang, B.C.; Tang, K. Handling constrained multiobjective optimization problems via bidirectional coevolution. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2021, 52, 10163–10176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Zheng, J.; Zou, J.; Yu, F.; Yang, S. A dual-population evolutionary algorithm based on adaptive constraint strength for constrained multi-objective optimization. Swarm Evol. Comput. 2023, 77, 101247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zuo, M.; Gong, D. Migration-based algorithm library enrichment for constrained multi-objective optimization and applications in algorithm selection. Inf. Sci. 2023, 649, 119593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Premkumar, M.; Kumar, C.; Dharma Raj, T.; Sundarsingh Jebaseelan, S.D.T.; Jangir, P.; Haes Alhelou, H. A reliable optimization framework using ensembled successive history adaptive differential evolutionary algorithm for optimal power flow problems. IET Gener. Transm. Distrib. 2023, 17, 1333–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Shao, H.; Cheng, J.; Zhao, X.; Yang, Y. Support tensor machine with dynamic penalty factors and its application to the fault diagnosis of rotating machinery with unbalanced data. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2020, 141, 106441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, R.; Meng, Z.; Zhou, H. A self-adaptive strategy based firefly algorithm for constrained engineering design problems. Appl. Soft Comput. 2021, 107, 107417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kale, I.R.; Kulkarni, A.J. Cohort intelligence with self-adaptive penalty function approach hybridized with colliding bodies optimization algorithm for discrete and mixed variable constrained problems. Complex Intell. Syst. 2021, 7, 1565–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deb, K.; Pratap, A.; Agarwal, S.; Meyarivan, T. A fast and elitist multiobjective genetic algorithm: NSGA-II. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2002, 6, 182–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Fang, Y.; Li, W.; Cai, X.; Wei, C.; Goodman, E. MOEA/D with angle-based constrained dominance principle for constrained multi-objective optimization problems. Appl. Soft Comput. 2019, 74, 621–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Wang, Y.; Song, W. A new fitness function with two rankings for evolutionary constrained multiobjective optimization. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2019, 51, 5005–5016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahama, T.; Sakai, S.; Iwane, N. Solving nonlinear constrained optimization problems by the ε constrained differential evolution. In Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man and Cybernetics, Taipei, Taiwan, 8–11 October 2006; Volume 3, pp. 2322–2327. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, Z.; Li, W.; Cai, X.; Huang, H.; Fang, Y.; You, Y.; Mo, J.; Wei, C.; Goodman, E. An improved epsilon constraint-handling method in MOEA/D for CMOPs with large infeasible regions. Soft Comput. 2019, 23, 12491–12510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; Liu, H.L.; Gu, F. An evolutionary algorithm with directed weights for constrained multi-objective optimization. Appl. Soft Comput. 2017, 60, 613–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younis, A.; Dong, Z. Adaptive surrogate assisted multi-objective optimization approach for highly nonlinear and complex engineering design problems. Appl. Soft Comput. 2024, 150, 111065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.Z.; Wang, Y. Handling constrained multiobjective optimization problems with constraints in both the decision and objective spaces. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2019, 23, 870–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, H.; Deb, K. An evolutionary many-objective optimization algorithm using reference-point based nondominated sorting approach, part II: Handling constraints and extending to an adaptive approach. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2013, 18, 602–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Cheng, R.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, X.; Tan, K.C.; Jin, Y. Paired offspring generation for constrained large-scale multiobjective optimization. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2020, 25, 448–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhu, M.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Xiang, Y.; Zhang, J. Tri-goal evolution framework for constrained many-objective optimization. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2018, 50, 3086–3099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ming, F.; Gong, W.; Zhen, H.; Li, S.; Wang, L.; Liao, Z. A simple two-stage evolutionary algorithm for constrained multi-objective optimization. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2021, 228, 107263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Feng, X.; Yu, H. A constrained multiobjective evolutionary algorithm with the two-archive weak cooperation. Inf. Sci. 2022, 615, 415–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Wei, H.; Tian, Y.; Cheng, R.; Zhang, X. A multi-stage evolutionary algorithm for multi-objective optimization with complex constraints. Inf. Sci. 2021, 560, 68–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.Z.; Qin, Y.; Song, W.; Zhang, J.; Li, K. Multiobjective-based constraint-handling technique for evolutionary constrained multiobjective optimization: A new perspective. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2022, 27, 1370–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverman, B.W. Density Estimation for Statistics and Data Analysis; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, J.; Ban, X.; Yu, K.; Qu, B.; Qiao, K.; Yue, C.; Chen, K.; Tan, K.C. A survey on evolutionary constrained multiobjective optimization. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2022, 27, 201–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Q.; Wang, Q.; Xiong, N.N.; Jiang, S.; Chen, L. Surrogate-assisted evolutionary algorithm for expensive constrained multi-objective discrete optimization problems. Complex Intell. Syst. 2022, 8, 2699–2718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Zhu, W.; Zhang, X.; Jin, Y. A practical tutorial on solving optimization problems via PlatEMO. Neurocomputing 2023, 518, 190–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, J.A.; Alamanos, A. A multi-objective optimization framework for water resources allocation considering stakeholder input. Environ. Sci. Proc. 2023, 25, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Chen, X.; Liu, Z.; Yang, J.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, Y. Multi-objective reliability-based design optimization for the reducer housing of electric vehicles. Eng. Optim. 2022, 54, 1324–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).