Gain-Preserving Data-Driven Approximation of the Koopman Operator and Its Application in Robust Controller Design
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Preliminaries
2.1. Koopman Operator and Its Data-Driven Approximation
2.1.1. Koopman Operator
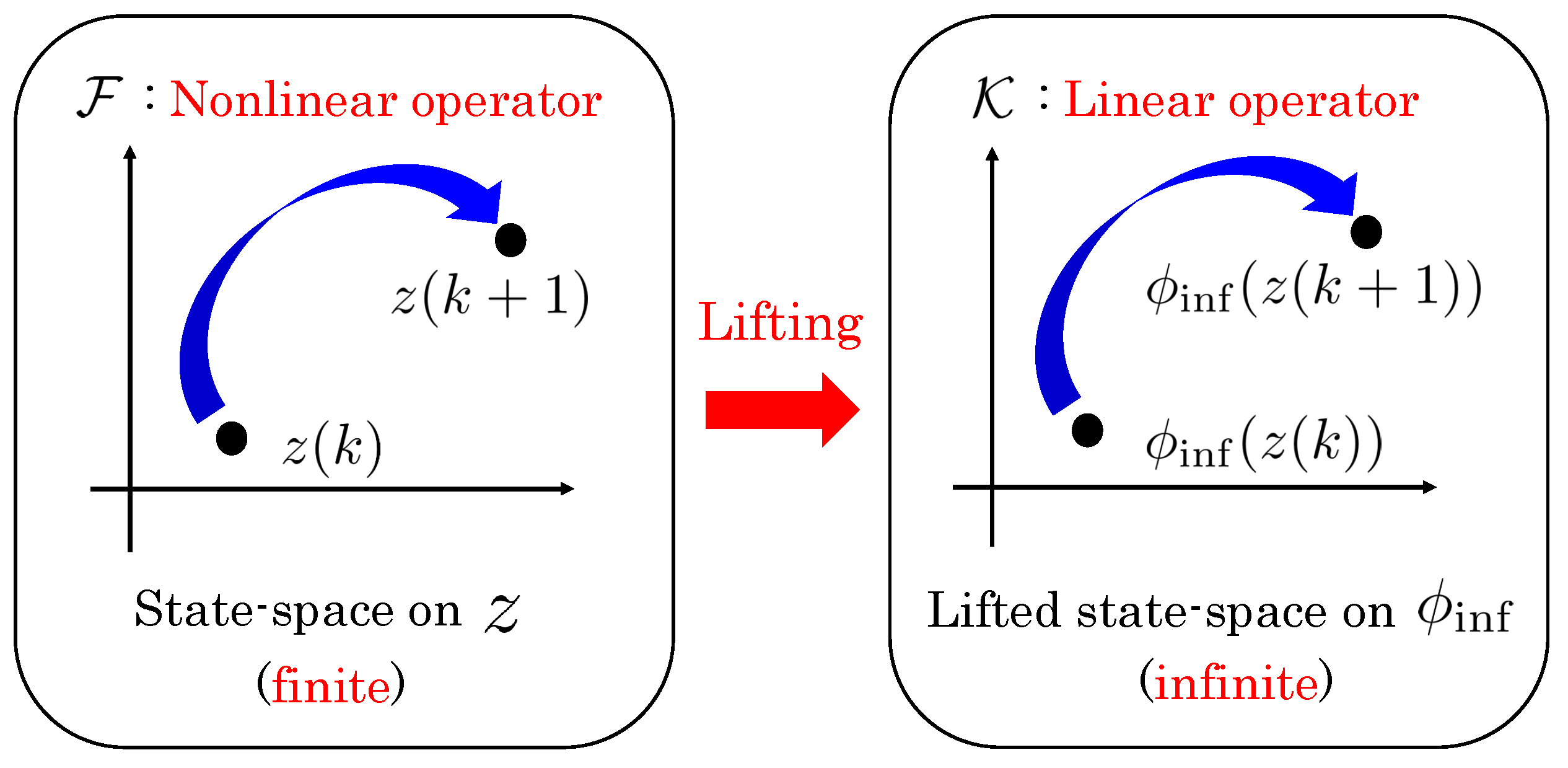
2.1.2. Approximation of the Koopman Operator
2.1.3. Data-Driven Approximation of Koopman Operator
2.2. Stability
2.2.1. Definition of Stability
- (i)
- holds.
- (ii)
- There exists symmetric matrix P such that the following inequalities hold.
2.2.2. Stability Analysis for Feedback System
2.3. Internal Model Control
3. Result 1: Gain-Preserving Data-Driven Modeling
3.1. Problem Setting
3.2. Convex Approximation of Problem 2
3.3. Sequential Convex Approximation of Problem 2
4. Result 2: Gain-Preserving Approximation of the Koopman Operator for Data-Driven Robust Controller Design
4.1. Data-Driven Modeling of Plant System
4.2. Data-Driven IMC with Gain Guarantee
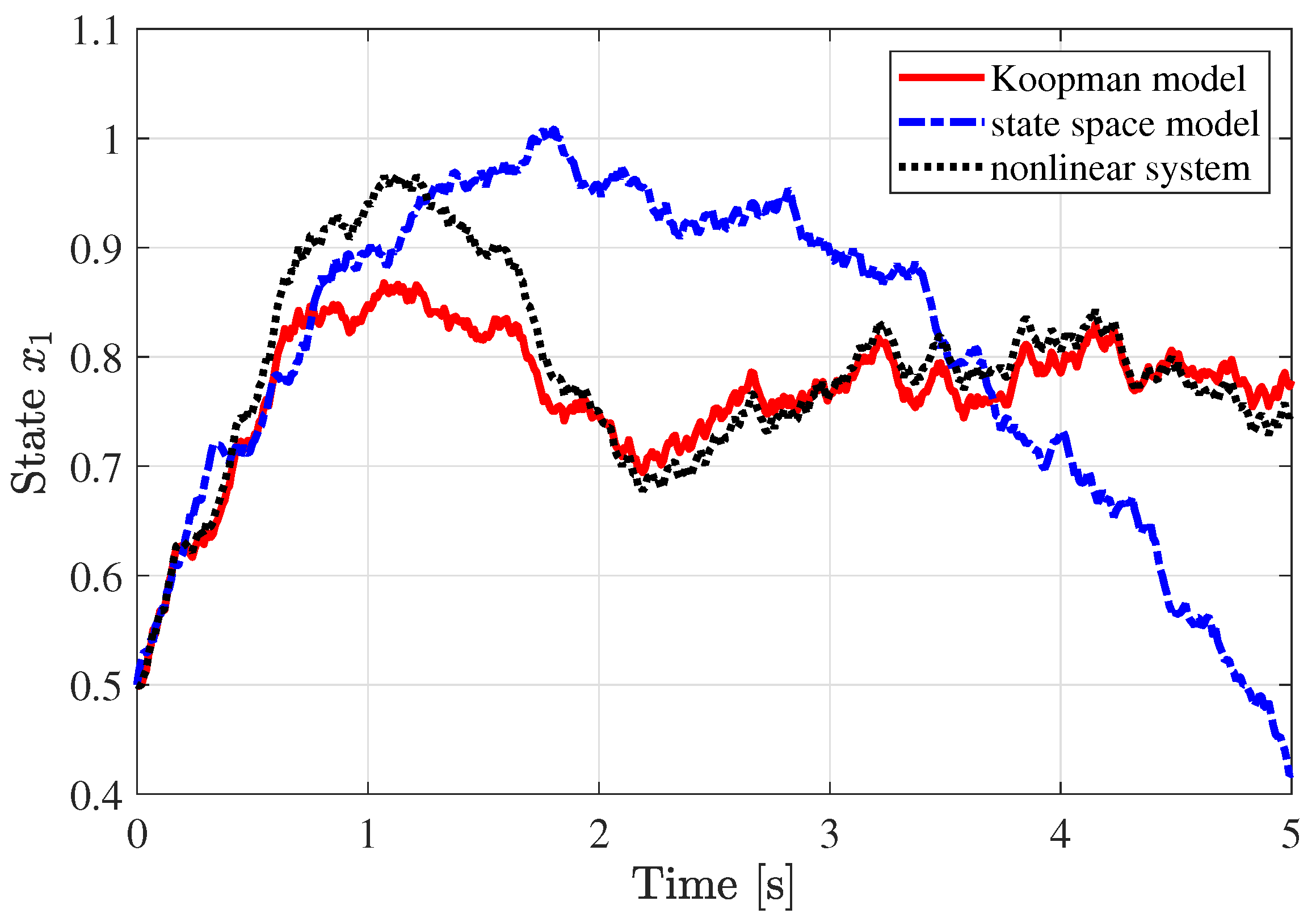
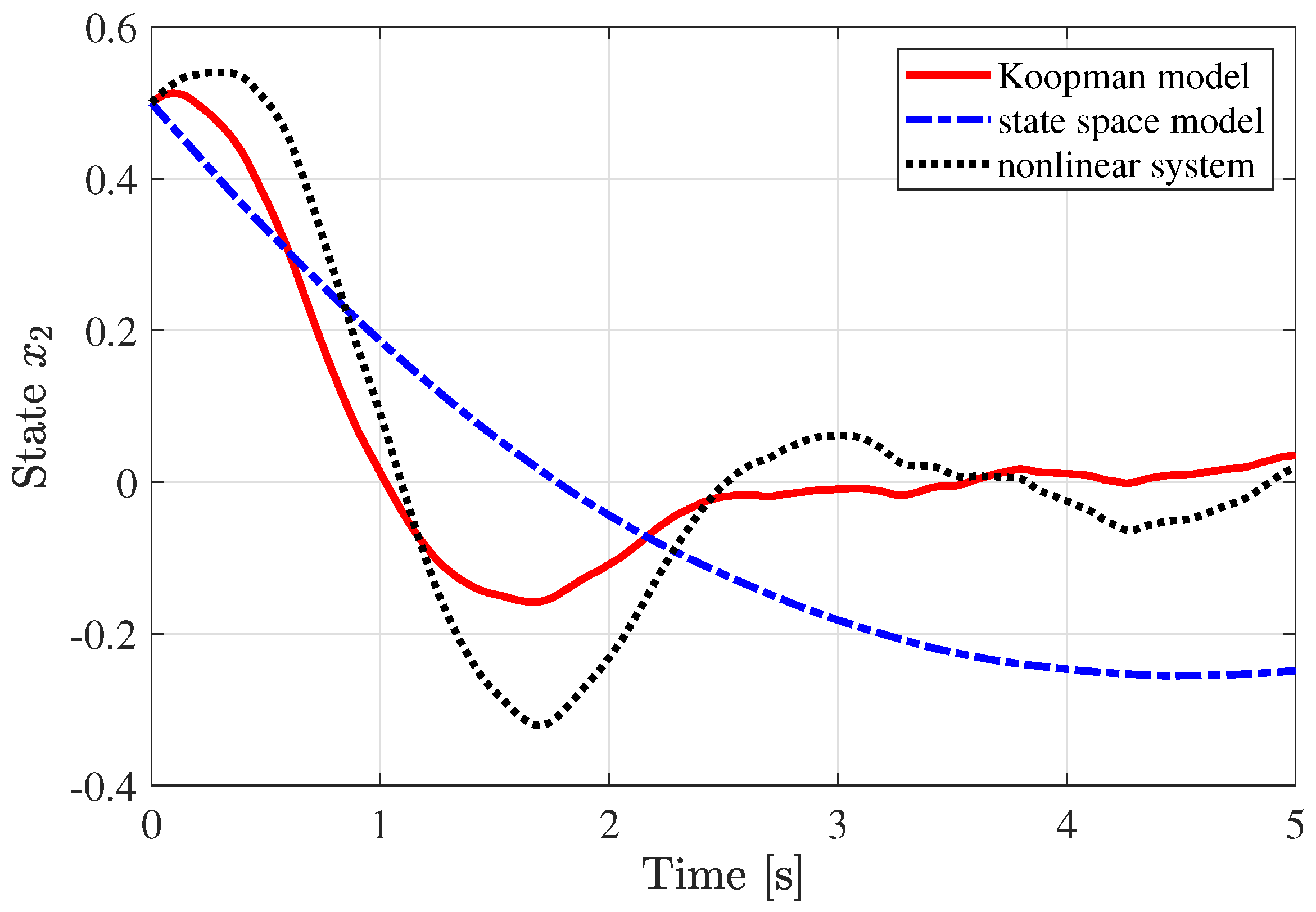
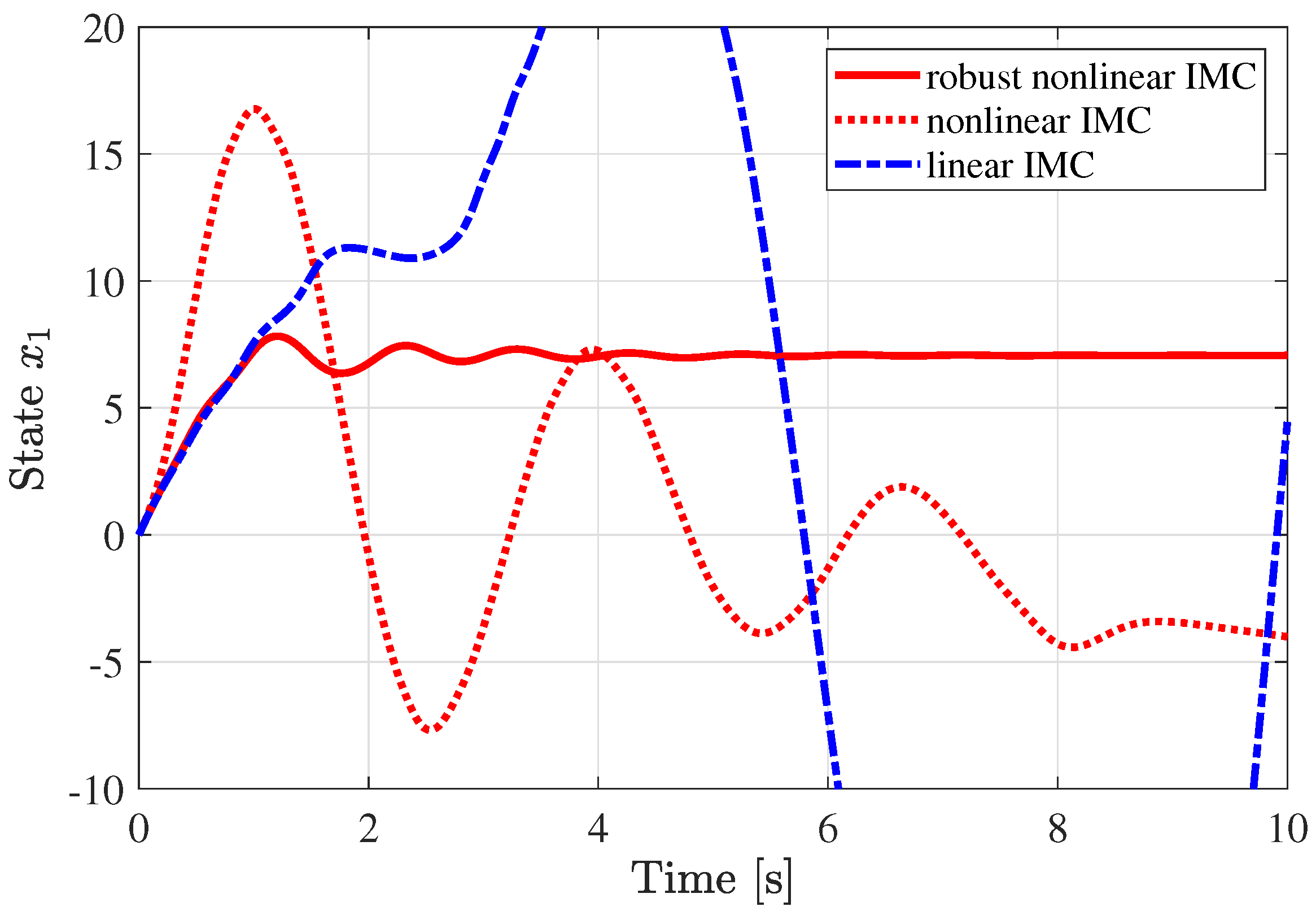
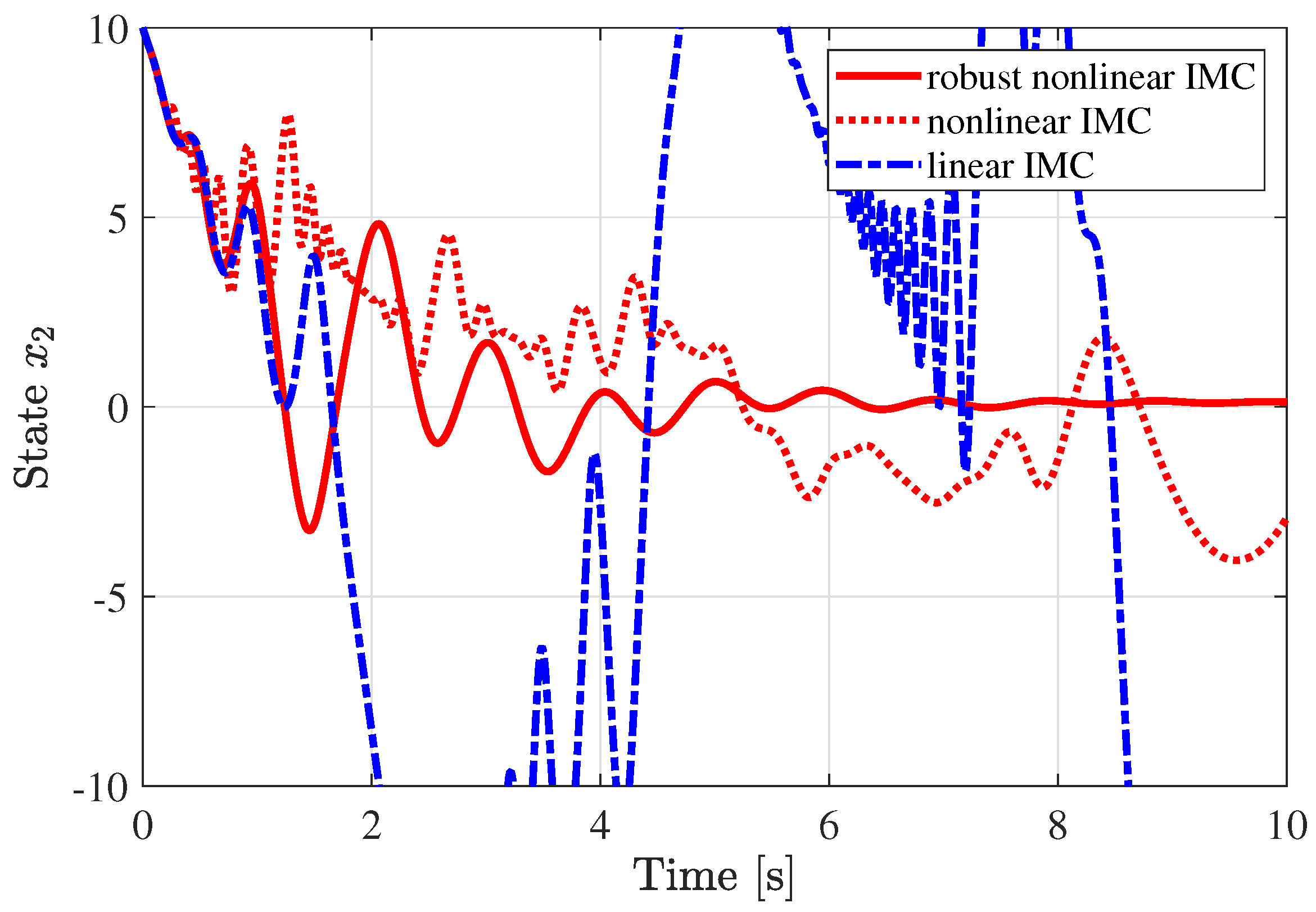
5. Numerical Experiment
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kutz, J.N.; Brunton, S.L.; Brunton, B.W.; Proctor, J.L. Dynamic Mode Decomposition: Data-Driven Modeling of Complex Systems; SIAM: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Ljung, L.; Andersson, C.; Tiels, K.; Schön, T.B. Deep learning and system identification. In Proceedings of the IFAC World Congress 2020, Berlin, Germany, 12–17 July 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Lacy, S.L.; Bernstein, D.S. Subspace identification with guaranteed stability using constrained optimization. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2003, 48, 1259–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, M.; Sugie, T. Subspace system identification considering both noise attenuation and use of prior knowledge. In Proceedings of the 35th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, Kobe, Japan, 11–13 December 1996; pp. 3662–3667. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, D.N.; De Callafon, R.A. Subspace identification with eigenvalue constraints. Automatica 2013, 49, 2468–2473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alenany, A.; Shang, H.; Soliman, M.; Ziedan, I. Improved subspace identification with prior information using constrained least squares. IET Control Theory Appl. 2011, 5, 1568–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimura, S.; Matsubayashi, A.; Inoue, M. System identification method inheriting steady-state characteristics of existing model. Int. J. Control 2019, 92, 2701–2711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goethals, I.; Van Gestel, T.; Suykens, J.; Van Dooren, P.; De Moor, B. Identification of positive real models in subspace identification by using regularization. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2003, 48, 1843–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoagg, J.B.; Lacy, S.L.; Erwin, R.S.; Bernstein, D.S. First-order-hold sampling of positive real systems and subspace identification of positive real models. In Proceedings of the 2004 American Control Conference, Boston, MA, USA, 30 June–2 July 2004; pp. 861–866. [Google Scholar]
- Abe, Y.; Inoue, M.; Adachi, S. Subspace identification method incorporated with a priori information characterized in frequency domain. In Proceedings of the 2016 European Control Conference, Aalborg, Denmark, 29 June–1 July 2016; pp. 1377–1382. [Google Scholar]
- Inoue, M. Subspace identification with moment matching. Automatica 2019, 99, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, K.; Doyle, J.C.; Glover, K. Robust and Optimal Control; Prentice Hall: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Brunton, S.L.; Brunton, B.W.; Proctor, J.L.; Kutz, J.N. Koopman invariant subspaces and finite linear representations of nonlinear dynamical systems for control. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0150171. [Google Scholar]
- Kaiser, E.; Kutz, J.N.; Brunton, S.L. Data-driven discovery of Koopman eigenfunctions for control. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1707.01146. [Google Scholar]
- Hara, K.; Inoue, M.; Sebe, N. Learning Koopman operator under dissipativity constraints. In Proceedings of the IFAC World Congress 2020, Berlin, Germany, 12–17 July 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Korda, M.; Mezić, I. Linear predictors for nonlinear dynamical systems: Koopman operator meets model predictive control. Automatica 2018, 93, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Narasingam, A.; Kwon, J.S.I. Koopman Lyapunov-based model predictive control of nonlinear chemical process systems. AIChE J. 2019, 65, e16743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Huang, B.; Vaidya, U. Optimal quadratic regulation of nonlinear system using Koopman operator. In Proceedings of the 2019 American Control Conference, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 10–12 July 2019; pp. 4911–4916. [Google Scholar]
- Broad, A.; Abraham, I.; Murphey, T.; Argall, B. Data-driven Koopman operators for model-based shared control of human–machine systems. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2020, 39, 1178–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peitz, S.; Otto, S.E.; Rowley, C.W. Data-driven model predictive control using interpolated Koopman generators. SIAM J. Appl. Dyn. Syst. 2020, 19, 2162–2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.; Vaidya, U.; Chen, Y. A convex data-driven approach for nonlinear control synthesis. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2006.15477. [Google Scholar]
- Uchida, D.; Yamashita, A.; Asama, H. Data-driven Koopman controller synthesis based on the extended H2 norm characterization. IEEE Control Syst. Lett. 2021, 5, 1795–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, Y.; Wang, R.; Jones, C.N. Koopman based data-driven predictive control. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2102.05122. [Google Scholar]
- Otto, S.E.; Rowley, C.W. Koopman operators for estimation and control of dynamical systems. Annu. Rev. Control Robot. Auton. Syst. 2021, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bevanda, P.; Sosnowski, S.; Hirche, S. Koopman operator dynamical models: Learning, analysis and control. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2102.02522. [Google Scholar]
- Mauroy, A.; Susuki, Y.; Mezić, I. The Koopman Operator in Systems and Control; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Sebe, N. Sequential convex overbounding approximation method for bilinear matrix inequality problems. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2018, 51, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, C.E.; Morari, M. Internal model control. A unifying review and some new results. Ind. Eng. Chem. Process. Des. Dev. 1982, 21, 308–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Economou, C.G.; Morari, M.; Palsson, B.O. Internal model control: Extension to nonlinear system. Ind. Eng. Chem. Process. Des. Dev. 1986, 25, 403–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.T.; Kaneko, O.; Yamamoto, S. Data-driven IMC for non-minimum phase systems-Laguerre expansion approach. In Proceedings of the 50th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control and 2011 European Control Conference, Orlando, FL, USA, 12–15 December 2011; pp. 476–481. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, H.T.; Kaneko, O.; Wadagaki, Y.; Yamamoto, S. Fictitious reference iterative tuning of internal model controllers for non-minimum phase plants. In Proceedings of the SICE Annual Conference 2011, Tokyo, Japan, 13–18 September 2011; pp. 2608–2613. [Google Scholar]
- Rojas, J.; Vilanova, R. Data-driven based IMC control. Int. J. Innov. Comput. Inf. Control 2012, 8, 1557–1574. [Google Scholar]
- Rueda-Escobedo, J.G.; Schiffer, J. Data-driven internal model control of second-order discrete Volterra systems. In Proceedings of the 59th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, Jeju, Korea, 14–18 December 2020; pp. 4572–4579. [Google Scholar]
- Desoer, C.A.; Vidyasagar, M. Feedback Systems: Input-Output Properties; SIAM: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Brogliato, B.; Lozano, R.; Maschke, B.; Egeland, O. Dissipative Systems Analysis and Control: Theory and Applications; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Saxena, S.; Hote, Y.V. Advances in internal model control technique: A review and future prospects. IETE Tech. Rev. 2012, 29, 461–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lofberg, J. YALMIP: A toolbox for modeling and optimization in MATLAB. In Proceedings of the 2004 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Taipei, Taiwan, 2–4 September 2004; pp. 284–289. [Google Scholar]
- Sturm, J.F. Using SeDuMi 1.02, a MATLAB toolbox for optimization over symmetric cones. Optim. Methods Softw. 1999, 11, 625–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Problem | Optimal Solution |
|---|---|
| Problem 2 | |
| Problem 3 | |
| Problem 4 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hara, K.; Inoue, M. Gain-Preserving Data-Driven Approximation of the Koopman Operator and Its Application in Robust Controller Design. Mathematics 2021, 9, 949. https://doi.org/10.3390/math9090949
Hara K, Inoue M. Gain-Preserving Data-Driven Approximation of the Koopman Operator and Its Application in Robust Controller Design. Mathematics. 2021; 9(9):949. https://doi.org/10.3390/math9090949
Chicago/Turabian StyleHara, Keita, and Masaki Inoue. 2021. "Gain-Preserving Data-Driven Approximation of the Koopman Operator and Its Application in Robust Controller Design" Mathematics 9, no. 9: 949. https://doi.org/10.3390/math9090949
APA StyleHara, K., & Inoue, M. (2021). Gain-Preserving Data-Driven Approximation of the Koopman Operator and Its Application in Robust Controller Design. Mathematics, 9(9), 949. https://doi.org/10.3390/math9090949






