A Robust Optimization Approach for E-Bus Charging and Discharging Scheduling with Vehicle-to-Grid Integration
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
3. Deterministic Optimization Model
3.1. Problem Description
3.2. Deterministic Optimization Model
4. Robust Optimization Model
4.1. Uncertainty Sets
4.2. Robust Optimization Model
4.3. Tractable Reformulation of Robust Counterparts
5. Computational Experiments
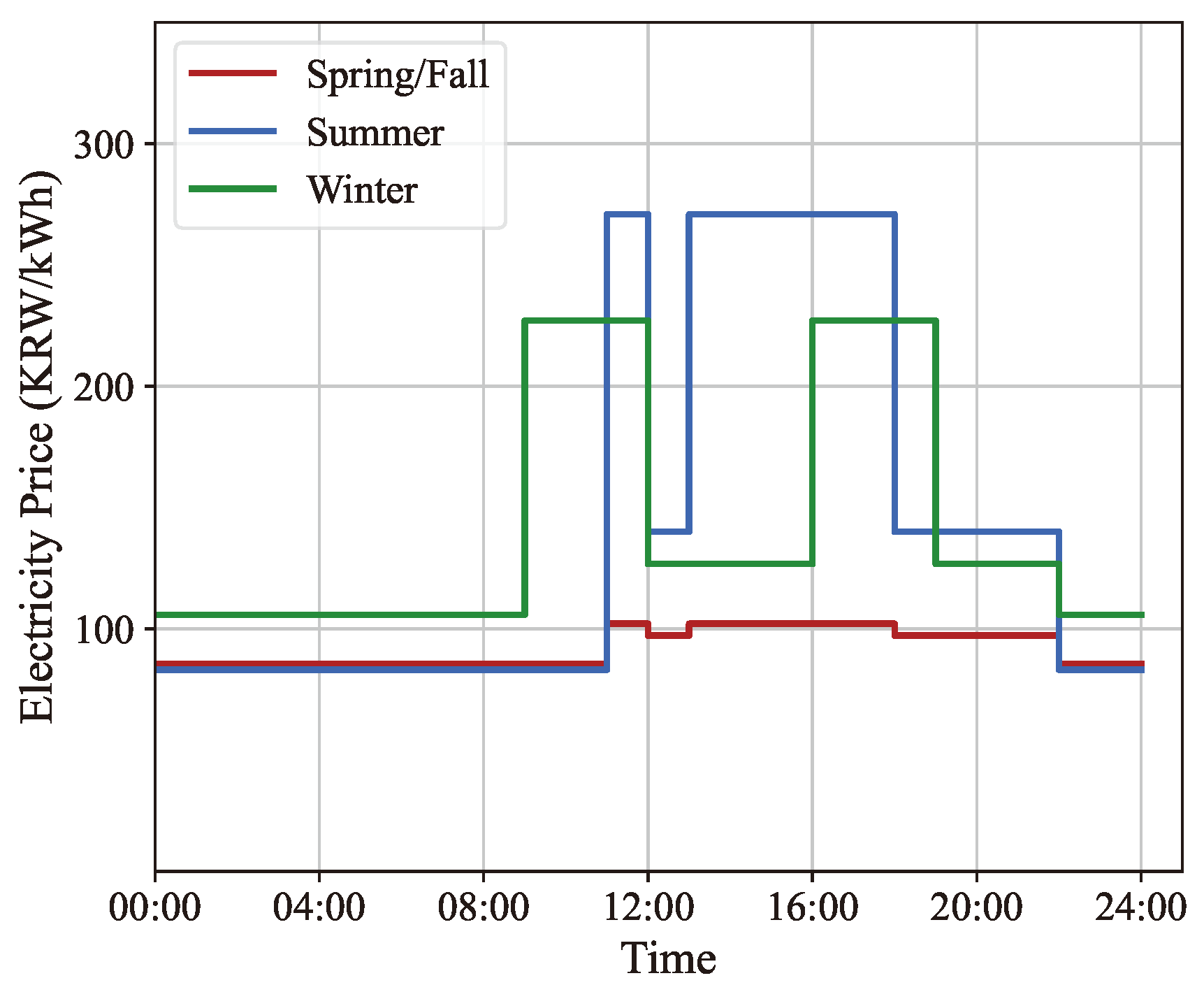
5.1. Test Instances and Parameters
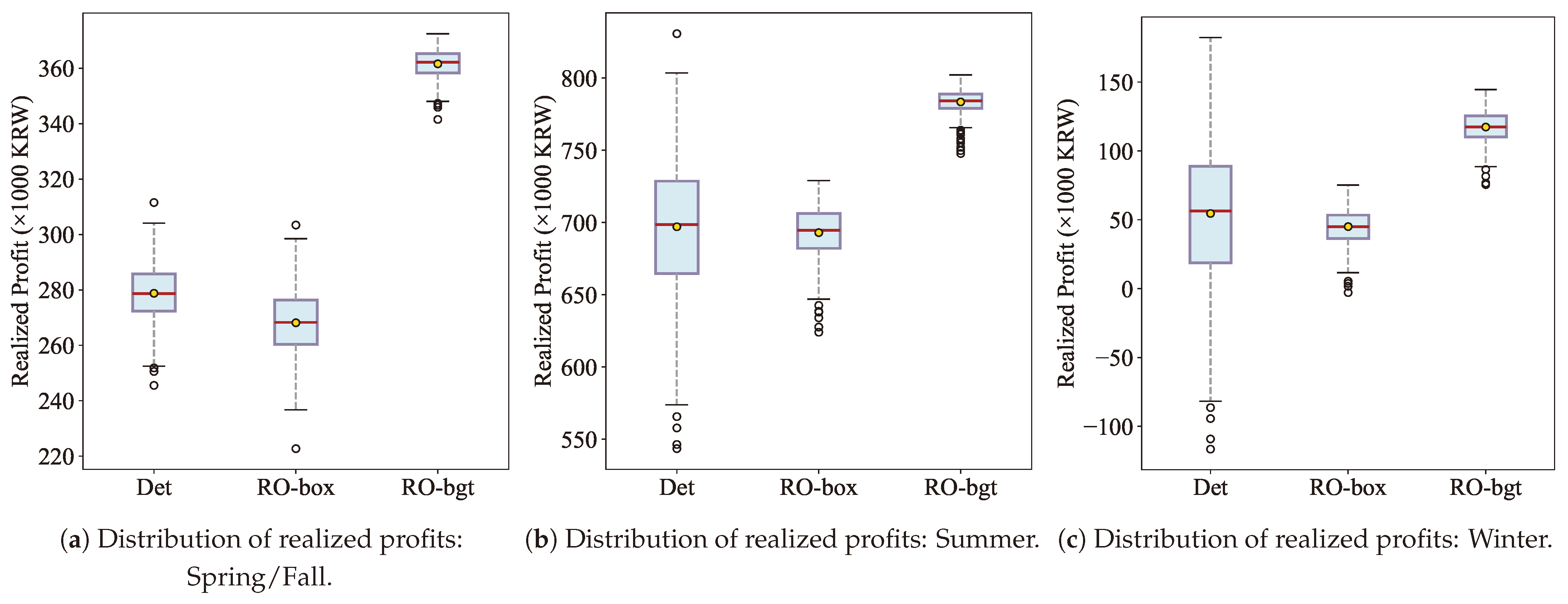
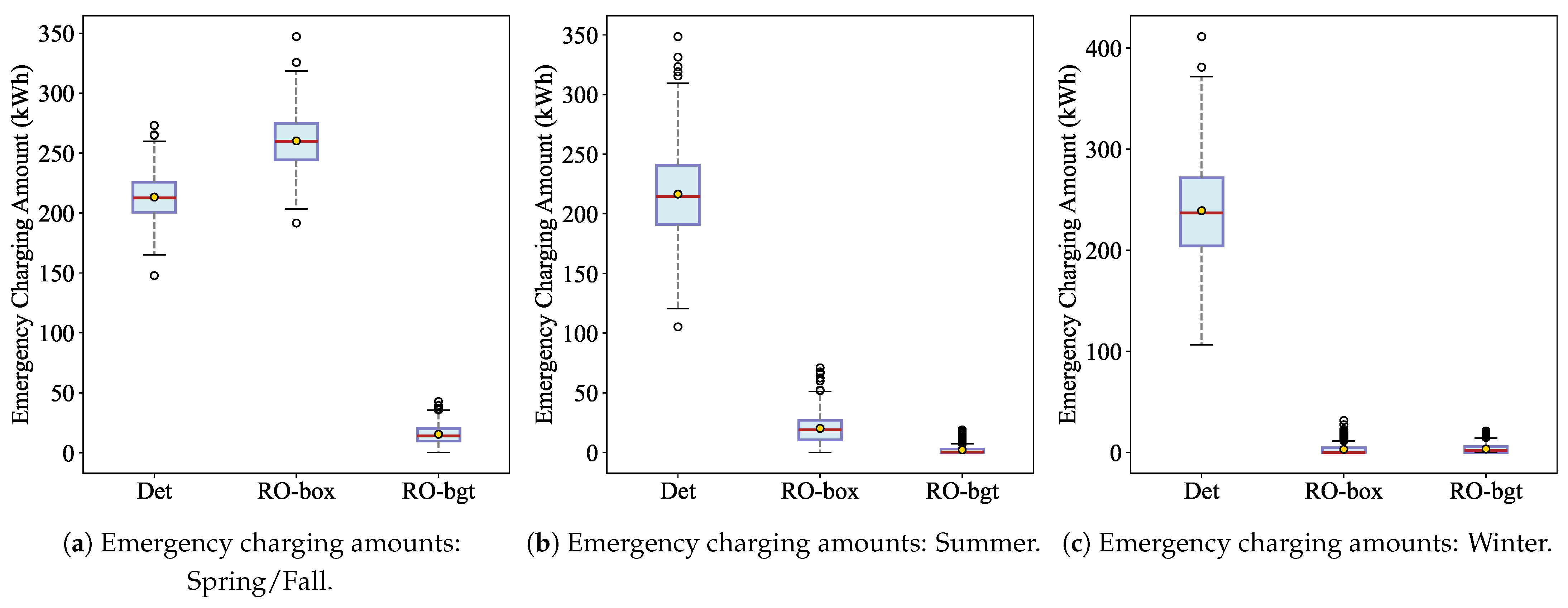
5.2. Performance of Robust Optimization Approach
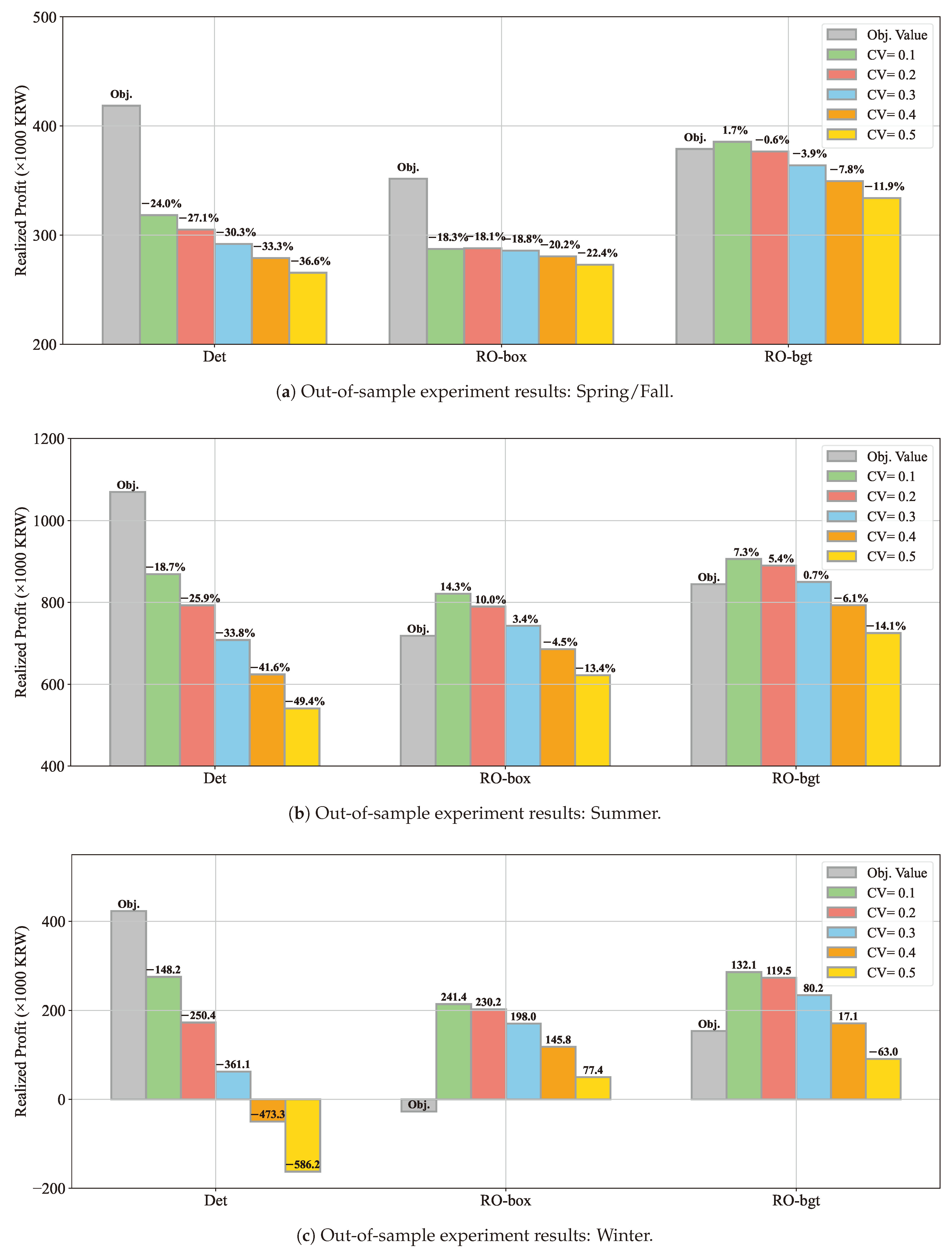
5.3. Out-of-Sample Validation
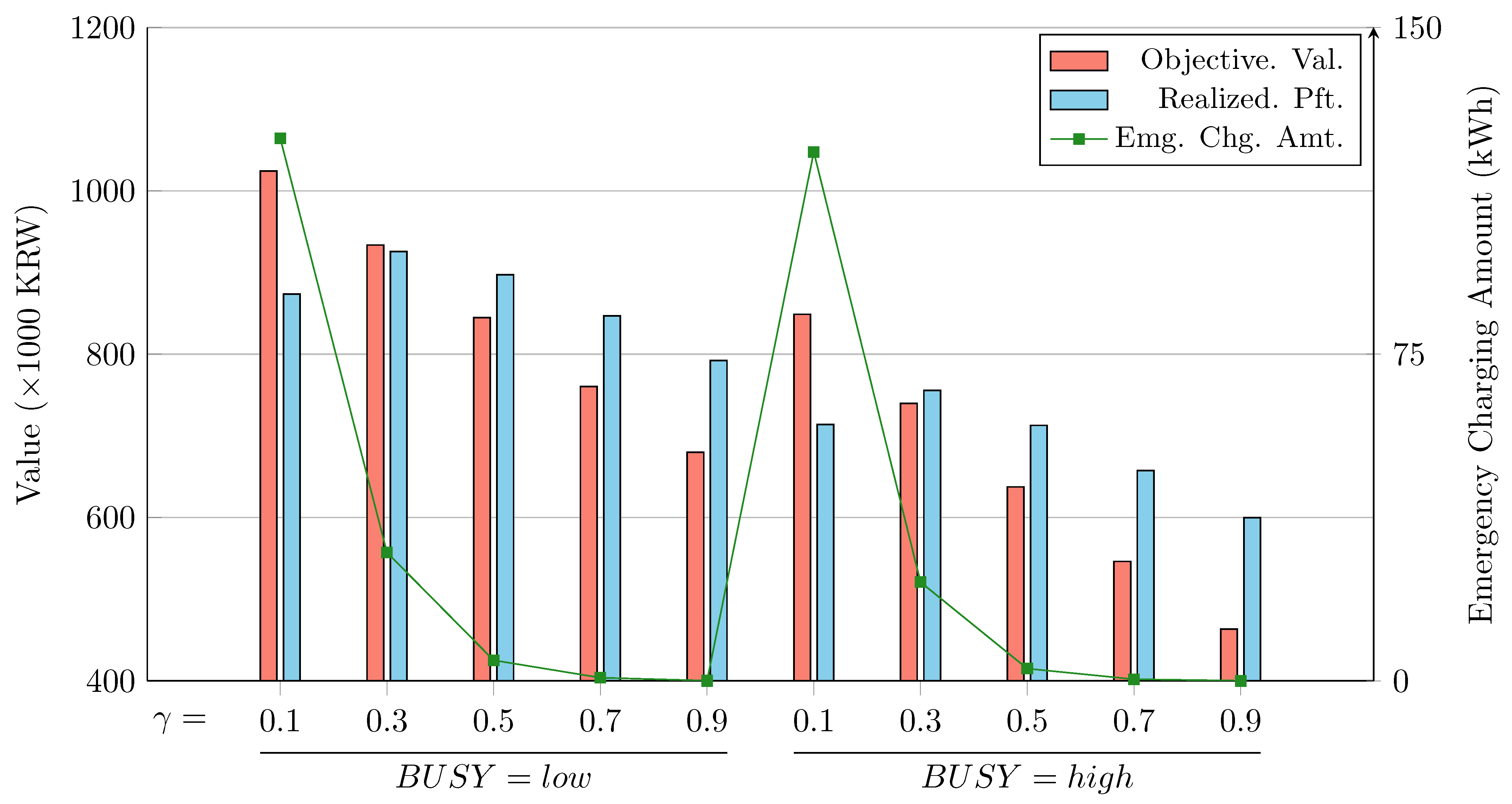
5.4. Impact of Budget Parameters
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Requia, W.J.; Mohamed, M.; Higgins, C.D.; Arain, A.; Ferguson, M. How clean are electric vehicles? Evidence-based review of the effects of electric mobility on air pollutants, greenhouse gas emissions and human health. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 185, 64–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Energy Agency. Global EV Outlook 2024. Available online: https://www.iea.org/reports/global-ev-outlook-2024 (accessed on 20 April 2025).
- Siemens. Siemens Technology Becoming Part of State-of-the-Art Bus Depot in Hamburg. Available online: https://press.siemens.com/global/en/pressrelease/siemens-technology-becoming-part-state-art-bus-depot-hamburg (accessed on 20 April 2025).
- Tribune, Q. Lusail Bus Depot, One of the World’s Largest E-Bus Depot, Inaugurated. Available online: https://www.qatar-tribune.com/article/26042/latest-news/lusail-bus-depot-one-of-the-worlds-largest-e-bus-depot-inaugurated (accessed on 20 April 2025).
- Ravi, S.S.; Aziz, M. Utilization of electric vehicles for vehicle-to-grid services: Progress and perspectives. Energies 2022, 15, 589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mal, S.; Chattopadhyay, A.; Yang, A.; Gadh, R. Electric vehicle smart charging and vehicle-to-grid operation. Int. J. Parallel Emergent Distrib. Syst. 2013, 28, 249–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guille, C.; Gross, G. A conceptual framework for the vehicle-to-grid (V2G) implementation. Energy Policy 2009, 37, 4379–4390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, J.; He, L.; Li, C.; Cao, Y.; Wang, J.; Fang, B.; Zeng, L.; Xiao, G. Coordinated control for large-scale EV charging facilities and energy storage devices participating in frequency regulation. Appl. Energy 2014, 123, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, L.; Zheng, Y.; Xiao, X.; Chan, C. Optimal scheduling for vehicle-to-grid operation with stochastic connection of plug-in electric vehicles to smart grid. Appl. Energy 2015, 146, 150–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinson, P.; Madsen, H. Benefits and challenges of electrical demand response: A critical review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 39, 686–699. [Google Scholar]
- Siano, P. Demand response and smart grids—A survey. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 30, 461–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asamer, J.; Graser, A.; Heilmann, B.; Ruthmair, M. Sensitivity analysis for energy demand estimation of electric vehicles. Transp. Res. Part Transp. Environ. 2016, 46, 182–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelletier, S.; Jabali, O.; Laporte, G. The electric vehicle routing problem with energy consumption uncertainty. Transp. Res. Part B Methodol. 2019, 126, 225–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, C.; Tang, J.; Ghosh, P. Optimizing electric vehicle charging: A customer’s perspective. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2013, 62, 2919–2927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Álvarez, J.; González, M.A.; Vela, C.R. Metaheuristics for solving a real-world electric vehicle charging scheduling problem. Appl. Soft Comput. 2018, 65, 292–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Lin, G.; Huang, S.; Zhou, Y.; Li, Y.; Rehtanz, C. Optimal EV charging scheduling by considering the limited number of chargers. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2020, 7, 1112–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honarmand, M.; Zakariazadeh, A.; Jadid, S. Optimal scheduling of electric vehicles in an intelligent parking lot considering vehicle-to-grid concept and battery condition. Energy 2014, 65, 572–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.; Ren, Y.; Pan, R.; Wang, L.; Chen, J. Fair and efficient electric vehicle charging scheduling optimization considering the maximum individual waiting time and operating cost. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2023, 72, 9808–9820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, M.; Kodaira, D.; Jin, Y.; Son, H.; Han, S. Development of an efficient vehicle-to-grid method for massive electric vehicle aggregation. Energy Rep. 2024, 11, 1659–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Liu, Z.; Song, Z. Optimal charging scheduling and management for a fast-charging battery electric bus system. Transp. Res. Part E Logist. Transp. Rev. 2020, 142, 102056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagherinezhad, A.; Palomino, A.D.; Li, B.; Parvania, M. Spatio-temporal electric bus charging optimization with transit network constraints. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2020, 56, 5741–5749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbrugge, B.; Rauf, A.M.; Rasool, H.; Abdel-Monem, M.; Geury, T.; El Baghdadi, M.; Hegazy, O. Real-time charging scheduling and optimization of electric buses in a depot. Energies 2022, 15, 5023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Z.; Li, J.; Bai, X.; Xie, C.; Chen, Z.; Xu, M.; Shang, W.L.; Li, H. An optimal charging scheduling model and algorithm for electric buses. Appl. Energy 2023, 332, 120512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Wang, Y.; Jia, S.; Liu, Z.; Wang, S. A Lagrangian relaxation approach for the electric bus charging scheduling optimisation problem. Transp. A Transp. Sci. 2023, 19, 2023690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Meng, Q.; Ong, G.P.; Wang, H. Electric bus charging scheduling on a bus network. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2024, 161, 104553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y.; Yu, B.; Tang, T. Charging facility planning and scheduling problems for battery electric bus systems: A comprehensive review. Transp. Res. Part E Logist. Transp. Rev. 2024, 183, 103463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noel, L.; McCormack, R. A cost benefit analysis of a V2G-capable electric school bus compared to a traditional diesel school bus. Appl. Energy 2014, 126, 246–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arif, S.M.; Lie, T.T.; Seet, B.C.; Ahsan, S.M.; Khan, H.A. Plug-in electric bus depot charging with PV and ESS and their impact on LV feeder. Energies 2020, 13, 2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafique, S.; Nizami, M.; Irshad, U.; Hossain, M.; Mukhopadhyay, S. A two-stage multi-objective stochastic optimization strategy to minimize cost for electric bus depot operators. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 332, 129856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertsimas, D.; Brown, D.B.; Caramanis, C. Theory and applications of robust optimization. SIAM Rev. 2011, 53, 464–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Z.; Wang, Z.; Ran, L. Smart charging and discharging of electric vehicles based on multi-objective robust optimization in smart cities. Appl. Energy 2023, 343, 121185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y. Optimal electric bus scheduling under travel time uncertainty: A robust model and solution method. J. Adv. Transp. 2021, 2021, 1191443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y.; Li, R. Robust optimization for integrated planning of electric-bus charger deployment and charging scheduling. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2022, 110, 103410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, R.; Li, S.; Zhang, P.; Lee, K.Y. Integration of renewable energy sources and electric vehicles in V2G network with adjustable robust optimization. Renew. Energy 2020, 153, 1067–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Z.; Ran, L.; Zhang, Y.; Ren, Y. Robust vehicle-to-grid power dispatching operations amid sociotechnical complexities. Appl. Energy 2021, 281, 115912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, L.; Wang, Y.Y.; Gopalakrishnan, S.; Namuduri, C.S.; Prasad, R.; Raghavan, M. Adaptive Fast-Charging of Multi-Pack Battery System in a Mobile Platform Having Dual Charge Ports. US Patent 11,336,101, 17 May 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Soyster, A.L. Convex programming with set-inclusive constraints and applications to inexact linear programming. Oper. Res. 1973, 21, 1154–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertsimas, D.; Sim, M. The price of robustness. Oper. Res. 2004, 52, 35–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertsimas, D.; Thiele, A. A robust optimization approach to inventory theory. Oper. Res. 2006, 54, 150–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ogaili, A.S.; Al-Shetwi, A.Q.; Al-Masri, H.M.; Babu, T.S.; Hoon, Y.; Alzaareer, K.; Babu, N.P. Review of the estimation methods of energy consumption for battery electric buses. Energies 2021, 14, 7578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rachna; Singh, A.K. Analyzing electric vehicle performance considering smooth roads with seasonal variation. Electr. Eng. 2024, 107, 3709–3723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Ref. | EV Fleet Type | V2G Integration | Uncertainty | Objective | Methods |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [14] | Private EVs | - | - | Aggregator revenue, Customer cost | Linear programming |
| [15] | Private EVs | - | - | Total tardiness | Metaheuristics |
| [16] | Private EVs | - | - | Charging cost | Bi-level programming |
| [17] | Private EVs in parking lots | ✓ | - | EV owner profit | Nonlinear programming |
| [18] | Private EVs | ✓ | – | Time-aware fairness, Cost efficiency | Bi-objective optimization |
| [19] | Private EVs | ✓ | – | Total costs | Multi-stage optimization |
| [20] | E-buses | – | – | Charging costs | Linear programming |
| [21] | E-buses | – | – | Operating costs | Second-order conic programming |
| [22] | E-buses | – | – | Charging costs | Real-time optimization |
| [23] | E-buses | – | – | Total costs | Lagrangian relaxation |
| [24] | E-buses | – | – | Charging time | Lagrangian relaxation |
| [25] | E-buses | – | – | Total costs | Branch-and-price, Adaptive large neighborhood search |
| [27] | E-school buses | ✓ | – | – | Comparative analysis |
| [28] | E-buses | ✓ | – | Daily profit | Mixed integer linear programming |
| [29] | E-buses | ✓ | Day-ahead forecast | Total costs | Mixed integer linear programming, Stochastic model |
| [31] | Private EVs | ✓ | PV Generation | Charging costs, Load fluctuation, PV consumption | Robust optimization |
| [32] | E-buses | – | Travel time | Operational cost | Robust optimization, Branch-and-price |
| [33] | E-buses | – | Energy consumption | Total costs | Robust optimization |
| [34] | Private EVs | ✓ | Wind power, EV SoCs | Total costs | Adjustable robust optimization |
| [35] | Private EVs | ✓ | Range anxiety | Total costs | Robust optimization, Benders decomposition |
| This study | E-buses | ✓ | Energy consumption, DR Requests | Total profits | Robust optimization |
| Sets | |
|---|---|
| set of buses () | |
| set of time periods () | |
| set of trips for bus i () | |
| set of time periods during which bus i is at the charging station | |
| set of time periods during which bus i is in operation | |
| set of time periods corresponding to peak hours ( | |
| set of time periods corresponding to k-th loadreduction requests | |
| set of load reduction requests ( | |
| set of ports () | |
| Parameters | |
| energy consumption of j-th trip of bus i | |
| / | start time/finish time of j-th trip of bus i |
| required load reduction amount of k-th request | |
| number of available chargers in period t | |
| charging and discharging efficiencies for bus i | |
| battery capacity of bus i | |
| / | maximum charging/discharging amount using port p |
| charging and discharging prices in period t | |
| expensive emergency charging price in period t | |
| Variables | |
| charging amount of bus i at period t | |
| discharging amount of bus i at period t | |
| if bus i is charged in period t with port p | |
| if bus i is discharged in period t with port p | |
| emergency charging amount of bus i at period t | |
| SoC level of bus i at the end of period t | |
| Obj. Value ( KRW) | Realized Profit ( KRW) | Emg. Chg. Amt (kWh) | Time (s) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spring /Fall | 10 | 137.4 | 115.1 | 124.2 | 101.4 | 91.7 | 125.1 | 64.9 | 90.7 | 8.2 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
| 20 | 279.0 | 234.5 | 252.6 | 208.6 | 192.8 | 254.3 | 120.4 | 164.9 | 14.9 | 2.3 | 2.5 | 2.4 | |
| 30 | 418.6 | 351.7 | 378.9 | 307.3 | 288.9 | 379.5 | 194.1 | 245.5 | 23.0 | 3.6 | 3.9 | 3.8 | |
| 40 | 558.5 | 468.7 | 505.6 | 414.7 | 382.8 | 505.0 | 240.8 | 335.4 | 28.6 | 5.0 | 5.3 | 5.1 | |
| 50 | 703.0 | 590.7 | 637.0 | 527.0 | 492.3 | 637.5 | 297.8 | 390.9 | 36.7 | 6.2 | 6.5 | 6.5 | |
| Summer | 10 | 338.1 | 222.9 | 263.2 | 253.5 | 252.2 | 282.0 | 68.4 | 11.3 | 1.5 | 61.0 | 15.4 | 1.3 |
| 20 | 720.8 | 485.6 | 570.4 | 549.1 | 543.2 | 606.5 | 136.9 | 22.5 | 2.9 | 2.9 | 4.5 | 5.0 | |
| 30 | 1069.3 | 718.4 | 844.6 | 810.2 | 799.7 | 897.2 | 202.7 | 37.2 | 4.7 | 6.9 | 5.3 | 8.6 | |
| 40 | 1443.5 | 966.5 | 1139.8 | 1088.8 | 1077.0 | 1210.3 | 275.3 | 46.5 | 6.0 | 6.9 | 9.0 | 8.1 | |
| 50 | 1804.2 | 1212.9 | 1429.6 | 1365.7 | 1352.2 | 1517.1 | 340.1 | 55.9 | 8.0 | 11.2 | 21.6 | 14.2 | |
| Winter | 10 | 126.5 | −27.6 | 36.3 | 52.0 | 57.3 | 79.9 | 79.2 | 2.9 | 1.0 | 1.7 | 26.9 | 2.4 |
| 20 | 291.1 | −11.5 | 110.6 | 140.5 | 145.2 | 195.5 | 153.9 | 4.0 | 1.7 | 62.5 | 3.6 | 5.5 | |
| 30 | 423.3 | −27.6 | 153.7 | 195.0 | 208.4 | 279.9 | 236.7 | 7.2 | 2.9 | 4.1 | 63.7 | 196.6 | |
| 40 | 580.6 | −32.8 | 215.1 | 270.9 | 282.7 | 383.6 | 311.3 | 9.8 | 3.6 | 175.1 | 8.7 | 227.4 | |
| 50 | 724.1 | −31.7 | 274.3 | 337.8 | 362.5 | 483.8 | 395.4 | 11.4 | 4.6 | 14.6 | 154.8 | 150.5 | |
| Average | 641.2 | 349.0 | 462.4 | 441.5 | 435.3 | 522.5 | 207.8 | 95.7 | 9.9 | 24.3 | 22.2 | 42.6 | |
| Obj. Value ( KRW) | Realized Profit ( KRW) | Emg. Chg. Amt (kWh) | Time (s) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spring /Fall | low | low | 418.6 | 351.7 | 378.9 | 307.3 | 288.9 | 379.5 | 194.1 | 245.5 | 23.0 | 3.6 | 3.9 | 3.8 |
| mid | 421.3 | 353.9 | 381.4 | 308.6 | 287.9 | 385.2 | 187.2 | 262.6 | 18.8 | 2.9 | 2.8 | 2.8 | ||
| high | 421.3 | 354.0 | 381.4 | 314.0 | 285.6 | 386.0 | 176.0 | 265.7 | 18.6 | 2.8 | 2.8 | 2.7 | ||
| high | low | 368.6 | 288.2 | 317.1 | 262.9 | 227.3 | 335.1 | 185.4 | 279.8 | 12.6 | 3.8 | 4.1 | 3.9 | |
| mid | 370.6 | 289.6 | 318.7 | 260.9 | 226.6 | 338.6 | 187.7 | 290.9 | 9.7 | 2.9 | 55.4 | 2.8 | ||
| high | 371.5 | 290.4 | 319.6 | 262.2 | 221.4 | 340.3 | 188.0 | 306.9 | 9.7 | 2.7 | 2.7 | 2.8 | ||
| Summer | low | low | 1069.3 | 718.4 | 844.6 | 810.2 | 799.7 | 897.2 | 202.7 | 37.2 | 4.7 | 6.9 | 5.3 | 8.6 |
| mid | 1155.2 | 766.2 | 909.5 | 881.8 | 847.3 | 962.8 | 199.0 | 37.0 | 3.3 | 3.0 | 3.0 | 2.9 | ||
| high | 1155.3 | 766.2 | 909.5 | 880.3 | 847.2 | 963.0 | 204.0 | 37.5 | 3.2 | 2.8 | 3.0 | 2.8 | ||
| high | low | 904.8 | 502.3 | 637.5 | 647.5 | 625.1 | 712.8 | 217.3 | 22.5 | 2.8 | 64.6 | 6.2 | 13.0 | |
| mid | 993.6 | 550.9 | 703.5 | 720.8 | 673.5 | 777.5 | 209.3 | 23.2 | 2.0 | 2.9 | 2.9 | 2.9 | ||
| high | 993.6 | 550.9 | 703.5 | 716.6 | 673.6 | 779.3 | 219.3 | 23.0 | 2.1 | 2.8 | 3.0 | 3.0 | ||
| Winter | low | low | 423.3 | −27.6 | 153.7 | 195.0 | 208.4 | 279.9 | 236.7 | 7.2 | 2.9 | 4.1 | 63.7 | 196.6 |
| mid | 502.4 | 5.3 | 207.3 | 259.6 | 238.9 | 330.9 | 226.5 | 8.4 | 2.1 | 3.0 | 3.1 | 3.0 | ||
| high | 502.4 | 5.3 | 207.3 | 258.7 | 238.8 | 330.5 | 223.7 | 7.5 | 2.4 | 3.0 | 3.1 | 3.0 | ||
| high | low | 293.0 | −199.3 | −13.1 | 65.3 | 80.8 | 144.2 | 261.7 | 5.0 | 1.9 | 6.0 | 124.9 | 215.4 | |
| mid | 425.0 | −132.0 | 84.4 | 168.3 | 147.5 | 242.2 | 251.7 | 5.3 | 1.2 | 3.6 | 3.6 | 3.6 | ||
| high | 425.0 | −132.0 | 84.4 | 163.6 | 146.8 | 241.6 | 255.6 | 6.4 | 1.1 | 3.7 | 3.9 | 3.8 | ||
| Average | 623.0 | 294.6 | 418.3 | 415.8 | 392.5 | 490.4 | 212.5 | 104.0 | 6.8 | 6.9 | 16.5 | 26.5 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kang, M.; Lee, B.; Lee, Y. A Robust Optimization Approach for E-Bus Charging and Discharging Scheduling with Vehicle-to-Grid Integration. Mathematics 2025, 13, 1380. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13091380
Kang M, Lee B, Lee Y. A Robust Optimization Approach for E-Bus Charging and Discharging Scheduling with Vehicle-to-Grid Integration. Mathematics. 2025; 13(9):1380. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13091380
Chicago/Turabian StyleKang, Mingyu, Bosung Lee, and Younsoo Lee. 2025. "A Robust Optimization Approach for E-Bus Charging and Discharging Scheduling with Vehicle-to-Grid Integration" Mathematics 13, no. 9: 1380. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13091380
APA StyleKang, M., Lee, B., & Lee, Y. (2025). A Robust Optimization Approach for E-Bus Charging and Discharging Scheduling with Vehicle-to-Grid Integration. Mathematics, 13(9), 1380. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13091380





