Adaptive Particle Swarm Optimization of PID Gain Tuning for Lower-Limb Human Exoskeleton in Virtual Environment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
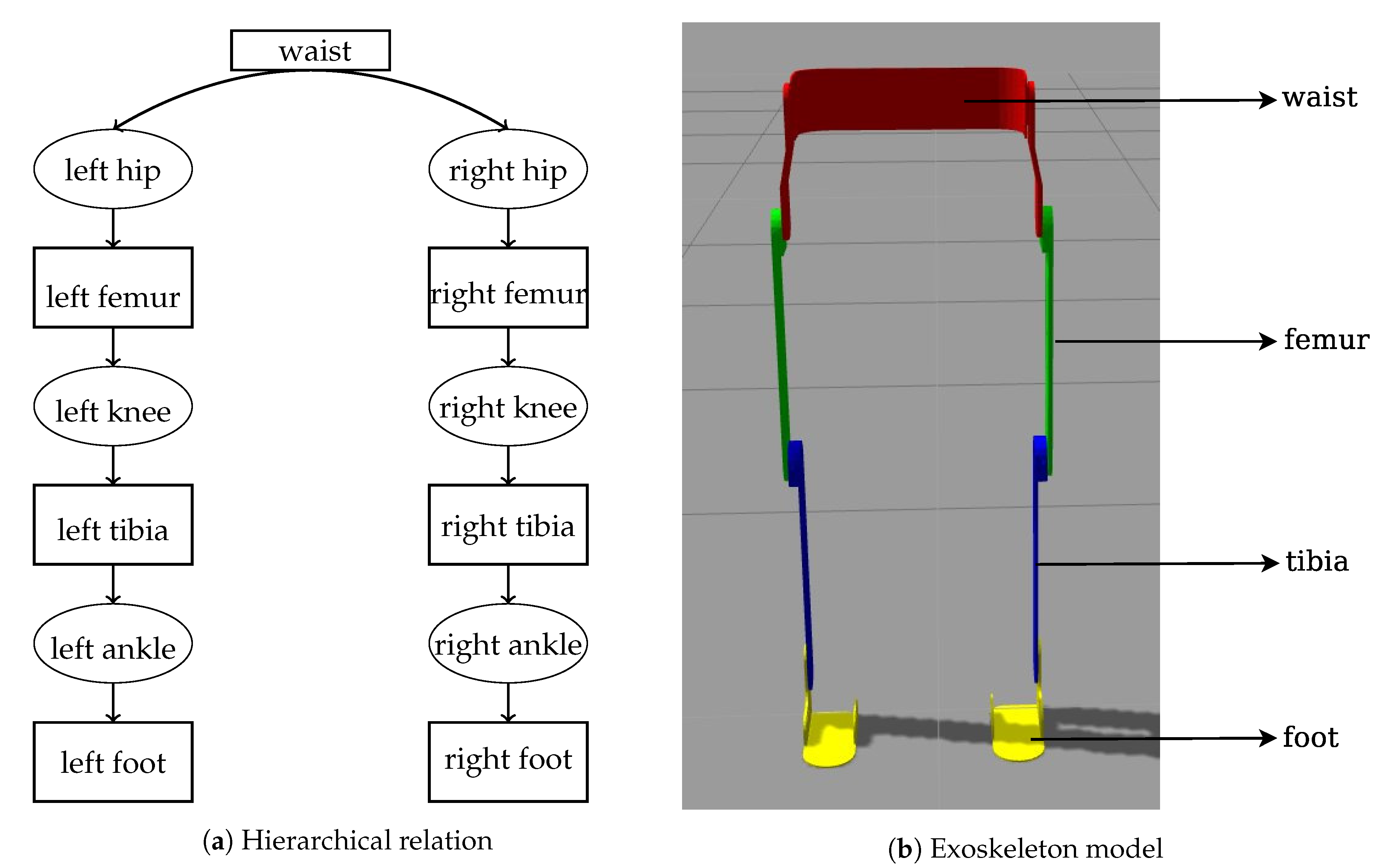
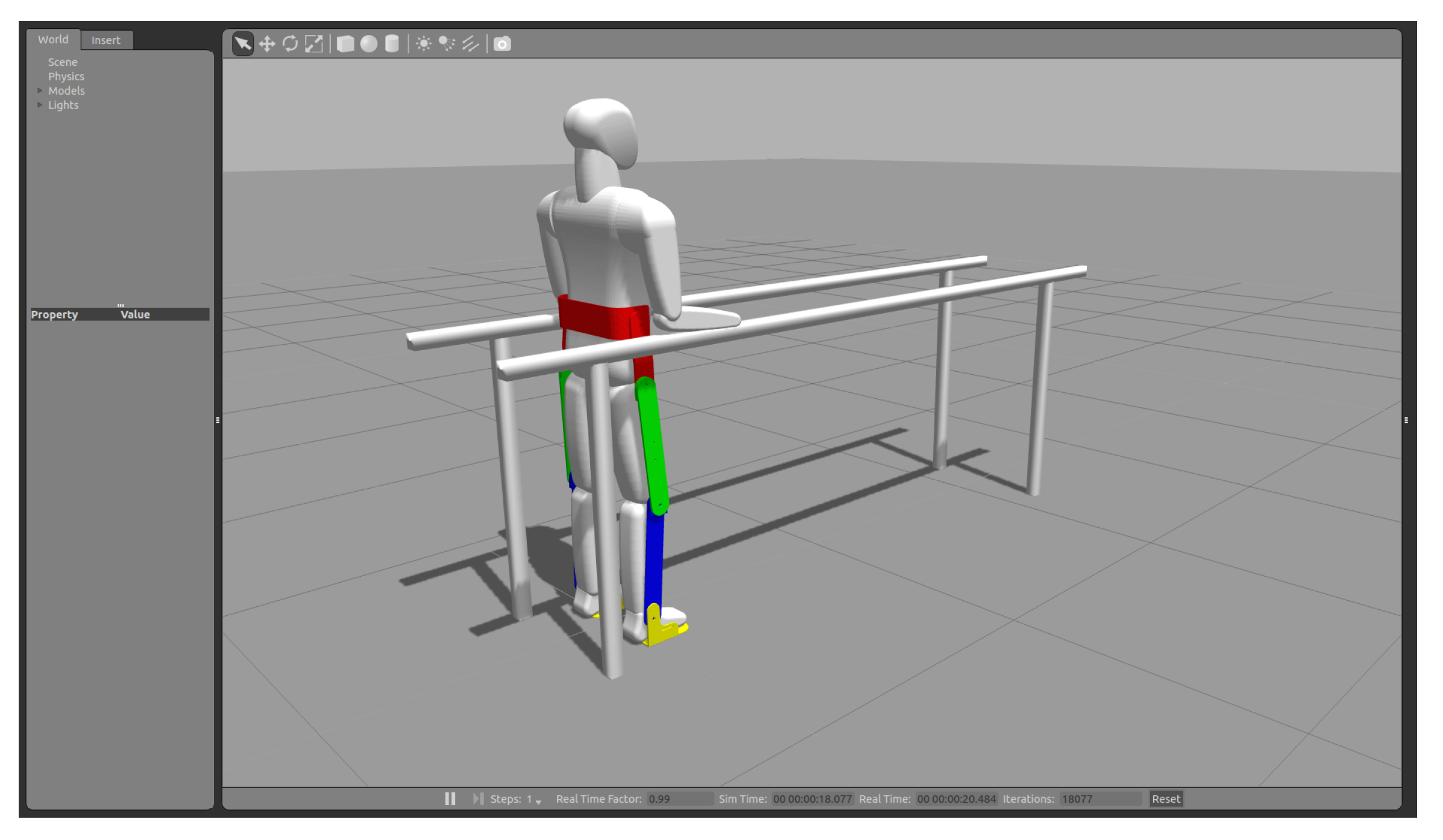
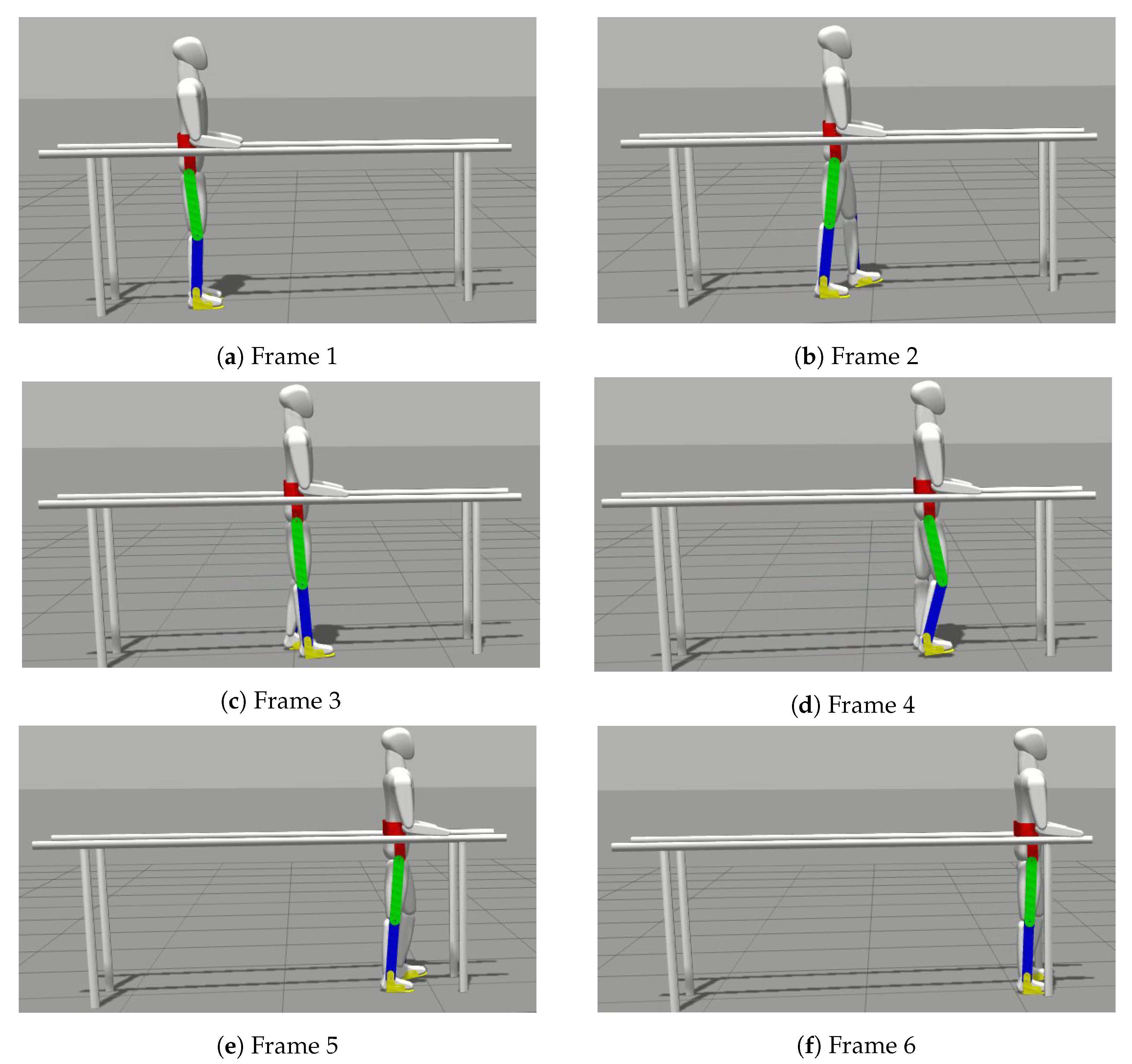
2. Human Exoskeleton Simulation in a Virtual Environment
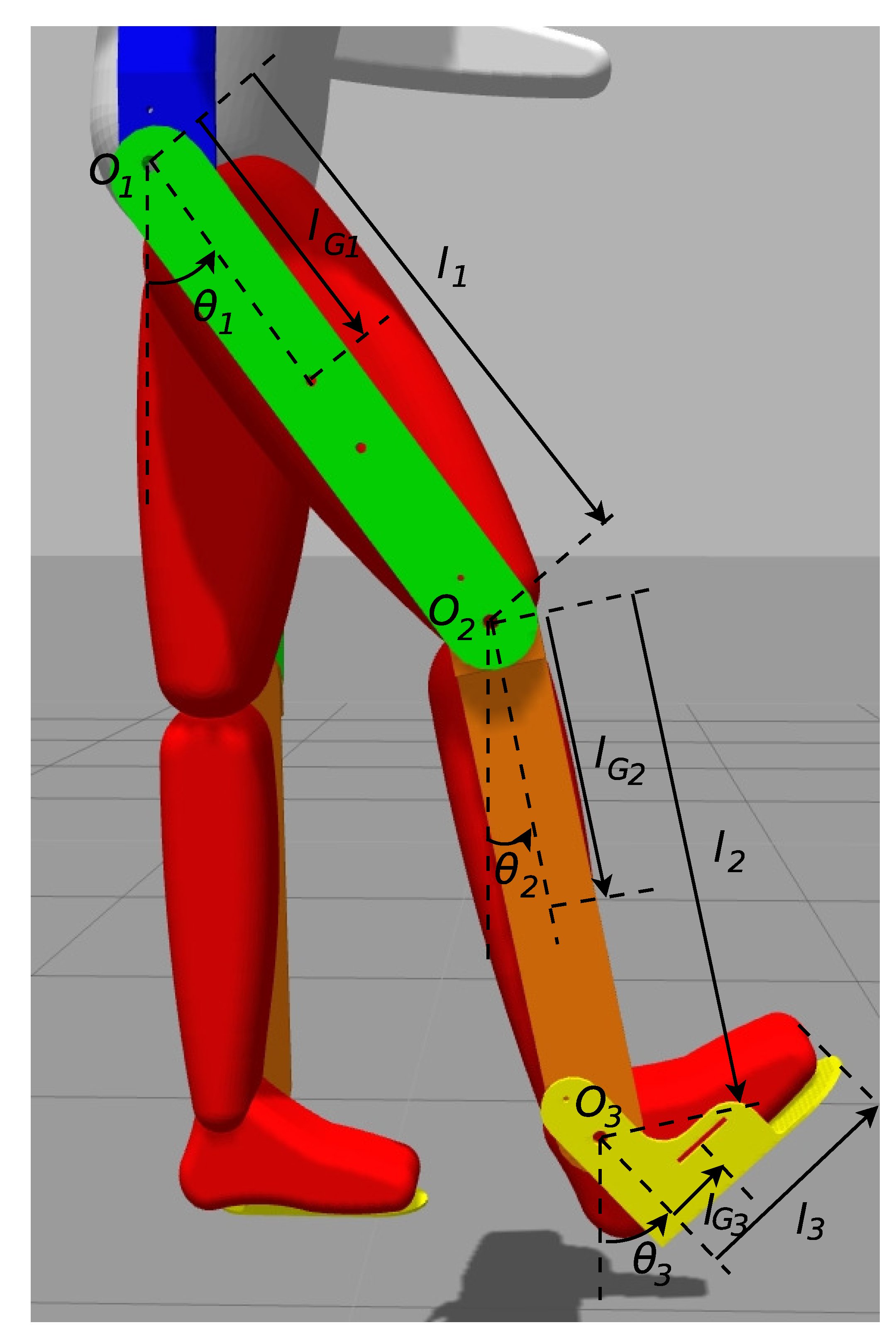
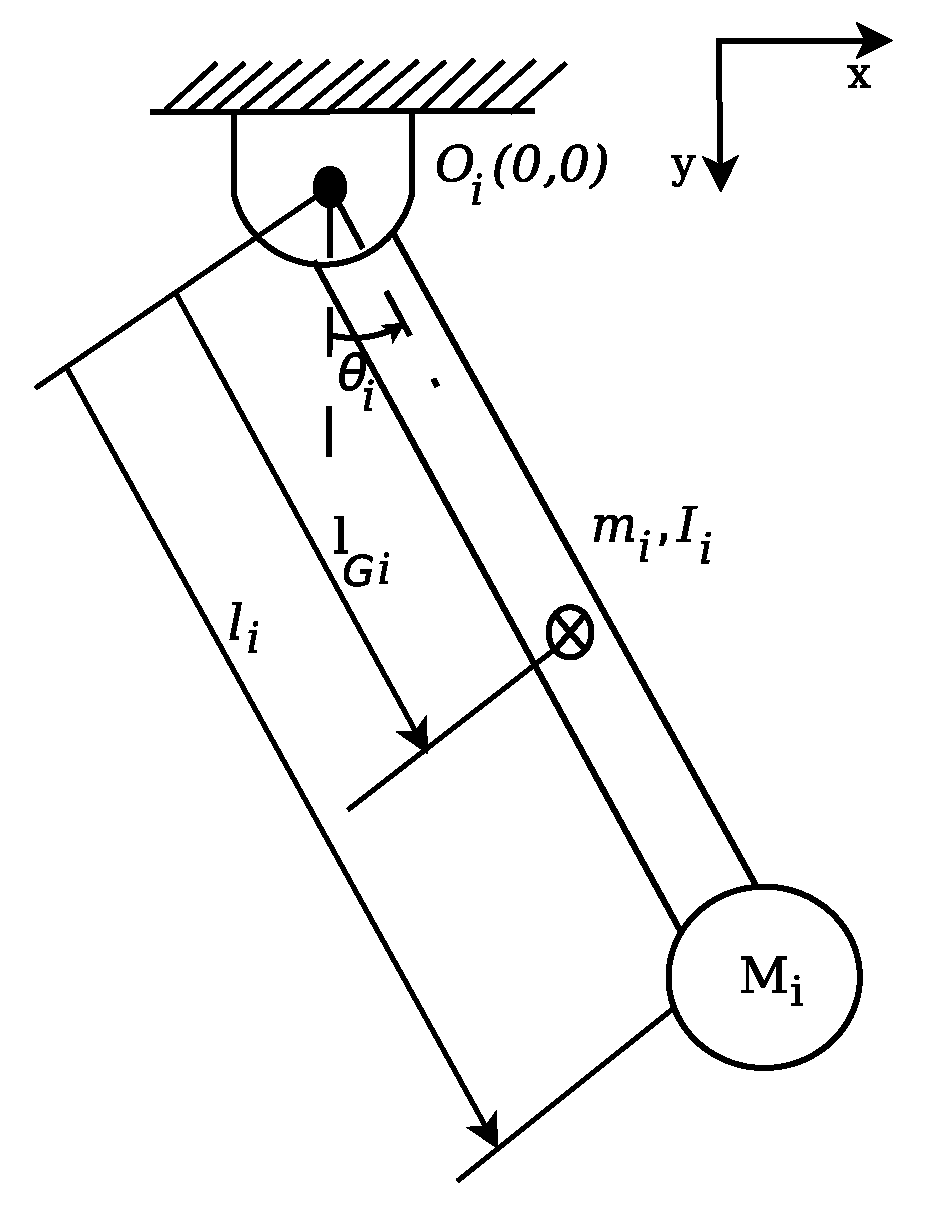
3. Human Exoskeleton Dynamic Modeling
4. Control System
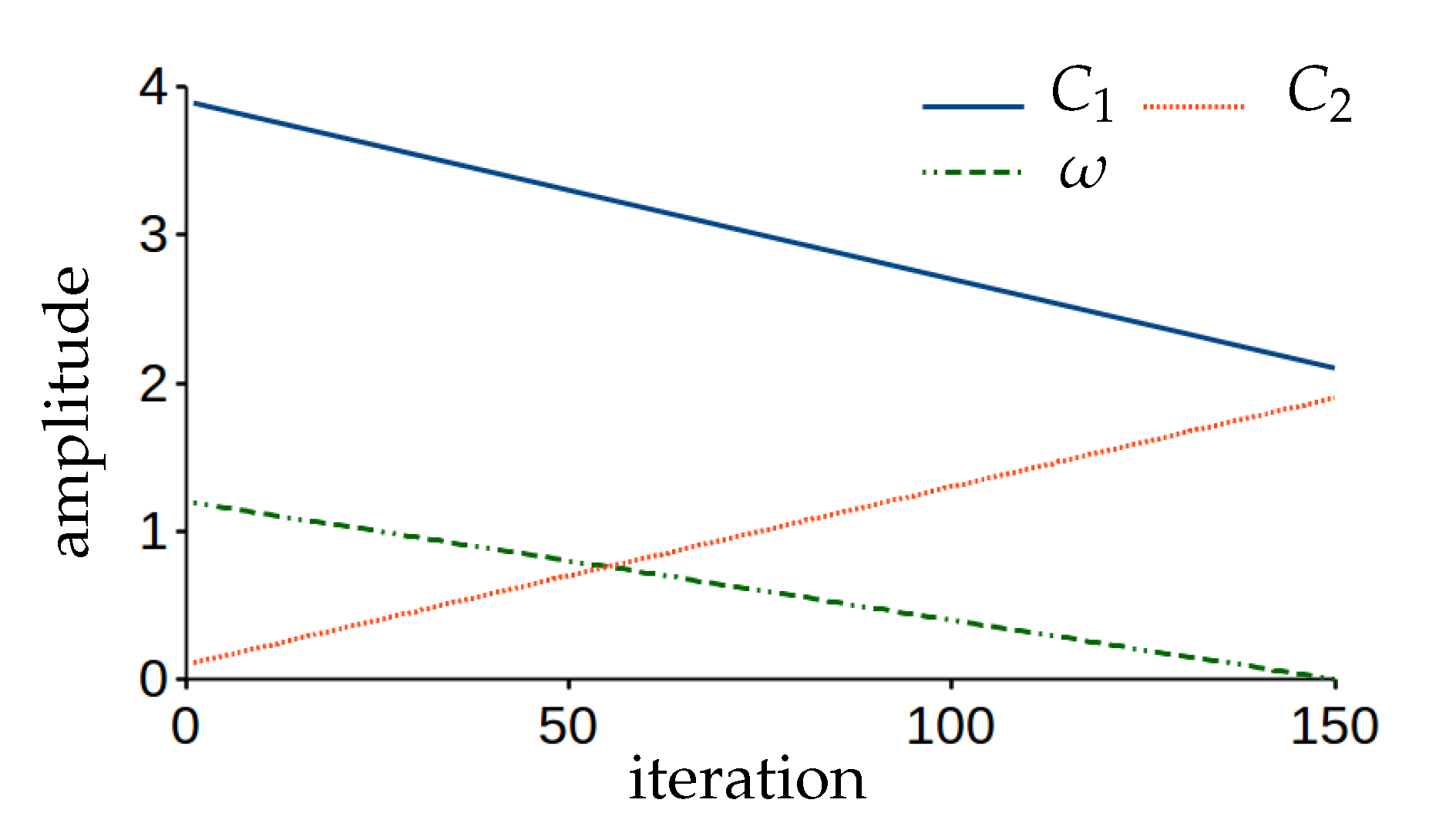
5. Optimization of the Controller’s Gains
| Algorithm 1 Combination of Ziegler–Nichols (Z-N) and adaptive particle swarm optimization (APSO). |
|
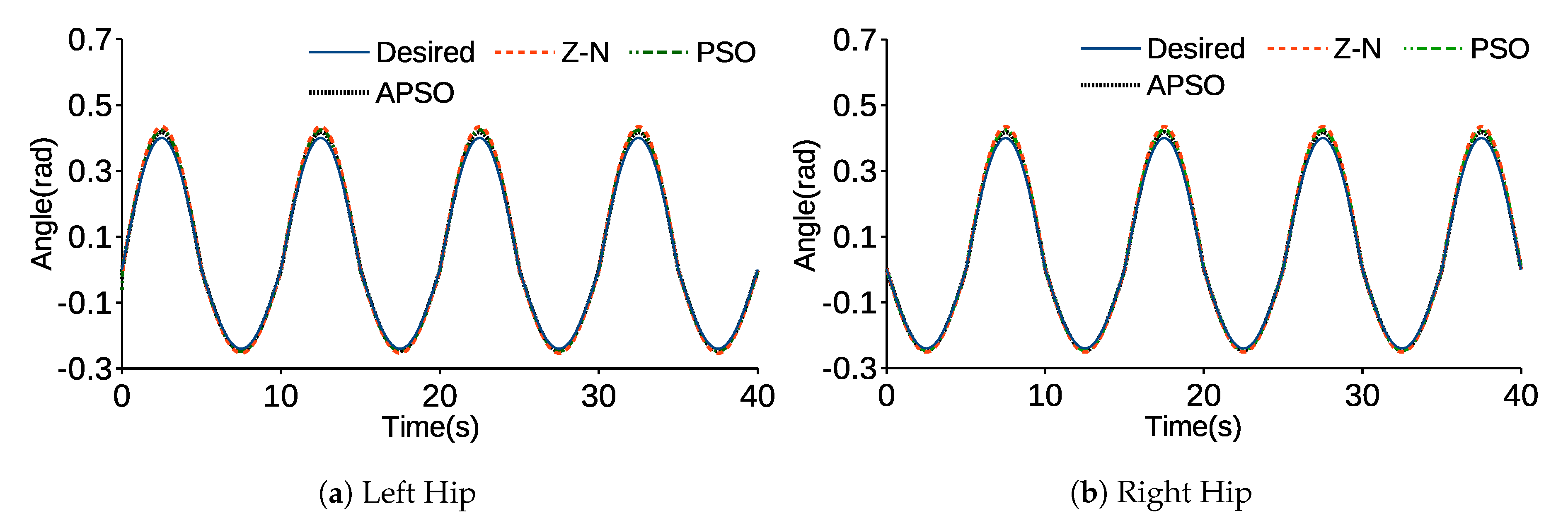
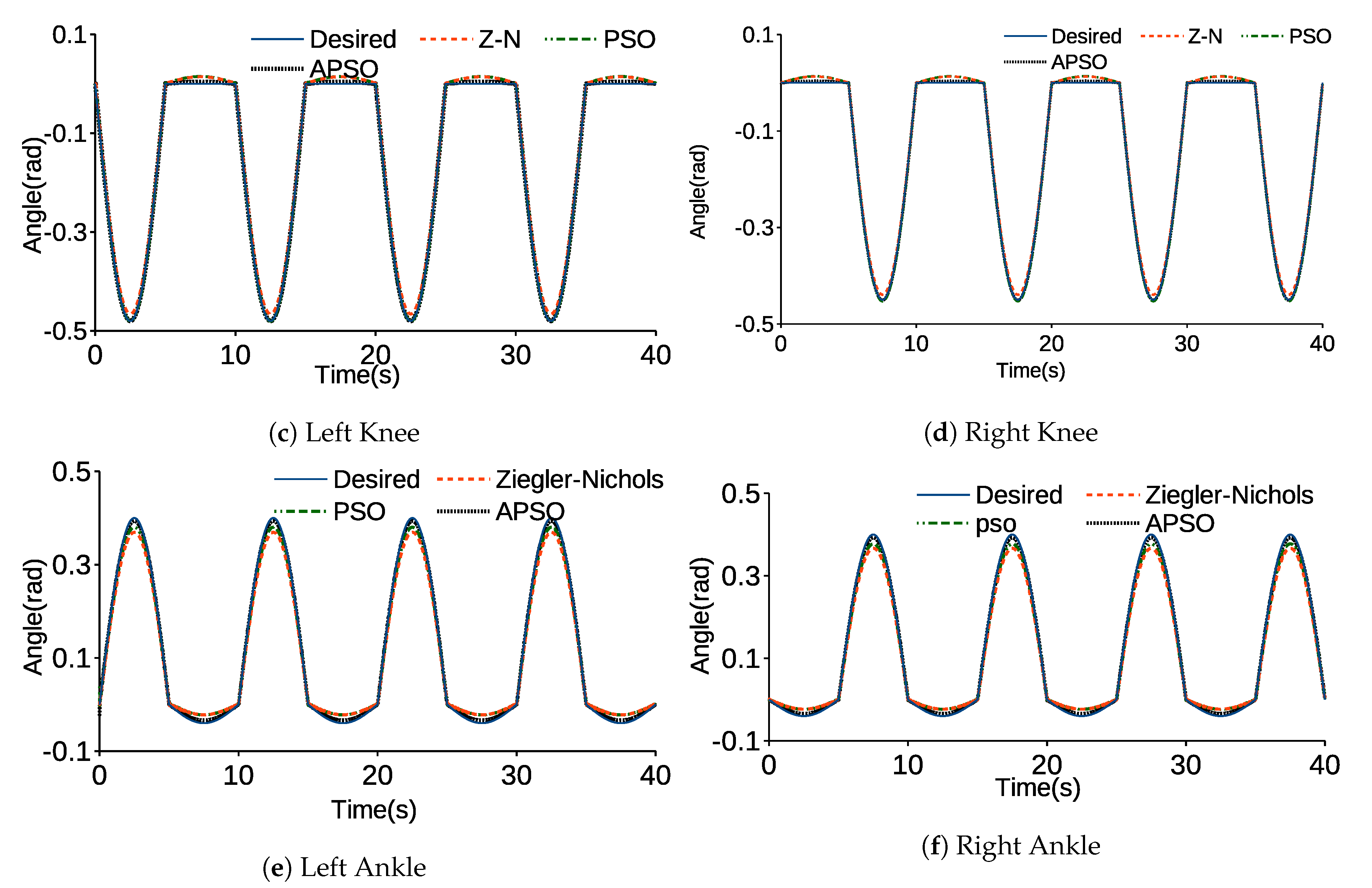
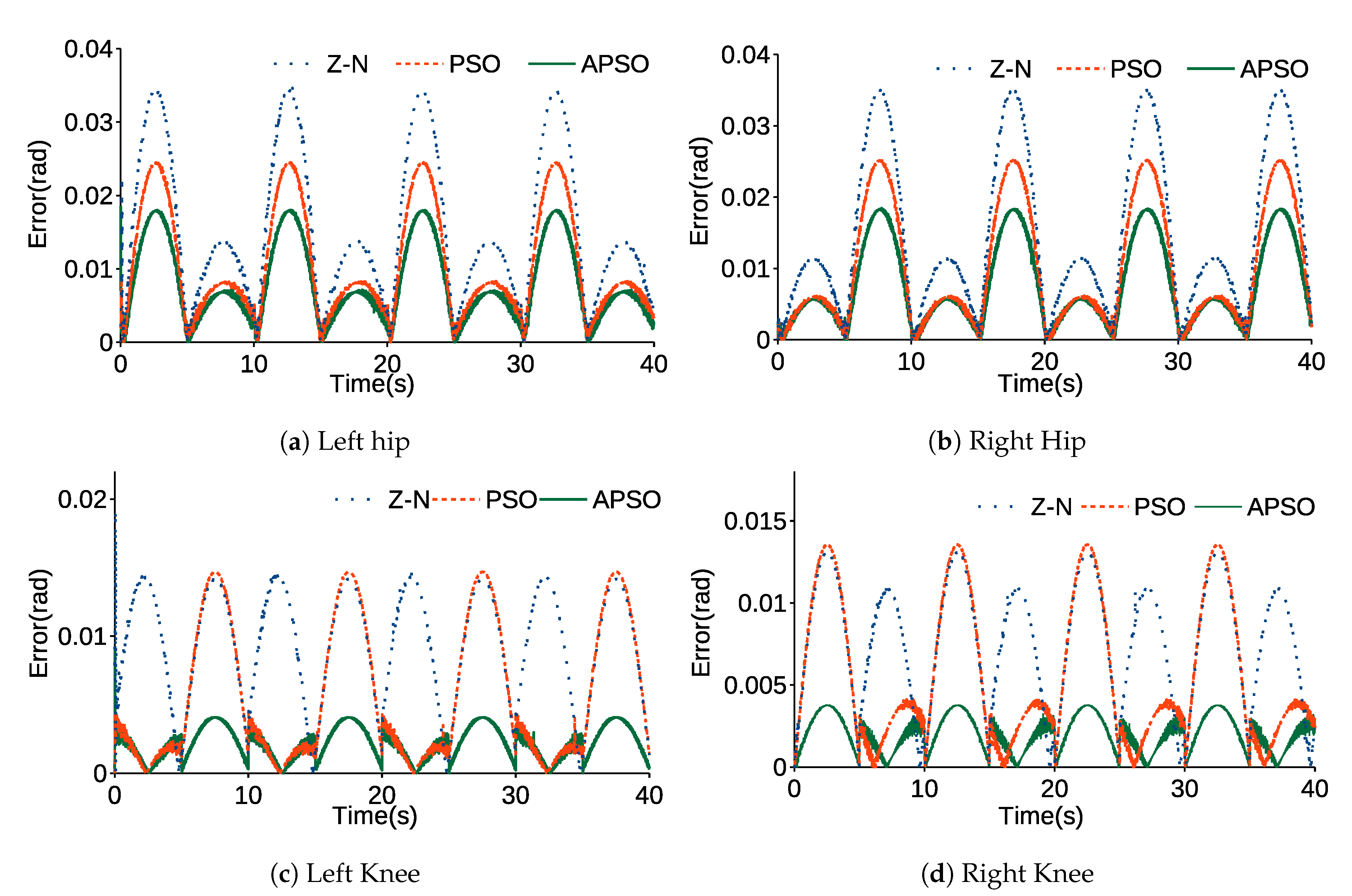
6. Results and Discussion
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, S.; Wang, L.; Meijneke, C.; Van Asseldonk, E.; Hoellinger, T.; Cheron, G.; Ivanenko, Y.; La Scaleia, V.; Sylos-Labini, F.; Molinari, M.; et al. Design and Control of the MINDWALKER Exoskeleton. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2015, 23, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Chen, W.; Chen, W.; Bai, S.; Zhang, J.; Wang, J. Design of a passive lower limb exoskeleton for walking assistance with gravity compensation. Mech. Mach. Theory 2020, 150, 103840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, S.A.; Ha, K.H.; Hartigan, C.; Goldfarb, M. An assistive control approach for a lower-limb exoskeleton to facilitate recovery of walking following stroke. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2015, 23, 441–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Zhong, C.H.; Zhao, X.; Ma, H.; Guan, X.; Li, X.; Liang, F.Y.; Cheng, J.C.Y.; Qin, L.; Law, S.W.; et al. A wearable exoskeleton suit for motion assistance to paralysed patients. J. Orthop. Transl. 2017, 11, 7–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kermavnar, T.; O’Sullivan, K.J.; Casey, V.; de Eyto, A.; O’Sullivan, L.W. Circumferential tissue compression at the lower limb during walking, and its effect on discomfort, pain and tissue oxygenation: Application to soft exoskeleton design. Appl. Ergon. 2020, 86, 103093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huo, W.; Mohammed, S.; Amirat, Y.; Kong, K. Active Impedance Control of a lower limb exoskeleton to assist sit-to-stand movement. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Stockholm, Sweden, 16–21 May 2016; pp. 3530–3536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daachi, M.E.; Madani, T.; Daachi, B.; Djouani, K. A radial basis function neural network adaptive controller to drive a powered lower limb knee joint orthosis. Appl. Soft Comput. J. 2015, 34, 324–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Chen, Z.; Yao, B.; Zhu, X.; Zhu, S.; Wang, Q.; Song, Y. Adaptive Robust Cascade Force Control of 1-DOF Hydraulic Exoskeleton for Human Performance Augmentation. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2017, 22, 589–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, R.; Li, Z.; Su, C.Y.; Xue, A. Development and learning control of a human limb with a rehabilitation exoskeleton. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2014, 61, 3776–3785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Huang, D.; Dong, X. Robust repetitive learning control of lower limb exoskeleton with hybrid electro-hydraulic system. In Proceedings of the 7th Data Driven Control and Learning Systems Conference, Enshi, China, 25–27 May 2018; pp. 718–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merayo, N.; Juárez, D.; Aguado, J.C.; De Miguel, I.; Durán, R.; Fernández, P.; Lorenzo, R.M.; Abril, E. PID Controller Based on a Self-Adaptive Neural Network to Ensure QoS Bandwidth Requirements in Passive Optical Networks. J. Opt. Commun. Netw. 2017, 9, 433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Castillo-Zamora, J.; Camarillo-Gomez, K.A.; Pérez-Soto, G.I.; Rodríguez-Reséndiz, J. Comparison of PD, PID and Sliding-Mode Position Controllers for V–Tail Quadcopter Stability. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 38086–38096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.; Dong, F.; Zhao, J.; Wang, L.; Wang, H.; Feng, Y. Combined Resonant Controller and Two-Degree-of-Freedom PID Controller for PMSLM Current Harmonics Suppression. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2018, 65, 7558–7568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.Y.; Park, J. Application of Particle Swarm Optimization to Economic Dispatch Problem: Advantages and Disadvantages. In Proceedings of the IEEE PES Power Systems Conference and Exposition, Atlanta, GA, USA, 29 October–1 November 2006; pp. 188–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdmouleh, Z.; Gastli, A.; Ben-brahim, L.; Haouari, M. Review of optimization techniques applied for the integration of distributed generation from renewable energy sources Review of optimization techniques applied for the integration of distributed generation from renewable energy sources. Renew. Energy 2017, 113, 266–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belkadi, A.; Oulhadj, H.; Touati, Y.; Khan, S.A.; Daachi, B. On the robust PID adaptive controller for exoskeletons: A particle swarm optimization based approach. Appl. Soft Comput. 2017, 60, 87–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durgadevi, S.; Sundari, K.T.; Raaghavi, D.; Akshaya, R. Comparative study of Controller Optimisation for CSTR using Particle Swarm Optimization Technique. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Electrical Energy Systems (ICEES), Chennai, India, 21–22 February 2019; pp. 2–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadigh, R.S.M. Optimizing PID Controller Coefficients Using Fractional Order Based on Intelligent Optimization Algorithms for Quadcopter. In Proceedings of the 6th RSI International Conference on Robotics and Mechatronics (IcRoM), Tehran, Iran, 23–25 October 2018; pp. 146–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Q.; Xia, X.; Feng, S.; Huang, M. Optimization design of LQR controller based on improved whale optimization algorithm. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Information and Computer Technologies (ICICT), Maui Island, HI, USA, 11–14 March 2020; pp. 380–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, D.; Gao, F.; Miao, Y.; Cao, R. Co-simulation research of a novel exoskeleton-human robot system on humanoid gaits with fuzzy-PID/PID algorithms. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2015, 79, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moharam, A.; El-Hosseini, M.A.; Ali, H.A. Design of optimal PID controller using hybrid differential evolution and particle swarm optimization with an aging leader and challengers. Appl. Soft Comput. 2016, 38, 727–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, D.K.; Barisal, A.K.; Tripathy, M. Load Frequency Control of Multi Area Interconnected Microgrid Power System using Grasshopper Optimization Algorithm Optimized Fuzzy PID Controller. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Recent Advances on Engineering, Technology and Computational Sciences (RAETCS), Allahabad, India, 6–8 February 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiri, M.S.; Ramli, R.; Tarmizi, M.A.A.; Ibrahim, M.F.; Danesh Narooei, K. Simulation and Control of a Six Degree of Freedom Lower Limb Exoskeleton. J. Kejuruter. 2020, 32, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiri, M.S.; Ramli, R.; Ibrahim, M.F. Hybrid design of PID controller for four DoF lower limb exoskeleton. Appl. Math. Model. 2019, 72, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiri, M.S.; Ramli, R.; Ibrahim, M.F. Genetically optimized parameter estimation of mathematical model for multi-joints hip–knee exoskeleton. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2020, 125, 103425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor Dempster, W. Space Requirements of the Seated Operator, Geometrical, Kinematic, and Mechanical Aspects of the Body with Special Reference to the Limb; Wright-Patterson Air Force Base: Green, OH, USA, 1955. [Google Scholar]
- Tözeren, A. Human Body Dynamics: Classical Mechanics and Human Movement; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- De Leva, P. Adjustments to Zatsiorsky-Seluyanov’s segment inertia parameters. J. Biomech. 1996, 29, 1223–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiri, M.S.; Ramli, R.; Ibrahim, M.F. Initialized Model Reference Adaptive Control for Lower Limb Exoskeleton. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 167210–167220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Chang, C. Hybrid Fuzzy PID Controller Design for a Mobile Robot. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Applied System Invention (ICASI), Chiba, Japan, 13–17 April 2018; pp. 650–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Rodríguez, I.D.; Han, S.; Keel, L.; Bhattacharyya, S. Advanced Tuning for Ziegler-Nichols Plants. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2017, 50, 1805–1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munlin, M.; Anantathanavit, M. New Social-Based Radius Particle Swarm Optimization. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Industrial Electronics and Applications (ICIEA), Siem Reap, Cambodia, 18–20 June 2017; pp. 838–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eberhart, R.; Kennedy, J. A new optimizer using particle swarm theory. In Proceedings of the Sixth International Symposium on Micro Machine and Human Science, Nagoya, Japan, 4–6 October 1995; pp. 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusuf, L.A.; Magaji, N. GA-PID controller for position control of inverted pendulum. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Adaptive Science and Technology (ICAST), Ota, Nigeria, 29–31 October 2015; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiri, M.S.; Ibrahim, M.F.; Ramli, R. Optimal parameter estimation for a DC motor using genetic algorithm. Int. J. Power Electron. Drive Syst. (IJPEDS) 2020, 11, 1047–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumathi, S.; Paneerselvam, S. Computational Intelligence Paradigms Theory and Applications, 1st ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Gao, J.; Song, R.; Li, R.; Li, Y.; Jiang, L. The design and control of a 3DOF lower limb rehabilitation robot. Mechatronics 2016, 33, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Exoskeleton | Femur | Tibia | Foot |
|---|---|---|---|
| m (kg) | 0.2943 | 0.2159 | 0.1150 |
| l (m) | 0.41 | 0.39 | 0.195 |
| I (kg m2) | |||
| (m) | 0.15 | 0.11 | 0.04 |
| Human | Femur | Tibia | Foot |
| m (kg) | 7.33 | 3.4503 | 1.075 |
| l (m) | 0.407 | 0.4334 | 0.275 |
| I (kg m2) | 0.1502 | 0.0505 | 0.0038 |
| (m) | 0.1763 | 0.1849 | 0.1179 |
| Link | Exoskeleton | Human Model |
|---|---|---|
| Femur | ||
| Tibia | ||
| Foot |
| Hip | 1656 | 4731.41 | 24.15 |
| Knee | 1314 | 3864.62 | 0.5 |
| Ankle | 101.90 | 615.57 | 4.26 |
| Joints | ||
|---|---|---|
| Right hip | ||
| Right knee | 0 | |
| Right ankle | ||
| Left hip | ||
| Left knee | 0 | |
| Left ankle |
| Joint | Left | Right | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hip | 0.0285 | 0.0080 | 0.0096 | 0.9983 | 0.0184 | 0.0077 | 0.0096 | 0.9983 |
| Knee | 0.0092 | 0.0021 | 0.0024 | 0.9998 | 0.0037 | 0.0019 | 0.0022 | 0.9998 |
| ankle | 0.023 | 0.0042 | 0.0047 | 0.9991 | 0.0088 | 0.0044 | 0.0049 | 0.9990 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Soleimani Amiri, M.; Ramli, R.; Ibrahim, M.F.; Abd Wahab, D.; Aliman, N. Adaptive Particle Swarm Optimization of PID Gain Tuning for Lower-Limb Human Exoskeleton in Virtual Environment. Mathematics 2020, 8, 2040. https://doi.org/10.3390/math8112040
Soleimani Amiri M, Ramli R, Ibrahim MF, Abd Wahab D, Aliman N. Adaptive Particle Swarm Optimization of PID Gain Tuning for Lower-Limb Human Exoskeleton in Virtual Environment. Mathematics. 2020; 8(11):2040. https://doi.org/10.3390/math8112040
Chicago/Turabian StyleSoleimani Amiri, Mohammad, Rizauddin Ramli, Mohd Faisal Ibrahim, Dzuraidah Abd Wahab, and Norazam Aliman. 2020. "Adaptive Particle Swarm Optimization of PID Gain Tuning for Lower-Limb Human Exoskeleton in Virtual Environment" Mathematics 8, no. 11: 2040. https://doi.org/10.3390/math8112040
APA StyleSoleimani Amiri, M., Ramli, R., Ibrahim, M. F., Abd Wahab, D., & Aliman, N. (2020). Adaptive Particle Swarm Optimization of PID Gain Tuning for Lower-Limb Human Exoskeleton in Virtual Environment. Mathematics, 8(11), 2040. https://doi.org/10.3390/math8112040





