Abstract
Electric vehicle (EV) charging systems are now integral to smart grids, increasing the need for robust and scalable cyberattack detection. This study presents an online intrusion detection system that leverages an Adaptive Random Forest classifier with Adaptive Windowing drift detection to identify real-time and evolving threats in EV charging infrastructures. The system is evaluated using real-world network traffic from the CICEVSE2024 dataset, ensuring practical applicability. For binary intrusion detection, the model achieves 0.9913 accuracy, 0.9999 precision, 0.9914 recall, and an F1-score of 0.9956, demonstrating highly accurate threat detection. It effectively manages concept drift, maintaining an average accuracy of 0.99 during drift events. In multiclass detection, the system attains 0.9840 accuracy, precision, and recall, with an F1-score of 0.9831 and an average drift event accuracy of 0.96. The system is computationally efficient, processing each instance in just 0.0037 s, making it well-suited for real-time deployment. These results confirm that online machine learning methods can effectively secure EV charging infrastructures. The source code is publicly available on GitHub, ensuring reproducibility and fostering further research. This study provides a scalable and efficient cybersecurity solution for protecting EV charging networks from evolving threats.
Keywords:
Adaptive Random Forest; anomaly detection; concept drift; drift detection; Electric Vehicle Charging Systems; Internet of Things; intrusion detection; network security; online machine learning; real-time system MSC:
68T05; 68M25
1. Introduction
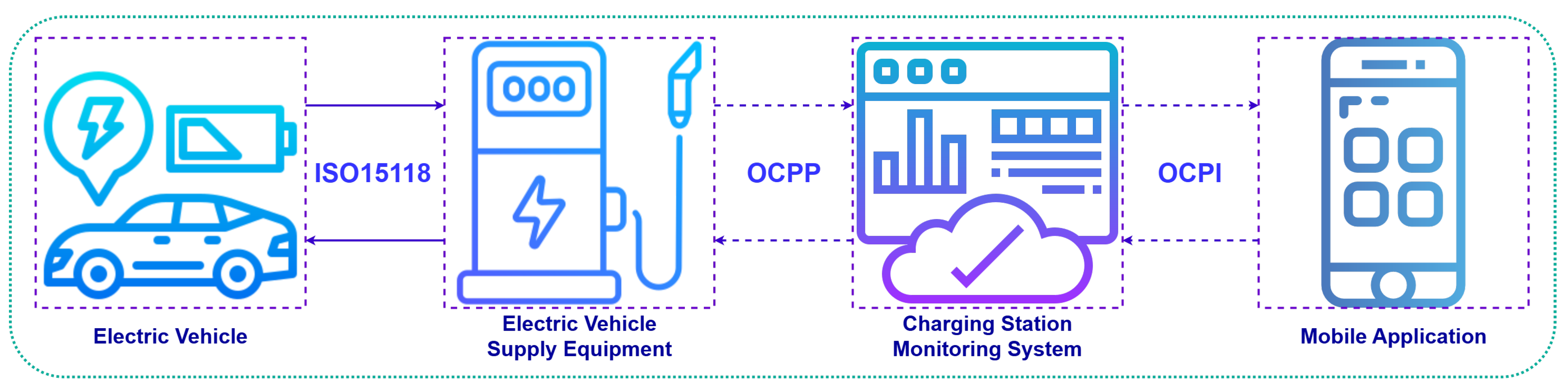
The rapid global adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) has increased the need for secure and efficient charging networks [1,2]. The EV charging station market, projected to grow from USD 7.3 billion in 2024 to USD 12.1 billion by 2030, highlights the urgency of building robust infrastructure [3]. Communication protocols such as ISO 15118 [4], Open Charge Point Protocol (OCPP) [5], and Open Charge Point Interface (OCPI) [6] play a central role in enabling interoperability between EVs, charging stations, and backend systems [7], but they also introduce potential security vulnerabilities (Figure 1).
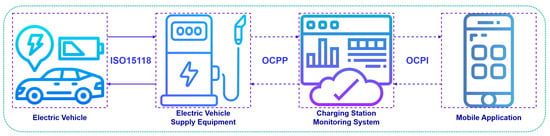
Figure 1.
Communication protocols in electric vehicle charging ecosystems.
ISO 15118 facilitates seamless communication between EVs and charging stations, supporting features like plug-and-charge and secure data exchange [8]. Yet, its misuse or exploitation could open doors to attacks, such as unauthorized vehicle access or data interception [9]. Similarly, OCPP, which standardizes communication between charging stations and their management systems, is critical for tasks like firmware updates and operational monitoring [10,11]. A breach in this protocol could disrupt station functionality or expose sensitive information [12]. OCPI, which governs cross-network communication for roaming and billing, adds another layer of complexity, as secure data exchange between multiple operators is essential to prevent fraud and maintain trust [13].
Cyber threats targeting these protocols are constantly evolving, requiring adaptive security measures capable of detecting new and emerging attack patterns [14]. Traditional intrusion detection systems (IDSs) [15,16], which rely on static models trained on historical data [17,18], struggle to keep up with these changes [19,20,21]. One major challenge is concept drift, where the statistical properties of cyber threat patterns shift over time, reducing the effectiveness of pre-trained models [22,23]. Concept drift is particularly problematic in cybersecurity, where attack strategies continually adapt to bypass detection mechanisms.
To address this issue, researchers have explored online learning techniques that continuously update models in response to new data. A key advancement in this domain is the ADaptive WINdowing (ADWIN) algorithm [24], which dynamically detects and adapts to concept drift in streaming data [25]. ADWIN ensures that outdated information is automatically discarded when significant distributional changes occur, making it a robust approach for evolving cybersecurity threats. Similarly, adaptive ensemble methods like Adaptive Random Forest (ARF) enhance drift detection by using a pool of decision trees, each adapting to different segments of evolving data streams.
Inspired by these advances, we introduce an online learning-based IDS for real-time anomaly detection in EV charging networks. Our method leverages the ARF classifier to process streaming data from ISO 15118, OCPP, and OCPI, ensuring continuous learning and adaptation. Key features include adaptive Naïve Bayes predictions at decision-tree leaves and selective feature usage [26], which improve detection accuracy while maintaining computational efficiency. By integrating concept drift detection into cybersecurity monitoring, our approach aims to enhance the resilience of EV charging networks against evolving threats.
This study introduces a novel approach to intrusion detection in Electric Vehicle Charging Systems (EVCS), with the following key contributions:
- First application of online learning—This is the first study to apply online learning for EVCS intrusion detection, enabling real-time adaptability to evolving data streams.
- Integration of ARF with drift detection—The ARF classifier is combined with ADWIN drift detection, providing robust handling of concept drifts and dynamic attack patterns.
- Real-time scalability—The system ensures efficient real-time performance and scalability for large, complex EVCS networks.
- EVCS-specific protocol Integration—The framework incorporates OCPP and ISO 15118 protocols, ensuring compatibility with existing EV infrastructure standards.
- Real-world deployment architecture—This work presents a practical and efficient design for intrusion detection in EVCS.
These contributions establish a robust and adaptive framework to address cybersecurity challenges in EVCS networks effectively.
The article is organized as follows: Section 2 provides a review of related works, summarizing previous research on intrusion detection in EVCS. Section 3 describes the proposed system in detail, including its design and implementation. Section 4 presents the results, outlining the experimental setup and evaluating performance for both binary and multiclass classification tasks. Section 5 discusses the findings, offering insights into the results and comparing them with existing studies. Finally, Section 6 highlights the key contributions of this work and concludes the study.
2. Related Works
IDSs have gained significant attention in recent years as essential components for ensuring the security and reliability of EV charging stations and associated networks. Various studies have explored the application of machine learning (ML) and deep learning (DL) methods for anomaly detection and threat mitigation in these systems. A widely adopted approach involves the use of sequential data analysis through advanced architectures such as stacked Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) models, which leverage electrical fingerprints and temporal features to detect complex cybersecurity threats in electric vehicle supply equipment (EVSE) [27]. Similarly, Gated Recurrent Unit (GRU) has been optimized using metaheuristic algorithms to classify attack types, with the addition of robust encryption mechanisms enhancing data security in real-time EVSE networks [28].
Privacy-preserving methods have also emerged as a crucial aspect of intrusion detection, with Federated Learning frameworks enabling collaborative model training across distributed charging stations without exposing sensitive data. These systems incorporate mechanisms such as utility-optimized local differential privacy and reinforcement learning to balance detection accuracy and privacy [29]. In addition to privacy-focused solutions, classical ML classifiers like Decision Tree, Random Forest, and Support Vector Machine have been applied to analyze network traffic patterns, showcasing their ability to efficiently categorize various attack types in Internet of Things (IoT)-enabled charging environments [30]. Some studies have further highlighted the importance of feature selection in improving classification performance, demonstrating that traditional models can remain competitive in detecting both known and novel threats [31].
Bio-inspired approaches have also gained traction, as demonstrated by the use of Grouping Cockroach Classifiers for intrusion detection in Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) networks. By modeling natural behaviors such as grouping and shelter attraction, these systems analyze network traffic anomalies with high adaptability and efficiency [32]. In addition, hybrid models such as the Squirrel Search-Optimized Attention-Deep Recurrent Neural Network (ADRNN) integrate metaheuristic optimization with attention mechanisms and DL, addressing both cybersecurity and cost optimization challenges in EV and Unmanned Aerial Vehicle charging systems [33].
Hybrid DL architectures have proven particularly effective in addressing the complexity of intrusion detection. For instance, models combining Convolutional Neural Network (CNN), LSTM, and GRU simultaneously capture spatial and temporal patterns in network traffic, making them well-suited for real-time detection in IoT-enabled charging stations [34]. Moreover, integrated frameworks addressing both intrusion detection and system efficiency have been proposed, incorporating sensor data and real-time monitoring to mitigate threats such as False Data Injection Attacks (FDIAs) and Distributed Denial of Service attacks. These systems leverage advanced techniques, including graph-based topology analysis and adaptive alarming modules, to dynamically adjust traffic thresholds and enhance response accuracy [35,36]. Other methods, such as combining graph theory with DL, enable topology reconstruction and attack detection, ensuring resiliency in smart grid networks under abnormal operating conditions [37].
Despite the considerable advancements in intrusion detection for EVCS, critical challenges persist in aligning existing methods with the dynamic and complex nature of these networks. While earlier works demonstrate the efficacy of various ML and DL techniques in identifying and mitigating cyber threats, many approaches fall short in addressing key issues such as concept drift [38], real-time adaptability, and compliance with EVSE-specific protocols like OCPP and ISO 15118. As outlined in Table 1, the reliance on offline learning models, limited scalability, and the absence of explicit mechanisms to handle evolving threats underscore the need for more innovative solutions. To overcome these limitations, Table 2 highlights the advantages of ARF over other online learning methods. ARF excels in explicit drift detection via ADWIN, ensemble-based robustness, and resilience to noisy data, making it a strong candidate for real-time cybersecurity in EVSE environments.

Table 1.
Comparative analysis of related works.

Table 2.
Comparison of online learning models for EVCS security.
3. Materials and Methods
This section presents the proposed online IDS for EVCS, which leverages online ML to process streaming network traffic, detect anomalies in real time, and adapt to evolving threats. The methodology covers data preparation, preprocessing, classifier initialization, metric evaluation, drift detection, and online training, ensuring efficient and accurate intrusion detection. The following subsections detail each component of the proposed approach.
3.1. Proposed Online Intrusion Detection System
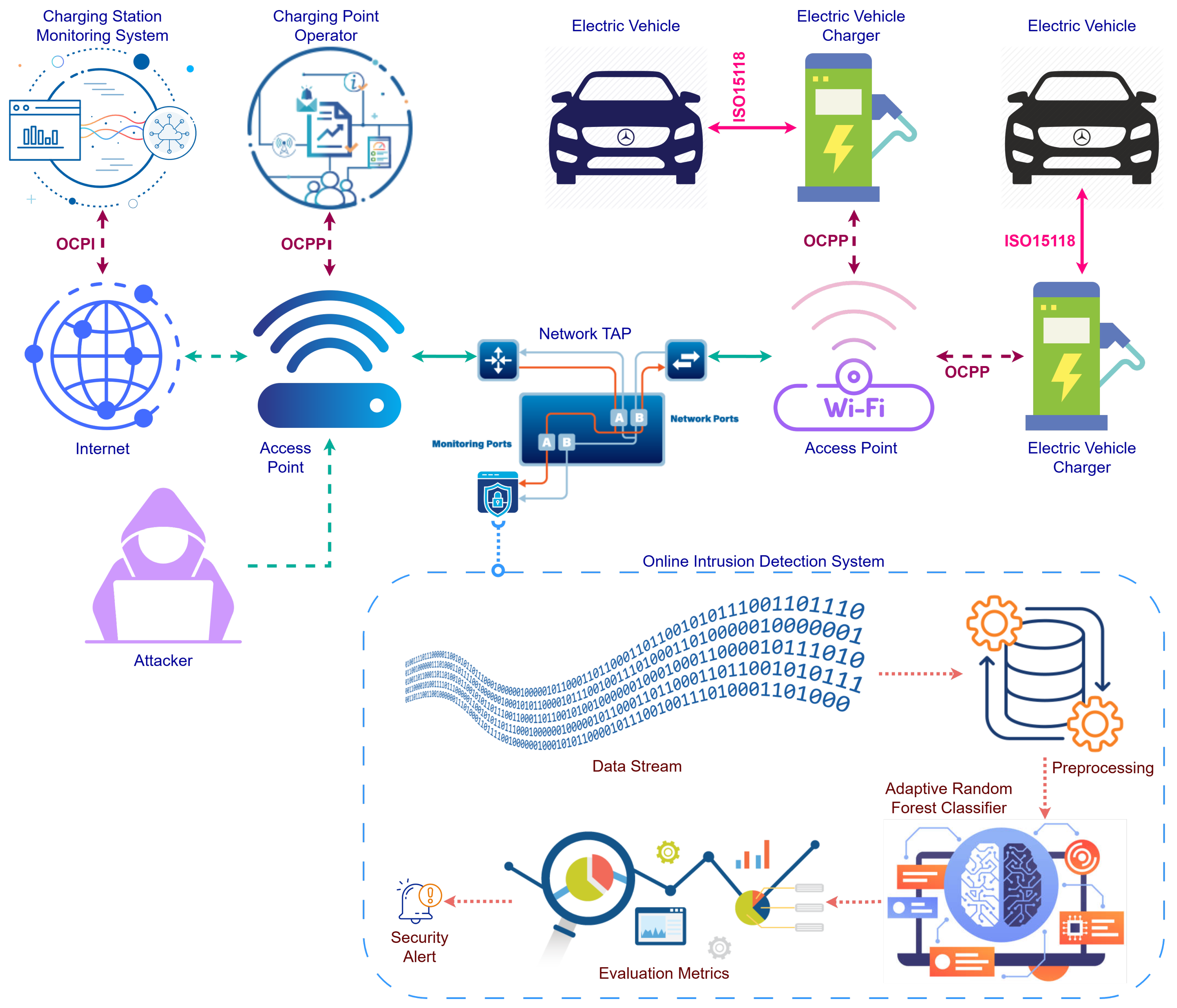
The proposed online IDS architecture is designed to ensure real-time monitoring and anomaly detection within EVCS [39]. Figure 2 illustrates the key components and communication flow of the proposed model, integrating the EVCS infrastructure, communication protocols, and a network monitoring mechanism [40].
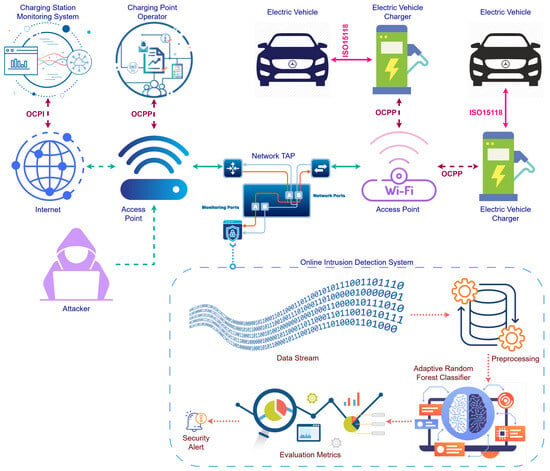
Figure 2.
Overall architecture of the proposed online intrusion detection.
At the core of the architecture is the Network Tap, which enables passive traffic monitoring without interrupting the normal operations of the EVCS. Network traffic, including data exchanges between EVs and charging stations, is captured and mirrored through this port for further analysis. The captured data undergoes preprocessing, where irrelevant information is filtered out, and essential features are extracted to form structured input for the intrusion detection model.
The online IDS employs the ARF Classifier [41], optimized for online learning scenarios. This model dynamically processes streaming data to detect both known and novel attack patterns. The ARF classifier incorporates a drift detection mechanism (ADWIN) to handle evolving attack behaviors, ensuring that the system adapts to changes in network conditions and threat landscapes [42].
Communication protocols such as ISO 15118, OCPP, and OCPI play a significant role in structuring the monitored data [13,43]. These protocols enable seamless interactions between EVs, charging stations, and backend systems, providing valuable context for intrusion detection. Any deviation from the expected protocol behavior is flagged as potentially malicious.
The architecture is designed for scalability and real-time adaptability, ensuring that the IDS remains effective in diverse operational environments. By leveraging real-time traffic monitoring and advanced ML techniques, the proposed online IDS provides a robust solution for enhancing the cybersecurity of EVCS networks.
3.2. Proposed Online Machine Learning
The proposed online ML system is designed to address the challenges of real-time anomaly detection in EVCS. The model supports both binary classification (e.g., distinguishing between malicious and legitimate traffic) and multiclass classification (e.g., identifying specific attack types). The system integrates data preparation and streaming, adaptive classification, metric evaluation, and drift detection to ensure robust and scalable performance in dynamic environments.
- Step 1: Data Preparation and Streaming
The initial phase of the proposed online ML system focuses on preparing the dataset and simulating a streaming environment to mimic real-world conditions [44]. Let the dataset be represented by the following equation:
where is the feature vector containing d attributes of network traffic data, and is the corresponding label. The labels can either be binary () for distinguishing between normal and malicious traffic or multiclass () for identifying specific attack types.
To ensure that the data is processed in a random order and reflects realistic conditions, the dataset is shuffled:
This ensures that the training and evaluation processes are unbiased and robust to variations in the data sequence.
Next, the shuffled dataset is fed into a streaming simulation. A data streaming iterator is constructed, providing instances sequentially, one at a time, from . This process is formalized as follows:
This streaming setup mimics the real-time arrival of network traffic data in EVCS, where incoming data is processed as it becomes available. By simulating streaming conditions, the proposed system ensures compatibility with dynamic environments where intrusion detection must operate continuously and adaptively.
This step lays the foundation for subsequent phases by creating a structured, randomized, and real-time data flow for online learning and evaluation.
- Step 2: Preprocessing and Classifier Initialization
The second phase of the proposed system focuses on preparing the input data through preprocessing and initializing the adaptive classification model [45]. This step ensures that the data is normalized for consistent processing and that the classifier is equipped to handle dynamic, real-time network traffic.
To standardize the input features, the StandardScaler is employed. This scaler transforms each feature in the input vector x to have zero mean and unit variance, ensuring that all features contribute equally to the model’s learning process. The transformation is defined as follows:
where is the mean of the feature across the dataset, and is the standard deviation of the feature. By normalizing the data, the system avoids issues associated with feature scaling discrepancies, which could otherwise impact the performance of the classifier.
The core of the system’s predictive capability lies in the ARF classifier, an ensemble learning model optimized for streaming data. The ARF classifier is composed of decision trees , with each tree operating independently. To enhance the robustness and diversity of the model, feature sampling is applied at each node split, where a random subset of features of size (where d is the total number of features) is selected. This randomization helps improve generalization and reduces the risk of overfitting. Additionally, the classifier incorporates a grace period mechanism, where each tree updates its structure only after every instances. This controlled update process ensures that the model balances responsiveness to new data while maintaining computational efficiency.
Predictions at the leaf nodes are handled by an integrated Naïve Bayes classifier, which computes the conditional probability of each label c based on feature likelihoods. The probability distribution is determined as follows:
where is the prior probability of class c, and is the likelihood of feature given class c. This probabilistic approach improves decision-making at the leaf level by incorporating statistical properties of the input data.
For binary classification, the final predicted label is determined using a majority voting mechanism among the ensemble of trees:
whereas in multiclass classification, the model leverages probabilistic aggregation across all decision trees to determine the most likely class label:
By combining preprocessing with a robust and adaptive classifier, this phase equips the system with the capability to handle high-dimensional, evolving data streams in real time. This ensures that the model is well-prepared to process the incoming data efficiently and adapt to changes in the network traffic patterns.
- Step 3: Metric Evaluation
The third phase of the proposed system focuses on evaluating the performance of the classifier in real time using a set of metrics. These metrics provide continuous feedback on the model’s ability to classify both binary and multiclass labels effectively, ensuring high reliability in detecting intrusions.
The proposed system utilizes four key metrics for performance evaluation. Accuracy measures the proportion of correctly predicted instances to the total number of instances:
This metric provides an overall measure of the model’s correctness.
Precision calculates the ratio of true positives to the total predicted positives, weighted by the class distribution in the case of multiclass classification:
where is the weight of class c, proportional to its occurrence in the dataset.
Recall measures the model’s ability to identify all true positives, weighted across all classes:
This metric ensures that the model captures all malicious activities effectively.
The F1-score is the harmonic mean of precision and recall, providing a balanced measure of the model’s performance:
The weighted F1-score accounts for imbalances in class distributions and provides an equitable evaluation metric.
Each of these metrics is updated dynamically after processing every new data instance. When an incoming instance arrives, the classifier first predicts the label . The system then compares y and , updating each metric accordingly. This continuous update process ensures that real-time insights are available regarding changes in model accuracy, precision, recall, and F1-score.
Real-time metric evaluation plays a crucial role in ensuring that the classifier remains effective in identifying normal and malicious traffic. It helps track trends in performance, such as sudden drops due to concept drift or class imbalance, and provides feedback that allows the system to fine-tune its components.
- Step 4: Drift Detection
The fourth phase of the proposed system addresses the challenge of concept drift, a phenomenon where the statistical properties of the data change over time. Concept drift is particularly relevant in dynamic environments like EVCS, where network traffic patterns and attack behaviors may evolve. To detect and adapt to such changes, the system employs the ADWIN algorithm, which continuously monitors the data stream for significant shifts in distribution.
Concept drift occurs when the underlying data distribution changes over time. This can result in reduced classifier performance, as the model is no longer aligned with the current data characteristics. Drift can manifest in various forms, including sudden drift, where an abrupt change in data distribution occurs, gradual drift, where shifts happen slowly over time, and recurring drift, where periodic changes in data distribution reappear after certain intervals. Since these drifts impact the classifier’s ability to maintain accurate predictions, it is essential for the system to detect such shifts in real time and adapt dynamically to maintain accuracy.
The ADWIN algorithm detects concept drift by maintaining a dynamic sliding window W of recent observations. This window is adaptively resized based on the detection of changes in the mean of the incoming data. The algorithm operates by splitting the window into two sub-windows:
where represents older data and contains more recent observations. If a significant difference is detected between the means of and , defined as follows:
where is a confidence threshold determined using Hoeffding’s inequality; a change is recognized as concept drift. When drift is detected, the older portion of the window () is discarded, and the system dynamically adjusts the window size to reflect the current data distribution.
To detect drift in real time, we employ ADWIN with its default parameters, ensuring efficient and adaptive change detection. The significance value is set to 0.002, controlling drift sensitivity, while the clock parameter is 32, determining how often ADWIN checks for changes, balancing detection speed and processing efficiency. The bucket compression mechanism uses a maximum of 5 buckets to optimize memory usage by merging historical data. Additionally, the minimum window length is set to 5, and the grace period is 10, preventing premature drift detection, reducing false positives, and ensuring responsiveness.
The drift detection mechanism is seamlessly integrated into the learning pipeline. For each incoming instance , the classifier first predicts the label based on the current learned model. The drift detector then evaluates whether the predicted label matches the true label by updating the function:
If a drift is detected, the system logs the drift event, including the instance index and timestamp, and updates or re-trains the classifier to align with the new data distribution.
The inclusion of drift detection provides several key advantages. The system dynamically adjusts to changing patterns in network traffic and attack behaviors, ensuring continuous adaptability. Additionally, by focusing only on recent data, unnecessary re-training on outdated information is avoided, making the system computationally efficient. This approach enhances resilience, maintaining high performance even when sudden or gradual changes in the data stream occur.
- Step 5: Online Training, Evaluation, and Drift Handling
The fifth and final phase of the proposed system integrates online learning, performance evaluation, and drift detection into a unified workflow. This phase ensures that the model continuously updates its classifier, evaluates its performance, and adapts dynamically to changes in data distribution.
For each streaming data instance , where x is the feature vector and y is the true label, the system executes a sequence of operations. First, the classifier predicts the label for the given instance using the following equation:
providing an immediate assessment of whether the instance is classified as normal or malicious. Following this, the classifier updates its internal parameters using the true label y as indicated here:
allowing it to incrementally incorporate new information as additional data arrives.
To continuously monitor the classifier’s effectiveness, the system dynamically evaluates its performance by updating key metrics such as accuracy, precision, recall, and F1-score, computed based on the comparison between the predicted and true labels:
These metrics provide real-time feedback on the model’s ability to correctly identify intrusions.
To maintain real-time efficiency, the system tracks execution times for each step, including the instance processing time () for prediction and learning, the metric computation time () for updating evaluation scores, and the drift detection time () for assessing distribution changes. The total time for processing N instances is computed as follows:
Tracking this timing information ensures that the system remains scalable and can handle high-speed data streams effectively.
Furthermore, the system maintains real-time logs of critical performance indicators, including classification metrics, drift detection events, instance indices, timestamps, and cumulative processing times. These logs serve as valuable resources for analyzing the system’s behavior and making improvements when necessary.
This integrated workflow enables the system to incrementally learn from each instance without requiring batch re-training. By dynamically updating performance metrics and adapting to detected drift, the system maintains high accuracy and robustness in evolving data environments.
3.3. Data Preprocessing
This study uses the CICEVSE2024 dataset, which represents a significant advancement in the development of realistic and comprehensive datasets for cybersecurity research in EVCS [46]. Designed using a carefully constructed testbed of real EV chargers and industry-standard communication protocols, such as ISO 15118 and OCPP, this dataset offers an authentic representation of EVCS operations under both normal and anomalous conditions. Its multi-faceted approach and rich feature set provide researchers with a robust foundation for evaluating and improving IDS.
Our focus is on network traffic data, which is captured using tools such as Wireshark and TCPdump. This data includes the complete spectrum of communication between EV chargers, vehicles, and backend systems. By monitoring packet-level interactions over protocols like OCPP and ISO 15118, the dataset captures the intricacies of normal operational behavior while simultaneously documenting deviations caused by malicious activities. This focus on communication channels ensures the dataset aligns closely with real-world EVCS operations, making it invaluable for researchers aiming to understand and mitigate cybersecurity risks in this domain.
To provide a broad representation of EVCS behavior, the dataset includes a range of experimental scenarios. Benign scenarios are carefully crafted to represent the normal operating states of EVCS. These include idle states, where the charger communicates with the backend management system without an active vehicle connection, and charging states, where the system actively engages in V2G communication while relaying data to the backend.
The CICEVSE2024 dataset was processed with great care to ensure it was ready for ML tasks. This preparation made it suitable for intrusion detection and classification within the context of EVCS. The process included steps such as integrating data, reducing features, and cleaning the dataset to improve its quality and make it effective for training advanced detection models.
The raw dataset consisted of CSV files stored in two directories labeled EVSE-A and EVSE-B. Each file represented specific scenarios or types of attacks observed in EVCS environments. To combine these data sources, all files in each directory were read and loaded into Pandas Data Frames. A unique label was assigned to each DataFrame, derived from the corresponding file name, to indicate the associated scenario or attack type. The labeled DataFrames were then combined within each directory, resulting in two comprehensive datasets. Finally, these two datasets were merged into a single DataFrame, providing a unified view of all recorded scenarios and attack types.
Further refinement was achieved by applying feature reduction techniques to remove unnecessary and redundant attributes. Columns with more than 80% zero values were identified and dropped, as they added little value in distinguishing between normal and anomalous behaviors. Attributes with many missing values, such as ‘requested_server_name’, ‘client_fingerprint’, ‘server_fingerprint’, ‘user_agent’, and ‘content_type’, were also removed to prevent inefficiency or bias. Additionally, columns related to network identifiers and addresses, such as ‘id’, ‘src_ip’, ‘src_mac’, ‘src_oui’, ‘src_port’, ‘dst_ip’, ‘dst_mac’, ‘dst_oui’, ‘dst_port’, ‘application_name’, and ‘application_category_name’, were excluded to focus on features that were more relevant to intrusion detection and to reduce the risk of overfitting.
To further improve the dataset’s quality, duplicate rows were identified and eliminated. This step removed over 1.46 million redundant entries, ensuring the dataset was free of unnecessary repetition and more efficient for training ML models. After these refinements, the dataset retained only unique and meaningful records, providing a clean and reliable foundation for subsequent analysis (Table 3).

Table 3.
Distribution of classes and attack records.
A key limitation of the CICEVSE2024 dataset is its significant class imbalance. While attack types like SYN Flood (259,481 samples) are well-represented, benign traffic (82 samples) is severely underrepresented, which may bias models toward attack detection while reducing their ability to identify normal traffic. Similarly, rare attack types, such as ICMP Fragmentation (28 samples), may lack sufficient training data for reliable classification.
4. Results
This section presents the evaluation of the proposed online IDS based on its implementation and performance. The experimental setup outlines the computing environment and configurations. The system’s effectiveness is assessed in two scenarios: binary classification and multiclass classification. The following subsections provide a detailed examination of the results.
4.1. Experimental Setup
The experimental setup for this study was designed to implement and evaluate the proposed online IDS efficiently. The experiments were conducted on a system running Windows 11, equipped with a 13th Gen Intel(R) Core(TM) i7-13700 processor (2.10 GHz) and 16.0 GB of RAM, providing sufficient computational power for real-time data processing and model evaluation.
Python (version 3.10.13) was used for implementation, leveraging libraries tailored for adaptive ML and data processing. The Pandas (version 2.2.3) library handled data cleaning and organization, while NumPy (version 1.26.4) supported numerical computations. Matplotlib (version 3.8.3) was utilized for visualizing model performance. The River (version 0.22.0) library formed the backbone of the system, enabling real-time data streaming with its stream module and constructing ML pipelines using compose and preprocessing [47]. The ARF classifier, implemented via the forest module, offered robust learning capabilities, while the metrics module enabled dynamic evaluation of accuracy, precision, recall, and F1-score [48]. The ADWIN drift detection mechanism from the drift module ensured the model adapted to changes in data distribution.
To ensure unbiased streaming simulations, the dataset was randomized using the shuffle utility from scikit-learn. Execution times for prediction, evaluation, and drift detection were tracked with Python’s time module, and timestamps for critical events were logged using the datetime module. The Counter class from Python’s collections module was used to efficiently manage class distributions and processed instance counts.
This experimental setup, combining powerful computational resources with specialized ML libraries, ensured the scalability and reliability of the online IDS. It provided a robust framework for addressing the dynamic and evolving cybersecurity challenges of EVCS.
The experimental code used in this study has been made publicly available in the following GitHub repository: https://github.com/TATU-hacker/Intrusion_Detection_on_Electric_Vehicle_Charging_Systems.git (uploaded on 8 January 2025). By sharing this code, we aim to facilitate reproducibility, encourage collaboration, and support further research in securing EVCS against evolving cyber threats.
4.2. Binary Classification Results
The binary classification results of the proposed online IDS highlight its exceptional performance in detecting and responding to malicious network traffic in EVCS.
The proposed online IDS demonstrated exceptional efficiency and adaptability during its evaluation, underscoring its suitability for real-time data streams in dynamic environments such as EVCS. Over the course of processing 1.2 million instances, the system achieved a total execution time of 4706.81 s, showcasing its ability to operate seamlessly under real-time conditions (Table 4). A detailed analysis revealed that only 6.59 s were spent updating performance metrics, including accuracy, precision, recall, and F1-score, while the ADWIN drift detection mechanism accounted for just 3.98 s. This lightweight design ensured that critical tasks, such as performance monitoring and drift detection, did not hinder the system’s responsiveness or scalability.

Table 4.
Execution times for binary classification.
The drift detection capability of the online IDS proved pivotal in maintaining its adaptability to evolving data distributions. Over the course of the experiment, 12 distinct drift events were detected at various points in the data stream, ranging from instance 18,047 to instance 1,213,183 (Table 5). The system’s integration of the ADWIN mechanism allowed it to promptly identify these changes with minimal computational overhead, ensuring real-time responsiveness. Despite the presence of drifts, the system consistently recalibrated its model to sustain high performance, maintaining an accuracy of 0.9913, precision of 0.9999, recall of 0.9914, and an F1-score of 0.9956. These metrics highlight the system’s robustness in addressing concept drift without sacrificing reliability.

Table 5.
Drift detected instances for binary classification.
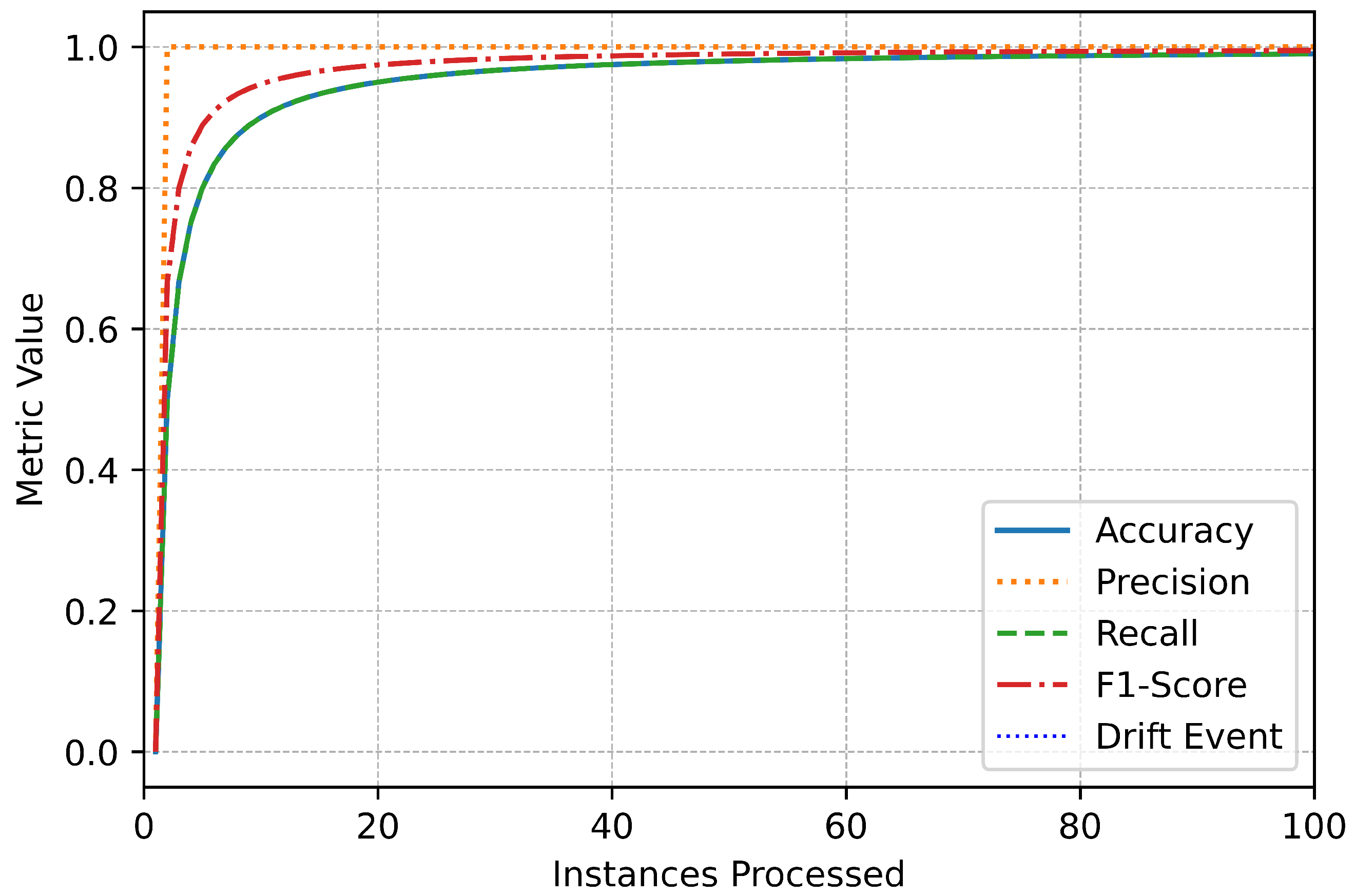
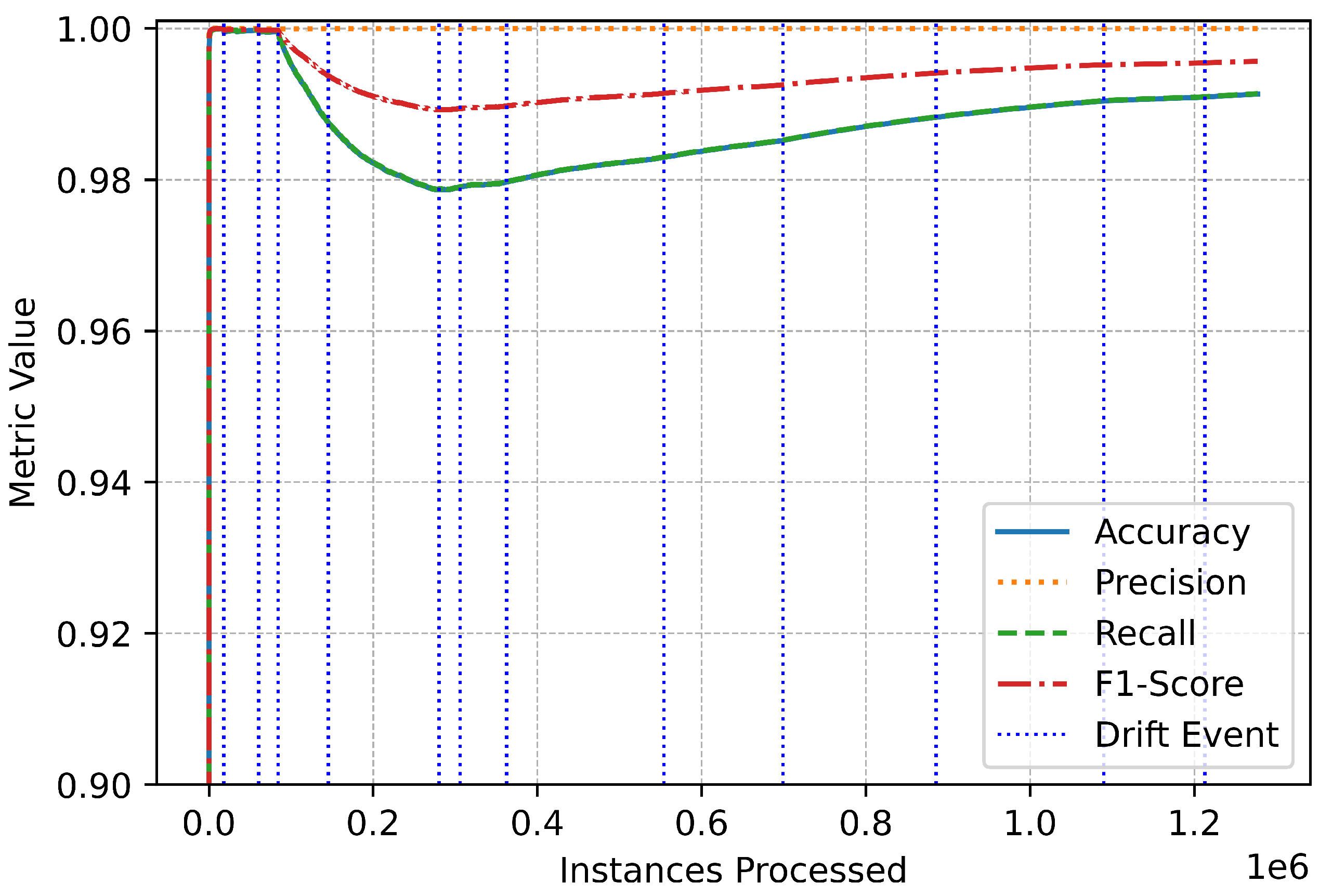
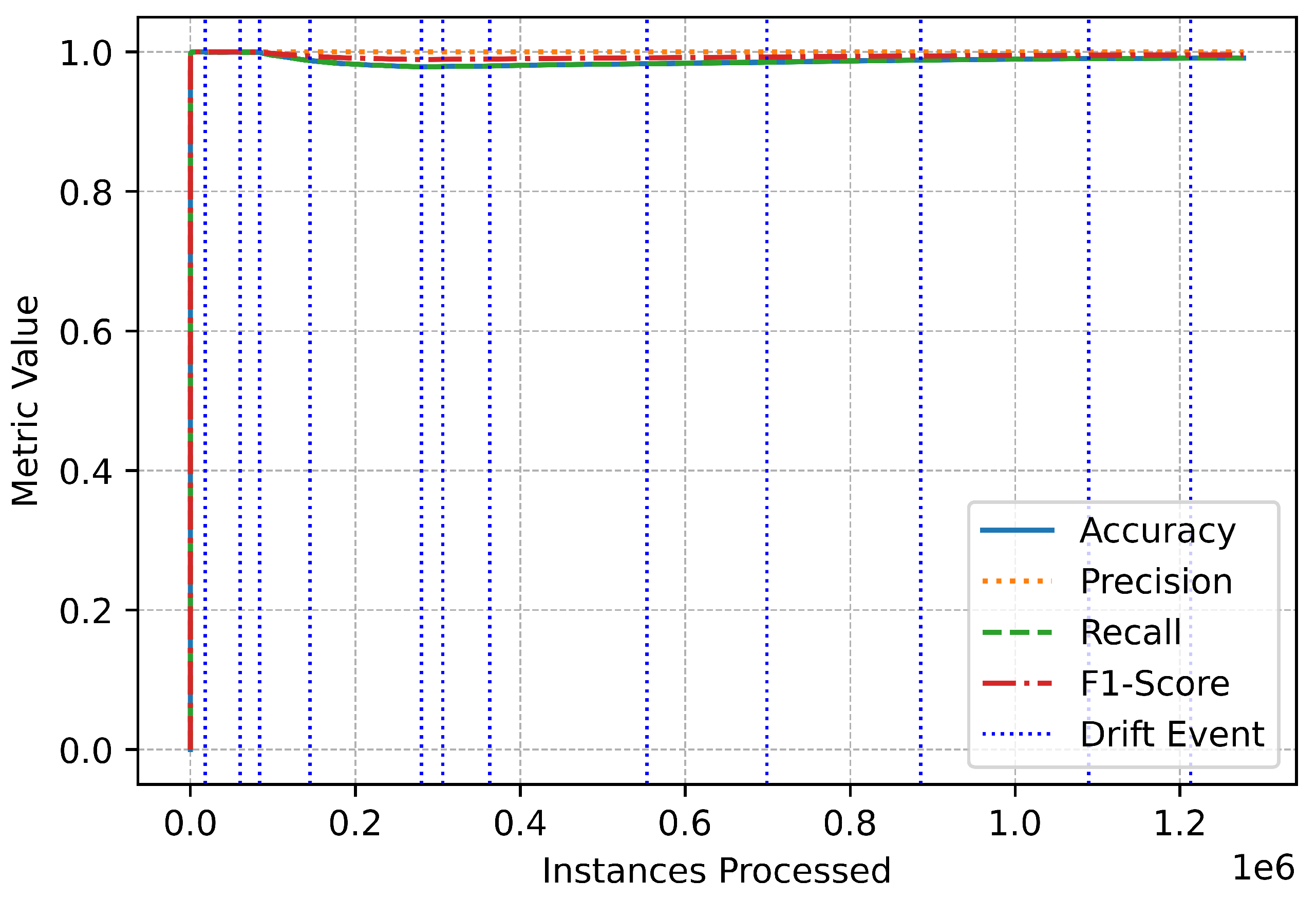
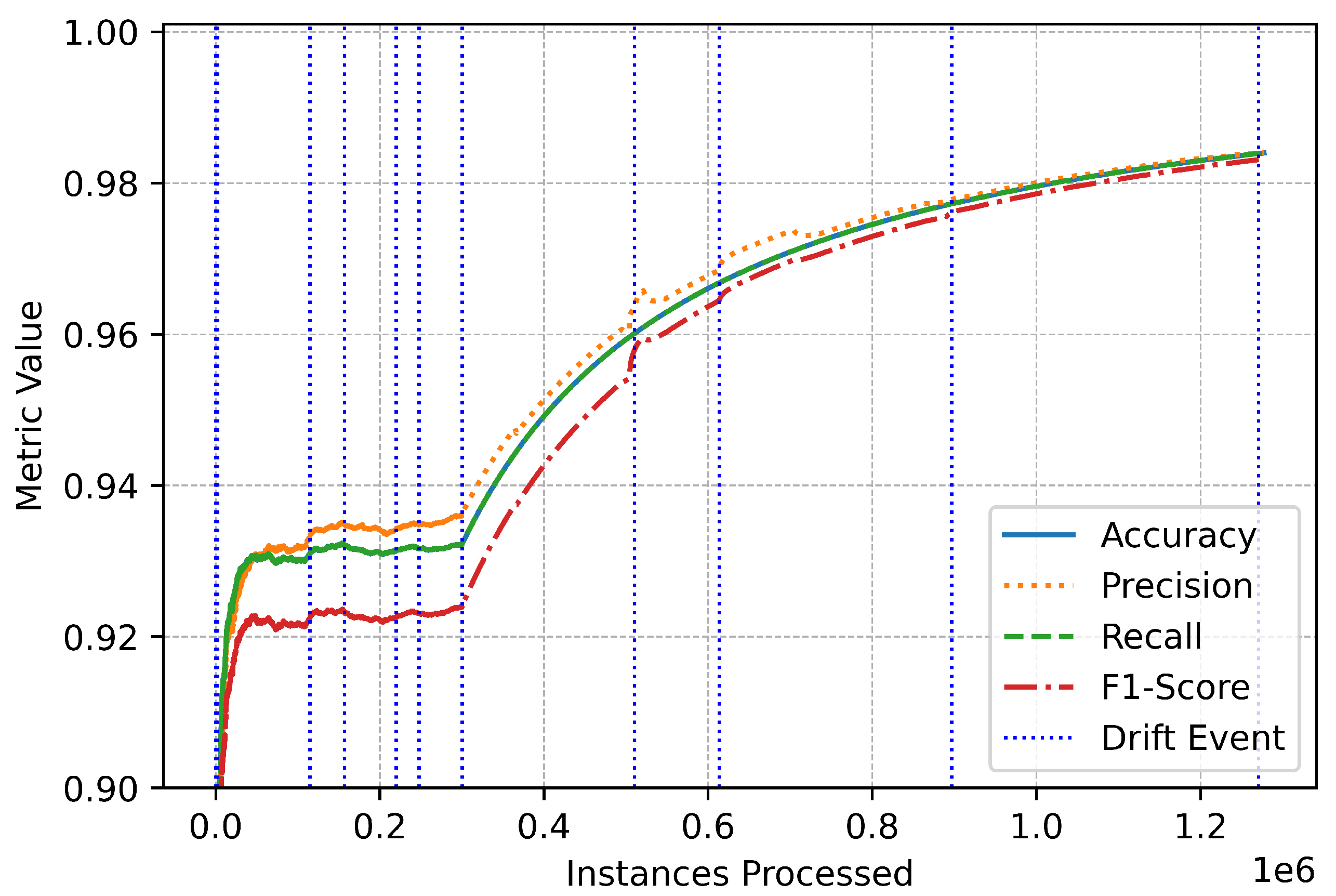
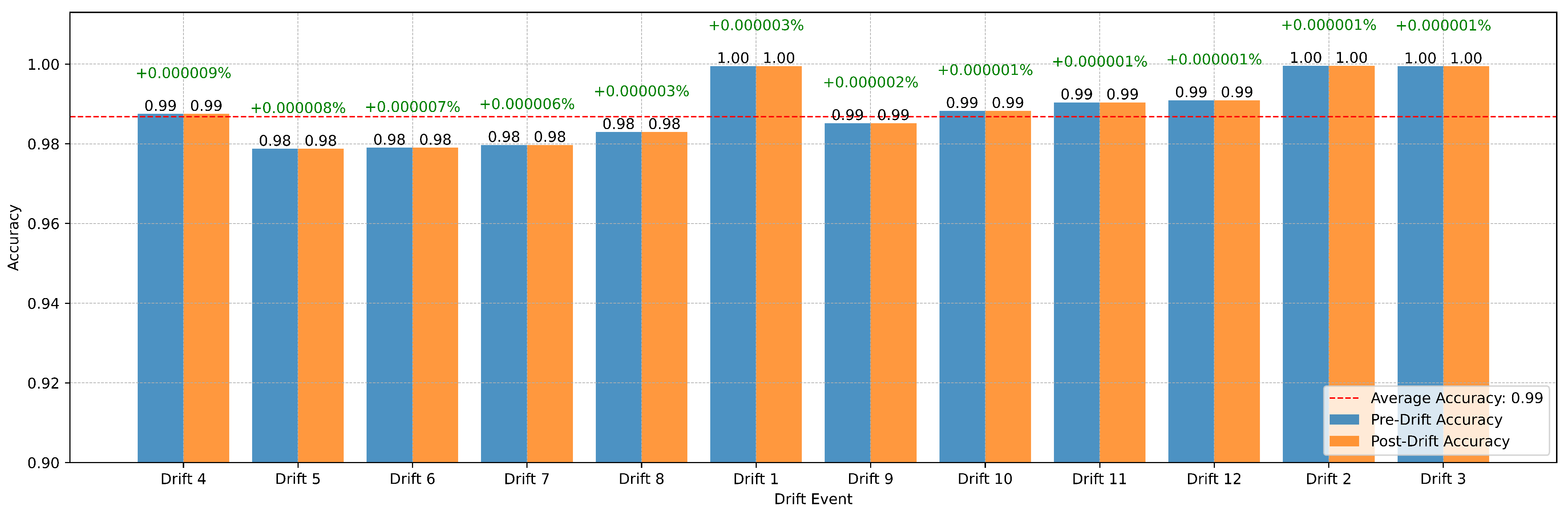
The metric trends further illustrate the system’s robustness and responsiveness (Figure 3). Performance metrics remained stable throughout the data stream, with only minor, temporary fluctuations during drift events (Figure 4). These variations highlight the system’s real-time adaptation to new patterns in the data. The swift stabilization of metrics following each drift event emphasizes the online IDS’s ability to recalibrate effectively without compromising overall performance (Figure 5). Vertical dotted lines in the performance graphs visually represent these drift events, showcasing the alignment between the system’s detection and adaptation processes (Figure 6).
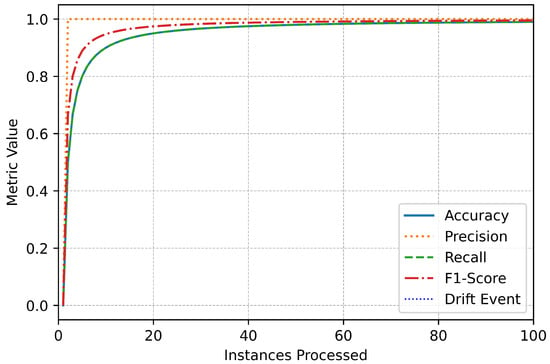
Figure 3.
Binary initial performance.
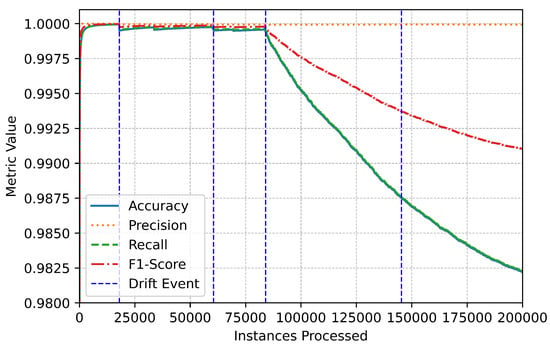
Figure 4.
Binary performance degradation.
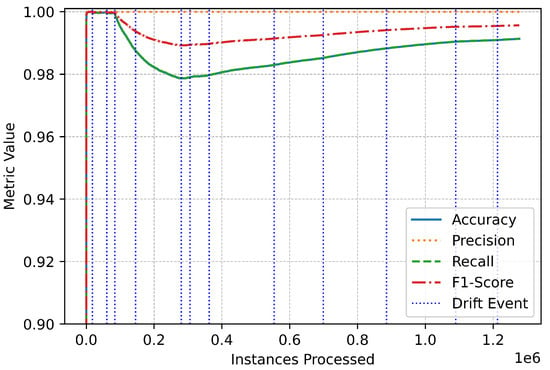
Figure 5.
Binary performance magnified.
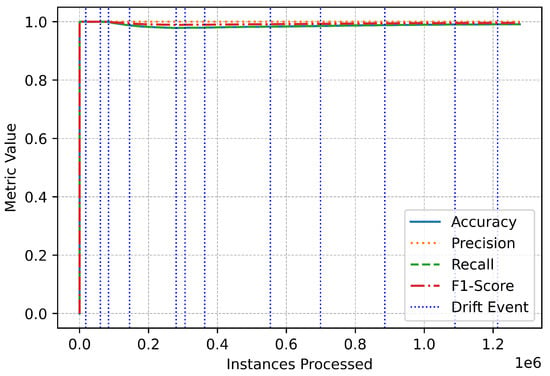
Figure 6.
Binary overall performance.
The lightweight and efficient drift detection mechanism ensured that the system remained responsive to shifts in data patterns caused by changes in traffic behavior or the emergence of new attack vectors. By swiftly detecting and adapting to these drifts, the online IDS maintained its ability to distinguish between benign and malicious traffic with exceptional precision and recall. The minimal time spent on drift detection and metric updates further underscores the system’s computational efficiency, making it suitable for high-speed streaming environments where timely decision-making is essential.
Overall, the online IDS balances computational efficiency with robust performance, ensuring adaptability and resilience in the face of evolving data patterns. Its ability to maintain exceptional accuracy and reliability, even under dynamic conditions, demonstrates its potential as a critical safeguard for modern infrastructures such as EVCS. The seamless integration of drift detection, real-time metric evaluation, and lightweight execution highlights the system’s practicality and effectiveness in addressing real-world cybersecurity challenges.
4.3. Multiclass Classification Results
The multiclass classification results of the proposed online IDS demonstrate its effectiveness in identifying and distinguishing between multiple attack types and benign network traffic within EVCS.
The proposed onine IDS demonstrated exceptional performance during the evaluation, achieving consistently high metrics. With an accuracy of 0.9840, the system reliably classified the vast majority of instances across all classes, ensuring accurate differentiation between benign traffic and multiple attack types. Its precision of 0.9840 highlights its ability to minimize false positives, ensuring benign activities are rarely misclassified as malicious. The system’s recall, also at 0.9840, reflects its strong sensitivity in identifying true positives across all attack categories, including less frequent ones. Finally, the F1-score of 0.9831 underscores the system’s balanced performance, combining precision and recall to deliver robust multiclass classification results. These metrics collectively affirm the system’s reliability, adaptability, and effectiveness in handling dynamic and diverse network traffic scenarios.
Drift detection was a key component of the system’s adaptive capabilities, allowing it to identify and respond to significant changes in data distribution. Over the course of the evaluation, a total of 11 drift events were detected at critical moments, such as at instance 383 and instance 1,270,815 (Table 6). These events reflect shifts in network traffic patterns, likely caused by the introduction of new attack behaviors or changing operational conditions. The integration of the ADWIN algorithm enabled the system to detect these drifts with exceptional efficiency, requiring only 4.56 s for drift detection across all instances. This responsiveness ensured that the system remained aligned with the latest data distribution, maintaining its high detection accuracy and adaptability in dynamic environments.

Table 6.
Drift detected instances for multiclass classification.
The overall execution time further underscores the system’s efficiency. Processing all instances required 4703.63 s, with metric computation accounting for just 4.88 s and drift detection contributing an additional 4.56 s (Table 7). These results highlight the computational efficiency of the online IDS, which seamlessly integrates real-time processes such as drift detection and metric updates without compromising its throughput. This balance of speed and adaptability makes the system suitable for high-speed data environments, where real-time decision-making is critical.

Table 7.
Execution times for multiclass classification.
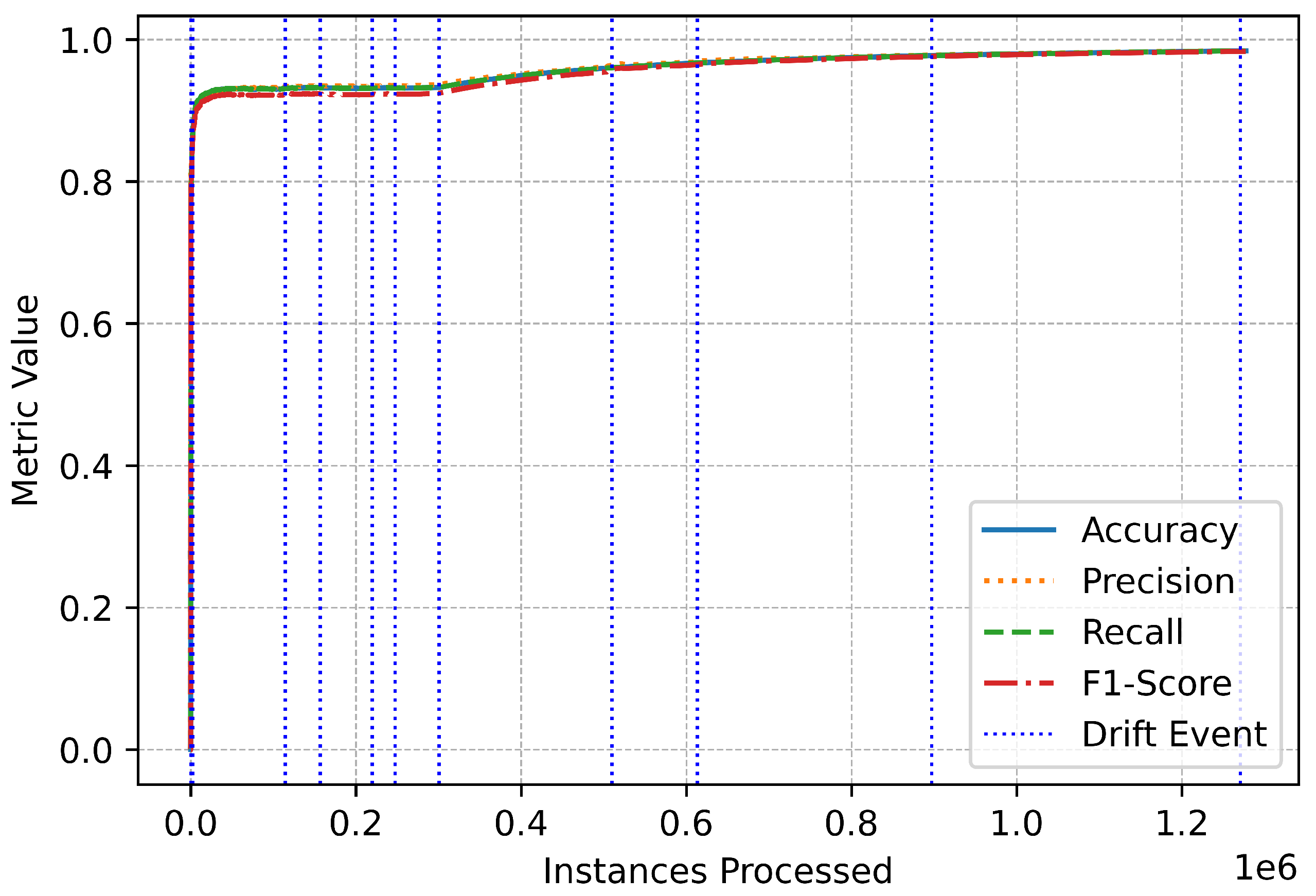
The trends observed in the performance metrics provide additional insights into the system’s reliability (Figure 7). Throughout the evaluation, accuracy, precision, recall, and F1-score remained consistently high, even during periods of drift (Figure 8). Brief fluctuations around drift events reflect the system’s dynamic adjustment to evolving data patterns, but these were quickly mitigated by its adaptive learning framework (Figure 9). The vertical markers representing drift events in the performance plots emphasize the online IDS’s responsiveness and ability to maintain stability in the face of changing data distributions (Figure 10).
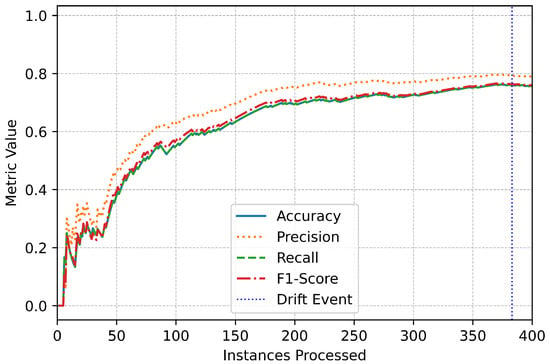
Figure 7.
Multiclass initial performance.
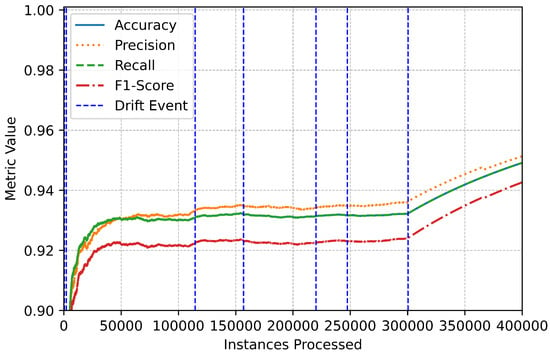
Figure 8.
Multiclass performance improvement.
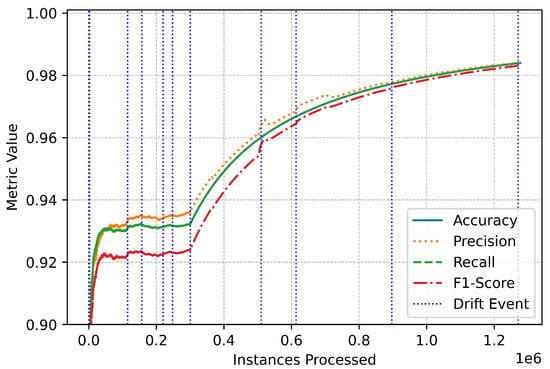
Figure 9.
Multiclass performance magnified.
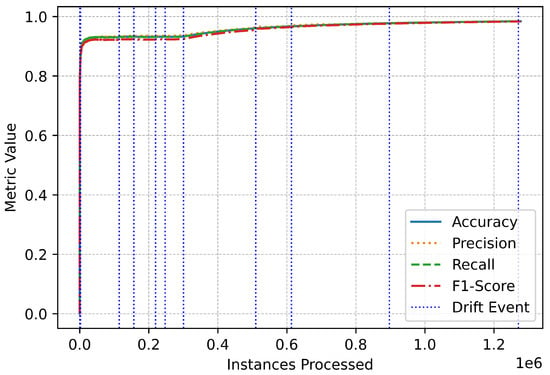
Figure 10.
Multiclass overall performance.
The proposed online IDS exhibits a robust combination of accuracy, adaptability, and computational efficiency. Its ability to detect and respond to drift, coupled with consistent metric trends and efficient execution, ensures its suitability for deployment in dynamic environments such as EVCS. This makes it a valuable tool for addressing the evolving cybersecurity challenges posed by modern, real-time systems.
5. Discussion
This section analyzes the performance of the proposed online IDS, focusing on its effectiveness in binary and multiclass classification. Additionally, a comparative analysis with existing studies highlights the system’s advantages and potential areas for improvement. The following subsections provide a detailed discussion of these aspects.
5.1. Discussion of Binary Classification
The evaluation of binary classification performance demonstrates the robustness and efficiency of the implemented framework, particularly in the context of drift detection and dynamic adaptation. The analysis encompasses three critical aspects: instance processing times, cumulative time contributions, and accuracy stability across drift events.
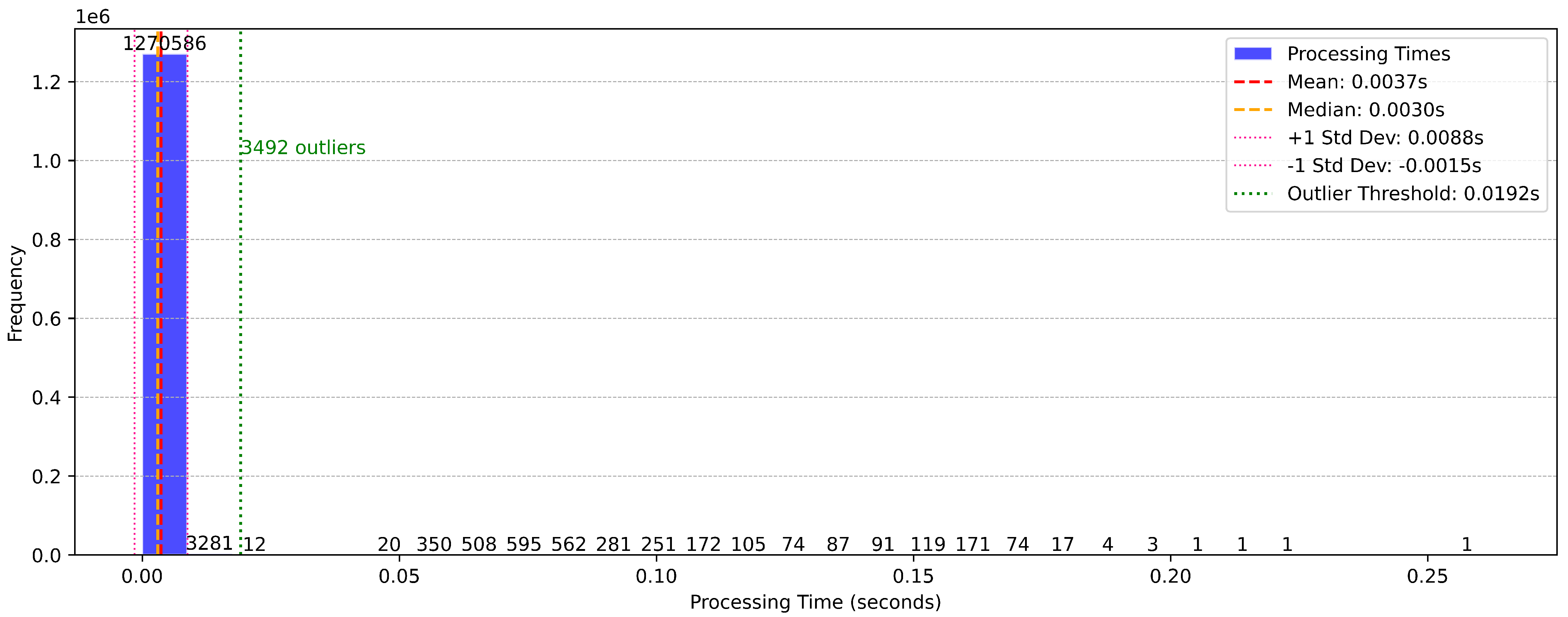
The distribution of processing times, as depicted in Figure 11, reveals a highly efficient system with a mean processing time of 0.0037 s and a median of 0.0030 s. The majority of instances are processed well within this range, with only 3492 instances exceeding the defined outlier threshold of 0.0192 s. These outliers, representing less than 0.3% of the total instances, highlight the framework’s ability to handle real-time data streams with negligible latency.
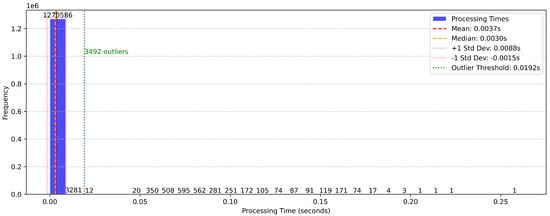
Figure 11.
Distribution of instance processing times in binary classification.
The narrow distribution of processing times underscores the system’s computational efficiency, a critical aspect for real-time applications. The presence of outliers, while minimal, could be attributed to transient computational overheads, such as memory allocation spikes or concurrent resource utilization. However, these occurrences are infrequent and do not significantly impact overall performance.
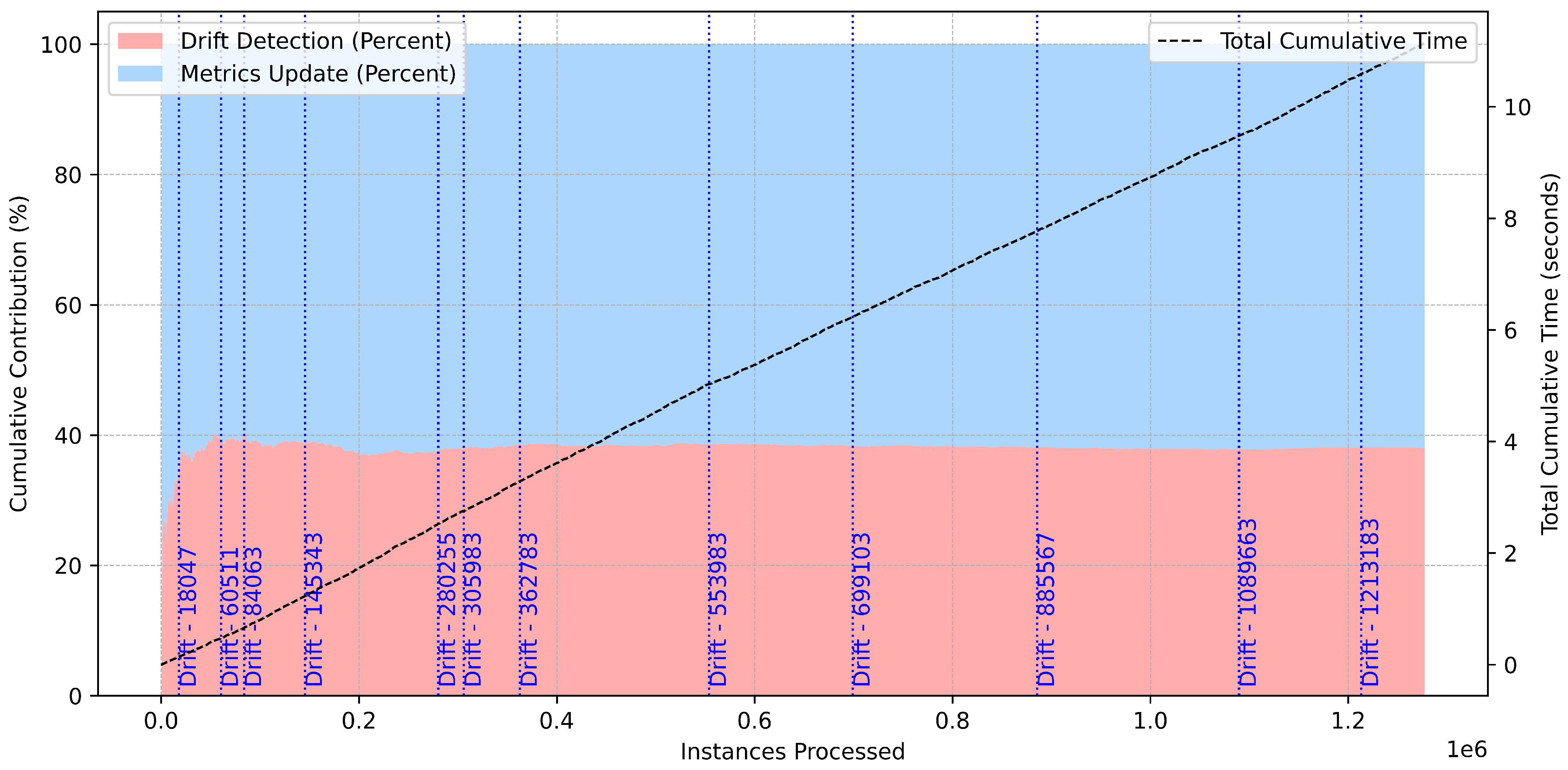
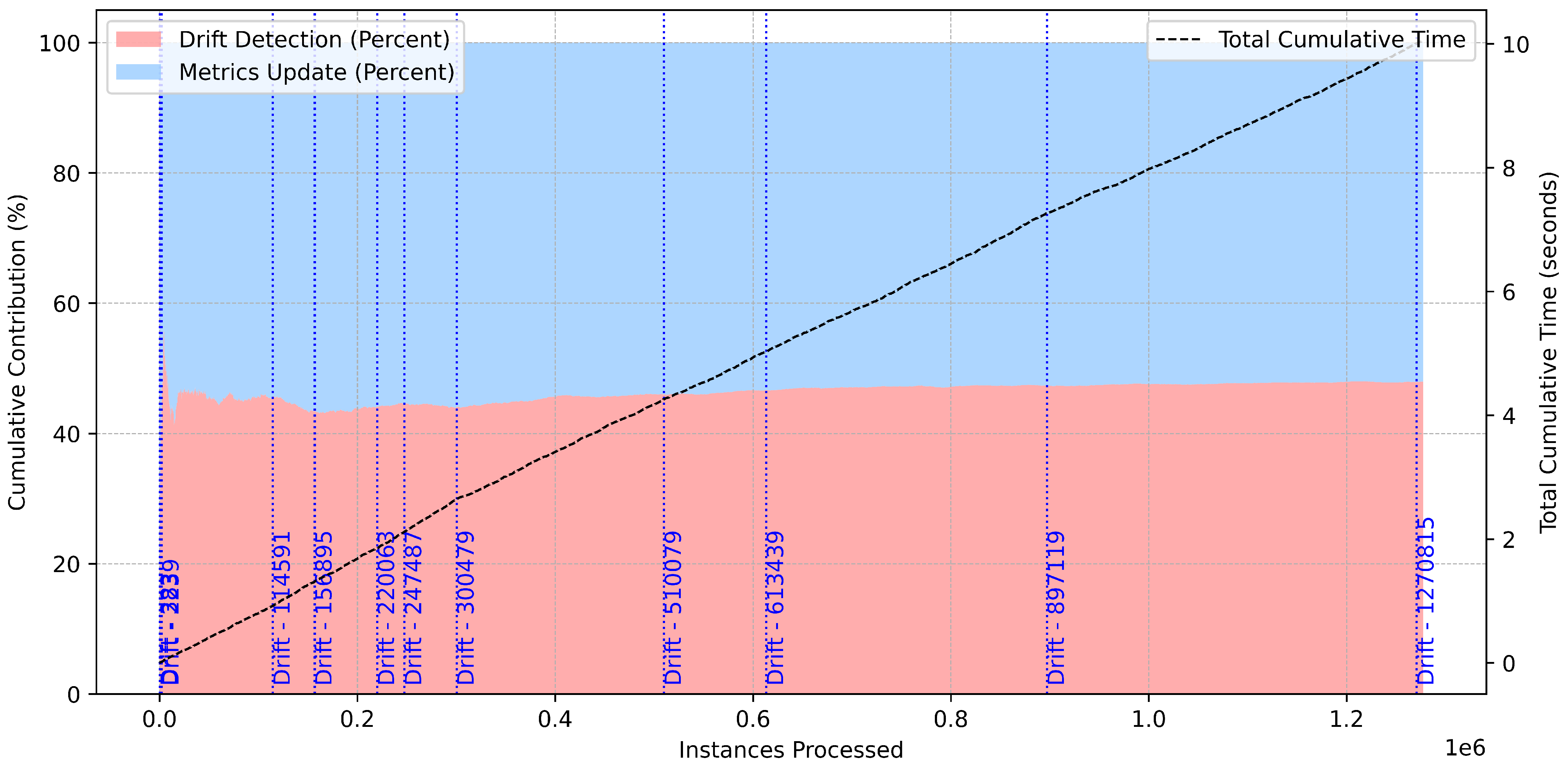
Figure 12 provides a detailed breakdown of cumulative time contributions for drift detection and metrics updates over 1.2 million processed instances. Drift detection accounts for approximately 40% of the cumulative time, while metrics updates comprise the remaining 60%. This distribution suggests a balanced allocation of computational resources between monitoring data stability and updating performance metrics.
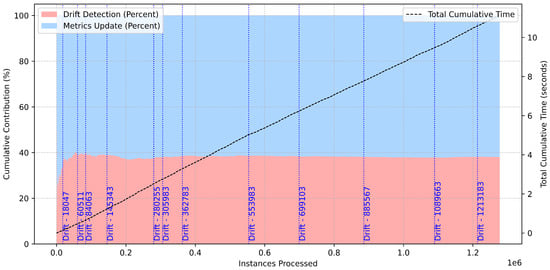
Figure 12.
Cumulative time analysis for binary classification.
The total cumulative time, which increases linearly with the number of processed instances, highlights the scalability of the framework. Notably, drift events–marked along the timeline–do not cause abrupt surges in cumulative time, indicating an efficient handling of drifts without disrupting the overall workflow. This behavior is crucial for maintaining real-time responsiveness in dynamic environments.
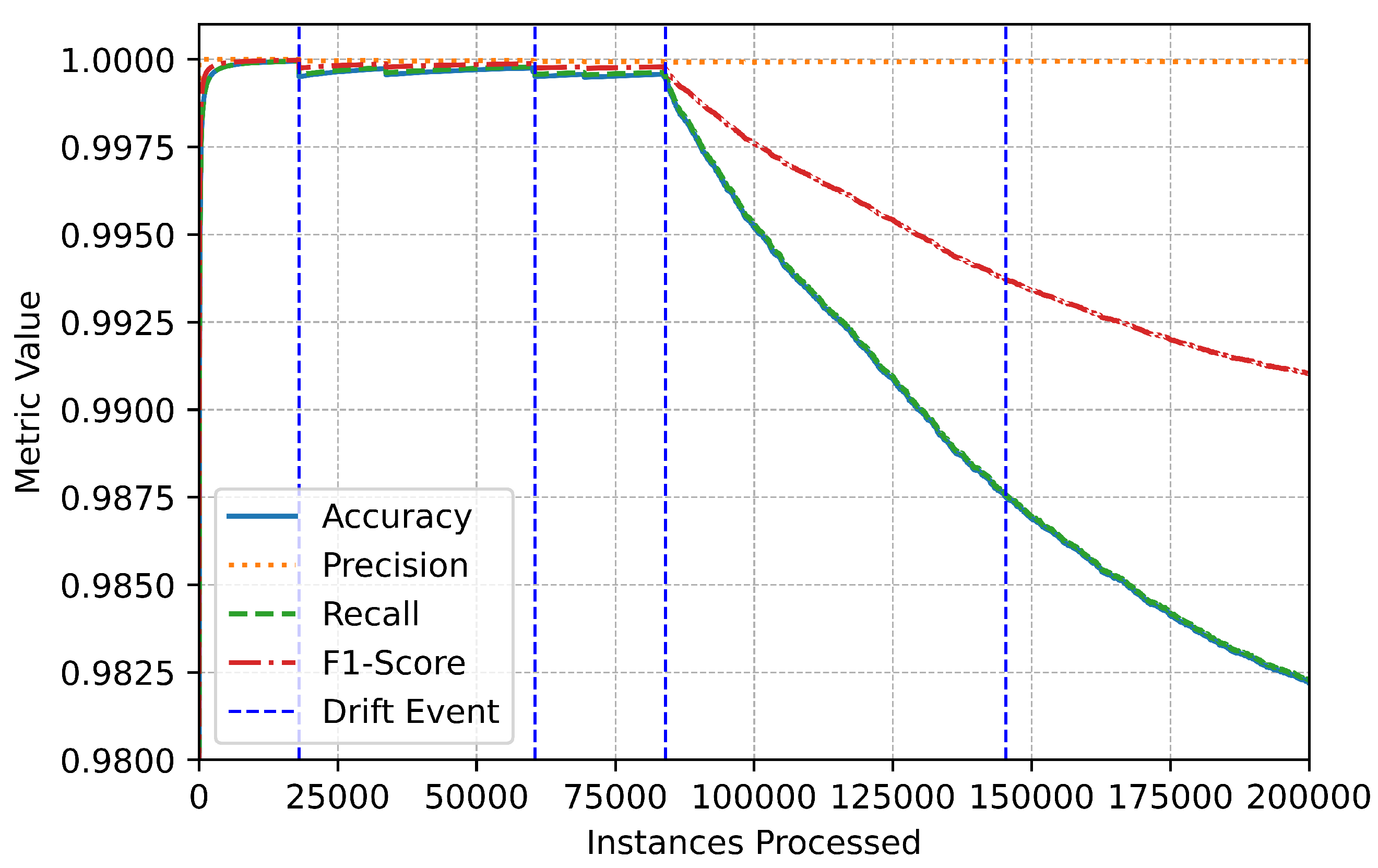
Figure 13 evaluates the impact of 12 detected drift events on the binary classification accuracy. Both pre-drift and post-drift accuracies remain consistently high, with an average accuracy of 0.99, indicating the framework’s resilience to data distribution changes. Percentage changes in accuracy across drift events are minimal, ranging from +0.000001% to +0.000009%, with no significant degradation observed.
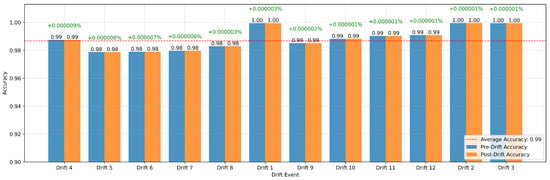
Figure 13.
Model accuracy before and after drift in binary classification.
This consistency suggests that the drift detection mechanism effectively triggers recalibration processes that maintain model performance. Furthermore, the slight positive changes in accuracy following most drift events highlight the system’s ability to adapt dynamically and optimize its predictions in response to evolving data patterns.
5.2. Discussion of Multiclass Classification
The multiclass classification analysis revealed critical insights into the model’s processing efficiency, cumulative time contributions, and adaptive performance in response to drift events. By integrating processing time statistics, cumulative contributions, and accuracy variations pre- and post-drift, this discussion highlights the model’s robustness and limitations in handling dynamic multiclass environments.
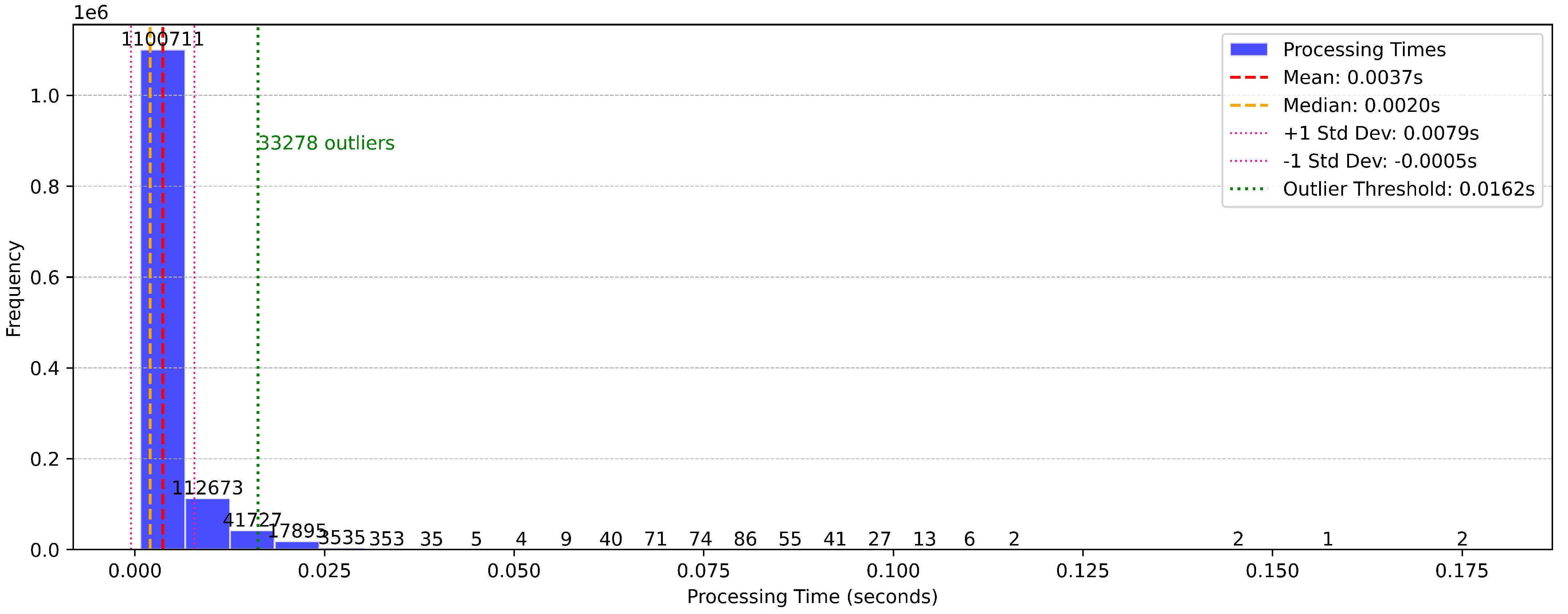
The distribution of processing times, as illustrated in Figure 14, reveals the model’s computational efficiency during the multiclass classification task. The mean processing time was calculated as 0.0037 s per instance, with a median of 0.0020 s. The narrow range between the mean and median, coupled with a standard deviation of 0.0079 s, highlights the consistency of processing times. A small fraction of outliers was identified, exceeding the outlier threshold of 0.0162 s. These outliers, though insignificant in volume, could reflect periods of increased complexity in processing, likely attributed to computational overhead during drift adaptation. The histogram visually emphasizes the predominance of efficient processing times, validating the model’s suitability for real-time applications.
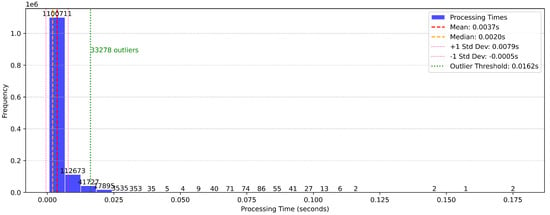
Figure 14.
Distribution of instance processing times in multiclass classification.
The cumulative time analysis provided additional insights into the balance between drift detection and metrics updates (Figure 15). Drift detection contributed approximately 45% to the cumulative time overhead, while metrics updates accounted for 55%, a proportion that reflects the system’s focus on maintaining model evaluation alongside adaptation to data distribution changes. Despite the presence of 11 drift events, the total cumulative time for both processes remained minimal, validating the system’s lightweight design. The stacked area plot highlights these contributions, with drift events annotated along the timeline to show the points of adaptation.
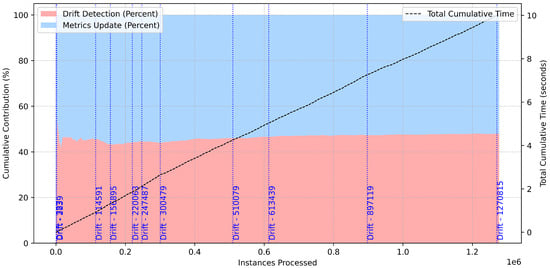
Figure 15.
Cumulative time analysis for multiclass classification.
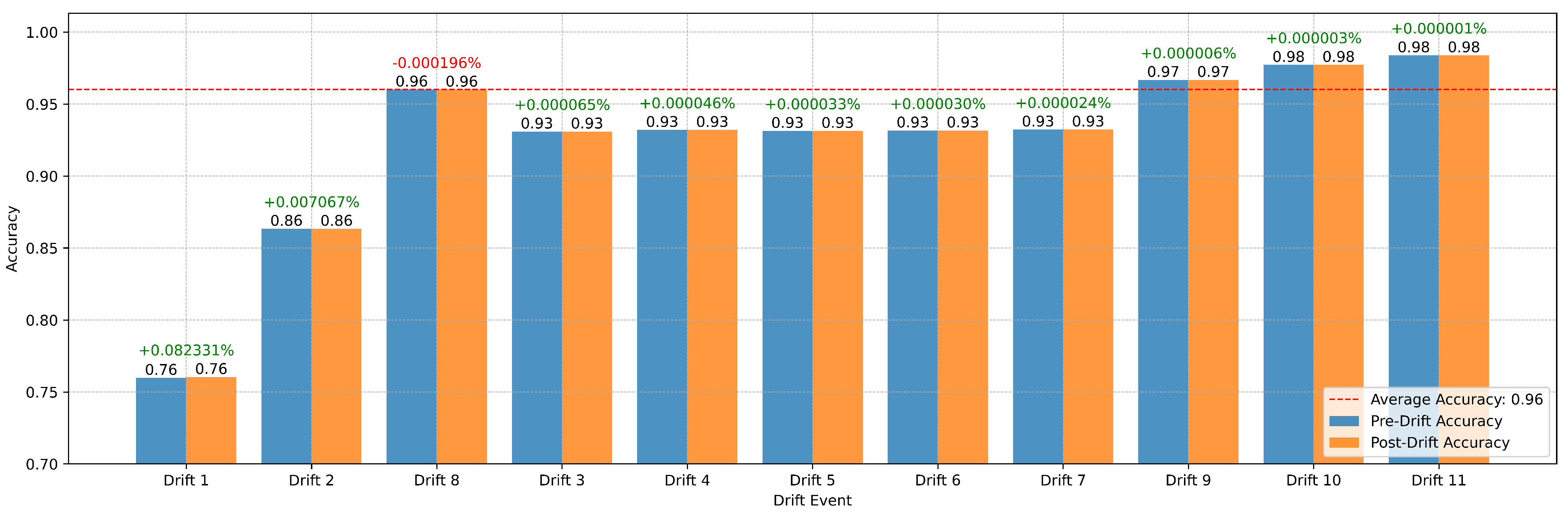
Figure 16 illustrates the model’s pre-drift and post-drift accuracy across 11 drift events. The average accuracy of 0.96, represented by the red dashed line, serves as a benchmark for evaluating the model’s adaptability. Notably, the model exhibited substantial improvement following Drift 1, where accuracy increased by +0.082331%, demonstrating effective adaptation to a significant data shift. Similarly, Drift 2 showed a moderate improvement of +0.007067%, indicating the model’s capacity to respond to evolving data distributions. However, Drift 3 displayed a minor accuracy drop of −0.000196%, suggesting challenges in fully adapting to specific data shifts. For most subsequent drift events, pre- and post-drift accuracies were nearly identical, with marginal improvements ranging from +0.000001% to +0.000033%, highlighting the model’s stability in less disruptive scenarios.
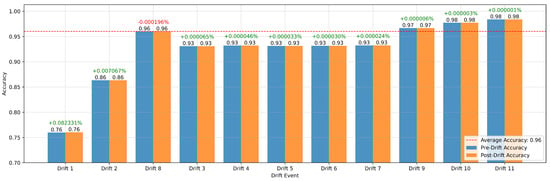
Figure 16.
Model accuracy before and after drift in multiclass classification.
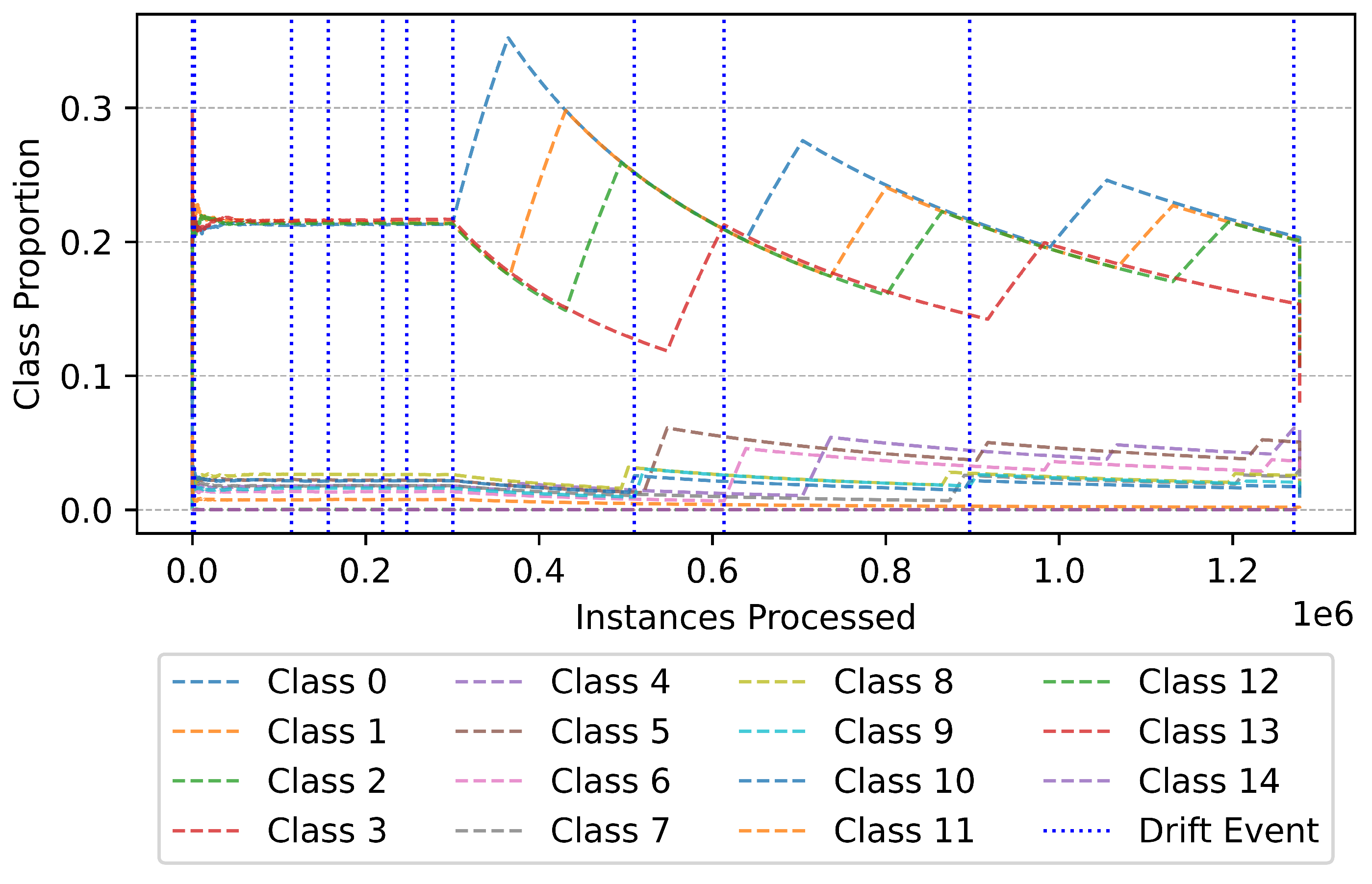
Figure 17 presents the overall trend of class distributions as instances are processed. A key observation from this figure is the periodic fluctuations in class proportions, signifying underlying concept drift within the dataset. Initially, the proportions remain stable, but as new data points are introduced, the distribution undergoes significant changes at multiple intervals, as indicated by the vertical blue dashed lines representing detected drift events. These shifts suggest that the data stream is non-stationary, reinforcing the necessity of an adaptive learning mechanism capable of dynamically adjusting to emerging patterns. The ability of the model to detect and respond to these drifts is pivotal in maintaining high classification accuracy over time.
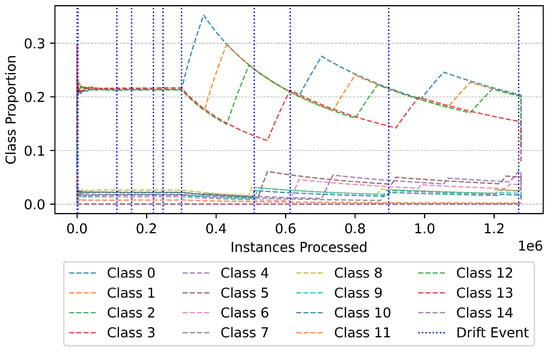
Figure 17.
Class distribution over time.
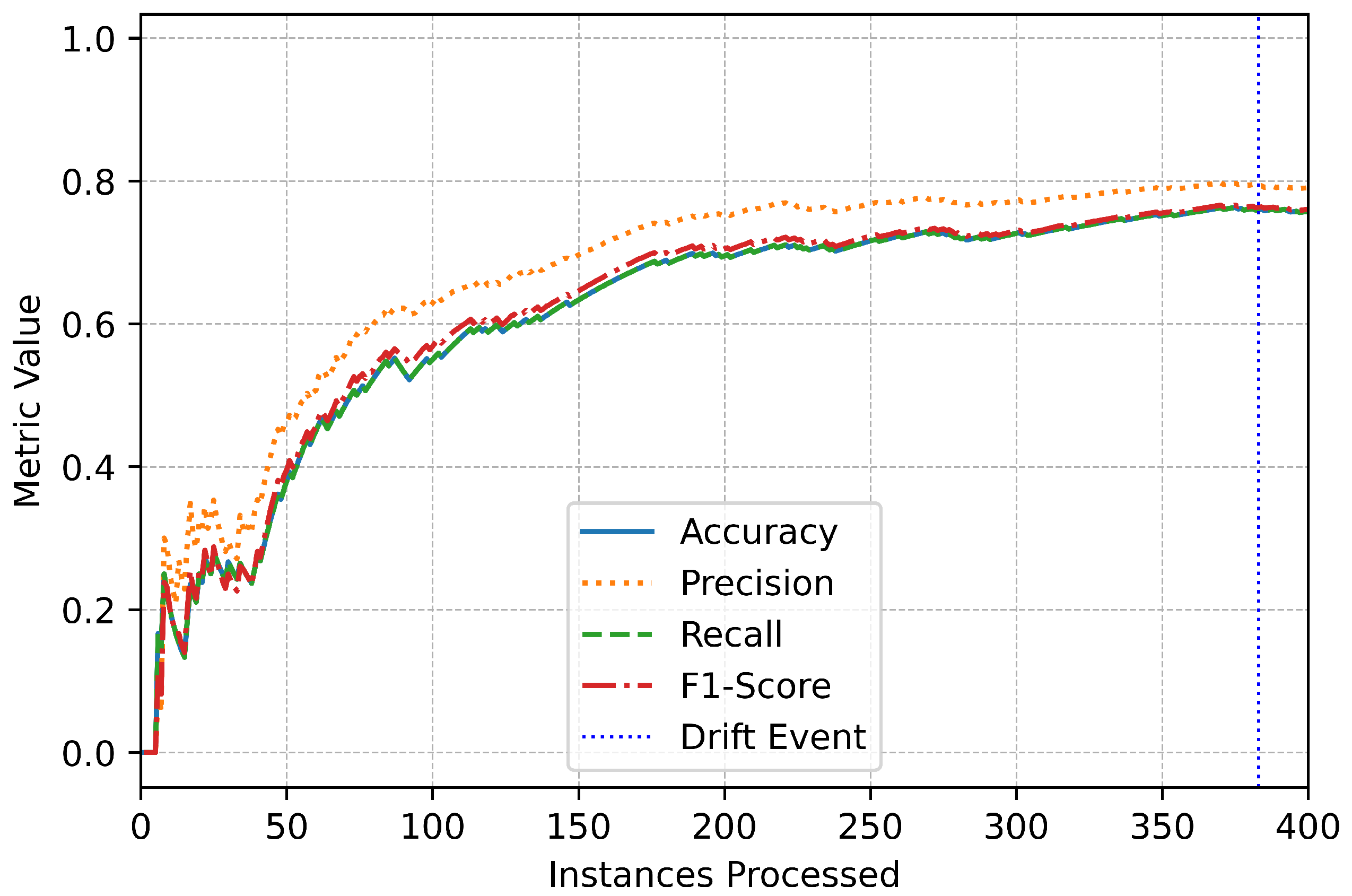
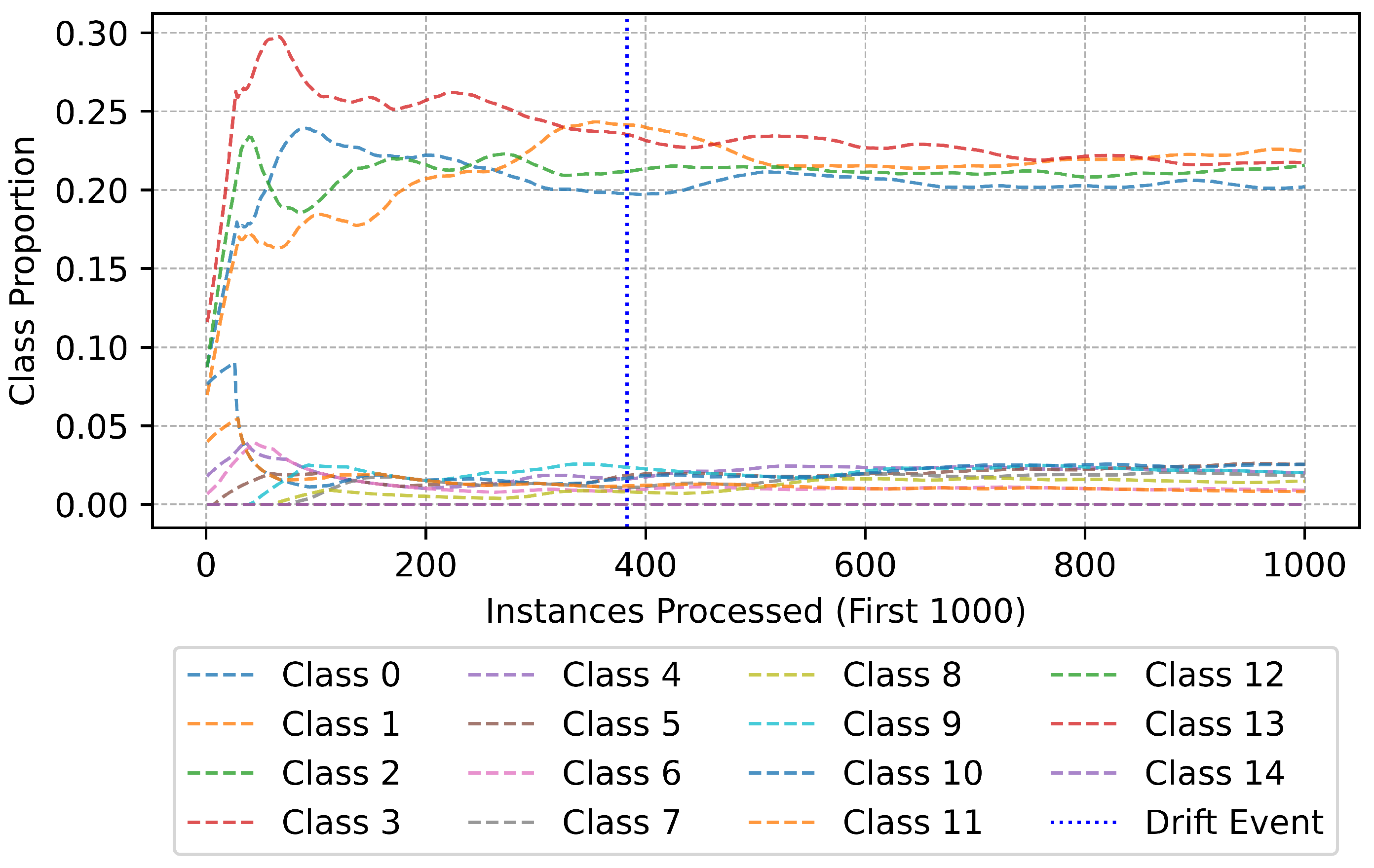
Zooming into the initial stages of data processing, Figure 18 focuses on the first 1000 instances. This phase is particularly important, as it captures the model’s behavior during its early adaptation period. A noticeable characteristic of this stage is the rapid fluctuation in class proportions, with certain classes experiencing a sharp increase in frequency before stabilizing. The occurrence of a drift event around the 400th instance marks a critical point in the model’s learning process, where it identifies and adjusts to an evolving data pattern. This highlights the efficiency of the ADWIN drift detection method in recognizing distributional changes early on, allowing the model to recalibrate its decision boundaries. Such early-stage fluctuations suggest that the model quickly learns an initial representation of the data, aligning itself with the underlying distribution.
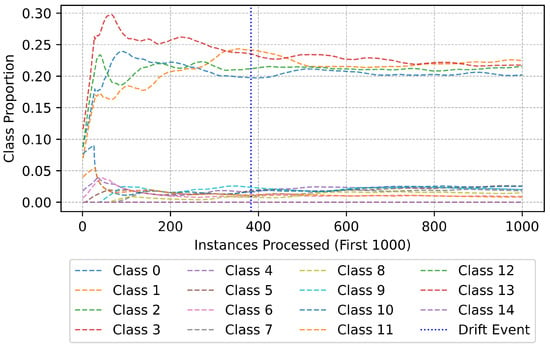
Figure 18.
Class distribution (first 1000 instances).
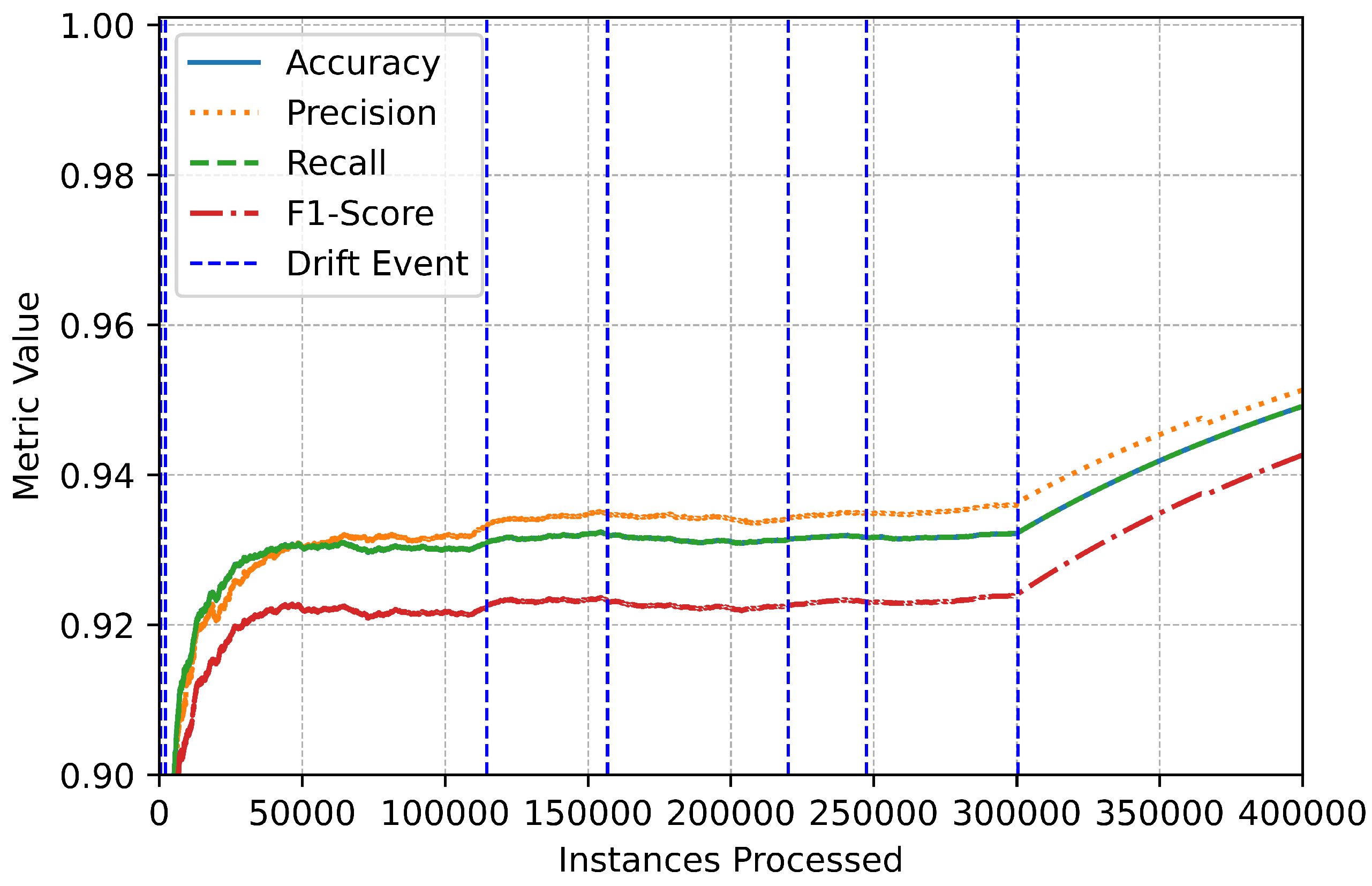
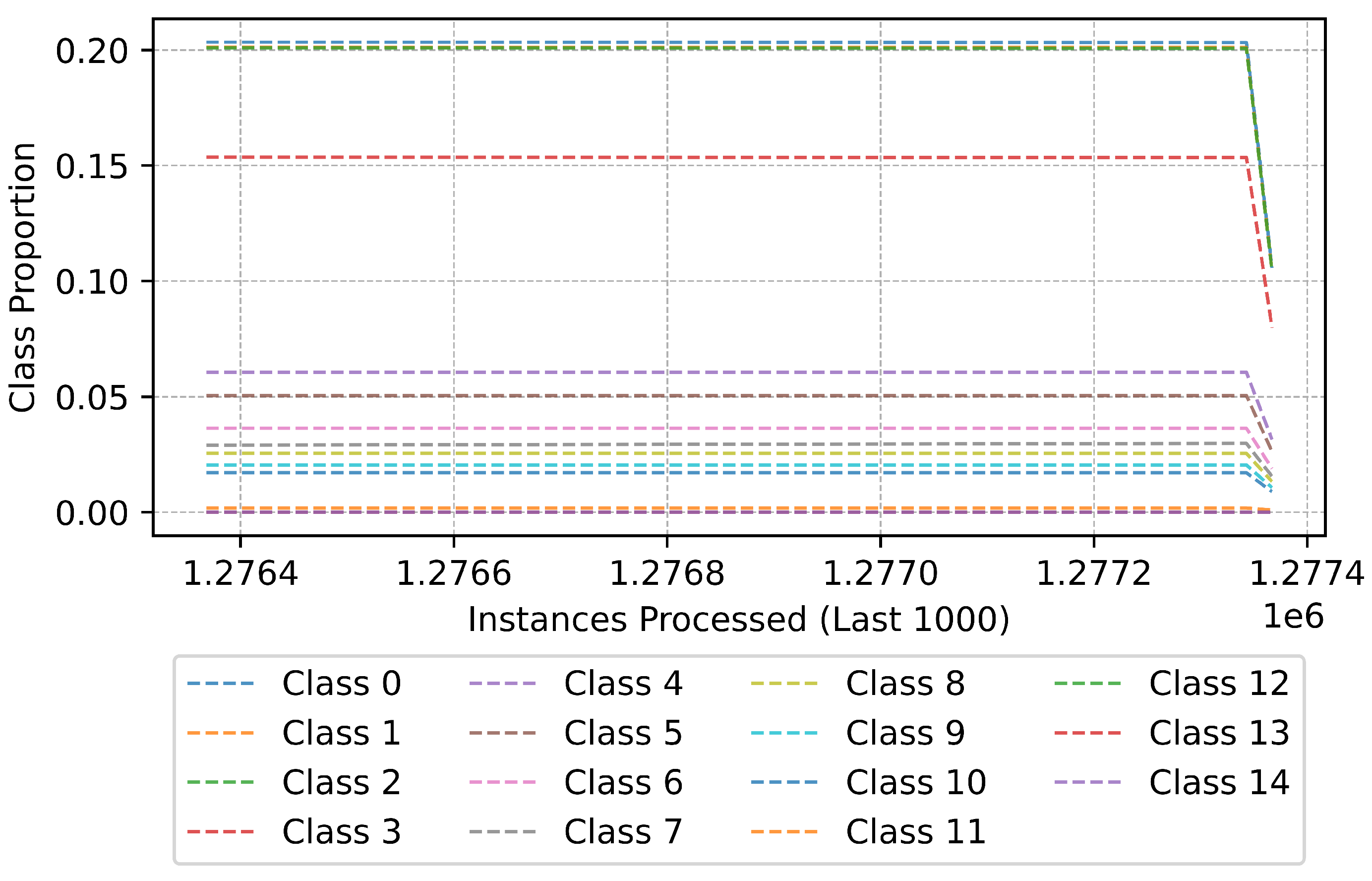
To examine the long-term stability of the model, Figure 19 provides a zoomed-in view of the last 1000 instances processed. In contrast to the initial phase, this segment showcases a relatively stable class distribution, indicating that the model has effectively adapted to prior drifts and established robust decision boundaries. While a drift event is detected near the end of processing, its impact on class proportions is minimal, demonstrating that the classifier has reached a steady-state performance. This stability is crucial in real-world applications, as it ensures that the model remains reliable even in the presence of minor distributional changes.
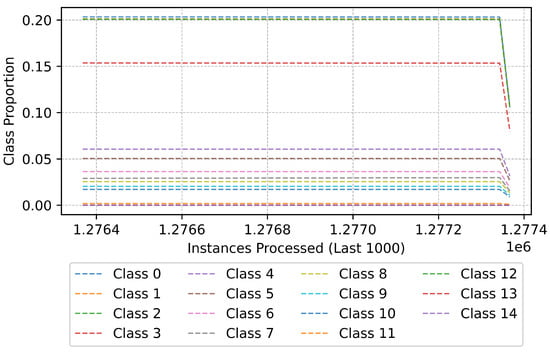
Figure 19.
Class distribution (last 1000 instances).
The findings underscore the model’s capacity to handle complex multiclass scenarios with high efficiency and stability. The processing time analysis validates the model’s capability for real-time classification, even in the presence of occasional computational outliers. The cumulative time contributions reflect a balanced allocation of resources between drift adaptation and performance evaluation, ensuring minimal delays during operation. The pre- and post-drift accuracy analysis further highlights the model’s resilience and adaptability, with significant gains in challenging scenarios and consistent performance across minor drifts.
However, the minor accuracy decline observed in Drift 3 suggests that further refinement of the drift detection and adaptation mechanisms is warranted, particularly for more complex data shifts. These results collectively demonstrate the model’s potential for deployment in real-world applications where multiclass data streams are subject to dynamic and evolving conditions.
5.3. Comparison with Existing Studies
To evaluate the effectiveness of the proposed adaptive IDS, we conducted a comparative analysis against existing models in the literature. Table 8 presents a performance comparison of various ML and DL approaches applied to the CICEVSE2024 dataset for intrusion detection.

Table 8.
Performance Comparison of Models.
Among previous studies utilizing offline learning methodologies, Buedi et al. [46] employed Random Forest and Support Vector Machine for multiclass classification (15 classes), reporting accuracies of 0.9374 and 0.9413, respectively. Bozömeroğlu et al. [49] leveraged a Decision Tree model, achieving an accuracy of 0.9999 for 13-class classification. Similarly, Purohit et al. [50] explored federated learning for binary classification, attaining an accuracy of 0.9697. Rahman et al. [51] investigated DL-based intrusion detection on host data, achieving an accuracy of 0.9754, while Benfarhat et al. [52] implemented a Temporal Convolutional Network (TCN), obtaining 1.0 accuracy for binary and five-class classification and 0.9300 for 17-class classification.
In contrast to these offline and federated learning models, our study introduces an online learning-based ARF approach, which continuously updates its model in response to evolving network traffic patterns. This adaptability enables real-time threat detection, a crucial advantage over static offline-trained models [53,54,55,56]. Our system demonstrated superior classification performance while maintaining computational efficiency. Specifically, for binary classification, our model achieved an accuracy of 0.9913, precision of 0.9999, recall of 0.9914, and an F1-score of 0.9956. For multiclass classification (15 classes), the model attained 0.9840 accuracy, precision, recall, and an F1-score of 0.9831.
Beyond classification performance, real-time drift detection and frequent model updates introduce computational overhead. To mitigate this, future work will explore selective model updates triggered only when performance drops below a predefined threshold, rather than after every instance. This strategy aims to balance efficiency and adaptability, reducing computational costs while maintaining robust classification performance.
Unlike conventional offline-trained models, which rely on predefined datasets and lack adaptability, our approach dynamically learns from streaming data, making it highly effective for real-world deployment in EV charging station security.
6. Conclusions
The rapid evolution of EVCS demands advanced cybersecurity frameworks to address dynamic and complex threats. This study introduces a groundbreaking intrusion detection framework that leverages online learning, real-time adaptability, and protocol integration, addressing critical gaps in the field.
This framework is the first to apply online learning to EVCS cybersecurity, shifting from static to dynamic detection. By continuously adapting to evolving data streams and attack patterns, the system enables seamless real-time updates without requiring retraining.
The integration of ARF with ADWIN drift detection ensures robust handling of concept drift, a significant challenge in streaming environments. ARF’s ensemble design provides stability, while ADWIN enables efficient detection of changing data distributions, allowing the system to address evolving cyberattacks with minimal latency.
The framework efficiently processes large-scale streaming datasets, a key requirement for EVCS networks. By minimizing computational overhead, it balances performance and resource efficiency, making it suitable for resource-constrained environments like charging stations.
Incorporating protocols such as OCPP and ISO 15118 enhances the framework’s practical relevance. These protocols ensure secure communication between EV infrastructure components, aligning the system with industry standards and addressing protocol-specific vulnerabilities.
The system’s performance is rigorously evaluated using metrics like accuracy, precision, recall, and F1-score. Detailed visual analytics highlight drift events and system performance trends, offering administrators actionable insights to optimize operations.
With a lightweight, efficient architecture, the framework is designed for real-world deployment. Its compatibility with EVSE protocols and real-time scalability ensures it acts as a robust defense against cyber threats in modern EV infrastructures.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, F.M.; methodology, F.M.; software, D.K.; validation, D.K.; formal analysis, U.G.; investigation, U.G.; data curation, F.M.; writing—original draft preparation, F.M. and U.G; writing—review and editing, D.K. and F.A.; visualization, U.G. and F.A.; supervision, F.A.; project administration, F.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Baronchelli, M.; Falabretti, D.; Gulotta, F. Power Demand Patterns of Public Electric Vehicle Charging: A 2030 Forecast Based on Real-Life Data. Sustainability 2025, 17, 1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldossary, M.; Alharbi, H.A.; Ayub, N. Optimizing Electric Vehicle (EV) Charging with Integrated Renewable Energy Sources: A Cloud-Based Forecasting Approach for Eco-Sustainability. Mathematics 2024, 12, 2627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Global EV Charging Station Market Is Projected to Reach USD 12.1 Billion by 2030. Available online: https://www.midaevse.com/news/global-ev-charging-station-market-is-projected-to-reach-usd-12-1-billion-by-2030/ (accessed on 8 May 2024).
- Mültin, M. ISO 15118 as the Enabler of Vehicle-to-Grid Applications. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference of Electrical and Electronic Technologies for Automotive, Milan, Italy, 9–11 July 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcaraz, C.; Lopez, J.; Wolthusen, S. OCPP Protocol: Security Threats and Challenges. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2017, 8, 2452–2459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priyasta, D.; Hadiyanto; Septiawan, R. An Overview of EV Roaming Protocols. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Energy, Environment, Epidemiology and Information System (ICENIS 2022), Semarang, Lndonesia, 9–10 August 2022; Volume 359, p. 05006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tejeida-Padilla, R.; Berdeja-Rocha, E.M.; Badillo-Piña, I.; Pérez-Matamoros, Z.; Amador-Santiago, J.E. A Comprehensive Review of Electric Charging Stations with a Systemic Approach. World Electr. Veh. J. 2024, 15, 571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, J.B.; Francisco, A.M.B.; Cabrita, C.; Monteiro, J.; Pacheco, A.; Cardoso, P.J.S. Development and Implementation of a Smart Charging System for Electric Vehicles Based on the ISO 15118 Standard. Energies 2024, 17, 3045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Kim, H.; Choi, J.Y. Improving TCP Performance in Vehicle-To-Grid (V2G) Communication. Electronics 2019, 8, 1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchner, S.R. OCPP Interoperability: A Unified Future of Charging. World Electr. Veh. J. 2024, 15, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsaini, S.; Ghogho, M.; Charaf, M.E.H. An OCPP-Based Approach for Electric Vehicle Charging Management. Energies 2022, 15, 6735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdare, S.; Brown, D.J.; Cao, Y.; Aljaidi, M.; Kumar, S.; Alanazi, R.; Jugran, M.; Vyas, P.; Kaiwartya, O. A Novel Charging Management and Security Framework for the Electric Vehicle (EV) Ecosystem. World Electr. Veh. J. 2024, 15, 392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillemin, S.; Choulet, R.; Guyot, G.; Hing, S. Electrical Vehicle Smart Charging Using the Open Charge Point Interface (OCPI) Protocol. Energies 2024, 17, 2873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agbedanu, P.R.; Yang, S.J.; Musabe, R.; Gatare, I.; Rwigema, J. A Scalable Approach to Internet of Things and Industrial Internet of Things Security: Evaluating Adaptive Self-Adjusting Memory K-Nearest Neighbor for Zero-Day Attack Detection. Sensors 2025, 25, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdusalomov, A.; Kilichev, D.; Nasimov, R.; Rakhmatullayev, I.; Im Cho, Y. Optimizing Smart Home Intrusion Detection with Harmony-Enhanced Extra Trees. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 117761–117786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erniyazov, S.; Kim, Y.M.; Jaleel, M.A.; Lim, C.G. Comprehensive Analysis and Improved Techniques for Anomaly Detection in Time Series Data with Autoencoder Models. Int. J. Adv. Sci. Eng. Inf. Technol. 2024, 14, 1861–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adewole, K.S.; Salau-Ibrahim, T.T.; Imoize, A.L.; Oladipo, I.D.; AbdulRaheem, M.; Awotunde, J.B.; Balogun, A.O.; Isiaka, R.M.; Aro, T.O. Empirical Analysis of Data Streaming and Batch Learning Models for Network Intrusion Detection. Electronics 2022, 11, 3109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilichev, D.; Kim, W. Hyperparameter Optimization for 1D-CNN-Based Network Intrusion Detection Using GA and PSO. Mathematics 2023, 11, 3724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, F.; Waqas Khan, Q.; Rizwan, A.; Alnashwan, R.; Atteia, G. A Machine Learning-Based Framework with Enhanced Feature Selection and Resampling for Improved Intrusion Detection. Mathematics 2024, 12, 1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Althiyabi, T.; Ahmad, I.; Alassafi, M.O. Enhancing IoT Security: A Few-Shot Learning Approach for Intrusion Detection. Mathematics 2024, 12, 1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakhimovich, A.M.; Kadirbergenovich, K.K.; Ishkobilovich, Z.M.; Kadirbergenovich, K.J. Logistic Regression with Multi-Connected Weights. J. Comput. Sci. 2024, 20, 1051–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, I.; Wan, Z.; Ahmad, A.; Ullah, S.S. A Hybrid Optimization Model for Efficient Detection and Classification of Malware in the Internet of Things. Mathematics 2024, 12, 1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakhimovich, M.A.; Kadirbergenovich, K.K.; Rakhmovich, O.U. Application of a Piecewise Linear Decision Tree Algorithm to Detect Phishing URLs in IoT Devices. In 12th World Conference “Intelligent System for Industrial Automation” (WCIS-2022); Aliev, R.A., Yusupbekov, N.R., Kacprzyk, J., Pedrycz, W., Babanli, M.B., Sadikoglu, F.M., Turabdjanov, S.M., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 47–54. [Google Scholar]
- Bifet, A.; Gavaldà, R. Learning from Time-Changing Data with Adaptive Windowing. In Proceedings of the 2007 SIAM International Conference on Data Mining (SDM), Minneapolis, MI, USA, 26–28 April 2007; pp. 443–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alalwany, E.; Alsharif, B.; Alotaibi, Y.; Alfahaid, A.; Mahgoub, I.; Ilyas, M. Stacking Ensemble Deep Learning for Real-Time Intrusion Detection in IoMT Environments. Sensors 2025, 25, 624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Ma, Z.; Ren, Z.; Wang, H.; Zhang, C.; Wan, Q.; Sun, D. Design of an Automatic Classification System for Educational Reform Documents Based on Naive Bayes Algorithm. Mathematics 2024, 12, 1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basnet, M.; Hasan Ali, M. Exploring cybersecurity issues in 5G enabled electric vehicle charging station with deep learning. IET Gener. Transm. Distrib. 2021, 15, 3435–3449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suriya, N.; Vijay Shankar, S. A novel ensembling of deep learning based intrusion detection system and scroll chaotic countermeasures for electric vehicle charging system. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2022, 43, 4789–4801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, S.; Badsha, S.; Sengupta, S.; Khalil, I.; Atiquzzaman, M. An Intelligent Privacy Preservation Scheme for EV Charging Infrastructure. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2023, 19, 1238–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ElKashlan, M.; Aslan, H.; Said Elsayed, M.; Jurcut, A.D.; Azer, M.A. Intrusion Detection for Electric Vehicle Charging Systems (EVCS). Algorithms 2023, 16, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ElKashlan, M.; Elsayed, M.S.; Jurcut, A.D.; Azer, M. A Machine Learning-Based Intrusion Detection System for IoT Electric Vehicle Charging Stations (EVCSs). Electronics 2023, 12, 1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekkaoui, K. Enhancing V2G Network Security: A Novel Cockroach Behavior-Based Machine Learning Classifier to Mitigate MitM and DoS Attacks. Adv. Electr. Comput. Eng. 2024, 24, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, R.; Selvan, M.P. A hybrid deep learning-based intrusion detection system for EV and UAV charging stations. Automatika 2024, 65, 1558–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilichev, D.; Turimov, D.; Kim, W. Next–Generation Intrusion Detection for IoT EVCS: Integrating CNN, LSTM, and GRU Models. Mathematics 2024, 12, 571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gul, M. Khan, O.; Elghitani, F.; Youssef, A.; Salama, M.; El-Saadany, E.F. Real-Time Congestion-Aware Charging Station Assignment Model for EVs. IEEE Internet Things J. 2024, 11, 11723–11736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, A.; Saha, R.; Kumar, G.; Conti, M. PETRAK: A solution against DDoS attacks in vehicular networks. Comput. Commun. 2024, 221, 142–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaldız, A.; Gökçek, T.; Ateş, Y.; Erdinç, O. Overview and advancement of power system topology addressing pre- and post-event strategies under abnormal operating conditions. Sustain. Energy Grids Netw. 2024, 40, 101562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Togbe, M.U.; Chabchoub, Y.; Boly, A.; Barry, M.; Chiky, R.; Bahri, M. Anomalies Detection Using Isolation in Concept-Drifting Data Streams. Computers 2021, 10, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shern, S.J.; Sarker, M.T.; Ramasamy, G.; Thiagarajah, S.P.; Al Farid, F.; Suganthi, S.T. Artificial Intelligence-Based Electric Vehicle Smart Charging System in Malaysia. World Electr. Veh. J. 2024, 15, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, A.; Osamy, W.; Alfawaz, O.; Khedr, A.M. EDCCS: Effective deterministic clustering scheme based compressive sensing to enhance IoT based WSNs. Wirel. Netw. 2022, 28, 2375–2391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Bifet, A.; Zhang, X.; Weiss, J.C.; Nejdl, W. FARF: A Fair and Adaptive Random Forests Classifier. In Advances in Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining; Karlapalem, K., Cheng, H., Ramakrishnan, N., Agrawal, R.K., Reddy, P.K., Srivastava, J., Chakraborty, T., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 245–256. [Google Scholar]
- Charusheela, C.; Lalitha, L. A comparative analysis of algorithm for detecting concept-drift. AIP Conf. Proc. 2024, 2742, 020090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Shin, M. TestShark: A Passive Conformance Testing System for ISO 15118 Using Wireshark. Energies 2024, 17, 5833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.; Liu, B.; Shao, C.; Yang, X.; Xu, S.; Zhu, C.; Yu, H. Multi-Label Learning with Distribution Matching Ensemble: An Adaptive and Just-In-Time Weighted Ensemble Learning Algorithm for Classifying a Nonstationary Online Multi-Label Data Stream. Symmetry 2025, 17, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Leng, X.; Wang, L.; Wang, N. Research on Fine-Tuning Optimization Strategies for Large Language Models in Tabular Data Processing. Biomimetics 2024, 9, 708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buedi, E.D.; Ghorbani, A.A.; Dadkhah, S.; Ferreira, R.L. Enhancing EV Charging Station Security Using a Multi-dimensional Dataset: CICEVSE2024. In Proceedings of the Data and Applications Security and Privacy XXXVIII, San Jose, CA, USA, 15–17 July 2024; Ferrara, A.L., Krishnan, R., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 171–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montiel, J.; Halford, M.; Mastelini, S.M.; Bolmier, G.; Sourty, R.; Vaysse, R.; Zouitine, A.; Gomes, H.M.; Read, J.; Abdessalem, T.; et al. River: Machine learning for streaming data in Python. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2021, 22, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Gomes, H.M.; Bifet, A.; Read, J.; Barddal, J.P.; Enembreck, F.; Pfharinger, B.; Holmes, G.; Abdessalem, T. Adaptive random forests for evolving data stream classification. Mach. Learn. 2017, 106, 1469–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozömeroğlu, H.; Gürkaş-Aydın, Z. Elektrikli Araç Şarj İstasyonlarının Siber Güvenliği: CIC-EVSE 2024 Veri Kümesi ile IDS Sistemlerinin Performans Analizi. In Proceedings of the 2024 17th International Conference on Information Security and Cryptology (ISCTürkiye), Ankara, Turkiye, 16–17 October 2024; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purohit, S.; Govindarasu, M. FL-EVCS: Federated Learning based Anomaly Detection for EV Charging Ecosystem. In Proceedings of the 2024 33rd International Conference on Computer Communications and Networks (ICCCN), Kailua-Kona, HI, USA, 29–31 July 2024; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Chayan, M.M.H.; Mehrin, K.; Sultana, A.; Hamed, M.M. Explainable Deep Learning for Cyber Attack Detection in Electric Vehicle Charging Stations. In Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Networking, Systems, and Security, Khulna Karak, Bangladesh, 19–21 December 2024; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benfarhat, I.; Goh, V.T.; Lim Siow, C.; Sheraz, M.; Chee Chuah, T. Temporal Convolutional Network Approach to Secure Open Charge Point Protocol (OCPP) in Electric Vehicle Charging. IEEE Access 2025, 13, 15272–15289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, H.M.; Yoo, J.; Agarwal, S. The Improved Network Intrusion Detection Techniques Using the Feature Engineering Approach with Boosting Classifiers. Mathematics 2024, 12, 3909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binbusayyis, A. Reinforcing Network Security: Network Attack Detection Using Random Grove Blend in Weighted MLP Layers. Mathematics 2024, 12, 1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, X.; Pan, M.; Chen, X.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, J.; Li, D.; Guo, B.; Zhu, Z. Research on Virus Propagation Network Intrusion Detection Based on Graph Neural Network. Mathematics 2024, 12, 1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlGhamdi, R. Design of Network Intrusion Detection System Using Lion Optimization-Based Feature Selection with Deep Learning Model. Mathematics 2023, 11, 4607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).