Online Investor Sentiment via Machine Learning
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Econometric Methodology
2.1. Model Setup
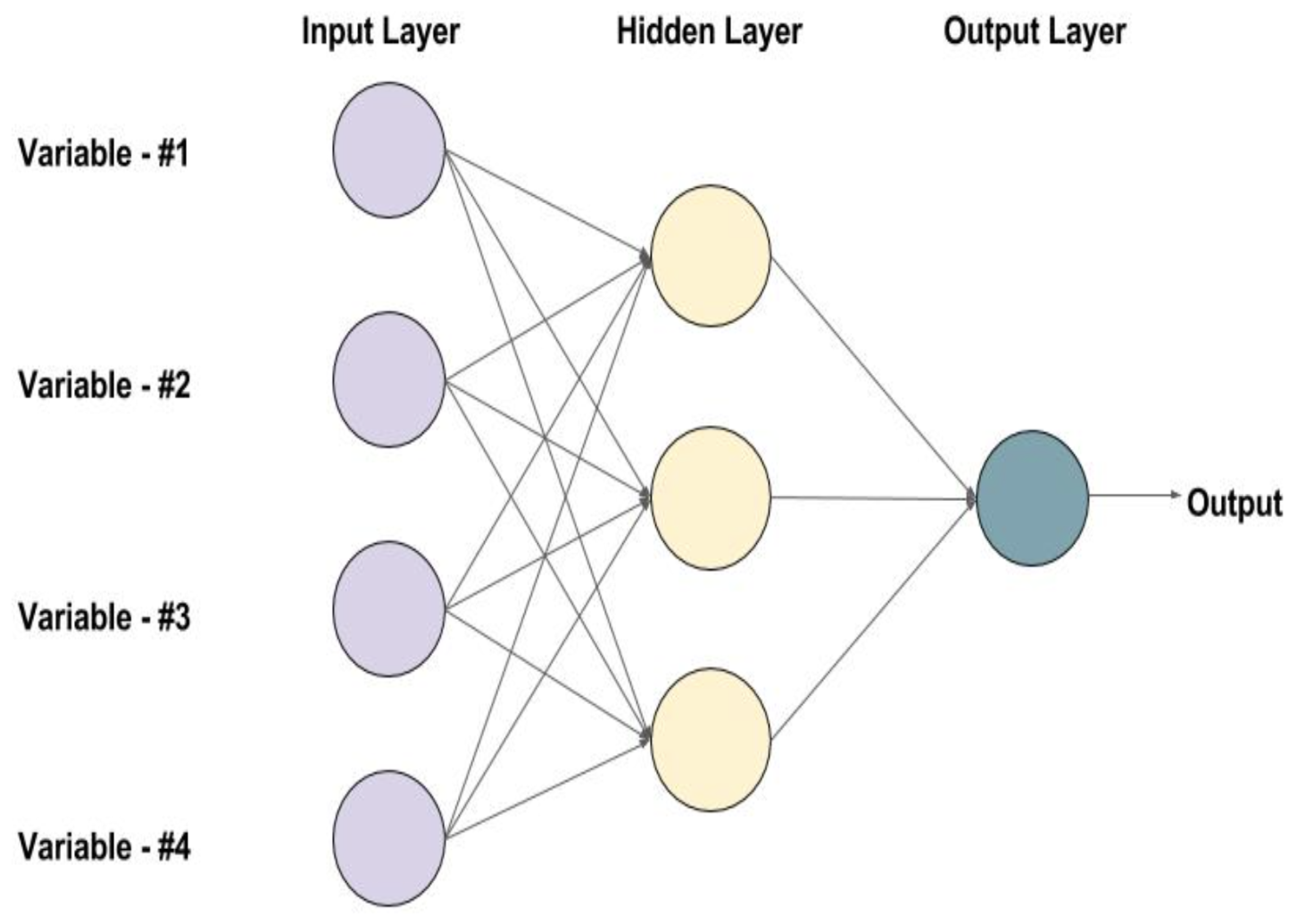
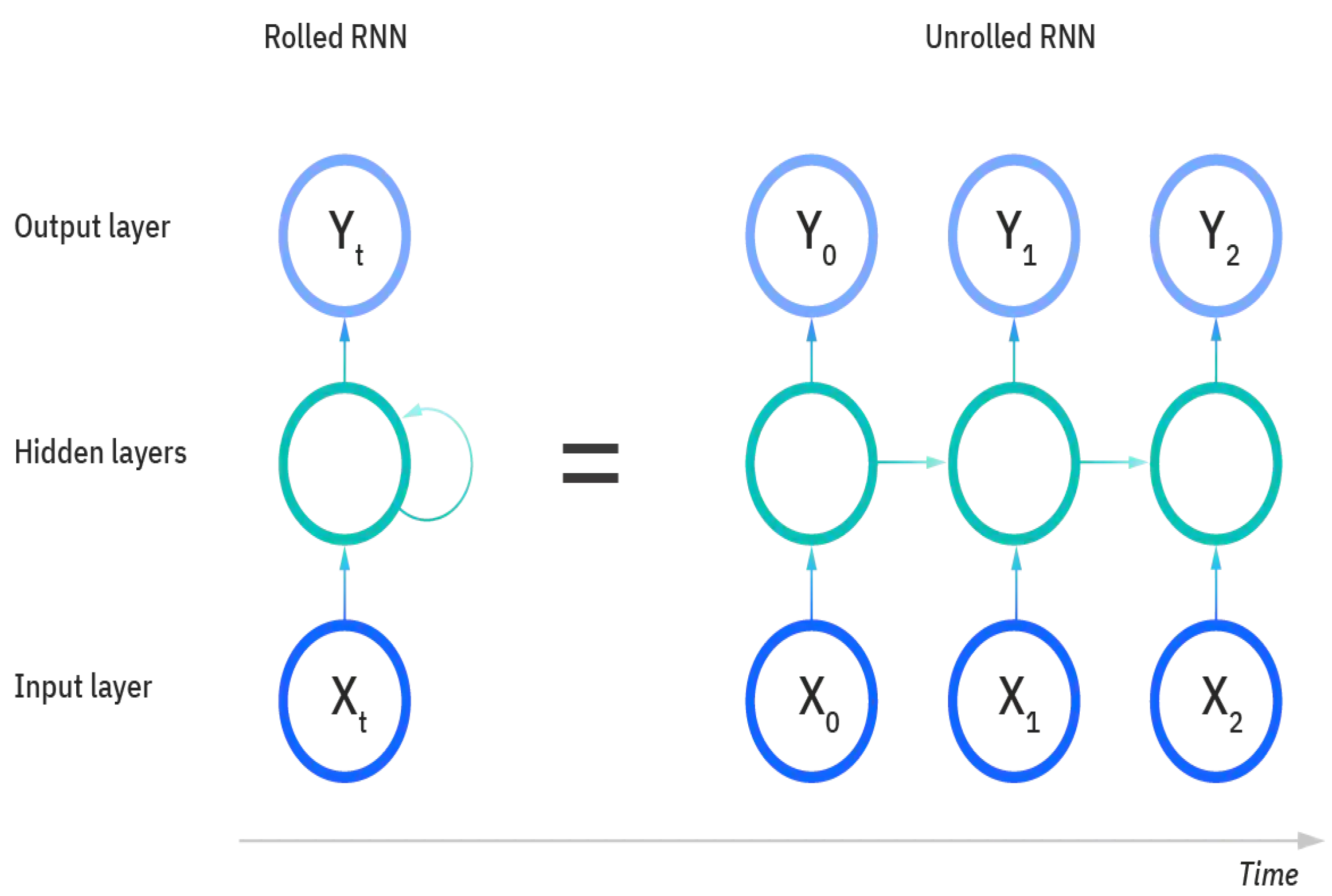
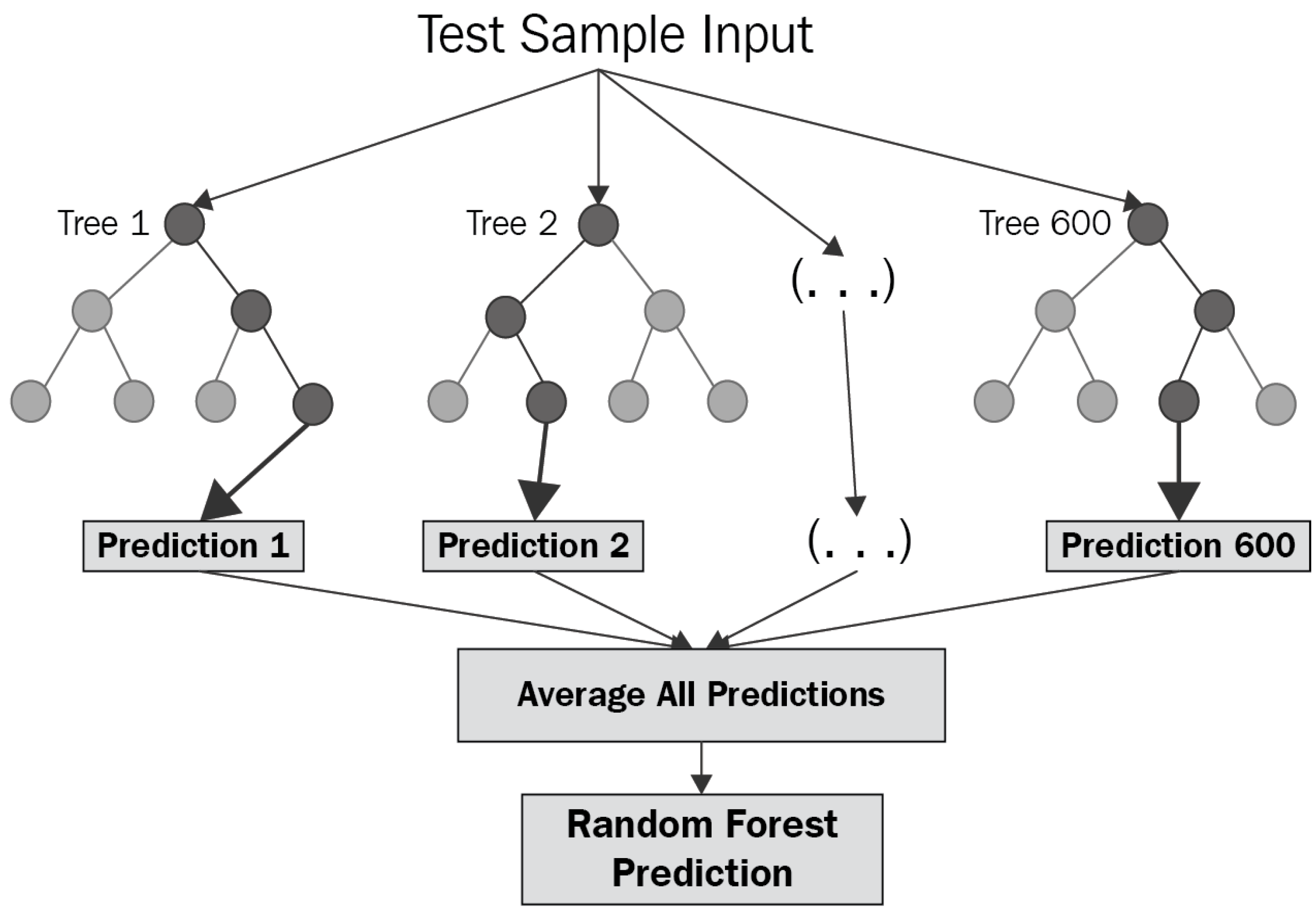
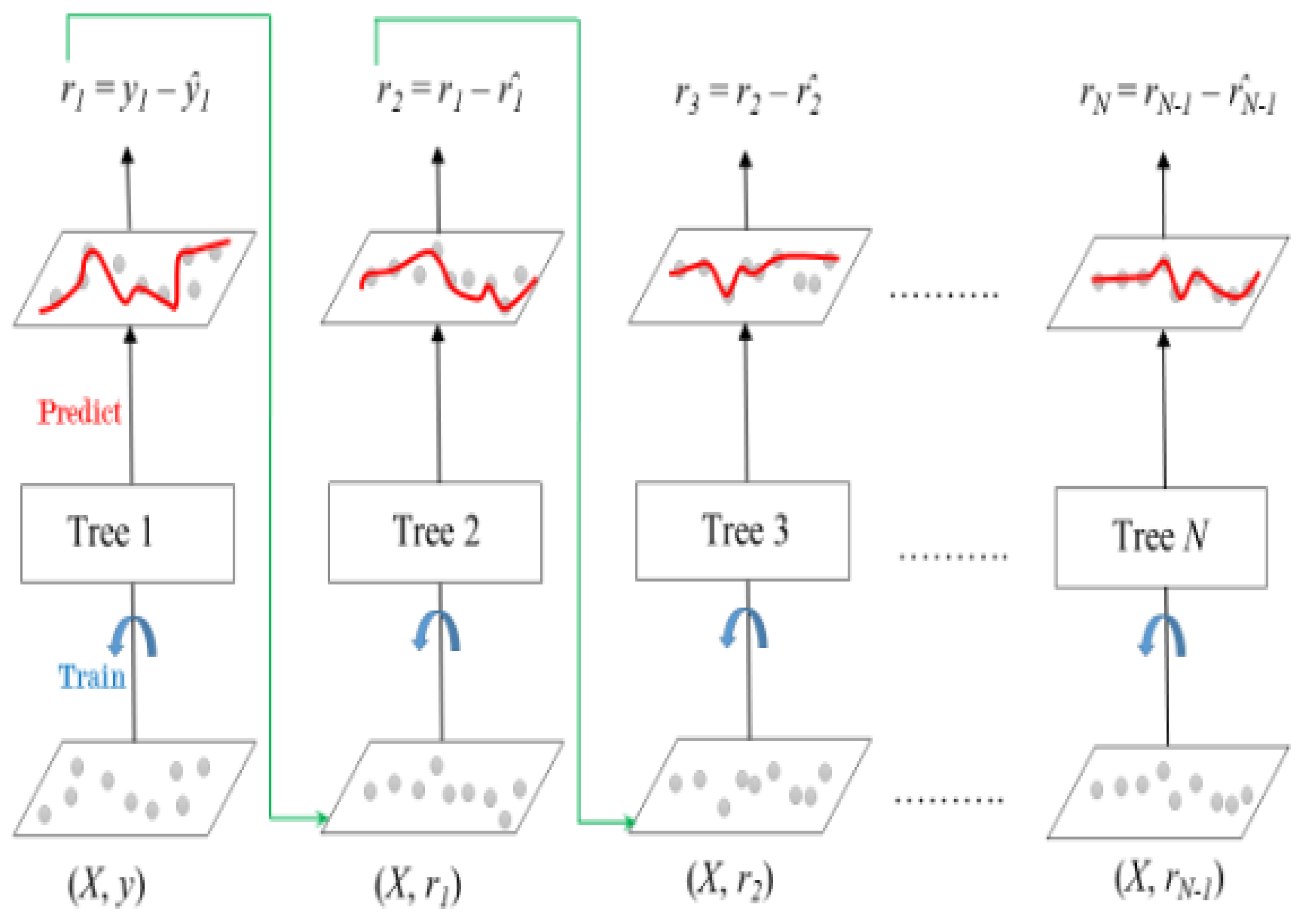
2.2. Machine Learning Methods
2.3. Choice of Tuning Parameters
3. Empirical Results
3.1. Data
3.2. Out-of-Sample Forecasting
3.3. Asset Allocation Implications
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rapach, D.; Zhou, G. Forecasting stock returns. In Handbook of Economic Forecasting; Elliott, G., Timmermann, A., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 328–383. [Google Scholar]
- Campbell, J.Y.; Thompson, S.B. Predicting excess stock returns out of sample: Can anything beat the historical average? Rev. Financ. Stud. 2008, 21, 1509–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; Chen, P. Online Investor Sentiment and Asset Returns; Working Paper; Department of Economics, University of Kansas: Lawrence, KS, USA, 2022; Available online: https://ideas.repec.org/p/kan/wpaper/202216.html (accessed on 23 November 2022).
- Markowitz, H. The utility of wealth. J. Political Econ. 1952, 60, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, M.; Wurgler, J. Investor sentiment and the cross-section of stock returns. Rev. Financ. Stud. 2006, 61, 1645–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, M.; Wurgler, J. Investor sentiment in the stock market. J. Econ. Perspect. 2007, 21, 129–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, G.W.; Cliff, M.T. Investor sentiment and the near-term stock market. J. Empir. Financ. 2004, 11, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Jiang, F.; Tu, J.; Zhou, G. Investor sentiment aligned: A powerful predictor of stock returns. Rev. Financ. Stud. 2015, 28, 791–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.; Lee, J.; Martin, X.; Zhou, G. Manager sentiment and stock returns. J. Financ. Econ. 2019, 132, 126–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemmon, M.; Portniaguina, E. Consumer confidence and asset prices: Some empirical evidence. Rev. Financ. Stud. 2006, 19, 1499–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, S.; Kelly, B.; Xiu, D. Empirical asset pricing via machine learning. Rev. Financ. Stud. 2020, 33, 2223–2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, G.; He, J.; Polson, N.G. Deep learning for predicting asset returns. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1804.09314. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, G.; Polson, N.G.; Xu, J. Deep learning in characteristics-sorted factor models. J. Financ. Quant. Anal. 2023, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Y. Machine Learning and Empirical Asset Pricing. Doctor of Business. Administration Dissertation, Olin Business School, Washington University in St. Louis, St. Louis, MI, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Ndikum, P. Machine learning algorithms for financial asset price forecasting. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.01504. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Pelger, M.; Zhu, J. Deep learning in asset pricing. Manag. Sci. 2024, 70, 714–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodfellow, I.; Pouget-Abadie, J.; Mirza, M.; Xu, B.; Warde-Farley, D.; Ozair, S.; Courville, A.; Bengio, Y. Generative adversarial networks. Commun. ACM 2020, 63, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, M.; Jiang, F.; Tang, G. Deep learning and factor investing in Chinese stock market. China Econ. Q. 2022, 22, 819–842. [Google Scholar]
- Bartov, E.; Faurel, L.; Mohanram, P.S. Can Twitter help predict firm-level earnings and stock returns? Account. Rev. 2018, 93, 25–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrendt, S.; Schmidt, A. The Twitter myth revisited: Intraday investor sentiment, Twitter activity and individual-level stock return volatility. J. Bank. Financ. 2018, 96, 355–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranco, G.; Aleksovski, D.; Caldarelli, G.; Grčar, M.; Mozetič, I. The effects of Twitter sentiment on stock price returns. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0138441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.Y.; Mo, S.Y.K.; Liu, A. Twitter financial community sentiment and its predictive relationship to stock market movement. Quant. Financ. 2015, 15, 1637–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renault, T. Intraday online investor sentiment and return patterns in the US stock market. J. Bank. Financ. 2017, 84, 25–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Naj, M.; Shen, J. Stock return predictability and investor sentiment: A high-frequency perspective. J. Bank. Financ. 2016, 73, 147–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.; Meng, L.; Tang, G. Media textual sentiment and Chinese stock return predictability. China Econ. Q. 2021, 12, 1323–1344. [Google Scholar]
- Majumder, S.; Singh, A.; Singh, A.; Karpenko, M.; Sharma, H.K.; Mukhopadhyay, S. On the analytical study of the service quality of Indian Railways under soft-computing paradigm. Transport 2024, 39, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tibshirani, R. Regression shrinkage and selection via the LASSO. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B 1996, 58, 267–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoerl, A.E.; Kennard, R.W. Ridge regression: Biased estimation for nonorthogonal problems. Technometrics 1970, 12, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, H.; Hastie, T. Regularization and variable selection via the elastic net. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B 2005, 67, 301–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cybenko, G. Approximation by superpositions of a sigmoidal function. Math. Control. Signals Syst. 1989, 2, 303–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornik, K.; Stinchcombe, M.; White, H. Multilayer feedforward networks are universal approximators. Neural Networks 1989, 2, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornik, K. Approximation capabilities of multilayer feedforward networks. Neural Netw. 1991, 4, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarotsky, D. Error bounds for approximations with deep ReLU networks. Neural Netw. 2017, 94, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elman, J.L. Finding structure in time. Cogn. Sci. 1990, 14, 179–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elman, J.L. Distributed representations, simple recurrent networks, and grammatical structure. Mach. Learn. 1991, 7, 195–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipton, Z.C.; Berkowitz, J.; Elkan, C. A critical review of recurrent neural networks for sequence learning. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1506.00019. [Google Scholar]
- Breiman, L. Random forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wager, S.; Athey, S. Estimation and inference of heterogeneous treatment effects using random forests. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 2018, 113, 1228–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coulombe, P.G. The macroeconomy as a random forest. J. Appl. Econom. 2024, 39, 401–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Bagging predictors. Mach. Learn. 1996, 24, 123–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Guestrin, C. XGBoost: A scalable tree boosting system. In Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–17 August 2016; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 785–794. [Google Scholar]
- Friedman, J.H. Greedy function approximation: A gradient boosting machine. Ann. Stat. 2001, 29, 1189–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; Fan, F.; Yao, Q. Functional-coefficient regression models for nonlinear time series. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 2000, 95, 941–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, J. Linear model selection by cross-validation. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1993, 88, 486–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; Gunawan; Sun, Y. A New Nonparametric Combination Forecasting with Structural Breaks; Working Paper; Department of Economics, University of Kansas: Lawrence, KS, USA, 2024; Available online: https://journals.ku.edu/econpapers/article/view/22878 (accessed on 23 September 2024).
- Kelly, B.; Xiu, D. Financial machine learning. Found. Trends Financ. 2023, 13, 205–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da, Z.; Engelberg, J.; Gao, P. The sum of all FEARS investor sentiment and asset prices. Rev. Financ. Stud. 2015, 28, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tetlock, P.C. Giving content to investor sentiment: The role of media in the stock market. J. Financ. 2007, 62, 1139–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tetlock, P.C.; Saar-Tsechansky, M.; Macskassy, S. More than words: Quantifying language to measure firms’ fundamentals. J. Financ. 2008, 63, 1437–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, W.J.; Yuen, K.K. Trimming and winsorization: A review. Stat. Pap. 1974, 15, 157–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, B.; Qureshi, S. Comparing out-of-sample performance of machine learning methods to forecast U.S. GDP growth. Comput. Econ. 2024, 62, 1567–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loughran, T.; McDonald, B. When is a liability not a liability? Textual analysis, dictionaries, and 10-Ks. J. Financ. 2011, 66, 35–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; Yuang, J.; Pan, Y. China economic policy uncertainty and its forecasting based on a new textual mining method. China J. Econom. 2023, 3, 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Loughran, T.; McDonald, B. Textual analysis in accounting and finance: A survey. J. Account. Res. 2016, 54, 1187–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Contribution | IRA Contribution | IRA | 401k | 401k Contribution | Roth Contribution | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Contribution | ||||||
| IRA contribution | ||||||
| IRA | ||||||
| 401k | ||||||
| 401k contribution | ||||||
| Roth contribution |
| J = 26 | J = 52 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type | RMSE | RMSLE | RMSE | RMSLE | ||
| XGBoost | 2.77 | 1.55 | 1.54 | 3.95 | 1.62 | 1.61 |
| RF | 0.45 | 1.61 | 1.60 | 1.55 | 1.68 | 1.67 |
| FNN | −0.77 | 1.86 | 1.84 | 0.03 | 2.12 | 2.11 |
| RNN | 0.18 | 1.63 | 1.63 | 0.75 | 1.72 | 1.74 |
| OLS | −19.58 | 1.69 | 1.69 | −30.07 | 1.86 | 1.85 |
| LASSO | −0.25 | 1.55 | 1.55 | −0.16 | 1.64 | 1.63 |
| Ridge | −0.49 | 1.55 | 1.55 | −0.30 | 1.63 | 1.63 |
| Elastic net | −0.03 | 1.56 | 1.55 | −0.03 | 1.63 | 1.62 |
| Aggregated Investor Sentiment Index | ||||||
| 2.08 | 1.53 | 1.53 | 1.85 | 1.62 | 1.61 | |
| 0.24 | 1.57 | 1.56 | 0.73 | 1.63 | 1.62 | |
| Index | = 1 | = 3 | = 5 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CER Gain | Sharpe Ratio | CER Gain | Sharpe Ratio | CER Gain | Sharpe Ratio | |
| XGBoost | 0.95 | 0.30 | 0.32 | 0.30 | 0.19 | 0.30 |
| RF | 0.62 | 0.24 | 0.21 | 0.24 | 0.12 | 0.24 |
| FNN | 0.05 | 0.31 | 0.02 | 0.31 | 0.01 | 0.31 |
| RNN | 0.17 | 0.33 | 0.06 | 0.33 | 0.03 | 0.33 |
| OLS | 1.03 | 0.14 | 0.34 | 0.14 | 0.21 | 0.14 |
| LASSO | 0.17 | 0.40 | 0.06 | 0.40 | 0.03 | 0.40 |
| Ridge | −0.03 | 0.28 | −0.01 | 0.28 | −0.01 | 0.28 |
| Elastic net | −0.01 | 0.29 | −0.002 | 0.29 | −0.001 | 0.29 |
| Aggregated Investor Sentiment Index | ||||||
| 0.56 | 0.30 | 0.19 | 0.30 | 0.11 | 0.30 | |
| 0.33 | 0.27 | 0.11 | 0.27 | 0.07 | 0.27 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cai, Z.; Chen, P. Online Investor Sentiment via Machine Learning. Mathematics 2024, 12, 3192. https://doi.org/10.3390/math12203192
Cai Z, Chen P. Online Investor Sentiment via Machine Learning. Mathematics. 2024; 12(20):3192. https://doi.org/10.3390/math12203192
Chicago/Turabian StyleCai, Zongwu, and Pixiong Chen. 2024. "Online Investor Sentiment via Machine Learning" Mathematics 12, no. 20: 3192. https://doi.org/10.3390/math12203192
APA StyleCai, Z., & Chen, P. (2024). Online Investor Sentiment via Machine Learning. Mathematics, 12(20), 3192. https://doi.org/10.3390/math12203192







