Simulation of Natural Convection in a Concentric Hexagonal Annulus Using the Lattice Boltzmann Method Combined with the Smoothed Profile Method
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Numerical Method
2.1. Solving Fluid Flow Using LBM
2.2. Solving Temperature Distribution with FDM
2.3. Evaluation of and with SPM
3. Simulation Results
3.1. Validation
3.2. Natural Convection in the Concentric Hexagonal Annulus
3.2.1. Streamlines and Isotherms Patterns Inside the Annulus
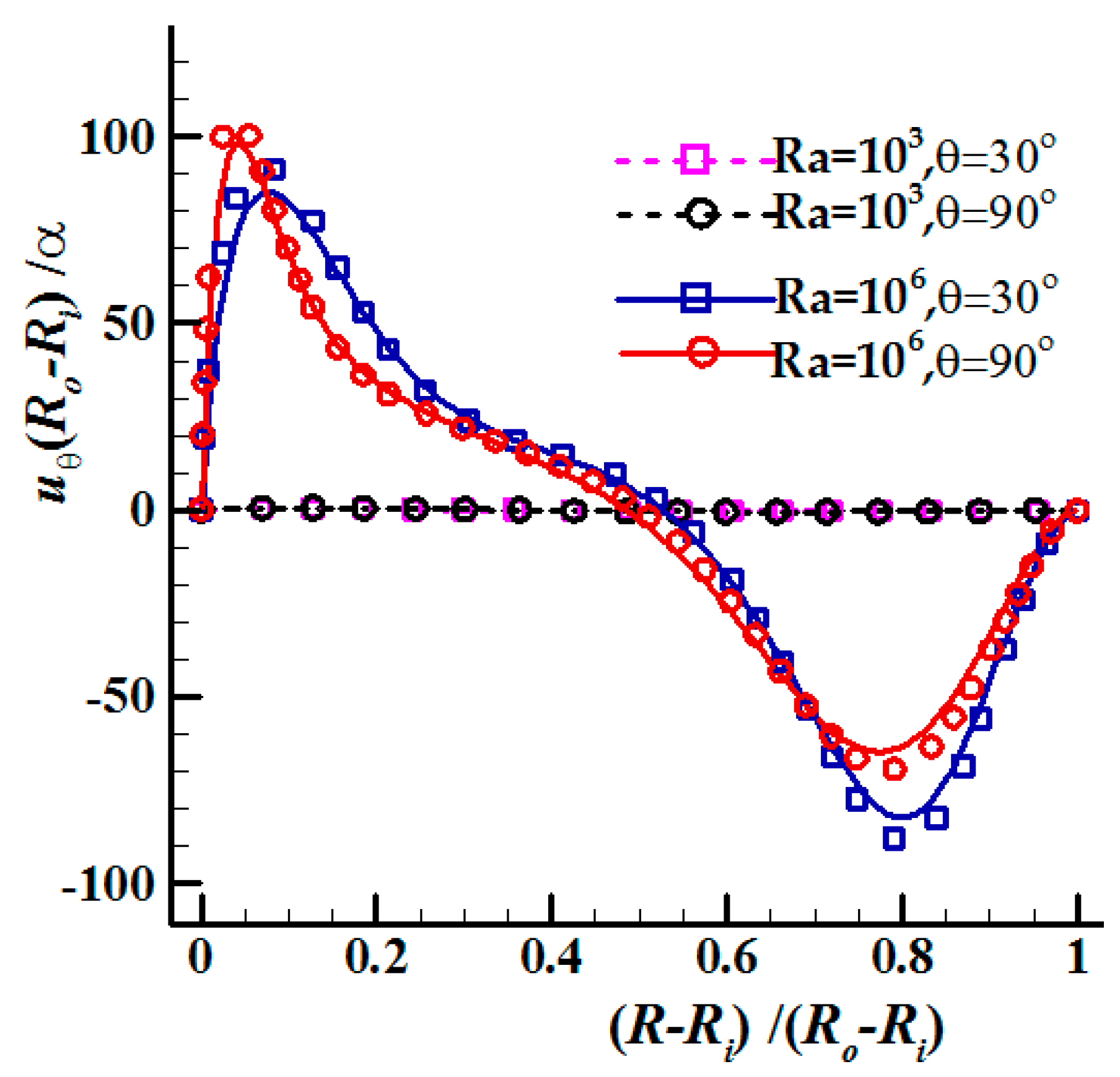
3.2.2. Temperature and Velocity Profiles
4. Conclusions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kuehn, T.H.; Goldstein, R.J. An experimental and theoretical study of natural convection in the annulus between horizontal concentric cylinders. J. Fluid Mech. 1976, 4, 695–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuehn, T.H.; Goldstein, R.J. An experimental study of natural convection heat transfer in concentric and eccentric horizontal cylindrical annuli. J. Heat Trans. 1978, 100, 635–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, R.D. An Experimental Study on the steady natural convection in a horizontal annulus with irregular boundaries. ASME-HTD 1980, 8, 89–95. [Google Scholar]
- Boyd, R.D. A unified theory for correlating steady laminar natural convective heat transfer data for horizontal annuli. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 1981, 24, 1545–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, K.S.; Won, Y.H.; Cho, C.H. Patterns of natural convection around a square cylinder placed concentrically in a horizontal circular cylinder. J. Heat Trans. 1983, 105, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raithby, G.D.; Galpin, P.F.; Van Doormaal, J.P. Prediction of heat and fluid flow in complex geometries using general orthogonal coordinates. Numer. Heat Trans. 1986, 9, 125–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glakpe, E.K.; Asfaw, A. Prediction of two-dimensional natural convection in enclosures with inner bodies of arbitrary shapes. Numer. Heat Trans. A 1991, 20, 279–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.L.; Wu, Q.J.; Tao, W.Q. Experimental study of natural convection heat transfer between a cylindrical envelope and an internal concentric heated octagonal cylinder with or without slots. ASME J. Heat Trans. 1991, 113, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peskin, C.S. Flow patterns around heart valves: A numerical method. J. Comp. Phys. 1972, 10, 252–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glowinski, R.; Pan, T.-W.; Helsa, T.; Joseph, D.D. A distributed lagrange multiplier/fictitious domain method for particulate flows. Int. J. Multiph. Flow. 1999, 25, 755–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakayama, Y.; Yamamoto, R. Simulation method to resolve hydrodynamic interactions in colloidal dispersions. Phys. Rev. E. 2005, 71, 036707-1–036707-7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Luo, X.; Maxey, R.M.; Karniadakis, G.E. Smoothed profile method for particulate flows: Error analysis and simulations. J. Comp. Phys. 2009, 228, 1750–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alapati, S.; Che, W.S.; Suh, Y.K. Simulation of sedimentation of a sphere in a viscous fluid using the lattice Boltzmann method combined with the smoothed profile method. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2015, 7, 794198-1–794198-12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Succi, S. The Lattice Boltzmann Equation for Fluid Dynamics and Beyond; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Alapati, S.; Kang, S.M.; Suh, Y.K. Parallel computation of two-phase flow in a microchannel using the lattice Boltzmann method. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2009, 23, 2492–2501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Palma, P.R.; Huber, C.; Viotti, P. A new lattice Boltzmann model for interface reactions between immiscible fluids. Adv. Water Resour. 2015, 82, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Huang, X.; Wang, S.; Kang, Y. Study on the bubble growth and departure with a lattice Boltzmann method. China Ocean Eng. 2020, 34, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dellar, P. Lattice Kinetic Schemes for Magnetohydrodynamics. J. Comp. Phys. 2002, 179, 95–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dellar, P. Lattice Boltzmann formulation for Braginskii magnetohydrodynamics. Comput. Fluids 2011, 46, 201–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fyta, M.; Melchionna, S.; Succi, S.; Kaxiras, E. Hydrodynamic correlations in the translocation of biopolymer through a nanopore: Theory and multiscale simulations. Phys. Rev. E 2008, 78, 036704-1–036704-7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alapati, S.; Fernandes, D.V.; Suh, Y.K. Numerical simulation of the electrophoretic transport of a biopolymer through a synthetic nanopore. Mol. Simulat. 2011, 37, 466–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alapati, S.; Fernandes, D.V.; Suh, Y.K. Numerical and theoretical study on the mechanism of biopolymer translocation process through a nanopore. J. Chem. Phys. 2011, 135, 055103-1–055103-11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Li, D.C.; Shu, S.; Niu, X.D. Modified momentum exchange method for fluid-particle interactions in the lattice Boltzmann method. Phys. Rev. E 2015, 91, 033301-1–033301-14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, H.Z.; Niu, X.D.; Shu, S.; Li, M.J.; Yamaguchi, H. A momentum exchange-based immersed boundary-lattice Boltzmann method for simulating a flexible filament in an incompressible flow. Comput. Math. Appl. 2014, 67, 1039–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohestani, A.; Rahnama, M.; Jafari, S.; Javaran, E.J. Non-circular particle treatment in smoothed profile method: A case study of elliptical particles sedimentation using lattice Boltzmann method. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2020, 41, 315–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Pan, G.; Zhang, Y.; Haeri, S. A relaxed multi-direct-forcing immersed boundary-cascaded lattice Boltzmann method accelerated on GPU. Comput. Phys. Commun. 2020, 248, 106980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikholeslami, M.; Bandpy, M.G.; Ganji, D.D. Magnetic field effects on natural convection around a horizontal circular cylinder inside a square enclosure filled with nanofluid. Int. Commun. Heat Mass. 2012, 39, 978–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikholeslami, M.; Bandpy, M.G.; Ganji, D.D. Lattice Boltzmann method for MHD natural convection heat transfer using nanofluid. Powder Technol. 2014, 254, 82–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, K.-H.; Liao, C.-C.; Lien, S.-Y.; Lin, C.-A. Thermal lattice Boltzmann simulations of natural convection with complex geometry. Comput. Fluids 2012, 69, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bararnia, H.; Soleimani, S.; Ganji, D.D. Lattice Boltzmann simulation of natural convection around a horizontal elliptic cylinder inside a square enclosure. Int. Commun. Heat Mass. 2011, 38, 1436–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikholeslami, M.; Bandpy, M.G.; Vajravelu, K. Lattice Boltzmann simulation of magnetohydrodynamic natural convection heat transfer of Al2O3-water nanofluid in a horizontal cylindrical enclosure with an inner triangular cylinder. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2015, 80, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moutaouakil, L.E.; Zrikem, Z.; Abdelbaki, A. Lattice Boltzmann simulation of natural convection in an annulus between a hexagonal cylinder and a square enclosure. Math. Probl. Eng. 2017, 2017, 3834170-1–3834170-11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, Y.; Niu, X.-D.; Shu, S.; Yuan, H.; Li, M. Natural convection in a concentric annulus: A lattice Boltzmann method study with boundary condition-enforced immersed boundary method. Adv. Appl. Math. Mech. 2013, 5, 321–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Li, D.; Shu, S.; Niu, X. Immersed boundary-lattice Boltzmann simulation of natural convection in a square enclosure with a cylinder covered by porous layer. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2016, 92, 1166–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khazaeli, R.; Mortazavi, S.; Ashrafizaadeh, M. Application of an immersed boundary treatment in simulation of natural convection problems with complex geometry via the lattice Boltzmann method. J. Appl. Fluid Mech. 2015, 8, 309–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Li, D.; Shu, S.; Niu, X. An efficient smoothed profile-lattice Boltzmann method for the simulation of forced and natural convection flows in complex geometries. Int. Commun. Heat Mass. 2015, 68, 188–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alapati, S.; Che, W.S.; Ahn, J.-W. Lattice Boltzmann method combined with the smoothed profile method for the simulation of particulate flows with heat transfer. Heat Transfer Eng. 2019, 40, 166–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladd, A.J.C. Numerical simulations of particulate suspensions via a discretized Boltzmann equation. Part 1. Theoretical foundation. J. Fluid Mech. 1994, 271, 285–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ladd, A.J.C. Numerical simulations of particulate suspensions via a discretized Boltzmann equation. Part 2. Numerical results. J. Fluid Mech. 1994, 271, 311–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bouzidi, M.; Firdaouss, M.; Lallemand, P. Momentum transfer of a Boltzmann-lattice fluid with boundaries. Phys. Fluids 2001, 13, 3452–3459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.; Mei, R.; Luo, L.-S.; Shyy, W. Viscous flow computations with the method of lattice Boltzmann equation. Prog. Aerosp. Sci. 2003, 39, 329–367. [Google Scholar]
- Mittal, R.; Iaccarino, G. Immersed boundary methods. Ann. Rev. Fluid Mech. 2005, 37, 239–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marshall, K.N.; Wedel, R.K.; Dammann, R.E. Development of Plastic Honeycomb Flat-Plate Solar Collectors; Lockheed Missiles & Space Company Inc.: Palo Alto, CA, USA, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Buchberg, H.; Edwards, D.K.; Mackenzie, J.D. Transparent Glass Honeycombs for Energy Loss Control; School of Engineering and Applied Science, University of California: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Marin, O.; Vinuesa, R.; Obabko, A.V.; Schlatter, P. Characterization of the secondary flow in hexagonal ducts. Phys. Fluids 2016, 28, 125101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliabadia, M.K.; Deldarb, S.; Hassanic, S.M. Effects of pin-fins geometry and nanofluid on the performance of a pin-fin miniature heat sink (PFMHS). Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2018, 148, 442–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadasivam, R.; Manglik, R.M.; Jog, M.A. Fully developed forced convection through trapezoidal and hexagonal ducts. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 1999, 42, 4321–4331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.Z. Transient and conjugate heat and mass transfer in hexagonal ducts with adsorbent walls. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2015, 84, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moukalled, F.; Acharya, S. Natural convection in the annulus between concentric horizontal circular and square cylinders. J. Thermophys. Heat Trans. 1996, 10, 524–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Ra | AR | Present | Previous [36] | Previous [49] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 104 | 0.2 | 2.042 | 2.035 | 2.071 |
| 0.4 | 3.202 | 3.173 | 3.331 | |
| 0.6 | 5.349 | 5.266 | 5.826 | |
| 105 | 0.2 | 3.714 | 3.751 | 3.825 |
| 0.4 | 4.843 | 4.893 | 5.080 | |
| 0.6 | 6.182 | 6.175 | 6.212 | |
| 106 | 0.2 | 5.959 | 6.115 | 6.107 |
| 0.4 | 8.718 | 8.897 | 9.374 | |
| 0.6 | 11.662 | 11.940 | 11.620 |
© 2020 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alapati, S. Simulation of Natural Convection in a Concentric Hexagonal Annulus Using the Lattice Boltzmann Method Combined with the Smoothed Profile Method. Mathematics 2020, 8, 1043. https://doi.org/10.3390/math8061043
Alapati S. Simulation of Natural Convection in a Concentric Hexagonal Annulus Using the Lattice Boltzmann Method Combined with the Smoothed Profile Method. Mathematics. 2020; 8(6):1043. https://doi.org/10.3390/math8061043
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlapati, Suresh. 2020. "Simulation of Natural Convection in a Concentric Hexagonal Annulus Using the Lattice Boltzmann Method Combined with the Smoothed Profile Method" Mathematics 8, no. 6: 1043. https://doi.org/10.3390/math8061043
APA StyleAlapati, S. (2020). Simulation of Natural Convection in a Concentric Hexagonal Annulus Using the Lattice Boltzmann Method Combined with the Smoothed Profile Method. Mathematics, 8(6), 1043. https://doi.org/10.3390/math8061043





