RMT: Real-Time Multi-Level Transformer for Detecting Downgrades of User Experience in Live Streams
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- We developed the Live Stream Quality of Experience (LSQE) dataset, which includes five million records from over 300,000 users in a 7-day period.
- We introduced a device-mask pretraining (DMP) method that applies a pretraining technique to cross-layer network device data, enabling a better understanding of cross-layer device correlations.
- We proposed a real-time QoE downgrade event prediction model based on a multi-layer Transformer. Experimental results show that the DMP task significantly improves the model’s prediction accuracy, and the proposed method outperforms baseline approaches.
2. Related Works
2.1. QoE/QoS Prediction for Live Video Quality Prediction
2.2. Transformer
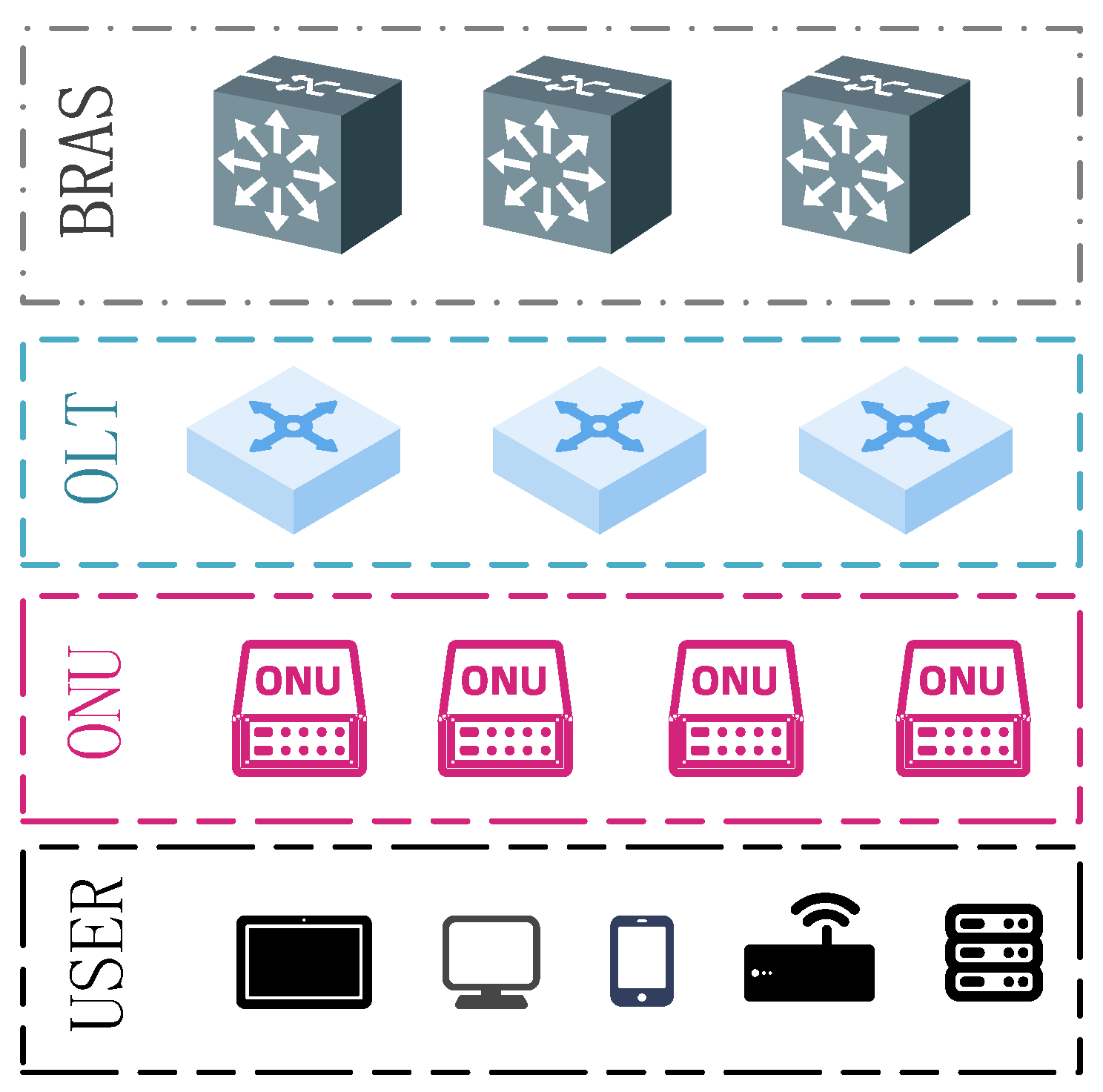
3. Live Stream Quality of Experience Dataset
- Table 1: BRAS layer—the BRAS (Broadband Remote Access Server) layer attributes encompass device-specific information (IP, model number, port/slot), traffic data (inbound/outbound rate differences, CRC error counts), and bandwidth metrics (inbound/outbound rates, utilization percentages). Additionally, it includes received optical power details (with maximum, minimum, and average power levels) to monitor the optical signal and a “QoE downgrade event Flag” to identify instances of degraded service quality.
- Table 2: OLT layer—attributes of the OLT (Optical Line Terminal) layer are categorized into device info and transmission details. Device info includes port IP, location city, device ID, and board performance. Transmission metrics cover inbound/outbound traffic rates, port bandwidth, and bandwidth utilization. It also provides optical power levels for both received and transmitted signals, contributing to assessing network performance, with a “QoE downgrade Flag” to denote QoE downgrade events.
- Table 3: ONU layer—the ONU (Optical Network Unit) layer attributes are broken down into device info (device ID, local identifier, city code, CPU, and memory usage) and transmission metrics, similar to the OLT layer. The transmission data include received and transmitted optical power levels, port bandwidth, bandwidth utilization, and the maximum number of user devices supported. Like the other layers, the table features a “QoE downgrade Flag” to denote QoE downgrade events.
| BRAS Layer | ||
|---|---|---|
| No. | Attributes | Description |
| 1 | BRAS IP | BRAS device data |
| 2 | BRAS Device IP | |
| 3 | BRAS Model Number | |
| 4 | BRAS Port/slot | |
| 5 | Inbound Rate Difference (%) | BRAS traffic, error rate, utilization data |
| 6 | Outbound Rate Difference (%) | |
| 7 | CRC Inbound Error Count | |
| 8 | CRC Outbound Error Count | |
| 9 | Inbound Rate (Gb/s) | |
| 10 | Outbound Rate (Gb/s) | |
| 11 | Bandwidth Utilization (%) | |
| 12 | Received Optical Power (dBm) | BRAS received optical power |
| 13 | Maximum Received Optical Power (dBm) | |
| 14 | Minimum Received Optical Power (dBm) | |
| 15 | Average Received Optical Power (dBm) | |
| 16 | QoE Downgrade Event Flag | Label |
| OLT Layer | ||
|---|---|---|
| No. | Attributes | Description |
| 1 | Port IP | Device info |
| 2 | Location City | |
| 3 | Device Id | |
| 4 | OLT Single Board Performance | |
| 5 | Port ID | OLT transmission info, including received and transmitted optical power |
| 6 | Inbound Rate (Gb/s) | |
| 7 | Outbound Rate (Gb/s) | |
| 8 | Port Bandwidth (Gb/s) | |
| 9 | Bandwidth Utilization (%) | |
| 10 | Received Optical Power (dBm) | |
| 11 | Transmitted Optical Power (dBm) | |
| 12 | QoE Downgrade Event Flag | Label |
| ONU Layer | ||
|---|---|---|
| No. | Attributes | Description |
| 1 | Device Id | Device info |
| 2 | Local Identifier | |
| 3 | City Code | |
| 4 | CPU Usage (%) | |
| 5 | Memory Usage (%) | |
| 6 | Received Optical Power (dBm) | ONU transmission info, including input and output. |
| 7 | Transmitted Optical Power (dBm) | |
| 8 | Port Bandwidth (Gb/s) | |
| 9 | Bandwidth Utilization (%) | |
| 10 | Max User Device Count | |
| 11 | QoE Downgrade Event Flag | Label |
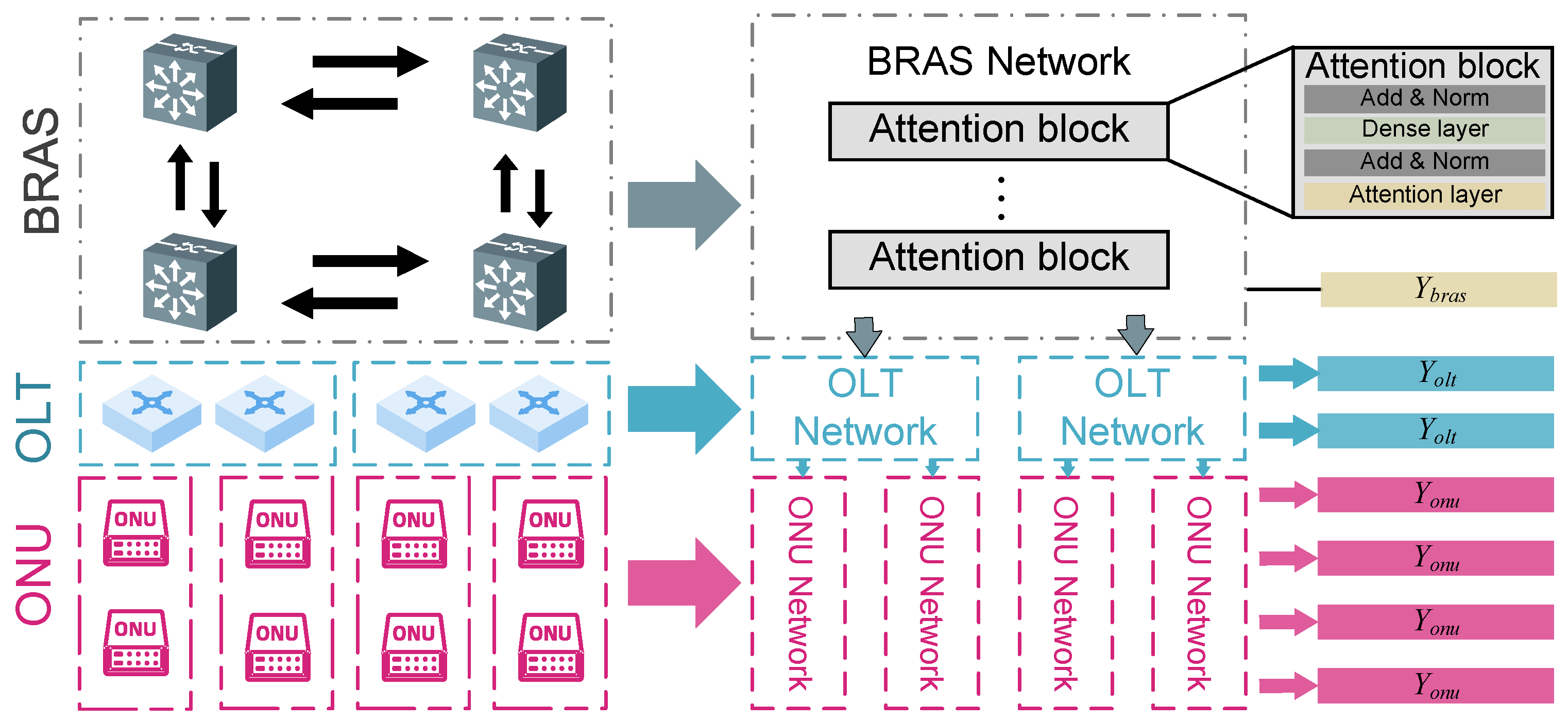
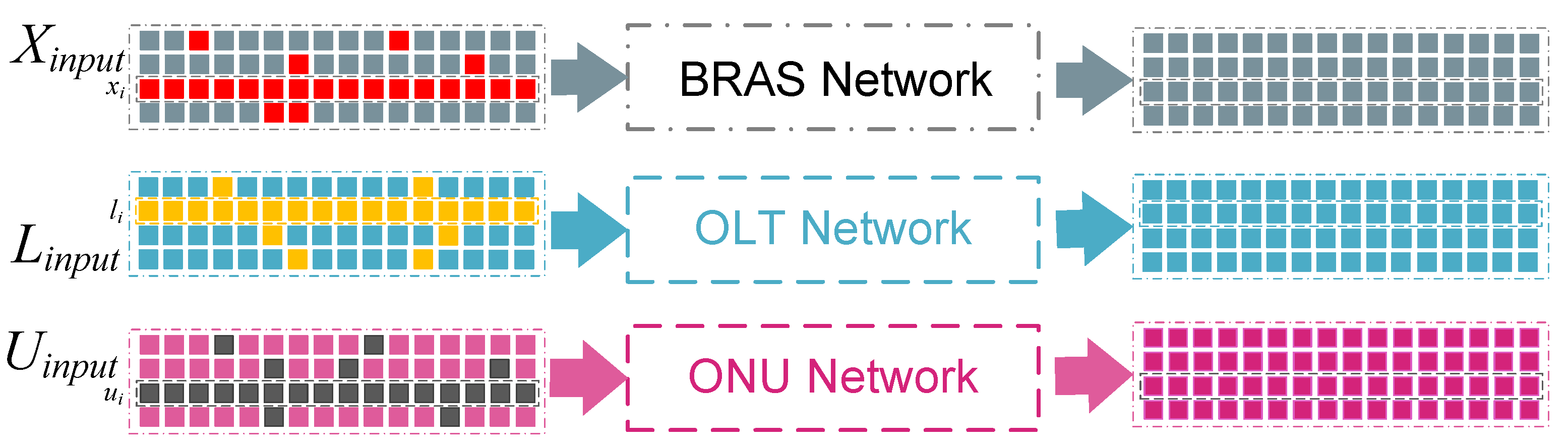
4. Multi-Level Transformer
4.1. BRAS, OLT, and ONU Network
4.2. Device-Masked Pretraining
4.3. Time-Delayed Fine-Tuning
5. Experiments
5.1. Experiments Settings and Details
- BRNN [15]: Bayesian-regularized neural networks for predicting QoE status, using patterns derived from objective QoE measurements and network statistics collected by the SDN controller to classify multimedia traffic.
- DRL [16]: An adaptive multimedia traffic control mechanism based on Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL), which integrates deep learning and reinforcement learning to learn from rewards through trial and error.
- CNN [12]: A hybrid model combining a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN), a recurrent neural network, and a Gaussian process classifier.
- LSTM [12]: An LSTM-based binary classifier that differentiates between live and on-demand streams in real-time with an accuracy exceeding 95%.
5.2. Experimental Results
5.2.1. Comparison with Other Methods
5.2.2. Ablation Study
6. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Farhady, H.; Lee, H.; Nakao, A. Software-Defined Networking: A survey. Comput. Netw. 2015, 81, 79–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, W.; Wen, Y.; Foh, C.H.; Niyato, D.; Xie, H. A Survey on Software-Defined Networking. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2015, 17, 27–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadros, C.N.; Rizk, M.R.; Mokhtar, B.M. Software defined network-based management for enhanced 5G network services. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 53997–54008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, M. Software-defined network function virtualization: A survey. IEEE Access 2015, 3, 2542–2553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eramo, V.; Miucci, E.; Ammar, M.; Lavacca, F.G. An approach for service function chain routing and virtual function network instance migration in network function virtualization architectures. IEEE/ACM Trans. Netw. 2017, 25, 2008–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begović, M.; Čaušević, S.; Avdagić-Golub, E. QoS Management in Software Defined Networks for IoT Environment: An Overview. Int. J. Qual. Res. 2021, 15, 171–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Said, O. Design and performance evaluation of QoE/QoS-oriented scheme for reliable data transmission in Internet of Things environments. Comput. Commun. 2022, 189, 158–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varyani, N.; Zhang, Z.L.; Dai, D. QROUTE: An Efficient Quality of Service (QoS) Routing Scheme for Software-Defined Overlay Networks. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 104109–104126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Lin, C.; Siahaan, E.; Chen, B.; Chuang, H. Mixed Sound Event Verification on Wireless Sensor Network for Home Automation. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2014, 10, 803–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsolkas, D.; Liotou, E.; Passas, N.; Merakos, L. A survey on parametric QoE estimation for popular services. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 2017, 77, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Choi, S.G. A study on a QoS/QoE correlation model for QoE evaluation on IPTV service. In Proceedings of the The 12th International Conference on Advanced Communication Technology (ICACT), Gangwon-Do, Republic of Korea, 7–10 February 2010; Volume 2, pp. 1377–1382. [Google Scholar]
- Lopez-Martin, M.; Carro, B.; Lloret, J.; Egea, S.; Sanchez-Esguevillas, A. Deep Learning Model for Multimedia Quality of Experience Prediction Based on Network Flow Packets. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2018, 56, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehr, S.K.; Jogalekar, P.; Medhi, D. Moving QoE for monitoring DASH video streaming: Models and a study of multiple mobile clients. J. Internet Serv. Appl. 2021, 12, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoßfeld, T.; Schatz, R.; Biersack, E.; Plissonneau, L. Internet video delivery in youtube: From traffic measurements to quality of experience. In Lecture Notes in Computer Science (Including Subseries Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence and Lecture Notes in 396 Bioinformatics); Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; Volume 7754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canovas, A.; Rego, A.; Romero, O.; Lloret, J. A robust multimedia traffic SDN-Based management system using patterns and models of QoE estimation with BRNN. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 2020, 150, 102498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Yuan, T.; Qiao, G.; Ren, Y. Deep Reinforcement Learning for Multimedia Traffic Control in Software Defined Networking. IEEE Netw. 2018, 32, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreolo, M.S.; Fabrega, J.M.; Martín, L.; Christodoulopoulos, K.; Varvarigos, E.; Fernández-Palacios, J.P. Flexgrid technologies enabling BRAS centralization in MANs. J. Opt. Commun. Netw. 2016, 8, A64–A75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, L.; Singh, A.; Sharma, V. Analysis on multiple optical line terminal passive optical network based open access network. Front. Optoelectron. 2019, 12, 208–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamza, B.J.; Saad, W.K.; Shayea, I.; Ahmad, N.; Mohamed, N.; Nandi, D.; Gholampour, G. Performance enhancement of SCM/WDM-RoF-XGPON system for bidirectional transmission with square root module. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 49487–49503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Butt, R.A.; Aslam, M.I. Simultaneous Upstream and Inter Optical Network Unit Communication for Next Generation PON. Eng. Proc. 2023, 32, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibarrola, E.; Davis, M.; Voisin, C.; Close, C.; Cristobo, L. A Machine Learning Management Model for QoE Enhancement in Next-Generation Wireless Ecosystems. In Proceedings of the 2018 ITU Kaleidoscope: Machine Learning for a 5G Future (ITU K), Santa Fe, Argentina, 26–28 November 2018; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, M.; Zhang, J.; Xu, K.; Zhu, L.; Liu, J.; Du, X. DeepQoE: Real-time Measurement of Video QoE from Encrypted Traffic with Deep Learning. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/ACM 28th International Symposium on Quality of Service (IWQoS), Hangzhou, China, 15–17 June 2020; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seshadrinathan, K.; Soundararajan, R.; Bovik, A.C.; Cormack, L.K. Study of subjective and objective quality assessment of video. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2010, 19, 1427–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phuong, M.; Lampert, C.H. The inductive bias of ReLU networks on orthogonally separable data. In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Learning Representations, ICLR 2021, Virtual Event, 3–7 May 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Yu, L.C.; Lai, K.R.; Zhang, X. Dimensional sentiment analysis using a regional CNN-LSTM model. In Proceedings of the 54th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, ACL 2016—Short Papers, Berlin, Germany, 7–12 August 2016; pp. 225–230. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Yu, L.C.; Lai, K.R.; Zhang, X. Investigating dynamic routing in tree-structured LSTM for sentiment analysis. In Proceedings of the 2019 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing and the 9th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing (EMNLP-IJCNLP); Association for Computational Linguistics: Hongkong, China, 2019; pp. 3432–3437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, L.; Abe, H.; Lee, C. RNN-based approach to TCP throughput prediction. In Proceedings of the 2020 Eighth International Symposium on Computing and Networking Workshops (CANDARW), Naha, Japan, 24–27 November 2020; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 391–395. [Google Scholar]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, Ł.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is all you need. In Proceedings of the 31st Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS 2017), Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017; pp. 5998–6009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devlin, J.; Chang, M.W.W.; Lee, K.; Toutanova, K. BERT: Pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding. In Proceedings of the 2019 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies (NAACL-HLT 2019); Association for Computational Linguistics: Kerrville, TX, USA, 2019; Volume 1, pp. 4171–4186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Zhou, P.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, Z.; Ju, Q.; Deng, H.; Wang, P. K-BERT: Enabling Language Representation with Knowledge Graph. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI-2020), New York, NY, USA, 7–12 February 2020; pp. 2901–2908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reimers, N.; Gurevych, I. Sentence-BERT: Sentence Embeddings using Siamese BERT-Networks. In Proceedings of the 2019 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing and the 9th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing, EMNLP-IJCNLP 2019, Hong Kong, China, 3–7 November 2019; Inui, K., Jiang, J., Ng, V., Wan, X., Eds.; Association for Computational Linguistics: Kerrville, TX, USA, 2019; pp. 3980–3990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.; Liao, L.C. Lexicon-based prompt for financial dimensional sentiment analysis. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 244, 122936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achiam, J.; Adler, S.; Agarwal, S.; Ahmad, L.; Akkaya, I.; Aleman, F.L.; Almeida, D.; Altenschmidt, J.; Altman, S.; Anadkat, S.; et al. Gpt-4 technical report. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2303.08774. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, T.B.; Mann, B.; Ryder, N.; Subbiah, M.; Kaplan, J.D.; Dhariwal, P.; Neelakantan, A.; Shyam, P.; Sastry, G.; Askell, A.; et al. Language models are few-shot learners. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2020, 33, 1877–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, L.; Wu, J.; Jiang, X.; Almeida, D.; Wainwright, C.; Mishkin, P.; Zhang, C.; Agarwal, S.; Slama, K.; Ray, A.; et al. Training language models to follow instructions with human feedback. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; Koyejo, S., Mohamed, S., Agarwal, A., Belgrave, D., Cho, K., Oh, A., Eds.; Curran Associates, Inc.: Red Hook, NY, USA, 2022; Volume 35, pp. 27730–27744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Lin, W.; Lin, S.; Wang, J.; Yu, L.-C. A Multi-dimensional Relation Model for Dimensional Sentiment Analysis. Inform. Sci. 2021, 579, 832–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Chen, X.; Xie, S.; Li, Y.; Dollar, P.; Girshick, R. Masked Autoencoders Are Scalable Vision Learners. In Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition(CVPR 2022), New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; IEEE Computer Society: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2022; pp. 15979–15988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.C.; Zhang, C.C.; Song, J.; Seon, J.; Yi, K.; Zhang, K.; Kweon, I.S.; Yi, J.S.K.; Zhang, K.; Kweon, I.S. A Survey on Masked Autoencoder for Self-supervised Learning in Vision and Beyond. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2208.00173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Yin, J.L.; Chen, B.H.; Liu, X. SRoUDA: Meta Self-Training for Robust Unsupervised Domain Adaptation. Proc. AAAI Conf. Artif. Intell. 2023, 37, 3852–3860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, C.; Cai, T.; Luo, S.; Zheng, S.; Ke, G.; He, D.; Shen, Y.; Liu, T.Y. Do Transformers Really Perform Badly for Graph Representation? In Proceedings of the Thirty-Fifth Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, New Orleans, LA, USA, 28 November–9 December 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Zheng, S.; Ke, G.; Shen, Y.; You, J.; He, J.; Luo, S.; Liu, C.; He, D.; Liu, T.Y. Benchmarking Graphormer on Large-Scale Molecular Modeling Datasets. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2203.04810. [Google Scholar]
| Layer | Method | Acc | Pre | Rec | F1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ONU | CNN | 0.715 | 0.641 | 0.767 | 0.699 |
| LSTM | 0.762 | 0.687 | 0.822 | 0.749 | |
| BRNN | 0.748 | 0.664 | 0.819 | 0.734 | |
| DRL | 0.776 | 0.712 | 0.832 | 0.768 | |
| MT(Ours) | 0.806 | 0.725 | 0.872 | 0.792 | |
| OLT | CNN | 0.665 | 0.611 | 0.727 | 0.659 |
| LSTM | 0.692 | 0.627 | 0.762 | 0.684 | |
| BRNN | 0.708 | 0.634 | 0.768 | 0.694 | |
| DRL | 0.716 | 0.682 | 0.802 | 0.718 | |
| MT(Ours) | 0.766 | 0.695 | 0.842 | 0.732 | |
| BRAS | CNN | 0.745 | 0.671 | 0.817 | 0.739 |
| LSTM | 0.822 | 0.747 | 0.872 | 0.809 | |
| BRNN | 0.808 | 0.694 | 0.879 | 0.774 | |
| DRL | 0.836 | 0.762 | 0.872 | 0.798 | |
| MT(Ours) | 0.856 | 0.765 | 0.912 | 0.822 |
| Layer | Method | Acc | Pre | Rec | F1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ONU | MT w/o DMP | 0.788 | 0.712 | 0.855 | 0.778 |
| MT w/ DMP | 0.806 | 0.725 | 0.872 | 0.792 | |
| OLT | MT w/o DMP | 0.756 | 0.682 | 0.832 | 0.725 |
| MT w/ DMP | 0.766 | 0.695 | 0.842 | 0.732 | |
| BRAS | MT w/o DMP | 0.836 | 0.762 | 0.872 | 0.798 |
| MT w/ DMP | 0.856 | 0.765 | 0.912 | 0.822 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, W.; Li, J.-P.; Li, X.-Y.; Lin, X.-Q. RMT: Real-Time Multi-Level Transformer for Detecting Downgrades of User Experience in Live Streams. Mathematics 2025, 13, 834. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13050834
Jiang W, Li J-P, Li X-Y, Lin X-Q. RMT: Real-Time Multi-Level Transformer for Detecting Downgrades of User Experience in Live Streams. Mathematics. 2025; 13(5):834. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13050834
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Wei, Jian-Ping Li, Xin-Yan Li, and Xuan-Qi Lin. 2025. "RMT: Real-Time Multi-Level Transformer for Detecting Downgrades of User Experience in Live Streams" Mathematics 13, no. 5: 834. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13050834
APA StyleJiang, W., Li, J.-P., Li, X.-Y., & Lin, X.-Q. (2025). RMT: Real-Time Multi-Level Transformer for Detecting Downgrades of User Experience in Live Streams. Mathematics, 13(5), 834. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13050834






