Ecoacoustics: A Quantitative Approach to Investigate the Ecological Role of Environmental Sounds
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Environmental Sound, General Characters, and Importance
3. Ecoacoustics as a New Scientific Discipline
- species distribution across the habitat,
- daily and seasonal changes of individual acoustic activity,
- intra- and inter-specific interactions,
- acoustic variation of individual species and populations across different landscape/waterscape configurations,
- acoustic biogeography (dialects) of species and populations, and
- seasonal fluctuations and density of populations.
4. Quantitative Methods in Ecoacoustics
4.1. Hardware
4.2. Ecoacoustic Metrics
- intensity indices that measure sound amplitude,
- complexity indices that measure the level of complexity (time, frequency, and/or amplitude), and
- soundscape indices that investigate the importance of geophonies, biophonies, and technophonies.
4.2.1. Intensity Indices
4.2.2. Complexity Indices
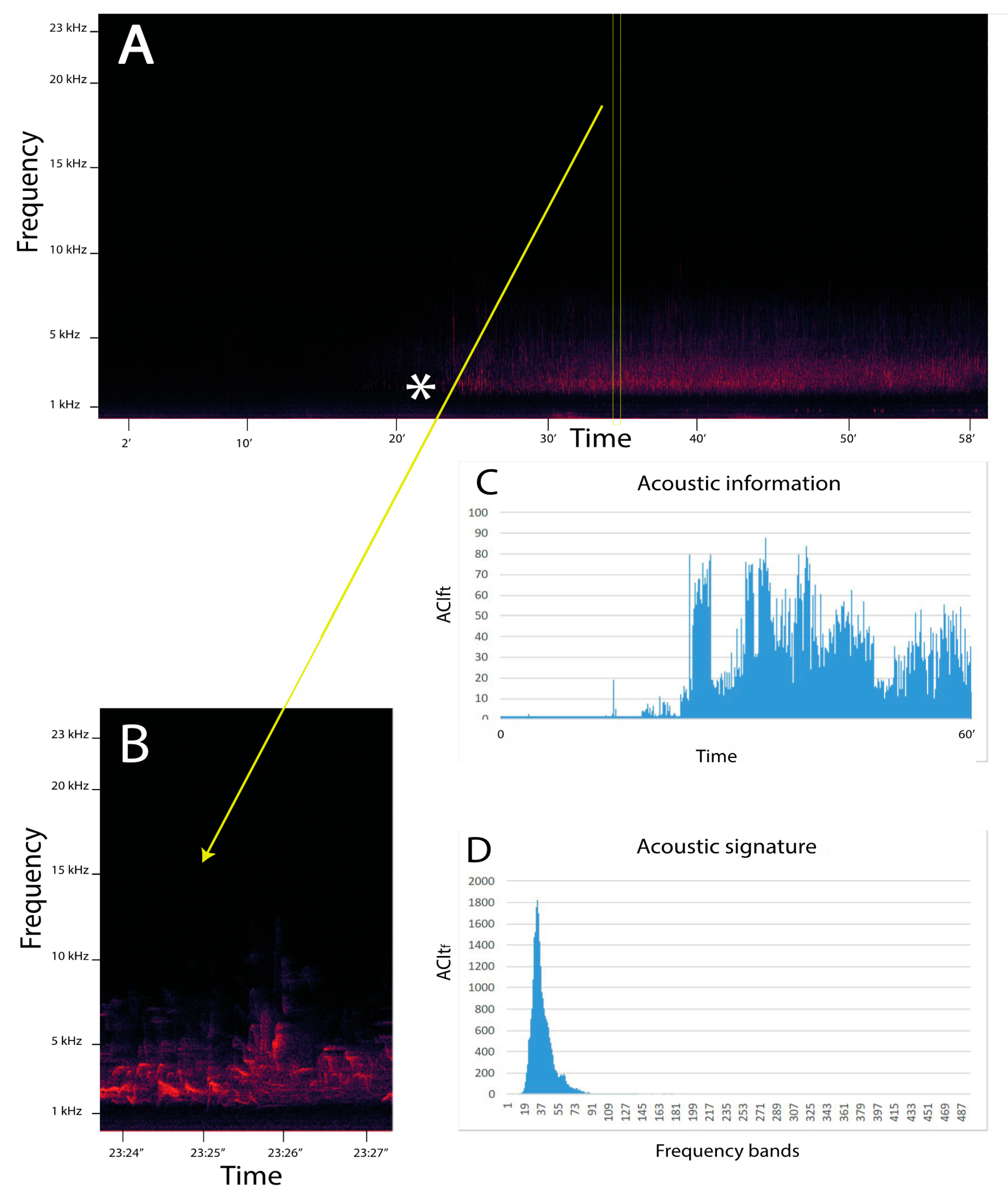
Characteristics of ACItf and ACIft
4.2.3. Soundscape Indices
Normalized Difference Soundscape Index
Ecoacoustic Event Detection and Identification Routine (EEDI)
4.3. Passive Acoustic Monitoring for Environmental Assessment and Long-Term Passive Ecoacoustic Monitoring
5. Discussion and Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Masood, E. Battle over biodiversity. Nature 2018, 560, 423–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibisch, P.; Hoffmann, M.T.; Kreft, S.; Pe’er, G.; Kati, V.; Biber-Freudenberger, L.; DellaSala, D.A.; Vale, M.M.; Hobson, P.R.; Selva, N. A global map of roadless areas and their conservation status. Science 2016, 354, 1423–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, L.R. The world food prospect. Science 1975, 190, 1053–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, L.R. World population growth, soil erosion, and food security. Science 1981, 214, 995–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erb, K.-H.; Fetzel, T.; Plutzar, C.; Kastner, T.; Lauk, C.; Mayer, A.; Niedertscheider, M.; Körner, C.; Haberl, H. Biomass turnover time in terrestrial ecosystems halved by land use. Nat. Geosci. 2016, 9, 674–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Galloway, J.N.; Townsend, A.R.; Erisman, J.W.; Bekunda, M.; Cai, Z.; Freney, J.R.; Martinelli, L.A.; Seitzinger, S.P.; Sutton, M.A. Transformation of the nitrogen cycle: Recent trends, questions, and potential solutions. Science 2008, 320, 889–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Kuang, W.; Zhang, C.; Chen, C. Impacts of impervious surface expansion on soil organic carbon—A spatially explicit study. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 17905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.-P.; Hansen, M.C.; Stehman, S.V.; Potapov, P.V.; Tyukavina, A.; Vermote, E.F.; Townshend, J.R. Global land change from 1982 to 2016. Nature 2018, 560, 639–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC. AR5 Climate Change 2014: Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability. 2014. Available online: https://ipcc-wg2.gov/AR5/report/ (accessed on 24 December 2018).
- Costanza, R.; d’Arge, R.; De Groot, R.; Farber, S.; Grasso, M.; Hannon, B.; Limburg, K.; Naeem, S.; O’neill, R.V.; Paruelo, J.; et al. The value of the world’s ecosystem services and natural capital. Nature 1997, 387, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocchini, D.; Boyd, D.S.; Féret, J.B.; Foody, G.M.; He, K.S.; Lausch, A.; Nagendra, H.; Wegmann, M.; Pettorelli, N. Satellite remote sensing to monitor species diversity: Potential and pitfalls. Remote Sens. Ecol. Conserv. 2015, 2, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer-Schönberger, V.; Cukier, K. Big Data: A Revolution That Will Transform How We Live, Work, and Think; Houghton Mifflin Harcourt: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, N.; Mittermeier, R.A.; Mittermeier, C.G.; Da Fonseca, G.A.; Kent, J. Biodiversity hotspots for conservation priorities. Nature 2000, 403, 853–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramirez, F.; Afàn, I.; Davis, L.S.; Chiaradia, A. Climate impacts on global hot spots of marine biodiversity. Science 2017, 3, e1601198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lundgren, J.G.; Fausti, S.W. Trading biodiversity for pest problems. Science 2015, 1, e1500558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sueur, J.; Pavoine, S.; Hamerlynck, O.; Duvail, S. Rapid acoustic survey for biodiversity appraisal. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e4065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carson, R. Silent Spring; Anniversary Edition; Houghton Mifflin Company: Boston, MA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Krause, B.; Farina, A. Using ecoacoustic methods to survey the impacts of climate change on biodiversity. Biol. Conserv. 2016, 195, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, S.; Narayanan, S.; Kuo, C.-C.J. Content Analysis for Acoustic Environment Classification in Mobile Robots; AAAI: Menlo Park, CA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Farina, A.; Lattanzi, E.; Malavasi, R.; Pieretti, N.; Piccioli, L. Avian soundscapes and cognitive landscapes: Theory, application and ecological perspectives. Landsc. Ecol. 2011, 26, 1257–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGregor, P.K.; Dabelsteen, T. Communication network. In Ecology and Evolution of Acoustic Communication in Birds; Kroodsma, D.E., Miller, E.H., Eds.; Cornell University Press: Ithaca, NY, USA, 1997; pp. 409–425. [Google Scholar]
- Gagliano, M.; Mancuso, S.; Robert, D. Toward understanding plant bioacoustics. Trends Plant Sci. 2012, 17, 323–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schöner, M.G.; Simon, R.; Schöner, C.R. Acoustic communication in plant-animal interactions. Curr. Opin. Plant Boil. 2016, 32, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, D.R.; Hopkins, C.D. Sound audible to migrating birds. Anim. Behav. 1974, 22, 672–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullet, T.C.; Farina, A.; Gage, S.H. The acoustic habitat hypothesis: An ecoacoustics perspective on species habitat selection. Biosemiotics 2017, 10, 319–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parmentier, E.; Berten, L.; Rigo, P.; Aubrun, F.; Nedelec, S.L.; Simpson, S.D.; Lecchini, D. The influence of various reef sounds on coral fish larvae behavior. J. Fish Biol. 2015, 86, 1507–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radford, C.A.; Stanley, J.A.; Jeffs, A.G. Adjacent coral reef habitats produce different underwater sound signatures. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2014, 505, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Au, W.W.L. The Sonar of Dolphins; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1993; Volume Xii, p. 278. [Google Scholar]
- Griffin, D.R. Listening in the Dark; Yale University Press: New Haven, CT, USA, 1959. [Google Scholar]
- Buchanan, K.L.; Catchpole, C.K.; Lewis, J.W.; Lodge, A. Song as indicator of parasitism in the sedge warbler. Anim. Behav. 1999, 57, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchanan, K.L.; Spencer, K.A.; Goldsmith, A.R.; Catchpole, C.K. Song as an honest signal of past developmental stress in the European starling (Sturnus vulgaris). Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. B Biol. Sci. 2002, 270, 1149–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kroodsma, D.E. The diversity and plasticity of birdsong. In Nature’s Music; Marler, P., Slabbekoorn, H., Eds.; Elsevier Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2004; pp. 108–131. [Google Scholar]
- Derryberry, E.P.; Danner, R.M.; Danner, J.E.; Derryberry, G.E.; Philips, J.N.; Lipshutz, S.E.; Gentry, K.; Luther, D.A. Patterns of song across natural and anthropogenic soundscapes suggest that white- crowned sparrows minimize acoustic masking and maximize signal content. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0154456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sebastian-Gonzalez, E.; Hart, P.J. Birdsong meme diversity in a fragmented habitat depends on landscape and species characteristics. Oikos 2017, 126, 1511–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cain, R.; Jennings, P.; Poxon, J. The development and application of the emotional dimensions of a soundscape. Appl. Acoust. 2013, 74, 232–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moscoso, P.; Peck, M.; Wibberley, S.; Eldridge, A. A systematic cross-disciplinary literature review on the association between soundscape and ecological/human wellbeing. PeerJ 2018, 6, e6570v2. [Google Scholar]
- Barber, J.R.; Crooks, K.R.; Fristrup, K.M. The costs of chronic noise exposure for terrestrial organisms. Trend Ecol. Evol. 2009, 25, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curry, C.M.; Des Brisay, P.G.; Rosa, P.; Koper, N. Noise source and individual physiology mediate effectiveness of bird songs adjusted to anthropogenic noise. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 3942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creel, S.; Fox, J.E.; Hardy, A.; Sands, J.; Garrott, B.; Peterson, R.O. Snowmobile activity and glucocorticoid stress responses in wolves and elk. Conserv. Biol. 2002, 16, 809–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCormick, M.I.; Allan, B.J.; Harding, H.; Simpson, S.D. Boat noise impacts risk assessment in a coral reef fish but effects depend on engine type. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 3847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, R.; Wright, A.J.; Ashe, E.; Blight, L.K.; Bruintjes, R.; Canessa, R.; Clark, C.W.; Cullis-Suzuki, S.; Dakin, D.T.; Erbe, C.; et al. Impacts of anthropogenic noise on marine life: Publication patterns, new discoveries, and future directions in research and management. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2015, 115, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaplan, M.B.; Solomon, S. A coming boom in commercial shipping? The potential for rapid growth of noise from commercial ships by 2030. Mar. Policy 2016, 73, 119–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, D.; Honarmand, M.; Pascual, J.; Perez-Mena, E.; Macias Garcia, C. Birds living near airports advance their dawn chorus and reduce overlap with aircraft noise. Behav. Ecol. 2014, 26, 435–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dominoni, D.M.; Greif, S.; Nemeth, E.; Brumm, H. Airport noise predicts song timing of European birds. Ecol. Evol. 2016, 6, 6151–6159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Phillips, J.; Derryberry, E.P. Urban sparrows respond to a sexually selected trait with increased aggression in noise. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 7505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, C.D.; Ortega, C.P.; Cruz, A. Noise pollution changes avian communities and species interactions. Curr. Biol. 2009, 19, 1415–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merchant, N.D.; Brookes, K.L.; Faulkner, R.C.; Bicknell, A.W.; Godley, B.J.; Witt, M.J. Underwater noise levels in UK waters. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 36942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- World Health Organization. Global Report on Urban Health: Equitable, Healthier Cities for Sustainable Development; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Babisch, W.; Beule, B.; Schust, M.; Kersten, N.; Ising, H. Traffic noise and risk of miocardial infarction. Epidemiology 2005, 16, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, E.A. A Study of Bird Song; Oxford University Press: London, UK, 1993; p. 335. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, L.I. Biological acoustics and the use of the sound spectrograph. Southwest. Nat. 1964, 9, 118–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morton, E. Ecological sources of selection on avian sounds. Am. Nat. 1975, 109, 17–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chappuis, C. Un exemple de L’influence du milieu sur les Emissions vocales des oiseaux: L’evolution de chants en foret equatoriale. Terre Et Vie 1971, 25, 183–202. [Google Scholar]
- Eyring, C.F. Jungle acoustics. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1946, 18, 257–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingard, U. A review of the influence of meteorological conditions on sound propagation. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1953, 108, 2412–2418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Embleton, T.F.W. Sound propagation in homogeneous deciduous and evergreen woods. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1963, 35, 1119–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aylor, D. Noise reduction by vegetation and ground. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1972, 51, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pijanowski, B.C.; Villanueva-Riveira, L.J.; Dumyahn, S.L.; Farina, A.; Krause, B.L.; Napoletano, B.M.; Gage, S.H.; Pieretti, N. Soundscape Ecology: The science of sound in the landscape. BioScience 2011, 61, 203–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pijanowski, B.C.; Farina, A.; Gage, S.H.; Dumyahn, S.L.; Krause, B.L. What is soundscape ecology? An introduction and overview of an emerging new science. Landsc. Ecol. 2011, 26, 1213–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sueur, J.; Farina, A. Ecoacoustics: The ecological investigation and interpretation of environmental sounds. Biosemiotics 2015, 8, 493–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farina, A.; Gage, S.H. Ecoacoustics: A new science. In Ecoacoustics; Farina, A., Gage, S.H., Eds.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Farina, A. Perspectives in ecoacoustics: A contribution to defining a discipline. J. Ecoacoust. 2018, 2, TRZD51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blumstein, D.T.; Mennill, D.J.; Clemins, P.; Girod, L.; Yao, K.; Patricelli, G.; Deppe, J.L.; Krakauer, A.H.; Clark, C.; Cortopassi, K.A.; et al. Acoustic monitoring in terrestrial environments using microphone arrays: Applications, technological considerations and prospectus. J. Appl. Ecol. 2011, 48, 758–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farina, A.; James, P. Acoustic community structure and dynamics: A fundamental component of ecoacoustics. Biosystems 2016, 147, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasc, A.; Sueur, J.; Pavoine, S.; Pellens, R.; Grandcolas, P. Biodiversity sampling using a global acoustic approach: Contrasting sites with microendemics in New Caledonia. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e65311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lellouch, L.; Pavoine, S.; Jiguet, F.; Glotin, H.; Sueur, J. Monitoring temporal change of bird communities with dissimilarity acoustic indices. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2014, 5, 495–505. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Farina, A. Soundscape Ecology; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2014; p. 315. [Google Scholar]
- Pavan, G. Fundamental of soundscape conservation. In Ecoacoustics; Farina, A., Gage, S., Eds.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 235–258. [Google Scholar]
- Farina, A.; Gage, S.H. The duality of sounds: Ambient and communication. In Ecoacoustics; Farina, A., Gage, S.H., Eds.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 13–29. [Google Scholar]
- Hill, A.P.; Prince, P.; Covarrubias, E.P.; Doncaster, C.P.; Snaddon, J.L.; Rogers, A. AudioMoth: Evaluation of a smart open acoustic device for monitoring biodiversity and the environment. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2018, 9, 1199–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sueur, J.; Farina, A.; Gasc, A.; Pieretti, N.; Pavoine, S. Acoustic indices for biodiversity assessment and landscape investigation. Acta Acust. United Acust. 2014, 100, 772–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Towsey, M.; Wimmer, J.; Williamson, I.; Roe, P. The use of acoustic indices to determine avian species richness in audio-recordings of the environment. Ecol. Inform. 2014, 21, 110–119. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, J.; Towsey, M.; Zhu, M.; Zhang, J.; Roe, P. An intelligent system for estimating frog community calling activity and species richness. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 82, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, A.; Fischer, M.; Tzanopoulos, J. Sound-mapping a conifeorus forest—Perspectives for biodiversity monitoring and noise mitigation. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0189843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, A.N.; Soldevilla, M.S.; Quinlan, J.A. Nocturnal patterns in fish chorusing off the coasts of Georgia and eastern Florida. Bull. Mar. Sci. 2017, 93, 455–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Depraetere, M.; Pavoine, S.; Jiguet, F.; Gasc, A.; Duvail, S.; Sueur, J. Monitoring animal diversity using acoustic indices: Implementation in a temperate woodland. Ecol. Indic. 2012, 13, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farina, A.; Morri, D. Source-sink e eco-field: Ipotesi ed evidenze sperimentali. In Proceedings of the X National Meeting of SIEP-IALE. Ecology and Landscape Governance: Experiences and Perspective, Bari, Italy, 2008; pp. 365–372. [Google Scholar]
- Lindseth, A.V.; Lobel, P.S. Underwater soundscape monitoring and fish bioacoustics: A review. Fishes 2018, 3, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieretti, N.; Farina, A.; Morri, D. A new methodology to infer the singing activity of an avian community: The acoustic complexity index (ACI). Ecol. Indic. 2011, 11, 868–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farina, A.; Pieretti, N.; Salutari, P.; Tognari, E.; Lombardi, A. The application of the acoustic complexity indices (ACI) to ecoacoustic event detection and identification (EEDI) model. Biosemiotics 2016, 9, 227–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levins, R. Evolution in Changing Environments: Some Theoretical Explorations; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 1968. [Google Scholar]
- Hurlbert, S.H. The measurement of niche overlap and some relatives. Ecology 1978, 59, 66–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieretti, N.; Duarte, M.H.L.; Sousa-Lima, R.S.; Rodrigues, M.; Young, R.J.; Farina, A. Determining temporal sampling schemes for passive acoustic studies in different tropical ecosystems. Trop. Conserv. Sci. 2015, 8, 215–2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farina, A.; Pieretti, N. Sonic environment and vegetation structure: A methodological approach for a soundscape analysis of a Mediterranean maqui. Ecol. Inform. 2014, 21, 120–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desjonquères, C.; Rybak, F.; Depraetere, M.; Gasc, A.; Le Viol, I.; Pavoine, S.; Sueur, J. First description of underwater acoustic diversity in three temperate ponds. PeerJ 2015, 3, e1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertucci, F.; Parmentier, E.; Lecellier, G.; Hawkins, A.D.; Lecchini, D. Acoustic indices provide information on the status of coral reefs: An example from Morea Island in the South Pacific. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 33326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolgan, M.; O’Brien, J.; Chorazyczewska, E.; Winfield, I.J.; McCullough, P.; Gammell, M. The soundscape of arctic charr spawning grounds in lotic and lentic environments: Can passive acoustic monitoring be used to detect spawning activities? Bioacoustics 2018, 27, 57–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolgan, M.; Amorim, M.C.; Fonseca, P.J.; Di Iorio, L.; Parmentier, E. Acoustic complexity of vocal fish communities: A field and controlled validation. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 10559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buxton, R.T.; Brown, E.; Sharman, L.; Gabriele, C.M.; McKenna, M.F. Using bioacoustics to examine shifts in songbird phenology. Ecol. Evol. 2016, 6, 4697–4710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Raynor, E.J.; Whalen, C.E.; Brown, M.B.; Powell, L.A. Grassland bird community and acoustic complexity appear unaffected by proximity to a wind energy facility in the Nebraska Sandhills. Condor 2017, 119, 484–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, M.H.L.; Sousa-Lima, R.S.; Young, R.J.; Farina, A.; Vacsoncelos, M.; Rodrigues, M.; Pieretti, N. The impact of noise open-vast mining on Atlantic forest biophony. Biol. Conserv. 2015, 191, 623–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilje, B.; Stack, S.; Sànchez-Azofeifa, A. Lianas abundance is positively related with the avian acoustic community in tropical forests. Forests 2017, 8, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McWilliam, J.N.; Hawkins, A.D. A comparison of inshore marine soundscapes. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2013, 446, 166–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieretti, N.; Lo Martire, M.; Farina, A.; Danovaro, R. Marine soundscape as an additional biodiversity monitoring tool: A case study from the Adriatic Sea (Mediterranean Sea). Ecol. Indic. 2017, 83, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceraulo, M.; Papale, E.; Caruso, F.; Filiciotto, F.; Grammauta, R.; Parisi, I.; Mazzola, S.; Farina, A.; Buscaino, G. Acoustic comparison of a patchy Mediterranean shallow water seascape: Posidonia oceanica meadow and sandy bottom habitats. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 85, 1030–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farina, A.; Gage, S.H.; Salutari, P. Testing the Ecoacoustics Event Detection and Identification (EEDI) Model on Mediterranean Soundscapes. Ecol. Indic. 2108, 85, 698–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasten, E.P.; Gage, S.H.; Fox, J.; Joo, W. The remote environmental assessment laboratory’s acoustic library: An archive for studying soundscape ecology. Ecol. Inform. 2012, 12, 50–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farina, A.; Belgrano, A. Eco-field: A new paradigm for landscape ecology. Ecol. Res. 2004, 19, 107–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farina, A.; Belgrano, A. The eco-field hypothesis: Toward a cognitive landscape. Landscape Ecology 2006, 21, 5–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farina, A.; Monacchi, D. A multiscaled approach to investigate the biosemiotics complexity of acoustic communities in two paleotropical and neotropical primary forests. Biosemiotics 2019. in preprint. [Google Scholar]
- Farina, A.; Pieretti, N.; Piccioli, L. The soundscape methodology for long-term bird monitoring: A Mediterranean Europe case-study. Ecol. Inform. 2011, 6, 354–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banner, K.M.; Irvine, K.M.; Rodhouse, T.J.; Wright, W.J.; Rodriguez, R.M.; Litt, A.R. Improving geographically extensive acoustic survey designs for modeling species occurrence with imperfect detection and misidentification. Ecol. Evol. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pine, M.K.; Wang, D.; Porter, L.; Wang, K. Investigating the spatiotemporal variation of fish choruses to help identify important foraging habitat for Indo-Pacific humpback dolphins, Sousa chinensis. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2017, 75, 510–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagens, S.V.; Rendall, A.R.; Whisson, D.A. Passive acoustic surveys for predicting species’s distributions: Optimising detection probability. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0199396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muirhead, C.A.; Warde, A.M.; Biedron, I.S.; Mihnovest, N.; Clark, C.W.; Rice, A.N. Seasonal acoustics occurrence of blue, fin, and North Atlantic right whales in the New York Bight. Aquat. Conserv. Mar. Frewhw. Ecosyst. 2018, 28, 744–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shonfield, J.; Heemskerk, S.; Bayne, E.M. Utility of Automated Species Recognition for Acoustic Monitoring of Owls. J. Raptor Res. 2018, 52, 42–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lillis, A.; Mooney, T.A. Snapping shrimp sound production patterns on Caribbean coral reefs: Relationships with celestial cycles and environmental variable. Coral Reefs 2018, 37, 597–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juanes, F. Visual and acoustic sensors for early detection of biological invasions: Current uses and future potential. J. Nat. Conserv. 2018, 42, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farina, A.; Pieretti, N.; Morganti, N. Acoustic patterns of an invasive species: The red-billed Leiothrix (Leiothrix lutea Scopoli 1786) in a Mediterranean shrubland. Bioacoustics 2013, 22, 175–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuller, S.; Axel, A.C.; Tucker, D.; Gage, S.H. Connecting soundscape to landscape: Which acoustic index best describes landscape configuration? Ecol. Indic. 2015, 58, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedoya, C.; Isaza, C.; Daza, J.M.; Lopez, J.D. Automatic identification of rainfall in acoustic recordings. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 75, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erbe, C.; Verma, A.; McCauley, R.; Gavrilov, A.; Parnum, I. The marine soundscape of the Perth Canyon. Prog. Oceanogr. 2015, 137, 38–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolfe, K.F.; Lani, S.; Sabra, K.G.; Kuperman, W.A. Monitoring deep-ocean temperatures using acoustic ambient noise. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2015, 42, 2878–2884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Monczak, A.; Berry, A.; Kehrer, C.; Montie, E.W. Long-term acoustic monitoring of fish calling provides baseline estimates of reproductive timelines in the May River estuary, southeastern USA. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2017, 581, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Linke, S.; Gifford, T.; Desjonquères, C.; Tonolla, D.; Aubin, T.; Barclay, L.; Karaconstantis, C.; Kennard, M.; Rybak, F.; Sueur, J. Freshwater ecoacoustics as a tool for continuous ecosystem monitoring. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2018, 16, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harris, S.A.; Shears, N.T.; Radford, C.A. Ecoacoustic indices as proxies for biodiversity on temperate reefs. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2015, 7, 713–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locascio, J.; Mann, D.; Wilcox, K.; Luther, M. Incorporation of acoustic sensors on a coastal ocean monitoring platform for measurements of biological activity. Mar. Technol. Soc. J. 2018, 52, 64–70. [Google Scholar]
- Putland, R.L.; Mackiewicz, A.G.; Mensinger, A.F. Localizing individual soniferous fish using passive acoustic monitoring. Ecol. Inform. 2018, 48, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McWilliam, J.N.; McCauley, R.D.; Erbe, C.; Parson, M.J.G. Soundscape diversity in the Great Barrier Reef: Lizard island, a case study. Bioacoustics 2018, 3, 295–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haver, S.M.; Gedamke, J.; Hatch, L.T.; Dziak, R.P.; Van Parijs, S.; McKenna, M.F.; Barlow, J.; Berchok, C.; DiDonato, E.; Hanson, B.; et al. Monitoring long-term soundscape trends in U.S. waters: The NOAA/NPS ocean noise reference station network. Mar. Policy 2018, 90, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandoval, L.; Barrantes, G.; Wilson, D.R. Conceptual and statistical problems with the use of the Shannon-Weiner entropy index in bioacoustics analyses. Bioacoustics 2018, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorge, F.C.; Machado, C.G.; da Cunha Nogueira, S.S.; Nogueira-Filho, S.L.G. The effectiveness of acoustic indices for forest monitoring in Atlantic rainforest fragments. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 91, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.-H.; Fang, S.-H.; Tsao, Y. Improving biodiversity assessment via unsupervised separation of biological sounds from long-duration recordings. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sueur, J.; Aubin, T.; Simonis, C. Seewave, a free modular tool for sound analysis and synthesis. Bioacoustics 2008, 18, 213–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sueur, J. Sound Analysis and Synthesis with R; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Lomolino, M.V.; Pijanowski, B.C.; Gasc, A. The silence of biogeography. J. Biogeogr. 2015, 42, 1187–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, R.Y.; Ellis, D.P.; Chmura, H.E.; Krause, J.S.; Pérez, J.H.; Sweet, S.K.; Gough, L.; Wingfield, J.C.; Boelman, N.T. Eavesdropping on the Arctic: Automated bioacoustics reveal dynamics in singbird breeding phenology. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eeaq1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, T.A.C.; Harding, H.R.; Wong, K.E.; Merchant, N.D.; Meekan, M.G.; McCormick, M.I.; Radford, A.N.; Simpson, S.D. Habitat degradation negatively affects auditory settlement behavior of coral reef fishes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 5193–5198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fairbrass, A.J.; Rennert, P.; Williams, C.; Titheridge, H.; Jones, K.E. Biases of acoustic indices measuring biodiversity in urban areas. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 83, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mugagga, P.; Basajjabaka, K.; Winberg, S. Sound source localisation on Android smartphones: A first step to using smartphones as auditory sensors for training AI systems with Big Data. In Proceedings of the AFRICON, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 14–17 September 2015; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Phillips, Y.F.; Towsey, M.; Roe, P. Revealing the ecological content of long-duration audio-recordings of the environmental though clustering and visualization. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0193345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Huang, K.; Cottman Fields, M.; Truskinger, A.; Roe, P.; Duan, S.; Dong, X.; Towsey, M.; Wimme, J. Managing and analysing big audio data for environmental monitoring. In Proceedings of the IEEE 16th International Conference on Computational Science and Engineering (CSE), Sydney, Australia, 3–5 December 2013; pp. 997–1004. [Google Scholar]
© 2018 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Farina, A. Ecoacoustics: A Quantitative Approach to Investigate the Ecological Role of Environmental Sounds. Mathematics 2019, 7, 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/math7010021
Farina A. Ecoacoustics: A Quantitative Approach to Investigate the Ecological Role of Environmental Sounds. Mathematics. 2019; 7(1):21. https://doi.org/10.3390/math7010021
Chicago/Turabian StyleFarina, Almo. 2019. "Ecoacoustics: A Quantitative Approach to Investigate the Ecological Role of Environmental Sounds" Mathematics 7, no. 1: 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/math7010021
APA StyleFarina, A. (2019). Ecoacoustics: A Quantitative Approach to Investigate the Ecological Role of Environmental Sounds. Mathematics, 7(1), 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/math7010021



