Combining Spatio-Temporal Context and Kalman Filtering for Visual Tracking
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. The Principle of Spatio-Temporal Context Tracking Algorithm and Kalman Filtering
2.1. The Basic Principle of STC Algorithm
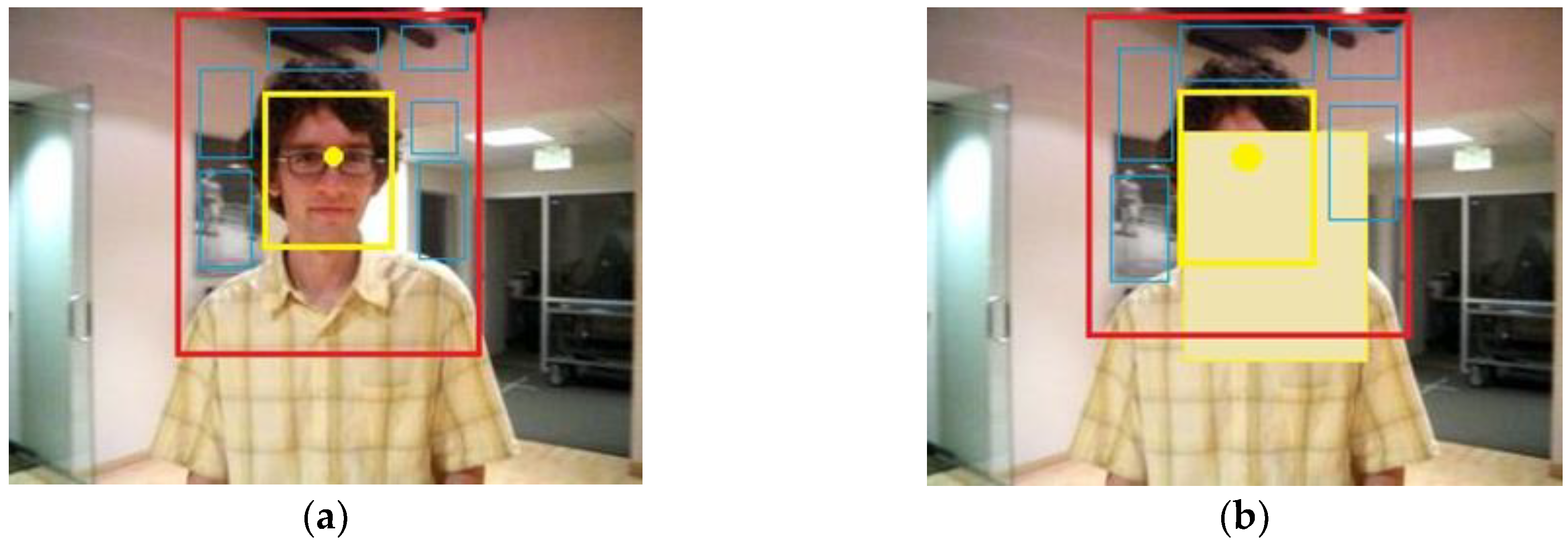
2.1.1. Spatial Context Model
2.1.2. Context Prior Model
2.1.3. Confidence Map
2.1.4. Fast Learning Spatial Context Model
2.1.5. Target Tracking
2.1.6. The Scale and Variance are Updated as
2.2. The Basic Principle of Kalman Filtering Algorithm
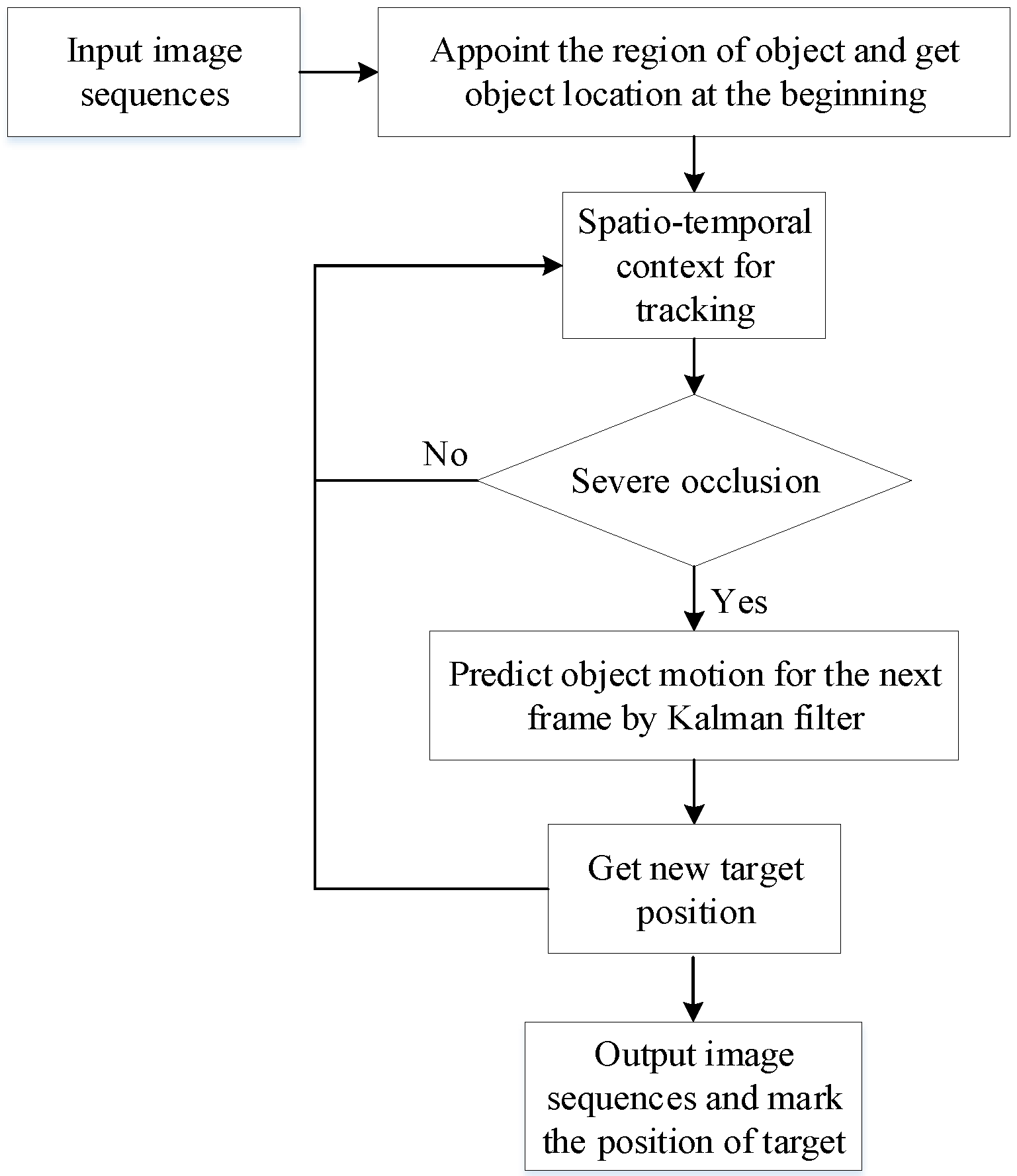
3. STC-KF Target Tracking Algorithm
4. Experimental Results and Analysis
4.1. Database Introduction
4.2. Experimental Results
4.2.1. Scene with Occlusion Condition
4.2.2. Scene with Illumination Changes Condition
4.2.3. Scene with Pose and Contour Variation Condition
5. Performance Analysis
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, M.; Kim, S. Robust appearance feature learning using pixel-wise discrimination for visual tracking. ETRI J. 2019, 41, 483–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, K.; Matas, J.; Svoboda, T. Tracking by an optimal sequence of linear predictors. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2009, 31, 677–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellis, L.; Dowson, N.; Matas, J. Linear regression and adaptive appearance models for fast simultaneous modeling and tracking. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2011, 95, 154–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalal, Z.; Mikolajczyk, K.; Matas, J. Forward Backward Error: Automatic Detection of Tracking Failures. In Proceedings of the 20th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR), Istanbul, Turkey, 23–26 August 2010; pp. 2756–2759. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Z.S.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, M.; Hou, Z.G.; Zhang, C.S. Gabor face recognition by multi-channel classifier fusion of supervised kernel manifold learning. Neurocomputing 2012, 97, 398–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzimiropoulos, G.; Zafeiriou, S.; Pantic, M. Sparse representations of image gradient orientations for visual recognition and tracking. In Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), Colorado Springs, CO, USA, 20–25 June 2011; pp. 26–33. [Google Scholar]
- Liwicki, S.; Zafeiriou, S.; Tzimiropoulos, G. Efficient online subspace learning with an indefinite kernel for visual tracking and recognition. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2012, 23, 1624–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, X.; Ling, H.B. Robust visual tracking and vehicle classification via sparse representation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2011, 33, 2259–2272. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.X.; Teng, S.H.; Liu, G.D.; Zhao, Z.S. Hierarchical sparse representation with deep dictionary for multi-modal classification. Neurocomputing 2017, 253, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horbert, E.; Rematas, K.; Leibe, B. Level-set person segmentation and tracking with multi-region appearance models and top-down shape information. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Barcelona, Spain, 6–13 November 2011; pp. 1871–1878. [Google Scholar]
- Nicolas, P.; Aurelie, B. Tracking with occlusions via graph cuts. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2011, 33, 144–157. [Google Scholar]
- Kalal, Z.; Mikolajczyk, K.; Matas, J. Tracking-Learning-Detection. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2012, 34, 1409–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pouya, B.; Seyed, A.C.; Musa, B.M.M. Upper body tracking using KLT and Kalman filter. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2012, 13, 185–191. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, G. Head pose estimation based on head tracking and the Kalman filter. Phys. Procedia 2011, 22, 420–427. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, Z.X.; Han, Y. Centroid weighted Kalman filter for visual object tracking. Measurement 2012, 45, 650–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Han, T.; Zhang, J. Target Tracking Algorithm Based on Kalman Filter and Optimization MeanShift. In LIDAR Imaging Detection and Target Recognition; Society of Photo-Optical Instrumentation Engineers (SPIE): Washington, DC, USA, 2017; p. 1060526. [Google Scholar]
- Gordon, N.J.; Salmond, D.J.; Smith, A.F.M. Novel Approach to Nonlinear/Non-Gaussian Bayesian State Estimation. IEE Proc. F Radar Signal Process. 1993, 140, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.Y.; Zhao, Q.J.; Zhao, L.J. Abrupt motion tracking using a visual saliency embedded particle filter. Pattern Recognit. 2014, 47, 1826–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, B. Tracking Algorithms Aided by the Pose of Target. IEEE Access. 2019, 7, 9627–9633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.P.; Liang, W.T.; Wang, J. A method of high maneuvering target dynamic tracking. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Energy, Environment and Materials Science, Guangzhou, China, 25–26 August 2015; pp. 25–26. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Fang, W.; Ding, W. Visual Tracking by Sequential Cellular Quantum-Behaved Particle Swarm Optimization, Bio-Inspired Computing—Theories and Applications (BIC-TA 2016). In International Conference on Bio-Inspired Computing: Theories and Applications; Springer: Singapore, 2016; pp. 86–94. [Google Scholar]
- Sengupta, S.; Peters, R.A. Learning to Track On-The-Fly Using a Particle Filter with Annealed-Weighted QPSO Modeled after a Singular Dirac Delta Potential. In Proceedings of the IEEE Symposium Series on Computational Intelligence (SSCI), Bangalore, India, 18–21 November 2018; pp. 1321–1330. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, K.H.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Q.S. Fast Visual Tracking via Dense Spatio-Temporal Context Learning. In European Conference on Computer Vision; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; pp. 127–141. [Google Scholar]
- Thang, B.D.; Nam, V.; Gerard, M. Context tracker: Exploring supporters and distracters in unconstrained environments. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Colorado Springs, CO, USA, 20–25 June 2011; pp. 1177–1184. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, M.; Wu, Y.; Hua, G. Context-aware visual tracking. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2009, 31, 1195–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liu, P.; Du, Y. Online convolution network tracking via spatio-temporal context. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2019, 78, 257–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalman, R.E. A New Approach to Linear Filtering and Prediction Problems. Trans. ASME J. Basic Eng. 1960, 82, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lagos-Álvarez, B.; Padilla, L.; Mateu, J.; Ferreira, G. A Kalman filter method for estimation and prediction of space–time data with an autoregressive structure. J. Stat. Plan. Inference 2019, 203, 117–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Lim, J.; Yang, M.H. Online Object Tracking: A Benchmark. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Portland, OR, USA, 23–28 June 2013; pp. 2411–2418. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Lim, J.; Yang, M.H. Object Tracking Benchmark. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2015, 37, 1834–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, J.Z.; Liu, W.X. Moving Target Detection and Tracking Algorithm Based on Context Information. IEEE Access. 2019, 7, 70966–70974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Huo, H.; Fang, T. Learning Deconvolutional Network for Object Tracking. IEEE Access. 2018, 6, 18032–18041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.S.; Sun, Q.; Yang, H.R. Compression artifacts reduction by improved generative adversarial networks. EURASIP J. Image Video Process. 2019, 62, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Li, J.; Yang, Y. Reliability verification-based convolutional neural networks for object tracking. IET Image Process. 2019, 13, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Algorithm Name | Video Name | Number of Frames | Correctly Track Frames |
|---|---|---|---|
| STC | car | 410 | 91 |
| KF-STC | car | 410 | 362 |
| Number of Frames | Target Real Coordinates | STC Tracking Coordinates | STC-KF Tracking Coordinates | STC Pixel Error | STC-KF Pixel Error |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50 | (120,62) | (124,63) | (121,61) | 4.1 | 1.4 |
| 100 | (164,63) | (169,68) | (160,60) | 7.1 | 5 |
| 150 | (142,44) | (144,46) | (143,42) | 2.8 | 2.2 |
| 200 | (128,31) | (136,31) | (129,29) | 8 | 2.2 |
| 250 | (180,74) | (180,70) | (182,73) | 4 | 2.1 |
| 300 | (126,60) | (120,53) | (130,59) | 9.2 | 4.1 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, H.; Wang, J.; Miao, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, Z.; Sun, Q.; Wu, D.O. Combining Spatio-Temporal Context and Kalman Filtering for Visual Tracking. Mathematics 2019, 7, 1059. https://doi.org/10.3390/math7111059
Yang H, Wang J, Miao Y, Yang Y, Zhao Z, Wang Z, Sun Q, Wu DO. Combining Spatio-Temporal Context and Kalman Filtering for Visual Tracking. Mathematics. 2019; 7(11):1059. https://doi.org/10.3390/math7111059
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Haoran, Juanjuan Wang, Yi Miao, Yulu Yang, Zengshun Zhao, Zhigang Wang, Qian Sun, and Dapeng Oliver Wu. 2019. "Combining Spatio-Temporal Context and Kalman Filtering for Visual Tracking" Mathematics 7, no. 11: 1059. https://doi.org/10.3390/math7111059
APA StyleYang, H., Wang, J., Miao, Y., Yang, Y., Zhao, Z., Wang, Z., Sun, Q., & Wu, D. O. (2019). Combining Spatio-Temporal Context and Kalman Filtering for Visual Tracking. Mathematics, 7(11), 1059. https://doi.org/10.3390/math7111059




