Probabilistic Non-Negative Matrix Factorization with Binary Components
Abstract
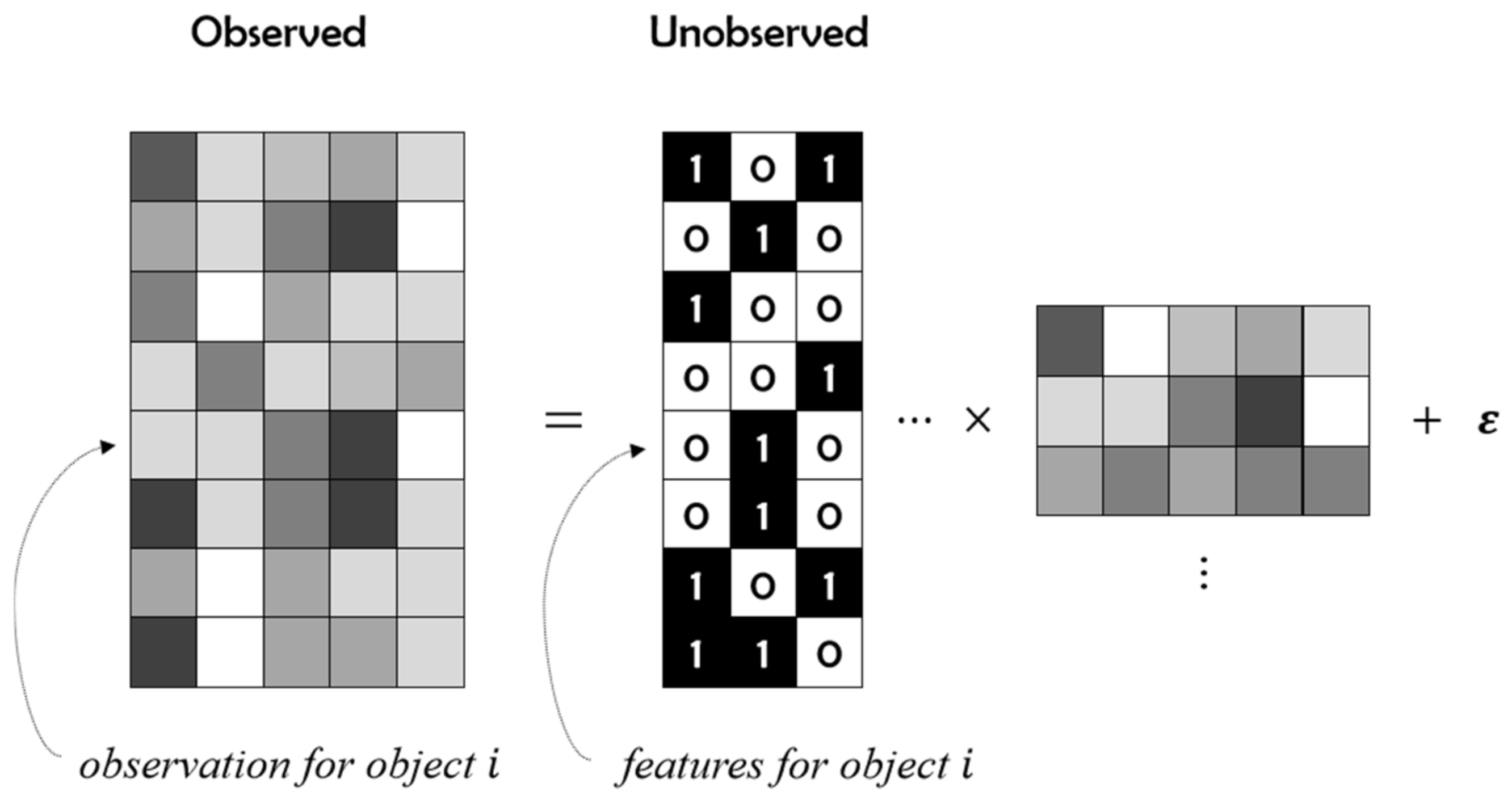
:1. Introduction
- (1)
- We present a pNMF with single binary component. Compared with other methods, the binary matrix can be regarded as the mapping from real object to binary codes, which is more intuitive.
- (2)
- IBP is applied to the pNMF and we explain its use as a prior in the variational Bayesian exponential Gaussian model. The real latent information is completely obtained by inference and the sensitivity of the model to initialization parameter setting is greatly reduced.
- (3)
- The experiments on the synthesized dataset and real-world datasets show the validity of the proposed method.
2. Related Work
2.1. Non-Negative Matrix Factorization
2.2. Indian Buffet Process
3. The Proposed Methods
3.1. Model Framework
3.2. The Solution of Weighted Matrix A
3.3. The Solution of Binary Matrix Z
3.4. Variational Inference Process
4. Experimental Result
4.1. Sythetic Dataset
4.2. Swimmer Dataset
4.3. Document Clustering
4.4. Face Feature Extraction
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Paatero, P.; Tapper, U. Positive matrix factorization: A non-negative factor model with optimal utilization of error estimates of data values. Environmetrics 1994, 5, 111–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Seung, H. Learning the parts of objects by nonnegative matrix factorization. Nature 1999, 401, 788–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramsay, J.O. Functional Data Analysis. In Encyclopedia of Statistical Sciences; Everitt, B.S., Howell, D.C., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2004; p. 4. [Google Scholar]
- Bach, F.; Mairal, J.; Ponce, J. Convex sparse matrix factorizations. arXiv 2008, arXiv:0812.1869. [Google Scholar]
- Zafeiriou, S.; Tefas, A.; Buciu, I.; Pitas, I. Exploiting discriminant information in nonnegative matrix factorization with application to frontal face verification. IEEE Trans. Neural. Netw. Learn Syst. 2006, 17, 683–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, H. Constrained nonnegative matrix factorization for image representation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2012, 34, 1299–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, D.; He, X.; Han, J.; Huang, T.S. Graph regularized nonnegative matrix factorization for data representation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2011, 33, 1548–1560. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, M.N.; Winther, O.; Hansen, L.K. Bayesian Non-Negative Matrix Factorization. In Independent Component Analysis and Signal Separation, Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Independent Component Analysis and Signal Separation, Paraty, Brazil, 15 March 2009; Adali, T., Christian, J., Romano, J.M.T., Barros, A.K., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2009; pp. 540–547. [Google Scholar]
- Wild, S.; Curry, J.; Dougherty, A. Improving non-negative matrix factorizations through structured initialization. Pattern Recognit. 2004, 37, 2217–2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Huang, K.; Zhang, R.; Hussain, A. Learning latent features with infinite nonnegative binary matrix trifactorization. IEEE Trans. Emerg. Top. Comput. 2018, 2, 450–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Fang, Y. A NMF algorithm for blind separation of uncorrelated signals. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Wavelet Analysis and Pattern Recognition, Beijing, China, 2 November 2007; Curran Associates Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2007; pp. 999–1003. [Google Scholar]
- Hoyer, P.O. Non-negative matrix factorization with sparseness constraints. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2004, 5, 1457–1469. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, Y.W.Y.; Turk, C.H.M. Fisher non-negative matrix factorization for learning local features. In Proceedings of the Asian Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea, 27 January 2004; Hong, K.S., Zhang, Z.Y., Eds.; Asian Federation of Computer Vision Societies: Seoul, Korea, 2004; pp. 27–30. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, C.J. Projected gradient methods for nonnegative matrix factorization. Neural Comput. 2007, 19, 2756–2779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guillamet, D.; Vitria, J.; Schiele, B. Introducing a weighted non-negative matrix factorization for image classification. Pattern Recogn. Lett. 2003, 24, 2447–2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinrich, J.L.; Mørup, M. Probabilistic Sparse Non-Negative Matrix Factorization. In Latent Variable Analysis and Signal Separation, Proceedings of the International Conference on Latent Variable Analysis and Signal Separation, Guildford, UK, 2 July 2018; Deville, Y., Gannot, S., Mason, R., Plumbley, M., Ward, D., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2018; pp. 488–498. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammadiha, N.; Kleijn, W.B.; Leijon, A. Gamma hidden Markov model as a probabilistic nonnegative matrix factorization. In Proceedings of the 21st European Signal Processing Conference (EUSIPCO 2013), Marrakech, Morocco, 9 September 2013; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Bayar, B.; Bouaynaya, N.; Shterenberg, R. Probabilistic non-negative matrix factorization: Theory and application to microarray data analysis. J. Bioinform. Comput. Biol. 2014, 12, 1450001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffiths, T.L.; Ghahramani, Z. The Indian buffet process: An introduction and review. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2011, 12, 1185–1224. [Google Scholar]
- Knowles, D.; Ghahramani, Z. Infinite Sparse Factor Analysis and Infinite Independent Components Analysis. In International Conference on Independent Component Analysis and Signal Separation, ICA’07, Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Independent Component Analysis and Signal Separation, London, UK, 12 August 2007; Davies, M.E., James, C.J., Abdallah, S.A., Plumbley, M.D., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2007; pp. 381–388. [Google Scholar]
- Teh, Y.W.; Grür, D.; Ghahramani, Z. Stick-Breaking Construction for the Indian Buffet Process. In Artificial Intelligence and Statistics, Proceedings of the Eleventh International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistic, San Juan, PR, USA, 21–24 March 2007; Meila, M., Shen, X., Eds.; PMLR: San Juan, PR, USA, 2007; pp. 556–563. [Google Scholar]
- Thibaux, R.; Jordan, M.I. Hierarchical Beta Processes and the Indian Buffet Process. In Artificial Intelligence and Statistics, Proceedings of the Eleventh International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistic, San Juan, PR, USA, 21–24 March 2007; Meila, M., Shen, X., Eds.; PMLR: San Juan, PR, USA, 2007; pp. 564–571. [Google Scholar]
- Gael, J.V.; The, Y.; Ghahramani, Z. The infinite factorial hidden Markov model. In Proceedings of the 21th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 8–10 December 2008; Koller, D., Schuurmans, D., Bengio, Y., Bottou, L., Eds.; Curran Associates Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2008; pp. 1697–1704. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, K.T.; Griffiths, T.L.; Jordan, M.I. The phylogenetic Indian buffet process: A non-exchangeable nonparametric prior for latent features. In Proceedings of the 24th Conference on Uncertainty in Artificial Intelligence, Helsinki, Finland, 9–12 July 2008; Mcallester, D., Myllymaki, P., Eds.; AUAI Press: Arlington, VA, USA, 2008; pp. 403–407. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, K.T.; Griffiths, T.L.; Jordan, M.I. Nonparametric latent feature models for link prediction. In Proceedings of the 22nd International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 7–10 December 2009; Bengio, Y., Schuurmans, D., Lafferty, J.D., Williams, C.K.I., Culotta, A., Eds.; Curran Associates Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 1276–1284. [Google Scholar]
- Meeds, E.; Ghahramani, Z.; Neal, R.; Roweis, S.T. Modeling dyadic data with binary latent factors. In Proceedings of the 19th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 4–7 December 2006; Schölkopf, B., Platt, J.C., Hoffman, T., Eds.; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2006; pp. 977–984. [Google Scholar]
- Wood, F.; Griffiths, T.L.; Ghahramani, Z.A. Non-parametric Bayesian method for inferring hidden causes. In Proceedings of the 22nd Conference in Uncertainty in Artificial Intelligence, Cambridge, MA, USA, 13–16 July 2006; AUAI Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2006; pp. 536–543. [Google Scholar]
- Navarro, D.; Griffiths, T. A nonparametric Bayesian method for inferring features from similarity judgments. In Proceedings of the 19th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 4–7 December 2006; Schölkopf, B., Platt, J.C., Hoffman, T., Eds.; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2006; pp. 1033–1040. [Google Scholar]
- Brouwer, T.; Frellsen, J.; Lió, P. Comparative study of inference methods for Bayesian nonnegative matrix factorization. In Proceedings of the Joint European Conference on Machine Learning and Knowledge Discovery in Databases, Skopje, Macedonia, 18 September 2017; Ceci, M., Hollmén, J., Todorovski, L., Vens, C., Džeroski, S., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2017; pp. 513–529. [Google Scholar]
- Bernardo, J.M.; Bayarri, M.J.; Berger, J.O.; Dawid, A.P.; Heckerman, D.; Smith, A.F.; West, M. The variational Bayesian EM algorithm for incomplete data: With application to scoring graphical model structures. Bayesian Stat. 2003, 7, 210. [Google Scholar]
- Chopin, N. Fast simulation of truncated Gaussian distributions. Stat. Comput. 2012, 21, 275–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mazet, V. Simulation d’une Distribution Gaussienne Tronquée sur un Intervalle Fini; Université de Strasbourg: Strasbourg, France, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, L.; Yu, J.; Pan, J. Feature Re-factorization-based data sparse representation. J. Beijing Univ. Technol. 2017, 43, 1666–1672. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, W.; Doshi-Velez, F. A characterization of the non-uniqueness of nonnegative matrix factorizations. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1604.00653. [Google Scholar]
- Xuan, J.; Lu, J.; Zhang, G.; Da Xu, R.Y.; Luo, X. Doubly nonparametric sparse nonnegative matrix factorization based on dependent Indian buffet processes. IEEE Trans. Neural. Netw. Learn. Syst. 2018, 29, 1835–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- MIT Center for Biological and Computation Learning. Available online: http://www.ai.mit.edu/projects/cbcl.old (accessed on 8 May 2020).












| Index | JC | FM | F1 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parametric Model or Algorithms | SNMF | 0.1678 | 0.2882 | 0.2870 |
| NMF | 0.1524 | 0.2729 | 0.2688 | |
| SP | 0.1691 | 0.3123 | 0.2737 | |
| Bayesian Non-parametric NMF Models | IBP | 0.1650 | 0.2770 | 0.2890 |
| Bivariate-Beta doubly IBP | 0.1720 | 0.2790 | 0.2930 | |
| Gaussian process doubly IBP | 0.1650 | 0.2630 | 0.2610 | |
| Ours | 0.1749 | 0.3173 | 0.2977 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, X.; Gao, J.; Liu, X.; Zhang, T.; Tang, Y. Probabilistic Non-Negative Matrix Factorization with Binary Components. Mathematics 2021, 9, 1189. https://doi.org/10.3390/math9111189
Ma X, Gao J, Liu X, Zhang T, Tang Y. Probabilistic Non-Negative Matrix Factorization with Binary Components. Mathematics. 2021; 9(11):1189. https://doi.org/10.3390/math9111189
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Xindi, Jie Gao, Xiaoyu Liu, Taiping Zhang, and Yuanyan Tang. 2021. "Probabilistic Non-Negative Matrix Factorization with Binary Components" Mathematics 9, no. 11: 1189. https://doi.org/10.3390/math9111189
APA StyleMa, X., Gao, J., Liu, X., Zhang, T., & Tang, Y. (2021). Probabilistic Non-Negative Matrix Factorization with Binary Components. Mathematics, 9(11), 1189. https://doi.org/10.3390/math9111189







