Fractional Order Magnetic Resonance Fingerprinting in the Human Cerebral Cortex
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bloch Equations
2.1.1. Time-Fractional Order Model
2.1.2. Integer Order Model
2.1.3. From Magnetisation to an MRI Signal
2.2. Parameter Estimation Using MRF
2.3. Relating MRI Data to the Bloch Model
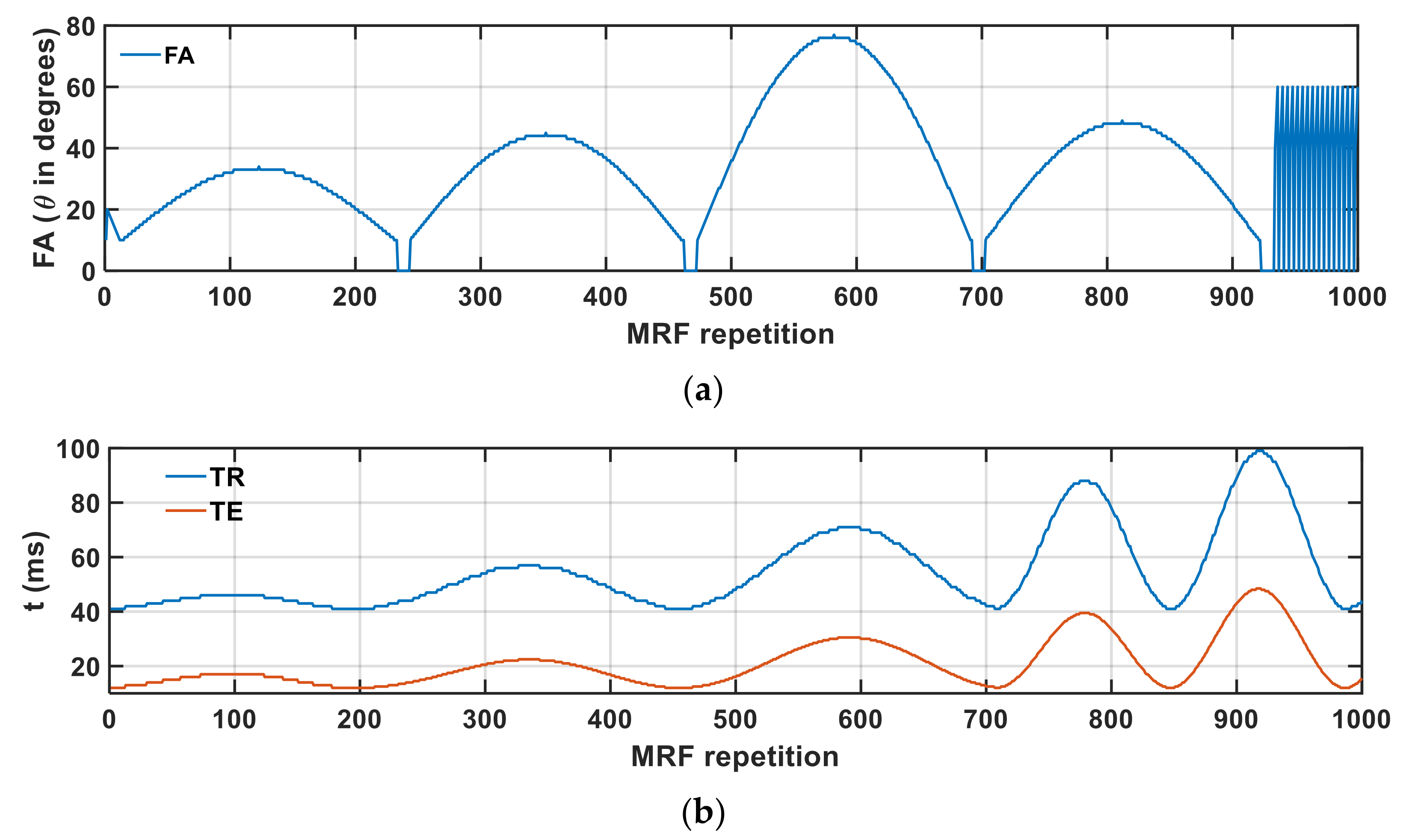
2.4. MRI Data Collection
2.5. Model Selection and Estimation Error
2.6. Human Brain Cortical Parcellation
3. Results
3.1. Expected Changes in the MRF Signal
3.2. Time-Fractional Bloch Model Parameter Sensitivity
3.3. Parameter Selectivity to Different Cortical Regions in the Human Brain
4. Discussion
4.1. MRF Parameter Discretisation and Matching
4.2. Role of and
4.3. Cortical Parcellation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A

References
- Kadamangudi, S.; Vegh, V.; Sood, S.; Reutens, D. Discrete frequency shift signatures explain GRE-MRI signal compartments. In Proceedings of the International Symposium in Magnetic Resonance in Medicine (ISMRM), Honolulu, HI, USA, 22–27 April 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Sepehrband, F.; Clark, K.A.; Ullmann, J.F.; Kurniawan, N.D.; Leanage, G.; Reutens, D.C.; Yang, Z. Brain tissue compartment density estimated using diffusion—Weighted MRI yields tissue parameters consistent with histology. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2015, 36, 3687–3702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sood, S.; Urriola, J.; Reutens, D.; O’Brien, K.; Bollmann, S.; Barth, M.; Vegh, V. Echo time—Dependent quantitative susceptibility mapping contains information on tissue properties. Magn. Reson. Med. 2017, 77, 1946–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thapaliya, K.; Vegh, V.; Bollmann, S.; Barth, M. Assessment of microstructural signal compartments across the corpus callosum using multi-echo gradient recalled echo at 7 T. NeuroImage 2017, 182, 407–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thapaliya, K.; Vegh, V.; Bollmann, S.; Reutens, D.; Barth, M. 7T GRE-MRI freqeuncy shifts obtained from signal compartments can differentiate normal from dysplastic tissue in focal epilepsy. In Proceedings of the International Symposium in Magnetic Resonance in Medicine (ISMRM), Paris, France, 16–21 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Q.; Reutens, D.; O’Brien, K.; Vegh, V. Tissue microstructure features derived from anomalous diffusion measurements in magnetic resonance imaging. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2017, 38, 1068–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Reutens, D.; Vegh, V. Can anomalous diffusion models in magnetic resonance imaging be used to characterise white matter tissue microstructure? NeuroImage 2018, 175, 122–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wharton, S.; Bowtell, R. Fiber orientation-dependent white matter contrast in gradient echo MRI. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 18559–18564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H.; Schneider, T.; Wheeler-Kingshott, C.A.; Alexander, D.C. NODDI: Practical in vivo neurite orientation dispersion and density imaging of the human brain. Neuroimage 2012, 61, 1000–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaman, M.M.; Sui, Y.; Wang, H.; Magin, R.L.; Li, Y.; Zhou, X.J. Differentiating low-and high-grade pediatric brain tumors using a continuous-time random-walk diffusion model at high b-values. Magn. Reson. Med. 2016, 76, 1149–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qin, S.; Liu, F.; Turner, I.W.; Yu, Q.; Yang, Q.; Vegh, V. Characterization of anomalous relaxation using the time—Fractional Bloch equation and multiple echo T2*—Weighted magnetic resonance imaging at 7 T. Magn. Reson. Med. 2017, 77, 1485–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Whittall, K.P.; MacKay, A.L.; Li, D.K. Are mono—Exponential fits to a few echoes sufficient to determine T2 relaxation for in vivo human brain? Magn. Reson.Med. Off. J. Int. Soc. Magn. Reson. Med. 1999, 41, 1255–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, W.C.; Leblanc, A.D.; Jhingran, S.G. The origin of biexponential T2 relaxation in muscle water. Magn. Reson. Med. 1993, 29, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Gelderen, P.; De Zwart, J.A.; Lee, J.; Sati, P.; Reich, D.S.; Duyn, J.H. Nonexponential T2* decay in white matter. Magn. Reson. Med. 2012, 67, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qin, S.; Liu, F.; Turner, I.; Vegh, V.; Yu, Q.; Yang, Q. Multi-term time-fractional Bloch equations and application in magnetic resonance imaging. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 2017, 319, 308–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Magin, R.L.; Hall, M.G.; Karaman, M.M.; Vegh, V. Fractional Calculus Models of Magnetic Resonance Phenomena: Relaxation and Diffusion. Crit. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2020, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.; Gulani, V.; Seiberlich, N.; Liu, K.; Sunshine, J.L.; Duerk, J.L.; Griswold, M.A. Magnetic resonance fingerprinting. Nature 2013, 495, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Poorman, M.E.; Martin, M.N.; Ma, D.; McGivney, D.F.; Gulani, V.; Griswold, M.A.; Keenan, K.E. Magnetic resonance fingerprinting Part 1: Potential uses, current challenges, and recommendations. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2020, 51, 675–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGivney, D.F.; Boyacıoğlu, R.; Jiang, Y.; Poorman, M.E.; Seiberlich, N.; Gulani, V.; Keenan, K.E.; Griswold, M.A.; Ma, D. Magnetic resonance fingerprinting review part 2: Technique and directions. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2020, 51, 993–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zou, L.; Ye, H.; Su, S.; Chang, Y.; Liu, X.; Liang, D. Application of Time-Fractional Order Bloch Equation in Magnetic Resonance Fingerprinting. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 16th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI 2019), Venice, Italy, 8–11 April 2019; pp. 1704–1707. [Google Scholar]
- Honey, C.J.; Thivierge, J.-P.; Sporns, O. Can structure predict function in the human brain? Neuroimage 2010, 52, 766–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebel, C.; Walker, L.; Leemans, A.; Phillips, L.; Beaulieu, C. Microstructural maturation of the human brain from childhood to adulthood. Neuroimage 2008, 40, 1044–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, S.E.; Janke Phd, A.L.; Chalk, J.B. Gray and white matter changes in Alzheimer’s disease: A diffusion tensor imaging study. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging Off. J. Int. Soc. Magn. Reson. Med. 2008, 27, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, I.A.; Rosenfeld, J.; Ahl, J.; Hahn, J.F.; Lüders, H. Intractable epilepsy and structural lesions of the brain: Mapping, resection strategies, and seizure outcome. Epilepsia 1991, 32, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubben, P.L. Brain Mapping: From Neural Basis of Cognition to Surgical Applications. In Surgical Neurology International; Duffau, H., Ed.; Springer: Wien, Austria, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen-Adad, J.; Polimeni, J.R.; Helmer, K.G.; Benner, T.; McNab, J.A.; Wald, L.L.; Rosen, B.R.; Mainero, C. T2* mapping and B0 orientation-dependence at 7 T reveal cyto-and myeloarchitecture organization of the human cortex. Neuroimage 2012, 60, 1006–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Does, M.D. Inferring brain tissue composition and microstructure via MR relaxometry. NeuroImage 2018, 182, 136–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geyer, S.; Weiss, M.; Reimann, K.; Lohmann, G.; Turner, R. Microstructural parcellation of the human cerebral cortex–from Brodmann’s post-mortem map to in vivo mapping with high-field magnetic resonance imaging. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2011, 5, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tardif, C.L.; Dinse, J.; Schäfer, A.; Turner, R.; Bazin, P.-L. Multi-modal surface-based alignment of cortical areas using intra-cortical T1 contrast. In Proceedings of the International Workshop on Multimodal Brain Image Analysis, Nagoya, Japan, 22 September 2013; pp. 222–232. [Google Scholar]
- Cercignani, M.; Bouyagoub, S. Brain microstructure by multi-modal MRI: Is the whole greater than the sum of its parts? Neuroimage 2018, 182, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, J.P.; Khabipova, D.; Gruetter, R. Studying cyto and myeloarchitecture of the human cortex at ultra-high field with quantitative imaging: R1, R2* and magnetic susceptibility. NeuroImage 2017, 147, 152–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stüber, C.; Morawski, M.; Schäfer, A.; Labadie, C.; Wähnert, M.; Leuze, C.; Streicher, M.; Barapatre, N.; Reimann, K.; Geyer, S. Myelin and iron concentration in the human brain: A quantitative study of MRI contrast. Neuroimage 2014, 93, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, L.J.; Kirilina, E.; Mohammadi, S.; Weiskopf, N. Microstructural imaging of human neocortex in vivo. Neuroimage 2018, 182, 184–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podlubny, I. Fractional Differential Equations: An Introduction to Fractional Derivatives, Fractional Differential Equations, to Methods of Their Solution and Some of Their Applications; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Medina, G.D.; Ojeda, N.R.; Pereira, J.H.; Romero, L.G. Fractional Laplace Transform and Fractional Calculus. Int. Math. Forum 2017, 12, 991–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrappa, R. Numerical evaluation of two and three parameter Mittag-Leffler functions. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 2015, 53, 1350–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Magin, R.L.; Li, W.; Velasco, M.P.; Trujillo, J.; Reiter, D.A.; Morgenstern, A.; Spencer, R.G. Anomalous NMR relaxation in cartilage matrix components and native cartilage: Fractional-order models. J. Magn. Reson. 2011, 210, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reiter, D.A.; Magin, R.L.; Li, W.; Trujillo, J.J.; Pilar Velasco, M.; Spencer, R.G. Anomalous T2 relaxation in normal and degraded cartilage. Magn. Reson. Med. 2016, 76, 953–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Poser, B.A.; Koopmans, P.; Witzel, T.; Wald, L.; Barth, M. Three dimensional echo-planar imaging at 7 T. Neuroimage 2010, 51, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Griswold, M.A.; Jakob, P.M.; Heidemann, R.M.; Nittka, M.; Jellus, V.; Wang, J.; Kiefer, B.; Haase, A. Generalized autocalibrating partially parallel acquisitions (GRAPPA). Magn. Reson. Med. Off. J. Int. Soc. Magn. Reson. Med. 2002, 47, 1202–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Frahm, J.; Haase, A.; Hänicke, W.; Matthaei, D.; Bomsdorf, H.; Helzel, T. Chemical shift selective MR imaging using a whole-body magnet. Radiology 1985, 156, 441–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edelman, R.; Hesselink, J.; Zlatkin, M. Wielopolski P and Schmitt F 1994 Echo-planar MR imaging. Radiology 1994, 192, 600–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buonincontri, G.; Schulte, R.; Cosottini, M.; Sawiak, S.; Tosetti, M. Spiral MRF at 7T with simultaneous B1 estimation. In Proceedings of the International Symposium for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine (ISMRM), Singapore , 7–13 May 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Buonincontri, G.; Schulte, R.F.; Cosottini, M.; Tosetti, M. Spiral MR fingerprinting at 7 T with simultaneous B1 estimation. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2017, 41, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rieger, B.; Zimmer, F.; Zapp, J.; Weingärtner, S.; Schad, L.R. Magnetic resonance fingerprinting using echo—Planar imaging: Joint quantification of T1 and relaxation times. Magn. Reson. Med. 2017, 78, 1724–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, Y.; Ishiguro, M.; Kitagawa, G. Akaike information criterion statistics. Dordr. Neth. D Reidel 1986, 81, 26853. [Google Scholar]
- Eickhoff, S.B.; Stephan, K.E.; Mohlberg, H.; Grefkes, C.; Fink, G.R.; Amunts, K.; Zilles, K. A new SPM toolbox for combining probabilistic cytoarchitectonic maps and functional imaging data. Neuroimage 2005, 25, 1325–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geyer, S.; Schleicher, A.; Zilles, K. Areas 3a, 3b, and 1 of human primary somatosensory cortex: 1. Microstructural organization and interindividual variability. Neuroimage 1999, 10, 63–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amunts, K.; Schleicher, A.; Bürgel, U.; Mohlberg, H.; Uylings, H.B.; Zilles, K. Broca’s region revisited: Cytoarchitecture and intersubject variability. J. Comp. Neurol. 1999, 412, 319–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geyer, S.; Ledberg, A.; Schleicher, A.; Kinomura, S.; Schormann, T.; Bürgel, U.; Klingberg, T.; Larsson, J.; Zilles, K.; Roland, P.E. Two different areas within the primary motor cortex of man. Nature 1996, 382, 805–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grefkes, C.; Geyer, S.; Schormann, T.; Roland, P.; Zilles, K. Human somatosensory area 2: Observer-independent cytoarchitectonic mapping, interindividual variability, and population map. Neuroimage 2001, 14, 617–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geyer, S. The Microstructural Border between the Motor and the Cognitive Domain in the Human Cerebral Cortex; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Amunts, K.; Malikovic, A.; Mohlberg, H.; Schormann, T.; Zilles, K. Brodmann’s areas 17 and 18 brought into stereotaxic space—Where and how variable? Neuroimage 2000, 11, 66–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagheri, S.M.; Vegh, V.; Reutens, D.C. Magnetic Resonance Fingerprinting (MRF) Can Reveal Microstructural Variations in the Brain Gray Matter. In Proceedings of the International Symposium in Magnetic Resonance in Medicine (ISMRM), Paris, France, 17–21 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Korb, J.-P.; Bryant, R.G. The physical basis for the magnetic field dependence of proton spin-lattice relaxation rates in proteins. J. Chem. Phys. 2001, 115, 10964–10974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abragam, A. The Principles of Nuclear Magnetism; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1961. [Google Scholar]











| Metric | RMSE Reduction (%) | |
|---|---|---|
| Median | 96.5 | 98.2 |
| Mean | 92.6 | 96.1 |
| Standard deviation | 9.6 | 5.4 |
| p-value | <10−9 | <10−9 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vegh, V.; Moinian, S.; Yang, Q.; Reutens, D.C. Fractional Order Magnetic Resonance Fingerprinting in the Human Cerebral Cortex. Mathematics 2021, 9, 1549. https://doi.org/10.3390/math9131549
Vegh V, Moinian S, Yang Q, Reutens DC. Fractional Order Magnetic Resonance Fingerprinting in the Human Cerebral Cortex. Mathematics. 2021; 9(13):1549. https://doi.org/10.3390/math9131549
Chicago/Turabian StyleVegh, Viktor, Shahrzad Moinian, Qianqian Yang, and David C. Reutens. 2021. "Fractional Order Magnetic Resonance Fingerprinting in the Human Cerebral Cortex" Mathematics 9, no. 13: 1549. https://doi.org/10.3390/math9131549
APA StyleVegh, V., Moinian, S., Yang, Q., & Reutens, D. C. (2021). Fractional Order Magnetic Resonance Fingerprinting in the Human Cerebral Cortex. Mathematics, 9(13), 1549. https://doi.org/10.3390/math9131549






