Deep Learning Chest CT for Clinically Precise Prediction of Sepsis-Induced Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome: A Protocol for an Observational Ambispective Cohort Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
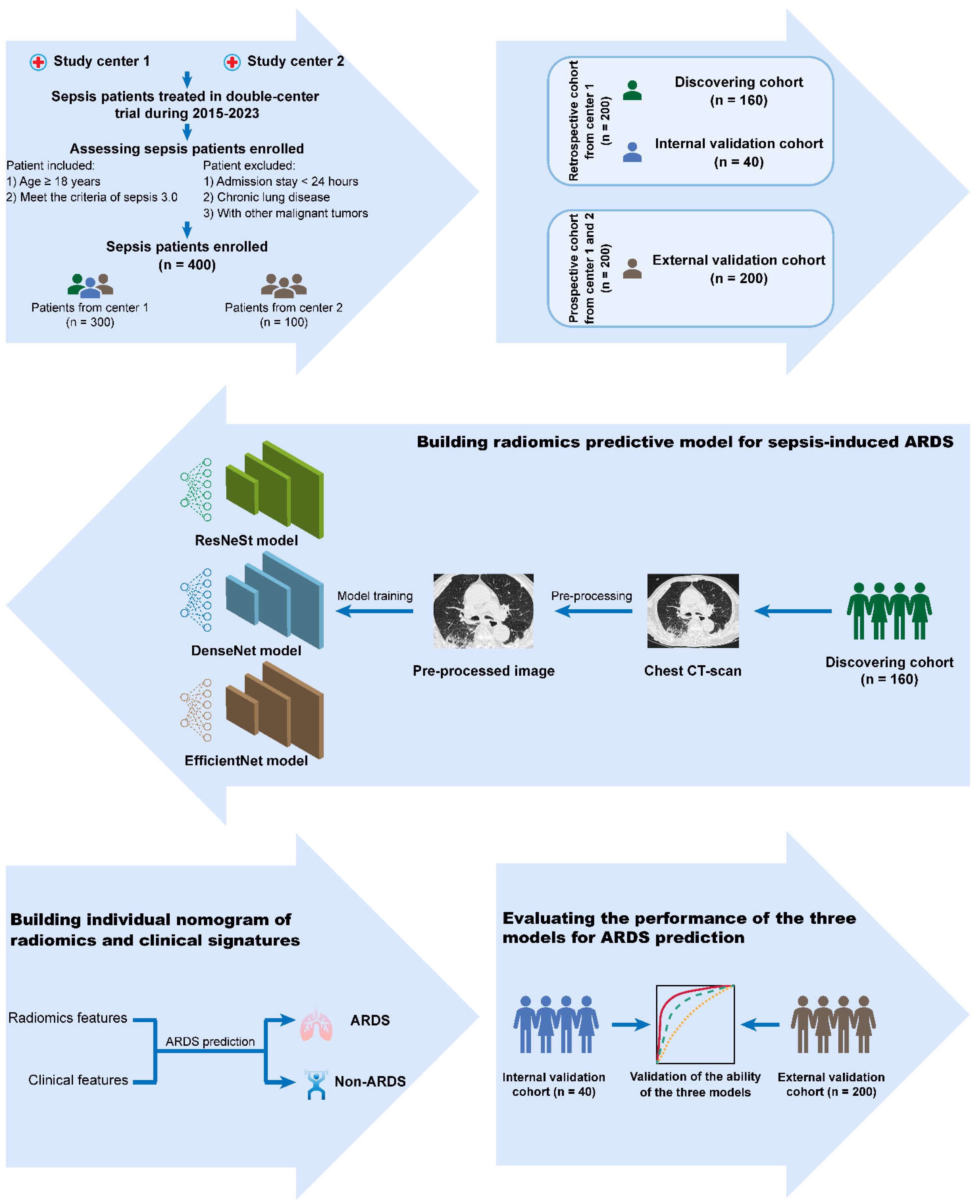
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Cohort Descriptions and Definitions
2.3. Sample Size Calculation
2.4. Data Collection
2.5. Work-Flow of Radiomics Analysis
2.6. Outcome Measures
- (1)
- Grade of pulmonary damage: patients will be classified as mild (200 < PaO2/FiO2 ≤ 300 mmHg), moderate (100 < PaO2/FiO2 ≤ 200 mmHg), or severe (PaO2/FiO2 ≤ 100 mmHg) at the moment of diagnosis of ARDS [2];
- (2)
- Ventilator-free days, VFD: defined as the number of days between successful weaning from mechanical ventilation and day 28 after ICU admission;
- (3)
- Respiratory organ failure-free days, RFFD: defined as the number of days between a day without evidence of respiratory organ failure [27];
- (4)
- 28-day mortality: all-cause mortality within 28 days following enrolment.
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Su, G.; Atakilit, A.; Li, J.T.; Wu, N.; Bhattacharya, M.; Zhu, J.; Shieh, J.E.; Li, E.; Chen, R.; Sun, S.; et al. Absence of integrin alphavbeta3 enhances vascular leak in mice by inhibiting endothelial cortical actin formation. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2012, 185, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranieri, V.M.; Rubenfeld, G.D.; Thompson, B.T.; Ferguson, N.D.; Caldwell, E.; Fan, E.; ARDS Definition of Task Force; Camporota, L.; Slutsky, A.S. Acute respiratory distress syndrome: The Berlin Definition. JAMA 2012, 307, 2526–2533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Q.; Zhang, M.; Girardi, C.; Bouhemad, B.; Kesecioglu, J.; Rouby, J.J. Computed tomography assessment of exogenous surfactant-induced lung reaeration in patients with acute lung injury. Crit. Care 2010, 14, R135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellani, G.; Laffey, J.G.; Pham, T.; Fan, E.; Brochard, L.; Esteban, A.; Gattinoni, L.; Van Haren, F.; Larsson, A.; McAuley, D.F.; et al. Epidemiology, Patterns of Care, and Mortality for Patients With Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome in Intensive Care Units in 50 Countries. JAMA 2016, 315, 788–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pais, F.M.; Sinha, P.; Liu, K.D.; Matthay, M.A. Influence of Clinical Factors and Exclusion Criteria on Mortality in ARDS Observational Studies and Randomized Controlled Trials. Respir. Care 2018, 63, 1060–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gajic, O.; Dabbagh, O.; Park, P.K.; Adesanya, A.; Chang, S.Y.; Hou, P.; Anderson, H.; Hoth, J.J.; Mikkelsen, M.E.; Gentile, N.T.; et al. Early identification of patients at risk of acute lung injury: Evaluation of lung injury prediction score in a multicenter cohort study. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2011, 183, 462–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singer, M.; Deutschman, C.S.; Seymour, C.W.; Shankar-Hari, M.; Annane, D.; Bauer, M.; Bellomo, R.; Bernard, G.R.; Chiche, J.-D.; Coopersmith, C.M.; et al. The Third International Consensus Definitions for Sepsis and Septic Shock (Sepsis-3). JAMA 2016, 315, 801–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venet, F.; Monneret, G. Advances in the understanding and treatment of sepsis-induced immunosuppression. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2018, 14, 121–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leissinger, M.; Kulkarni, R.; Zemans, R.L.; Downey, G.P.; Jeyaseelan, S. Investigating the role of nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-like receptors in bacterial lung infection. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2014, 189, 1461–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calfee, C.S.; Delucchi, K.; Parsons, P.E.; Thompson, B.T.; Ware, L.B.; Matthay, M.A. Subphenotypes in acute respiratory distress syndrome: Latent class analysis of data from two randomised controlled trials. Lancet Respir. Med. 2014, 2, 611–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Li, P.; Goodwin, A.J.; Cook, J.A.; Halushka, P.V.; Chang, E.; Zingarelli, B.; Fan, H. Exosomes from endothelial progenitor cells improve outcomes of the lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury. Crit. Care 2019, 23, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bos, L.D.; Schouten, L.R.; van Vught, L.A.; Wiewel, M.A.; Ong, D.; Cremer, O.; Artigas, A.; Martin-Loeches, I.; Hoogendijk, A.J.; van der Poll, T.; et al. Identification and validation of distinct biological phenotypes in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome by cluster analysis. Thorax 2017, 72, 876–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laffey, J.G.; Madotto, F.; Bellani, G.; Pham, T.; Fan, E.; Brochard, L.; Amin, P.; Arabi, Y.; Bajwa, E.K.; Bruhn, A.; et al. Geo-economic variations in epidemiology, patterns of care, and outcomes in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome: Insights from the LUNG SAFE prospective cohort study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2017, 5, 627–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fialkow, L.; Fochesatto, F.L.; Bozzetti, M.C.; Milani, A.R.; Rodrigues, F.E.; Ladniuk, R.M.; Pierozan, P.; de Moura, R.M.; Prolla, J.C.; Vachon, E.; et al. Neutrophil apoptosis: A marker of disease severity in sepsis and sepsis-induced acute respiratory distress syndrome. Crit. Care 2006, 10, R155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giamarellos-Bourboulis, E.J.; Tsaganos, T.; Spyridaki, E.; Mouktaroudi, M.; Plachouras, D.; Vaki, I.; Karagianni, V.; Antonopoulou, A.; Veloni, V.; Giamarellou, H. Early changes of CD4-positive lymphocytes and NK cells in patients with severe Gram-negative sepsis. Crit. Care 2006, 10, R166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conway, M.A.; Datta, D.; Shankar-Hari, M.; Stephen, J.; Weir, C.J.; Rennie, J.; Antonelli, J.; Bateman, A.; Warner, N.; Judge, K.; et al. Cell-surface signatures of immune dysfunction risk-stratify critically ill patients: INFECT study. Intensiv. Care Med. 2018, 44, 627–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, D.C.; Huang, Q.; Wang, X. Significance of clinical phenomes of patients with COVID-19 infection: A learning from 3795 patients in 80 reports. Clin. Transl. Med. 2020, 10, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKinney, S.M.; Sieniek, M.; Godbole, V.; Godwin, J.; Antropova, N.; Ashrafian, H.; Back, T.; Chesus, M.; Corrado, G.S.; Darzi, A.; et al. International evaluation of an AI system for breast cancer screening. Nature 2020, 577, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moons, K.G.; Altman, D.G.; Reitsma, J.B.; Ioannidis, J.P.; Macaskill, P.; Steyerberg, E.W.; Vickers, A.J.; Ransohoff, D.F.; Collins, G.S. Transparent Reporting of a multivariable prediction model for Individual Prognosis or Diagnosis (TRIPOD): Explanation and elaboration. Ann. Intern. Med. 2015, 162, W1–W73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunliffe, A.; Armato, S.R.; Castillo, R.; Pham, N.; Guerrero, T.; Al-Hallaq, H.A. Lung texture in serial thoracic computed tomography scans: Correlation of radiomics-based features with radiation therapy dose and radiation pneumonitis development. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2015, 91, 1048–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevransky, J.E.; Levy, M.M.; Marini, J.J. Mechanical ventilation in sepsis-induced acute lung injury/acute respiratory distress syndrome: An evidence-based review. Crit. Care Med. 2004, 32, S548–S553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubenfeld, G.D.; Caldwell, E.; Peabody, E.; Weaver, J.; Martin, D.P.; Neff, M.; Stern, E.J.; Hudson, L.D. Incidence and outcomes of acute lung injury. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 353, 1685–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, P.A.; Taylor, R.; Thielke, R.; Payne, J.; Gonzalez, N.; Conde, J.G. Research electronic data capture (REDCap)--a metadata-driven methodology and workflow process for providing translational research informatics support. J. Biomed. Inform. 2009, 42, 377–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Wu, C.R.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Zhu, Y.; Lin, H.B.; Zhang, Z.; Sun, Y.; He, T.; Mueller, J.; Manmatha, R.; et al. ResNeSt: Split-Attention Networks. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.08955. [Google Scholar]
- Iandola, F.; Moskewicz, M.; Karayev, S.; Girshick, R.; Darrell, T.; Keutzer, K. Densenet: Implementing efficient convnet descriptor pyramids. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1404.1869. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, M.; Le, Q.V. Efficientnet: Rethinking model scaling for convolutional neural networks. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1905.11946. [Google Scholar]
- Perkins, G.D.; Gates, S.; Park, D.; Gao, F.; Knox, C.; Holloway, B.; McAuley, D.F.; Ryan, J.; Marzouk, J.; Cooke, M.W.; et al. The beta agonist lung injury trial prevention. A randomized controlled trial. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2014, 189, 674–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random Forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tibshirani, R. Regression shrinkage and selection via the LASSO. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B 1996, 58, 267–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shekar, K.; Davies, A.R.; Mullany, D.V.; Tiruvoipati, R.; Fraser, J.F. To ventilate, oscillate, or cannulate? J. Crit. Care 2013, 28, 655–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthay, M.A.; McAuley, D.F.; Ware, L.B. Clinical trials in acute respiratory distress syndrome: Challenges and opportunities. Lancet Respir. Med. 2017, 5, 524–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerin, C.; Reignier, J.; Richard, J.C.; Beuret, P.; Gacouin, A.; Boulain, T.; Mercier, E.; Badet, M.; Mercat, A.; Baudin, O.; et al. Prone positioning in severe acute respiratory distress syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 2159–2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, A.; Jones, D.; Bailey, M.; Beca, J.; Bellomo, R.; Blackwell, N.; Forrest, P.; Gattas, D.; Granger, E.; Jackson, A.; et al. Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation for 2009 Influenza A(H1N1) Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. JAMA 2009, 302, 1888–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trillo-Alvarez, C.; Cartin-Ceba, R.; Kor, D.J.; Kojicic, M.; Kashyap, R.; Thakur, S.; Thakur, L.; Herasevich, V.; Malinchoc, M.; Gajic, O. Acute lung injury prediction score: Derivation and validation in a population-based sample. Eur. Respir. J. 2011, 37, 604–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolinay, T.; Kim, Y.S.; Howrylak, J.; Hunninghake, G.M.; An, C.H.; Fredenburgh, L.; Massaro, A.F.; Rogers, A.; Gazourian, L.; Nakahira, K.; et al. Inflammasome-regulated cytokines are critical mediators of acute lung injury. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2012, 185, 1225–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kangelaris, K.N.; Prakash, A.; Liu, K.D.; Aouizerat, B.; Woodruff, P.G.; Erle, D.J.; Rogers, A.; Seeley, E.J.; Chu, J.; Liu, T.; et al. Increased expression of neutrophil-related genes in patients with early sepsis-induced ARDS. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2015, 308, L1102–L1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bos, L.; Scicluna, B.P.; Ong, D.; Cremer, O.; van der Poll, T.; Schultz, M.J. Understanding Heterogeneity in Biologic Phenotypes of Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome by Leukocyte Expression Profiles. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 200, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colen, R.R.; Fujii, T.; Bilen, M.A.; Kotrotsou, A.; Abrol, S.; Hess, K.R.; Hajjar, J.; Suarez-Almazor, M.E.; Alshawa, A.; Hong, D.S.; et al. Radiomics to predict immunotherapy-induced pneumonitis: Proof of concept. Investig. New Drugs 2018, 36, 601–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirano, Y.; Aziz, M.; Yang, W.L.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, M.; Ochani, M.; Khader, A.; Wang, P. Neutralization of osteopontin attenuates neutrophil migration in sepsis-induced acute lung injury. Crit. Care 2015, 19, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, I.; Kim, M.; Choe, K.; Song, E.; Seo, H.; Hwang, Y.; Ahn, J.; Lee, S.-H.; Lee, J.H.; Jo, Y.H.; et al. Neutrophils disturb pulmonary microcirculation in sepsis-induced acute lung injury. Eur. Respir. J. 2019, 53, 1800786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, H.; Gu, Y.; Liu, X.; Yi, X.; Li, Z.; Yu, Y.; Yu, T.; Li, L. Deep Learning Chest CT for Clinically Precise Prediction of Sepsis-Induced Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome: A Protocol for an Observational Ambispective Cohort Study. Healthcare 2022, 10, 2150. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare10112150
Li H, Gu Y, Liu X, Yi X, Li Z, Yu Y, Yu T, Li L. Deep Learning Chest CT for Clinically Precise Prediction of Sepsis-Induced Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome: A Protocol for an Observational Ambispective Cohort Study. Healthcare. 2022; 10(11):2150. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare10112150
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Han, Yang Gu, Xun Liu, Xiaoling Yi, Ziying Li, Yunfang Yu, Tao Yu, and Li Li. 2022. "Deep Learning Chest CT for Clinically Precise Prediction of Sepsis-Induced Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome: A Protocol for an Observational Ambispective Cohort Study" Healthcare 10, no. 11: 2150. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare10112150
APA StyleLi, H., Gu, Y., Liu, X., Yi, X., Li, Z., Yu, Y., Yu, T., & Li, L. (2022). Deep Learning Chest CT for Clinically Precise Prediction of Sepsis-Induced Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome: A Protocol for an Observational Ambispective Cohort Study. Healthcare, 10(11), 2150. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare10112150





