Optimization of Magnetic Pump Impeller Based on Blade Load Curve and Internal Flow Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Numerical Simulation and Experiment
2.1. Theoretical Basis
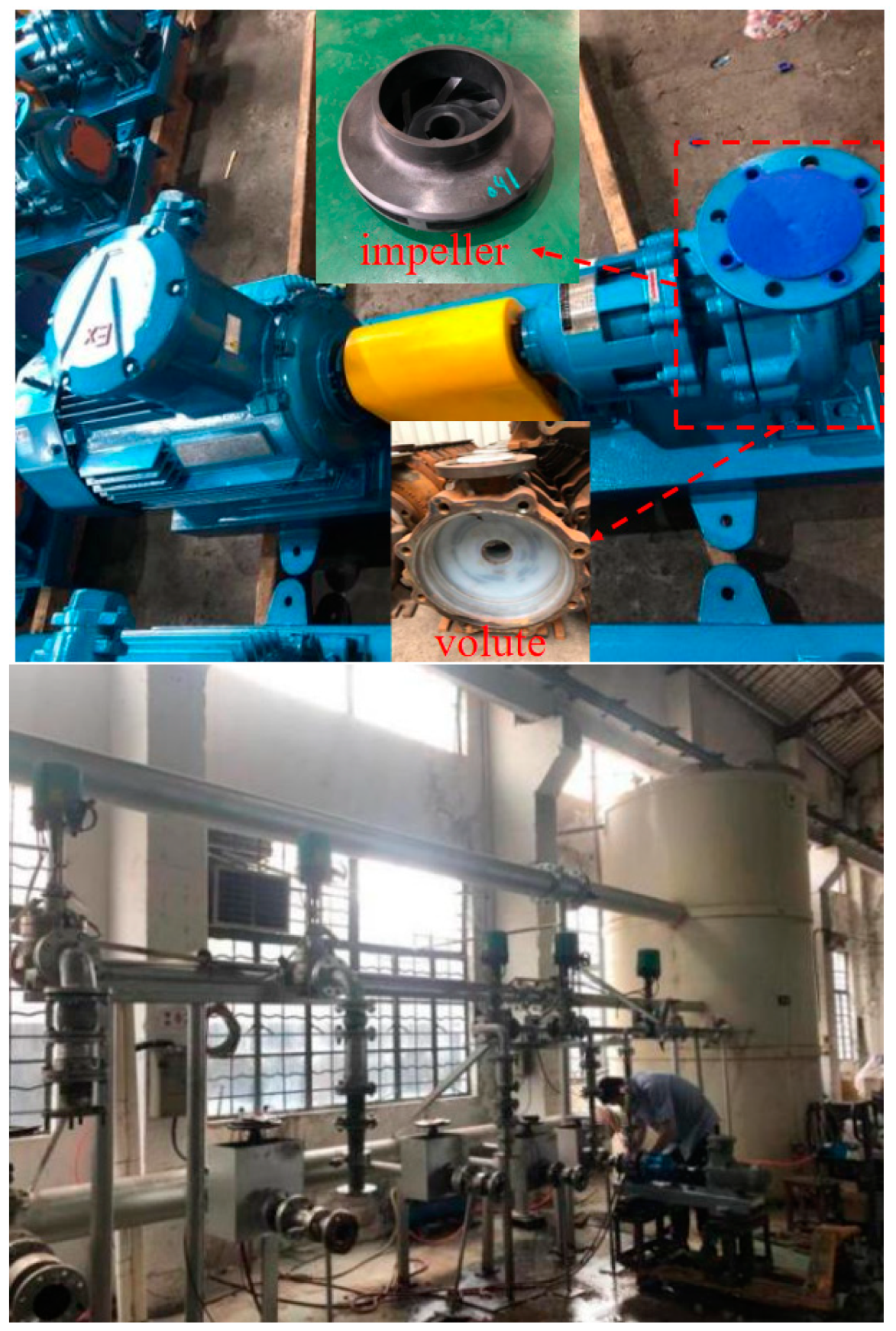
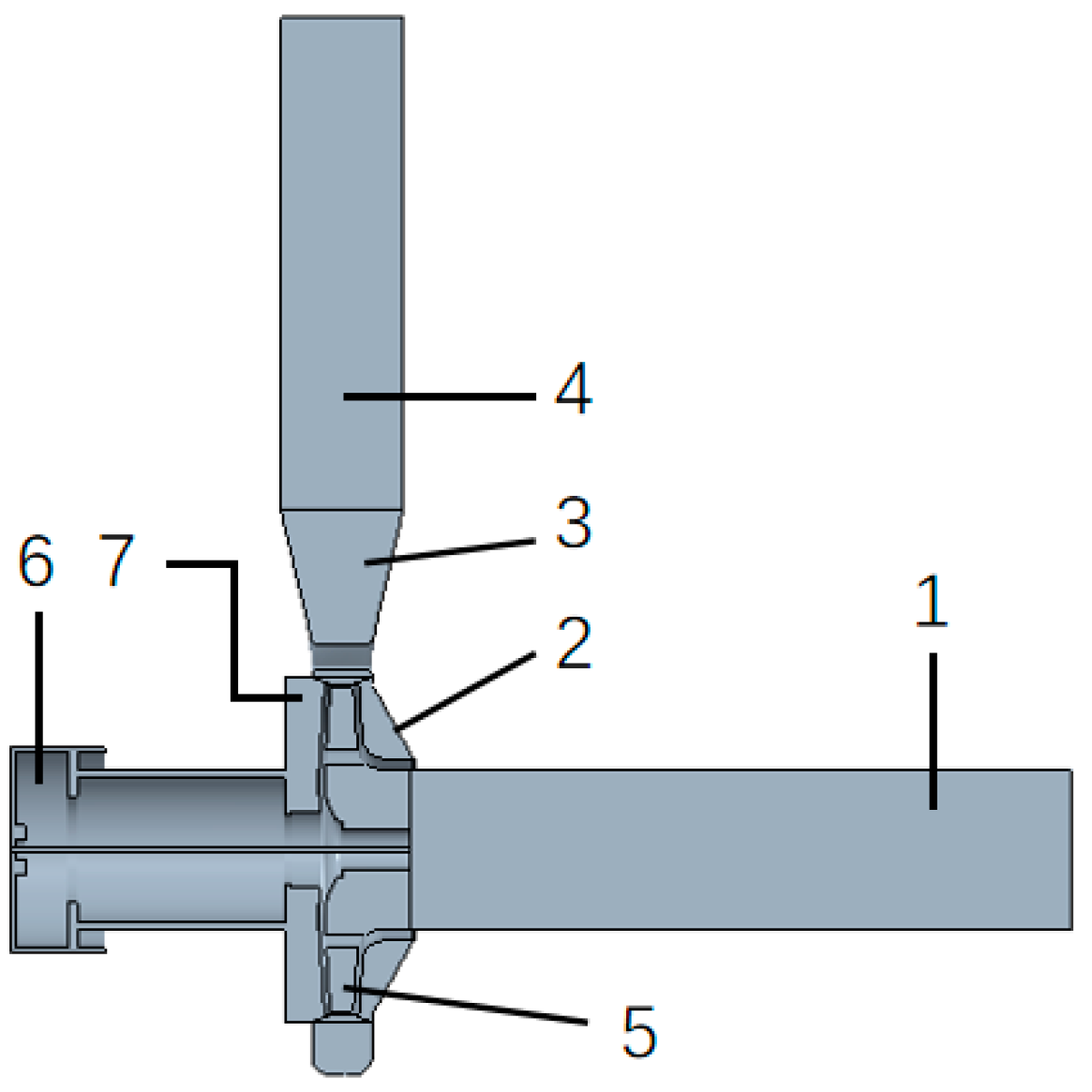
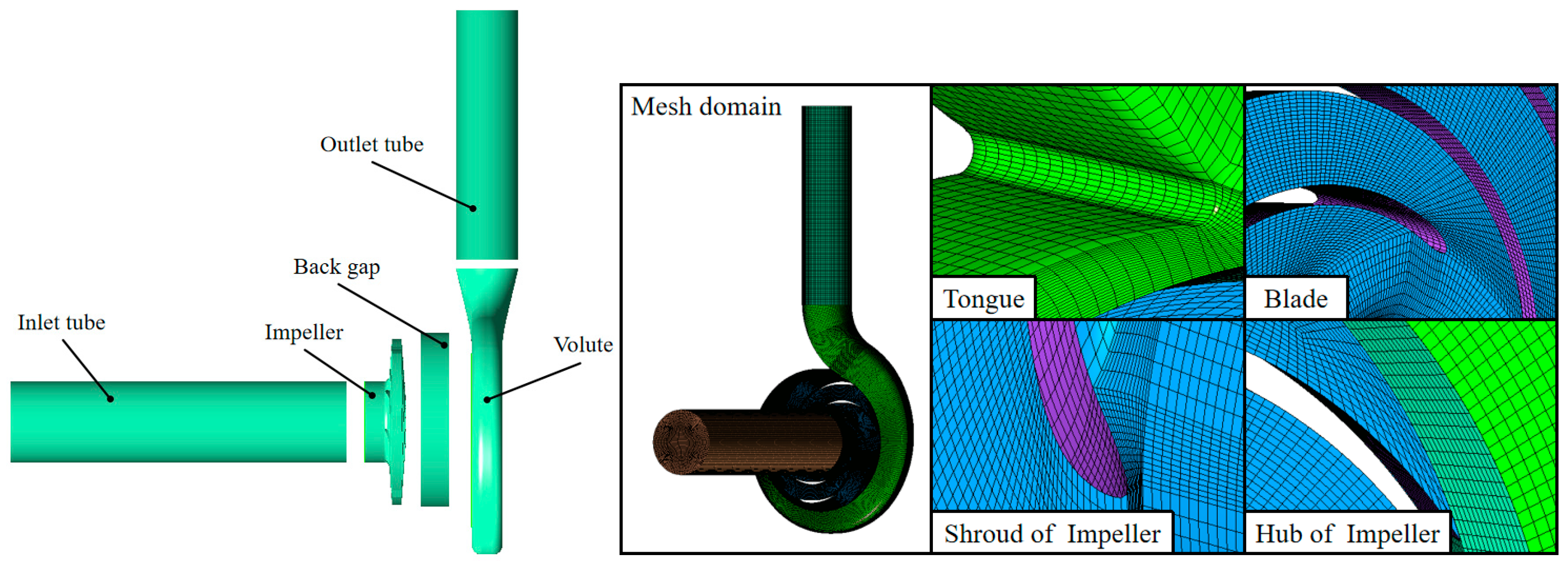
2.2. Physical Model and Computational Domain Model
2.3. Grid Generation
3. Research Methods
3.1. Numerical Simulation
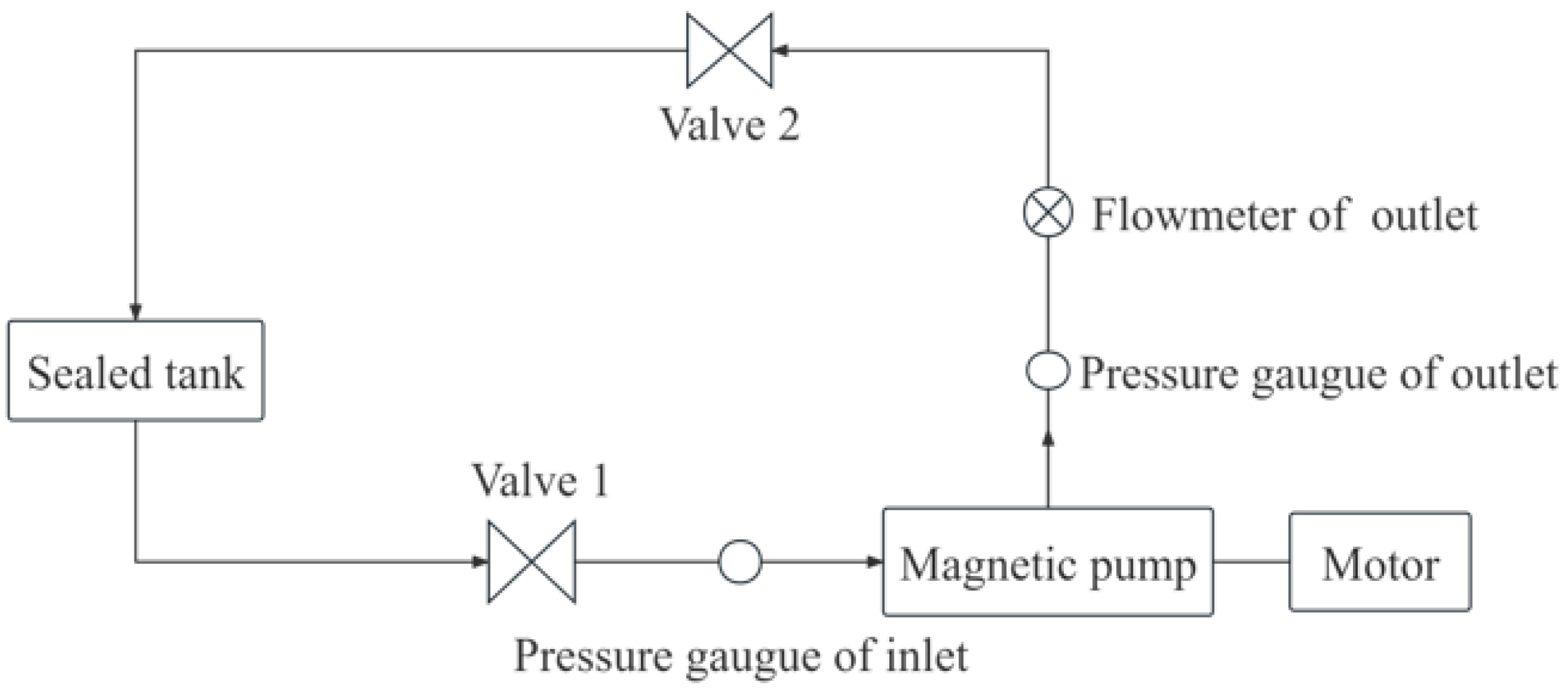
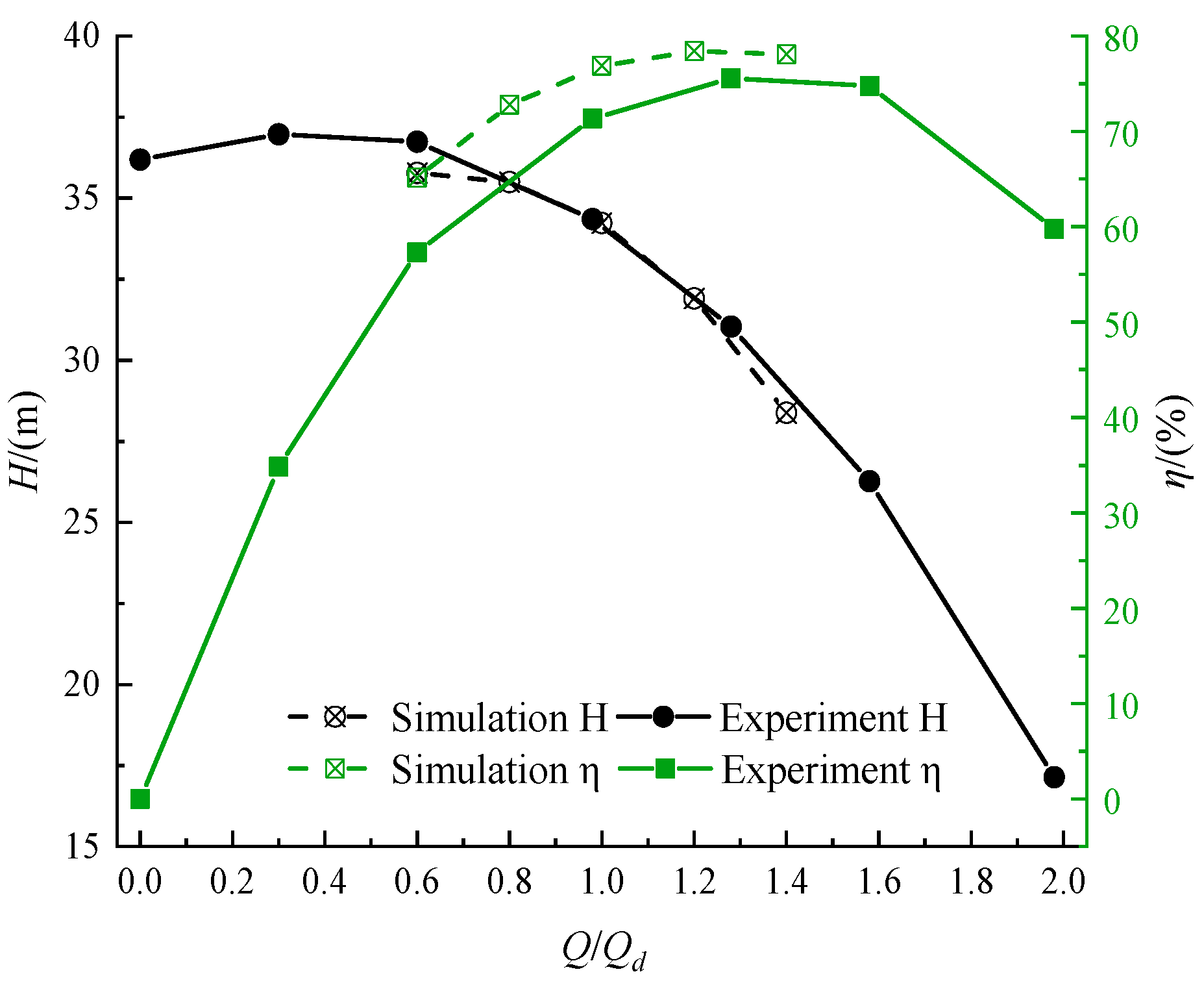
3.2. Experimental Verification
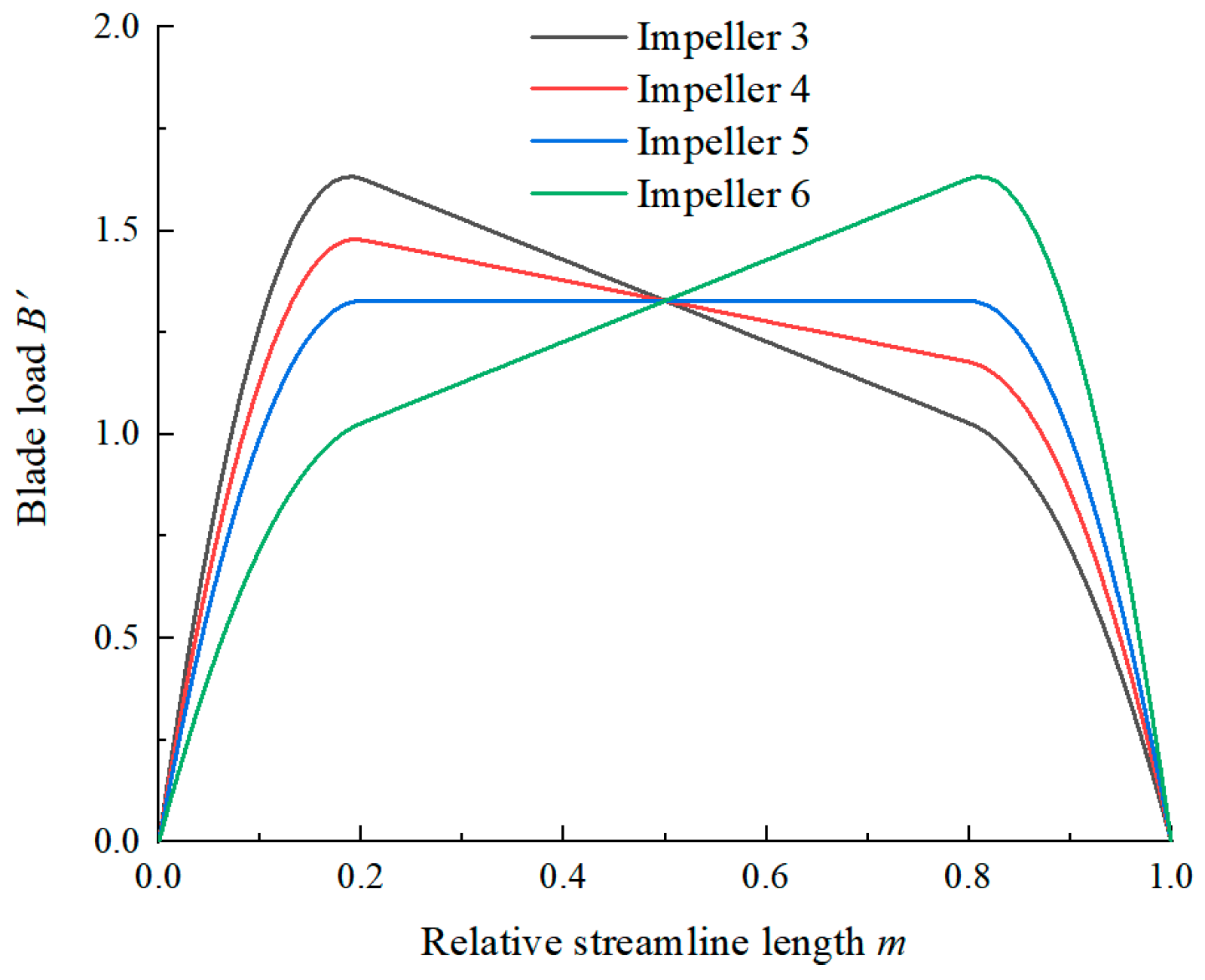
3.3. Optimal Design of Impeller
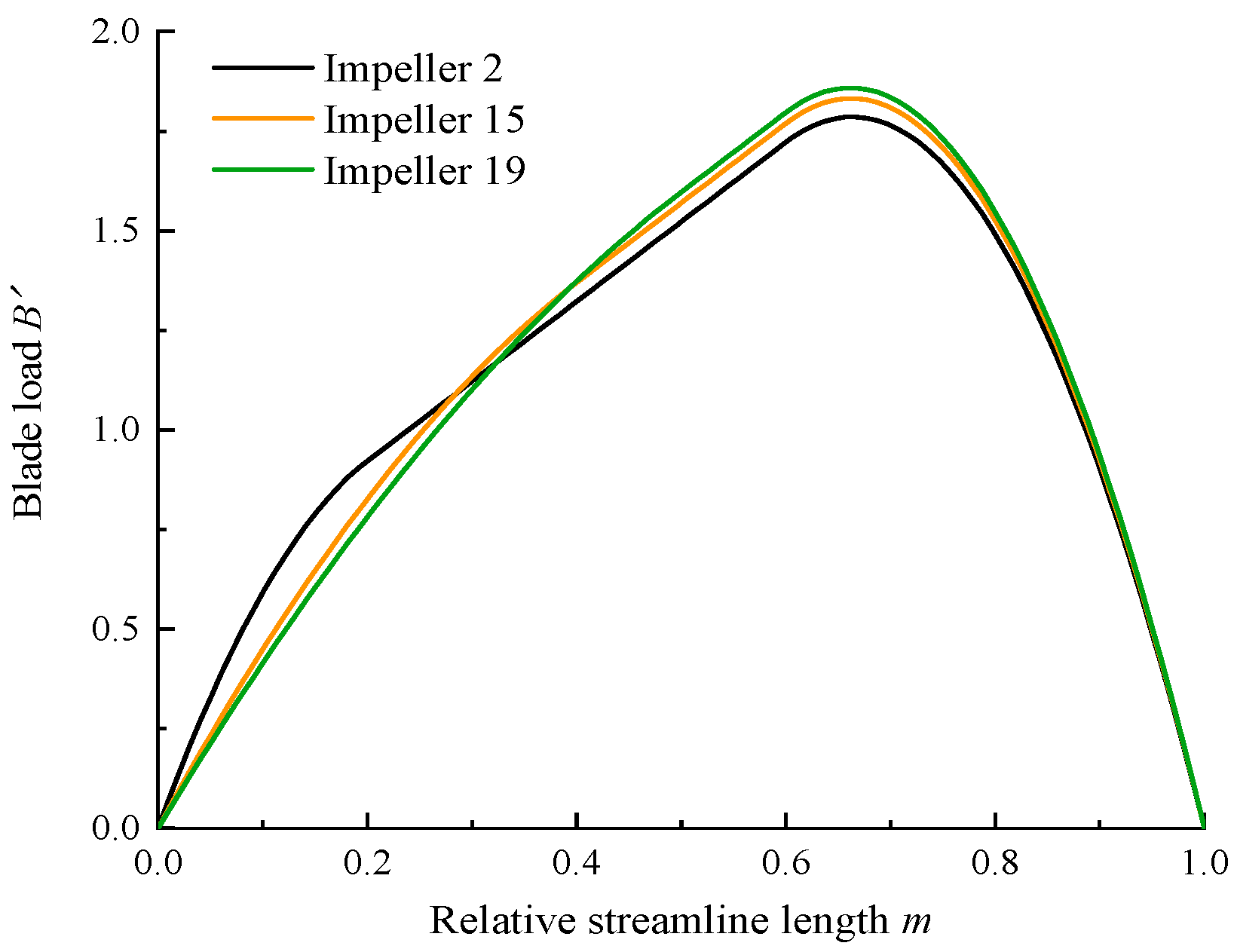
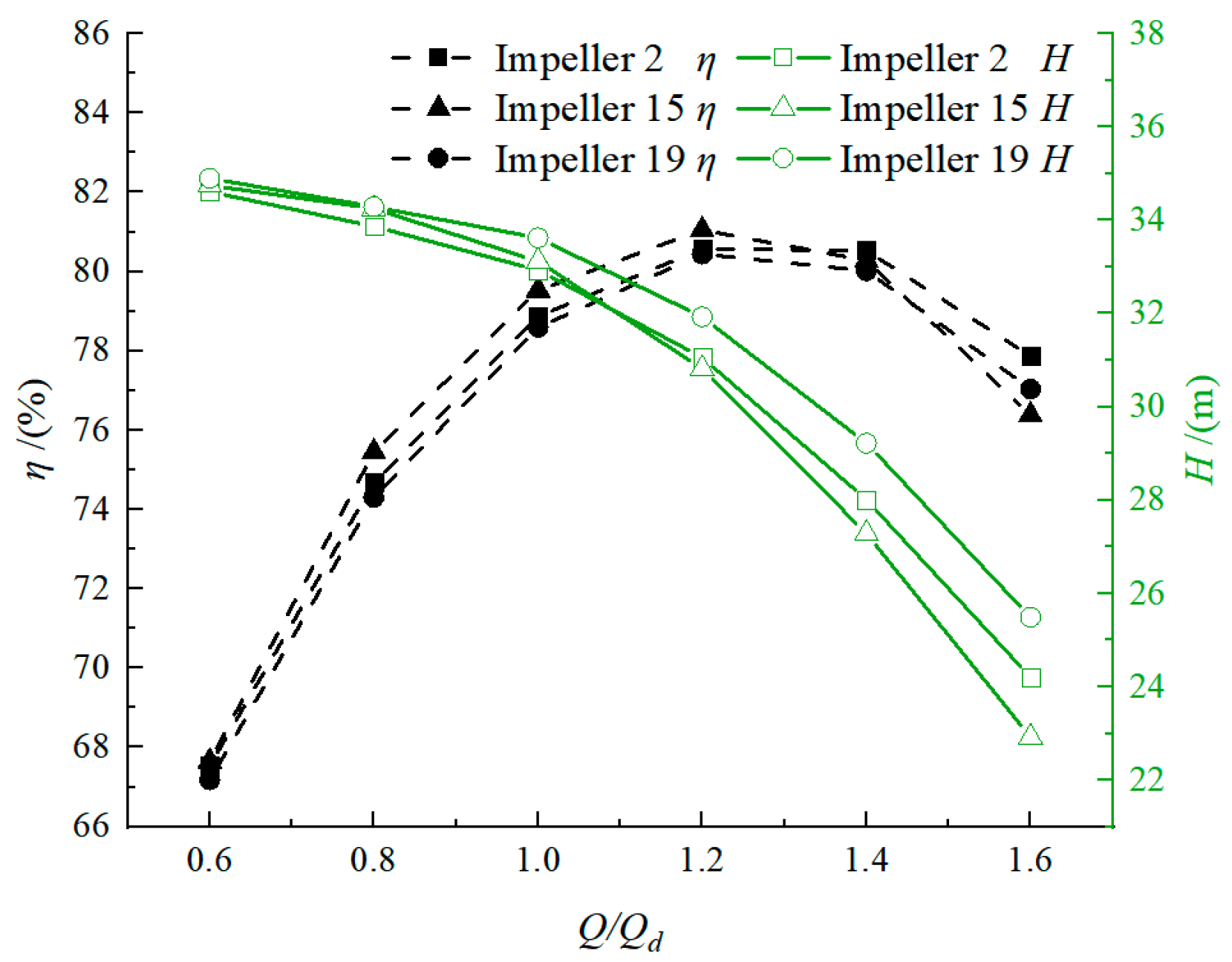
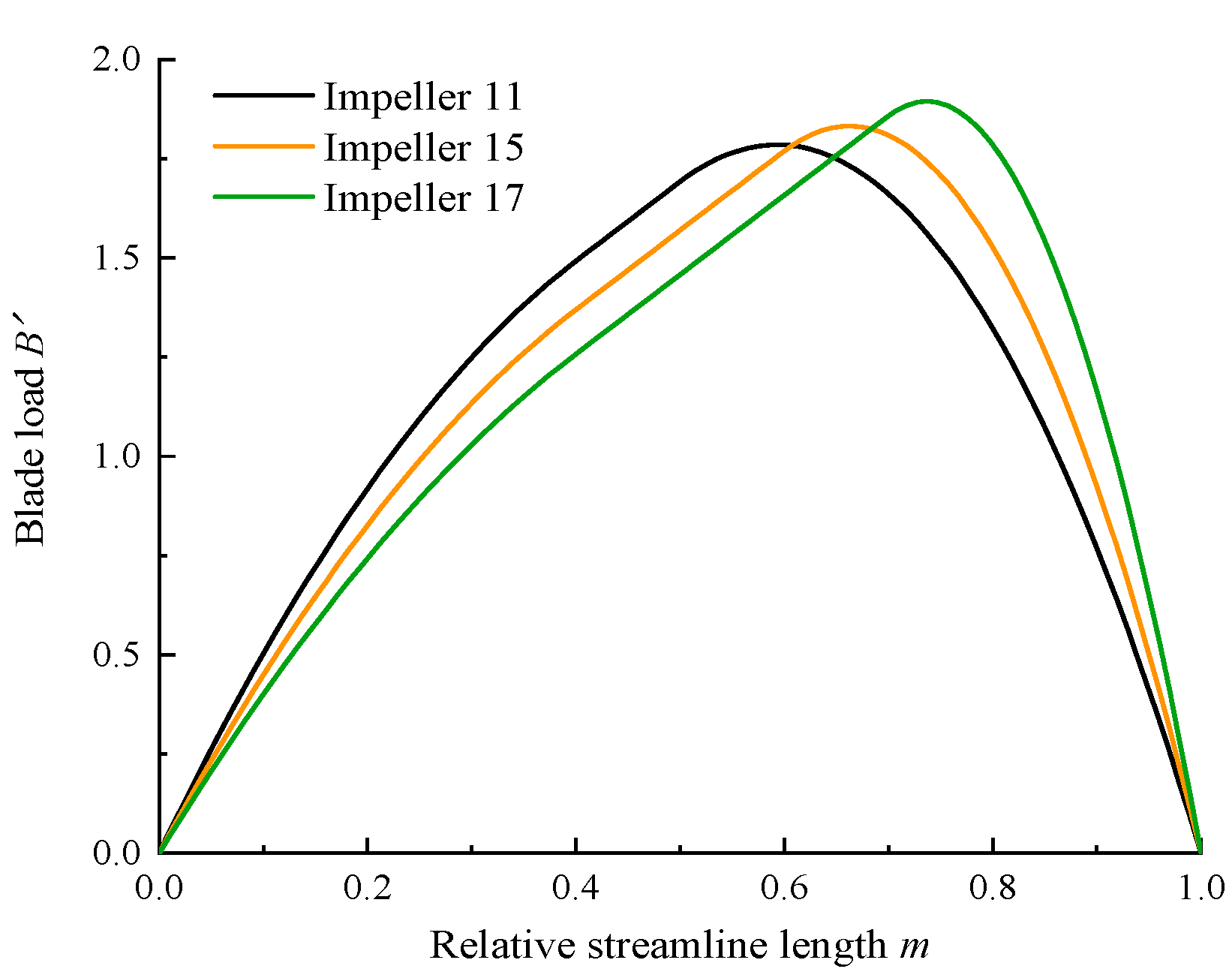
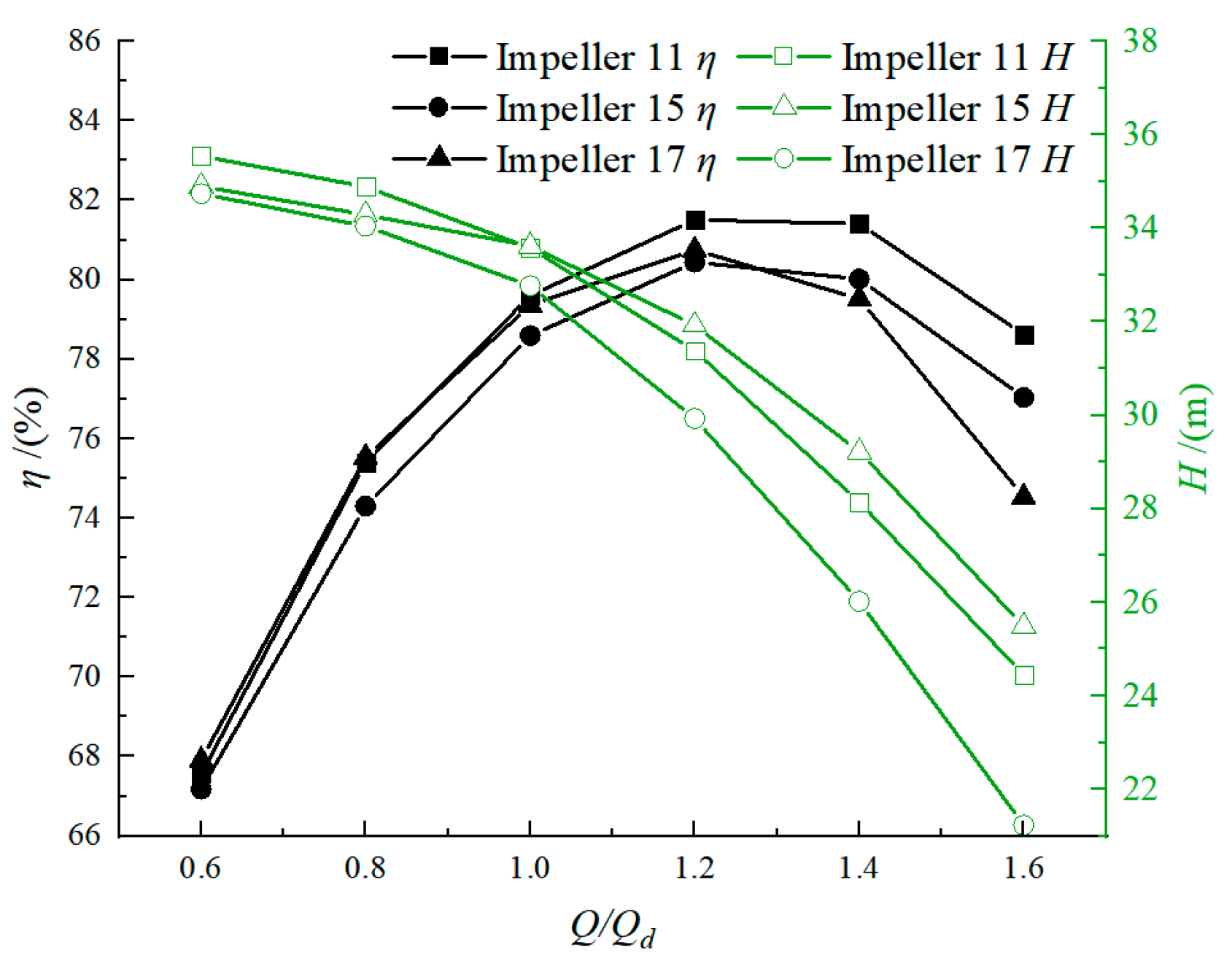
3.4. Comparative Analysis of Optimization Results
4. Analysis of Unsteady Internal Flow in Impeller Based on Blade Load Curve
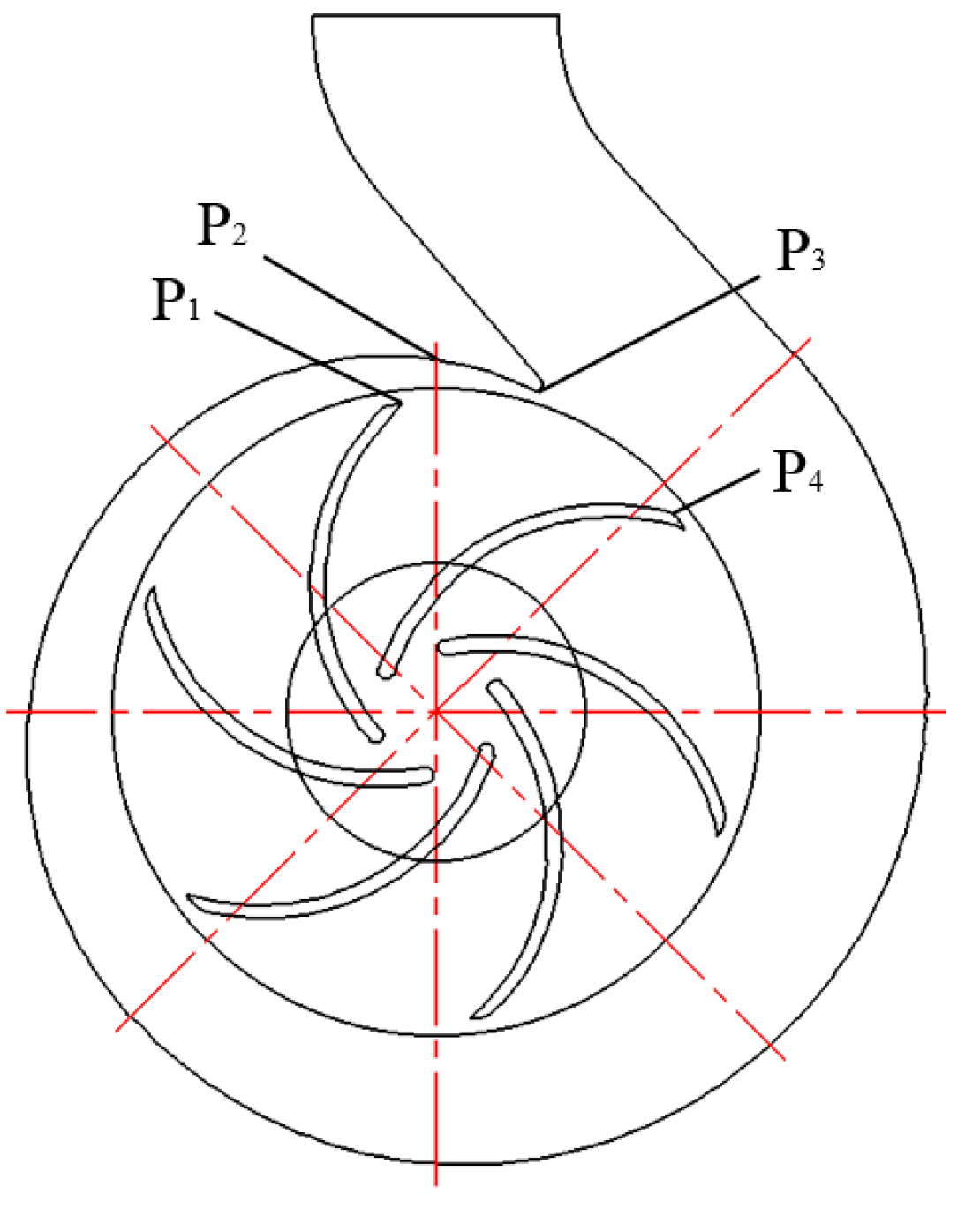
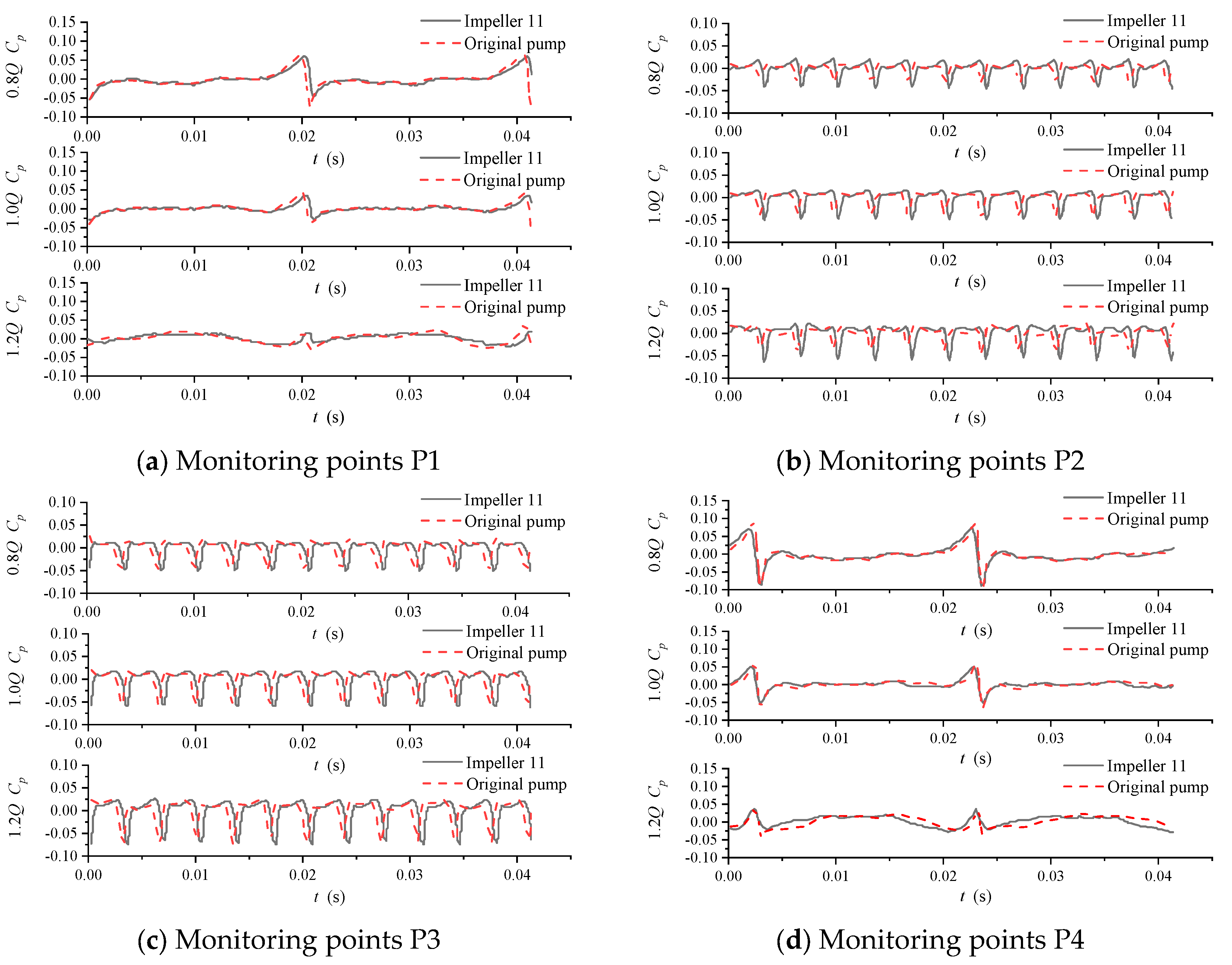
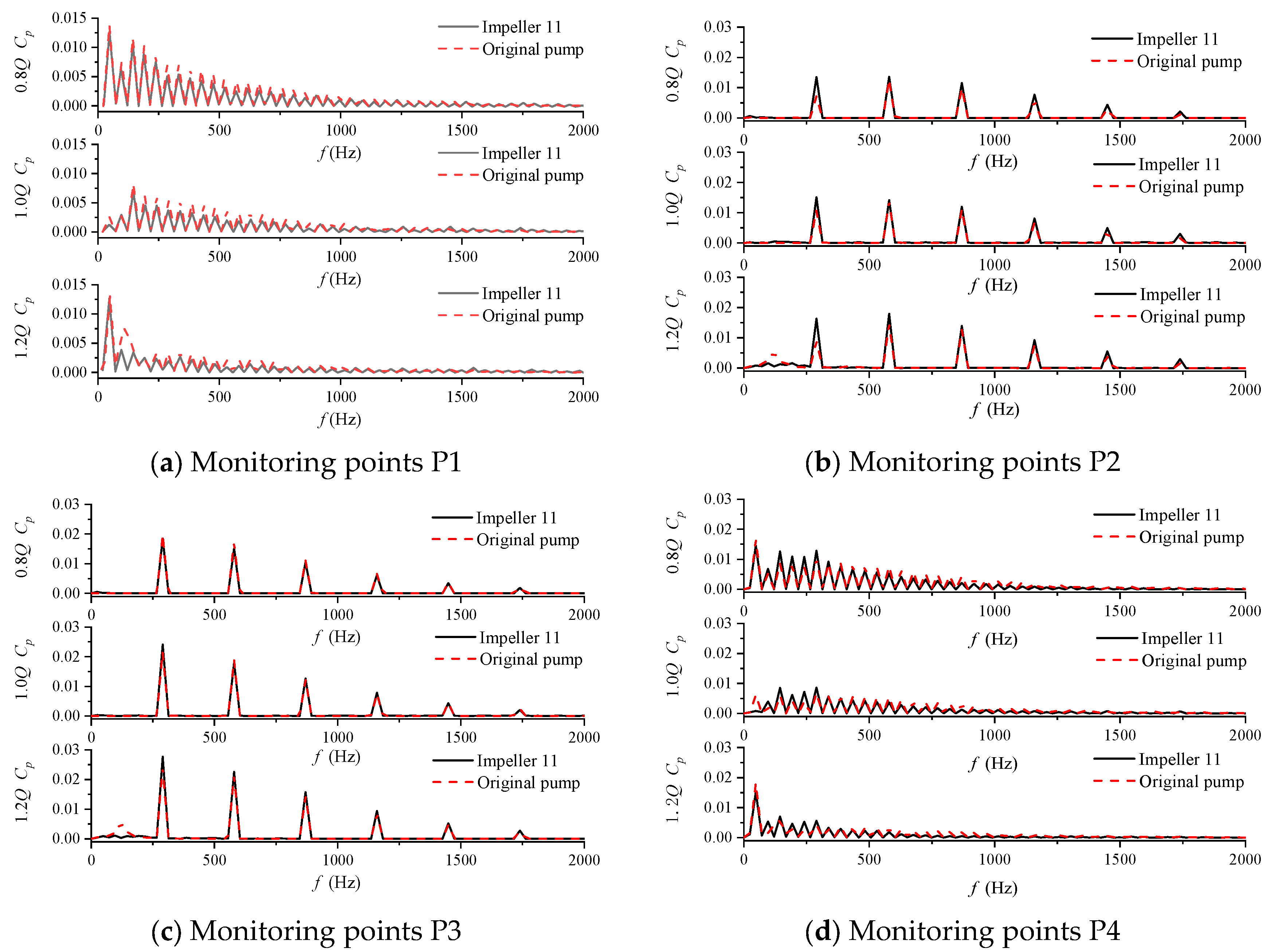
4.1. Comparative Analysis of Pressure Pulsation
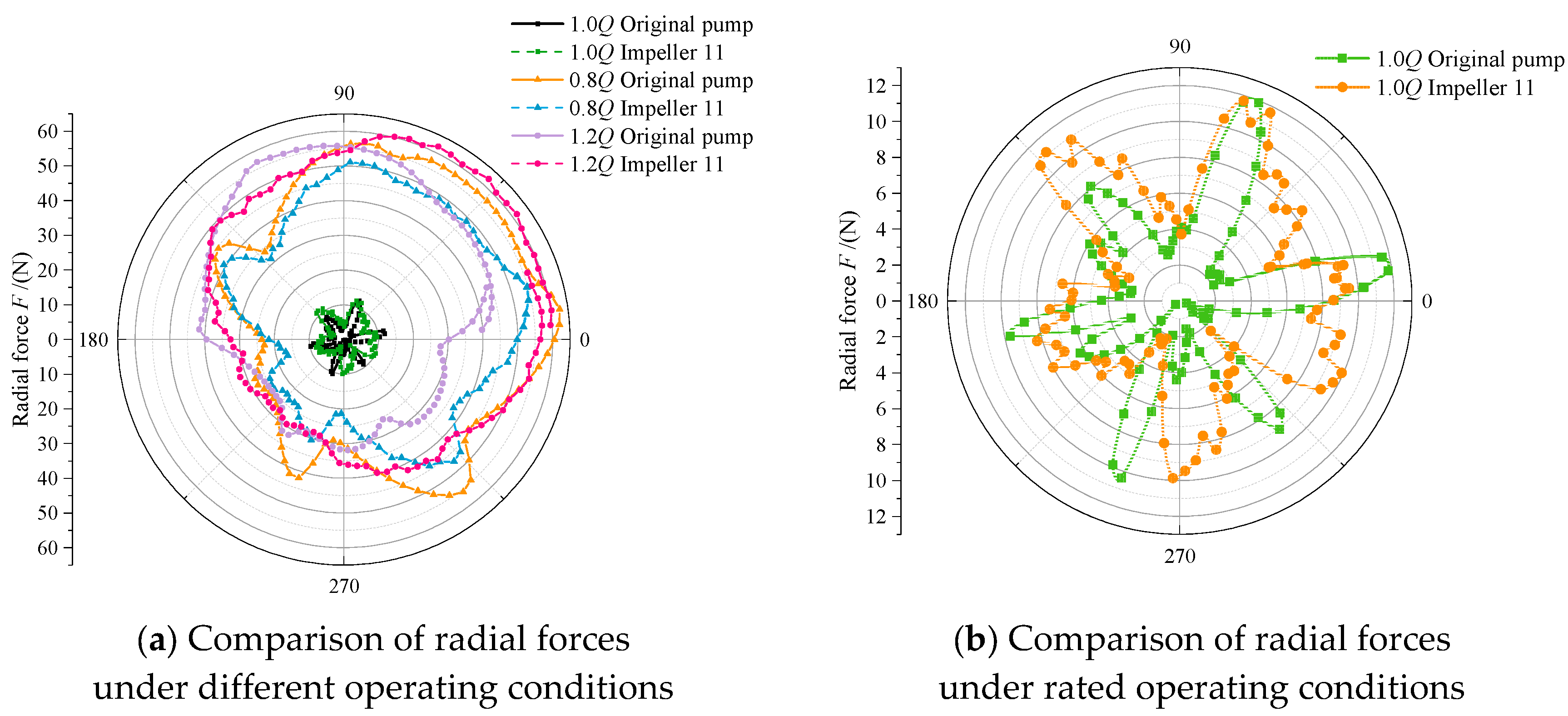
4.2. Comparative Analysis of Radial Force Distribution
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brodersen, S. Magnetic-drive pumps: Technology and new applications. Hydrocarb. Process. 2001, 80, 45–48. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, K. What the future holds for magnetic drive pumps. World Pumps 2007, 2007, 28–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Davila, G.; Zangeneh, M. Multi-objective optimization of a high specific speed centrifugal volute pump using three-dimensional inverse design coupled with computational fluid dynamics simulations. J. Fluids Eng. 2021, 143, 021202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.H. A general theory of three-dimensional flow in subsonic and supersonic turbomachines of axial, radial, and mixed-flow types. Trans. Am. Soc. Mech. Eng. 1952, 74, 1363–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zangeneh, M. Inviscid-viscous interaction method for three-dimensional inverse design of centrifugal impellers. J. Turbomach. 1994, 116, 280–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Zhao, X. Inverse method of centrifugal pump blade based on Gaussian process regression. Math. Probl. Eng. 2020, 2020, 4605625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.Y.; Wang, F.J.; An, D.S.; Yao, Z.; Xiao, R.; Lu, L.; He, C.; Zou, Z. A general alternate loading technique and its applications in the inverse designs of centrifugal and mixed-flow pump impellers. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2021, 64, 898–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.M.; Wang, X.F.; Wang, W.; Zhou, F.M. Application of the modified inverse design method in the optimization of the runner blade of a mixed-flow pump. Chin. J. Mech. Eng. 2018, 31, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Yang, A.L.; Lang, D.P.; Dai, R. Blade design loads on the flow exciting force in centrifugal pump. In Proceedings of the 26th IAHR Symposium on Hydraulic Machinery and Systems, Beijing, China, 19–23 August 2012. PTS 1-7.2013. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, B.; Wang, X.; Tan, L.; Zhou, D.; Zhao, Y.; Cao, S. Optimization design of a reversible pump–turbine runner with high efficiency and stability. Renew. Energy 2015, 81, 366–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, R.X.; Akins, R.A.; Lee, C.E.; Taylor, H.F. Fiber-optic pressure sensors detect cavitation and flow instabilities in centrifugal pumps. World Pumps 1996, 1996, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Zhang, Z.; Xia, C.; Liu, Z. Experimental investigation of pressure fluctuation, vibration, and noise in a multistage pump. Shock. Vib. 2018, 2018, 2784079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Liu, J.; Liu, X.; Xie, T. Numerical study of pressure pulsation of centrifugal pumps with the compressible mode. J. Therm. Sci. 2019, 28, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhou, L.; Shi, W.; He, Z.; Han, Y.; Xiao, Y. Interstage difference of pressure pulsation in a three-stage electrical submersible pump. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2021, 196, 107653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Jiang, J.; Gao, B.; Liu, X. DDES analysis of unsteady flow evolution and pressure pulsation at off-design condition of a centrifugal pump. Renew. Energy 2020, 153, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, B.; Liu, J.X.; Zhai, L.; Han, A. Analysis of the performance and pressure pulsation in a high-speed centrifugal pump with different hub-cutting angles. Mod. Phys. Lett. B 2023, 37, 2350117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BIPM. Évaluation des Données de Mesur—Guide Pour l’Expression del’Incertitude de Mesure; JCGM 100:2008; BIPM: Paris, France, 2008. [Google Scholar]




| Parameter | Symbol | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Design flow rate | Q | 50 | m3/h |
| Design speed | n | 2900 | r/min |
| Head | H | 32 | m |
| Shaft power | P | 7.5 | kW |
| Inner diameter | D | 85 | mm |
| Number of impeller blades | Z1 | 6 | / |
| Wrap angle | Z2 | 100 | ° |
| Component | Grid 1 | Grid 2 | Grid 3 | Grid 4 | Grid 5 | Grid 6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| The number of grids | 1,060,773 | 1,720,188 | 1,929,446 | 2,484,601 | 2,882,167 | 3,372,629 |
| H(m) | 35.88 | 35.94 | 35.98 | 36.09 | 36.12 | 36.14 |
| η(%) | 74.64 | 74.39 | 74.42 | 74.5 | 74.48 | 74.49 |
| AL | PL | SL | 1.0Q·η(%) | 1.0Q·H/(m) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.2 | 0.6 | 1 | 78.79 | 32.95 |
| 2 | 0.2 | 0.6 | 2 | 78.87 | 32.93 |
| 3 | 0.2 | 0.8 | −1 | 77.27 | 34.73 |
| 4 | 0.2 | 0.8 | −0.5 | 77.72 | 35.27 |
| 5 | 0.2 | 0.8 | 0 | 78.88 | 32.52 |
| 6 | 0.2 | 0.8 | 1 | 79.47 | 32.61 |
| 7 | 0.3 | 0.7 | 1 | 79.37 | 32.89 |
| 8 | 0.3 | 0.7 | 2 | 79.51 | 32.66 |
| 9 | 0.4 | 0.5 | −1 | 78.56 | 34.1 |
| 10 | 0.4 | 0.5 | 0 | 78.8 | 33.15 |
| 11 | 0.4 | 0.5 | 2 | 79.6 | 33.58 |
| 12 | 0.4 | 0.6 | −1 | 78.0 | 35.55 |
| 13 | 0.4 | 0.6 | 0 | 79.02 | 32.95 |
| 14 | 0.4 | 0.6 | 1 | 79.23 | 32.96 |
| 15 | 0.4 | 0.6 | 2 | 79.53 | 33.12 |
| 16 | 0.4 | 0.7 | 1 | 79.42 | 32.95 |
| 17 | 0.4 | 0.7 | 2 | 79.36 | 32.93 |
| 18 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 1 | 78.64 | 34.73 |
| 19 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 2 | 78.59 | 35.27 |
| AL | PL | SL | 0.6Q/(%) | 0.8Q/(%) | 1.0Q/(%) | 1.2Q/(%) | 1.4Q/(%) | 1.6Q(%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | 0.2 | 0.8 | −1 | 65.15 | 72.63 | 77.27 | 79.49 | 79.03 | 76.33 |
| 4 | 0.2 | 0.8 | −0.5 | 65.05 | 73.08 | 77.72 | 80.06 | 80.2 | 78.65 |
| 5 | 0.2 | 0.8 | 0 | 67.69 | 74.83 | 78.88 | 80.73 | 80.57 | 77.86 |
| 6 | 0.2 | 0.8 | 1 | 67.78 | 75.28 | 79.47 | 81.24 | 80.42 | 76.92 |
| AL | PL | SL | 0.6Q/(%) | 0.8Q/(%) | 1.0Q(%) | 1.2Q/(%) | 1.4Q/(%) | 1.6Q(%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | 0.2 | 0.8 | −1 | 36.47 | 36.33 | 34.73 | 32.6 | 28.87 | 24.98 |
| 4 | 0.2 | 0.8 | −0.5 | 37.15 | 36.93 | 35.27 | 33.646 | 30.24 | 26.85 |
| 5 | 0.2 | 0.8 | 0 | 34.37 | 33.66 | 32.52 | 30.56 | 27.6 | 23.84 |
| 6 | 0.2 | 0.8 | 1 | 34.47 | 33.88 | 32.61 | 30.39 | 26.78 | 22.47 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, R.; Wang, J.; Qian, W.; Geng, L. Optimization of Magnetic Pump Impeller Based on Blade Load Curve and Internal Flow Study. Mathematics 2024, 12, 607. https://doi.org/10.3390/math12040607
Zhang R, Wang J, Qian W, Geng L. Optimization of Magnetic Pump Impeller Based on Blade Load Curve and Internal Flow Study. Mathematics. 2024; 12(4):607. https://doi.org/10.3390/math12040607
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Ruijie, Jiaqiong Wang, Wenfei Qian, and Linlin Geng. 2024. "Optimization of Magnetic Pump Impeller Based on Blade Load Curve and Internal Flow Study" Mathematics 12, no. 4: 607. https://doi.org/10.3390/math12040607
APA StyleZhang, R., Wang, J., Qian, W., & Geng, L. (2024). Optimization of Magnetic Pump Impeller Based on Blade Load Curve and Internal Flow Study. Mathematics, 12(4), 607. https://doi.org/10.3390/math12040607




