An Efficient Micro Grid Optimization Theory
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Related Research
3. Micro Grid Optimization Theory
4. Conditional Equation
4.1. Conditional Equation for Peak Control
4.2. Conditional Equation for Power Usage Flattening
4.3. Conditional Equation for Demand Response Power
4.4. Conditional Equation for Net Zero Operation
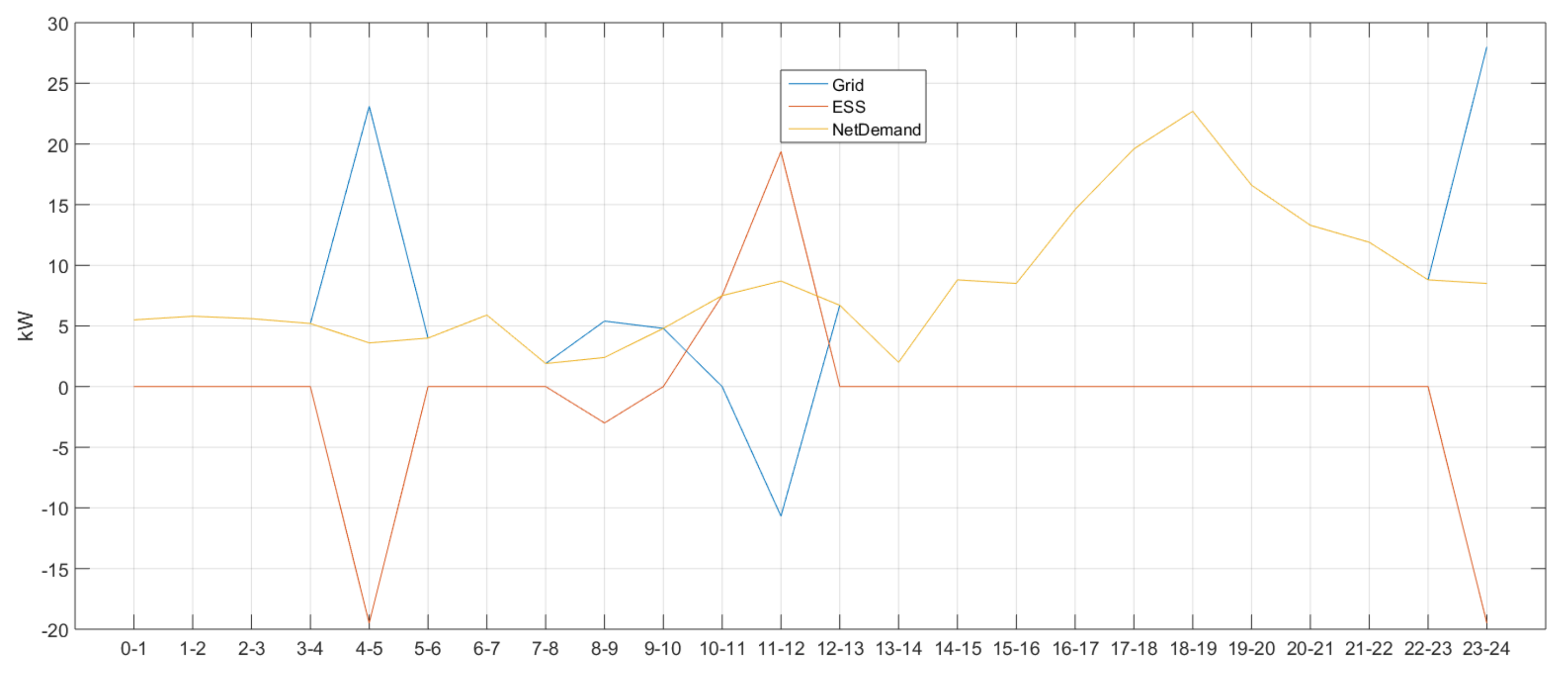
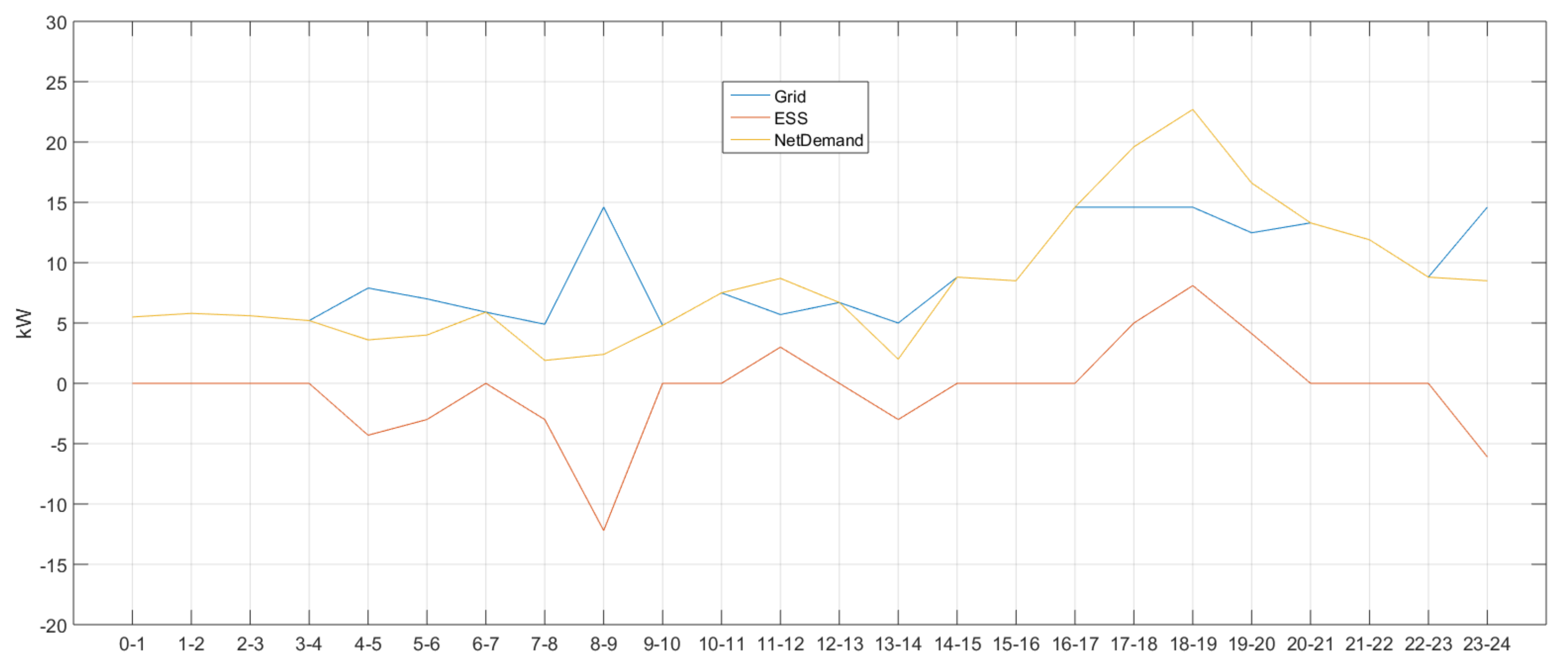
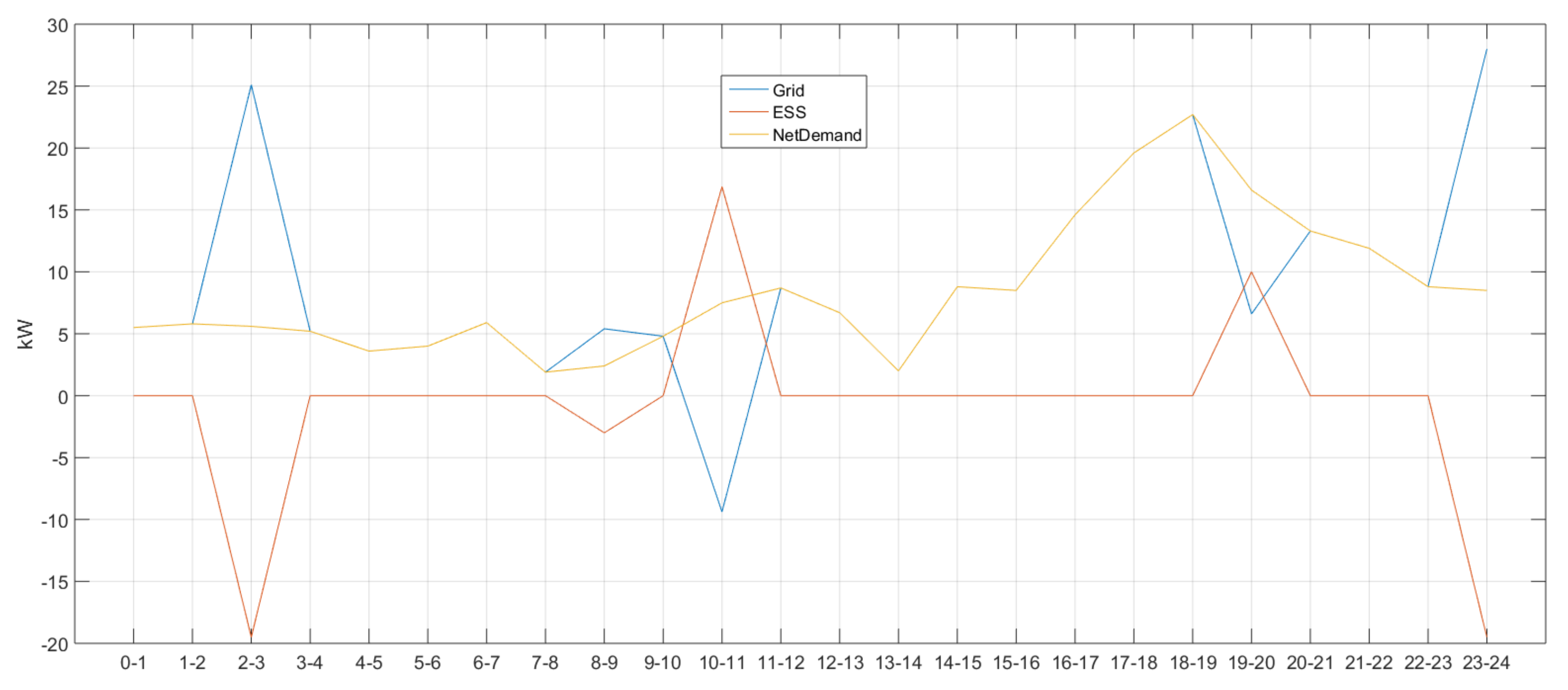
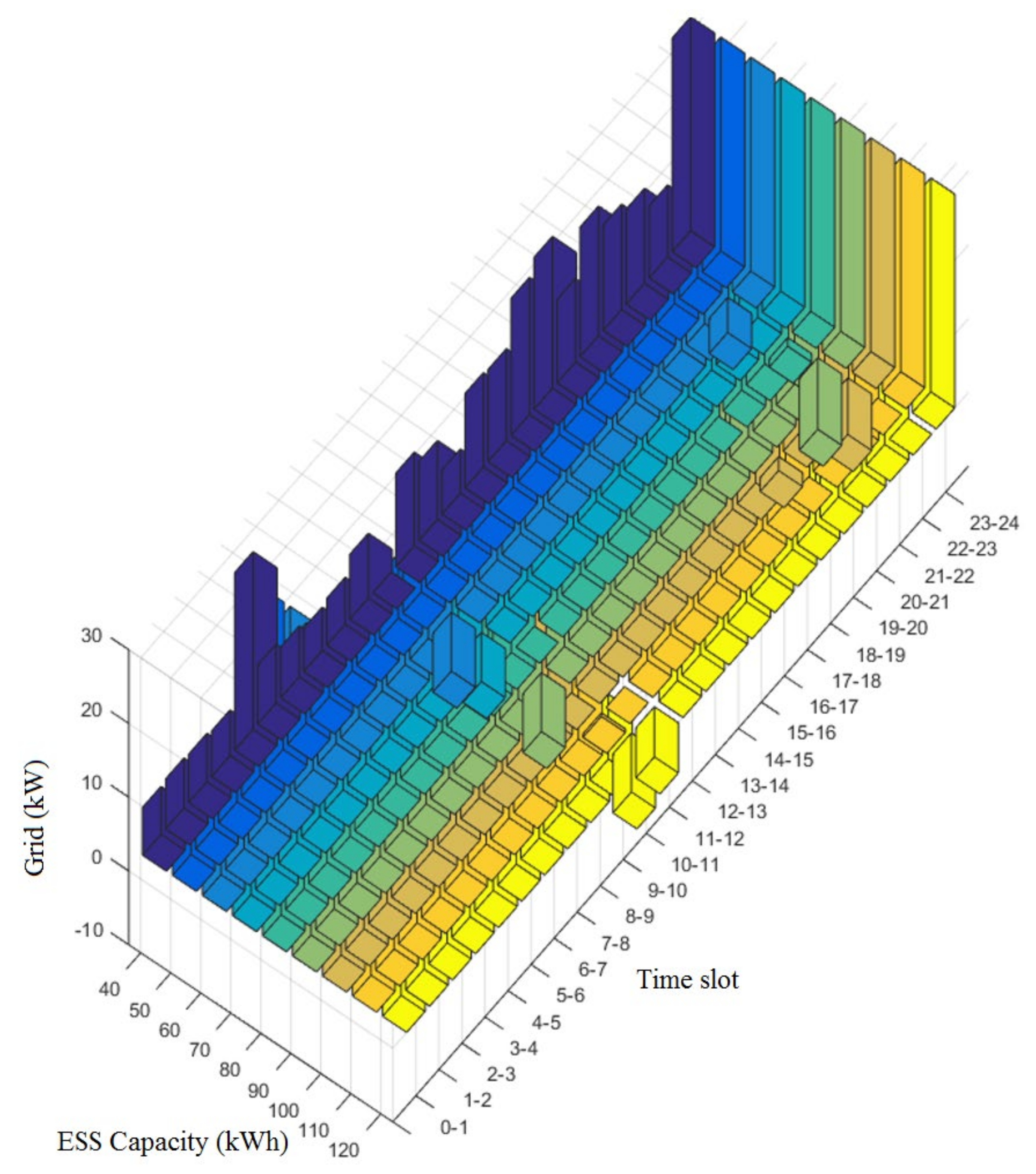
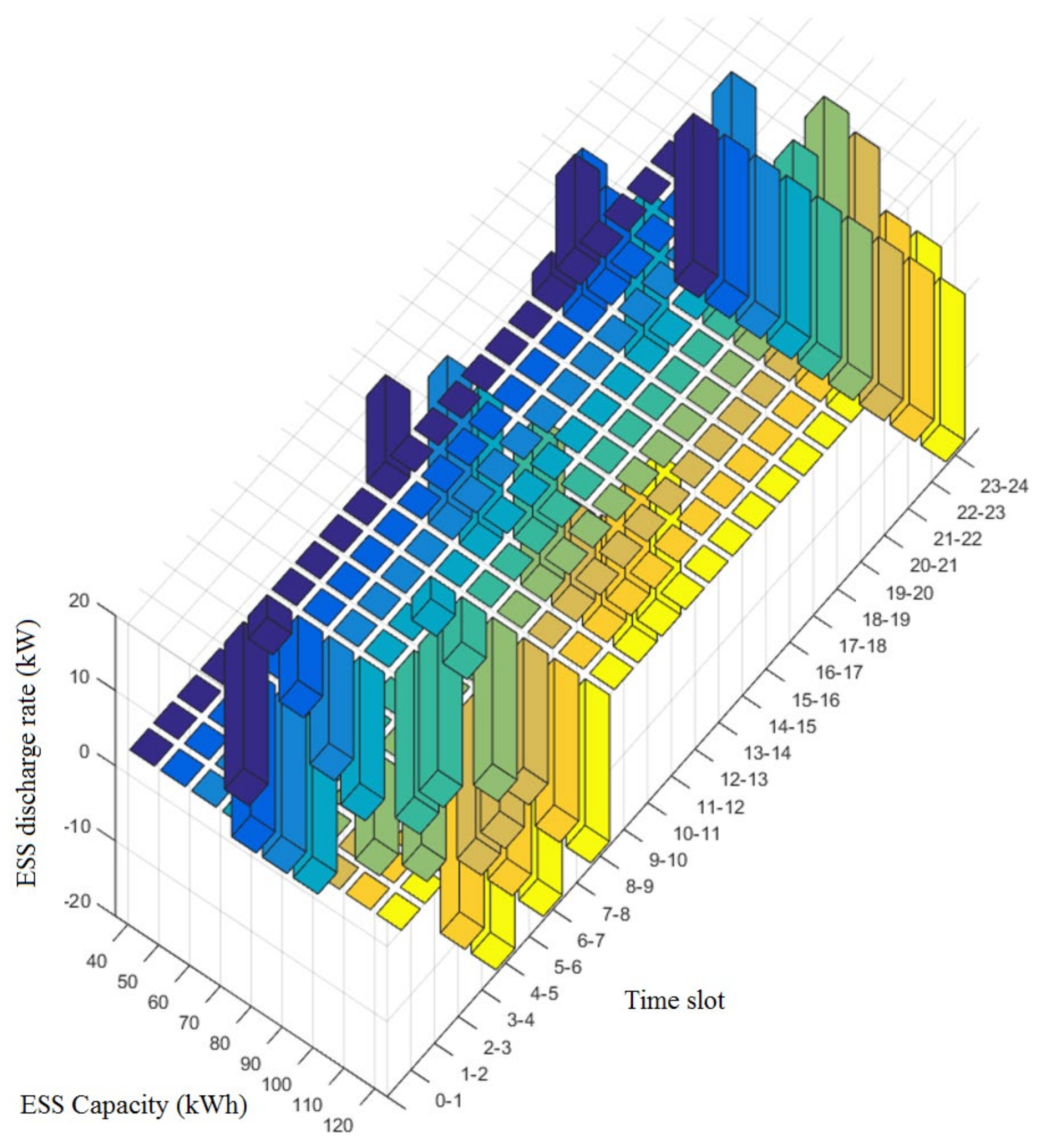
5. Performance Evaluation
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DERs | distributed energy resources |
| DR | demand response |
| EMS | energy management system |
| PV | photovoltaic |
| ESS | energy storage system |
| WT | wind turbine |
| SoC | state of charge |
References
- Huh, J.-H. Smart Grid Test Bed Using OPNET and Power Line Communication; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2017; pp. 1–425. [Google Scholar]
- Mun, J.H.; Ko, J.S.; Choi, J.S.; Jang, M.G.; Chung, D.H. Efficiency optimization control of SynRM drive using multi-AFLC. In Proceedings of the 2010 International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems, Incheon, Korea, 11–13 October 2010; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 908–913. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, J.S.; Ko, J.-S.; Chung, D.-H. Efficiency Analysis of PV tracking system with PSA Algorithm. J. Korean Inst. Illum. Electr. Install. Eng. 2009, 23, 36–44. [Google Scholar]
- Park, D.-M.; Kim, S.-K.; Seo, Y.-S. S-mote: SMART Home Framework for Common Household Appliances in IoT Network. J. Inf. Process. Syst. KIPS 2019, 15, 449–456. [Google Scholar]
- Arcos-Aviles, D.; Pascual, J.; Marroyo, L.; Sanchis, P.; Guinjoan, F. Fuzzy logic-based energy management system design for residential grid-connected microgrids. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2016, 9, 530–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Ma, Y.; Liu, W.; Ranade, S.J.; Luo, Y. Distributed optimal active power dispatch under constraints for smart grids. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 64, 5084–5094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamarra, C.; Guerrero, J.M. Computational optimization techniques applied to microgrids planning: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 48, 413–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, H.; Kinoshita, T. A new challenge of microgrid operation. Commun. Comput. Inf. Sci. 2010, 78, 250–260. [Google Scholar]
- Mohanpurkar, M.; Ouroua, A.; Hovsapian, R.; Luo, Y.; Singh, M.; Muljadi, E.; Gevorgian, V.; Donalek, P. Real-time co-simulation of adjustable-speed pumped storage hydro for transient stability analysis. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2018, 154, 276–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Yang, X.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, M.; Li, Z. Microgrid multi-objective economic dispatch optimization. Proc. CSEE 2013, 33, 57–66. [Google Scholar]
- Saad, W.; Han, Z.; Poor, H.V.; Basar, T. Game-theoretic methods for the smart grid: An overview of microgrid systems, demand-side management, and smart grid communications. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2012, 29, 86–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.; Basir, R.; Jidin, R.; Pasupuleti, J. Multi-agent based distributed control architecture for microgrid energy management and optimization. Energy Convers. Manag. 2016, 112, 288–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hori, H.; Ishigaki, Y.; Kimura, Y.; Mai, T.X.; Ozaki, T.; Yokose, T. Energy management system (sEMSA) achieving energy cost minimization. SEI Tech. Rev. 2015, 81, 56–62. Available online: https://global-sei.com/technology/tr/bn81/pdf/81-11.pdf (accessed on 20 September 2018).
- Huh, J.-H.; Seo, K. Hybrid AMI design for Smart Grid using the Game Theory model. Adv. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2015, 108, 86–92. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Wang, R.; Liu, Y.; Guo, B. Optimal operation of a smart residential microgrid based on model predictive control by considering uncertainties and storage impacts. Sol. Energy 2015, 122, 1052–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Chung, J.Y.; Xiao, J.; Hong, J.W.-K.; Boutaba, R. On the design and implementation of a home energy management system. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Wireless and Pervasive Computing, Hong Kong, China, 23–25 February 2011; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Ali, A.; El-Hag, A.; Bahadiri, M.; Harbaji, M.; El Haj, Y.A. Smart Home Renewable Energy Management System. Energy Procedia 2011, 12, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Zeng, P.; Li, S.; Zang, C.; Li, H. A Novel Multiobjective Optimization Algorithm for Home Energy Management System in Smart Grid. Math. Probl. Eng. 2015, 2015, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rodriguez, D.I.H.; Braun, M. A comparative study of optimization-and rule-based control for microgrid operation. In Proceedings of the Power and Energy Student Summit (PESS), Dortmund, Germany, 13–14 January 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Luna, A.C.; Diaz, N.L.; Graells, M.; Vasquez, J.C.; Guerrero, J.M.; Aldana, N.L.D. Mixed-Integer-Linear-Programming-Based Energy Management System for Hybrid PV-Wind-Battery Microgrids: Modeling, Design, and Experimental Verification. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2016, 32, 2769–2783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, H.; Eseye, A.T.; Zhang, J.; Zheng, D. Optimal energy management for industrial microgrids with high-penetration renewables. Prot. Control Mod. Power Syst. 2017, 2, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ju, C.; Wang, P.; Goel, L.; Xu, Y. A Two-Layer Energy Management System for Microgrids with Hybrid Energy Storage Considering Degradation Costs. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2017, 9, 6047–6057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, F.A.; Koivo, H.N. System modelling and online optimal management of microgrid with battery storage. Renew. Energy Power Qual. J. 2007, 1, 74–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, F.A.; Koivo, H.N. Online Management of MicroGrid with Battery Storage Using Multiobjective Optimization. In Proceedings of the 2007 International Conference on Power Engineering, Energy and Electrical Drives, Setubal, Portugal, 12–14 April 2007; pp. 231–236. [Google Scholar]
- Parisio, A.; Glielmo, L. Energy efficient microgrid management using model predictive control. In Proceedings of the 50th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control and European Control Conference, Orlando, FL, USA, 12–15 December 2011; pp. 5449–5454. [Google Scholar]
- Malysz, P.; Sirouspour, S.; Emadi, A. An Optimal Energy Storage Control Strategy for Grid-connected Microgrids. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2014, 5, 1785–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Xie, X.; Chu, C.-C.; Gadh, R. Distributed Optimal Energy Management in Microgrids. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2014, 6, 1137–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, K.; Menzel, K. A Guideline for the Implementation of an Energy Management System in Facility Management Organisations. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2019, 887, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, S.; Wang, Z.; Yan, X.; He, G. Appliance Flexibility Analysis Considering User Behavior in Home Energy Management System Using Smart Plugs. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2018, 66, 1391–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eissa, M. Developing incentive demand response with commercial energy management system (CEMS) based on diffusion model, smart meters and new communication protocol. Appl. Energy 2019, 236, 273–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nge, C.L.; Ranaweera, I.U.; Midtgård, O.-M.; Norum, L. A real-time energy management system for smart grid integrated photovoltaic generation with battery storage. Renew. Energy 2019, 130, 774–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gazafroudi, A.S.; Soares, J.; Ghazvini, M.A.F.; Pinto, T.; Vale, Z.; Corchado, J.M. Stochastic interval-based optimal offering model for residential energy management systems by household owners. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2019, 105, 201–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alasali, F.; Haben, S.; Holderbaum, W. Energy management systems for a network of electrified cranes with energy storage. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2019, 106, 210–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapaloglou, S.; Nesiadis, A.; Iliadis, P.; Atsonios, K.; Nikolopoulos, N.; Grammelis, P.; Yiakopoulos, C.; Antoniadis, I.; Kakaras, E. Smart energy management algorithm for load smoothing and peak shaving based on load forecasting of an island’s power system. Appl. Energy 2019, 238, 627–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, J.M.G.; Pouresmaeil, E.; Canizares, C.A.; Bhattacharya, K.; Mosaddegh, A.; Solanki, B.V.; Gonzalez, J.M.; Solanki, B. Smart Residential Load Simulator for Energy Management in Smart Grids. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2018, 66, 1443–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Sun, Z.; Chen, Z. Rule-based energy management strategy of a lithium-ion battery, supercapacitor and PEM fuel cell system. Energy Procedia 2019, 158, 2555–2560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farmani, F.; Parvizimosaed, M.; Monsef, H.; Rahimi-Kian, A. A conceptual model of a smart energy management system for a residential building equipped with CCHP system. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2018, 95, 523–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Zhou, L.; Ren, H.; Liu, X.; Talari, S.; Shafie-Khah, M.; Catalao, J.P.S. Multi-Objective Optimization Model of Source–Load–Storage Synergetic Dispatch for a Building Energy Management System Based on TOU Price Demand Response. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2018, 54, 1017–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, D.; Deblecker, O.; Ioakimidis, C.S. Optimal operation of an energy management system for a grid-connected smart building considering photovoltaics’ uncertainty and stochastic electric vehicles’ driving schedule. Appl. Energy 2018, 210, 1188–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Meer, D.; Mouli, G.R.C.; Mouli, G.M.-E.; Elizondo, L.R.; Bauer, P.; Morales-Espana, G. Energy Management System with PV Power Forecast to Optimally Charge EVs at the Workplace. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2016, 14, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nunna, H.S.V.S.K.; Battula, S.; Doolla, S.; Srinivasan, D. Energy Management in Smart Distribution Systems with Vehicle-to-Grid Integrated Microgrids. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2016, 9, 4004–4016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizivahed, A.; Naderi, E.; Narimani, H.; Fathi, M.; Narimani, M.R. A New Bi-Objective Approach to Energy Management in Distribution Networks with Energy Storage Systems. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2017, 9, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indragandhi, V.; Logesh, R.; Subramaniyaswamy, V.; Vijayakumar, V.; Siarry, P.; Uden, L. Multi-objective optimization and energy management in renewable based AC/DC microgrid. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2018, 70, 179–198. [Google Scholar]
- Pilloni, V.; Floris, A.; Meloni, A.; Atzori, L. Smart Home Energy Management Including Renewable Sources: A QoE-driven Approach. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2016, 9, 2006–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ali, I.; Hussain, S.M.S. Communication Design for Energy Management Automation in Microgrid. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2016, 9, 2055–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.-J.; Wang, J.; Gupta, V.; Chen, C. Distributed Energy Management for Networked Microgrids Using Online ADMM With Regret. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2018, 9, 847–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.Y.; Jin, Y.G.; Yoon, Y.T. Determining the Optimal Reserve Capacity in a Microgrid with Islanded Operation. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2016, 31, 1369–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eom, S.; Huh, J.-H. The Opening Capability for Security against Privacy Infringements in the Smart Grid Environment. Mathematics 2018, 6, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jung, S.; Huh, J.-H. Demand Response Resource Energy Optimization System for Residential Buildings: Smart Grid Approach. In Advanced Multimedia and Ubiquitous Engineering; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 517–522. [Google Scholar]








| Variables | Definitions |
|---|---|
| Power (kW) obtained with new and renewable energy generation in time zone k | |
| Power (kW) transmitted from PV to ESS in time zone k | |
| Power (kW) transmitted from PV to load in time zone k | |
| Amount of power (kWh) stored in time zone k | |
| Power (kW) discharged in time zone k | |
| Power (kW) transmitted from ESS to load in time zone k | |
| Power (kW) transmitted from ESS to power grid in time zone k | |
| Power (kW) charged to ESS in time zone k | |
| Power (kW) received from power grid in time zone k | |
| Power (kW) transmitted from power grid to ESS in time zone k | |
| Power (kW) transmitted from power grid to load in time zone k | |
| Power (kW) transmitted from power grid to in time zone k | |
| Power (kW) consumed by load in time zone k |
| Variables | Definitions |
|---|---|
| PV data in time zone k | |
| Load data in time zone k | |
| PV data set in time zone 1–(k-1) | |
| Load data set in time zone 1–(k-1) | |
| Data storage in time zone k | |
| Function (or algorithm) to predict PV | |
| Function (or algorithm) to predict load | |
| PV value calculated based on PV prediction in time zone k | |
| : | n PV data predicted based on D_PV [k] |
| Load value calculated based on load prediction in time zone k | |
| : | n load data predicted based on |
| Set of constants | |
| Power unit price info | |
| External operating conditions info | |
| ESS performance info | |
| Other constants including SoC range setting in each time zone, etc. | |
| Objective function coefficient vector | |
| Set of matrices or vectors representing constraints | |
| Function (or algorithm) for the calculation of optimal solutions | |
| ESS operation schedule |
| Range of ESS Charging Power | Range of ESS Discharging Power | SoC by Time Zone | ESS Capacity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3–19.5 kW | 3–19.5 kW | 0.05–0.95 | 40 kWh |
| Time Zone | 0–1 | 1–2 | 2–3 | 3–4 | 4–5 | 5–6 | 6–7 | 7–8 | 8–9 | 9–10 | 10–11 | 11–12 |
| Demand (kW) | 5.5 | 5.8 | 5.6 | 5.2 | 3.6 | 4 | 5.9 | 7.9 | 11.4 | 16.8 | 25.5 | 26.7 |
| Time Zone | 12–13 | 13–14 | 14–15 | 15–16 | 16–17 | 17–18 | 18–19 | 19–20 | 20–21 | 21–22 | 22–23 | 23–24 |
| Demand (kW) | 24.7 | 23 | 23.8 | 23.5 | 23.6 | 24.6 | 22.7 | 16.6 | 13.3 | 11.9 | 8.8 | 8.5 |
| Time Zone | 0–1 | 1–2 | 2–3 | 3–4 | 4–5 | 5–6 | 6–7 | 7–8 | 8–9 | 9–10 | 10–11 | 11–12 |
| Supply (kW) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 6 | 9 | 12 | 18 | 18 |
| Time Zone | 12–13 | 13–14 | 14–15 | 15–16 | 16–17 | 17–18 | 18–19 | 19–20 | 20–21 | 21–22 | 22–23 | 23–24 |
| Supply (kW) | 18 | 21 | 15 | 15 | 9 | 6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Time Zone | 0–1 | 1–2 | 2–3 | 3–4 | 4–5 | 5–6 | 6–7 | 7–8 | 8–9 | 9–10 | 10–11 | 11–12 |
| Unit Price for Purchase | 66.1 | 66.1 | 66.1 | 66.1 | 66.1 | 66.1 | 66.1 | 66.1 | 66.1 | 96.5 | 111.3 | 111.3 |
| Unit Price for Sales | 66.1 | 66.1 | 66.1 | 66.1 | 66.1 | 66.1 | 66.1 | 66.1 | 66.1 | 96.5 | 111.3 | 111.3 |
| Time Zone | 12–13 | 13–14 | 14–15 | 15–16 | 16–17 | 17–18 | 18–19 | 19–20 | 20–21 | 21–22 | 22–23 | 23–24 |
| Unit Price for Purchase | 96.5 | 96.5 | 96.5 | 96.5 | 96.5 | 111.3 | 111.3 | 111.3 | 96.5 | 96.5 | 111.3 | 66.1 |
| Unit Price for Sales | 96.5 | 96.5 | 96.5 | 96.5 | 96.5 | 111.3 | 111.3 | 111.3 | 96.5 | 96.5 | 111.3 | 66.1 |
| Time Zone | Peak Setting | |
|---|---|---|
| Condition | 17–18, 18–19, 19–20 | 15 kW |
| - | Time Zone | Demand Response Setting |
|---|---|---|
| Condition | 17–18, 18–19, 19–20 | 10 kWh |
| - | Time Zone |
|---|---|
| Condition | 3–4, 4–5 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jung, S.; Yoon, Y.T.; Huh, J.-H. An Efficient Micro Grid Optimization Theory. Mathematics 2020, 8, 560. https://doi.org/10.3390/math8040560
Jung S, Yoon YT, Huh J-H. An Efficient Micro Grid Optimization Theory. Mathematics. 2020; 8(4):560. https://doi.org/10.3390/math8040560
Chicago/Turabian StyleJung, Sooyoung, Yong Tae Yoon, and Jun-Ho Huh. 2020. "An Efficient Micro Grid Optimization Theory" Mathematics 8, no. 4: 560. https://doi.org/10.3390/math8040560
APA StyleJung, S., Yoon, Y. T., & Huh, J.-H. (2020). An Efficient Micro Grid Optimization Theory. Mathematics, 8(4), 560. https://doi.org/10.3390/math8040560






