A Self-Learning Based Preference Model for Portfolio Optimization
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Multi-Criteria Decision Making System for Portfolio Optimization MV-IMCDM
2.1. MV Model
2.2. MV-IMCDM
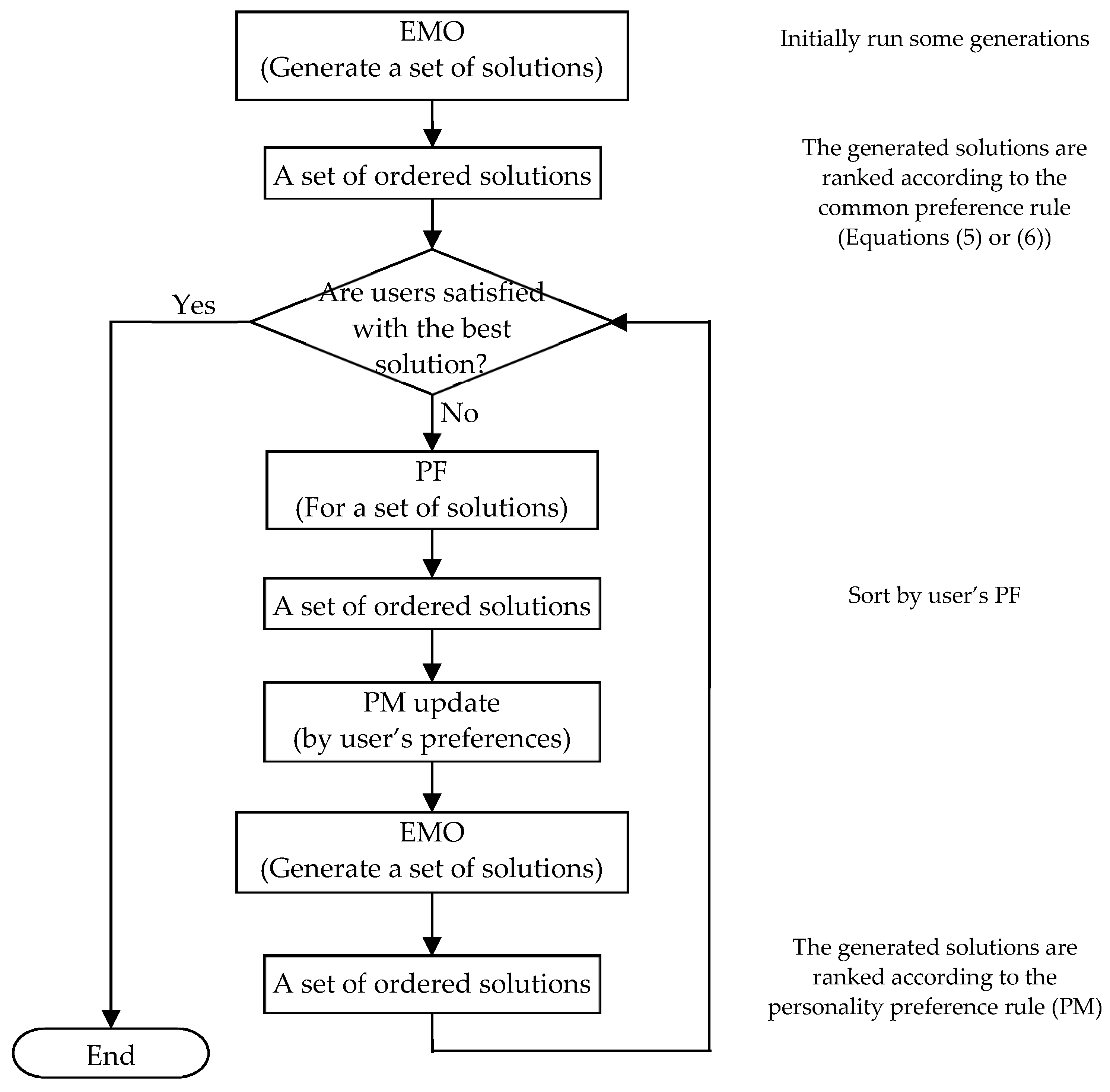
3. The Self-Learning Based Preference Model DT-PM
3.1. Construction of DT-PM
3.2. Sample Space of DT-PM
3.3. Guidance of DT-PM
4. Experimental Evaluation
4.1. Experimental Design
4.2. Experimental Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Acronyms | Explanation |
| ABC | Artificial bee colony |
| DM | Decision maker |
| DT | Decision tree |
| DT-PM | Decision tree-preference model |
| EMO | Evolutionary multi-objective optimization |
| G-PM | General polynomial-preference model |
| IMCDM | Interactive multi-criteria decision making |
| L-PM | Linear-preference model |
| MOEA/D | Multi-objective evolutionary algorithm based on decomposition |
| MV | Mean variance |
| MV-IMCDM | Mean variance-Interactive multi-criterion decision making |
| PF | Preference feedback |
| PM | Preference model |
| NPGA-II | Niched pareto genetic algorithm II |
| PSO | Particle swarm optimization |
| SPEA2 | Strength Pareto evolutionary algorithm 2 |
Appendix A
| Stock Category and Code | Company Stock Code | Company in Short | Expected Return |
|---|---|---|---|
| agriculture, forestry, husbandry, fishery (A) | 002458 | Yisheng Stock | 0.146350 |
| mining (B) | 601899 | Zijin Mining | 0.035467 |
| manufacturing (C) | 600809 | Shanxi Fenjiu | 0.087283 |
| electricity, heating, gas, water, supply (D) | 601139 | Shenzhen Gas | 0.037375 |
| architecture (E) | 002140 | Donghua Tech | 0.038983 |
| wholesale, retailer (F) | 603708 | Jiajiayue | 0.041692 |
| transportation, storage, post (G) | 601111 | Air China | 0.026667 |
| accommodation, catering (H) | 000428 | Huatian Hotel | 0.007550 |
| information (I) | 600570 | Hangseng Elec | 0.063117 |
| finance (J) | 000001 | Pingan Bank | 0.052067 |
| estate (K) | 600383 | Jingdi Group | 0.043716 |
| lease, business service (L) | 601888 | CITS | 0.036816 |
| science, technique (M) | 002887 | Huayang Intl | 0.035520 |
| irrigation, environment, infrastructure (N) | 000069 | Green Ecology | 0.024300 |
| education (P) | 002607 | Zhonggong Edu | 0.043266 |
| sanitation, society (Q) | 300015 | Aier Eye | 0.059350 |
| culture, PE, entertainment (R) | 300251 | Ray Media | 0.043150 |
| composite (S) | 600455 | Broadcom Shares | 0.044383 |
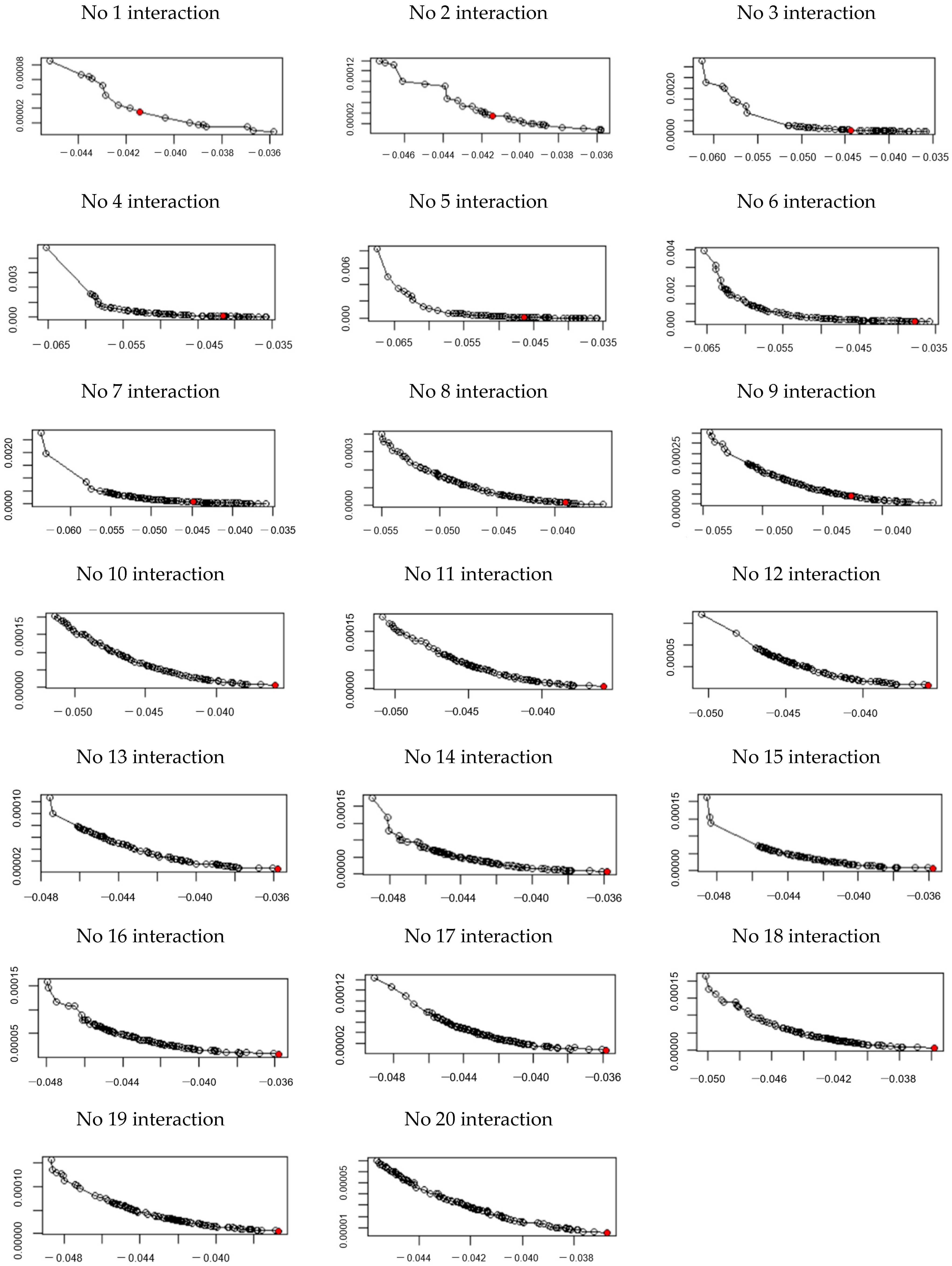
References
- Markowitz, H. Portfolio selection. J. Financ. 1952, 7, 77–91. [Google Scholar]
- Markowitz, H. Portfolio Selection: Efficient Diversification of Investments; Yale University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1959. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, N.; Yuan, C. Research on credit business operation efficiency of commercial banks based on portfolio theory. Syst. Eng. Theory Prac. 2019, 39, 1643–1650. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Qin, Z.; Kar, S. Mean-variance-skewness model for portfolio selection with fuzzy returns. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2010, 202, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrgott, M.; Klamroth, K.; Schwehm, C.J. An MCDM approach to portfolio optimization. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2004, 155, 752–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konno, H.; Yamazaki, H. Mean-absolute deviation portfolio optimization model and its applications to Tokyo stock market. Manag. Sci. 1991, 37, 519–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Young, M.R. A minimax portfolio selection rule with linear programming solution. Manag. Sci. 1998, 44, 673–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jorion, P. Value at Risk: A New Benchmark for Measuring Derivatives Risk; Irwin Professional Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 1996; pp. 1–624. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, X.; Sun, X.; Zhu, S.; Jiang, R.; Li, D. Portfolio optimization with nonparametric value at risk: A block coordinate descent method. Inf. J. Comput. 2018, 30, 454–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speranza, M.G. A heuristic algorithm for a portfolio optimization model applied to the Milan stock market. Comput. Oper. Res. 1996, 23, 433–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardoroudi, N.D.; Keshvari, A.; Kallio, M.; Korhonen, P.J. Solving cardinality constrained mean-variance portfolio problems via MILP. Ann. Oper. Res. 2017, 254, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paiva, F.D.; Cardoso, R.T.N.; Hanaoka, G.P.; Duarte, W.M. Decision-making for financial trading: A fusion approach of machine learning and portfolio selection. Expert Sust. Appl. 2019, 115, 635–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Kim, W.C.; Fabozzi, F.J. Portfolio selection with conservative short-selling. Financ. Res. Lett. 2016, 18, 363–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Han, R.; Wang, W. Prediction-based portfolio optimization models using deep neural networks. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 115393–115405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ertenlice, O.; Kalayci, C.B. A survey of swarm intelligence for portfolio optimization: Algorithms and applications. Swarm Evol. Comput. 2018, 39, 36–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altinoz, M.; Altinoz, O.T. Systematic initialization approaches for portfolio optimization problems. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 57779–57794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anagnostopoulos, K.P.; Mamanis, G. The mean-variance cardinality constrained portfolio optimization problem: An experimental evaluation of five multiobjective evolutionary algorithms. Expert Syst. Appl. 2011, 38, 14208–14217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Rodríguez, S.; Quintana, D.; Galván, I.M.; Viñuela, P.I. Portfolio optimization using SPEA2 with resampling. In Proceedings of the Intelligent Data Engineering and Automated Learning (IDEAL 2011), Norwich, UK, 7–9 September 2011; pp. 127–134. [Google Scholar]
- He, Y.; Aranha, C. Solving portfolio optimization problems using MOEA/D and levy flight. Adv. Data Sci. Adapt. Anal. 2020, 12, 1–34. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Zhou, Y. Robust multiobjective portfolio with higher moments. Expert Syst. Appl. 2018, 100, 165–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Sheng, H.; Wang, J.; Wang, S. Artificial bee colony algorithm based on novel mechanism for fuzzy portfolio selection. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy. Syst. 2019, 27, 966–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kizys, R.; Juan, A.A.; Sawik, B.; Calvet, L. A biased-randomized iterated local search algorithm for rich portfolio optimization. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 3509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xin, B.; Chen, L.; Chen, J.; Ishibuchi, H.; Hirota, K.; Liu, B. Interactive multiobjective optimization: A review of the state-of-the-art. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 41256–41279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branke, J.; Branke, J.; Deb, K.; Miettinen, K.; Slowiński, R. Multiobjective Optimization: Interactive and Evolutionary Approaches; Springer-Verlag: West Berlin, Germany, 2008; pp. 1–470. [Google Scholar]
- Köksalan, M.; Wallenius, J.; Zionts, S. An early history of multiple criteria decision making. J. Multi-Criteria Decis. Anal. 2016, 20, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meignan, D.; Knust, S.; Frayret, J.-M.; Pesant, G.; Gaud, N. A review and taxonomy of interactive optimization methods in operations research. ACM Trans. Interact. Intell. Syst. 2015, 5, 1–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allmendinger, R.W.; Ehrgott, M.; Gandibleux, X.; Geiger, M.J.; Klamroth, K.; Luque, M. Navigation in multiobjective optimization methods. J. Multi-Criteria Decis. Anal. 2017, 24, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, S.; Geiger, M.J.; de Almeida, A.T. Multiple Criteria Decision Making and Aiding; Springer: West Berlin, Germany, 2019; pp. 1–309. [Google Scholar]
- Deb, K.; Sundar, J. Reference point based multi-objective optimization using evolutionary algorithms. In Proceedings of the 8th Annual Conference on Genetic and Evolutionary Computation, Seattle, WA, USA; 2006; pp. 635–642. [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz, A.B.; Saborido, R.; Bermúdez, J.D.; Luque, M.; Vercher, E. Preference-based evolutionary multi-objective optimization for portfolio selection: A new credibilistic model under investor preferences. J. Glob. Optim. 2020, 76, 295–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou-Kangas, Y.; Miettinen, K. Decision making in multiobjective optimization problems under uncertainty: Balancing between robustness and quality. OR Spectr. 2019, 41, 391–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hafiz, F.; Swain, A.; Mendes, E. Multi-objective evolutionary framework for non-linear system identification: A comprehensive investigation. Neurocomputing 2020, 386, 257–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ruiz, F.; Luque, M.; Cabello, J.M. A classification of the weighting schemes in reference point procedures for multiobjective programming. J. Oper. Res. Soc. 2009, 60, 544–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deb, K.; Kumar, A. Interactive evolutionary multi-objective optimization and decision-making using reference direction method. In Proceedings of the 9th Annual Conference on Genetic and Evolutionary Computation, London, UK, 7–11 July 2007; pp. 781–788. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; He, Q.; Li, Y.; Zhu, Z. Multi-areas outstanding covering optimization method of HF network based on preference ranking elimination NSGAII algorithm. J. Electron. Inf. Technol. 2017, 8, 1779–1787. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, R.; Wang, R.; Feng, W.; Huang, J.; Jiao, L. Interactive reference region based multi-objective evolutionary algorithm through decomposition. IEEE Access 2016, 4, 7331–7346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Yu, G.; Zheng, J.; Zou, J. A preference-based multi-objective evolutionary algorithm using preference selection radius. Soft. Comput. 2017, 21, 5025–5051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battiti, R.; Passerini, A. Brain computer evolutionary multiobjective optimization: A genetic algorithm adapting to the decision maker. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2010, 14, 671–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhlisullina, D.; Passerini, A.; Battiti, R. Learning to diversify in complex interactive multiobjective optimization. In Proceedings of the 10th Metaheuristics International Conference (MIC 2013), Singapore, 5–8 August 2013; pp. 230–239. [Google Scholar]
- March, J.G. Bounded rationality, ambiguity, and the engineering of choice. Bell J. Econ. 1978, 9, 587–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larichev, O.I. Cognitive validity in design of decision-aiding techniques. J. Multi-Criteria Decis. Anal. 1992, 1, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowler, J.W.; Gel, E.S.; Köksalan, M.; Korhonen, P.J.; Marquis, J.L.; Wallenius, J. Interactive evolutionary multi-objective optimization for quasi-concave preference functions. Eur. J. Oper Res. 2010, 206, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köksalan, M.; Karahan, I. An interactive territory defining evolutionary algorithm: iTDEA. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2010, 14, 702–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deb, K.; Sinha, A.; Korhonen, P.J.; Wallenius, J. An interactive evolutionary multiobjective optimization method based on progressively approximated value functions. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2010, 14, 723–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pascoletti, A.; Serafini, P. Scalarizing vector optimization problems. J. Optim. Theory Appl. 1984, 42, 499–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branke, J.; Corrente, S.; Greco, S.; Słowiński, R.; Zielniewicz, P. Using Choquet integral as preference model in interactive evolutionary multiobjective optimization. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2016, 250, 884–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, S.; Li, F.; Liu, Y.; Wang, S. A self-adaptive preference model based on dynamic feature analysis for interactive portfolio optimization. Int. J. Mach. Learn. Cybern. 2020, 11, 1253–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubinstein, A.; Ni, X. Modeling Bounded Rationality; China Renmin University Press: Beijing, China, 2005; pp. 1–220. [Google Scholar]
- Kolm, P.N.; Tütüncü, R.; Fabozzi, F.J. 60 Years of portfolio optimization: Practical challenges and current trends. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2014, 234, 356–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlou, A.; Doumpos, M.; Zopounidis, C. The robustness of portfolio efficient frontiers: A comparative analysis of bi-objective and multi-objective approaches. Manag. Decis. 2018, 57, 300–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deb, K.; Pratap, A.; Agarwal, S.; Meyarivan, T. A fast and elitist multiobjective genetic algorithm: NSGA-II. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2002, 6, 182–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Q.; Li, H. MOEA/D: A multiobjective evolutionary algorithm based on decomposition. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2007, 11, 712–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhang, Q. Multiobjective optimization problems with complicated pareto sets, MOEA/D and NSGA-II. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2009, 13, 284–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuate, O.; Schütze, O.; Grasso, F.; Tlelo-Cuautle, E. Sizing CMOS operational transconductance amplifiers applying NSGA-II and MOEAD. In Proceedings of the 2019 42nd International Convention on Information and Communication Technology, Electronics and Microelectronics (MIPRO), Opatija, Croatia, 20–24 May 2019; pp. 149–152. [Google Scholar]
- Mishra, S.K.; Panda, G.; Majhi, R. A comparative performance assessment of a set of multiobjective algorithms for constrained portfolio assets selection. Swarm Evol. Comput. 2014, 16, 38–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajabi, M.; Khaloozadeh, H. Investigation and comparison of the performance of multi-objective evolutionary algorithms based on decomposition and dominance in portfolio optimization. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Electrical Engineering (ICEE), Mashhad, Iran, 8–10 May 2018; pp. 923–929. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Li, H.; Maringer, D.G.; Tsang, E.P.K. MOEA/D with NBI-style Tchebycheff approach for portfolio management. In Proceedings of the IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation, Barcelona, Spain, 18–23 July 2010; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, H.; Pei, L.; Jiao, L.; Yang, S.; Hou, B. Review of parallel deep neural network. Chin. J. Comput. 2018, 41, 1861–1881. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, J.; Hu, W. Recent advances in bayesian machine learning. J. Comput. Res. Dev. 2015, 52, 16–26. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Yang, L.; Yang, M. Multitier ensemble classifiers for malicious network traffic detection. J. Commun. 2018, 39, 155–165. [Google Scholar]
- Grąbczewski, K. Meta-Learning in Decision Tree Induction; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 1–343. [Google Scholar]
- Safavian, S.R.; Landgrebe, D. A survey of decision tree classifier methodology. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 1991, 21, 660–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bramer, M. Principles of Data Mining/Edition 4; Springer-Verlag: London, UK, 2020; pp. 1–571. [Google Scholar]
- Loh, W.Y. Fifty years of classification and regression trees. Int. Stat. Rev. 2014, 82, 329–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, S.; Yan, Y. Financial Data; Tsinghua University Press: Beijing, China, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Resset Financial Research Database. Beijing Juyuan Resset Data Technology Co., Ltd. ed. DB/OL. Available online: http://www.resset.cn/ (accessed on 26 May 2021).
- Pal, S.; Qu, B.; Das, S.; Suganthan, P.N. Linear antenna array synthesis with constrained multi-objective differential evolution. Prog. Electromagn. Res. 2010, 21, 87–111. [Google Scholar]
- Basak, A.; Pal, S.; Pandi, V.R.; Panigrahi, B.K.; Mallick, M.K.; Mohapatra, A. A novel multi-objective formulation for hydrothermal power scheduling based on reservoir end volume relaxation. In Proceedings of the 2010 International Conference on Swarm, Evolutionary, and Memetic Computing, Hyderabad, India, 18–19 December 2010; pp. 718–726. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Zhou, A.; Zhang, G. An MOEA/D with multiple differential evolution mutation operators. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation (CEC), Beijing, China, 6–11 July 2014; pp. 397–404. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, A.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, G. A multiobjective evolutionary algorithm based on decomposition and probability model. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation, Brisbane, Australia, 10–15 June 2012; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Ozbey, O.; Karwan, M.H. An interactive approach for multicriteria decision making using a Tchebycheff utility function approximation. J. Multi-Criteria Decis. Anal. 2014, 21, 153–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Xin, B.; Chen, J.; Li, J. A virtual-decision-maker library considering personalities and dynamically changing preference structures for interactive multi-objective optimization. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation (CEC), Donostia, Spain, 5–8 June 2017; pp. 636–641. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Y.C.; Cheam, X.J.; Chen, C.Y.; Kuo, S.Y.; Chou, Y.H. A novel portfolio optimization with short selling using GNQTS and trend ratio. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics (SMC), Miyazaki, Japan, 7–10 October 2018; pp. 1564–1569. [Google Scholar]
- Teplá, L. Optimal portfolio policies with borrowing and shortsale constraints. J. Econ. Dyn. Control 2000, 24, 1623–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, C.; Lari-Lavassani, A.; Li, X. Dynamic mean-variance portfolio selection with borrowing constraint. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2010, 200, 312–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Li, R. A portfolio selection model with borrowing constraint based on possibility theory. Appl. Soft Comput. 2012, 12, 754–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbons, M.R.; Ross, S.A.; Shanken, J. A test of efficiency of a given portfolio. Econometrica 1989, 57, 1121–1152. [Google Scholar]
- Agrrawal, P. Using index ETFs for multi-asset class investing: Shifting the efficient frontier up. J. Index Invest. 2013, 4, 83–94. [Google Scholar]
- Petchrompo, S.; Wannakrairot, A.; Parlikad, A.K. Pruning pareto optimal solutions for multi-objective portfolio asset management. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| PMs | Diff | Acc |
|---|---|---|
| DT-PM | 28.537 × 10−9 | 0.913 |
| L-PM | 451.72 × 10−9 | 0.483 |
| G-PM | 2.054 × 10−9 | 0.979 |
| PMs | Diff | Acc |
|---|---|---|
| DT-PM | 0.6042 × 10−9 | 0.929 |
| L-PM | 253.233 × 10−9 | 0.628 |
| G-PM | 5.726 × 10−9 | 0.822 |
| PMs | Diff | Acc |
|---|---|---|
| DT-PM | 1.669 × 10−7 | 0.948 |
| L-PM | 236.043 × 10−7 | 0.554 |
| G-PM | 11.759 × 10−7 | 0.831 |
| PMs | Diff | Acc |
|---|---|---|
| DT-PM | 2.485 × 10−4 | 0.887 |
| G-PM | 3.722 × 10−4 | 0.573 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, S.; Li, D.; Jia, J.; Liu, Y. A Self-Learning Based Preference Model for Portfolio Optimization. Mathematics 2021, 9, 2621. https://doi.org/10.3390/math9202621
Hu S, Li D, Jia J, Liu Y. A Self-Learning Based Preference Model for Portfolio Optimization. Mathematics. 2021; 9(20):2621. https://doi.org/10.3390/math9202621
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Shicheng, Danping Li, Junmin Jia, and Yang Liu. 2021. "A Self-Learning Based Preference Model for Portfolio Optimization" Mathematics 9, no. 20: 2621. https://doi.org/10.3390/math9202621
APA StyleHu, S., Li, D., Jia, J., & Liu, Y. (2021). A Self-Learning Based Preference Model for Portfolio Optimization. Mathematics, 9(20), 2621. https://doi.org/10.3390/math9202621





