Strategic Investment in an International Infrastructure Capital: Nonlinear Equilibrium Paths in a Dynamic Game between Two Symmetric Countries
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Model
2.1. Preference and Demand
2.2. Firm Behavior
- Case (i)
- Two way trade in all varieties (i.e., and );
- Case (ii)
- One way trade in which only home firms export their varieties to foreign countries (i.e., and );
- Case (iii)
- One way trade in which only foreign firms export their varieties to home countries (i.e., and );
- Case (iv)
- No firm exports to the other country (i.e., ).
2.3. Market Equilibrium
3. Dynamic Game of Infrastructure Investment
4. Properties of the Dynamic Equilibrium
4.1. Open-Loop Nash Equilibrium
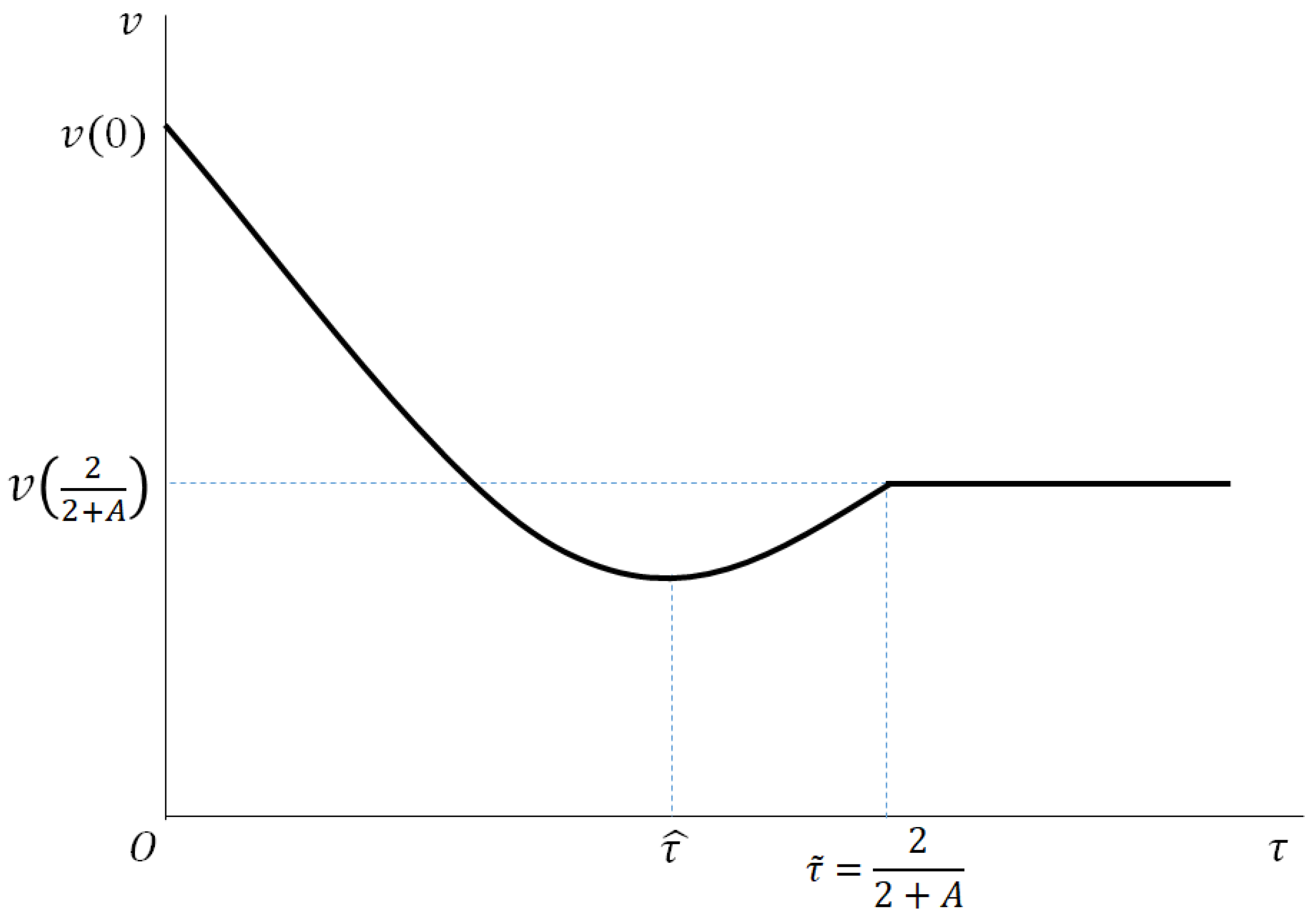
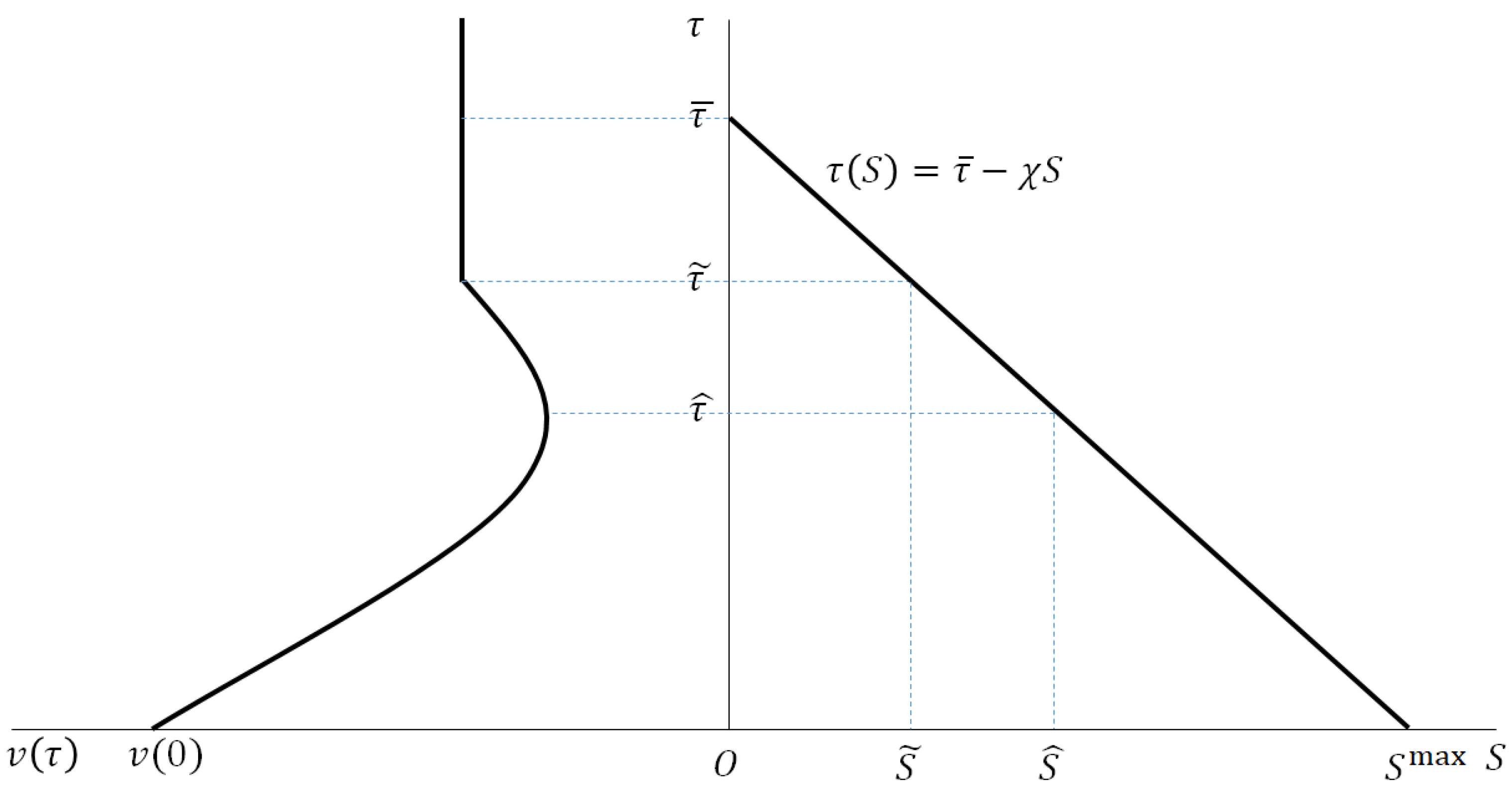
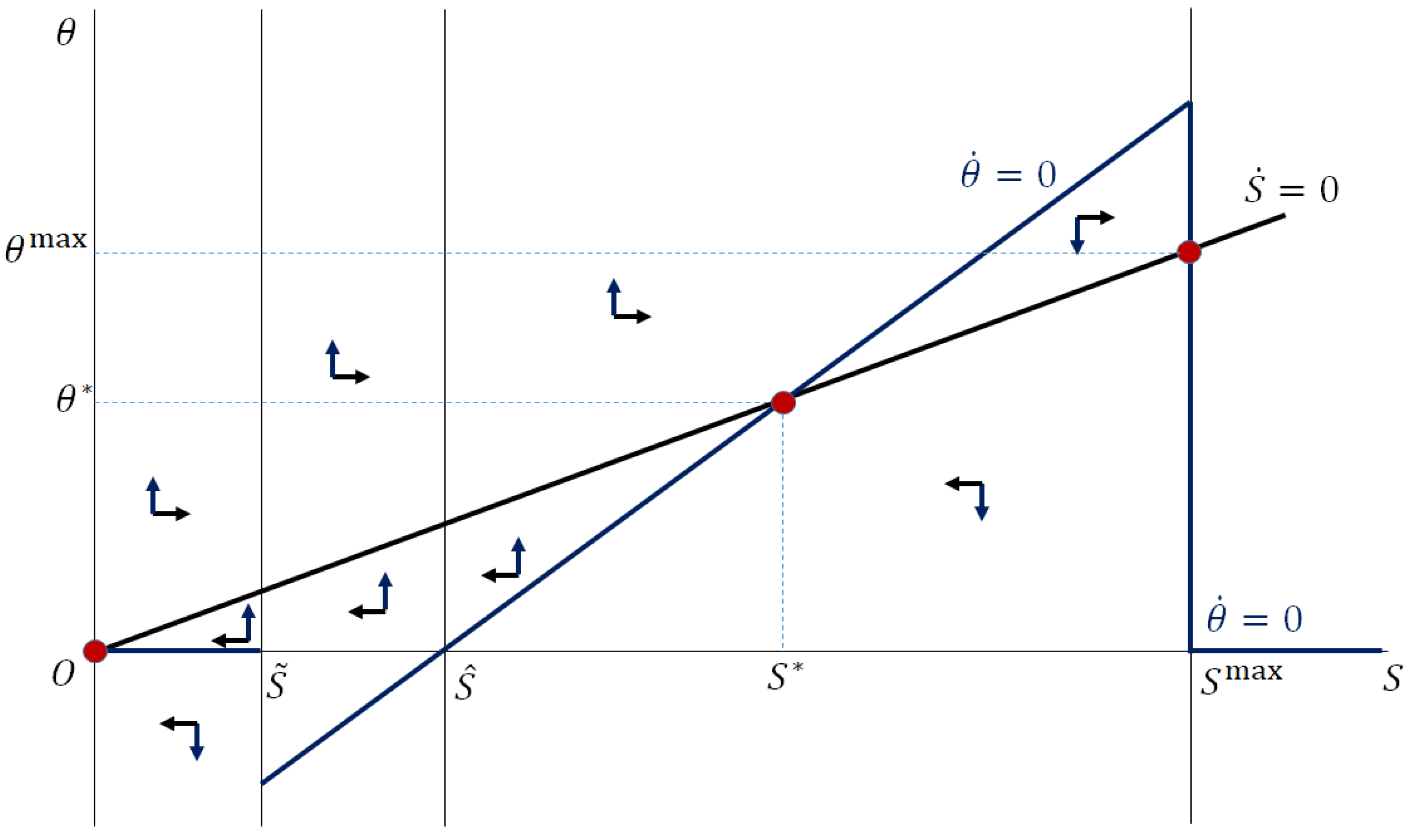
4.1.1. The Locus
4.1.2. The Locus
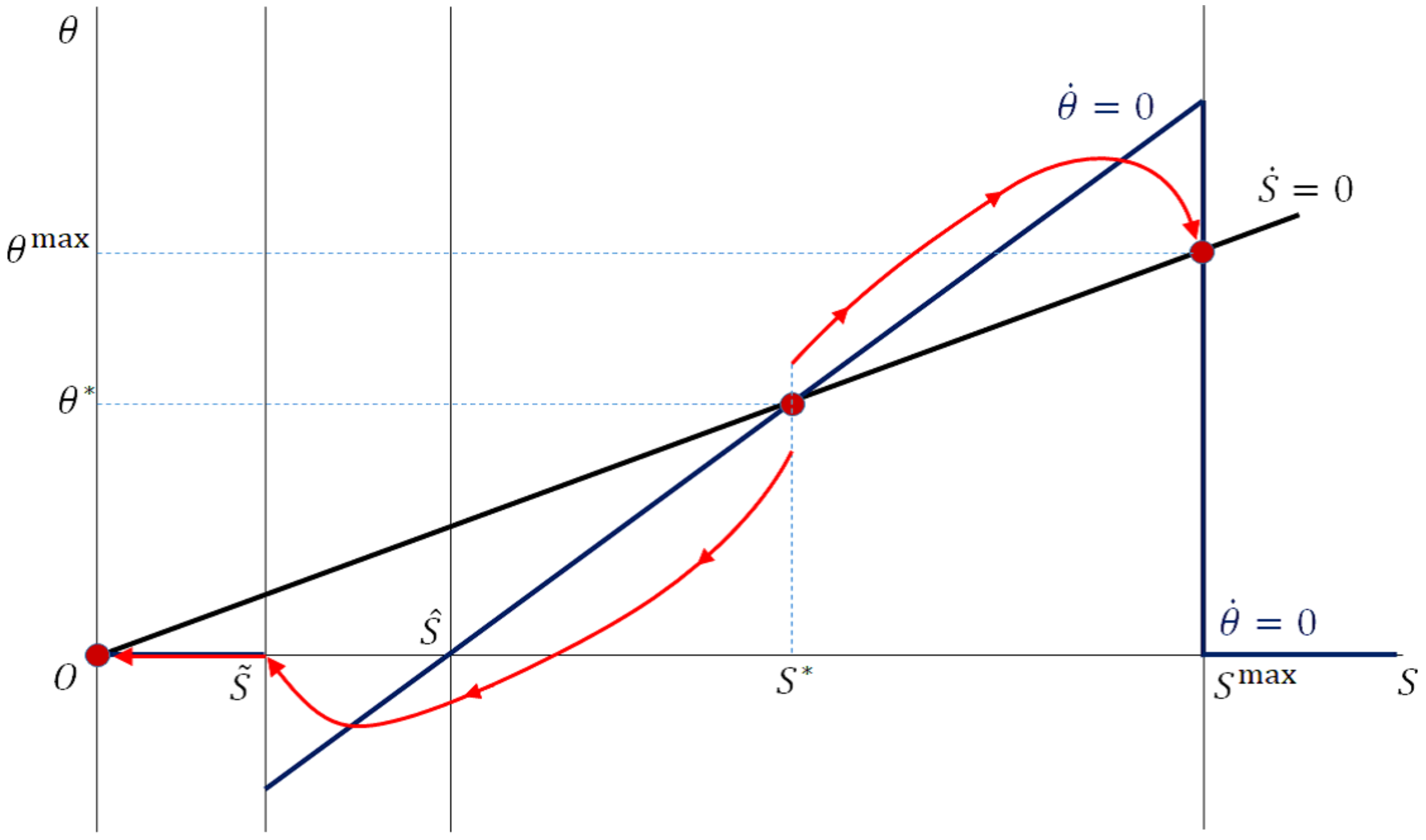
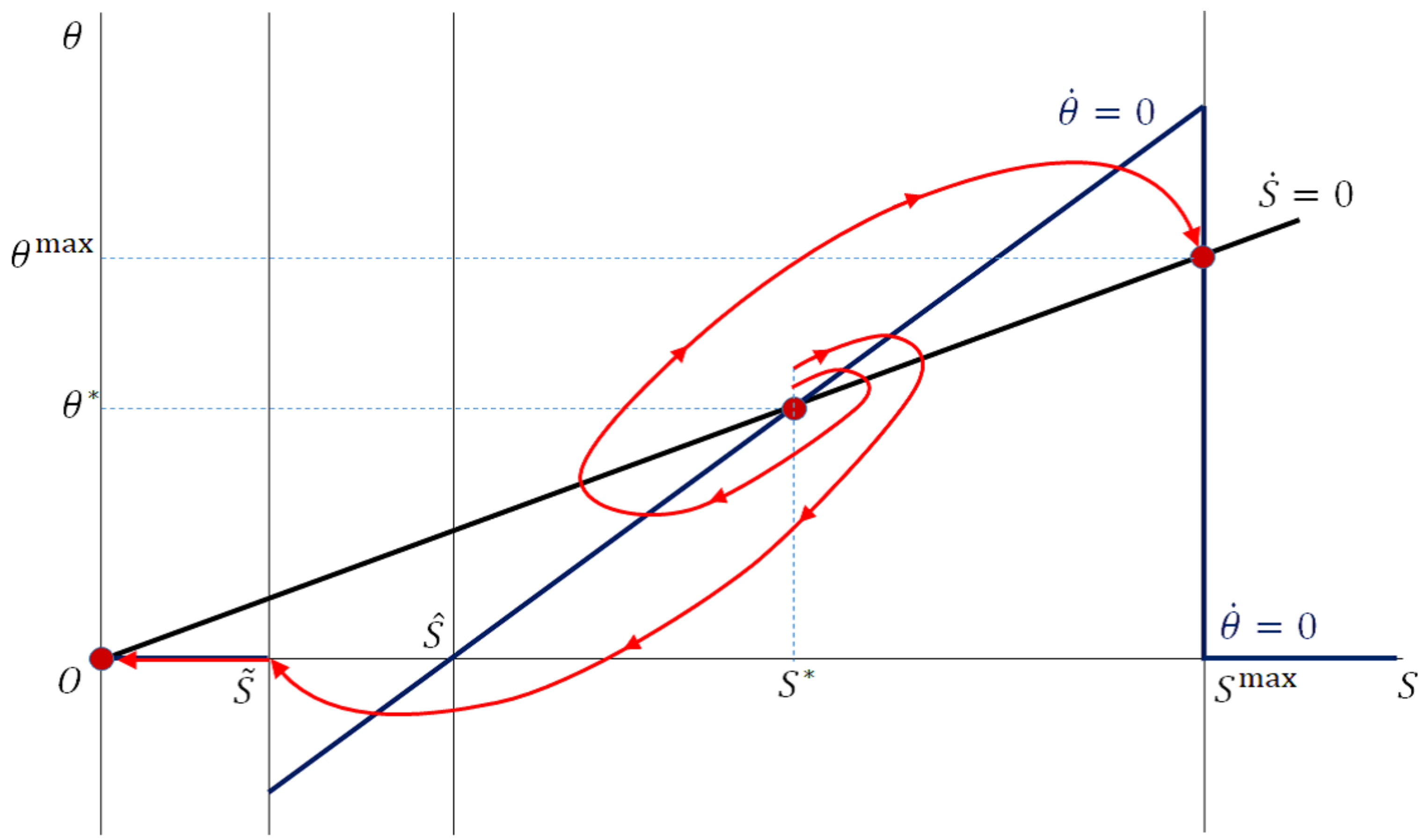
4.1.3. Steady States
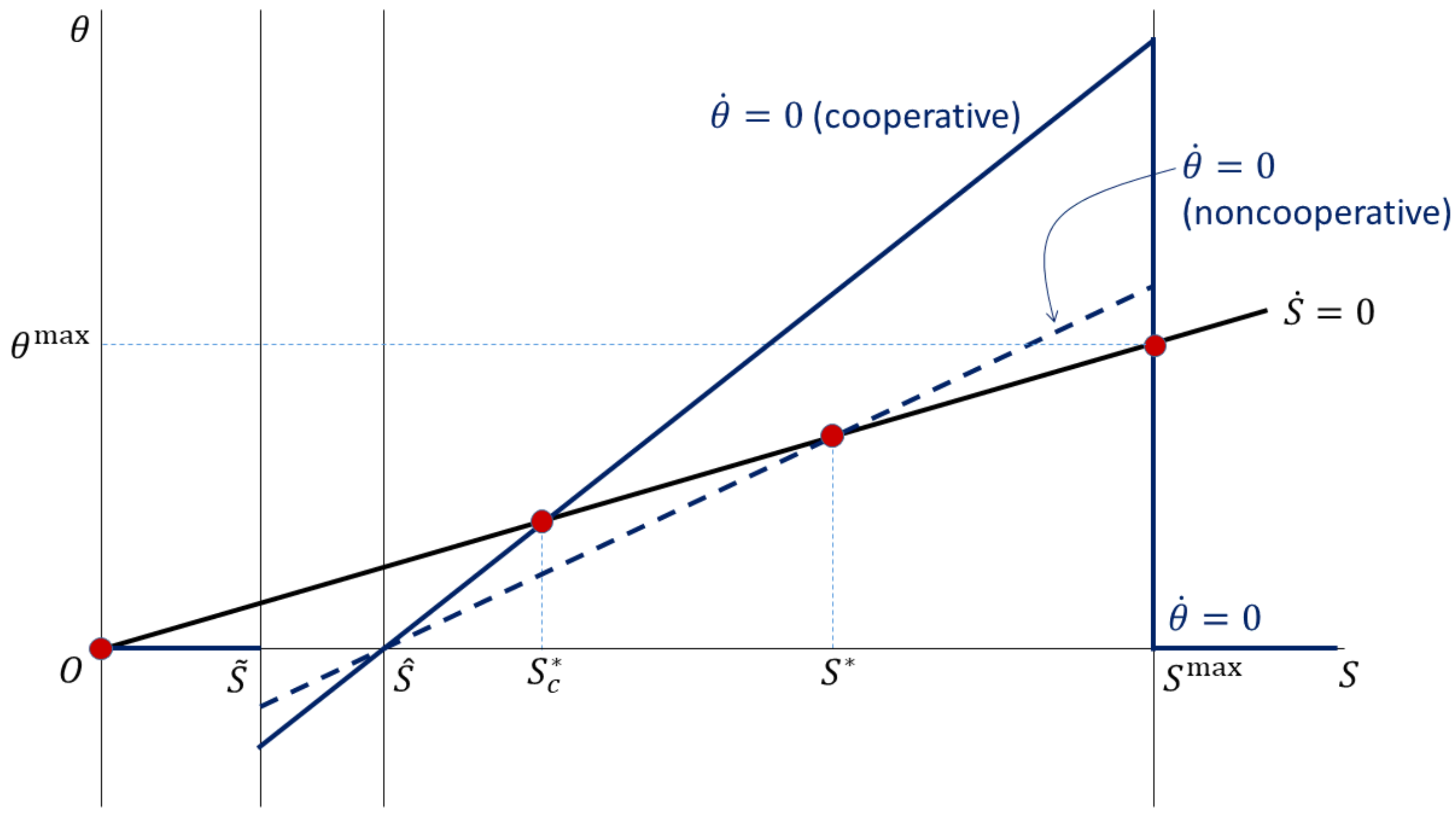
4.2. Comparison with the Cooperative Solution
5. Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Derivation of Equilibrium Prices and Outputs
Case (i): Two Way Trade in All Varieties (qHF > 0 and qFH > 0)
Case (ii): One Way Trade in which Only Home Firms Export to Foreign Countries (qHF > 0 and qFH = 0)
Case (iii): One Way Trade in Which Only Foreign Firms Export to Home Countries (qHF = 0 and qFH > 0)
Case (iv): No Firm Exports to the Other Country (qHF = qFH = 0)
Equilibrium Outputs: Summary
Appendix B. Proof of Proposition 1
Case (i): qHF > 0 and qFH > 0
Case (ii): qHF > 0 and qFH = 0
Case (iii): qHF = 0 and qFH > 0
Case (iv): qHF = qFH = 0
Proof of the Proposition
References
- Anderson, J.E.; van Wincoop, E. Trade costs. J. Econ. Lit. 2004, 42, 691–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arvis, J.-F.; Duval, Y.; Shepherd, B.; Utoktham, C.; Raj, A. Trade Costs in the Developing World: 1996–2010. World Trade Rev. 2016, 15, 451–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jacks, D.S.; Meissner, C.M.; Novy, D. Trade Booms, Trade Busts, and Trade Costs. J. Int. Econ. 2011, 83, 185–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Donaldson, D. Railroads of the Raj: Estimating the Impact of Transportation Infrastructure. Am. Econ. Rev. 2018, 108, 899–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Allen, T.; Arkolakis, C. Trade and the Topography of the Spatial Economy. Q. J. Econ. 2014, 129, 1085–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Felbermayr, G.J.; Tarasov, A. Trade and the Spatial Distribution of Transport Infrastructure, CESifo Working Paper Series No. 5634. 2015. Available online: https://ideas.repec.org/p/ces/ceswps/_5634.html (accessed on 29 December 2020).
- Bond, E.W. Transportation Infrastructure Investments And Trade Liberalization. Jpn. Econ. Rev. 2006, 57, 483–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochman, G.; Tabakis, C.; Zilberman, D. The Impact of International Trade on Institutions and Infrastructure. J. Comp. Econ. 2013, 41, 126–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, P.; Rogers, C. Industrial Location and Public Infrastructure. J. Int. Econ. 1995, 39, 335–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mun, S.; Nakagawa, S. Pricing and Investment of Cross-border Transport Infrastructure. Reg. Sci. Urban Econ. 2010, 40, 228–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsubuku, M. Endogenous Transport Costs and Firm Agglomeration in New Trade Theory. Pap. Reg. Sci. 2016, 95, 353–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.A.; Marcouiller, D. Insecurity and the Pattern of Trade: An Empirical Investigation. Rev. Econ. Stat. 2002, 84, 342–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Francois, J.; Manchin, M. Institutions, Infrastructure, and Trade. World Dev. 2013, 46, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Freund, C.L.; Weinhold, D. The Effect of the Internet on International Trade. J. Int. Econ. 2004, 62, 171–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Limão, N.; Venables, A.J. Infrastructure, Geographical Disadvantage, Transport Costs and Trade. World Bank Econ. Rev. 2001, 15, 451–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, T.; Arkolakis, C. The Welfare Effects of Transportation Infrastructure Improvements. Unpublished manuscript. Available online: https://ideas.repec.org/p/nbr/nberwo/25487.html (accessed on 29 December 2020).
- Bougheas, S.; Demetriades, P.O.; Morgenroth, E.L.W. Infrastructure, Transport Costs and Trade. J. Int. Econ. 1999, 47, 169–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bougheas, S.; Demetriades, P.O.; Morgenroth, E.L.W. International aspects of public infrastructure investment. Can. J. Econ. 2003, 36, 884–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brancaccio, G.; Kalouptsidiy, M.; Papageorgiouz, T. Geography, Search Frictions and Endogenous Trade Costs, NBER Working Paper No. 23581. 2017. Available online: https://econpapers.repec.org/paper/nbrnberwo/23581.htm (accessed on 29 December 2020).
- Fajgelbaum, P.D.; Schaal, E. Optimal Transport Networks in Spatial Equilibrium, NBER Working Paper No. 23200. 2017. [Google Scholar]
- McMillan, J. A Dynamic Analysis of Public Intermediate Goods Supply in Open Economy. Int. Econ. Rev. 1978, 19, 665–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bougheas, S.; Demetriades, P.O.; Mamuneas, T.P. Infrastructure, Specialization, and Economic Growth. Can. J. Econ. 2000, 33, 506–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanase, A.; Tawada, M. History-Dependent Paths and Trade Gains in a Small Open Economy with a Public Intermediate Good. Int. Econ. Rev. 2012, 53, 303–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanase, A.; Tawada, M. Public Infrastructure for Production and International Trade in a Small Open Economy: A Dynamic Analysis. J. Econ. 2017, 121, 51–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanase, A.; Tawada, M. Public Infrastructure and Trade in a Dynamic Two-country Model. Rev. Int. Econ. 2020, 28, 447–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, L.; Lambertini, L.; Mantovani, A. Endogenous transportation technology in a Cournot Differential Game with Intraindustry Trade. Jpn. World Econ. 2009, 21, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Devereux, M.B.; Mansoorian, A. International Fiscal Policy Coordination and Economic Growth. Int. Econ. Rev. 1992, 33, 249–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fershtman, C.; Nitzan, S. Dynamic Voluntary Provision of Public Goods. Eur. Econ. Rev. 1991, 35, 1057–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figuières, C.; Prieur, F.; Tisball, M. Public Infrastructure, Non-cooperative Investments, and Endogenous Growth. Can. J. Econ. 2013, 46, 587–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Han, Y.; Pieretti, P.; Zanaj, S.; Zou, B. Asymmetric Competition among Nation States: A Differential Game Approach. J. Public Econ. 2014, 119, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Itaya, J.-I.; Shimomura, K. A Dynamic Conjectural Variations Model in the Private Provision of Public Goods: A Differential Game Approach. J. Public Econ. 2001, 81, 153–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krugman, P. History versus Expectations. Q. J. Econ. 1991, 106, 651–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuyama, K. Increasing Returns, Industrialization, and Indeterminacy of Equilibrium. Q. J. Econ. 1991, 106, 617–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fukao, K.; Benabou, R. History versus Expectations: A Comment. Q. J. Econ. 1993, 108, 535–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skiba, A.K. Optimal Growth with a Convex-concave Production Function. Econometrica 1978, 46, 527–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deissenberg, C.; Feichtinger, G.; Semmler, W.; Wirl, F. Multiple Equilibria, History Dependence, and Global Dynamics in Intertemporal Optimization Models. In Economic Complexity (International Symposia in Economic Theory and Econometrics); Barnett, W.A., Deissenberger, C., Feichtinger, G., Eds.; Emerald Group Publishing: Bingley, UK, 2004; Volume 14, pp. 91–122. [Google Scholar]
- Hartl, R.F.; Kort, P.M.; Feichtinger, G.; Wirl, F. Multiple Equilibria and Thresholds Due to Relative Investment Costs. J. Optim. Theory Appl. 2004, 123, 49–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyama, D. History versus Expectations in Economic Geography Reconsidered. J. Econ. Dyn. Control 2009, 33, 394–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wagener, F.O.O. Skiba Points and Heteroclinic Bifurcations, with Applications to the Shallow Lake System. J. Econ. Dyn. Control 2003, 27, 1533–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirl, F. Indeterminacy and History Dependence of Strategically Interacting Players. Econ. Lett. 2016, 145, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ottaviano, G.I.P.; Tabuchi, T.; Thisse, J.-F. Agglomeration and Trade Revisited. Int. Econ. Rev. 2002, 43, 409–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furusawa, T.; Konishi, H. Free Trade Networks. J. Int. Econ. 2007, 72, 310–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhelobodko, E.; Kokovin, S.; Parenti, M.; Thisse, J.-F. Monopolistic Competition: Beyond the Constant Elasticity of Substitution. Econometrica 2012, 80, 2765–2784. [Google Scholar]
- Brander, J.; Krugman, P. A ‘Reciprocal Dumping’ Model of International Trade. J. Int. Econ. 1983, 15, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Friberg, R.; Ganslandt, M. Reciprocal Dumping with Product Differentiation. Rev. Int. Econ. 2008, 16, 942–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujiwara, K. Trade Liberalization in a Differentiated Duopoly Reconsidered. Res. Econ. 2009, 63, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, J.; Oladi, R. International Trade and Welfare with Differentiated Goods and Strategic Asymmetry, Mimeo. Available online: http://www.etsg.org/ETSG2018/papers/006.pdf (accessed on 29 December 2020).
- Yanase, A.; Long, N.V. Trade Costs and Strategic Investment in Infrastructure in a Dynamic Global Economy with Symmetric Countries, CIRANO Working Papers 2020s-59. 2020. Available online: https://ideas.repec.org/p/ces/ceswps/_8707.html (accessed on 29 December 2020).


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yanase, A.; Long, N.V. Strategic Investment in an International Infrastructure Capital: Nonlinear Equilibrium Paths in a Dynamic Game between Two Symmetric Countries. Mathematics 2021, 9, 63. https://doi.org/10.3390/math9010063
Yanase A, Long NV. Strategic Investment in an International Infrastructure Capital: Nonlinear Equilibrium Paths in a Dynamic Game between Two Symmetric Countries. Mathematics. 2021; 9(1):63. https://doi.org/10.3390/math9010063
Chicago/Turabian StyleYanase, Akihiko, and Ngo Van Long. 2021. "Strategic Investment in an International Infrastructure Capital: Nonlinear Equilibrium Paths in a Dynamic Game between Two Symmetric Countries" Mathematics 9, no. 1: 63. https://doi.org/10.3390/math9010063
APA StyleYanase, A., & Long, N. V. (2021). Strategic Investment in an International Infrastructure Capital: Nonlinear Equilibrium Paths in a Dynamic Game between Two Symmetric Countries. Mathematics, 9(1), 63. https://doi.org/10.3390/math9010063




