On the Inversion of the Mellin Convolution
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Properties of Mellin Convolution
- For , there are real constants A, , such that when τ is small (say, for );
- For , there are real constants B, , such that , when τ is large (say, for );
- It holds that .
- The Mellin convolution is commutative and associative, and its unit element is .
- For and , it is true thatmeaning that is an eigenfunction of the Mellin convolution with an eigenvalue of the Mellin transform of , ).
- For [10]This power function has the following property:This property is of great importance because of the structure of –log-exponential monomials.
- The Parseval equality holds true:
- If is not identically null for any interval in , it defines the bilateral systems represented by (2).
- The case where defines the right systems that output the response is given by
- When the left systems are defined by
- For a function with a Mellin transform , it follows that
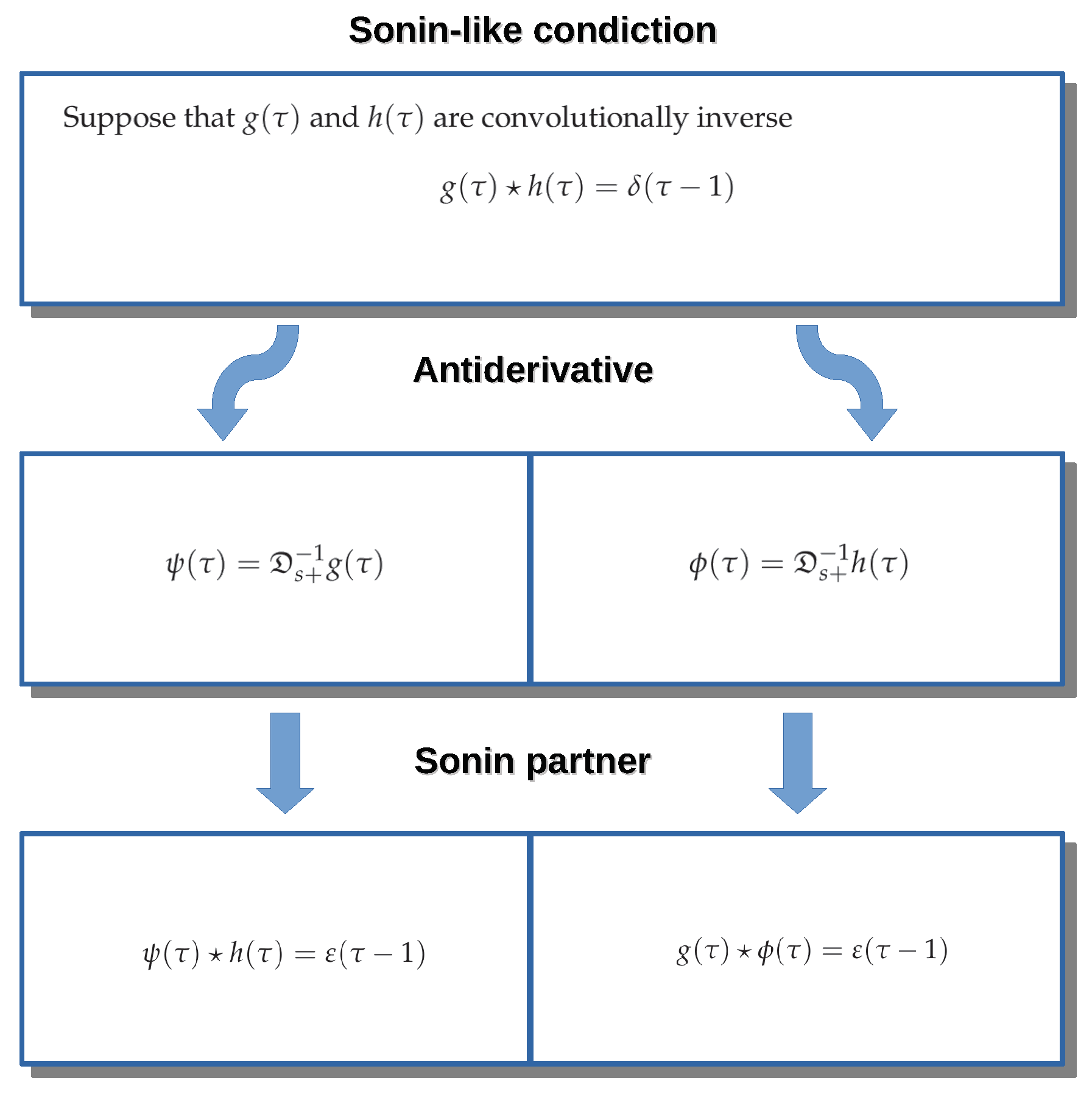
3. Sonin-like Condition
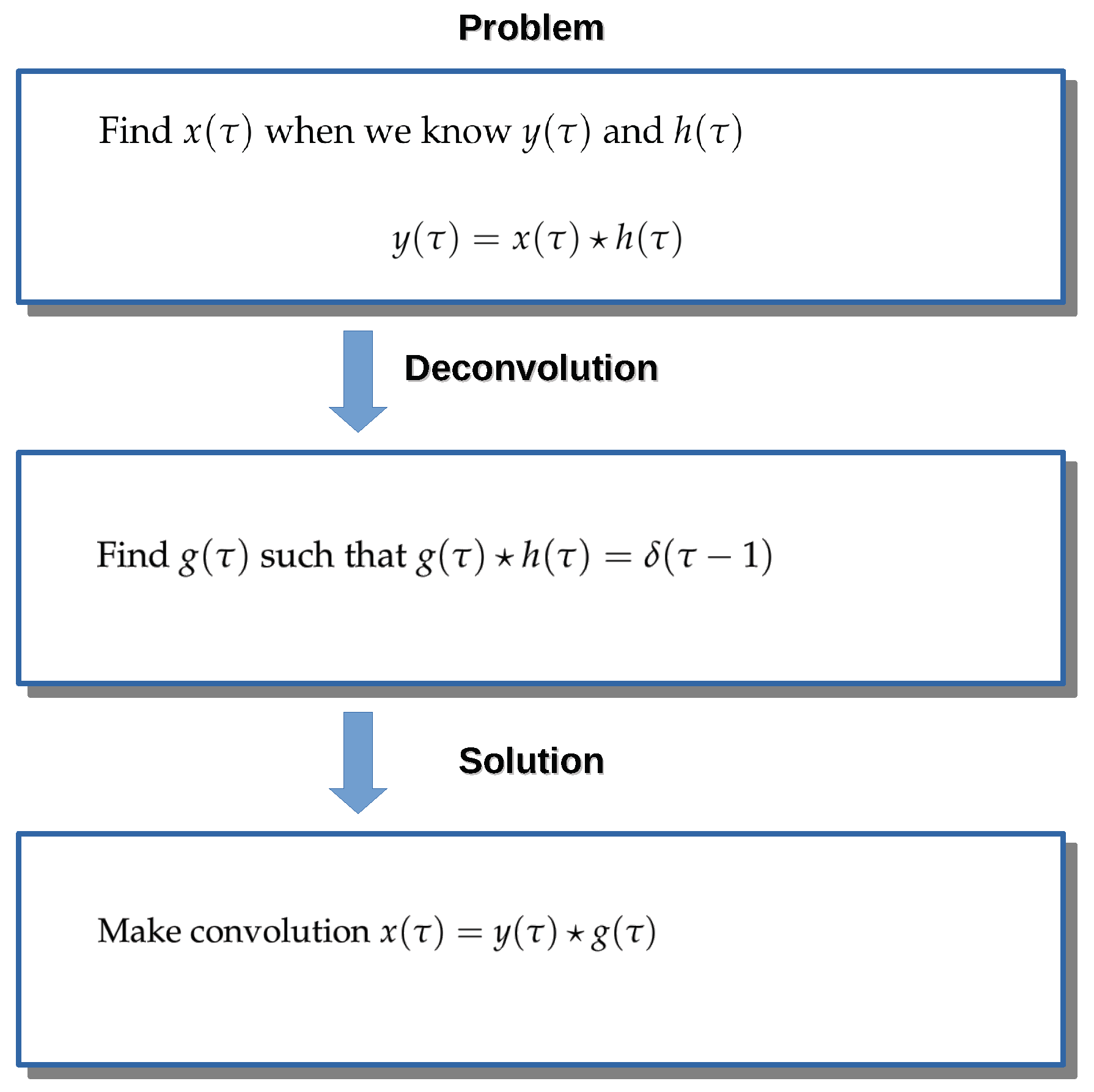
4. Mellin Deconvolution Problem
5. Scale-Invariant Linear Systems
5.1. Integer-Order Scale-Invariant Linear Systems
5.2. Non-Integer-Order Commensurate Scale-Invariant Linear Systems
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Proofs
References
- Hirschman, I.; Widder, D. The Convolution Transform; Courier Corporation: North Chelmsford, MA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Domínguez, A. A History of the Convolution Operation [Retrospectroscope]. IEEE Pulse 2015, 6, 38–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, M.J. Signals and Systems: Analysis Using Transform Methods and Matlab; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Ortigueira, M.D.; Machado, J.T. The 21st century systems: An updated vision of continuous-time fractional models. IEEE Circuits Syst. Mag. 2022, 22, 36–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braccini, C.; Gambardella, G. Form-invariant linear filtering: Theory and applications. IEEE Trans. Acoust. Speech Signal Process. 1986, 34, 1612–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazici, B.; Kashyap, R.L. A class of second-order stationary self-similar processes for 1/f phenomena. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 1997, 45, 396–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, L. The scale representation. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 1993, 41, 3275–3292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortigueira, M.D. On the fractional linear scale invariant systems. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2010, 58, 6406–6410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortigueira, M.; Bohannan, G. Fractional scale calculus: Hadamard vs. Liouville. Fractal Fract. 2023, 7, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bengochea, G.; Ortigueira, M. An Operational Approach to Fractional Scale-Invariant Linear Systems. Fractal Fract. 2023, 7, 524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Singh, P.; Aggarwal, P.; Joshi, S.D. Unified framework for linear scale invariant signals, systems, and transforms: A tutorial. Digit. Signal Process. 2025, 157, 104880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossmann, A.; Morlet, J. Decomposition of Hardy functions into square integrable wavelets of constant shape. SIAM J. Math. Anal. 1984, 15, 723–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallat, S.G. Multiresolution Representations and Wavelets; University of Pennsylvania: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Heil, C.E.; Walnut, D.F. Continuous and discrete wavelet transforms. SIAM Rev. 1989, 31, 628–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nottale, L. The theory of scale relativity. Int. J. Mod. Phys. A 1992, 7, 4899–4936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nottale, L. Non-differentiable space-time and scale relativity. In Proceedings of the International Colloquium Geometrie au XXe Siecle, Paris, France, 24–29 September 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Borgnat, P.; Amblard, P.O.; Flandrin, P. Scale invariances and Lamperti transformations for stochastic processes. J. Phys. A Math. Gen. 2005, 38, 2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butzer, P.; Jansche, S. A direct approach to the Mellin transform. J. Fourier Anal. Appl. 1997, 3, 325–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertrand, J.; Bertrand, P.; Ovarlez, J. The Mellin transform. In The Transforms and Applications Handbook; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.; Cao, J.; Kim, J.; Zhang, W. A Mellin transform approach to pricing barrier options under stochastic elasticity of variance. Appl. Stoch. Models Bus. Ind. 2023, 39, 160–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fikioris, G. Mellin-Transform Method for Integral Evaluation: Introduction and Applications to Electromagnetics; Springer Nature: New York, NY, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, X.; Gamboa, J.; Hamidfar, T.; Shahriar, S. Investigation of frequency invariance in automated event recognition using resonant atomic media. In Proceedings of the Practical Holography XXXVIII: Displays, Materials, and Applications, San Francisco, CA, USA, 27 January–1 February 2024; Blanche, P.A.J., Lee, S.H., Eds.; International Society for Optics and Photonics. SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2024; Volume 12910, p. 129100E. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vashisth, S.; Singh, H.; Yadav, A.; Singh, K. Image encryption using fractional Mellin transform, structured phase filters, and phase retrieval. Optik 2014, 125, 5309–5315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luchko, Y.; Kiryakova, V. The Mellin integral transform in fractional calculus. Fract. Calc. Appl. Anal. 2013, 16, 405–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, T.; Rehman, M. Generalized Mellin transform and its applications in fractional calculus. Comput. Appl. Math. 2022, 41, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarasov, V.E. Scale-invariant general fractional calculus: Mellin convolution operators. Fractal Fract. 2023, 7, 481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luchko, Y.; Yamamoto, M. The general fractional derivative and related fractional differential equations. Mathematics 2020, 8, 2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortigueira, M. Searching for Sonine kernels. Fract. Calc. Appl. Anal. 2024; submitted. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prost, R.; Goutte, R. Linear systems identification by Mellin deconvolution. Int. J. Control 1976, 23, 713–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prost, R.; Goutte, B. Performances of the method of linear systems identification by Mellin deconvolution. Int. J. Control 1977, 25, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shtrauss, V. Decomposition of multi-exponential and related signals–Functional filtering approach. WSEAS Trans. Signal Process. 2008, 4, 44–52. [Google Scholar]
- Kaiser, H. Applications of Mellin-Barnes Integrals to Deconvolution Problems. Ph.D. Thesis, Justus-Liebig-University of Giessen, Giessen, Germany, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Brenner, S.; Johannes, J.; Siebel, M. Multiplicative deconvolution under unknown error distribution. Electron. J. Stat. 2024, 18, 4795–4850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gel’fand, I.; Shilov, G. Generalized Functions: Properties and Operations; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1964. [Google Scholar]
- Abel, N. Oplösning af et par opgaver ved hjelp af bestemte integraler. Mag. Naturvidenskaberne 1823, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Sonine, N. Sur la généralisation d’une formule d’Abel. Acta Math. 1884, 4, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X. An equivalent formulation of Sonine condition. Appl. Math. Lett. 2024, 153, 109069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanton, J. Convolution and deconvolution: Two mathematical tools to help performing tests in research and industry. Int. J. Metrol. Qual. Eng. 2021, 12, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bengochea, G.; Verde-Star, L. Linear algebraic foundations of the operational calculi. Adv. Appl. Math. 2011, 47, 330–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortigueira, M.; Machado, J. The 21st century systems: An updated vision of discrete-time fractional models. IEEE Circuits Syst. Mag. 2022, 22, 6–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorenflo, R.; Kilbas, A.; Mainardi, F.; Rogosin, S. Mittag-Leffler Functions, Related Topics and Applications; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bengochea, G.; Ortigueira, M.; Arroyo-Cabañas, F. On the Inversion of the Mellin Convolution. Mathematics 2025, 13, 432. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13030432
Bengochea G, Ortigueira M, Arroyo-Cabañas F. On the Inversion of the Mellin Convolution. Mathematics. 2025; 13(3):432. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13030432
Chicago/Turabian StyleBengochea, Gabriel, Manuel Ortigueira, and Fernando Arroyo-Cabañas. 2025. "On the Inversion of the Mellin Convolution" Mathematics 13, no. 3: 432. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13030432
APA StyleBengochea, G., Ortigueira, M., & Arroyo-Cabañas, F. (2025). On the Inversion of the Mellin Convolution. Mathematics, 13(3), 432. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13030432







